Figure 3.
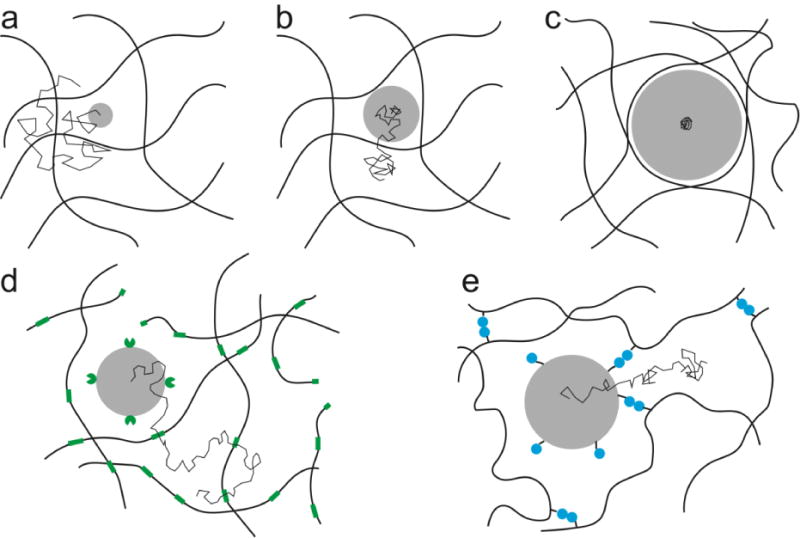
Steric effects on diffusion in gels (a-c) and mechanisms to modulate steric hindrance (d-e). Thin lines represent thermal motion of the particle. a) Particles smaller than the mesh size diffuse freely in interstitial fluid. b) Particles on the order of the mesh size have significant steric hindrance but eventually penetrate gels. c) Large particles are trapped. d) Particles that cleave gel polymers may diffuse more quickly. Notched green circles attached to particle are lytic enzymes; green segments of gel polymer are substrates for the enzymes. e) Particles may reversibly disrupt gel crosslinks (blue-blue contacts), allowing enhanced diffusion without irreversibly degrading the gel.
