Abstract
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common form of kidney cancer. While cure remains exceptionally infrequent in RCC patients with systemic or recurrent disease, current targeted molecular strategies, including multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), notably changed the treatment paradigm of advanced renal cancer. Yet, complete and durable responses have been noted in only a few cases. Our studies reveal that sunitinib triggers two resistance-promoting signaling pathways in RCC cells, which emanate from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response: a PERK-driven ER stress response that induces expression of the pro-tumorigenic cytokines IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α, and a TRAF2-mediated NF-κB survival program that protects tumor cells against cell death. PERK blockade completely prevents sunitinib-induced expression of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α, whereas NF-κB inhibition reinstates sensitivity of RCC cells to sunitinib both in vitro and in vivo. Taken together, our findings indicate that ER stress response may contribute to sunitinib resistance in RCC patients.
Introduction
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a lethal disease with rising incidence1. It is categorized into various subtypes, with clear cell RCC (ccRCC) representing about 75% of all RCC tumors2. Currently, there is no curative treatment for patients who present with metastatic disease or those who recur following definitive surgical therapy for localized ccRCC. Cure remains exceptionally rare in these patients. However, current targeted molecular strategies, including tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), have resulted in a doubling of progression-free survival and significant gains in overall survival (median 18–30 months), thereby fundamentally changing the treatment paradigm of advanced kidney cancer3,4. Unfortunately, about 21% of ccRCC patients are primarily refractory to the treatment with TKIs, showing neither disease stabilization nor clinical benefits2. Moreover, most patients that respond initially will typically progress within 12 months of starting therapy. Median overall survival in patients with metastatic ccRCC treated with TKIs remains in the region of 24 months5,6.
A family of NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa B) transcription factors functions as a key regulator of a variety of biological processes, including immunity, cell adaptation and survival, proliferation, and apoptosis7. Multiple studies have established the role of NF-κB regulated genes in malignant transformation, metastatic tumor progression and resistance to therapeutic regimens8. The aberrant activation of NF-κB results in upregulation of anti-apoptotic and pro-tumorigenic genes and promotes survival and migration of cancer cells8,9. A number of studies reported that constitutive NF-κB activity was observed in a variety of cancer types10. In addition, the activity of NF-κB may be induced by several stress factors including anticancer therapy11. A recent report by Tam et al. demonstrated a functional crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and activation of NF-κB12. ER functions include translation, modification and folding of secreted proteins. Misfolded proteins remain in the ER and are subjected to re-folding or degradation13. ER homeostasis may be disrupted by a variety of physiological and pathological stimuli resulting in accumulation of misfolded or unfolded proteins. Such accumulation, termed as ER stress, activates a cell signaling program, known as unfolded protein response (UPR), in order to restore ER homeostasis14. Activation of three types of ER stress sensors - protein kinase R (PKR)-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1α) and activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6)- by dissociation from ER chaperone, GRP78, induces the UPR15. Activated PERK phosphorylates translation initiation factor eIF2α, thus triggering suppression of protein translation. However, expression of ATF4 protein is increased upon activation of the PERK branch16. IRE1α represents the most evolutionary conservative branch of the UPR17. Activated IRE1α interacts with TRAF2, which results in downstream activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and NF-κB pathways12. In addition, an active RNAse domain of IRE1α exerts regulated IRE1α-dependent decay (RIDD of mRNA) activity. A transcription factor, X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1), which functions as for ER quality control genes, is generated by IRE1α-mediated processing of mRNA18,19. Activation of ATF6 depends on the dissociation from GRP78 and proteolytic cleavage. The cleaved ATF6 fragment translocates into the nucleus and upregulates transcription of target genes20. Recent studies demonstrate a link between ER stress and survival of cancer cells. The activation of pro-survival mechanisms by ER stress, such as an autophagy, may compromise the efficacy of anticancer therapy21. In contrast, persistent or severe ER stress results in apoptotic cell death22.
In the present study, we demonstrate, for the first time, that sunitinib triggers two resistance-promoting signaling pathways in ccRCC cells. These pathways emanate from the ER stress response: first, a PERK-driven ER stress response induces expression of the pro-tumorigenic cytokines interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Second, a TRAF2-mediated NF-κB transcriptional survival program protects tumor cells against cell death. PERK blockade using pharmacological or genetic approaches completely prevents sunitinib-induced expression of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α, whereas NF-κB inhibition reinstates sensitivity of ccRCC cells to sunitinib both in vitro and in vivo. Our findings suggest that induction of ER stress may contribute to TKI resistance in RCC patients.
