Key Points
Question
Have racial/ethnic disparities in the receipt of live donor kidney transplantation (LDKT) narrowed over the last 2 decades in the United States?
Findings
In this study of 453 162 adult first-time kidney transplantation candidates, the cumulative incidence of LDKT receipt at 2 years after appearing on the waiting list increased from 7.0% in 1995 to 11.4% in 2014 among white patients, decreased from 3.4% to 2.9% among black patients, decreased from 6.8% to 5.9% among Hispanic patients, and increased from 5.1% to 5.6% among Asian patients, which represent a significant increase in racial/ethnic disparities over time.
Meaning
Racial/ethnic disparities in receipt of LDKT increased from 1995-1999 to 2010-2014, suggesting that national strategies to reduce LDKT disparities have not been effective.
Abstract
Importance
Over the past 2 decades, there has been increased attention and effort to reduce disparities in live donor kidney transplantation (LDKT) for black, Hispanic, and Asian patients with end-stage kidney disease. The goal of this study was to investigate whether these efforts have been successful.
Objective
To estimate changes over time in racial/ethnic disparities in LDKT in the United States, accounting for differences in death and deceased donor kidney transplantation.
Design, Setting, and Participants
A secondary analysis of a prospectively maintained cohort study conducted in the United States of 453 162 adult first-time kidney transplantation candidates included in the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients between January 1, 1995, and December 31, 2014, with follow-up through December 31, 2016.
Exposures
Race/ethnicity.
Main Outcomes and Measures
The primary study outcome was time to LDKT. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards and competing risk models were constructed to assess changes in racial/ethnic disparities in LDKT among adults on the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list and interaction terms were used to test the statistical significance of temporal changes in racial/ethnic differences in receipt of LDKT. The adjusted subhazard ratios are estimates derived from the multivariable competing risk models. Data were categorized into 5-year increments (1995-1999, 2000-2004, 2005-2009, 2010-2014) to allow for an adequate sample size in each analytical cell.
Results
Among 453 162 adult kidney transplantation candidates (mean [SD] age, 50.9 [13.1] years; 39% were women; 48% were white; 30%, black; 16%, Hispanic; and 6%, Asian), 59 516 (13.1%) received LDKT. Overall, there were 39 509 LDKTs among white patients, 8926 among black patients, 8357 among Hispanic patients, and 2724 among Asian patients. In 1995, the cumulative incidence of LDKT at 2 years after appearing on the waiting list was 7.0% among white patients, 3.4% among black patients, 6.8% among Hispanic patients, and 5.1% among Asian patients. In 2014, the cumulative incidence of LDKT was 11.4% among white patients, 2.9% among black patients, 5.9% among Hispanic patients, and 5.6% among Asian patients. From 1995-1999 to 2010-2014, racial/ethnic disparities in the receipt of LDKT increased (P < .001 for all statistical interaction terms in adjusted models comparing white patients vs black, Hispanic, and Asian patients). In 1995-1999, compared with receipt of LDKT among white patients, the adjusted subhazard ratio was 0.45 (95% CI, 0.42-0.48) among black patients, 0.83 (95% CI, 0.77-0.88) among Hispanic patients, and 0.56 (95% CI, 0.50-0.63) among Asian patients. In 2010-2014, compared with receipt of LDKT among white patients, the adjusted subhazard ratio was 0.27 (95% CI, 0.26-0.28) among black patients, 0.52 (95% CI, 0.50-0.54) among Hispanic patients, and 0.42 (95% CI, 0.39-0.45) among Asian patients.
Conclusions and Relevance
Among adult first-time kidney transplantation candidates in the United States who were added to the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list between 1995 and 2014, disparities in the receipt of live donor kidney transplantation increased from 1995-1999 to 2010-2014. These findings suggest that national strategies for addressing disparities in receipt of live donor kidney transplantation should be revisited.
This study uses Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients registry data to compare kidney transplantation rates among white, black, Hispanic, and Asian recipient candidates in 1995-1999 vs 2010-2014.
Introduction
Live donor kidney transplantation accounts for approximately one-third of kidney transplants performed in the United States. Live donor kidney transplantation is associated with improved clinical outcomes and quality of life for clinically suitable patients with end-stage kidney disease compared with receiving long-term dialysis treatment or deceased donor kidney transplantation. National data since 1988 show that patients from racial/ethnic minority groups are less likely to receive live donor kidney transplantation than white patients despite having a disproportionately higher burden of end-stage kidney disease. Prior studies suggested that racial/ethnic disparities in live donor kidney transplantation may be attributable to barriers encountered at multiple steps along the path to successful live donor kidney transplantation. The steps during which these barriers may be encountered include during referral, identification and pursuit of potential living donors, evaluation, and treatment decision making by the clinician, potential donor, and potential recipient.
Over the last 2 decades, dozens of interventions addressing racial/ethnic disparities in live donor kidney transplantation have been developed and implemented in single-center and small multicenter environments. These interventions have addressed a wide range of barriers including knowledge, concerns, and clinical characteristics of the live donor kidney transplantation recipient and donor; beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors of health care clinicians; and awareness, attitudes, and disease burden of the US population. In addition to these programs, US policy makers have enacted federal and state legislation over the past 2 decades that primarily targeted the reduction of economic barriers for potential living donors.
The primary goal of this study was to assess whether racial/ethnic disparities in live donor kidney transplantation have narrowed over the last 2 decades.
Methods
Data Source
This study was reviewed by the institutional review board at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. The board determined that the study qualified for an exemption under the Code of Federal Regulations because the study participants cannot be identified directly or through linked identifiers. The study used data from the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients (SRTR).
The SRTR system includes data on all donors, candidates, and transplantation recipients in the United States that are submitted by the members of the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN). The Health Resources and Services Administration within the US Department of Health and Human Services oversees the activities of the OPTN and SRTR contractors. Data from the SRTR were linked at the 5-digit zip code level with neighborhood socioeconomic status and poverty data using the American Community Surveys from the US Census.
Study Design
The study population included adults (aged ≥18 years) on the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list for a first kidney transplantation between January 1, 1995, and December 31, 2014. On the OPTN adult kidney transplantation registration forms, which were completed by clinicians at the transplantation center, the race/ethnicity of all candidates included in this study was designated using 1 of the following fixed categories: white, black/African American, Hispanic/Latino, or Asian. This study was not sufficiently powered to examine temporal changes in live donor kidney transplantation disparities among candidates identified as American Indian or Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander, or multiracial due to the small population sizes during some of the years. Five candidates (0.001%) did not have a racial/ethnic assignment and were excluded from the study. The primary study outcome of time to live donor kidney transplantation was determined by the transplant date documented on the OPTN forms by the transplantation center.
Statistical Analysis
Descriptive Data Analysis
Clinical and demographic characteristics were stratified by kidney transplantation candidate race/ethnicity and year of placement on the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list. Wilcoxon rank sum (for continuous variables) and χ2 tests (for categorical variables) were performed to compare distributions and assess statistical significance. Kaplan-Meier methods, which accounted for the competing risks of deceased donor kidney transplantation and mortality, were used to assess candidate racial/ethnic differences in the estimated cumulative incidence of live donor kidney transplantation at 2 years after appearing on the waiting list. In addition, among live donor kidney transplantation recipients, racial/ethnic differences in recipient and donor characteristics were assessed over time. Wilcoxon rank sum and χ2 tests were performed to assess statistical significance between racial/ethnic differences.
Cox Proportional Hazards and Competing Risk Models
Associations between race/ethnicity and time to live donor kidney transplantation were analyzed using multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression models that estimated adjusted hazard ratios. The data were categorized into 5-year increments (1995-1999, 2000-2004, 2005-2009, 2010-2014) based on the date of candidate placement on the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list to allow for an adequate sample size in each analytical cell. Patients were followed up for 2 years after placement on the waiting list.
