Abstract
Importance
The association of maternal use of folic acid and multivitamin supplements before and during pregnancy with the risk of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in offspring is unclear.
Objective
To examine the associations between the use of maternal folic acid and multivitamin supplements before and during pregnancy and the risk of ASD in offspring.
Design, Setting, and Participants
A case-control cohort study of 45 300 Israeli children born between January 1, 2003, and December 31, 2007, were followed up from birth to January 26, 2015, for the risk of ASD. The cases were all children diagnosed with ASD and the controls were a random sample of 33% of all live-born children.
Exposures
Maternal vitamin supplements were classified for folic acid (vitamin B9), multivitamin supplements (Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical A11 codes vitamins A, B, C, and D), and any combination thereof exposed in the intervals before and during pregnancy.
Main Outcomes and Measures
The association between maternal vitamin supplementation and the risk of ASD in offspring was quantified with relative risks (RRs) and their 95% CIs fitting Cox proportional hazards regression models adjusted for confounders. Sensitivity analyses were performed to test the robustness of the results.
Results
Of the 45 300 children in the study (22 090 girls and 23 210 boys; mean [SD] age, 10.0 [1.4] years at the end of follow-up), 572 (1.3%) received a diagnosis of ASD. Maternal exposure to folic acid and/or multivitamin supplements before pregnancy was statistically significantly associated with a lower likelihood of ASD in the offspring compared with no exposure before pregnancy (RR, 0.39; 95% CI, 0.30-0.50; P < .001). Maternal exposure to folic acid and/or multivitamin supplements during pregnancy was statistically significantly associated with a lower likelihood of ASD in offspring compared with no exposure during pregnancy (RR, 0.27; 95% CI, 0.22-0.33; P < .001). Corresponding RRs were estimated for maternal exposure to folic acid before pregnancy (RR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.42-0.74; P = .001), maternal exposure to folic acid during pregnancy (RR, 0.32; 95% CI, 0.26-0.41; P < .001), maternal exposure to multivitamin supplements before pregnancy (RR, 0.36; 95% CI, 0.24-0.52; P < .001), and maternal exposure to multivitamin supplements during pregnancy (RR, 0.35; 95% CI, 0.28-0.44; P < .001). The results generally remained statistically significant across sensitivity analyses.
Conclusions and Relevance
Maternal exposure to folic acid and multivitamin supplements before and during pregnancy is associated with a reduced risk of ASD in the offspring compared with the offspring of mothers without such exposure.
This case-control cohort study examines the associations between the use of maternal folic acid and multivitamin supplements before and during pregnancy and the risk of autism spectrum disorders in offspring.
Key Points
Question
Does maternal folic acid and/or multivitamin supplement use before and/or during pregnancy increase the risk of autism spectrum disorder in offspring?
Findings
In this case-control cohort study of 45 300 offspring, statistically significant associations between maternal vitamin supplement use before and/or during pregnancy and reduced risk of autism spectrum disorder in offspring were observed.
Meaning
A reduced risk of autism spectrum disorder in children born to women who used the specified vitamin supplements before and during pregnancy has important public health implications; possible mechanisms include epigenetic modifications.
Introduction
Maternal vitamin deficiency during pregnancy is inconsistently associated with cognitive functioning in offspring. However, maternal vitamin D deficiency may have specific associations with the risk of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and intellectual disability (ID) in offspring. Furthermore, maternal vitamin deficiency has also been linked with increased neural tube defects, the incidence of which can be reduced by folic acid (FA) supplementation. Hence, FA and multivitamin supplements are routinely recommended to pregnant women.
Epidemiologic studies report inconsistent associations between maternal supplementation with multivitamins or FA before and during pregnancy and the risk of ASD in offspring. Case-control studies in California identified a reduced risk of ASD in offspring with FA exposure 12 weeks before and 4 weeks into pregnancy; this risk was moderated by genetic variants involved in folate use. In population-based Norwegian studies, FA supplementation from 4 weeks before and 8 weeks into pregnancy was associated with reduced risks of ASD and linguistic delay, a key feature of ASD. However, in studies from Denmark of the same exposure interval, maternal FA and multivitamin supplement use did not significantly reduce the risk of ASD in offspring. In the Stockholm Youth Cohort, multivitamin (but not FA) use reported at approximately 10 weeks into pregnancy was associated with a reduced risk of ASD with ID but not ASD without ID. Our study aims to examine the association between maternal supplementation with FA and multivitamins before and/or during pregnancy and the risk of ASD in offspring.
Methods
Population
A case-cohort study was established by linking health care registers from the Meuhedet health care organization that covers 35% of Israelis until the age of 15 years (eAppendix in the Supplement). Linked health care registers included the Family Relations Register, the Diagnostic Classification Register (records health care dates of diagnosis and codes in accordance with the International Classification of Diseases, Eighth Revision, and the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision), and the Prescription Register (records all prescribed and dispensed medications based on the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical [ATC] Classification System).
We identified all children with ASD and a randomly selected one-third of all children born live between January 1, 2003, and December 31, 2007. The cohort was followed up from birth to January 26, 2015. All children had complete birth date, sex, and parental information. The study was approved by the University of Haifa Institutional Review Board and the Helsinki Ethics Committee of the Meuhedet. Each body that approved the study granted a waiver of informed consent because the study data were deidentified (eAppendix in the Supplement).
