ABSTRACT
Darunavir (DRV) has bimodal activity against HIV-1 protease, enzymatic inhibition and protease dimerization inhibition, and has an extremely high genetic barrier against development of drug resistance. We previously generated a highly DRV-resistant HIV-1 variant (HIVDRVRP51). We also reported that four amino acid substitutions (V32I, L33F, I54M, and I84V) identified in the protease of HIVDRVRP51 are largely responsible for its high-level resistance to DRV. Here, we attempted to elucidate the role of each of the four amino acid substitutions in the development of DRV resistance. We found that V32I is a key substitution, which rarely occurs, but once it occurs, it predisposes HIV-1 to develop high-level DRV resistance. When two infectious recombinant HIV-1 clones carrying I54M and I84V (rHIVI54M and rHIVI84V, respectively) were selected in the presence of DRV, V32I emerged, and the virus rapidly developed high-level DRV resistance. rHIVV32I also developed high-level DRV resistance. However, wild-type HIVNL4-3 (rHIVWT) failed to acquire V32I and did not develop DRV resistance. Compared to rHIVWT, rHIVV32I was highly susceptible to DRV and had significantly reduced fitness, explaining why V32I did not emerge upon selection of rHIVWT with DRV. When the only substitution is at residue 32, structural analysis revealed much stronger van der Waals interactions between DRV and I-32 than between DRV and V-32. These results suggest that V32I is a critical amino acid substitution in multiple pathways toward HIV-1’s DRV resistance development and elucidate, at least in part, a mechanism of DRV’s high genetic barrier to development of drug resistance. The results also show that attention should be paid to the initiation or continuation of DRV-containing regimens in people with HIV-1 containing the V32I substitution.
KEYWORDS: darunavir, genetic barrier, drug resistance, dual mechanism, HIV-1, V32I, protease inhibitors
IMPORTANCE
Darunavir (DRV) is the only protease inhibitor (PI) recommended as a first-line therapeutic and represents the most widely used PI for treating HIV-1-infected individuals. DRV possesses a high genetic barrier to development of HIV-1’s drug resistance. However, the mechanism(s) of the DRV’s high genetic barrier remains unclear. Here, we show that the preexistence of certain single amino acid substitutions such as V32I, I54M, A71V, and I84V in HIV-1 protease facilitates the development of high-level DRV resistance. Interestingly, all in vitro-selected highly DRV-resistant HIV-1 variants acquired V32I but never emerged in wild-type HIV (HIVWT), and V32I itself rendered HIV-1 more sensitive to DRV and reduced viral fitness compared to HIVWT, strongly suggesting that the emergence of V32I plays a critical role in the development of HIV-1’s resistance to DRV. Our results would be of benefit in the treatment of HIV-1-infected patients receiving DRV-containing regimens.
INTRODUCTION
Combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) for HIV-1 infection and AIDS available at this time potently suppresses the replication of HIV-1 and significantly extends the life expectancy of HIV-1-infected individuals (1, 2). However, our ability to provide effective long-term cART remains a complex issue, since many of those individuals who initially achieve favorable viral suppression to undetected levels eventually suffer treatment failure. Nevertheless, in regard to the propensity of HIV-1 to develop resistance to antiretroviral agents, protease inhibitors (PIs) generally have high genetic barrier against resistance. In particular, the latest FDA-approved PI, darunavir (DRV), the only PI recommended for first-line therapy (3), has a favorable genetic barrier apparently because of its dual mechanism of action, (i) protease enzymatic inhibition activity and (ii) protease dimerization inhibition activity (4–6), and it currently represents the most widely used PI for treating HIV-1-infected individuals. Indeed, it has been shown that multiple attempts to select HIV-1 variants resistant to DRV have failed when such selection attempts were made using a single wild-type HIV-1 strain as a starting virus population (7–12), although DRV resistance has been observed clinically (13, 14). In this regard, we previously generated highly DRV-resistant HIV-1 variants in vitro (HIV-1DRVRP10, HIV-1DRVRP30, and HIV-1DRVRP51) by employing a mixture of eight multidrug-resistant HIV-1 variants as a starting HIV-1 population (8). The most DRV-resistant isolate, HIV-1DRVRP51, had acquired four major amino acid substitutions in its protease (V32I, L33F, I54M, and I84V), which have been shown to be responsible for the DRV resistance of HIV-1DRVRP51 (5, 6). Moreover, the emergence of DRV-resistant HIV-1 variants has also been reported in patients receiving long-term DRV-containing cART (13), and those with such DRV-resistant HIV-1 variants have experienced treatment failure (14).
In the present study, we attempted to elucidate the mechanism by which HIV-1 eventually acquires resistance to DRV. We demonstrate that one of the four critical amino acid substitutions, V32I, serves as a key substitution, which rarely occurs in in vitro selection attempts, but once it occurs, it predisposes HIV-1 to develop high-level DRV resistance. The present data not only explain the mechanisms of DRV’s high genetic barrier well but also suggest that the initiation or continuation of DRV-containing regimens in individuals harboring HIV-1 variants with a V32I substitution must be carefully considered and monitored.
RESULTS
Failure of selection of DRV-resistant HIV-1 variants as wild-type HIV-1 strains were used as starting virus populations.
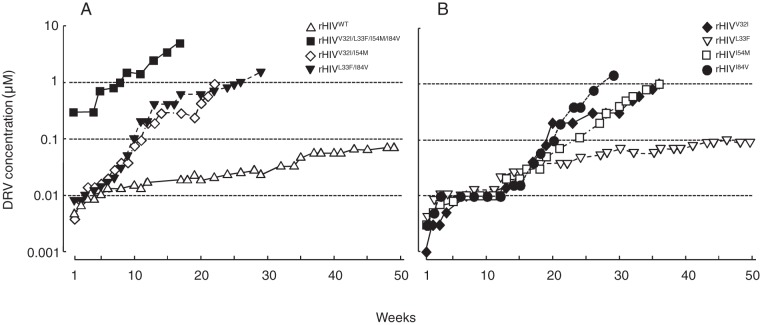
Our group and others have previously reported that the selection of wild-type HIV-1 strains in the presence of each of eight FDA-approved protease inhibitors (PIs) (ritonavir, indinavir, nelfinavir, saquinavir, amprenavir [APV], lopinavir, tipranavir, and atazanavir) readily gave HIV-1 variants resistant to each PI over 20 to 67 weeks (7–10, 15, 16). However, when HIV-1 was selected against DRV using standardized selection protocols, the development of HIV-1 variants resistant to DRV was not seen or much delayed, and no significant DRV resistance-associated amino acid substitutions were identified (7–12). Figure 1A shows that during selection of an infectious HIV-1NL4-3 clone (rHIVWT) in the presence of DRV, rHIVWT failed to replicate in the presence of >0.075 μM DRV even after 50 weeks of selection, in line with our previous findings (8–11).
FIG 1 .
In vitro selection of highly DRV-resistant variants using various infectious HIV-1 clones. The impact of four amino acid substitutions, V32I, L33F, I54M, and I84V, on the development of DRV resistance was examined. (A and B) rHIVWT, rHIVV32I/I54M, rHIVL33F/I84V, and rHIVV32I/L33F/I54M/I84V (A) and rHIVV32I, rHIVL33F, rHIVI54M, and rHIVI84V (B) were propagated in the presence of increasing concentrations of DRV in MT-4 cells. At the conclusion of each passage, cell-free supernatant was harvested from the culture and subsequently added to a following culture replenished with the same number of uninfected target cells, and the virus was further propagated. This passage was repeated every 1 to 3 weeks for a total of 17 to 50 weeks.
As previously reported, the highly DRV-resistant HIV-1 variant, HIVDRVRP51, contains four major DRV resistance-associated amino acid substitutions (V32I, L33F, I54M, and I84V) in its protease (8), which are responsible for the loss of DRV’s protease dimerization inhibition activity (5). However, the role of each of the four substitutions in the development of HIV-1’s DRV resistance has remained to be determined. Thus, we newly generated a panel of recombinant infectious HIV-1 clones using the site-directed mutagenesis method. When three such recombinant clones (rHIVV32I/L33F/I54M/I84V, rHIVV32I/I54M, and rHIVL33F/I84V) were propagated in increasing concentrations of DRV, rHIVV32I/L33F/I54M/I84V readily acquired high-level DRV resistance and replicated in the presence of 5 μM DRV by 17 weeks of selection (Fig. 1A), followed by rHIVV32I/I54M and rHIVL33F/I84V, which vigorously replicated in the presence of 1 μM DRV by the end of 22 and 26 weeks of selection, respectively (Fig. 1A). rHIVV32I, rHIVI54M, and rHIVI84V acquired DRV resistance somewhat slower than the double and quadruple mutants tested above, but they did replicate in the presence of ≥1 μM DRV by the end of 36 weeks of selection (Fig. 1B), while rHIVL33F failed to acquire DRV resistance by the end of week 50 of selection (Fig. 1B).
The V32I substitution predisposes HIV-1 to acquisition of DRV resistance.