Patients were censored at the first documented date of death; receipt of deceased donor kidney transplantation; at 2 years after initial placement on the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list; at the date of removal from the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list due to reasons other than receipt of kidney transplantation or death; or at the end of the study observation period on December 31, 2016. The decision to censor patients at 2 years after appearing on the waiting list was informed by a prior study of national data reporting that most live donor kidney transplantations occurred within the first 6 months of being listed.
All regression models were adjusted for biologically plausible confounders (age, sex, body mass index [calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared], panel reactive antibody, and ABO blood type) measured at the time of appearing on the waiting list. Statistical interaction terms were used in regression models to formally test the statistical significance of temporal changes in racial/ethnic disparities in the receipt of live donor kidney transplantation. To evaluate whether differences in live donor kidney transplantation were related to differences in deceased donor kidney transplantation or death (ie, informative censoring), the main analyses were repeated using competing risk models according to the methods of Fine and Gray (estimating adjusted subhazard ratios). The analyses in which death and deceased donor kidney transplantation were treated as separate competing risk events were adjusted for the same variables described above.
Sensitivity Analysis
To test the robustness of the estimates, all analyses were repeated in (1) a contemporary cohort of kidney transplantation candidates who were added to the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list between 2000 and 2014, (2) an expanded cohort of kidney transplantation candidates who were added to the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list between 1995 and 2014 plus candidates who received live donor kidney transplantation preemptively between 1995 and 2014 without placement on the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list, and (3) a reduced cohort of active status only kidney transplantation candidates who were added to the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list between 1995 and 2014.
Additional models were used to examine the extent to which the racial/ethnic differences in potential mediators of (1) health care access and socioeconomic status factors (neighborhood poverty level, education level, health insurance type, time receiving dialysis) and (2) transplantation center factors (distance to center, kidney transplantation candidate volume, percentage of nonwhite kidney transplantation candidates, median time to deceased donor kidney transplantation, live donor kidney transplantation volume) influenced the primary findings. To estimate the influence of these potential mediators on racial/ethnic disparities in live donor kidney transplantation, these factors were incrementally incorporated into the Cox regression and the competing risk models.
Model Testing and Statistical Significance
Complementary log-log plots and Schoenfeld residuals were examined to assess the proportional hazards assumption. The variance inflation factor and Eigen values were used to test for colinearity among the vector of explanatory variables. The standard SRTR risk adjustment approach was used for handling missing data. With the SRTR approach, missing variable levels were modeled separately from known variable levels in the regression models. The robustness of estimates was tested by comparing results from an alternate modeling approach to handle missing data (multiple imputation), and the inferences remained the same for the study outcomes of interest. The correction for false-discovery rate and the Bonferroni correction were used to account for multiple comparisons.
A 2-tailed P value <.05 was considered statistically significant. All analyses were conducted using Stata version 14.1 (StataCorp).
Results
Population Characteristics
Among 453 162 adult kidney transplantation candidates identified within the SRTR between 1995 and 2014 (mean [SD] age, 50.9 [13.1] years; 39% were women; 48% were white [n = 217 040]; 30%, black [n = 135 333]; 16%, Hispanic [n = 71 912]; and 6%, Asian [n = 28 877]), 59 516 (13.1%) received live donor kidney transplantation. Study participants were censored due to the following reasons: death (n = 30 653), deceased donor kidney transplantation (n = 86 008), waiting list removal due to reasons other than receipt of kidney transplantation or death (n = 50 748), or at 2 years after initial listing (n = 226 237). Of all live donor kidney transplantation recipients, 87.5% received live donor kidney transplantation within 2 years of placement on the waiting list and these outcomes were included in the study. After 2 years of placement on the waiting list, which is outside the study scope, 12.5% of patients received live donor kidney transplantations.
Mean age, body mass index, and prevalence of end-stage kidney disease secondary to diabetes increased from 1995 to 2014. Black and Hispanic patients were younger and also less likely to have college degrees than Asian and white patients. The prevalence of private health insurance was highest among white and Asian patients, and the prevalence of Medicare as the primary coverage was highest among black and Hispanic patients. The prevalence of end-stage kidney disease due to hypertension or diabetes was highest among black and Hispanic patients, whereas the prevalence of end-stage kidney disease due to glomerular diseases or other causes was highest among white and Asian patients. Black and Hispanic patients spent the longest time receiving dialysis and had the highest prevalence of body mass index of 35 or greater (Table 1 and Table 2).
Table 1. Characteristics of US Adult Kidney Transplantation Candidates by Period Listed on Transplant Waiting List, 1995-1999 and 2000-2004a.
| Baseline Characteristics | Transplant Waiting List Cohortb |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995-1999 | 2000-2004 | |||||||
| White (n = 42 210) |
Black (n = 22 855) |
Hispanic (n = 8937) |
Asian (n = 3771) |
White (n = 46 633) |
Black (n = 28 794) |
Hispanic (n = 14 549) |
Asian (n = 5727) |
|
| Age, mean (SD), y | 48.3 (12.8) | 45.6 (12.5) | 45.9 (13.0) | 46.8 (12.6) | 51.9 (12.8) | 47.9 (12.5) | 48.2 (13.2) | 49.7 (13.1) |