Results
Sunitinib induces NF-κB activation and augments expression of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α
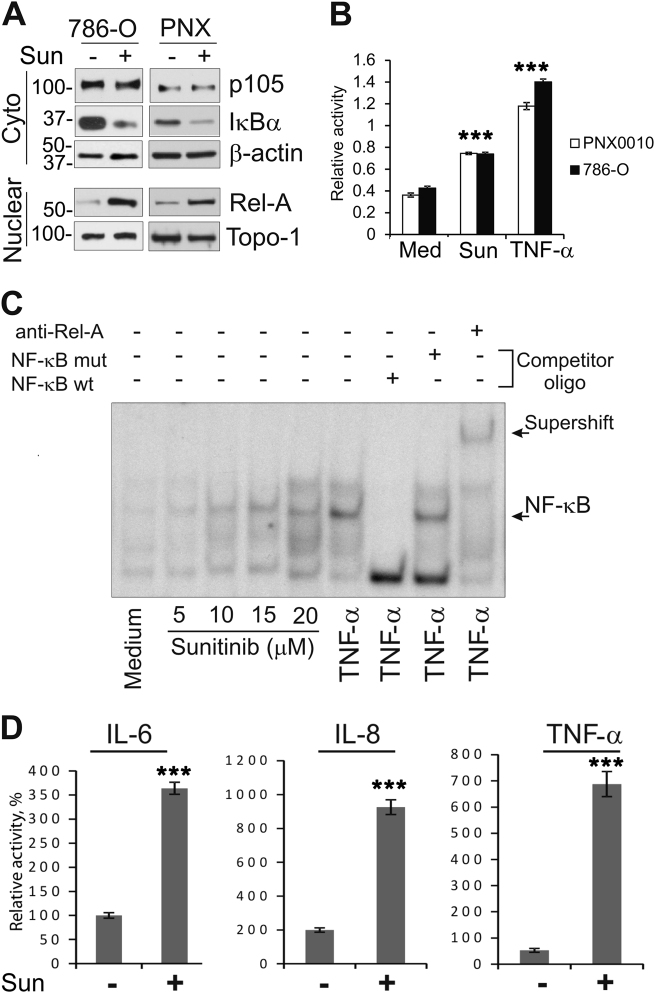
In addition to inhibition of angiogenesis, TKIs also exert a direct cytotoxic effect on tumor cells23–26. Importantly, studies by Gotink et al. using human clinical specimens established that intratumor sunitinib levels are significantly higher than the corresponding plasma concentrations (9.5 ± 2.4 μmol/L vs. 0.3 ± 0.1 μmol/L, respectively)23. Recent studies have shown that resistance of tumor cells to various therapeutic agents could be driven, at least in part, by the augmented activation of NF-κB signaling in response to drug exposure27. We evaluated the level of NF-κB activity in established 786-O and patient-derived PNX0010 ccRCC cells treated with sunitinib. Treatment with sunitinib triggered the activation of NF-κB in both 786-O and PNX0010 RCC cells as assessed by western blot analysis of nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts. Sunitinib-induced degradation of the inhibitory subunit IκBα is accompanied by the nuclear translocation of Rel-A (Fig. 1a). Importantly, we did not observe any noticeable changes in NF-κB1 (p105) levels (Fig. 1a). These findings indicate that treatment with sunitinib promotes activation of canonical but not non-canonical NF-κB signaling. The results of western blot analysis were validated using TransAm assay (Fig. 1b) and EMSA (Fig. 1c). We carried out supershift assays to demonstrate that the observed bands are specific for NF-κB (Fig. 1c). Notably, sunitinib-mediated NF-κB activation coincided with the elevated expression of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α (Fig. 1d).
Fig. 1. Treatment with sunitinib activates NF-κB and upregulates expression of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α in ccRCC cells.
a Sunitinib (Sun) induces degradation of IκBα and promotes nuclear translocation of Rel-A in 786-O and PNX0010 ccRCC cells. Cells were treated with 10 μM of sunitinib for 3 h. Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were subjected to western blot analysis using specific antibodies. b 786-O and PNX0010 cells were treated with 10 μM of sunitinib for 4 h. NF-κB (p65) DNA binding activity was examined using TransAM assay. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. ***P < 0.0001 when compared with cells cultured in medium only (Med). c 786-O cells were treated as described above. NF-κB activity was examined by EMSA in nuclear extracts prepared from 786-O cells. Supershift analysis using p50 antibody was performed to confirm that the observed bands are specific for NF-κB. d Sunitinib augments expression of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α in ccRCC cells. 786-O cells were treated with 10 μM of sunitinib for 10 h. The levels of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α were evaluated by ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. ***P < 0.0005 when compared with cells cultured in medium only
Sunitinib-mediated activation of NF-κB depends on the IRE1α/TRAF2/IKKβ axis of the ER stress response
Recent studies by Tam et al. indicate that activation of NF-κB may be triggered via ER stress response12. Therefore, we examined the potential contribution of the distinct branches of ER stress response in the regulation of sunitinib-mediated activation of NF-κB signaling. Sunitinib-induced NF-κB activation in 786-O RCC cells, as demonstrated by IκBα degradation and Rel-A phosphorylation, corresponds with the eIF2α phosphorylation, upregulation of ATF4 protein expression and dephosphorylation of IRE1α (Fig. 2a). Treatment with sunitinib and thapsigargin, a well-established ER stress inducer, in the presence or absence of either PERK inhibitor GSK2656157 or IRE1α inhibitor 4μ8C did not affect the expression level of Rel-A protein in 786-O cells (Supplementary Fig. 1). We also observed no changes in full-length and cleaved ATF6 protein levels (Fig. 2a), suggesting that the effect of sunitinib may be restricted to the IRE1α and PERK arms.
Fig. 2. Sunitinib activates ER stress response in ccRCC cells.