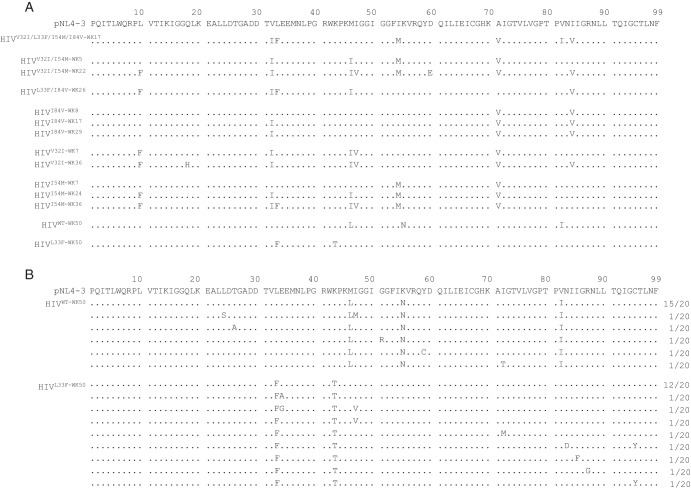
In order to clarify which amino acid substitutions emerged in each of the HIV-1 clones, the amino acid sequence of the protease-encoding region of each variant was directly determined using proviral DNA isolated from the HIV-1-producing MT-4 cells at various time points of selection. HIVWT examined at week 50 of selection (HIVWT-WK50) had acquired three substitutions, M46L, K55N, and V82I, by 50 weeks. HIVL33F-WK50, which apparently did not acquire DRV resistance (Fig. 1B), had acquired only K43T, whose significance in the development of PI resistance is well-known (17) (Fig. 2A). It was noteworthy that all six clones that eventually developed DRV resistance (HIVV32I/L33F/I54M/I84V-WK17, HIVV32I/I54M-WK22, HIVL33F/I84V-WK26, HIVI84V-WK29, HIVV32I-WK36, and HIVI54M-WK36) (Fig. 1) contained the V32I substitution, although other substitutions such as L10F, L33F, M46I, A71V, and I84V had been acquired in a subset of the six clones (Fig. 2A), suggesting that V32I substitution might have played an important role in the pathway of DRV resistance development. We, therefore, further asked whether the two clones that did not develop DRV resistance by the end of 50 weeks of selection (HIVWT-WK50 and HIVL33F-WK50) had not acquired V32I (Fig. 2A). As shown in Fig. 2B, V32I was not seen in any of the 20 clones examined for HIVWT-WK50 and HIVL33F-WK50, suggesting that the emergence of V32I might have been associated with the eventual development of DRV resistance in the 6 clones described above. It was also noted that in five of the six clones, A71V had emerged in quite early stages of DRV selection (by the end of 5 to 8 weeks of selection), followed by the emergence of V32I substitution. It is possible that the presence of A71V might predispose to HIV-1’s acquisition of V32I.
FIG 2 .
Emergence of the V32I substitution during the selection of highly DRV-resistant HIV-1 variants but not in HIVWT and HIVL33F. (A) Amino acid sequences deduced from the nucleotide sequence of the protease-encoding region (direct sequencing) were determined using proviral DNA. In the selection with DRV, proviral DNA was extracted at week 50 for HIVWT and HIVL33F, at week 36 for HIVV32I, at weeks 7, 24, and 36 for HIVI54M, at weeks 8, 17 and 29 for HIVI84V, at week 22 for HIVV32I/I54M, at week 26 for HIVL33F/I84V, and at week 17 for HIVV32I/L33F/I54M/I84V. (B) Absence of the V32I substitution in two infectious clones, rHIVWT and rHIVL33F, which were selected with DRV over 50 weeks. Two clones, rHIVWT and rHIVL33F, selected with DRV over 50 weeks (generating HIVWT-WK50 and HIVL33F-WK50, respectively), apparently failed to develop DRV resistance as shown in Fig. 1. To confirm the absence of V32I, HIVWT-WK50 and HIVL33F-WK50 were further cloned (20 clones), and each clone generated was sequenced. Note that the V32I substitution did not emerge in either of the virus populations. The consensus sequence of pNL4-3 is illustrated at the top of panels A and B as a reference. Amino acids that are identical to those in the consensus sequence at individual amino acid positions are indicated by dots. The fractions of the virus which each clone is presumed to have originated from over the total number of clones examined are shown to the right of the sequences.
V32I renders rHIVWT highly susceptible to DRV.
We next attempted to determine how each of the four amino acid substitutions contributed to the high-level DRV resistance of HIVDRVRP51. To this end, we first replaced the Gag- and protease-encoding genes of HIVNL4-3 with genes derived from HIVDRVRP51 and obtained a recombinant infectious HIV-1 clone, designated rHIVDRVRP51. This rHIVDRVRP51 clone was confirmed to be highly resistant to DRV, showing a 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 330 nM, 106-fold greater than that of rHIVWT (Table 1). We then reverted each of the four substitutions to the wild-type amino acid in rHIVDRVRP51 via site-directed mutagenesis. A newly generated infectious clone, rHIVDRVRP51I32V, in which the substitution V32I was reverted back to Val, was found to be only moderately resistant to DRV with an IC50 of 29 nM. The IC50s of rHIVDRVRP51F33L, rHIVDRVRP51M54I, and rHIVDRVRP51V84I turned out to be 120, 43, and 28 nM, respectively (Table 1). These data strongly suggested that the order of the magnitude of contribution to the high-level DRV resistance was V32I ≈ I84V > I54M >> L33F. We subsequently introduced all four substitutions or each single substitution into HIVNL4-3 (rHIVWT), generating rHIVV32I/L33F/I54M/I84V, rHIVV32I, rHIVL33F, rHIVI54M, and rHIVI84V. As expected, rHIVV32I/L33F/I54M/I84V proved to be highly resistant to DRV with an IC50 of 639 nM, while rHIVL33F, rHIVI54M, and rHIVI84V were as sensitive as rHIVWT with IC50s of ~3 nM, virtually identical to that of rHIVWT, in line with our previous report (5). It is noteworthy that rHIVV32I was hypersensitive to DRV with an IC50 of 0.2 nM, 16.7-fold more sensitive to DRV compared to rHIVWT (Table 1), suggesting that since the emergence of DRV-hypersensitive HIVV32I would be prohibitive in the presence of DRV, rHIVWT is not likely to directly acquire V32I substitution.
TABLE 1 .
Antiviral activity of DRV against HIV-1 clones carrying various mutations in protease
| Infectious clone | Amino acid substitution(s) in PR | IC50 (mean ± SD) (nM) (fold change)a |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRV | APVb | AZTc | RALd | ||
| rHIVWT | None | 3.1 ± 0.3 | 24 ± 2 | 30 ± 9 | 4.9 ± 3.2 |
| rHIVDRVRP51I32V | L10I, I15V, K20R, L24I, L33F, M36I, M46L, I54M, L63P, K70Q, V82I, I84V, L89M |
29 ± 8 (9) | ND | ND | ND |
| rHIVDRVRP51F33L | L10I, I15V, K20R, L24I, V32I, M36I, M46L, I54M, L63P, K70Q, V82I, I84V, L89M |
120 ± 33 (38) | ND | ND | ND |
| rHIVDRVRP51M54I | L10I, I15V, K20R, L24I, V32I, L33F, M36I, M46L, L63P, K70Q, V82I, I84V, L89M |
43 ± 15 (14) | ND | ND | ND |
| rHIVDRVRP51V84I | L10I, I15V, K20R, L24I, V32I, L33F, M36I, M46L, I54M, L63P, K70Q, V82I, L89M |
28 ± 6 (9) | ND | ND | ND |
| rHIVDRVRP51 | L10I, I15V, K20R, L24I, V32I, L33F, M36I, M46L, I54M, L63P, K70Q, V82I, I84V, L89M |
330 ± 10 (106) | ND | ND | ND |
| rHIVV32I/L33F/I54M/I84V | V32I, L33F, I54M, I84V | 639 ± 17 (205) | ND | ND | ND |
| rHIVV32I | V32I | 0.2 ± 0.05 (0.06) | 31 ± 3 (1.3) | 32 ± 6 (1.1) | 4.7 ± 0.5 (1.0) |
| rHIVL33F | L33F | 3.2 ± 0.1 (1.0) | 35 ± 2 (1.3) | 45 ± 12 (1.5) | 5.6 ± 1.1 (1.1) |
| rHIVI54M | I54M | 2.7 ± 0.1 (0.9) | 324 ± 86 (13) | 34 ± 17 (1.1) | 5.1 ± 2.2 (1.0) |
| rHIVI84V | I84V | 3.3 ± 0.3 (1.1) | 313 ± 98 (13) | 44 ± 18 (1.5) | 6.4 ± 6.0 (1.3) |
Data shown represent mean IC50 values (±1 standard deviation) derived from the results of three independent experiments conducted in triplicate. The IC50s were determined by employing MT-4 cells exposed to each infectious HIV-1 clone (50 TCID50s) in the presence of each inhibitor and using the inhibition of p24 Gag protein production as an end point. The fold change values in parentheses were calculated by dividing IC50s against each virus by the IC50 against rHIVWT. ND, not determined.
APV, amprenavir, a protease inhibitor.
AZT, zidovudine, a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor.
RAL, raltegravir, an integrase strand transfer inhibitor.