| Age group, y | ||||||||
| 18-44 | 16 014 (37.9) | 10 149 (44.4) | 3893 (43.6) | 1552 (41.2) | 12 243 (26.3) | 10 764 (37.4) | 5270 (36.2) | 1889 (33.0) |
| 45-60 | 18 095 (42.9) | 9814 (42.9) | 3784 (42.3) | 1665 (44.2) | 21 527 (46.2) | 13 119 (45.6) | 6420 (44.1) | 2545 (44.4) |
| >60 | 8101 (19.2) | 2892 (12.7) | 1260 (14.1) | 554 (14.7) | 12 863 (27.6) | 4911 (17.1) | 2859 (19.7) | 1293 (22.6) |
| Female sex | 16 403 (38.9) | 9856 (43.1) | 3557 (39.8) | 1729 (45.8) | 18 152 (38.9) | 12 497 (43.4) | 5737 (39.4) | 2539 (44.3) |
| Body mass indexc | ||||||||
| <30 | 30 883 (73.2) | 15 285 (66.9) | 6653 (74.4) | 3307 (87.7) | 30 719 (65.9) | 17 487 (60.7) | 10 162 (69.8) | 4927 (86.0) |
| 30-34.9 | 6489 (15.4) | 4062 (17.8) | 1375 (15.4) | 228 (6.0) | 9790 (21.0) | 6553 (22.8) | 2823 (19.4) | 541 (9.4) |
| >34.9 | 2926 (6.9) | 2266 (9.9) | 588 (6.6) | 92 (2.4) | 5076 (10.9) | 4090 (14.2) | 1327 (9.1) | 168 (2.9) |
| Peak PRA or CPRA, median (IQR) | 0 (0-5) | 0 (0-13) | 0 (0-10) | 0 (0-8) | 0 (0-5) | 0 (0-16) | 0 (0-9) | 0 (0-7) |
| Primary cause of end-stage kidney disease | ||||||||
| Diabetes | 9049 (21.4) | 3257 (14.3) | 1832 (20.5) | 464 (12.3) | 7847 (16.8) | 4617 (16.0) | 3854 (26.5) | 1111 (19.4) |
| Hypertension | 5123 (12.1) | 9156 (40.1) | 1657 (18.5) | 744 (19.7) | 6746 (14.5) | 11 499 (39.9) | 3035 (20.9) | 1265 (22.1) |
| Glomerular disease | 9008 (21.3) | 4052 (17.7) | 1897 (21.2) | 1205 (32.0) | 9517 (20.4) | 4849 (16.8) | 2569 (17.7) | 1586 (27.7) |
| Cystic disease | 5127 (12.1) | 631 (2.8) | 469 (5.2) | 177 (4.7) | 6137 (13.2) | 867 (3.0) | 675 (4.6) | 210 (3.7) |
| Other cause | 13 903 (32.9) | 5759 (25.2) | 3082 (34.5) | 1181 (31.3) | 16 386 (35.1) | 6962 (24.2) | 4416 (30.4) | 1555 (27.2) |
| ABO blood type | ||||||||
| O | 19 326 (45.8) | 11 446 (50.1) | 5124 (57.3) | 1486 (39.4) | 21 391 (45.9) | 14 447 (50.2) | 8499 (58.4) | 2283 (39.9) |
| A | 16 546 (39.2) | 5789 (25.3) | 2740 (30.7) | 1054 (28.0) | 18 195 (39.0) | 7285 (25.3) | 4251 (29.2) | 1484 (25.9) |
| B | 4714 (11.2) | 4674 (20.5) | 888 (9.9) | 984 (26.1) | 5270 (11.3) | 5992 (20.8) | 1453 (10.0) | 1587 (27.7) |
| AB | 1624 (3.8) | 946 (4.1) | 185 (2.1) | 247 (6.5) | 1777 (3.8) | 1070 (3.7) | 346 (2.4) | 373 (6.5) |
| Health Care Access and Socioeconomic Status | ||||||||
| Primary health insurance coveraged | ||||||||
| Private | 21 600 (51.2) | 7211 (31.6) | 2582 (28.9) | 1706 (45.2) | 25 062 (53.7) | 10 390 (36.1) | 4646 (31.9) | 2921 (51.0) |
| Medicare | 17 370 (41.2) | 12 744 (55.8) | 4879 (54.6) | 1375 (36.5) | 18 166 (39.0) | 14 688 (51.0) | 7416 (51.0) | 1927 (33.6) |
| Medicaid | 1787 (4.2) | 2193 (9.6) | 1232 (13.8) | 486 (12.9) | 1814 (3.9) | 2489 (8.6) | 2191 (15.1) | 691 (12.1) |
| Other coverage | 1229 (2.9) | 600 (2.6) | 228 (2.6) | 193 (5.1) | 1582 (3.4) | 1227 (4.3) | 293 (2.0) | 187 (3.3) |
| Highest level of educationd | ||||||||
| <College degree | 24 519 (58.1) | 15 124 (66.2) | 6212 (69.5) | 1765 (46.8) | 28 244 (60.6) | 19 243 (66.8) | 10 621 (73.0) | 3197 (55.8) |
| College degree | 5512 (13.1) | 1819 (8.0) | 519 (5.8) | 633 (16.8) | 6429 (13.8) | 2579 (9.0) | 759 (5.2) | 800 (14.0) |
| Graduate or professional degree | 2316 (5.5) | 588 (2.6) | 160 (1.8) | 315 (8.4) | 2978 (6.4) | 880 (3.1) | 219 (1.5) | 445 (7.8) |
| Time receiving renal replacement therapy, yd | ||||||||
| Median (IQR) | 0.2 (0-0.9) | 0.3 (0-1.4) | 0.4 (0-1.4) | 0.3 (0-1.1) | 0.5 (0-1.4) | 1.2 (0.5-2.6) | 1.1 (0.5-2.3) | 0.7 (0.2-1.8) |
| <1 | 32 815 (77.7) | 15 575 (68.1) | 5918 (66.2) | 2761 (73.2) | 30 009 (64.4) | 12 756 (44.3) | 6690 (46.0) | 3359 (58.7) |
| 1-2 | 5300 (12.6) | 3318 (14.5) | 1508 (16.9) | 499 (13.2) | 8565 (18.4) | 6521 (22.6) | 3615 (24.8) | 1070 (18.7) |
| >2 | 4095 (9.7) | 3962 (17.3) | 1511 (16.9) | 511 (13.6) | 8059 (17.3) | 9517 (33.1) | 4244 (29.2) | 1298 (22.7) |
| Neighborhood poverty level of households, %d,e | ||||||||
| <5 | 8075 (19.1) | 647 (2.8) | 203 (2.3) | 785 (20.8) | 9299 (19.9) | 966 (3.4) | 312 (2.1) | 1321 (23.1) |
| 5-19 | 28 867 (68.4) | 5791 (25.3) | 2460 (27.5) | 2067 (54.8) | 32 561 (69.8) | 7877 (27.4) | 4152 (28.5) | 3212 (56.1) |
| ≥20 | 3293 (7.8) | 15 353 (67.2) | 5828 (65.2) | 711 (18.9) | 3606 (7.7) | 19 150 (66.5) | 9559 (65.7) | 997 (17.4) |
| Met Transplantation Center Criteriad | ||||||||
| Median patient distance >160 km to centerf | 8501 (20.1) | 2658 (11.6) | 1698 (19.0) | 517 (13.7) | 9347 (20.0) | 3684 (12.8) | 3157 (21.7) | 562 (9.8) |
| Kidney transplantation volume ≥1100 patients | 36 894 (87.4) | 20 145 (88.1) | 7940 (88.8) | 3242 (86.0) | 37 617 (80.7) | 24 028 (83.4) | 12 583 (86.5) | 4682 (81.8) |
| Estimate of nonwhite kidney transplantation candidates >50% | 17 219 (40.8) | 15 179 (66.4) | 7348 (82.2) | 2777 (73.6) | 20 525 (44.0) | 20 224 (70.2) | 12 341 (84.8) | 4472 (78.1) |
| Median time >3 y to deceased donor kidney transplantation | 18 299 (43.4) | 12 478 (54.6) | 5102 (57.1) | 2353 (62.4) | 28 976 (62.1) | 20 711 (71.9) | 12 188 (83.8) | 4865 (84.9) |
| Cumulative live donor kidney transplantation volume ≥40 | 36 778 (87.1) | 19 660 (86.0) | 7516 (84.1) | 3239 (85.9) | 43 786 (93.9) | 26 423 (91.8) | 13 205 (90.8) | 5357 (93.5) |
Abbreviations: CPRA, calculated panel reactive antibody; PRA, panel reactive antibody.
Complete data were available from 453 162 patients for age, sex, primary cause of end-stage kidney disease, time receiving renal replacement therapy, ABO blood type, and the transplantation center criteria except for median patient distance to center.
Data are expressed as No. (%) unless otherwise indicated. Results were calculated based on complete data from patients by listing year. The following variables were missing data for some of the patients: primary health insurance coverage (0.1% missing overall, 0.5% in 1995-1999, 0% in 2000-2004, 0.1% in 2005-2009, 0% in 2010-2014), highest level of education (13.1% missing overall, 23.5% in 1995-1999, 20.2% in 2000-2004, 11.8% in 2005-2009, 4.3% in 2010-2014), body mass index (1.6% missing overall, 4.6% in 1995-1999, 2.1% in 2000-2004, 1.2% in 2005-2009, 0.2% in 2010-2014), peak PRA or CPRA (2.0% missing overall, 3.6% in 1995-1999, 3.1% in 2000-2004, 2.4% in 2005-2009, 0% in 2010-2014), neighborhood poverty level of households (2.6% missing overall, 4.7% in 1995-1999, 2.8% in 2000-2004, 2.1% in 2005-2009, 1.7% in 2010-2014), and median patient distance to center (1.1% missing overall, 2.8% in 1995-1999, 1.2% in 2000-2004, 0.6% in 2005-2009, 0.5% in 2010-2014).
Calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared.
These variables were not included as covariates in the primary models. Kidney transplantation volume and estimate of nonwhite kidney transplantation candidates were calculated based on the prevalence at the middle time point of the period interval.
Based on US Census estimates of residents living below the federal poverty level within the zip code where the candidate resided at the time of appearing on the waiting list.
Distance determined using zip code data.
Table 2. Characteristics of US Adult Kidney Transplantation Candidates by Period Listed on Transplant Waiting List, 2005-2009 and 2010-2014a.
| Baseline Characteristics | Transplant Waiting List Cohortb |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005-2009 | 2010-2014 | |||||||
| White (n = 61 768) |
Black (n = 39 006) |
Hispanic (n = 21 918) |
Asian (n = 8563) |
White (n = 66 429) |
Black (n = 44 678) |
Hispanic (n = 26 508) |
Asian (n = 10 816) |
|
| Age, mean (SD), y | 53.9 (12.8) | 49.8 (12.5) | 49.6 (13.4) | 51.8 (13.1) | 55.0 (12.8) | 50.9 (12.3) | 50.3 (13.0) | 52.8 (13.0) |
| Age group, y | ||||||||
| 18-44 | 13 314 (21.6) | 12 805 (32.8) | 7172 (32.7) | 2392 (27.9) | 13 019 (19.6) | 13 301 (29.8) | 7981 (30.1) | 2779 (25.7) |
| 45-60 | 27 376 (44.3) | 17 915 (45.9) | 9750 (44.5) | 3661 (42.8) | 27 350 (41.2) | 20 368 (45.6) | 12 179 (45.9) | 4449 (41.1) |
| >60 | 21 078 (34.1) | 8286 (21.2) | 4996 (22.8) | 2510 (29.3) | 26 060 (39.2) | 11 009 (24.6) | 6348 (23.9) | 3588 (33.2) |
| Female sex | 22 979 (37.2) | 16 742 (42.9) | 8441 (38.5) | 3609 (42.1) | 24 321 (36.6) | 18 489 (41.4) | 9641 (36.4) | 4396 (40.6) |
| Body mass indexc | ||||||||
| <30 | 36 578 (59.2) | 21 247 (54.5) | 14 060 (64.1) | 7052 (82.4) | 36 097 (54.3) | 22 383 (50.1) | 15 499 (58.5) | 8527 (78.8) |
| 30-34.9 | 15 280 (24.7) | 10 177 (26.1) | 5132 (23.4) | 1049 (12.3) | 18 202 (27.4) | 12 522 (28.0) | 7210 (27.2) | 1697 (15.7) |
| >34.9 | 9151 (14.8) | 7053 (18.1) | 2552 (11.6) | 375 (4.4) | 12 006 (18.1) | 9713 (21.7) | 3761 (14.2) | 567 (5.2) |
| Peak PRA or CPRA, median (IQR) | 0 (0-9) | 0 (0-27) | 0 (0-15) | 0 (0-13) | 0 (0-0) | 0 (0-21) | 0 (0-3) | 0 (0-6) |
| Primary cause of end-stage kidney disease | ||||||||
| Diabetes | 16 838 (27.3) | 11 828 (30.3) | 9799 (44.7) | 2995 (35.0) | 19 514 (29.4) | 15 608 (34.9) | 13 044 (49.2) | 4082 (37.7) |
| Hypertension | 10 305 (16.7) | 15 000 (38.5) | 4598 (21.0) | 1897 (22.2) | 11 041 (16.6) | 16 773 (37.5) | 4920 (18.6) | 2228 (20.6) |
| Glomerular disease | 11 151 (18.1) | 6024 (15.4) | 3286 (15.0) | 1993 (23.3) | 12 023 (18.1) | 6434 (14.4) | 3785 (14.3) | 2546 (23.5) |
| Cystic disease | 8140 (13.2) | 1247 (3.2) | 1006 (4.6) | 355 (4.1) | 8497 (12.8) | 1460 (3.3) | 1201 (4.5) | 480 (4.4) |
| Other cause | 15 334 (24.8) | 4907 (12.6) | 3229 (14.7) | 1323 (15.5) | 15 354 (23.1) | 4403 (9.9) | 3558 (13.4) | 1480 (13.7) |
| ABO blood type | ||||||||
| O | 27 761 (44.9) | 19 594 (50.2) | 13 049 (59.5) | 3354 (39.2) | 29 668 (44.7) | 22 518 (50.4) | 15 603 (58.9) | 4274 (39.5) |
| A | 24 731 (40.0) | 9734 (25.0) | 6248 (28.5) | 2123 (24.8) | 26 919 (40.5) | 11 162 (25.0) | 7696 (29.0) | 2693 (24.9) |
| B | 6940 (11.2) | 7992 (20.5) | 2163 (9.9) | 2497 (29.2) | 7285 (11.0) | 9218 (20.6) | 2629 (9.9) | 3134 (29.0) |
| AB | 2336 (3.8) | 1686 (4.3) | 458 (2.1) | 589 (6.9) | 2557 (3.8) | 1780 (4.0) | 580 (2.2) | 715 (6.6) |
| Health Care Access and Socioeconomic Status | ||||||||
| Primary health insurance coveraged | ||||||||
| Private | 33 537 (54.3) | 14 787 (37.9) | 7347 (33.5) | 4579 (53.5) | 34 418 (51.8) | 16 381 (36.7) | 9068 (34.2) | 5458 (50.5) |
| Medicare | 24 056 (38.9) | 19 977 (51.2) | 10 995 (50.2) | 2791 (32.6) | 27 732 (41.7) | 23 302 (52.2) | 13 859 (52.3) | 3981 (36.8) |
| Medicaid | 2523 (4.1) | 3057 (7.8) | 3129 (14.3) | 984 (11.5) | 2631 (4.0) | 3613 (8.1) | 3171 (12.0) | 1184 (10.9) |
| Other coverage | 1615 (2.6) | 1166 (3.0) | 429 (2.0) | 198 (2.3) | 1641 (2.5) | 1378 (3.1) | 409 (1.5) | 192 (1.8) |
| Highest level of educationd | ||||||||
| <College degree | 39 070 (63.3) | 28 053 (71.9) | 17 380 (79.3) | 4838 (56.5) | 42 996 (64.7) | 33 520 (75.0) | 22 494 (84.9) | 6176 (57.1) |
| College degree | 10 278 (16.6) | 4645 (11.9) | 1414 (6.5) | 1809 (21.1) | 13 633 (20.5) | 6639 (14.9) | 2194 (8.3) | 2778 (25.7) |
| Graduate or professional degree | 5258 (8.5) | 1707 (4.4) | 414 (1.9) | 871 (10.2) | 6992 (10.5) | 2604 (5.8) | 636 (2.4) | 1409 (13.0) |
| Time receiving renal replacement therapy, yd | ||||||||
| Median (IQR) | 0.4 (0-1.3) | 1.2 (0.4-2.7) | 1.1 (0.4-2.3) | 0.7 (0-1.7) | 0.3 (0-1.2) | 1.1 (0.3-2.8) | 1.0 (0.3-2.3) | 0.6 (0-1.5) |
| <1 | 41 853 (67.8) | 17 190 (44.1) | 10 486 (47.8) | 5238 (61.2) | 47 023 (70.8) | 20 601 (46.1) | 13 285 (50.1) | 6927 (64.0) |
| 1-2 | 10 012 (16.2) | 8493 (21.8) | 4899 (22.4) | 1518 (17.7) | 9553 (14.4) | 9032 (20.2) | 5589 (21.1) | 1855 (17.2) |
| >2 | 9903 (16.0) | 13 323 (34.2) | 6533 (29.8) | 1807 (21.1) | 9853 (14.8) | 15 045 (33.7) | 7634 (28.8) | 2034 (18.8) |
| Neighborhood poverty level of households, %d,e | ||||||||
| <5 | 12 911 (20.9) | 1522 (3.9) | 531 (2.4) | 2162 (25.2) | 14 671 (22.1) | 1973 (4.4) | 733 (2.8) | 2782 (25.7) |