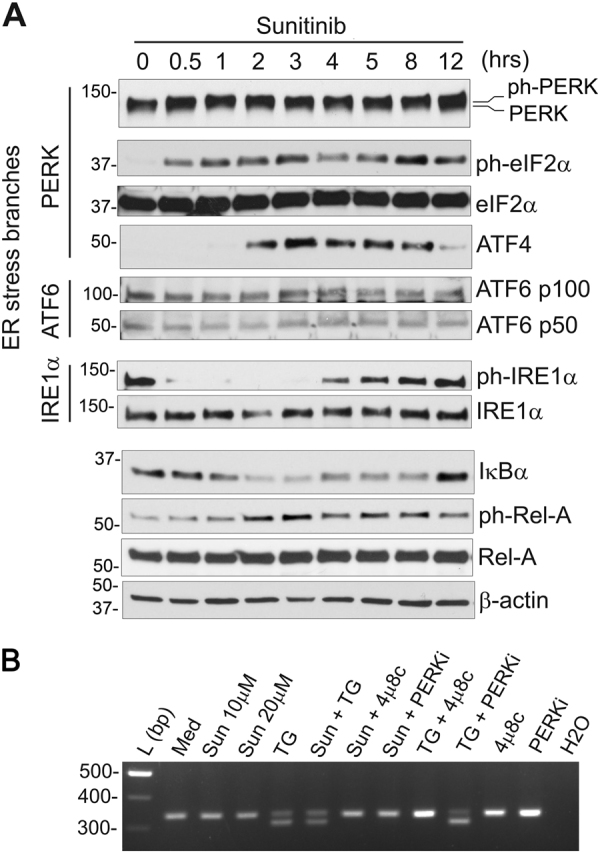
a Time-course of sunitinib-induced ER stress and NF-κB activation. 786-O ccRCC cells were treated with 10 μM of sunitinib for the indicated periods of time. Total cell lysates were subjected to western blot analysis using specific antibodies. b Treatment with sunitinib does not affect IRE1α-mediated Xbp1 splicing under ER stress conditions. 786-O cells were pre-treated with 5 μM of the PERK inhibitor GSK2656157 (PERKi) or 1 μM of the IRE1α inhibitor 4μ8c for 1 h followed by incubation in the presence or absence of sunitinib (10 μM) (Sun) or thapsigargin (1 μM) (TG) for 4 h. To explore whether treatment with sunitinib affects Xbp1 splicing under ER stress, 786-O cells were pre-incubated with sunitinib (10 μM) for 1 h followed by treatment with thapsigargin (1 μM) for 4 h. Total RNA was subjected to RT-PCR with specific primers spanning Xbp1 cleavage site. RT-PCR products were then separated in 2.5% agarose gel to detect spliced (lower band, 311 bp) and unspliced (upper band, 337 bp) fragments
Recent studies demonstrate that sunitinib inhibits autophosphorylation of IRE1α, but may stabilize the active conformation of IRE1α ATP-binding site28,29. Our studies support these findings demonstrating that sunitinib does not inhibit RNAse activity of IRE1α under ER stress conditions (Fig. 2b).
In order to further substantiate our findings, we generated IRE1α, PERK and TRAF2 knockout sub-lines of 786-O cells using CRISPR/Cas9 technology. 786-O cells with IKKβ knockout were used as a control. As expected, knockout of IKKβ completely abolished sunitinib-induced NF-κB activation (Fig. 3). Also, no activation of NF-κB was detected in 786-O-IRE1α and -TRAF2 knockout cell lines treated with sunitinib. In contrast, knockout of PERK had no effect on sunitinib-induced NF-κB activation (Fig. 3), indicating that PERK arm of the ER stress response is not involved in the regulation of the NF-κB activation under these conditions.
Fig. 3. Sunitinib-mediated NF-κB activation depends on IRE1α/TRAF2/IKKβ branch of ER stress.
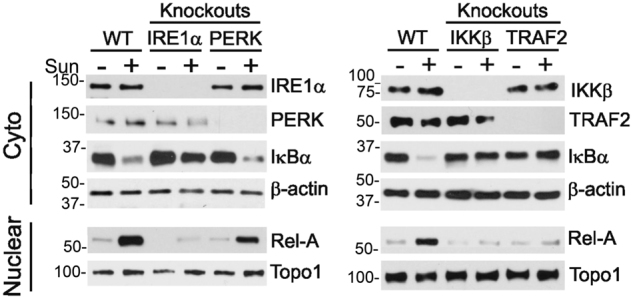
Wild type (WT) 786-O cells and their knockout counterparts were treated with 10 μM of sunitinib (Sun) for 3 h. Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were subjected to western blot analysis using specific antibodies
Critical roles of NF-κB and PERK branch of ER stress in sunitinib-mediated expression of pro-tumorigenic IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α cytokines
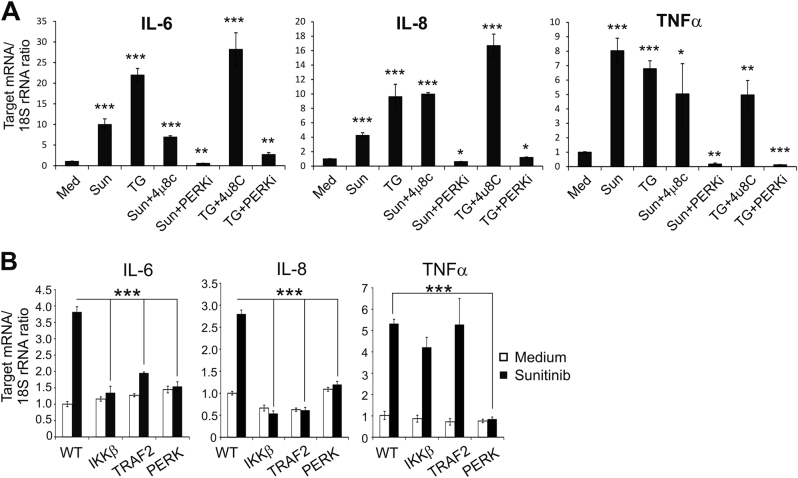
Both sunitinib and thapsigargin notably upregulated the expression of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α in 786-O cells (Fig. 4a). Pretreatment with a selective PERK inhibitor, GSK2656157, completely suppressed both thapsigargin and sunitinib-induced expression of all tested cytokines. In contrast, the addition of IRE1α inhibitor 4μ8C did not affect the expression levels of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α (Fig. 4a). These findings indicate that augmented expression of these molecules is mediated through the PERK branch of the ER stress.
