Abstract
Polygonumins A, a new compound, was isolated from the stem of Polygonum minus. Based on NMR results, the compound’s structure is identical to that of vanicoside A, comprising four phenylpropanoid ester units and a sucrose unit. The structure differences were located at C-3″″′. The cytotoxic activity of polygonumins A was evaluated on several cancer cell lines by a cell viability assay using tetrazolium dye 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT). The compound showed the highest antiproliferative (p < 0.05) activities against K562 (Human Leukaemia Cell Line), MCF7 (Human breast adenocarcinoma cell line), and HCT116 (Colorectal cancer cells) cells. Cytotoxic studies against V79–4 cells were carried out and showed that polygonumins A was toxic at 50 µg/ml, suggesting that this compound may be used as an anticancer drug without affecting normal cells. Polygonumins A also showed promising activity as an HIV-1 protease inhibitor with 56% relative inhibition. Molecular docking results indicated that the compound possesses high binding affinity towards the HIV protease over the low binding free energy range of -10.5 to -11.3 kcal/mol. P. minus is used in Malaysian traditional medicine for the treatment of tumour cells. This is the first report on the use of P. minus as an HIV-1 protease inhibitor.
Introduction
The use of traditional herbal medicine is widespread, and plants are sources of many natural antioxidants that might serve as leads for the development of novel drugs. Natural antioxidants and bioactive compounds derived from traditional herbal medicines have received increasing attention for their potential use in treating certain human diseases. For example, traditional herbal medicine has been used widely in cancer patients1 and to treat neurodegenerative disorders2.
Polygonum minus, also known as kesum, is an aromatic plant in the Polygonaceae family, which primarily grows in temperate regions. The plant originates from Southeast Asian countries such as Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, and Indonesia, where it is widely used as a spice and flavouring agent in the food industry. P. minus is abundant in Malaysia, where it has recently been listed in the National Agro-Food Policy by the Malaysian government to promote its production as a way to boost the agricultural economy. P. minus has also been recognized by the Malaysian government in the Herbal Product Blueprint as an essential oil-producing crop3. Kesum oil is a source of natural aliphatic aldehydes and could be commercially produced in North East Victoria and Australia4. In Japan, China, and Europe, kesum has long been used as a hot spice. The sprouts of kesum are a traditional vegetable in Japan and are often used in ‘sashimi’5.
In addition to its use as a spice in the food industry, P. minus has been reported for its use as a herbal medicine. Kesum leaf decoctions are traditionally used in indigestion relief, as ingredients in shampoo to remove dandruff6, and as postnatal tonics7. P. minus has been reported to exhibit anti-microbial activity8, anti-inflammatory activity9 and cytotoxic activity against HeLa (human cervical carcinoma) cells10 and gastric cytoprotective activity11. P. minus has also been reported to be a source of natural antioxidants for its high total phenolic content and reducing capacity12–14. The pharmacological properties of P. minus are based on its chemical constituents. Therefore, numerous studies on the profiling of metabolites have been performed on P. minus in the search for its active compounds15–17.
Encouraged by the aforementioned findings, we aimed to isolate novel bioactive compounds from kesum in our continued investigations on kesum as a medicinal plant. In the present study, we isolated a new polyoxygenated aromatic compound (polygonumins A) from the stem of kesum. Polygonumins A demonstrated cytotoxic activities against several cancer cell lines, which indicated that it has potential value in the treatment of cancers such as leukaemia. These data provide baseline information for possible use in controlling cancer diseases, particularly leukaemia. In addition, the present study was undertaken to evaluate the antioxidant and anticholinesterase activities of P. minus. We also examined the potential of polygonumins A to serve as an HIV-1 protease inhibitor. Finally, a molecular docking study was performed to support our findings, which could lead to a new drug discovery in the near future.
Results and Discussion
Polygonumins A structure
Spectroscopy data indicated that polygonumins A has a molecular formula of C52H50O21, as supported by HRESIMS [M + Na]+ at m/z 1033.2697 (1033.9642 ([M + Na]+ calc.) or [M]+ at m/z 1010.2697 (1010.9642 ([M]+ calc.).