| 5-19 | 43 469 (70.4) | 12 089 (31.0) | 6507 (29.7) | 4818 (56.3) | 46 408 (69.9) | 14 597 (32.7) | 8127 (30.7) | 5922 (54.8) |
| ≥20 | 4170 (6.8) | 24 491 (62.8) | 14 360 (65.5) | 1401 (16.4) | 4315 (6.5) | 27 259 (61.0) | 17 202 (64.9) | 1930 (17.8) |
| Met Transplantation Center Criteriad | ||||||||
| Median patient distance >160 km to centerf | 12 796 (20.7) | 5079 (13.0) | 5075 (23.2) | 957 (11.2) | 14 949 (22.5) | 6443 (14.4) | 6151 (23.2) | 1317 (12.2) |
| Kidney transplantation volume ≥1100 patients | 42 461 (68.7) | 29 469 (75.5) | 16 386 (74.8) | 6451 (75.3) | 13 706 (20.6) | 10 987 (24.6) | 8578 (32.4) | 3931 (36.3) |
| Estimate of nonwhite kidney transplantation candidates >50% | 27 889 (45.2) | 27 935 (71.6) | 18 638 (85.0) | 6597 (77.0) | 30 025 (45.2) | 32 409 (72.5) | 22 555 (85.1) | 8490 (78.5) |
| Median time >3 y to deceased donor kidney transplantation | 42 227 (68.4) | 30 035 (77.0) | 18 015 (82.2) | 7272 (84.9) | 56 390 (84.9) | 40 948 (91.7) | 24 462 (92.3) | 10 144 (93.8) |
| Cumulative live donor kidney transplantation volume ≥40 | 56 846 (92.0) | 35 230 (90.3) | 19 949 (91.0) | 7962 (93.0) | 60 406 (90.9) | 39 059 (87.4) | 23 444 (88.4) | 9788 (90.5) |
Abbreviations: CPRA, calculated panel reactive antibody; PRA, panel reactive antibody.
Complete data were available from 453 162 patients for age, sex, primary cause of end-stage kidney disease, time receiving renal replacement therapy, ABO blood type, and the transplantation center criteria except for median patient distance to center.
Data are expressed as No. (%) unless otherwise indicated. Results were calculated based on complete data from patients by listing year. The following variables were missing data for some of the patients: primary health insurance coverage (0.1% missing overall, 0.5% in 1995-1999, 0% in 2000-2004, 0.1% in 2005-2009, 0% in 2010-2014), highest level of education (13.1% missing overall, 23.5% in 1995-1999, 20.2% in 2000-2004, 11.8% in 2005-2009, 4.3% in 2010-2014), body mass index (1.6% missing overall, 4.6% in 1995-1999, 2.1% in 2000-2004, 1.2% in 2005-2009, 0.2% in 2010-2014), peak PRA or CPRA (2.0% missing overall, 3.6% in 1995-1999, 3.1% in 2000-2004, 2.4% in 2005-2009, 0% in 2010-2014), neighborhood poverty level of households (2.6% missing overall, 4.7% in 1995-1999, 2.8% in 2000-2004, 2.1% in 2005-2009, 1.7% in 2010-2014), and median patient distance to center (1.1% missing overall, 2.8% in 1995-1999, 1.2% in 2000-2004, 0.6% in 2005-2009, 0.5% in 2010-2014).
Calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared.
These variables were not included as covariates in the primary models. Kidney transplantation volume and estimate of nonwhite kidney transplantation candidates were calculated based on the prevalence at the middle time point of the period interval.
Based on US Census estimates of residents living below the federal poverty level within the zip code where the candidate resided at the time of appearing on the waiting list.
Distance determined using zip code data.
Temporal Changes in Receipt of Live Donor Kidney Transplantation by Candidate Race/Ethnicity
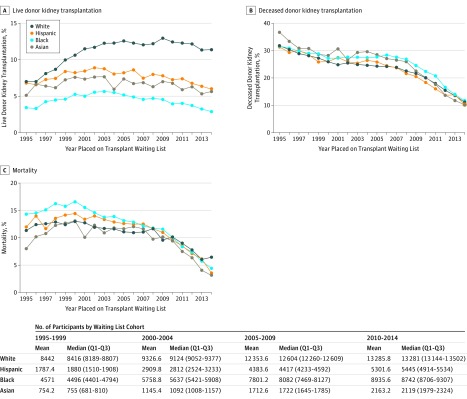
In 1995, the cumulative incidence of live donor kidney transplantation at 2 years after placement on the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list was 7.0% among white patients, 3.4% among black patients, 6.8% among Hispanic patients, and 5.1% among Asian patients; in 2014, the cumulative incidence of live donor kidney transplantation at 2 years after placement on the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list was 11.4% among white patients, 2.9% among black patients, 5.9% among Hispanic patients, and 5.6% among Asian patients (Figure 1A). Temporal changes in racial/ethnic differences in receipt of deceased donor kidney transplantation (Figure 1B) and mortality (Figure 1C) also were observed during the study period.
Figure 1. Temporal Trends in Live Donor Kidney Transplantation, Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation, and Mortality Among US Adults on the Kidney Transplantation Waiting List.
The graphs illustrate the Kaplan-Meier estimated cumulative incidence at 2 years of being on the waiting list among kidney transplantation candidates.
In 1995-1999, there were 5472 live donor kidney transplantations within 2 years of placement on the waiting list among white patients, 1351 among black patients, 999 among Hispanic patients, and 316 among Asian patients. In 2000-2004, there were 9096 live donor kidney transplantations among white patients, 2445 among black patients, 1963 among Hispanic patients, and 605 among Asian patients. In 2005-2009, there were 12 293 live donor kidney transplantations among white patients, 2718 among black patients, 2628 among Hispanic patients, and 834 among Asian patients. In 2010-2014, there were 12 648 live donor kidney transplantations among white patients, 2412 among black patients, 2767 among Hispanic patients, and 969 among Asian patients (Table 3).
Table 3. Crude Live Donor Kidney Transplantation, Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation, and Mortality Within 2 Years of Being Placed on Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation Waiting List by Candidate Race/Ethnicity.