Fig. 4. Sunitinib-induced expression of IL-6, IL-8 and TNFα depends on activation of PERK branch of ER stress.
a Induction of ER stress in ccRCC cells results in upregulation of IL-6, IL-8 and TNFα expression. 786-O cells were pre-treated with 5 μM of the PERK inhibitor, GSK2656157 (PERKi) or 1 μM of the IRE1α inhibitor 4μ8 C for 1 h followed by incubation in the presence or absence of sunitinib (10 μM) (Sun) or thapsigargin (1 μM) (TG) for 4 h. Cytokines expression levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. *P < 0.05; **P < 0,001; ***P < 0.0005 when compared with cells cultured in medium only (Med). b The effects of IKKβ, TRAF2 and PERK knockouts on sunitinib-induced cytokine production in 786-O cells. Wild-type (WT) 786-O cells and their knockout counterparts were treated with 10 μM of sunitinib for 3 h. Cytokines expression levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. ***P < 0.0005
Studies with IKKβ, TRAF2 and PERK knockout sub-lines of 786-O cells demonstrated that activation of both NF-κB and PERK was essential for sunitinib-induced production of IL-6 and IL-8 in tumor cells (Fig. 4b). In contrast, the expression of TNF-α was dependent on PERK activity only (Fig. 4b). These findings suggest that both NF-κB and PERK may serve as attractive therapeutic targets to modulate TKI-induced cytokine response in RCC tumors.
Activation of NF-κB promotes survival of RCC cells during sunitinib treatment
Short hairpin RNA-mediated knockdown of IKKβ or expression of dominant-negative (DN) IκBα reinstated sensitivity of 786-O cells to sunitinib-induced apoptosis (Fig. 5a). Furthermore, treatment with IKKβ inhibitor, IKK-16, also overcame resistance to sunitinib and sorafenib in 786-O cells (Fig. 5b). Interestingly, the results of quantitative reverse transcriptase-PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis did not reveal substantial changes in the expression levels of pro- and anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members in sunitinib-treated 786-O cells (Supplementary Fig. 2). Taken together, our results suggest that NF-κB activation is essential for survival of RCC cells upon TKIs treatment, whereas PERK activity is critical for the production of pro-tumorigenic cytokines by tumor cells. To corroborate our in vitro finding, we examined the effect of concomitant treatment with IKK-16 and sunitinib on tumor growth using PNX0010 RCC xenograft model. The combined treatment with IKK-16 and sunitinib notably inhibited growth of PNX0010 tumors (Fig. 6). Importantly, this treatment was well tolerated by all experimental animals. These data support our hypothesis that NF-κB contributes to the activation of intrinsic resistance mechanisms promoting RCC cell survival during TKI treatment.
Fig. 5. NF-κB activation promotes survival of ccRCC cells treated with sunitinib.
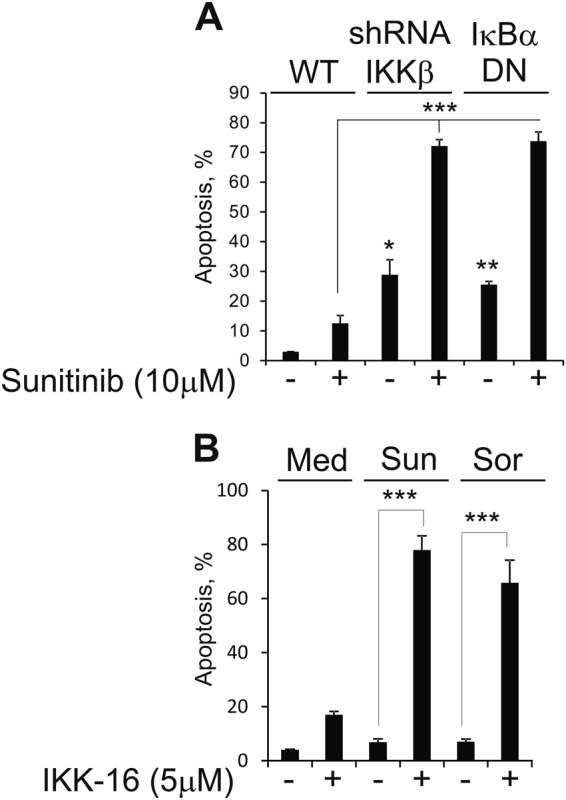
a Wild type (WT) 786-O cells, IKKβ knockout subline and cells expressing HA-tagged dominant-negative mutant IκBα (S32A/S36A) were treated with 10 μM of sunitinib for 24 h. Apoptosis was examined using APO-BRDU kit followed by flow cytometry analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. *P = 0.0002; **P < 0.0001; ***P < 0.0001 when compared with WT 786-O cells treated with sunitinib. b 786-O cells were treated with either 10 μM of sunitinib (Sun) or 10 μM of sorafenib (Sor) for 24 h with or without IKKβ inhibitor, IKK-16 (5 μM). Apoptosis was examined using APO-BRDU kit followed by flow cytometry analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± S.D. ***P < 0.0001.
Fig. 6. Treatment with IKK-16 overcomes resistance to sunitinib in a xenograft animal model of human ccRCC.