Since the presence of A71V might predispose HIV-1 to its acquisition of V32I as discussed above, we generated various recombinant infectious HIV-1 clones and determined their susceptibility to DRV (Table 2). The addition of A71V to rHIVV32I that was hypersensitive to DRV (IC50 = 0.2 nM), generating rHIVV32I/A71V, abrogated the DRV hypersensitivity of rHIVV32I to DRV and the IC50 of rHIVV32I/A71V became virtually the same as that of rHIVWT (2.8 versus 3.1 nM). Two clones, rHIVV32I/I54M and rHIVV32I/I84V, were also found hypersensitive to DRV with IC50s of 1.7 and 0.42 nM, suggesting that these two clones would not emerge in the presence of DRV. However, the addition of A71V to these two clones, generating rHIVV32I/I54M/A71V and rHIVV32I/A71V/I84V, acquired significant resistance to DRV with their IC50s of 27 and 35 nM, respectively (Table 2). These data strongly suggest that while the A71V substitution by itself confers no particular DRV resistance on HIV-1, combining it with the V32I substitution appears to suppress the hypersusceptibility phenotype conferred by V32I substitution and retains the wild-type level of susceptibility of rHIVA71V—as if the effect of V32I substitution were suppressed. Furthermore, when the A71V substitution is combined with V32I and I54M or V32I and I84V (both of which by themselves appear to be hypersensitive on their own), the resultant HIV-1 yields high-level DRV resistance (Table 2).
TABLE 2 .
Antiviral activity of DRV against HIV-1 clones carrying V32I, I54M, A71V, and/or I84V
| Infectious clone | Amino acid substitution(s) in PR | IC50 (mean ± SD) (nM) (fold change)a |
|---|---|---|
| rHIVWT | None | 3.1 ± 0.3b |
| rHIVV32I | V32I | 0.2 ± 0.05 (0.06)b |
| rHIVA71V | A71V | 3.3 ± 0.2 (1.1) |
| rHIVV32I/A71V | V32I, A71V | 2.8 ± 0.2 (0.9) |
| rHIVV32I/I54M | V32I, I54M | 1.7 ± 0.4 (0.5) |
| rHIVV32I/I84V | V32I, I84V | 0.42 ± 0.13 (0.13) |
| rHIVV32I/I54M/A71V | V32I, I54M, A71V | 27 ± 5 (8.6) |
| rHIVV32I/A71V/I84V | V32I, A71V, I84V | 35 ± 2 (11) |
Data shown represent mean IC50 values (±1 standard deviation) derived from the results of three independent experiments conducted in triplicate. The IC50s were determined employing MT-4 cells exposed to each infectious HIV-1 clone (50 TCID50s) in the presence of DRV and using the inhibition of p24 Gag protein production as an end point. The fold change values in parentheses were calculated by dividing IC50s against each virus by the IC50 against rHIVWT.
These values are from Table 1 and serve as reference values.
A71V predisposes HIV-1 to its acquisition of high-level DRV resistance.
We further attempted to examine whether the addition of A71V to rHIVWT, generating rHIVA71V, renders rHIVWT inclined to eventually develop high-level DRV resistance. Figure 3 shows that the selection of rHIVA71V with DRV led to the emergence of high-level DRV resistance. Since the M46I substitution is often seen in various PI-resistant HIV-1 variants (18) and that substitution was also seen in the present study (Fig. 2A), we also generated rHIVM46I and selected it in the presence of DRV. However, DRV selection of rHIVM46I did not result in the emergence of high-level DRV-resistant variants (Fig. 3). These data strongly suggest that the presence of A71V predisposes HIV-1 to its acquisition of V32I in the pathway toward HIV-1’s acquisition of high-level DRV resistance at least when rHIVWT (HIV-1NL4-3) was employed as a starting viral population in the selection with DRV.
FIG 3 .
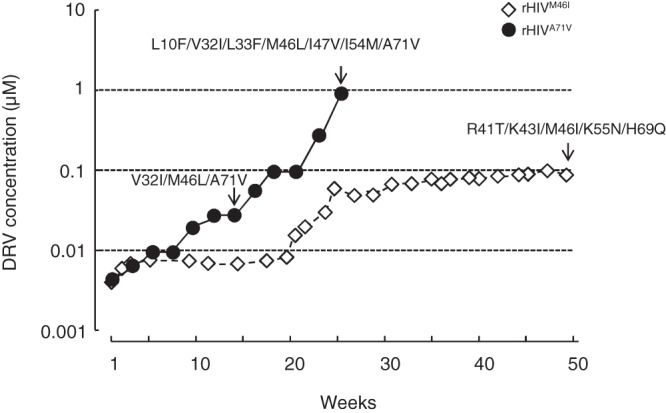
rHIVA71V rapidly develops DRV resistance, acquiring the V32I substitution. rHIVM46I and rHIVA71V were propagated in the presence of increasing concentrations of DRV in MT-4 cells. The selection was carried out in a cell-free manner over a total of 23 or 50 weeks. Amino acid substitutions identified in the protease of rHIVA71V at 14 and 23 weeks and that of rHIVM46I at 50 weeks are shown, indicated by arrows. Note that rHIVM46I apparently failed to develop DRV resistance, while rHIVA71V rapidly developed DRV resistance, acquiring the V32I substitution.
V32I increases DRV’s protease dimerization inhibition and reduces viral fitness.
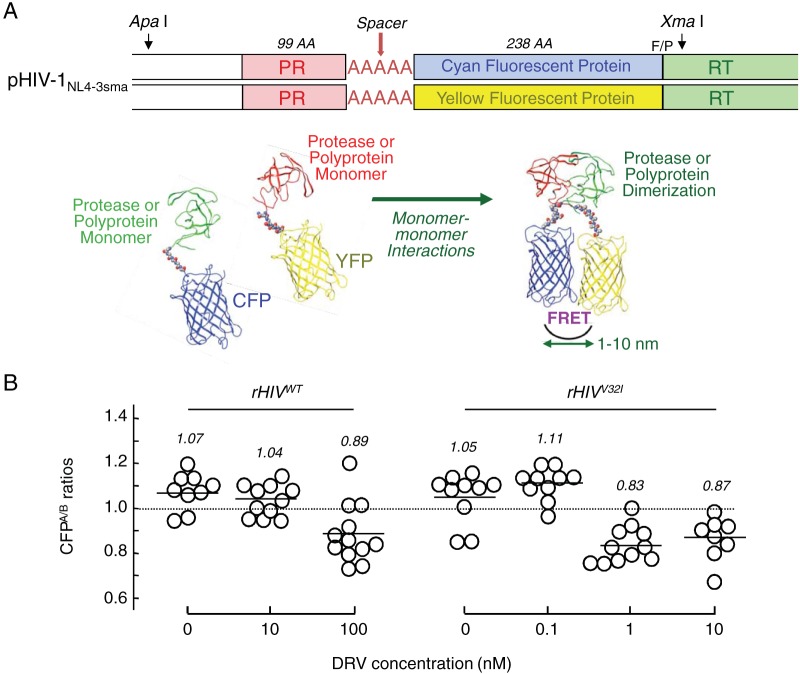
Since the potent activity of DRV against HIV-1 is associated with the bimodal anti-HIV-1 activity (4–6), (i) protease’s enzymatic activity inhibition and (ii) protease dimerization inhibition, our observation as described above that rHIVV32I was hypersensitive to DRV prompted us to examine the susceptibility of rHIVV32I to DRV’s protease dimerization inhibition activity. As assessed by the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based HIV-1 expression assay (Fig. 4A), the mean CFPA/B ratios (ratio of intensities of cyan fluorescent protein [CFP] fluorescence after photobleaching to those of CFP fluorescence before photobleaching) determined for rHIVWT in the absence of DRV and in the presence of 10 nM DRV were 1.07 and 1.04, respectively, indicating that protease dimerization occurred (Fig. 4B). In the presence of 100 nM DRV, the ratio was 0.89, indicating that 100 nM DRV blocked dimerization. However, when rHIVV32I was used in the assay, as little as 1 nM DRV blocked protease dimerization, giving a CFPA/B ratio of 0.83 (Fig. 4B). These data indicate that rHIVV32I was much more sensitive to DRV’s dimerization inhibition (by a factor of 100) than rHIVWT.
FIG 4 .
DRV’s protease dimerization inhibition activity also increases against HIVV32I compared to HIVWT. (A, top) Plasmids encoding full-length molecular infectious HIVNL4-3 clones, which produce CFP- or YFP-tagged protease (PR), were generated using the PCR-mediated recombination method as described in Materials and Methods. A linker consisting of five alanines was inserted between PR and each fluorescent protein. The phenylalanine-proline site (F/P) that PR cleaves was introduced between the fluorescent protein and reverse transcriptase (RT). AA, amino acids. (Bottom) Structural representations of PR monomers and dimer in association with the linker atoms and fluorescent proteins are shown below the schematic representation of the plasmids. FRET occurs when the two fluorescent proteins come close in the proximity of 1 to 10 nm. If an agent that inhibits the dimerization of 2-PR monomer subunits is present when the CFP- and YFP-tagged PR monomers are produced within the cell upon cotransfection, FRET does not occur. (B) COS-7 cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding either of full-length molecular infectious HIVNL4-3 clones producing CFP- or YFP-tagged wild-type protease (HIVWT) and cultured in the presence or absence of various concentrations of DRV. COS-7 cells were also cotransfected with plasmids encoding either of HIVNL4-3 clones producing CFP- or YFP-tagged V32I-carrying protease (HIVV32I). After 72 h, cultured cells were examined in the FRET-HIV-1 assay system and the CFPA/B ratios (y axis) were determined. The mean values of the ratios obtained are shown as bars. A CFPA/B ratio that is greater than 1 signifies that protease dimerization occurred, whereas a ratio that is less than 1 signifies the disruption of protease dimerization. All the experiments were conducted in a blind fashion. For rHIVWT, the P values were 0.3816 for the CFPA/B ratio in the absence of drug (CFPA/BNo Drug) versus the CFPA/B ratio in the presence of 10 nM DRV (CFPA/B10-DRV), 0.004 for CFPA/BNo Drug versus CFPA/B100-DRV. For rHIVV32I, the P values were 0.1111 for CFPA/BNo Drug versus CFPA/B0.1-DRV, 0.001 for CFPA/BNo Drug versus CFPA/B1-DRV, and 0.0086 for CFPA/BNo Drug versus CFPA/B10-DRV.
