Figure 2.
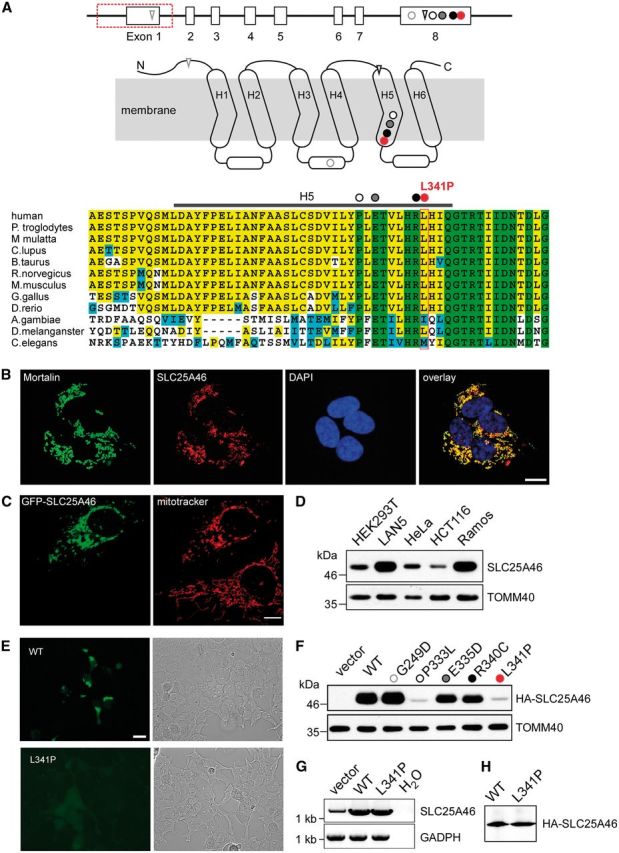
SLC25A46 localizes to the mitochondria with differential mutant protein stability. Genomic structure of SLC25A46, with 8 exons represented by open boxes and the exonic deletion demarcated by a red box along with the mutation c.1022T>C in red in relationship to other recently reported mutations: circle = missense; triangle = frameshift. Predicted membrane-spanning 2D structure of SLC25A46 with three sequence repeats (Repeat 1–3), each with two transmembrane helices linked by an elongated loop with a short alpha-helix. The homozygous nucleotide variant c.1022T>C identified in Family 1 is predicted to alter a highly conserved residue L341 in H5, represented by a red circle in the diagram as well as the alignment of protein sequences encoded by orthologues in human and other eukaryotic organisms. The homozygous 1897-nucleotide deletion identified in Family 2 is predicted to delete exon 1, which contains the start codon ATG, with the next in-frame ATG in exon 4 predicted to encode M147 in the H1-H2 linker. The four previously described missense mutations in exon 8 are predicted to alter highly conserved G249 (grey open circle) in the linker between H3 and H4, and in H5 P333 (black open circle), E335 (grey closed circle), and R340 (black closed circle). The two frameshift mutations in A are predicted to introduce premature stops in the N terminus and H5. (B) Localization to the mitochondria of SLC25A46 by immunohistochemical analysis. LAN5 cells were fixed and incubated with antibodies against the mitochondrial marker mortalin and SLC25A46. Cell nuclei were marked with DAPI (scale bar = 10 µm). (C) Mitochondrial localization of SLC25A46 by mitochondrial labelling with MitoTracker® in a transiently transfected HeLa cell overexpressing GFP-tagged SLC25A46. Note the fragmentation of the mitochondria in the cell overexpressing GFP-SLC25A46, in contrast to the typical extensive long tubular mitochondrial network in the cell below, which was not transfected and not overexpressing SLC25A46. (D) Western blotting analysis of differential SLC25A46 expression in isolated mitochondria from the indicated cell lines. TOMM40 is included as loading control. (E) Visualization under fluorescent microscopy (left) or bright field (right) of transiently transfected HEK293 cells with plasmid constructs for GFP-tagged wild-type (WT) or L341P mutant SLC25A46, demonstrating markedly diminished fluorescent signal intensity of the mutant transfected cells compared to that in cells transfected with the wild-type construct. (F) Western blot analysis of HA-tagged mutant compared to the wild-type SLC25A46 probed with anti-HA antibodies. HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with the pCDNA3 vector containing HA-tagged SLC25A46. TOMM40 is included as a blotting control. (G) Quantitative RT-PCR demonstrated comparable levels of the L341P mutant and the wild-type mRNA. (H) In vitro transcription and translation reaction was performed on the same mRNA as in G.