FTIR spectra showed absorption bands at (cm−1) 3334.8 (hydroxyl); 2953.3 (C-H aliphatic); 1704 (C-carbonyl) and 1629.4; 1605.3, and 1513.7 (aromatics rings). 1H NMR spectra (acetoned6, 600 MHz) δH (ppm) 4.21 (m, 1 H, H-1a); 4.41 (m, 1 H, H-1b); 5.62 (d, 7.8, 1 H, H-3); 4.83 (ddd, 13.2, 10.2, 3.6, 1 H, H-4); 4.31 (m, 1 H, H-5); 4.61 (dd, 12.0, 3.0, 1 H, H-6a); 4.47 (m, 1 H, H-6b); 5.77 (d, 3.6, 1 H, H-1′); 4.67 (t, 7.8, 1 H, H-2′); 4.47 (m, 1 H, H-3′); 4.98 (t, 10.2, 1 H, H-4′); 4.11 (br t, 9.6, 1 H, H-5′); 4.41 (m, 1 H, H-6′a); 4.21 (m, 1 H, H-6′b); 7.55 (d, 8.4, 1 H, H-2″); 6.94 (d, 8.4, 1 H, H-3″); 6.94 (d, 8.4, 1 H, H-5″); 7.55 (d, 8.4, 1 H, H-6″); 7.57 (d, 8.4, 2 H, H-2″′/6′″); 7.57 (d, 8.4, 2 H, H-2”″/6″″); 7.55 (d, 8.4, 2 H, H-2″″′/6″″′); 6.90 (m, 2 H, H-3″′/5″′); 6.90 (m, 2 H, H-3″″/5″″), 6.94 (d, 8.4, 2 H, H3″″′/5″″′); 7.78 (d, 15.6, 1 H, H-7″); 7.72 (d, 15.6, 1 H, H-7″′); 7.68 (d, 10.2, 1 H, H-7″″); 7.64 (dd, 13.2, 1.2, 1 H, H-7″″′); 6.51 (d, 14.4, 1 H, H-8″); 6.48 (d, 13.8, 1 H; H-8″′); 6.43 (d, 12.6, 1 H, H-8″″); 6.42 (d, 16.2, 1 H, H-8″″′). 13C NMR spectra (acetoned6, 125 MHz) δC (ppm) 65.0 (C-1); 102.7 (C-2); 78.2 (C-3); 72.7 (C-4); 80.4 (C-5); 64.2 (C-6); 89.1 (C-1′); 73.2 (C-2′); 68.6 (C-3′); 71.4 (C-4′); 68.8 (C-5′); 63.1 (C-6′); 126.1(C-1″); 130.21 (C-2″); 115.9 (C-3″); 159.81 (C-4″); 115.9 (C-5″); 130.21 (C-6″); 130.24(C-2″′/6″′); 130.3(C-2″″/6″″); 130.4(C-2″″′/6″″′); 115.8 (3″′/5″′); 115.9 (3″″/5″″); 116.0 (3″″′/5″″′); 159.84 (C-4“′); 159.9 (C-4″″); 160.2 (C-4″″′); 169.6 (C=O1); 170.1 (C=O2); 20.0 (C-methyl1) and 20.1 (C-methyl2).
According to HRESIMS data, polygonumins A has a molecular weight of m/z 1010.2697 and a molecular formula of C52H50O21. FTIR spectra indicated that the compound has various functional groups i.e., hydroxyl absorbance at 3334.8 cm−1, aliphatic carbon absorbance at 2953.3 cm−1, carbonyl absorbance at 1704 cm−1 and aromatic absorbance at 1629.4, 1605.3, and 1513.7 cm−1. The results are supported by NMR data (1H and 13C NMR), which showed that the structure of polygonumins A comprises four phenylpropanoid units and a sucrose unit, which could be well distinguished from the structure of vanicoside A. NMR data for vanicoside A and polygonumins A are compared in Table 1 and Fig. 1.
Table 1.