Ascertainment of ASD and ID
Children with a clinical impression of probable ASD undergo evaluation by a panel of experts consisting of social workers, a psychologist, and either a trained psychiatrist, developmental behavioral pediatrician, or child neurologist. The final ASD diagnosis is determined by a board-recognized developmental behavioral pediatrician. Since 1995, diagnoses of ASD are stored in a database maintained by Meuhedet as a distinct subset of the Diagnostic Classification Register. We defined ASD using the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision code 299.0, 299.1, or 299.8. Intellectual disability is diagnosed in a similar manner as ASD, except that the evaluation also includes psychometric cognitive testing (diagnostic codes are in the eAppendix in the Supplement).
Covariates
Information was obtained about sex, birth year, socioeconomic status (high vs low), a maternal and paternal psychiatric diagnosis by childbirth (present or absent), maternal and paternal age at childbirth, and parity. Parental psychiatric history was ascertained from a recorded diagnosis of at least 1 episode of a psychiatric disorder (eAppendix in the Supplement).
Exposure
The Meuhedet Prescription Register holds information on drugs dispensed by a majority of pharmacies nationwide since 1996, including drug names, prescription and dispensation dates, number of pills dispensed, and ATC codes. Using the ATC codes of dispensed drugs, we extracted information on dispensed FA and multivitamin supplements (eAppendix in the Supplement). In Israel, food is not fortified with FA, but FA supplementation is recommended before and during pregnancy.
Using the ATC codes, vitamin supplements were classified as FA and/or multivitamin supplements, an FA supplement, and a multivitamin supplement. For each of the 3 vitamin supplement classifications, the redeemed dispensations were categorized into the following 2 time intervals: before pregnancy (540-271 days before childbirth) and during pregnancy (270 days before childbirth up to the date of childbirth).
For each dispensation, assuming 1 pill per day, we defined an exposure period as the date the pills were dispensed until the date the pills would be finished. If an exposure period occurred entirely during a defined time interval, we defined the woman as being exposed during that time interval.
Statistical Analysis
Relative risks (RRs) of ASD and the associated 2-sided 95% CIs were estimated by the hazard ratios from Cox proportional hazards regression models. All models were fitted using age as the underlying time scale. For each exposure, a crude model was fitted without adjusting for any other covariate than the exposure. Each model was also adjusted with all the aforementioned covariates. Because we used a case-cohort study design, all models were estimated using sampling weights to correct for the sampling of controls. As a consequence, if not adjusted for properly, the SEs may be underestimated, resulting in CIs that are too narrow; to correct for this, we used robust SEs. The use of robust SEs also adjusted for the potential within-maternal correlations due to multiple births from the same mother. Each child was followed up from birth until the first diagnosis of ASD, death, or end of follow-up in 2015, whichever came first. The RRs of ASD among children whose mothers were exposed to FA and/or multivitamin supplements before and/or during pregnancy were compared with the reference group of children whose mothers had no exposure in each corresponding interval. Folic acid and/or multivitamin exposure, FA exposure, and multivitamin exposure were analyzed separately. P < .05 (2-sided) was considered statistically significant. All analyses were performed in R, version 3.4.1, using the survival library.
Sensitivity Analyses
The robustness of the primary results was tested in sensitivity analyses. First, we examined maternal vitamin supplementation before but not during pregnancy, during but not before pregnancy, and before and during pregnancy, and compared the group in each time interval with the reference group without maternal vitamin supplementation in each of the aforementioned intervals.
Second, we examined maternal vitamin supplementation with exposure before pregnancy compared with exposure during pregnancy. Third, we examined the exposure interval of 4 weeks before pregnancy to 8 weeks into pregnancy, compared with the reference group of children with no exposure in this interval for direct comparison with prior studies that have examined this exposure interval. Fourth, we examined maternal vitamin supplementation 2 years before pregnancy, during pregnancy, and 2 years before and during pregnancy, compared with the reference group without vitamin supplementation in each of the aforementioned intervals. We examined the 2 years before pregnancy because vitamin use in this time interval has not been studied previously, to our knowledge, and is a negative control group.
Several potential sources of confounding factors were examined. First, we repeated the primary analysis among singleton births because associations between multiple births with vitamin exposure before conception and assisted reproductive technologies have been reported. Second, we repeated the primary analysis for male and female offspring separately. Third, to investigate the role of maternal vitamin deficiency, we repeated the primary analysis for the offspring of women with and without a diagnosis of vitamin deficiency separately (eAppendix in the Supplement). Fourth, we repeated the primary analysis for offspring with both parents diagnosed with a psychiatric disorder and then for offspring with neither parent diagnosed with a psychiatric disorder. Fifth, we refitted the primary analysis confined to mothers with low socioeconomic status because socioeconomic status has been shown to be associated with risk of ASD. Sixth, we refitted the primary analysis for the outcome diagnosis of ASD with and then without ID. Finally, the proportional hazards assumption for the Cox proportional hazards regression models was examined using Schoenfeld residuals.