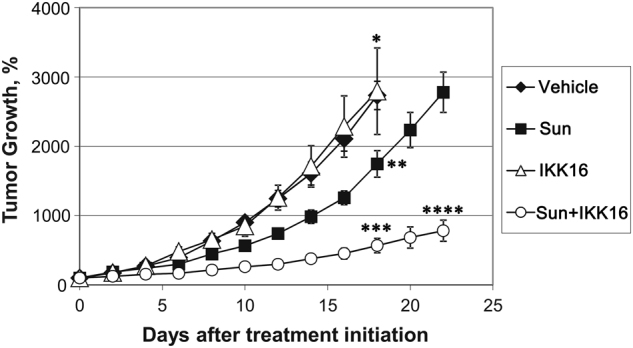
Subcutaneous PNX0010 tumors were established in 6-week-old male C.B17icr-scid mice. Treatment with sunitinib (Sun), IKK-16 or combination was carried out as described in Materials and methods section. Values are means (n = 5) ±SEM. *P = 0.0069 when compared vehicle with sunitinib treatment; **P < 0.0001 when compared sunitinib with sunitinib + IKK-16 treatment; ***P < 0.0001 when compared vehicle with sunitinib + IKK-16 treatment; ****P < 0.0001 when compared sunitinib with sunitinib + IKK-16 treatment at the end of the experiment.
Discussion
There are two fundamental mechanisms underlining resistance of RCC to TKIs. First, extrinsic mechanisms bypass TKI-mediated antiangiogenic activity by providing alternative means for TKI-resistant intra-tumoral blood vessel growth. For instance, production of alternative pro-angiogenic factors, such as fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) and placenta growth factor (PlGF), or downregulation of angiostatic chemokines, such as Cxcl9, or induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, that is, IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, by tumor cells have been implicated in the mechanisms of TKI resistance30–32. Second, intrinsic mechanisms of TKI resistance include activation of alternative pro-survival signaling pathways within the tumor cells that make these cells refractory to TKI-mediated death. NF-κB is one of the most important cell survival pathways known to play a critical role in resistance to chemo- and radiotherapy in various solid and hematologic malignancies33–35.
Along with others, we have demonstrated that, in addition to the inhibition of angiogenesis, sunitinib can exert a direct cytotoxic effect on tumor cells23–26. Our current findings indicate that sunitinib triggers two resistance-promoting signaling pathways in RCC cells, both of which emanate from the ER stress response: a PERK-driven ER stress response that induces expression of the pro-tumorigenic cytokines IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α, and a TRAF2-mediated NF-κB transcriptional survival program that protects tumor cells against cell death (Fig. 7). Potentially, ER stress may activate NF-κB, at least in part, indirectly via autocrine TNF-α production. However, this possibility can be excluded based on our findings showing that knockout of PERK does not affect sunitinib-mediated NF-κB activation in 786-O cells (Fig. 3), despite the fact that PERK knockout or pretreatment of cells with PERK inhibitor, GSK2656157 (Figs. 4a, b) results in complete inhibition of TNF-α production.
Fig. 7.
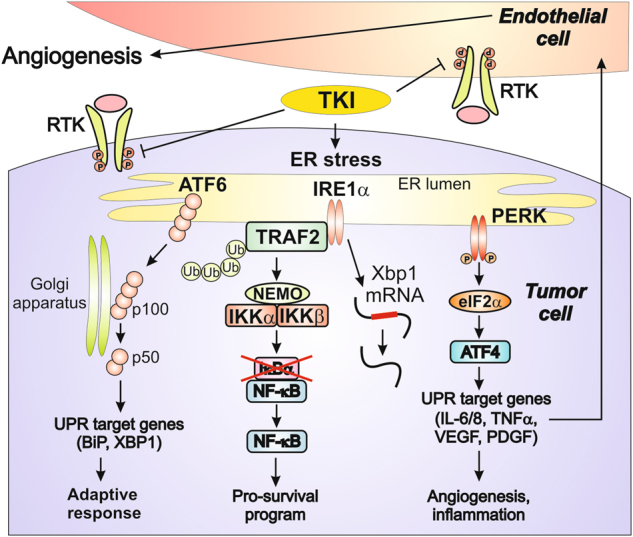
Potential mechanisms of TKI-mediated activation of ER stress and NF-κB signaling
Similar to data obtained by Tam et al., our experiments demonstrate that sunitinib-mediated activation of NF-κB depends on IRE1α branch of ER stress. Indeed, knockout of IRE1α dramatically affects NF-κB activity induced by sunitinib12. Our studies indicate that IRE1α-dependent activation of NF-κB in sunitinib-treated cells occurs concomitantly with reduction of IRE1α phosphorylation. Normally, IRE1α’s RNAse activity depends on its kinase trans-autophosphorylation36. However, sunitinib may stimulate IRE1α RNAse activity independently of its trans-autophosphorylation by stabilizing the active conformation of its ATP-binding site28,29. Our data indicate that sunitinib suppressed IRE1α kinase activity, but did not affect its RNAse activity. We therefore hypothesize that, in spite of the negative effect of sunitinib on IRE1α phosphorylation, sunitinib stabilizes its active conformation, thereby facilitating interaction with TRAF2 resulting in IKKβ-dependent activation of NF-κB.
It was reported previously that treatment with TKIs results in upregulation of pro-angiogenic and pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α24,32,37. Our current study demonstrates that, in addition to the well-established NF-κB-dependent regulation of IL-6 and IL-8 expression, PERK activity is also critical for the augmented expression of these cytokines upon treatment with sunitinib. Our data indicate that the sunitinib-induced expression of TNF-α depends on PERK activity only. Indeed, downregulation of NF-κB activation via TRAF2 or IKKβ knockout failed to prevent sunitinib-mediated upregulation of TNF-α expression. However, treatment with a selective PERK inhibitor, GSK2656157, completely suppressed both thapsigargin- and sunitinib-mediated expression of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α. Our data are in strong agreement with the recent study by Wang et al. demonstrating that PERK/ATF4 branch of ER stress controls angiogenic switch in human cancer cells in response to glucose deprivation38. Therefore, PERK could serve as an attractive therapeutic target to modulate TKI-induced cytokine response.
