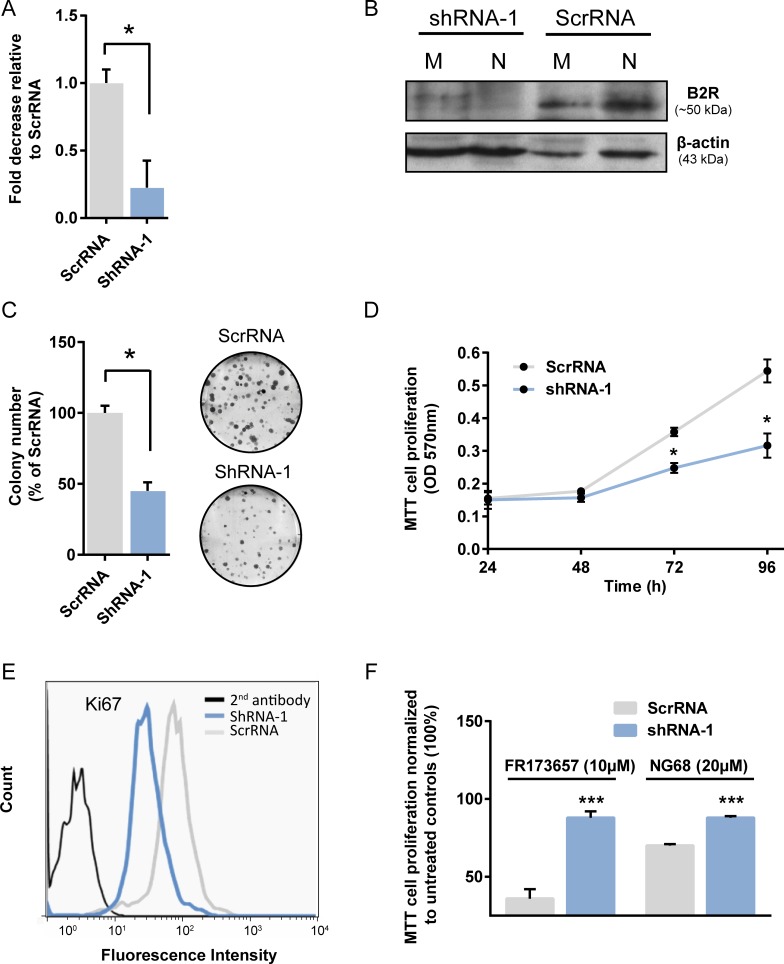
Figure 8. Stable B2R knockdown affects basal growth and cytocidal activity of CP-B2RAs in MDA-MB-231 cells.
(A–B) Knockdown efficiency of B2R was assessed using quantitative real-time PCR and western blot analyses. (A) Graph indicates the mean ± s.e.m. from 3 independent experiments. (B) The autoradiograms shown are representative of two experiments. (C–D) Effects of B2R depletion on clonogenic and proliferative potential of MDA-MB-231 cells under basal conditions. Clonogenicity and MTT cell proliferation experiments performed as described in Figures 3 and 4, and under Materials. (C) Graph indicates the mean ± s.e.m. from 3 independent experiments. Representative images of methylene blue-stained colonies of MDA-MB-231 cells expressing B2R shRNA or a scrambled shRNA are shown on the right side. (D) Data are as mean ± s.e.m. of 6–8 experiments. (E) Altered expression of the proliferation marker Ki67 in MDA-MB-231 B2R knockdown cells measured by FACS. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (F) Effects of B2R depletion on the cytostatic activities of CP-B2RAs against MDA-MB-231 cells determined by MTT assays. Data are as mean ± s.e.m. of 6–8 experiments. Basal viability of ScrRNA was comparable to that of shRNA-1 (not shown). All statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t-test for unpaired samples. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 versus the indicated group or corresponding time points.