Results
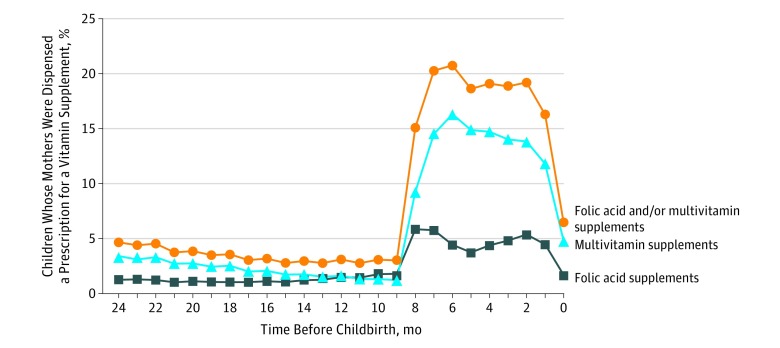
Children born before 2003 were not included in the analysis owing to a lack of reliable information on maternal vitamin dispensation before 2002. We included children born from 2003 onward to ascertain maternal vitamin use up to 270 days before birth. Of 45 300 children born to 26 702 mothers, 572 (1.3%) received a diagnosis of ASD. The raw dispensation rate indicated that most dispensations occurred around the first trimester (Figure 1). There were 11 917 children (26.3%) born to mothers exposed to FA and/or multivitamin supplements before pregnancy and 21 884 children (48.3%) born to mothers exposed to FA and/or multivitamin supplements during pregnancy (eTable 1 in the Supplement).
Figure 1. Proportion of Vitamin Supplement Dispensations Before Childbirth.
Dispensations of folic acid and/or multivitamin vitamin supplements, folic acid supplements, and multivitamin supplements before childbirth.
FA and/or Multivitamin Supplements and Risk of ASD
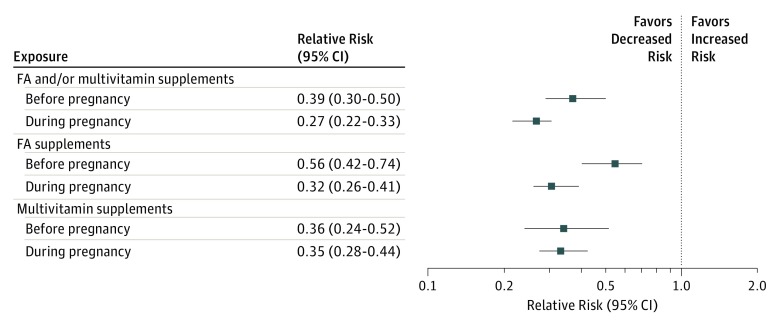
The crude RR of ASD in children of mothers exposed to FA and/or multivitamin supplements before pregnancy compared with children of unexposed mothers in the same interval was estimated at 0.41 (95% CI, 0.32-0.53) and at 0.39 (95% CI, 0.30-0.50) after covariate adjustment (Figure 2). The crude RR of ASD in children of mothers exposed during pregnancy to FA and/or multivitamin supplements compared with children of unexposed mothers in the same interval was estimated at 0.27 (95% CI, 0.22-0.34) and at 0.27 (95% CI, 0.22-0.33) after covariate adjustment (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Adjusted Relative Risk of Autism Spectrum Disorder in Offspring to Mothers Exposed to Folic Acid (FA) and/or Multivitamin Supplements, FA Supplements, or Multivitamin Supplements in the Periods Before and During Pregnancy.
The solid boxes represent the estimated relative risk adjusted for the study covariates, and the lines represent the corresponding 95% CI. For each exposure, the reference group was children whose mothers had no exposure in each corresponding interval.
FA Supplements and the Risk of ASD
The crude RR of ASD in children of mothers exposed before pregnancy to FA compared with children of unexposed mothers in the same interval was estimated at 0.62 (95% CI, 0.47-0.83) and at 0.56 (95% CI, 0.42-0.74) after covariate adjustment (Figure 2). The crude RR of ASD in children of mothers exposed during pregnancy to FA compared with children of unexposed mothers in the same interval was estimated at 0.34 (95% CI, 0.27-0.43) and at 0.32 (95% CI, 0.26-0.41) after covariate adjustment (Figure 2).
Multivitamin Supplements and Risk of ASD
The crude RR of ASD in children of mothers exposed before pregnancy to multivitamin supplements compared with children of unexposed mothers in the same interval was estimated at 0.34 (95% CI, 0.23-0.49) and at 0.36 (95% CI, 0.24-0.52) after covariate adjustment (Figure 2). The crude RR of ASD in children of mothers exposed during pregnancy to multivitamin supplements compared with children of unexposed mothers in the same interval was estimated at 0.36 (95% CI, 0.29-0.45) and at 0.35 (95% CI, 0.28-0.44) after covariate adjustment (Figure 2).