Our study demonstrates for the first time that sunitinib activates NF-κB signaling via IRE1α-mediated mechanism. Knockout of IRE1α completely blocked sunitinib-induced NF-κB activation in 786-O cells (Fig. 3). In addition, our findings indicate that, although PERK activity is essential for sunitinib-mediated expression of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α, such activity is dispensable for cell survival. Indeed, pretreatment of 786-O cells with PERK inhibitor GSK2656157 failed to sensitize cells to sunitinib (data not shown). A recent study by Han et al. suggested pro-survival effect of PERK/eIF2α branch of ER stress pathway39. The authors reported that BiP/GRP78 depletion results in decreased PERK phosphorylation and suppression of activity of its downstream target, eIF2α. However, these findings are in strong controversy with general biological functions of BiP/GRP78. This chaperone acts as the main binding partner of three ER sensors, specifically ATF6, IRE1α and PERK, keeping them inactive in sequestration40,41. Moreover, a number of publications documented that depletion of BiP/GRP78 results in activation of ER stress pathways, including PERK branch42,43.
The current study demonstrates for the first time that sunitinib induces two resistance-promoting signaling pathways, both of which originate from the ER stress response: a PERK-driven pathway that regulates the expression of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α cytokines, and a TRAF2-mediated NF-κB pro-survival pathway. Taken together, our findings indicate that ER stress response may contribute to sunitinib resistance in RCC patients.
Materials and methods
Cells and culture conditions
The 786-O human ccRCC cells (CRL-1932) and the 293T human embryonic kidney cells (CRL-3216) were obtained from ATCC (Rockville, MD). Authentication of 786-O and 293T cells were performed by IDEXX BioResearch (West Sacramento, CA). The PNX0010 patient-derived ccRCC cell line44 was a kind gift of Vladimir Khazak, Ph.D. (Priaxon Inc., Philadelphia, PA). Initial stocks were cryopreserved, and at every 6-month interval a fresh aliquot of frozen cells was used for the experiments. Cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 (Bio-Whittaker, Walkersville, MD) supplemented with 10% FBS (Hyclone, Logan, UT), penicillin (100 U/ml), streptomycin (100 μg/ml), sodium pyruvate (1 mM) and non-essential amino acids (0.1 mM) under conditions indicated in the figure legends.
Antibodies and reagents
Antibodies to Rel-A (#8242), phospho-Rel-A (S536) (#3033), NF-κB1 (p105/p50) (#13586), TRAF2 (#4712), IKKβ (#8943), IRE1α (#3294), PERK (#5683), eIF2α (#5234), phospho-eIF2α (S51) (#9721) and ATF4 (#11815) were obtained from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA). ATF6 (sc-22799), Topo-1 (sc-32736), IκBα (sc-203), β-actin (sc-130300) and HA-probe (sc-7392) antibodies were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc. (Santa Cruz, CA). Phospho-IRE1α (S724) (#GTX63722) antibody was obtained from GeneTex (Irvine, CA). IKK-16 (#S2882) and GSK2656157 (#S7033) were obtained from Selleckchem (Radnor, PA). Sunitinib (#S-8803) was obtained from LC Laboratories (Woburn, MA). TNF-α (#CYT-223) was obtained from ProSpec (East Brunswick, NJ). 4μ8C (#412512) was obtained from Calbiochem (Burlington, MA).
Western blot analysis
Cell lysates preparation and western blot analysis were performed as described previously45.
ESMA and Gel-Supershift assays
ESMA and Gel-Supershift assays were performed as described previously46.
qRT-PCR and Xbp1 splicing analysis
Total RNA was isolated using Quick-RNA™ MiniPrep (#R1054) (Zymo Research, Orange, CA) following DNase I (#M0303S) (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA) treatment. Then, RNA was purified using RNA Clean and Concentrator Kit (#R1015) (Zymo Research, Orange, CA). Total RNA (1 μg) was reverse transcribed in final volume of 20 μl with 100 U of Superscript III Reverse Transcriptase (#18080-051) (Life Science, Gaithersburg, MD) and 75 ng of random hexamer primers according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After reverse transcription, complementary DNA (cDNA) samples were diluted 40 times and 5 μl of diluted cDNA were amplified by real-time PCR using TNF-α TaqMan Gene Expression Assay (ID# Hs.PT.58.45380900), IL-6 TaqMan Gene Expression Assay (ID# Hs.PT.53a.24948568), IL-8 TaqMan Gene Expression Assay (ID# Hs.PT.56a.39926886.g), Bcl-2 TaqMan Gene Expression Assay (ID# Hs.PT.56a.654557.g), Bcl-2A1 TaqMan Gene Expression Assay (ID# Hs.PT.56a.1995943), BIM TaqMan Gene Expression Assay (ID# Hs.PT.58.27975199) and Mcl1 TaqMan Gene Expression Assay (ID# Hs.PT.58.1431437). Custom 18S rRNA Mini qPCR assay was used as internal amplification control. The amplicon was detected with a forward primer 5′-GCTCTTTCTCGATTCCGT-3′, reverse primer 5′-CCAGAGTCTCGTTCGTTATC-3′ and probe 5′-TTCTTAGTTGGTGGAGCGATTTGT-3′ labeled with 6-FAM and quenched with Jowa-Black FQ. All assays and primers were obtained from IDT DNA Technologies (Coralville, IA). Each sample was run in triplicate for each gene in a 20 μl reaction using TaqMan Gene Expression Master Mix according to the manufacturer’s instructions (#4369016) (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). Reactions were carried out in an Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR System. Relative expression was analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCt method47.