V32I compromises the replication fitness of rHIVWT, but the addition of A71V mitigates the compromised fitness.
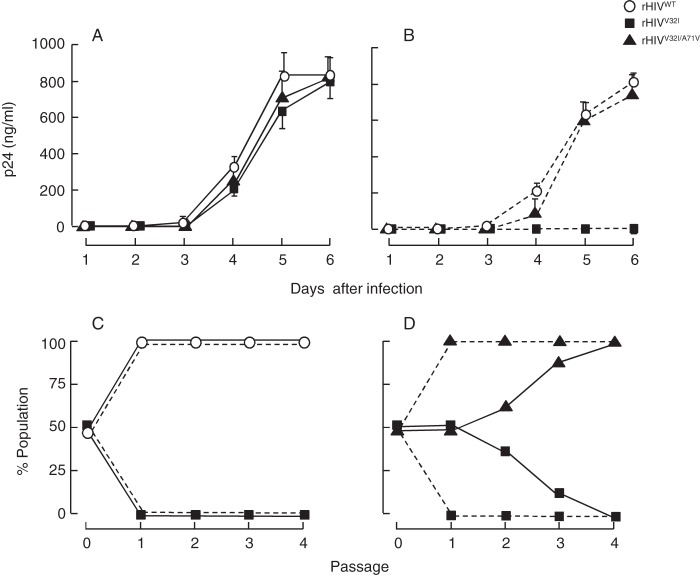
We further attempted to examine the replication kinetics of three infectious clones, rHIVWT, rHIVV32I, and rHIVV32I/A71V in the presence or absence of DRV. The replication kinetic profiles of these three clones were apparently comparable in the absence of DRV (Fig. 5A), although the replication of rHIVV32I was, as expected, totally suppressed in the presence of 3 nM DRV (Fig. 5B). We therefore determined detailed replication fitness of rHIVWT and rHIVV32I employing the competitive HIV-1 replication assay (CHRA) as previously described (19). It was clearly shown that rHIVV32I had compromised replication fitness compared to rHIVWT both in the presence and absence of 3 nM DRV (Fig. 5C). Interestingly, the addition of A71V substitution to rHIVV32I clearly mitigated the compromised replication fitness of rHIVV32I (Fig. 5D). These data suggest that the presence of A71V enables and probably accelerates the emergence of V32I.
FIG 5 .
V32I reduces the viral fitness of HIV-1, while A71V recovers the compromised fitness. Replication profiles of rHIVWT, rHIVV32I, and rHIVV32I/A71V were examined. (A and B) Replication kinetics of the three clones were examined. MT-4 cells (105) were exposed to each infectious clone (calibrated to have 10 ng of p24 Gag of each preparation) and cultured in the absence (A) or presence (B) of 3 nM DRV. Virus replication was monitored by the amounts of p24 Gag produced in the culture supernatants. The results shown are representative of results from three independent experiments. The failure of rHIVV32I replication in the presence of 3 nM DRV suggests that rHIVV32I is more susceptible to DRV than rHIVWT and rHIVV32I/A71V are. (C and D) The replication profiles of HIVWT versus HIVV32I and HIVV32I versus HIVV32I/A71V in the absence (solid line) or presence (dashed line) of 3 nM DRV were examined using the competitive HIV replication assay (19). MT-4 cells (105) were exposed to an equal amount of two infectious clones to be compared and cultured for 7 days. The cell-free supernatant harvested at the conclusion of each culture passage (7 days) in the absence (solid line) or presence (dashed line) of 3 nM DRV was transferred to fresh MT-4 cell culture. High-molecular-weight DNA extracted from infected cells at the end of each passage was subjected to nucleotide sequencing, and percent populations of the mixture were estimated by the heights of the electropherogram obtained through the sequencing. The proportions of Val and Ile at position 32 in protease (panel C) and of Ala and Val at position 71 in protease (panel D) were determined.
The V32I substitution increases van der Waals interactions with DRV.
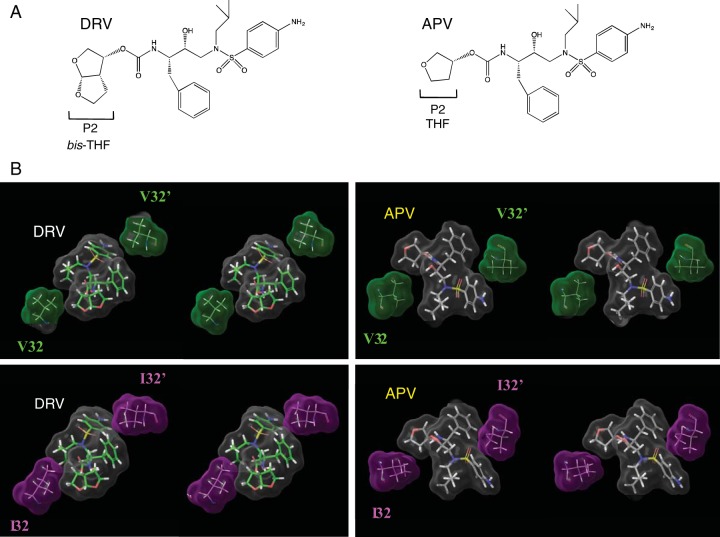
We analyzed the structural interactions of DRV with Val32 by analyzing the crystal structure of DRV-HIV-1 protease (PDB identifier [ID] or accession no. 4HLA) (20). Connolly surfaces for DRV, Val32 and Val32′, were generated and the interactions among the surfaces were analyzed. As shown in the top left portions of Fig. 6A and B, Val32 has good interactions with the bis-tetrahydrofuranylurethane (bis-THF), while Val32′ interacts with the aminobenzene moieties of DRV. We then analyzed the interactions of V32I mutant protease (PRV32I) with DRV. As shown in the bottom left panel of Fig. 6B, bis-THF has enhanced interactions with substituted Ile32 than with Val32 of wild-type protease (PRWT). The substituted Ile32′ also has enhanced interactions with the aminobenzene group of DRV than does Val32 in PRWT. Overall, the Connolly surface interactions suggested better interactions of DRV with both Ile32 and Ile32′ of V32I-substituted protease (PRV32I) than with Val32 and Val32′ of PRWT. We further analyzed the interactions of amprenavir (APV) with PRWT in comparison with PRV32I. APV has a THF group as the P2 ligand (Fig. 6A), and it does interact with Val32 (top right panel of Fig. 6B). However, there are no changes in the interactions of the THF group with Ile32 (bottom right panel of Fig. 6B). In contrast, as described above, the P2 bis-THF of DRV has much better interactions with Ile32 than it does with Val32. The changes in the interactions of APV on the P2′ site with Ile32′ over Val32 are similar to the corresponding changes in the interactions of DRV. In conclusion, the presence of the bis-THF group in DRV (compared to THF in APV) is responsible for the increased van der Waals interactions with Ile32 of PRV32I. This increase in van der Waals interactions must be partly responsible for the increased susceptibility of rHIVV32I to DRV.
FIG 6 .
Comparison of binding fashion of DRV or APV to PRVal32 or PRIle32. (A) In the structure, DRV contains a bis-tetrahydrofuranyl urethane (bis-THF) at the P2 site instead of APV’s tetrahydrofuranyl urethane (THF) moiety. (B) The Connolly surface interactions of DRV or APV with residue 32 are shown in stereo. Surface colors are as follows: gray for DRV or APV, green for V32, and magenta for I32. DRV is shown with green carbons, and APV is shown with gray carbons. The figure shows that DRV has better interaction with substituted I32 than with wild-type V32. The interactions of APV with V32 or I32 are similar.
DISCUSSION
DRV, the latest FDA-approved PI, is the only PI recommended for first-line therapy (3) and has a favorable genetic barrier against emergence of resistant variants. The latter might be because of its dual mechanism of action: (i) protease enzymatic inhibition activity and (ii) protease dimerization inhibition activity (4–6). DRV currently represents the most widely used PI for treating HIV-1-infected individuals. The relatively rare emergence of HIV-1 variants resistant to DRV in the setting of clinical applications was noted, which was explained with the findings in the early phase of clinical development of DRV that multiple attempts to select DRV-resistant HIV-1 variants failed when such selection attempts were conducted using a single wild-type HIV-1 strain as a starting virus population (7–12). However, when a mixture of eight multidrug-resistant HIV-1 variants was employed as a starting HIV-1 population (8), highly DRV-resistant HIV-1 variants (HIV-1DRVRP10, HIV-1DRVRP30, and HIV-1DRVRP51) emerged relatively quickly (8). In fact, the emergence of DRV-resistant HIV-1 variants has been reported in patients receiving long-term DRV-containing cART (13).