Sensitivity Analyses
Sensitivity analysis showed that exposure during compared with before pregnancy showed statistically insignificant risk reductions for FA and/or multivitamin exposure and FA exposure, but showed an insignificant increase in risk for multivitamin exposure (Table, model 2). Maternal exposure to FA and/or multivitamin supplements from 4 weeks before to 8 weeks into pregnancy was associated with a statistically significant reduction in the risk of ASD in offspring compared with offspring of mothers with no exposure in that time interval (Table, model 3). Across the vitamin supplement classifications examined, maternal exposure during the 2 years before pregnancy was associated with a significant reduction in the risk of ASD in offspring compared with the reference group never exposed, not exposed during the 2-year period before pregnancy, or not exposed during pregnancy (model 4 in the Table; eTables 2 and 3 in the Supplement).
Table. Sensitivity Analyses of the Adjusted Cox Proportional Hazards Regression Modelsa.
| Model, Exposure Interval | Exposure Groups: Dispensed Vitamin Supplement Classification | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Folic Acid and/or Multivitamin Supplements | Folic Acid | Multivitamin Supplements | ||||
| RR (95% CI) | P Valueb | RR (95% CI) | P Valueb | RR (95% CI) | P Valueb | |
| 1, Comparing maternal exposure to vitamin supplements in mutually exclusive exposure intervalsc | ||||||
| Before pregnancy onlyd | 0.25 (0.17-0.36) | <.001 | 0.31 (0.19-0.48) | <.001 | 0.25 (0.14-0.42) | <.001 |
| During pregnancy onlyd | 0.21 (0.17-0.27) | <.001 | 0.25 (0.19-0.33) | <.001 | 0.32 (0.25-0.41) | <.001 |
| Before and during pregnancyd | 0.19 (0.13-0.27) | <.001 | 0.35 (0.24-0.50) | <.001 | 0.23 (0.13-0.40) | <.001 |
| 2, Comparing maternal exposure to vitamin supplements before pregnancy with maternal exposure to vitamin supplements during pregnancyc | ||||||
| During pregnancy onlye | 0.83 (0.54-1.27) | .39 | 0.84 (0.50-1.42) | .52 | 1.27 (0.72-2.27) | .41 |
| 3, Comparing maternal exposure to vitamin supplements from 4 wk before up to 8 wk into pregnancy with no maternal exposure to vitamin supplements in the same intervalc | ||||||
| Exposure from 4 wk before up to 8 wk into pregnancyf | 0.40 (0.31-0.51) | <.001 | 0.41 (0.31-0.55) | <.001 | 0.36 (0.26-0.49) | <.001 |
| 4, Comparing maternal exposure to vitamin supplements 2 y before pregnancy with maternal exposure to vitamin supplements during pregnancy in mutually exclusive exposure intervalsc | ||||||
| During the 2nd year before pregnancy onlyg | 0.12 (0.07-0.20) | <.001 | 0.23 (0.14-0.38) | <.001 | 0.15 (0.09-0.27) | <.001 |
| During pregnancy onlyg | 0.23 (0.18-0.29) | <.001 | 0.30 (0.23-0.39) | <.001 | 0.37 (0.28-0.47) | <.001 |
| During the 2nd year before pregnancy and during pregnancy onlyg | 0.13 (0.09-0.21) | <.001 | 0.13 (0.07-0.25) | <.001 | 0.16 (0.09-0.28) | <.001 |
| 5, Comparing maternal exposure to vitamin supplements before pregnancy and maternal exposure to vitamin supplements during pregnancy in singletons onlyh | ||||||
| Before pregnancyi | 0.42 (0.29-0.62) | <.001 | 0.53 (0.35-0.79) | .002 | 0.24 (0.12-0.52) | <.001 |
| During pregnancyi | 0.26 (0.19-0.35) | <.001 | 0.37 (0.27-0.50) | <.001 | 0.38 (0.28-0.52) | <.001 |
| 6, Comparing maternal exposure to vitamin supplements before pregnancy and maternal exposure to vitamin supplements during pregnancy in male offspring onlyh | ||||||
| Before pregnancyi | 0.38 (0.29-0.51) | <.001 | 0.57 (0.42-0.79) | <.001 | 0.32 (0.21-0.50) | <.001 |
| During pregnancyj | 0.30 (0.24-0.37) | <.001 | 0.33 (0.26-0.43) | <.001 | 0.38 (0.29-0.48) | <.001 |
| 7, Comparing maternal exposure to vitamin supplements before pregnancy and maternal exposure to vitamin supplements during pregnancy in female offspring onlyh | ||||||
| Before pregnancyi | 0.40 (0.22-0.75) | .004 | 0.49 (0.24-0.99) | .05 | 0.49 (0.23-1.07) | .07 |
| During pregnancyj | 0.14 (0.08-0.26) | <.001 | 0.28 (0.16-0.49) | <.001 | 0.25 (0.14-0.45) | <.001 |
| 8, Comparing maternal exposure to vitamin supplements before pregnancy and maternal exposure to vitamin supplements during pregnancy in offspring of low SES parentsh | ||||||
| Before pregnancyi | 0.32 (0.20-0.51) | <.001 | 0.46 (0.27-0.81) | .006 | 0.35 (0.19-0.63) | <.001 |
| During pregnancyj | 0.20 (0.14-0.29) | <.001 | 0.23 (0.15-0.35) | <.001 | 0.26 (0.17-0.38) | <.001 |