Comparison of NMR data (1H and 13C) between vanicoside A and polygonumins A.
| C | Vanicoside A* | Polygonumins A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1H (300 MHz) | 13C (75 MHz) | 1H (600 MHz) | 13C (125 MHz) | |
| 1 | 4.25, 4.6 m | 63.80 | 4.21 (m, 1 H), 4.41 (m, 1 H) |
65.0 |
| 2 | — | 102.12 | — | 102.7 |
| 3 | 5.61 d (8.4) | 77.64 | 5.62 (d, 7.8, 1 H) | 78.2 |
| 4 | 4.65 m | 72.65 | 4.83 (ddd, 13.2, 10.2, 3.6, 1 H) | 72.7 |
| 5 | 4.3 m | 79.82 | 4.31 (m, 1 H) | 80.4 |
| 6 | 4.6 m | 64.55 | 4.61 (dd, 12.0, 3.0, 1 H), 4.47 (m, 1 H) | 64.2 |
| 1′ | 5.66 d (3.6) | 89.18 | 5.77 (d, 3.6, 1 H) | 89.1 |
| 2′ | 4.69 m | 73.01 | 4.67 (t, 7.8, 1 H) | 73.2 |
| 3′ | 3.9 m | 70.79 | 4.47 (m, 1 H) | 68.6 |
| 4′ | 3.51 dd (9.4, 9.4) | 70.66 | 4.98 (t, 10.2, 1 H) | 71.4 |
| 5′ | 4.3 m | 70.79 | 4.11 (br t, 9.6, 1 H) | 68.8 |
| 6′ | 4.3, 4.35 m | 64.49 | 4.41 (m, 1 H), 4.21 (m, 1 H) | 63.1 |
| 1″, 1″′ | — | 125.69 | — | 126.1 |
| — | 125.77 | — | 126.04 | |
| — | 125.84 | — | 125.91 | |
| — | 126.38 | — | 125.9 | |
| 2″ | 7.33 d (1.8) | 110.08 | 7.55 (d, 8.4, 1 H) | 130.21 |
| 3″ | — | 148.97b | 6.94 (d, 8.4, 1 H) | 115.9 |
| 4″ | — | 147.62b | — | 159.81 |
| 5″ | 6.81 | 114.94 | 6.94 (d, 8.4, 1 H) | 115.9 |
| 6″ | 7.11 dd (1.8, 8.2) | 123.24 | 7.55 (d, 8.4, 1 H) | 130.21 |
| 7″, 7′″″ | 7.58, 7.62, 7.64, 7.72 ea d (16) | 7.78 (d, 15.6, 1 H) | 146.1 | |
| 144.92 | 7.72 (d, 15.6, 1 H) | 145.3 | ||
| 145.91 | 7.68 (d, 10.2, 1 H) | 145.2 | ||
| 145.10 | 7.64 (dd, 13.2, 1.2, 1 H) | 145.1 | ||
| 8″, 8′″″ | 6.33, 6.40, 6.45, 6.53 ea d (16) | 113.41 | 6.51 (d, 14.4, 1 H) | 113.6 |
| 113.87 | 6.48 (d, 13.8, 1 H) | 114.1 | ||
| 113.97 | 6.43 (d, 12.6, 1 H) | 114.2 | ||
| 114.53 | 6.42 (d, 16.2, 1 H) | 114.3 | ||
| 9″, 9′″″ | — | 165.93 | — | 166.0 |
| 165.96 | — | 166.04 | ||
| 166.46 | — | 166.5 | ||
| 166.64 | — | 166.6 | ||
| 2/6′″−2/6″″′ | 7.45–7.65 m | 130.02 | 7.57 (d, 8.4, 2 H) | 130.24 |
| 130.06 | 7.57 (d, 8.4, 2 H) | 130.3 | ||
| 130.31 | 7.55 (d, 8.4, 2 H) | 130.4 | ||