| Period Placed on Transplantation Waiting List |
White | Black | Hispanic | Asian | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Totala | No. (%) | Totala | No. (%) | Totala | No. (%) | Totala | No. (%) | |
| Live Donor Kidney Transplantations | ||||||||
| 1995-1999 | 42 210 | 5472 (13.0) | 22 855 | 1351 (5.9) | 8937 | 999 (11.2) | 3771 | 316 (8.4) |
| 2000-2004 | 46 633 | 9096 (19.5) | 28 794 | 2445 (8.5) | 14 549 | 1963 (13.5) | 5727 | 605 (10.6) |
| 2005-2009 | 61 768 | 12 293 (19.9) | 39 006 | 2718 (7.0) | 21 918 | 2628 (12.0) | 8563 | 834 (9.7) |
| 2010-2014 | 66 429 | 12 648 (19.0) | 44 678 | 2412 (5.4) | 26 508 | 2767 (10.4) | 10 816 | 969 (9.0) |
| Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantations | ||||||||
| 1995-1999 | 42 210 | 13 836 (32.8) | 22 855 | 5440 (23.8) | 8937 | 2294 (25.7) | 3771 | 862 (22.9) |
| 2000-2004 | 46 633 | 11 789 (25.3) | 28 794 | 5243 (18.2) | 14 549 | 2491 (17.1) | 5727 | 903 (15.8) |
| 2005-2009 | 61 768 | 12 179 (19.7) | 39 006 | 6402 (16.4) | 21 918 | 3083 (14.1) | 8563 | 1130 (13.2) |
| 2010-2014 | 66 429 | 9683 (14.6) | 44 678 | 6130 (13.7) | 26 508 | 3214 (12.1) | 10 816 | 1329 (12.3) |
| Deaths | ||||||||
| 1995-1999 | 42 210 | 3405 (8.1) | 22 855 | 1762 (7.7) | 8937 | 627 (7.0) | 3771 | 191 (5.1) |
| 2000-2004 | 46 633 | 3849 (8.3) | 28 794 | 2300 (8.0) | 14 549 | 1048 (7.2) | 5727 | 359 (6.3) |
| 2005-2009 | 61 768 | 4470 (7.2) | 39 006 | 2539 (6.5) | 21 918 | 1359 (6.2) | 8563 | 445 (5.2) |
| 2010-2014 | 66 429 | 4115 (6.2) | 44 678 | 2334 (5.2) | 26 508 | 1378 (5.2) | 10 816 | 472 (4.4) |
Indicates the cumulative number of kidney transplantation candidates placed on the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list.
In the models that treated death and deceased donor kidney transplantation as competing risks, adjusted for biologically plausible confounders, and compared receipt of live donor kidney transplantation in the 1995-1999 cohort, the adjusted subhazard ratio for the receipt of live donor kidney transplantation in the 2010-2014 cohort was 1.86 (95% CI, 1.80-1.92) among white patients, 1.13 (95% CI, 1.06-1.21) among black patients, 1.17 (95% CI, 1.09-1.26) among Hispanic patients, and 1.39 (95% CI, 1.23-1.58) among Asian patients (Table 4). Results from unadjusted models (Table 4), Cox models (eTable 1 in the Supplement), and sensitivity analysis models (eTable 2, eTable 3, eTable 4, and eTable 5 in the Supplement) also reflect racial/ethnic differences in temporal changes in the receipt of live donor kidney transplantation.
Table 4. Temporal Changes in Live Donor Kidney Transplantation by Race/Ethnicity.
| Period Placed on Transplantation Waiting List |
Unadjusted Model, Crude Hazard Ratio (95% CI)a | Competing Risk Model, Adjusted Subhazard Ratio (95% CI)a,b | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | Black | Hispanic | Asian | White | Black | Hispanic | Asian | |
| 1995-1999 | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] | 1 [Reference] |
| 2000-2004 | 1.52 (1.47-1.57) | 1.44 (1.35-1.54) | 1.20 (1.12-1.30) | 1.27 (1.11-1.45) | 1.65 (1.59-1.70) | 1.54 (1.44-1.65) | 1.32 (1.22-1.42) | 1.42 (1.24-1.62) |
| 2005-2009 | 1.56 (1.51-1.61) | 1.18 (1.11-1.26) | 1.07 (0.99-1.15) | 1.17 (1.02-1.33) | 1.93 (1.87-2.00) | 1.45 (1.36-1.55) | 1.36 (1.26-1.46) | 1.51 (1.33-1.72) |
| 2010-2014 | 1.47 (1.43-1.52) | 0.91 (0.85-0.97) | 0.92 (0.86-0.99) | 1.06 (0.93-1.20) | 1.86 (1.80-1.92) | 1.13 (1.06-1.21) | 1.17 (1.09-1.26) | 1.39 (1.23-1.58) |
From regression models comparing live donor kidney transplantation in recent candidate cohorts (2000-2004, 2005-2009, and 2010-2014) vs the earliest cohort (1995-1999).
From competing risk models performed according to the methods of Fine and Gray. The competing risk models were adjusted for differences in biologically plausible confounders, including age (continuous), sex (male and female), body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared; ≤30, >30, or missing), panel reactive antibody (continuous), primary cause of end-stage kidney disease (diabetes, hypertension, or other), and ABO blood type (O, A, B, AB).
Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Receipt of Live Donor Kidney Transplantation From 1995-1999 to 2010-2014
From 1995-1999 to 2010-2014, racial/ethnic disparities in the receipt of live donor kidney transplantation increased (P < .001 for all statistical interaction terms in adjusted models comparing white patients vs black, Hispanic, and Asian patients). In models that treated death and deceased donor kidney transplantation as competing risks and adjusted for biologically plausible confounders in the 1995-1999 cohort compared with the receipt of live donor kidney transplantation among white patients, the adjusted subhazard ratio was 0.45 (95% CI, 0.42-0.48) among black patients, 0.83 (95% CI, 0.77-0.88) among Hispanic patients, and 0.56 (95% CI, 0.50-0.63) among Asian patients (Table 5).
Table 5. Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Live Donor Kidney Transplantation From 1995-1999 to 2010-2014.
| Period Placed on Transplantation Waiting List |
Unadjusted Model, Crude Hazard Ratio (95% CI)a | Competing Risk Model, Adjusted Subhazard Ratio (95% CI)a,b | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | Black | Hispanic | Asian | White | Black | Hispanic | Asian | |
| 1995-1999 | 1 [Reference] | 0.42 (0.39-0.44) | 0.82 (0.77-0.88) | 0.60 (0.54-0.68) | 1 [Reference] | 0.45 (0.42-0.48) | 0.83 (0.77-0.88) | 0.56 (0.50-0.63) |
| 2000-2004 | 1 [Reference] | 0.40 (0.38-0.41) | 0.65 (0.62-0.68) | 0.51 (0.47-0.55) | 1 [Reference] | 0.42 (0.40-0.44) | 0.66 (0.63-0.69) | 0.48 (0.44-0.52) |
| 2005-2009 | 1 [Reference] | 0.32 (0.30-0.33) | 0.56 (0.54-0.59) | 0.45 (0.42-0.49) | 1 [Reference] | 0.34 (0.32-0.35) | 0.58 (0.56-0.60) | 0.44 (0.41-0.47) |
| 2010-2014 | 1 [Reference] | 0.26 (0.25-0.27) | 0.51 (0.49-0.53) | 0.44 (0.41-0.46) | 1 [Reference] | 0.27 (0.26-0.28) | 0.52 (0.50-0.54) | 0.42 (0.39-0.45) |
From regression models comparing live donor kidney transplantation in white patients vs black, Hispanic, and Asian patients in 1995-1999, 2000-2004, 2005-2009, and 2010-2014.
From competing risk models performed according to the methods of Fine and Gray. The competing risk models were adjusted for differences in biologically plausible confounders, including age (continuous), sex (male and female), body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared; ≤30, >30, or missing), panel reactive antibody (continuous), primary cause of end-stage kidney disease (diabetes, hypertension, or other), and ABO blood type (O, A, B, AB). An estimated adjusted subhazard ratio of greater than 1 suggests that the racial/ethnic group is more likely to receive live donor kidney transplantation compared with white candidates. An estimated adjusted subhazard ratio of less than 1 suggests that the racial/ethnic group is less likely to receive live donor kidney transplantation compared with white candidates. P < .001 for all statistical interaction terms in the adjusted models comparing white patients vs black, Hispanic, and Asian patients.