| 9, Comparing maternal exposure to vitamin supplements before pregnancy and maternal exposure to vitamin supplements during pregnancy in offspring of parents with a psychiatric diagnosis at time of childbirth (present in both parents)h | ||||||
| Before pregnancyi | 0.47 (0.28-0.79) | .004 | 0.75 (0.44-1.28) | 0.29 | 0.37 (0.16-0.82) | .02 |
| During pregnancyj | 0.28 (0.18-0.43) | <.001 | 0.30 (0.19-0.48) | <.001 | 0.37 (0.23-0.59) | <.001 |
| 10, Comparing maternal exposure to vitamin supplements before pregnancy and maternal exposure to vitamin supplements during pregnancy in offspring of parents without a psychiatric diagnosis at time of childbirth (absent in both parents)h | ||||||
| Before pregnancyi | 0.38 (0.24-0.61) | <.001 | 0.50 (0.29-0.84) | .009 | 0.31 (0.15-0.62) | .001 |
| During pregnancyj | 0.26 (0.19-0.37) | <.001 | 0.34 (0.23-0.50) | <.001 | 0.38 (0.26-0.54) | <.001 |
| 11, Comparing maternal exposure to vitamin supplements before pregnancy and maternal exposure to vitamin supplements during pregnancy in offspring of mothers with a documented vitamin deficiency at time of childbirthc | ||||||
| Before pregnancyi | 1.02 (0.58-1.81) | .94 | 1.56 (0.88-2.78) | .13 | 0.50 (0.20-1.26) | .14 |
| During pregnancyj | 0.24 (0.13-0.47) | <.001 | 0.46 (0.26-0.83) | .009 | 0.38 (0.19-0.78) | .008 |
| 12, Comparing maternal exposure to vitamin supplements before pregnancy and maternal exposure to vitamin supplements during pregnancy in offspring of mothers without a documented vitamin deficiency at time of childbirthc | ||||||
| Before pregnancyi | 0.32 (0.23-0.44) | <.001 | 0.44 (0.31-0.62) | <.001 | 0.34 (0.23-0.53) | <.001 |
| During pregnancyj | 0.27 (0.22-0.34) | <.001 | 0.31 (0.24-0.40) | <.001 | 0.35 (0.28-0.45) | <.001 |
| 13, Comparing maternal exposure to vitamin supplements before pregnancy and maternal exposure to vitamin supplements during pregnancy, with an outcome of offspring with ASD with IDc | ||||||
| Before pregnancyi | 0.49 (0.21-1.11) | .09 | 0.66 (0.25-1.76) | .41 | 0.33 (0.08-1.35) | .12 |
| During pregnancyj | 0.24 (0.12-0.49) | <.001 | 0.12 (0.04-0.36) | <.001 | 0.37 (0.18-0.78) | .009 |
| 14, Comparing maternal exposure to vitamin supplements before pregnancy and maternal exposure to vitamin supplements during pregnancy with an outcome of offspring of ASD without IDc | ||||||
| Before pregnancyi | 0.38 (0.28-0.50) | <.001 | 0.55 (0.40-0.74) | <.001 | 0.36 (0.24-0.53) | <.001 |
| During pregnancyj | 0.27 (0.22-0.33) | <.001 | 0.35 (0.28-0.44) | <.001 | 0.35 (0.28-0.44) | <.001 |
| 15, Covariates in primary analysis and maternal vitamin deficiencyh | ||||||
| Before pregnancyi | 0.41 (0.31-0.53) | <.001 | 0.60 (0.45-0.80) | <.001 | 0.36 (0.25-0.53) | <.001 |
| During pregnancyj | 0.27 (0.22-0.33) | <.001 | 0.33 (0.26-0.41) | <.001 | 0.36 (0.28-0.45) | <.001 |
Abbreviations, ASD, autism spectrum disorder, ID, intellectual disability, RR, relative risk, SES, socioeconomic status.
Each numbered model (1-15) consists of 3 adjusted models, 1 for each vitamin supplement classification.
P value that tests the hypothesis RR = 0 vs RR ≠ 0.
Covariates: models were adjusted for the same covariates as the primary analysis (birth year, sex, SES (high vs low), a maternal and paternal psychiatric diagnosis at childbirth (present or absent), maternal and paternal age at childbirth, and parity.
Reference group: not exposed.
Reference group: before pregnancy.
Reference group: no exposure from 4 weeks before to 8 weeks into pregnancy.
Reference group: never exposed, or not exposed during the 2-year-period before pregnancy or not exposed during pregnancy.
Differences to the primary analysis were singletons (model 5), the parity covariate was not included and the potential within-maternal correlations due to multiple births was not applicable; subsets of male and female offspring (models 6 and 7, respectively), the sex covariate was not included; the low SES group (model 8), the SES covariate was not included; parental psychiatric diagnoses were not included as covariates (models 9 and 10); and model 15 that included all the covariates in primary analysis and the presence or absence of a maternal vitamin deficiency as a covariate.
Reference group: before pregnancy refers to exposure to vitamin supplement intake during the interval from 271 to 540 days before childbirth, compared with the reference category of exposure not before pregnancy.
Reference group: during pregnancy refers to vitamin supplement intake during the interval from 270 days before childbirth to childbirth, compared with the reference category of exposure not during pregnancy.