For Xbp1 splicing analysis, 1 μl of reverse transcription reaction mixture was amplified with specific primers spanning Xbp1 cleavage site (forward 5′-AGCAAGTGGTAGATTTAGAAGA-3′ and reverse 5′- GTCCAAGTTGTCCAGAATG-3′). RT-PCR products were then separated in 2.5% agarose gel to detect spliced (311 bp) and unspliced (337 bp) fragments.
Generation of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout cell lines
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout was performed using pLentiCRISPRv2 lentiviral vector48 (Addgene plasmid # 52961, a gift from Feng Zhang). Double-stranded DNA oligos (Supplementary materials, Table 1) targeting the desired genomic region were cloned into pLentiCRISPRv2 following the protocol provided by F. Zhang laboratory (available online at www.addgene.org). 293T cells were concomitantly transfected with following plasmids, pLentiCRISPRv2, psPAX2 (Addgene plasmid # 12260) and pVSV-G (Clontech, Mountain View, CA) using TransIT-2020 Transfection reagent (MIR 5400) (Mirus, Madison, WI). Supernatant of 293T cells containing lentiviral particles was collected 48 h after transfection and filtered through 0.22 μm PVDF syringe filters. The infection of 786-O cells was performed in 10 cm dishes in presence of 4 μg/ml Polybrene (Hexadimethrine bromide) in 9 ml of cellular media by addition of 1 ml of 293T filtered supernatant. Forty-eight hours after infection, puromycin (1 μg/ml) was added to the cellular media for further selection of infected cells. After 10–14 days, cells were analyzed by western blotting for the knockouts efficacy.
Generation of cells expressing DN IκBα
Open Reading Frame of DN IκBα (S32A/S36A) was amplified using pCMV-IκBα(S32A/S36A)-HA vector (a kind gift from N. Dulin, Ph.D., University of Chicago, IL) as a template and re-cloned into pLV-CMV-H4-puro lentiviral construct. Generation of lentiviral particles and infection of 786-O cells was performed as described previously49.
Analysis of apoptosis
DNA fragmentation was detected using APO-BRDU kit (#AU1001) (The Phoenix Flow Systems, Inc., San Diego, CA) as described previously50.
Measurement of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α proteins
IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α protein levels in cell culture supernatants were determined by ELISA kits (#D6050, #D8000C and #DTA00C, respectively) (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN).
Assessment of in vivo tumor growth
For in vivo studies, 2 × 106 of PNX0010 cells were injected subcutaneously in the flank region of 6-week-old male C.B17/icr-scid mice using a 27-gauge needle. All animal procedures were done in accordance with institutional guidelines on animal care and with appropriate institutional certification. Animals were fed sterile AIN-93M diet (Harlan Teklad, Madison, WI) and water ad libitum. Ten days after the injection of tumor cells, animals were randomly assigned to the control or experimental groups (n = 5 mice/group). The mice were treated daily with (i) 0.15 M NaCl with 2% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) solution (vehicle); (ii) sunitinib malate (20 mg/kg in 0.15 M NaCl with 2% DMSO solution, P.O.); (iii) IKK-16 (10 mg/kg, in 0.15 M NaCl with 2% DMSO, I.P.); or (iv) sunitinib and IKK-16 combined. Tumors were measured twice weekly and their volumes were calculated by the formula: [volume = 0.52 × (width)2 × length].
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables are presented as mean (±SD). Comparison of continuous variables was performed using a two-sided Student’s t-test. A P-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support of the Laboratory Animal Facility at Fox Chase Cancer Center. We thank Dr. N. Dulin for pCMV-IκBα(S32A/S36A)-HA vector. This work was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health Grants RO3 CA216173 (to PM) and RO3 CA167671 (to VMK), and the Department of Defense Impact Award PC160049 (to VMK).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Edited by T. Kaufmann
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper at (10.1038/s41419-018-0388-1).
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Edited by T Kaufmann.
References
- 1.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016;66:7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Duran I, et al. Resistance to targeted therapies in renal cancer: the importance of changing the mechanism of action. Target. Oncol. 2017;12:19–35. doi: 10.1007/s11523-016-0463-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rini BI. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma: many treatment options, one patient. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009;27:3225–3234. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.19.9836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Rini BI. New strategies in kidney cancer: therapeutic advances through understanding the molecular basis of response and resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010;16:1348–1354. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bridgeman VL, et al. Preclinical evidence that trametinib enhances the response to antiangiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitors in renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016;15:172–183. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Motzer RJ, McCann L, Deen K. Pazopanib versus sunitinib in renal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013;369:1970–731. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1303989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hoesel B, Schmid JA. The complexity of NF-kappa B signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer. 2013;12:86. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chaturvedi MM, Sung B, Yadav VR, Kannappan R, Aggarwal BB. NF-kappaB addiction and its role in cancer: ‘one size does not fit all’. Oncogene. 2011;30:1615–1630. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Oya M, et al. Increased nuclear factor-kappa B activation is related to the tumor development of renal cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2003;24:377–384. doi: 10.1093/carcin/24.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wu D, et al. NF-kappaB expression and outcomes in solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. 2015;94:e1687. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang CY, Cusack JC, Jr., Liu R, Baldwin AS., Jr. Control of inducible chemoresistance: enhanced anti-tumor therapy through increased apoptosis by inhibition of NF-kappaB. Nat. Med. 1999;5:412–417. doi: 10.1038/7410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tam AB, Mercado EL, Hoffmann A, Niwa M. ER stress activates NF-kappaB by integrating functions of basal IKK activity, IRE1 and PERK. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e45078. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Anelli T, Sitia R. Protein quality control in the early secretory pathway. EMBO J. 2008;27:315–327. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kim I, Xu W, Reed JC. Cell death and endoplasmic reticulum stress: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008;7:1013–1030. doi: 10.1038/nrd2755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gardner BM, Pincus D, Gotthardt K, Gallagher CM, Walter P. Endoplasmic reticulum stress sensing in the unfolded protein response. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013;5:a013169–a013169. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a013169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kilberg MS, Shan J, Su N. ATF4-dependent transcription mediates signaling of amino acid limitation. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009;20:436–443. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2009.05.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mori K. Signalling pathways in the unfolded protein response: development from yeast to mammals. J. Biochem. 