In the 2010-2014 cohort, compared with receipt of live donor kidney transplantation among white patients, the adjusted subhazard ratio was 0.27 (95% CI, 0.26-0.28) among black patients, 0.52 (95% CI, 0.50-0.54) among Hispanic patients, and 0.42 (95% CI, 0.39-0.45) among Asian patients (Table 5). Inferences from unadjusted competing risk models (Table 5), Cox models (eTable 1 in the Supplement), and sensitivity analysis models (eTable 2, eTable 3, eTable 4, and eTable 5 in the Supplement) were similar to inferences from adjusted competing risk models.
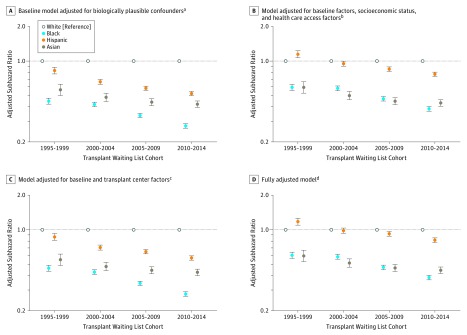
Potential Mechanisms Influencing Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Receipt of Live Donor Kidney Transplantation
Findings from exploratory models suggest that among black and Hispanic patients, adjustments for differences in health care access and socioeconomic status factors were more strongly related to attenuating disparities in live donor kidney transplantation than transplantation center factors. However, even in fully adjusted models, live donor kidney transplantation disparities substantially increased over time for black and Hispanic patients (Figure 2). In additional stratified models, the magnitude of the increase over time in racial/ethnic disparities in the receipt of live donor kidney transplantation was greater for black patients and Hispanic patients (1) living in poorer (vs wealthier) neighborhoods, (2) without (vs with) a college degree, and (3) with Medicare (vs private) insurance (eTable 2 in the Supplement).
Figure 2. Robustness of Estimates of Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Receipt of Live Donor Kidney Transplantation (Primary Outcome) From 1995-1999 to 2010-2014.
The adjusted subhazard ratios were estimated using competing risk models according to the methods of Fine and Gray. Estimated adjusted subhazard ratios greater than 1 suggest that the racial/ethnic group is more likely to receive live donor kidney transplantation compared with white candidates. Estimated adjusted subhazard ratios less than 1 suggest that the racial/ethnic group is less likely to receive live donor kidney transplantation compared with white candidates. The error bars indicate 95% CIs.
aIncludes age, sex, body mass index, panel reactive antibody, end-stage kidney disease etiology, and ABO blood type.
bIncludes neighborhood poverty level, education level, health insurance status, and amount of time receiving renal replacement therapy.
cIncludes distance to center, total number of kidney transplantation candidates, percentage of nonwhite kidney transplantation candidates, median time to deceased donor kidney transplantation, total number of live donor kidney transplantations performed, and total number of live donor kidney transplantations not on the waiting list.
dIncludes all baseline, socioeconomic status, health care, and transplantation center factors (footnotes a-c).
Characteristics of Live Donor Kidney Transplantation Recipients and Donors From 1995-1999 to 2010-2014
In secondary models, temporal changes in live donor kidney transplantation recipient and donor characteristics were explored by race/ethnicity. Across all racial/ethnic groups, live donor kidney transplantation recipients in 2010-2014 were more likely to be older, male, have a college degree, and receive preemptive live donor kidney transplantation than those in 1995-1999. Donors of live donor kidney transplantation in 2010-2014 were more likely to be older or female, and less likely to be biologically related or concordant by race/ethnicity with the recipient compared with donors of live donor kidney transplantation in 1995-1999 (eTable 6 in the Supplement).
Discussion
In this national study of more than 450 000 adult kidney transplantation candidates in the United States who were added to the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list between 1995 and 2014, racial/ethnic disparities in the receipt of live donor kidney transplantation increased from 1995-1999 to 2010-2014. Exploratory study findings suggest that racial/ethnic differences in health care access and socioeconomic status factors may be related to the increasing racial/ethnic disparities in the receipt of live donor kidney transplantation among black and Hispanic patients.
These findings are consistent with and build on prior study findings that racial/ethnic disparities in socioeconomic status measures, including education and health insurance coverage, may be associated with racial/ethnic differences in the receipt and timing of specialist kidney care from a nephrologist prior to end-stage kidney disease. Delays in the receipt of kidney care may also contribute to reported racial/ethnic differences in the quality and timing of patient-clinician and family-clinician discussions about live donor kidney transplantation as a treatment option.
Secondary study findings that live donor kidney transplantation recipients in 2010-2014 were less likely to have a biologically related donor than those in 1995-1999 are consistent with prior work documenting a decrease in national rates of living donation from relatives in the United States. Declines in living donation from relatives may reflect an increasing prevalence of risk factors for end-stage kidney disease (eg, obesity, diabetes, and hypertension) and other clinical contraindications to live donation within the families of kidney transplantation candidates. In this study, the prevalence of end-stage kidney disease due to diabetes or hypertension increased to greater than 72% for black patients and 68% for Hispanic patients compared with 46% for white patients. Familial clustering of end-stage kidney disease risk factors may also contribute to the difficulties reported by black and Hispanic patients in identifying suitable living donors within their families and close social networks.
An important policy change in deceased donor organ allocation occurred during the study period. In 2003, the United Network for Organ Sharing, which oversees OPTN, approved a change in deceased donor kidney allocation that eliminated the priority points given to HLA-B matching. Previous studies reported that this change was associated with a reduction in the disparity between black and white patients in the receipt of deceased donor kidney transplantation.
Consistent with prior studies, there was a similar reduction in the racial disparity in deceased donor kidney transplantation in this study. Findings from models accounting for deceased donor kidney transplantation and death as competing risks yielded similar results to models censoring for deceased donor kidney transplantation and death. Racial/ethnic disparities in live donor kidney transplantation increased in recent years, even after accounting for differences in deceased donor kidney transplantation and death.
In addition, study findings of an increasing prevalence of Hispanic adult kidney transplantation candidates and an increase in disparities in live donor kidney transplantation reinforce calls for culturally targeted programs to overcome barriers to live donor kidney transplantation in the Hispanic community. A recent review of culturally competent strategies to increase knowledge regarding live donor kidney transplantation in Hispanic communities concluded that only 3 culturally targeted interventions have been developed and evaluated since 2010. These interventions, including a mass and social media campaign, exposure to a bilingual website, and transplantation center provision of live donor kidney transplantation education and culturally and linguistically competent care, were found to be effective in increasing knowledge about live donor kidney transplantation. Increased live donor kidney transplantation knowledge in Hispanic communities and culturally appropriate decision support may be important for addressing disparities in patients’ willingness to identify and approach potential donors in their families and close social networks.
Findings from this study suggest that current efforts to reduce live donor kidney transplantation disparities need to be revisited, perhaps with a national strategy initiative. Although center-level patient engagement strategies are important for removing disincentives to live donor kidney transplantation, the implementation of national, evidence-based strategies to address live donor kidney transplantation disparities would likely be more effective.
Potential strategies could include national dissemination of evidence-based culturally and linguistically appropriate live donor kidney transplantation educational materials, online communities, patient navigation services, and policies to standardize and increase the availability of kidney exchanges and chains to help overcome immunological barriers for recipient-donor pairs. Collaborations among researchers, patient advocates, and policy makers are also needed to monitor the effects of legislative efforts on racial/ethnic minorities and to directly target identified barriers to achieving transplantation equity.
This study has several strengths. The first is the ability to comprehensively analyze 2 decades of national data to assess temporal changes in live donor kidney transplantation by race/ethnicity. A second strength is the ability to examine a well-characterized US population of adult kidney transplantation candidates with comprehensive follow-up for transplantation, death, or waiting list removal. A third strength of the study is the ability to account for differences in many important characteristics that might confound or potentially mediate observed associations.