Sensitivity analyses of possible sources of confounding replicated the statistical significance in the primary analysis (Table), with some exceptions. Among female offspring, maternal exposure to multivitamin supplementation before pregnancy (crude RR [eTable 3 in the Supplement] and adjusted RR [Table]) and FA supplementation before pregnancy (crude RR [eTable 3 in the Supplement, model 7]) had a null association with the risk of ASD in offspring. Among offspring to both parents with a psychiatric condition, maternal exposure to FA before pregnancy had a null association with the risk of ASD in offspring (Table, model 9). Among children of mothers with a vitamin deficiency, across the classifications of vitamin supplements examined, maternal exposure before pregnancy had a null association with the risk of ASD in offspring (Table, model 11). Across the vitamin supplement classifications examined, maternal exposure before pregnancy was not statistically significantly associated with the risk of a comorbid diagnosis of ASD with ID in offspring (Table, model 13). Inspection of the Schoenfeld residuals did not suggest any violation of the proportional hazards assumption for the primary exposures (eFigures 1-3 in the Supplement).
Discussion
This study of 45 300 children revealed a decreased risk of ASD in children born to mothers who used FA and/or multivitamin supplements before and/or during pregnancy compared with those who had not. Sensitivity analysis examining the risk in different intervals, controlling for different sources of confounding, and checking analytic assumptions underlying the statistical analysis did not generally attenuate the observed risk reduction. The association between the use of multivitamin supplements and the risk of ASD was similar in male and female offspring. However, the analysis for female offspring had low power due to the small sample size. Also, among offspring whose parents had a psychiatric condition, FA supplementation before pregnancy did not significantly reduce the risk of ASD. This finding may reflect noncompliance, higher rates of vitamin deficiency, or poor diet among persons with psychiatric conditions. Across the vitamin supplement classes examined, maternal exposure before pregnancy did not reduce the risk of ASD with ID in offspring, possibly owing to the combination of rare outcome and rare exposure.
We examined whether the reduced RR of ASD was due to a vitamin deficiency. Folate deficiency before pregnancy has been associated with adverse childhood outcomes and ASD traits. The reduction in the risk of ASD in offspring after maternal exposure to FA and multivitamin supplements remained after adjusting for the presence of vitamin deficiency in the mother. However, among offspring of women with a vitamin deficiency who were already receiving supplementation before pregnancy, the risk of ASD was not reduced (Table), a result that rules out the possibility that the association is solely due to confounding. Future studies of the underlying biological mechanisms could help us understand the potential modifiable mechanisms in the possible causes of ASD.
Maternal FA and/or multivitamin supplement exposure before and during pregnancy reduced the risk of ASD in offspring. Our results are consistent with those from a Norwegian birth cohort study showing that maternal FA use from 4 weeks before and 8 weeks into pregnancy is associated with a reduced risk of ASD in offspring. This interval is considered relevant to the development of the central nervous system, includes neural tube closure, and is implicated in the development of basic brain structures. These results were, however, not replicated in Danish studies on maternal use of FA and multivitamin supplements. Unique to our study, to our knowledge, is the ability to examine the association between multivitamin exposure and ASD for an extended period preceding pregnancy. Maternal exposure to FA and multivitamin supplements 2 years before pregnancy was associated with a reduced risk of ASD in offspring (Table, model 4). The risk of ASD associated with maternal vitamin exposure was similar before and during pregnancy (Table, model 2). Our study could not determine whether this result is due to the vitamin or to unmeasured confounding by other conditions, such as preterm birth, or lifestyle factors. Future research is warranted to examine the association between vitamin exposure before pregnancy and outcomes in offspring further.
Limitations
The present results require cautious interpretation given several limitations. The effect of confounding was notable, and we cannot rule out remaining residual confounding. Furthermore, our study had a limited sample size and lacked the ability to conduct a sibling control analysis. The underlying indication for the supplement dispensation is unknown. We cannot rule out the possibility that the observed risk reduction is due to other causes associated with the dispensation. However, most dispensations appeared to occur around pregnancy (Figure 1).
Misclassifications of exposure may have occurred and biased the estimated risk reduction. Some mothers may have used over-the-counter supplements that were not prescribed by the health care professional (ie, use of the supplements was not recorded). This form of misclassification is in the direction of false negatives. False-negative classification of exposure may narrow the difference between the exposed and unexposed groups, resulting in a more conservative comparison than one without false-negative misclassification. This suggests that if women classified as false negative were accurately identified, the results would be more pronounced than they are.
Although registry data avoid recall biases associated with survey-based methods, they still may be subject to bias, such as false-positive misclassification due to noncompliance. To address this limitation, the analysis consisted of continuous exposure over time. A continuous rather than a single dispensation pattern may reflect a conservative estimate of ongoing vitamin supplement use.
The rates of vitamin supplementation in our study largely resemble those found in prior registry-based research in Norway. The prevalence of mutually exclusive FA and/or multivitamin supplements (derived from eTable 2: model 1 in the Supplement) was 26 668 (58.8%) overall (vs 44.4% in the study in Norway), was 7133 (15.8%) before and during pregnancy (vs 15.9% in the study in Norway), was 14 751 (32.6%) during pregnancy only (vs 27.3% in the study in Norway), and was 4784 (10.6%) before pregnancy only (vs 1.3% in the study in Norway). Differences may be attributable in part to government guidelines in Norway for FA supplement use for the first 12 weeks of pregnancy.