| 3/5″′−3/5″″′ | 6.85–6.89 m | 115.63 | 6.90 (m, 2 H) | 115.8 |
| 115.64 | 6.90 (m, 2 H) | 115.9 | ||
| 115.73 | 6.94 (d, 8.4, 2 H) | 116.0 | ||
| 4′″ − 4″″′ | — | 159.53 | — | 159.84 |
| 159.63 | — | 159.9 | ||
| 159.81 | — | 160.2 | ||
| 1″″″ (C=O) | — | 170.12 (1) | — | 170.1 (1) |
| 2″″″ | 2.06 s | 20.03 (1) | 1.99 (s, 3 H) | 20.0 (1) |
| 1″″″′ | 3.85 s | 55.25 | — | 169.6 (2) |
| 2″″″′ | 1.99 (s, 3 H) | 20.1 (1) | ||
| 7.33 d (1.8, OH phenolic) | 7.83, 7.64 (4 OH phenolic) | |||
| 4.21 4.41 2 (OH glucose) | ||||
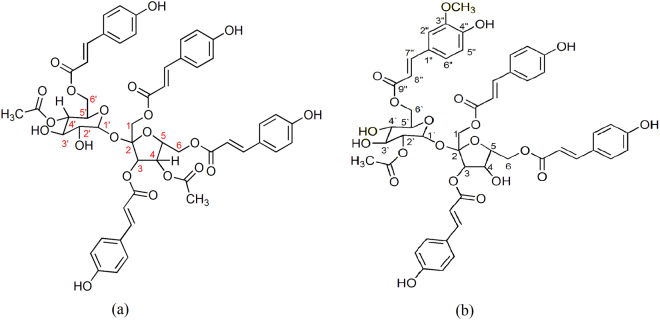
Figure 1.
Structure of (a) polygonumins A (b) vanicoside A.
Vanicoside A has a molecular formula of C51H50O21 and a molecular weight of 998 mass units18. The structural differences between vanicoside A and polygonumins A are located at C-3″″′. Carbon C-3″″′ of vanicoside A binds a methoxyl unit with δC and δH chemical shifts of 55.25 ppm and 3.85 ppm, respectively. Carbon C-3″″′ of polygonumins A binds a proton unit with a chemical shift δH of 6.94 (d, 8.4, 1 H). Furthermore, structural differences between vanicoside A and polygonumins A are observed for the substituents at C-4, C-2′ and C-4′. In vanicoside A, the substituents at C-4, C-2′ and C-4′ are hydroxyl, ethanoyl and hydroxyl units, respectively. However, the substituents at C-4, C-2′ and C-4′ in polygonumins A are ethanoyl, hydroxyl, and ethanoyl units, respectively. In the HMBC spectrum of polygonumins A in particular, the first ethanoyl unit shows long-range 1H-13C correlations between the signal δH 4.98 ppm (H-4′) and the carbonyl signal δC 170.1 ppm (C-2′″″″) and between the signal δH 1.99 ppm (H-1″″″′) and the carbonyl signal δC 170.1 ppm (C-2′″″″). The second ethanoyl unit of polygonumins A shows long-range 1H-13C correlations between the signal δH 4.83 ppm (H-4) and the carbonyl signal δC 169.6 ppm (C-2″″″) and between the signal δH 1.99 ppm (H-1″″″′) and the carbonyl signal δC 169.6 ppm (C-2″″″) (Fig. 2).
Figure 2.
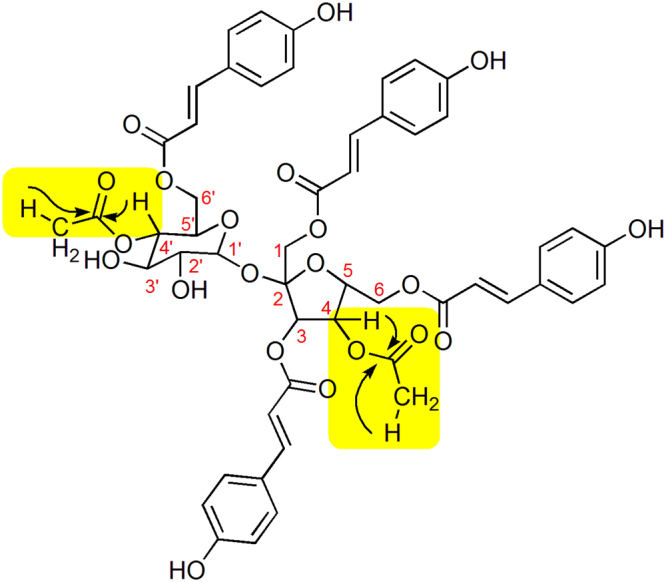
HMBC Polygonumins A.