Limitations
The study also has a number of limitations. The first is that the study was limited by the variables available in the SRTR, including clinician-reported race/ethnicity and comorbidities, which has some potential for misclassification bias. The second limitation is the inability to further subcategorize the broad racial/ethnic categories available in the national registry (ie, Hispanic/Latino, Asian, black/African American, and white) to identify unique barriers to live donor kidney transplantation in more disadvantaged racial/ethnic subgroups. The third is the inability to assess the extent to which potential racial/ethnic differences in preferences about and willingness to pursue live donor kidney transplantation among kidney transplantation candidates may be related to our observed findings. The fourth limitation is that the study was unable to account for individual-level patient income. Even though zip-code level measures are important proxies, the future availability of individual-level income in national registries would allow researchers to better delineate the extent to which trends in individual-level income may have contributed to changes in racial/ethnic disparities in live donor kidney transplantation.
Conclusions
Among adult first-time kidney transplantation candidates in the United States who were added to the deceased donor kidney transplantation waiting list between 1995 and 2014, disparities in the receipt of live donor kidney transplantation increased from 1995-1999 to 2010-2014. These findings suggest that national strategies for addressing disparities in receipt of live donor kidney transplantation should be revisited.
eTable 1. Sensitivity analysis: Cox regression model results
eTable 2. Sensitivity analysis: models stratified by age categories, neighborhood poverty, education, and health insurance type
eTable 3. Sensitivity analysis: contemporary reference cohort
eTable 4. Sensitivity analysis: inclusion of non-waitlisted LDKT recipients
eTable 5. Sensitivity analysis: restricted to active status waitlist candidates
eTable 6. Characteristics of LDKT recipients and donors by race/ethnicity, from 1995-1999 to 2010-2014
References
- 1.US Renal Data System 2016 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients 2015 SRTR annual data report. https://srtr.transplant.hrsa.gov/annual_reports/Default.aspx. Accessed July 12, 2017.
- 3.Gore JL, Danovitch GM, Litwin MS, Pham PT, Singer JS. Disparities in the utilization of live donor renal transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2009;9(5):1124-1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hall EC, James NT, Garonzik Wang JM, et al. Center-level factors and racial disparities in living donor kidney transplantation. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;59(6):849-857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Purnell TS, Hall YN, Boulware LE. Understanding and overcoming barriers to living kidney donation among racial and ethnic minorities in the United States. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2012;19(4):244-251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rodrigue JR, Kazley AS, Mandelbrot DA, Hays R, LaPointe Rudow D, Baliga P; American Society of Transplantation . Living donor kidney transplantation: overcoming disparities in live kidney donation in the US—recommendations from a consensus conference. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10(9):1687-1695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Schweitzer EJ, Yoon S, Hart J, et al. Increased living donor volunteer rates with a formal recipient family education program. Am J Kidney Dis. 1997;29(5):739-745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rodrigue JR, Cornell DL, Kaplan B, Howard RJ. A randomized trial of a home-based educational approach to increase live donor kidney transplantation: effects in blacks and whites. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;51(4):663-670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Waterman AD, McSorley AM, Peipert JD, et al. Explore transplant at home: a randomized control trial of an educational intervention to increase transplant knowledge for black and white socioeconomically disadvantaged dialysis patients. BMC Nephrol. 2015;16:150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Garonzik-Wang JM, Berger JC, Ros RL, et al. Live donor champion: finding live kidney donors by separating the advocate from the patient. Transplantation. 2012;93(11):1147-1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Moore DR, Feurer ID, Zavala EY, et al. A web-based application for initial screening of living kidney donors: development, implementation and evaluation. Am J Transplant. 2013;13(2):450-457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Boulware LE, Hill-Briggs F, Kraus ES, et al. Effectiveness of educational and social worker interventions to activate patients’ discussion and pursuit of preemptive living donor kidney transplantation: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;61(3):476-486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Arriola KR, Powell CL, Thompson NJ, Perryman JP, Basu M. Living donor transplant education for African American patients with end-stage renal disease. Prog Transplant. 2014;24(4):362-370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ephraim PL, Powe NR, Rabb H, et al. The providing resources to enhance African American patients’ readiness to make decisions about kidney disease (PREPARED) study: protocol of a randomized controlled trial. BMC Nephrol. 2012;13:135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Boulware LE, Troll MU, Plantinga LC, Powe NR. The association of state and national legislation with living kidney donation rates in the United States: a national study. Am J Transplant. 2008;8(7):1451-1470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Protection of Human Participants, 45 CFR §46.101[b].
- 17.Fine JP, Gray RJ. A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J Am Stat Assoc. 1999;94(446):496-509. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Patzer RE, McClellan WM. Influence of race, ethnicity and socioeconomic status on kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012;8(9):533-541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Purnell TS, Xu P, Leca N, Hall YN. Racial differences in determinants of live donor kidney transplantation in the United States. Am J Transplant. 2013;13(6):1557-1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Johansen KL, Zhang R, Huang Y, Patzer RE, Kutner NG. Association of race and insurance type with delayed assessment for kidney transplantation among patients initiating dialysis in the United States. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;7(9):1490-1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Boulware LE, Meoni LA, Fink NE, et al. Preferences, knowledge, communication and patient-physician discussion of living kidney transplantation in African American families. Am J Transplant. 2005;5(6):1503-1512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rodrigue JR, Schold JD, Mandelbrot DA. The decline in living kidney donation in the United States: random variation or cause for concern? Transplantation. 2013;96(9):767-773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM. Prevalence of childhood and adult obesity in the United States, 2011-2012. JAMA. 2014;311(8):806-814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Selvin E, Parrinello CM, Sacks DB, Coresh J. Trends in prevalence and control of diabetes in the United States, 1988-1994 and 1999-2010. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160(8):517-525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Egan BM, Zhao Y, Axon RN. US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension, 1988-2008. JAMA. 2010;303(20):2043-2050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Grams ME, Chow EK, Segev DL, Coresh J. Lifetime incidence of CKD stages 3-5 in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(2):245-252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Freedman BI, Spray BJ, Tuttle AB, Buckalew VM Jr. The familial risk of end-stage renal disease in African Americans. Am J Kidney Dis. 1993;21(4):387-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ashby VB, Port FK, Wolfe RA, et al. Transplanting kidneys without points for HLA-B matching: consequences of the policy change. Am J Transplant. 2011;11(8):1712-1718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hall EC, Massie AB, James NT, et al. Effect of eliminating priority points for HLA-B matching on racial disparities in kidney transplant rates. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011;58(5):813-816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gordon EJ. Culturally competent strategies for increasing knowledge of live kidney donation in the Hispanic community. Curr Transplant Rep. 2017;4:32. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gordon EJ, Caicedo JC, Ladner DP, Reddy E, Abecassis MM. Transplant center provision of education and culturally and linguistically competent care: a national study. Am J Transplant. 2010;10(12):2701-2707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Alvaro EM, Siegel JT, Crano WD, Dominick A. A mass mediated intervention on Hispanic live kidney donation. J Health Commun. 2010;15(4):374-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gordon EJ, Reddy E, Gil S, et al. Culturally competent transplant program improves Hispanics’ knowledge and attitudes about live kidney donation and transplant. Prog Transplant. 2014;24(1):56-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eTable 1. Sensitivity analysis: Cox regression model results
eTable 2. Sensitivity analysis: models stratified by age categories, neighborhood poverty, education, and health insurance type
eTable 3. Sensitivity analysis: contemporary reference cohort
eTable 4. Sensitivity analysis: inclusion of non-waitlisted LDKT recipients
eTable 5. Sensitivity analysis: restricted to active status waitlist candidates
eTable 6. Characteristics of LDKT recipients and donors by race/ethnicity, from 1995-1999 to 2010-2014