The extent to which dispensed vitamins are consumed is unknown, and ATC codes cannot distinguish between multivitamin preparations with and multivitamin preparations without FA. Also, we lack information about the mothers’ whole-blood folate levels, which, to our knowledge, is unavailable for women of reproductive age in Israel. Research has shown that second-trimester prenatal vitamin use and maternal whole-blood folate levels are not associated with a proxy of autism-like behaviors. The lack of association between whole-blood folate levels and autistic behaviors may reflect the timing of biomarker measures relative to developmental periods, confounding, or other moderators. Although our exposure rates resembled those in prior studies, future research should account for whole-blood folate levels during pregnancy.
The combination of rare outcome and rare exposure (eTable 2 in the Supplement) precluded defining adequately powered exposures by mutually exclusive time intervals across all analyses. This may be expected in observational studies like ours. Still, mutually exclusive exposure by time interval was included in the sensitivity analysis (Table, model 1).
Another study limitation was our lack of information on gestational age, decreasing the accuracy of exposure classifications. The use of birth date to ascertain exposure increases the possibility that preterm births were misclassified. Hence, future studies are warranted to replicate these findings.
Finally, causality cannot be inferred from observational epidemiologic studies such as this one. However, observational epidemiologic studies are more pragmatic and ethical than randomized clinical trials to examine the pregnancy period.
Conclusions
Maternal exposure to FA and multivitamin supplements before and during pregnancy is associated with a reduced risk of ASD in offspring compared with offspring of mothers without such exposure. Reduced risk of ASD in offspring is a consideration for public health policy that may be realized by extended use of FA and multivitamin supplements during pregnancy.
eAppendix. Methods
eTable 1. Descriptive Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Cases and Controls
eTable 2. Descriptive Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Cases and Controls: Exposures in Sensitivity Analyses
eTable 3. Unadjusted Relative Risk (RR) Estimates and 95% Confidence Intervals From Sensitivity Analysis
eFigure 1. Schoenfeld Residual Plots to Assess Proportional Hazards for the Primary Exposures to Folic Acid and/or Multivitamin Before and During Pregnancy
eFigure 2. Schoenfeld Residual Plots to Assess Proportional Hazards for the Primary Exposures to Folic Acid Before and During Pregnancy
eFigure 3. Schoenfeld Residual Plots to Assess Proportional Hazards for the Primary Exposures to Multivitamin Supplement Before and During Pregnancy
eReferences
References
- 1.Veena SR, Gale CR, Krishnaveni GV, Kehoe SH, Srinivasan K, Fall CH. Association between maternal nutritional status in pregnancy and offspring cognitive function during childhood and adolescence; a systematic review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016;16:220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Magnusson C, Lundberg M, Lee BK, et al. Maternal vitamin D deficiency and the risk of autism spectrum disorders: population-based study. BJPsych Open. 2016;2(2):170-172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Smithells RW, Sheppard S, Schorah CJ. Vitamin deficiencies and neural tube defects. Arch Dis Child. 1976;51(12):944-950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.De Wals P, Tairou F, Van Allen MI, et al. Reduction in neural-tube defects after folic acid fortification in Canada. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(2):135-142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Williams J, Mai CT, Mulinare J, et al. ; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Updated estimates of neural tube defects prevented by mandatory folic Acid fortification—United States, 1995-2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64(1):1-5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Czeizel AE, Dudás I. Prevention of the first occurrence of neural-tube defects by periconceptional vitamin supplementation. N Engl J Med. 1992;327(26):1832-1835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gao Y, Sheng C, Xie RH, et al. New perspective on impact of folic acid supplementation during pregnancy on neurodevelopment/autism in the offspring children—a systematic review. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0165626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, Curry SJ, et al. ; US Preventive Services Task Force . Folic acid supplementation for the prevention of neural tube defects: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2017;317(2):183-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schmidt RJ, Hansen RL, Hartiala J, et al. Prenatal vitamins, one-carbon metabolism gene variants, and risk for autism. Epidemiology. 2011;22(4):476-485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schmidt RJ, Tancredi DJ, Ozonoff S, et al. Maternal periconceptional folic acid intake and risk of autism spectrum disorders and developmental delay in the CHARGE (CHildhood Autism Risks from Genetics and Environment) case-control study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;96(1):80-89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Surén P, Roth C, Bresnahan M, et al. Association between maternal use of folic acid supplements and risk of autism spectrum disorders in children. JAMA. 2013;309(6):570-577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Roth C, Magnus P, Schjølberg S, et al. Folic acid supplements in pregnancy and severe language delay in children. JAMA. 2011;306(14):1566-1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hollander E, Kolevzon A, Coyle JT. Textbook of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Pub; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Virk J, Liew Z, Olsen J, Nohr EA, Catov JM, Ritz B. Preconceptional and prenatal supplementary folic acid and multivitamin intake and autism spectrum disorders. Autism. 2016;20(6):710-718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Strøm M, Granström C, Lyall K, Ascherio A, Olsen SF. Research letter: folic acid supplementation and intake of folate in pregnancy in relation to offspring risk of autism spectrum disorder [published online September 26, 2017]. Psychol Med. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717002410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.DeVilbiss EA, Magnusson C, Gardner RM, et al. Antenatal nutritional supplementation and autism spectrum disorders in the Stockholm Youth Cohort: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2017;359:j4273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Davidovitch M, Hemo B, Manning-Courtney P, Fombonne E. Prevalence and incidence of autism spectrum disorder in an Israeli population. J Autism Dev Disord. 2013;43(4):785-793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.King MD, Fountain C, Dakhlallah D, Bearman PS. Estimated autism risk and older reproductive age. Am J Public Health. 2009;99(9):1673-1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zlotogora J, Amitai Y, Leventhal A. Surveillance of neural tube defects in Israel: the effect of the recommendation for periconceptional folic acid. Isr Med Assoc J. 2006;8(9):601-604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Borgan O, Langholz B, Samuelsen SO, Goldstein L, Pogoda J. Exposure stratified case-cohort designs. Lifetime Data Anal. 2000;6(1):39-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Barlow WE. Robust variance estimation for the case-cohort design. Biometrics. 1994;50(4):1064-1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.R Development Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Therneau T. A package for survival analysis in S. R package version 2.38. http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/survival/index.html. 2015.