In the present study, we attempted to elucidate the mechanisms by which DRV rarely allows HIV-1 to develop DRV-resistant HIV-1 variants so that novel PIs that more profoundly resist against the emergence of resistant variants can be designed. Here, we demonstrate that one of the four critical amino acid substitutions responsible for DRV resistance, V32I, serves as a key substitution; it rarely occurs in in vitro selection attempts, but once it occurs, it predisposes HIV-1 to develop high-level DRV resistance. As shown in Fig. 7A, when we selected three infectious clones (rHIVWT, rHIVL33F, and rHIVM46I) with DRV, none of those clones developed DRV resistance. However, when two clones (rHIVV32I and rHIVI54M) were selected, rHIVV32I and rHIVI54M relatively rapidly acquired A71V by 7 weeks of selection and rHIVI54M subsequently acquired V32I as well. These virus isolates continued to acquire multiple amino acid substitutions, became highly resistant to DRV, and propagated well despite the presence of 1 µM DRV by 36 weeks of selection (Fig. 1B and Fig. 2A). The A71V substitution is relatively frequently seen as a secondary mutation in clinically isolated HIV-1 variants resistant to FDA-approved PIs (21). The A71V substitution has been seen in 20.4, 20.1, and 6.2% of nelfinavir-, lopinavir (LPV)-, and atazanavir-experienced patients, respectively (22, 23), compared to 3.5 to 5.4% of HIV-1 isolates from PI-naive patients (22, 23). In one study by Sterrantino et al. (24), involving 1,104 patients receiving DRV-containing regimens, 118 patients (10.7%) experienced treatment failure. This study (24) showed that V32I and I84V substitutions in protease played a significant role, but there was no mention of A71V. In contrast, a set of data compiled for NDA21-976/S003 and NDA21-976/S004 clearly indicates that 10 amino acid substitutions including L10F, V32I, L33F, S37N, M46I, I47V, I50V, L63P, A71V, and I84V are the most prevalent (https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2008/021976s003s004lbl.pdf). Nevertheless, no detailed analysis on the role of A71V in the development of DRV resistance has been reported.
FIG 7 .
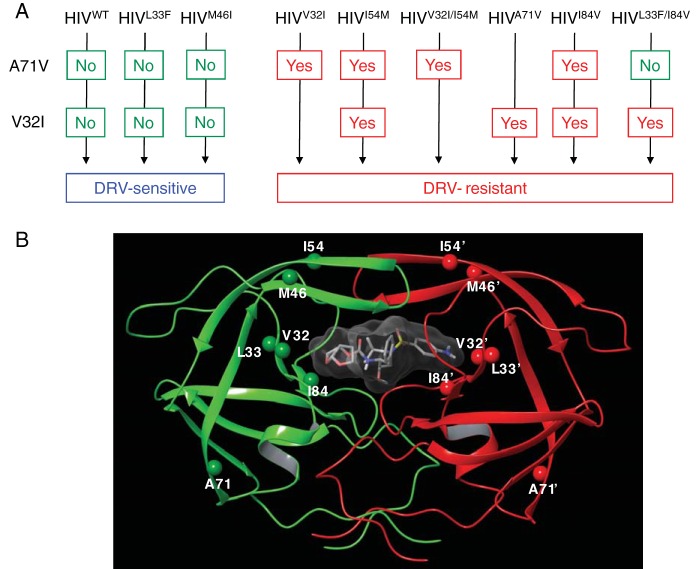
The mature dimerized HIV-1 protease in complex with DRV and proposed pathway of development of DRV resistance. (A) Proposed pathway of development of DRV resistance of HIV-1. Upon DRV selection, rHIVWT, rHIVL33F, and rHIVM46I clones did not develop DRV resistance. rHIVV32I and rHIVI54M relatively rapidly acquired A71V, and rHIVI54M subsequently acquired V32I. These clones continued to acquire multiple amino acid substitutions and became highly resistant to DRV. Upon DRV selection, rHIVV32I/I54M quickly acquired A71V and became highly resistant to DRV. rHIVA71V acquired V32I and eventually became resistant to DRV. rHIVI84V quickly acquired A71V, subsequently acquired V32I, and became resistant to DRV. rHIVL33F/I84V continued to propagate in the presence of DRV, acquired V32I but without acquiring A71V, and became resistant to DRV. rHIVL33F/I84V’s acquisition of high-level DRV resistance despite the absence of A71V strongly suggest that its DRV resistance acquisition involved alternate albeit unidentified pathway of DRV resistance development. (B) The locations of V32, L33F, M46, I54, A71, and I84 are shown in the dimerized protease. V32, I54, and I84 are located in the active site of the dimerized protease; however, A71 is distant from the active site.
When rHIVV32I/I54M was selected, this clone acquired A71V more quickly by 5 weeks of selection and became capable of replicating in the presence of 1 µM DRV by 22 weeks of selection (Fig. 1A). When rHIVA71V was selected, this clone acquired V32I and other amino acid substitutions and became capable of propagating in the presence of 1 µM DRV by 25 weeks of selection (Fig. 3). When rHIVI84V was selected, this clone quickly acquired A71V by 8 weeks of selection, subsequently acquired V32I by 17 weeks of selection, and was replicating in the presence of 1 µM DRV by 29 weeks of selection (Fig. 1B and Fig. 2A). It is interesting that when rHIVL33F/I84V was selected, this clone continued to propagate in the presence of increasing concentrations of DRV, acquired V32I (as examined at week 26) but without acquiring A71V, and became capable of propagating in the presence of 1 µM DRV by 26 weeks of selection. rHIVL33F/I84V’s acquisition of high-level DRV resistance despite the absence of A71V strongly suggested that its DRV resistance acquisition involved an alternate albeit unidentified pathway of DRV resistance development. The reason why the three clones (rHIVWT, rHIVL33F, and rHIVM46I) failed to develop DRV resistance is unknown at this time, although it is possible that the acquisition of A71V, a secondary substitution observed among HIV-1 isolates resistant to various PIs (25, 26), might render each clone more susceptible to DRV and/or compromise their replication fitness, and A71V substitution rarely emerged. It is noteworthy that the IC50s of rHIVWT and rHIVA71V were virtually the same (3.1 and 3.3 µM, respectively), although the cell-based assay for determining IC50s employed is as short as 7 days and it is of limited significance in strictly comparing the susceptibility or replication fitness of HIV-1.
It should be noted that all the highly DRV-resistant HIV-1 variants (HIV-1DRVRP10, HIV-1DRVRP30, and HIV-1DRVRP51) did not contain the A71V substitution as the PR-encoding gene of those variants were directly sequenced, although when a highly drug-resistant clinical HIV-1 isolate, HIVc, was selected with DRV, that isolate eventually acquired A71V by passage 50 (8). As discussed above, in regard to the selection results of rHIVL33F/I84V, which developed high-level DRV resistance without acquiring A71V, the development of high-level DRV resistance in cases of HIV-1DRVRP10, HIV-1DRVRP30, and HIV-1DRVRP51 also involved alternative albeit unidentified pathways in the development of DRV resistance.
In the present study, we concluded that the V32I substitution serves as a key substitution, which rarely occurs in the presence of DRV without other DRV resistance-predisposing amino acid substitutions, but once it occurs, it significantly predisposes HIV-1 to develop high-level DRV resistance. As summarized in the proposed pathway of development of DRV resistance (Fig. 7B), all three resultant highly DRV-resistant variants (HIV-1DRVRP10, HIV-1DRVRP30, and HIV-1DRVRP51) contained the V32I substitution (8), and all the HIV-1 infectious clones that were selected with DRV and developed high-level DRV resistance also contained the substitution. In fact, the presence of the V32I substitution has been significantly associated with treatment failure in those receiving DRV-containing regimens. The study by Lambert-Niclot et al. (27) reported that the V32I substitution was seen in 24% of clinical HIV-1 isolates from 54 multiple-PI-experienced but non-DRV-exposed HIV-1-infected individuals, but the prevalence of the substitution increased to 57% in those who subsequently received DRV-containing regimens and underwent treatment failure with such regimens. The study by Delaugerre et al. showed that the V32I substitution was present in 64% of HIV-1 isolates from 25 DRV-naive patients after treatment failure (28). Sterrantino et al. also reported that among 1,104 patients receiving DRV-containing regimens, the substitution was seen in 20.3% of HIV-1 isolates from 118 patients undergoing treatment failure but in only 7.5% of 986 patients responding to the regimens (24). It is noteworthy that V32I was reportedly involved in the development of pan-PI resistance including DRV resistance as estimated by an independent correlation network analysis of amino acid substitutions identified in HIV-1 proteases studied from more than 10,000 patients receiving PI-containing regimens (29). These data suggest that the V32I substitution is strongly associated with the development of DRV resistance.