2009;146:743–750. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvp166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Acosta-Alvear D, et al. XBP1 controls diverse cell type- and condition-specific transcriptional regulatory networks. Mol. Cell. 2007;27:53–66. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.06.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Maurel M, Chevet E, Tavernier J, Gerlo S. Getting RIDD of RNA: IRE1 in cell fate regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014;39:245–254. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Maurel M, et al. Controlling the unfolded protein response-mediated life and death decisions in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015;33:57–66. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mahoney E, Byrd JC, Johnson AJ. Autophagy and ER stress play an essential role in the mechanism of action and drug resistance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor flavopiridol. Autophagy. 2013;9:434–435. doi: 10.4161/auto.23027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rao RV, et al. Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program: role of the ER chaperone GRP78. FEBS Lett. 2002;514:122–128. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02289-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gotink KJ, et al. Lysosomal sequestration of sunitinib: a novel mechanism of drug resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011;17:7337–7346. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kutikov A, et al. Interleukin-6: a potential biomarker of resistance to multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Urology. 2011;78(968):e967–911. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2011.07.1384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Makhov PB, et al. Modulation of Akt/mTOR signaling overcomes sunitinib resistance in renal and prostate cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012;11:1510–1517. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Xin H, et al. Sunitinib inhibition of Stat3 induces renal cell carcinoma tumor cell apoptosis and reduces immunosuppressive cells. Cancer Res. 2009;69:2506–2513. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Nakanishi C, Toi M. Nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitors as sensitizers to anticancer drugs. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2005;5:297–309. doi: 10.1038/nrc1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wang L, et al. Divergent allosteric control of the IRE1alpha endoribonuclease using kinase inhibitors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012;8:982–989. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Han D, et al. IRE1alpha kinase activation modes control alternate endoribonuclease outputs to determine divergent cell fates. Cell. 2009;138:562–575. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bhatt RS, et al. Renal cancer resistance to antiangiogenic therapy is delayed by restoration of angiostatic signaling. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010;9:2793–2802. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Casanovas O, Hicklin DJ, Bergers G, Hanahan D. Drug resistance by evasion of antiangiogenic targeting of VEGF signaling in late-stage pancreatic islet tumors. Cancer Cell. 2005;8:299–309. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2005.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Huang D, et al. Interleukin-8 mediates resistance to antiangiogenic agent sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010;70:1063–1071. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kim DS, Park SS, Nam BH, Kim IH, Kim SY. Reversal of drug resistance in breast cancer cells by transglutaminase 2 inhibition and nuclear factor-kappaB inactivation. Cancer Res. 2006;66:10936–10943. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rushworth SA, et al. The high Nrf2 expression in human acute myeloid leukemia is driven by NF-kappaB and underlies its chemo-resistance. Blood. 2012;120:5188–5198. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-04-422121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Veuger SJ, Hunter JE, Durkacz BW. Ionizing radiation-induced NF-kappaB activation requires PARP-1 function to confer radioresistance. Oncogene. 2009;28:832–842. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ali MM, et al. Structure of the Ire1 autophosphorylation complex and implications for the unfolded protein response. EMBO J. 2011;30:894–905. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mikami S, et al. Expression of TNF-alpha and CD44 is implicated in poor prognosis, cancer cell invasion, metastasis and resistance to the sunitinib treatment in clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Int J. Cancer. 2015;136:1504–1514. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wang Y, et al. The unfolded protein response induces the angiogenic switch in human tumor cells through the PERK/ATF4 pathway. Cancer Res. 2012;72:5396–5406. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Han KS, et al. Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum chaperone protein glucose-regulated protein 78 potentiates antiangiogenic therapy in renal cell carcinoma through inactivation of the PERK/eIF2alpha pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6:34818–34830. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lee AS. The ER chaperone and signaling regulator GRP78/BiP as a monitor of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Methods. 2005;35:373–381. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2004.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wang M, Wey S, Zhang Y, Ye R, Lee AS. Role of the unfolded protein response regulator GRP78/BiP in development, cancer, and neurological disorders. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2009;11:2307–2316. doi: 10.1089/ars.2009.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Booth L, et al. OSU-03012 suppresses GRP78/BiP expression that causes PERK-dependent increases in tumor cell killing. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2012;13:224–236. doi: 10.4161/cbt.13.4.18877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Paton AW, et al. AB5 subtilase cytotoxin inactivates the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP. Nature. 2006;443:548–552. doi: 10.1038/nature05124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kirsanov KI, et al. Minor grove binding ligands disrupt PARP-1 activation pathways. Oncotarget. 2014;5:428–437. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Uzzo RG, et al. Zinc inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB activation and sensitizes prostate cancer cells to cytotoxic agents. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002;8:3579–3583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Golovine K, et al. Overexpression of the zinc uptake transporter hZIP1 inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB and reduces the malignant potential of prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008;14:5376–5384. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sanjana NE, Shalem O, Zhang F. Improved vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat. Methods. 2014;11:783–784. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Makhov P, et al. Piperlongumine promotes autophagy via inhibition of Akt/mTOR signalling and mediates cancer cell death. Br. J. Cancer. 2014;110:899–907. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Makhov P, et al. Zinc chelation induces rapid depletion of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis and sensitizes prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15:1745–1751. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2008.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.