- 24.Lipsitch M, Tchetgen Tchetgen E, Cohen T. Negative controls: a tool for detecting confounding and bias in observational studies. Epidemiology. 2010;21(3):383-388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Czeizel AE, Métneki J, Dudás I. Higher rate of multiple births after periconceptional vitamin supplementation. N Engl J Med. 1994;330(23):1687-1688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bailey LB, Berry RJ. Folic acid supplementation and the occurrence of congenital heart defects, orofacial clefts, multiple births, and miscarriage. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;81(5):1213S-1217S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Baron-Cohen S, Lombardo MV, Auyeung B, Ashwin E, Chakrabarti B, Knickmeyer R. Why are autism spectrum conditions more prevalent in males? PLoS Biol. 2011;9(6):e1001081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.DeVilbiss EA, Gardner RM, Newschaffer CJ, Lee BK. Maternal folate status as a risk factor for autism spectrum disorders: a review of existing evidence. Br J Nutr. 2015;114(5):663-672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Brown S, Birtwistle J, Roe L, Thompson C. The unhealthy lifestyle of people with schizophrenia. Psychol Med. 1999;29(3):697-701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.McGrath J. Hypothesis: is low prenatal vitamin D a risk-modifying factor for schizophrenia? Schizophr Res. 1999;40(3):173-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kane JM, Kishimoto T, Correll CU. Non-adherence to medication in patients with psychotic disorders: epidemiology, contributing factors and management strategies. World Psychiatry. 2013;12(3):216-226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Black MM. Effects of vitamin B12 and folate deficiency on brain development in children. Food Nutr Bull. 2008;29(2)(suppl):S126-S131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Steenweg-de Graaff J, Ghassabian A, Jaddoe VW, Tiemeier H, Roza SJ. Folate concentrations during pregnancy and autistic traits in the offspring: the Generation R Study. Eur J Public Health. 2015;25(3):431-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Braun JM, Froehlich T, Kalkbrenner A, et al. Brief report: are autistic-behaviors in children related to prenatal vitamin use and maternal whole blood folate concentrations? J Autism Dev Disord. 2014;44(10):2602-2607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lyall K, Schmidt RJ, Hertz-Picciotto I. Maternal lifestyle and environmental risk factors for autism spectrum disorders. Int J Epidemiol. 2014;43(2):443-464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rai D, Lee BK, Dalman C, Newschaffer C, Lewis G, Magnusson C. Antidepressants during pregnancy and autism in offspring: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2017;358:j2811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nilsen RM, Vollset SE, Rasmussen SA, Ueland PM, Daltveit AK. Folic acid and multivitamin supplement use and risk of placental abruption: a population-based registry study. Am J Epidemiol. 2008;167(7):867-874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ericson A, Källén B, Aberg A. Use of multivitamins and folic acid in early pregnancy and multiple births in Sweden. Twin Res. 2001;4(2):63-66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Li Q, Andrade SE, Cooper WO, et al. Validation of an algorithm to estimate gestational age in electronic health plan databases. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2013;22(5):524-532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Macklin R. Enrolling pregnant women in biomedical research. Lancet. 2010;375(9715):632-633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
eAppendix. Methods
eTable 1. Descriptive Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Cases and Controls
eTable 2. Descriptive Characteristics of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Cases and Controls: Exposures in Sensitivity Analyses
eTable 3. Unadjusted Relative Risk (RR) Estimates and 95% Confidence Intervals From Sensitivity Analysis
eFigure 1. Schoenfeld Residual Plots to Assess Proportional Hazards for the Primary Exposures to Folic Acid and/or Multivitamin Before and During Pregnancy
eFigure 2. Schoenfeld Residual Plots to Assess Proportional Hazards for the Primary Exposures to Folic Acid Before and During Pregnancy
eFigure 3. Schoenfeld Residual Plots to Assess Proportional Hazards for the Primary Exposures to Multivitamin Supplement Before and During Pregnancy
eReferences