It is noteworthy that the key amino acid substitutions focused on in the present study, including not only V32I but also L33F, I54M, and I84V, as a single substitution do not by themselves confer resistance to DRV. Importantly, the V32I substitution did confer hypersusceptibility to DRV, while the other three substitutions did not significantly change the susceptibility (Table 1). These substitutions are part of rHIVDRVRP51, which is highly resistant to DRV (106-fold-greater IC50 compared to DRV’s IC50 against rHIVWT). However, when we introduced the reversion of each of those substitutions into the highly DRV-resistant rHIVDRVRP51, three partially reverted clones (rHIVDRVRP51I32V, rHIVDRVRP51M54I, and rHIVDRVRP51V84I) became significantly less resistant to DRV (9- to 14-fold) and rHIVDRVRP51F33L also became less resistant to DRV (38-fold) (Table 1). These data strongly suggest that these four substitutions are unusual in that they somehow affect the ability of other mutations in the background to confer high-level DRV resistance. In particular, considering that the V32I substitution is seen in some HIV-1 variants resistant to other PIs than DRV (21, 30), the V32I substitution is not necessarily specific to DRV resistance but likely associated with pan-PI resistance as well.
It is also noteworthy that substitutions other than the four key substitutions present in rHIVDRVRP51 might be DRV specific; however, considering that rHIVDRVRP51 is highly resistant to all the existing FDA-approved PIs examined as shown in previous reports (8, 10), it is also possible that substitutions other than the key substitutions are responsible for the acquisition of HIV-1 of pan-PI resistance. The exact mechanism as to how other substitutions play a role(s) in conferring DRV-specific resistance or pan-PI resistance remains to be determined. Structurally, it is plausible to presume that the four key substitutions change the structure of PR in some global way that is important for optimal PR functions while conferring DRV resistance. In any event, the data together strongly suggest that the V32I substitution (and the three associated substitutions as a single substitution) is not by itself a DRV resistance-associated mutation, but does facilitate DRV resistance when present.
Structurally, A71 is located distant from the enzymatic active site and the hydrophobic cavity of PR (Fig. 7B). Skálová et al. (31) reported that mutations can result in the movement of β-sheets, which causes structural changes far away from the location of the mutation. They propose that there are hydrogen bonds involving multiple β-sheets between residues 71 and 64, residues 65 and 14, and residues 13 and 20. The side chain of A71 is orientated toward the hydrophobic cavity of PR, and changing alanine to valine requires more space to hold valine’s bulkier side chain. The A71V substitution likely changes the configuration of the A71-containing β-sheet and the hydrogen bond network propagating to the binding pocket, changing the shape of the “ligand binding tunnel,” and affecting the interactions, in which the catalytic site amino acid residues (Asp25 and Asp25′) are involved (31). These structural insights can help explain why the IC50 of rHIVV32I/A71V is comparable to that of rHIVWT (Table 2), while rHIVV32I/I54M and rHIVV32I/I84V were still highly sensitive to DRV (Table 2). Furthermore, A71V compensated for the compromised viral fitness by acquisition of V32I (Fig. 5).
DRV has good van der Waals interactions with several protease residues. The bis-THF moiety of DRV has van der Waals interactions with Val32, and our structural modeling indicated that the interactions are substantially strengthened with substitution to Ile32 (Fig. 6B). In contrast, the THF moiety of APV, being significantly smaller, has similar interactions with both Val32 as well as Ile32 (Fig. 6B). These data partly explain why rHIVV32I is more sensitive to DRV, whereas the antiviral activity of APV does not change (Table 1). It is also noteworthy that HIV-1 carrying a single primary resistance-associated amino acid substitution may increase PI susceptibility when it occurs alone but increase PI resistance when it occurs in combination with other mutations (32).
The detailed structural analysis of the major amino acid substitutions conferring high-level DRV resistance on HIV-1 including V32I, L33F, I54M, and I84V remains to be conducted. In this regard, we have expressed and purified several mutated proteases associated with DRV resistance such as that from highly DRV-resistant HIV-1DRVRP51 (5) that contains various amino acid substitutions including V32I, L33F, I54M, and I84V, generated crystals of such proteases complexed with DRV and other PIs, and are analyzing the crystallographic structures of those complexes, which should give more in-depth insights in the understanding of the mechanism of the high genetic barrier of DRV. This molecular insight should be of help for the development of future PIs.
Amino acid codon substitutions in the HIV-1 genome that confer drug resistance are one of the major reasons for treatment failure. Hence, treatment guidelines recommend using genotyping tests prior to initiation of cART (3, 33). de Meyer et al. reported that 11 amino acid substitutions, V11I, V32I, L33F, I47V, I50V, I54L/M, G73S, L76V, I84V, and L89V, which appear to be associated with HIV-1 resistance against DRV, were identified among HIV-1 variants isolated from patients treated with DRV-including regimens on POWER studies. Some of these amino acid substitutions are reportedly associated with diminished virological response to DRV-containing regimens (34). However, to the best of our knowledge, no detailed studies on each of the amino acid substitutions have been reported. In the present study, at least four amino acid substitutions, V32I, I54M, A71V, and I84V, obviously facilitate a high level of DRV resistance (Fig. 1B and Fig. 3), even though HIV-1 clones carrying each of the mutations showed sensitivity to DRV (Tables 1 and 2). These four mutations are commonly seen as PI-associated amino acid substitutions (21), and V32I (3.9%), I54M (1.3%), and I84V (14.5%) were actually found in 1,021 genotypes from patients who failed in regimens including PIs other than DRV (30). In addition, A71V is also known as one of the common polymorphisms found in several percent PI-naive patients (22, 23). Therefore, it is necessary to be careful when patients infected with HIV-1 carrying the four mutations are treated with DRV-containing regimens. The present data not only explain well the mechanisms of DRV’s high genetic barrier but also suggest that the initiation or continuation of DRV-containing regimens in individuals harboring HIV-1 variants with V32I substitution must be carefully considered and monitored.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cells and antiviral agents.
MT-4 cells were grown in RPMI 1640-based culture medium, while COS-7 cells were propagated in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium. These media were supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (FCS) (PAA Laboratories GmbH, Linz, Austria) plus 50 U of penicillin and 50 μg of kanamycin per ml. Darunavir (DRV) was synthesized as previously described (35). Amprenavir (APV), zidovudine (AZT), and raltegravir (RAL) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO).
Drug susceptibility assay.
The susceptibility of infectious molecular HIV-1 clones to various antiviral agents was determined as previously described (36). Briefly, MT-4 cells (105/ml) were exposed to 50 50% tissue culture infectious doses (TCID50s) of each infectious molecular HIV-1 clone in the presence or absence of various concentrations of each antiviral agent and were incubated at 37°C. On day 7 of culture each week, the supernatants were harvested, and the amounts of p24 Gag protein were determined by using a fully automated chemiluminescent-enzyme immunoassay system (Lumipulse G1200; Fujirebio Inc., Tokyo, Japan). The drug concentrations that suppressed the production of p24 Gag protein by 50% (50% inhibitory concentrations [IC50s]) were determined by comparing the average level of p24 production in drug-free control cell cultures. All assays were performed in triplicate.
Selection of highly DRV-resistant HIV-1 variants in vitro.
Drug-resistant HIV-1 variants against DRV were generated as previously described (15, 37). Briefly, in the first passage, MT-4 cells (5 × 105) were exposed to 500 TCID50s of each infectious molecular HIV-1 clone and cultured in the presence of DRV at an initial concentration of an IC50. On the last day of each passage (week 1 to 3), 1.5 ml of the cell-free supernatant was harvested and transferred to a culture of fresh uninfected MT-4 cells in the presence of increased concentrations of the drug for the following round of culture. In this round of culture, three drug concentrations (increased by one-, two-, and threefold compared to the previous concentration) were employed. When the replication of HIV-1 in the culture was confirmed by substantial p24 Gag protein production (greater than 200 ng/ml), the highest drug concentration among the three concentrations was used to continue selection (for the next round of culture). This protocol was repetitively used until the drug concentration reached the targeted concentration. Proviral DNA samples obtained from the lysates of infected cells were subjected to nucleotide sequencing.
Determination of nucleotide sequences.
Molecular cloning and determination of the nucleotide sequences of HIV-1 strains passaged in the presence of each compound were performed as previously described (15). In brief, high-molecular-weight DNA was extracted from HIV-1-infected MT-4 cells by using the InstaGene Matrix (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA) and was subjected to molecular cloning, followed by sequence determination. The primers used for the PCR with the entire Gag- and protease-encoding regions of the HIV-1 genome were LTR F2 (5′-GAG ACT CTG GTA ACT AGA GAT C-3′) and Ksma2.1 (5′-CCA TCC CGG GCT TTA ATT TTA CTG GTA C-3′). The PCR mixture consisted of 1 μl of proviral DNA solution, 10 μl of Premix Taq (Ex Taq version; TaKaRa Bio Inc., Otsu, Japan), and 10 pmol of each of the PCR primers in a total volume of 20 μl. The PCR conditions used were as follows: (i) an initial step of 1 min at 95°C; (ii) 30 cycles, with 1 cycle consisting of 40 s at 95°C, 20 s at 55°C, and 2 min at 72°C; (iii) a final extension step of 10 min at 72°C. The PCR products were purified with spin columns (MicroSpin S-400 HR columns; Amersham Biosciences Corp., Piscataway, NJ), cloned directly, and subjected to sequencing with a model 3130 automated DNA sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA).
Generation of recombinant HIV-1 clones.
The PCR products obtained as described above were digested with two enzymes ApaI and XmaI, and the resulting fragments were introduced into pHIV-1NLSma designed to have an XmaI site by changing two nucleotides (2590 and 2593) of pHIV-1NL4-3. To generate HIV-1 clones carrying the intended mutation(s), site-directed mutagenesis using the QuikChange site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) was used, and the genomic fragments containing the mutation(s) were introduced into pHIV-1NLSma. Determination of the nucleotide sequences of plasmids confirmed that each clone had the desired mutations but no unintended mutations. Each recombinant plasmid was transfected into COS-7 cells with Lipofectamine 2000 reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA), and infectious virions thus obtained were harvested 72 h after transfection and stored at −80°C until use.
Competitive HIV-1 replication assay.
In order to compare the replicative capability or fitness of two titrated infectious clones, the competitive HIV-1 replication assay (19) was conducted. Briefly, a fixed amount (200 TCID50s) of one infectious clone was combined with three different amounts (100, 200, and 300 TCID50s) of the other infectious HIV-1 clone and added to the culture of MT-4 cells. On the following day, one-third of the infected MT-4 cells were harvested and washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and cellular DNA was extracted and subjected to PCR and sequencing as described above. The proportions of the mixture were estimated by the heights of the electropherogram obtained from direct sequencing. The HIV-1 coculture, which best approximated a 50:50 mixture on day 1, was further propagated in the assay. Every 7 days, the cell-free supernatants of virus coculture were transmitted to fresh uninfected MT-4 cells. The cells harvested at the end of each passage (7 days) were subjected to direct DNA sequencing, and viral population changes in terms of percent population of each clone were determined. The persistence of the original amino acid substitutions was confirmed for all infectious clones used in the assay.
Generation of FRET-based HIV-1 expression system.
The intermolecular fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based HIV-1 expression assay employing protease (PR) monomers tagged with cyan and yellow fluorescent protein (CFP and YFP, respectively) was performed as previously described (4). In brief, CFP- and YFP-tagged HIV-1 protease constructs were generated using BD Creator DNA cloning kits (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA). For the generation of full-length molecular infectious clones containing CFP- or YFP-tagged protease, the PCR-mediated recombination method was used (38). A linker consisting of five alanines was inserted between protease and fluorescent proteins. The phenylalanine-proline site where HIV-1 protease cleaves was also introduced between the fluorescent protein and reverse transcriptase. DNA fragments obtained were subsequently joined by using the PCR-mediated recombination reaction performed under the standard conditions for Ex Taq polymerase (TaKaRa Bio Inc., Otsu, Japan). The amplified PCR products were cloned into the pCR-XL-TOPO vector according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Gateway Cloning System; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). PCR products containing the HIV-PRWTCFP and HIV-PRWTYFP-coding genes were generated with pCR-XL-TOPO vector as the templates, followed by digestion with both ApaI and XmaI, and the ApaI-XmaI fragment was introduced into pHIV-1NLSma, generating pHIV-PRWTCFP and pHIV-PRWTYFP, respectively.
FRET procedure.
COS-7 cells plated on EZ view cover-glass bottom culture plates (Iwaki, Tokyo, Japan) were transfected with pHIV-PRWTCFP and pHIV-PRWTYFP using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions in the presence of various concentrations of DRV, cultured for 72 h, and analyzed under a Leica TCS SP8 confocal microscope (Leica Microsystems, Inc., Wetzlar, Germany) at room temperature as previously described (4). DRV was added to the culture medium simultaneously with plasmid transfection. Results of FRET were determined by quenching of CFP (donor) fluorescence and an increase in YFP (acceptor) fluorescence (sensitized emission), since part of the energy of CFP is transferred to YFP instead of being emitted. The changes in the CFP and YFP fluorescence intensity in the images of selected regions were examined and quantified using Leica Application Suite X software. Background values were obtained from the regions where no cells were present and were subtracted from the values for the cells examined for all calculations. The ratios of intensities of CFP fluorescence after photobleaching to CFP fluorescence before photobleaching (CFPA/B ratios) were determined. It is well established that CFPA/B ratios of greater than 1.0 indicate that CFP- and YFP-tagged proteins were associated, and it was interpreted as evidence that protease subunits had dimerized. CFPA/B ratios of less than 1 indicate that the two subunits were not associated and were interpreted as inhibition of protease dimerization (4).
Structural analysis.
We used the coordinates from the X-ray crystal structures of DRV-PRWT complex (PDB ID 4HLA) (20) and APV-PRWT complex (PDB ID 1HPV) (39). Hydrogens were added to the crystal structure, the protonation states of aspartates were assigned, and a restrained minimization was performed followed by a full minimization. Val-32 in the structures was “mutated” to Ile, and the structures were again fully minimized using OPLS3 force field, and used for subsequent analysis. Connolly molecular surfaces for the inhibitors and selected protease residues from the active site were generated using a water sphere with a radius of 1.4 Å as a probe. MAESTRO (version 10.7.015, release 2016-3) and associated software tools from Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY), were used for model building, visualization, and analysis.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This project was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, by grants for the Promotion of AIDS Research from the Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Labor of Japan, by grants from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT), by a grant from the National Center for Global Health and Medicine (NCGM) Research Institute (to H.M.), and by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (GM53386 to A.K.G.). This work was also supported in part by the Platform Project for Supporting Drug Discovery and Life Science Research (Platform for Drug Discovery, Informatics, and Structural Life Science) funded by MEXT and AMED.
This study utilized the high-performance computational capabilities of the Biowulf Linux cluster at the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD (https://hpc.nih.gov/).
Footnotes
Citation Aoki M, Das D, Hayashi H, Aoki-Ogata H, Takamatsu Y, Ghosh AK, Mitsuya H. 2018. Mechanism of darunavir (DRV)’s high genetic barrier to HIV-1 resistance: a key V32I substitution in protease rarely occurs, but once it occurs, it predisposes HIV-1 to develop DRV resistance. mBio 9:e02425-17. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02425-17.
REFERENCES
- 1.Samji H, Cescon A, Hogg RS, Modur SP, Althoff KN, Buchacz K, Burchell AN, Cohen M, Gebo KA, Gill MJ, Justice A, Kirk G, Klein MB, Korthuis PT, Martin J, Napravnik S, Rourke SB, Sterling TR, Silverberg MJ, Deeks S, Jacobson LP, Bosch RJ, Kitahata MM, Goedert JJ, Moore R, Gange SJ, North American AIDS Cohort Collaboration on Research and Design (NA-ACCORD) of IeDEA . 2013. Closing the gap: increases in life expectancy among treated HIV-positive individuals in the United States and Canada. PLoS One 8:e81355. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Marcus JL, Chao CR, Leyden WA, Xu L, Quesenberry CP Jr, Klein DB, Towner WJ, Horberg MA, Silverberg MJ. 2016. Narrowing the gap in life expectancy between HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected individuals with access to care. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 73:39–46. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000001014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.DHHS Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents 2017. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in adults and adolescents living with HIV. DHHS Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents, Office of AIDS Research Advisory Council, US Department of Health and Human Services, Washington, DC. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Koh Y, Matsumi S, Das D, Amano M, Davis DA, Li J, Leschenko S, Baldridge A, Shioda T, Yarchoan R, Ghosh AK, Mitsuya H. 2007. Potent inhibition of HIV-1 replication by novel non-peptidyl small molecule inhibitors of protease dimerization. J Biol Chem 282:28709–28720. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703938200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Koh Y, Aoki M, Danish ML, Aoki-Ogata H, Amano M, Das D, Shafer RW, Ghosh AK, Mitsuya H. 2011. Loss of protease dimerization inhibition activity of darunavir is associated with the acquisition of resistance to darunavir by HIV-1. J Virol 85:10079–10089. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05121-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hayashi H, Takamune N, Nirasawa T, Aoki M, Morishita Y, Das D, Koh Y, Ghosh AK, Misumi S, Mitsuya H. 2014. Dimerization of HIV-1 protease occurs through two steps relating to the mechanism of protease dimerization inhibition by darunavir. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:12234–12239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1400027111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.De Meyer S, Azijn H, Surleraux D, Jochmans D, Tahri A, Pauwels R, Wigerinck P, de Béthune MP. 2005. TMC114, a novel human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease inhibitor active against protease inhibitor-resistant viruses, including a broad range of clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:2314–2321. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.6.2314-2321.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Koh Y, Amano M, Towata T, Danish M, Leshchenko-Yashchuk S, Das D, Nakayama M, Tojo Y, Ghosh AK, Mitsuya H. 2010. In vitro selection of highly darunavir-resistant and replication-competent HIV-1 variants by using a mixture of clinical HIV-1 isolates resistant to multiple conventional protease inhibitors. J Virol 84:11961–11969. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00967-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Aoki M, Hayashi H, Yedidi RS, Martyr CD, Takamatsu Y, Aoki-Ogata H, Nakamura T, Nakata H, Das D, Yamagata Y, Ghosh AK, Mitsuya H. 2015. C-5-modified tetrahydropyrano-tetrahydofuran-derived protease inhibitors (PIs) exert potent inhibition of the replication of HIV-1 variants highly resistant to various PIs, including darunavir. J Virol 90:2180–2194. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01829-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Aoki M, Hayashi H, Rao KV, Das D, Higashi-Kuwata N, Bulut H, Aoki-Ogata H, Takamatsu Y, Yedidi RS, Davis DA, Hattori SI, Nishida N, Hasegawa K, Takamune N, Nyalapatla PR, Osswald HL, Jono H, Saito H, Yarchoan R, Misumi S, Ghosh AK, Mitsuya H. 2017. A novel central nervous system-penetrating protease inhibitor overcomes human immunodeficiency virus 1 resistance with unprecedented aM to pM potency. eLife 6:e28020. doi: 10.7554/eLife.28020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ide K, Aoki M, Amano M, Koh Y, Yedidi RS, Das D, Leschenko S, Chapsal B, Ghosh AK, Mitsuya H. 2011. Novel HIV-1 protease inhibitors (PIs) containing a bicyclic P2 functional moiety, tetrahydropyrano-tetrahydrofuran, that are potent against multi-PI-resistant HIV-1 variants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:1717–1727. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01540-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dierynck I, Van Marck H, Van Ginderen M, Jonckers TH, Nalam MN, Schiffer CA, Raoof A, Kraus G, Picchio G. 2011. TMC310911, a novel human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease inhibitor, shows in vitro an improved resistance profile and higher genetic barrier to resistance compared with current protease inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:5723–5731. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00748-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mitsuya Y, Liu TF, Rhee SY, Fessel WJ, Shafer RW. 2007. Prevalence of darunavir resistance-associated mutations: patterns of occurrence and association with past treatment. J Infect Dis 196:1177–1179. doi: 10.1086/521624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tang MW, Shafer RW. 2012. HIV-1 antiretroviral resistance: scientific principles and clinical applications. Drugs 72:e1–e25. doi: 10.2165/11633630-000000000-00000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Aoki M, Venzon DJ, Koh Y, Aoki-Ogata H, Miyakawa T, Yoshimura K, Maeda K, Mitsuya H. 2009. Non-cleavage site gag mutations in amprenavir -resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) predispose HIV-1 to rapid acquisition of amprenavir resistance but delay development of resistance to other protease inhibitors. J Virol 83:3059–3068. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02539-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Doyon L, Tremblay S, Bourgon L, Wardrop E, Cordingley MG. 2005. Selection and characterization of HIV-1 showing reduced susceptibility to the non-peptidic protease inhibitor tipranavir. Antiviral Res 68:27–35. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2005.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Svicher V, Ceccherini-Silberstein F, Erba F, Santoro M, Gori C, Bellocchi MC, Giannella S, Trotta MP, Monforte A, Antinori A, Perno CF. 2005. Novel human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease mutations potentially involved in resistance to protease inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:2015–2025. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.5.2015-2025.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shafer RW. 2006. Rationale and uses of a public HIV drug-resistance database. J Infect Dis 194(Suppl 1):S51–S58. doi: 10.1086/505356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kosalaraksa P, Kavlick MF, Maroun V, Le R, Mitsuya H. 1999. Comparative fitness of multi-dideoxynucleoside-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) in an in vitro competitive HIV-1 replication assay. J Virol 73:5356–5363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yedidi RS, Maeda K, Fyvie WS, Steffey M, Davis DA, Palmer I, Aoki M, Kaufman JD, Stahl SJ, Garimella H, Das D, Wingfield PT, Ghosh AK, Mitsuya H. 2013. P2′ benzene carboxylic acid moiety is associated with decrease in cellular uptake: evaluation of novel nonpeptidic HIV-1 protease inhibitors containing P2 bis-tetrahydrofuran moiety. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:4920–4927. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00868-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wensing AM, Calvez V, Gunthard HF, Johnson VA, Paredes R, Pillay D, Shafer RW, Richman DD. 2017. 2017 update of the drug resistance mutations in HIV-1. Top Antivir Med 24:132–133. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Garriga C, Pérez-Elías MJ, Delgado R, Ruiz L, Nájera R, Pumarola T, del Mar Alonso-Socas M, García-Bujalance S, Menéndez-Arias L, Spanish Group for the Study of Antiretroviral Drug Resistance . 2007. Mutational patterns and correlated amino acid substitutions in the HIV-1 protease after virological failure to nelfinavir- and lopinavir/ritonavir-based treatments. J Med Virol 79:1617–1628. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dolling DI, Dunn DT, Sutherland KA, Pillay D, Mbisa JL, Parry CM, Post FA, Sabin CA, Cane PA, UK HIV Drug Resistance Database (UKHDRD), UK Collaborative HIV Cohort Study (UK CHIC) . 2013. Low frequency of genotypic resistance in HIV-1-infected patients failing an atazanavir-containing regimen: a clinical cohort study. J Antimicrob Chemother 68:2339–2343. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sterrantino G, Zaccarelli M, Colao G, Baldanti F, Di Giambenedetto S, Carli T, Maggiolo F, Zazzi M, ARCA Database Study Group . 2012. Genotypic resistance profiles associated with virological failure to darunavir-containing regimens: a cross-sectional analysis. Infection 40:311–318. doi: 10.1007/s15010-011-0237-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Clemente JC, Hemrajani R, Blum LE, Goodenow MM, Dunn BM. 2003. Secondary mutations M36I and A71V in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease can provide an advantage for the emergence of the primary mutation D30N. Biochemistry 42:15029–15035. doi: 10.1021/bi035701y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chang MW, Torbett BE. 2011. Accessory mutations maintain stability in drug-resistant HIV-1 protease. J Mol Biol 410:756–760. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.03.038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lambert-Niclot S, Flandre P, Canestri A, Peytavin G, Blanc C, Agher R, Soulié C, Wirden M, Katlama C, Calvez V, Marcelin AG. 2008. Factors associated with the selection of mutations conferring resistance to protease inhibitors (PIs) in PI-experienced patients displaying treatment failure on darunavir. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:491–496. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00909-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Delaugerre C, Pavie J, Palmer P, Ghosn J, Blanche S, Roudiere L, Dominguez S, Mortier E, Molina JM, de Truchis P. 2008. Pattern and impact of emerging resistance mutations in treatment experienced patients failing darunavir-containing regimen. AIDS 22:1809–1813. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e328307f24a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Varghese V, Mitsuya Y, Fessel WJ, Liu TF, Melikian GL, Katzenstein DA, Schiffer CA, Holmes SP, Shafer RW. 2013. Prototypical recombinant multi-protease-inhibitor-resistant infectious molecular clones of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57:4290–4299. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00614-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Poveda E, de Mendoza C, Martin-Carbonero L, Corral A, Briz V, González-Lahoz J, Soriano V. 2007. Prevalence of darunavir resistance mutations in HIV-1-infected patients failing other protease inhibitors. J Antimicrob Chemother 60:885–888. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkm276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Skálová T, Dohnalek J, Duskova J, Petrokova H, Hradílek M, Soucek M, Konvalinka J, Hasek J. 2006. HIV-1 protease mutations and inhibitor modifications monitored on a series of complexes. Structural basis for the effect of the A71V mutation on the active site. J Med Chem 49:5777–5784. doi: 10.1021/jm0605583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Henderson GJ, Lee SK, Irlbeck DM, Harris J, Kline M, Pollom E, Parkin N, Swanstrom R. 2012. Interplay between single resistance-associated mutations in the HIV-1 protease and viral infectivity, protease activity, and inhibitor sensitivity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:623–633. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05549-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Günthard HF, Aberg JA, Eron JJ, Hoy JF, Telenti A, Benson CA, Burger DM, Cahn P, Gallant JE, Glesby MJ, Reiss P, Saag MS, Thomas DL, Jacobsen DM, Volberding PA, International Antiviral Society–USA Panel . 2014. Antiretroviral treatment of adult HIV infection: 2014 recommendations of the International Antiviral Society–USA Panel. JAMA 312:410–425. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.8722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.de Meyer S, Vangeneugden T, van Baelen B, de Paepe E, van Marck H, Picchio G, Lefebvre E, de Béthune MP. 2008. Resistance profile of darunavir: combined 24-week results from the POWER trials. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 24:379–388. doi: 10.1089/aid.2007.0173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ghosh AK, Leshchenko S, Noetzel M. 2004. Stereoselective photochemical 1,3-dioxolane addition to 5-alkoxymethyl-2(5H)-furanone: synthesis of bis-tetrahydrofuranyl ligand for HIV protease inhibitor UIC-94017 (TMC-114). J Org Chem 69:7822–7829. doi: 10.1021/jo049156y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yoshimura K, Kato R, Yusa K, Kavlick MF, Maroun V, Nguyen A, Mimoto T, Ueno T, Shintani M, Falloon J, Masur H, Hayashi H, Erickson J, Mitsuya H. 1999. JE-2147: a dipeptide protease inhibitor (PI) that potently inhibits multi-PI-resistant HIV-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:8675–8680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.15.8675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Aoki M, Danish ML, Aoki-Ogata H, Amano M, Ide K, Das D, Koh Y, Mitsuya H. 2012. Loss of the protease dimerization inhibition activity of tipranavir (TPV) and its association with the acquisition of resistance to TPV by HIV-1. J Virol 86:13384–13396. doi: 10.1128/JVI.07234-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Fang G, Weiser B, Visosky A, Moran T, Burger H. 1999. PCR-mediated recombination: a general method applied to construct chimeric infectious molecular clones of plasma-derived HIV-1 RNA. Nat Med 5:239–242. doi: 10.1038/5607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kim EE, Baker CT, Dwyer MD, Murcko MA, Rao BG, Tung RD, Navia MA. 1995. Crystal structure of HIV-1 protease in complex with VX-478, a potent and orally bioavailable inhibitor of the enzyme. J Am Chem Soc 117:1181–1182. doi: 10.1021/ja00108a056. [DOI] [Google Scholar]