Biological activities
It has been recommended that in selecting plant medicines for cancer treatment, ethnopharmacological uses in cancer-relevant diseases such as inflammation, infection, and immune and skin disorders should be taken into account19. In the present investigation, polygonumins A, a novel compound isolated from the stem of P. minus, was first evaluated for its antiproliferative activities against HCT116, C33A, H1299, MCF7, A549, and K-562 cancer cell lines using the MTT assay and then for its activities in radical scavenging and acetylcholinesterase inhibition. The activity towards HIV-1 protease inhibitor was also evaluated, as the newly isolated compound has a structure similar to that of vanicoside A.
The IC50 values inhibiting cell proliferation were determined, and the results are summarized in Table 2. The results showed that polygonumins A exhibited cytotoxicity against all tested cell lines except for the A549 cell line. Considering the cutoff point of 4 µg/ml for potential anticancer compounds20, values below this set point were obtained for this compound in HCT116 (IC50 3.24 µg/ml), K562 (IC50 2.25 µg/ml) and MCF7 (IC50 2.87 µg/ml), indicating that polygonumins A could be defined as an anticancer compound. Polygonumins A was most effective against K562 (human leukaemia cell line), with an IC50 of 2.25 µg/ml, lower than that of doxorubicin (2.97 µg/ml), highlighting the anti-leukaemia potential of polygonumins A. It has been well observed that leukaemia is more sensitive to chemotherapy than other malignancies are21,22.
Table 2.
Biological activities of polygonumins A, vanicoside A and vanicoside B.
| PolygonuminsA | Vanicoside A | Vanicoside B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biological activity | IC50 (µg/ml)a | |||
| Cytotoxic activity | HCT116 Doxorubicineb C33A Doxorubicine H1299 Doxorubicine MCF7 Doxorubicine A549 Doxorubicine K562 Doxorubicine V79-4 cells |
3.24 ± 0.73 2.97 ± 0.17 36.84 ± 7.16* 0.90 ± 0.1 4.71 ± 0.68* 10.12 ± 0.35 2.87 ± 0.28* 0.52 ± 0.1 — 3.13±0.11 2.25 ± 0.24 2.13 ± 0.54 >50 |
— | Inhibitory effects on two-stage carcinogenesis of mouse skin tumor48 |
| Compound isolated from Polygonum pensylvanicum showed Cyototoxic activity againts MCF cell line18 | Compound isolated from Polygonum pensylvanicum showed Cyototoxic activity againts MCF cell line18 | |||
| Antioxidant Activity (DPPH scavenging activity) (Total Phenolic Content (mg GAE/g) (Reducing Power Assay (EC50 (µg/ml)) |
Polygonumins A Gallic acidb Ascorbic acidb Polygonumins A Polygonumins A Gallic acid |
812.83 ± 41.11* 35.48 ± 1.03 63.12 ± 1.11 124.0625 ±0.88 89.3 ± 2.3 59.3 ± 0.58 |
Isolation from Polygonum hydropiper showed significant DPPH scavenging activity at 26 μg/ml49 — |
— |
| Anticholinesterase activity | Polygonumins A Tacrineb |
1980 ± 25.02* 2.54 ± 0.01 |
— | Anticholinesterase activity at 90 μg/ml was reported in Polygonum sachalinensis33 |
| α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity | n.d | Inhibitory activity was observed at 225 μg/ml in Polygonum sachalinense33 | ||
| β-glucosidase Inhibitory activity | n.d | IC 50 of 59.8 μg/ml was observed in Polygonum sachalinense50 | IC 50 of 48.3±1.39 was observed in Polygonum sachalinense50 | |
| Antimicrobial activity | n.d | Compound isolated from Polygonum sachalinense showed antimicrobial activity againts fish pathogen Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida51 | Isolated from Polygonum sachalinense showed antimicrobial activity againts fish pathogen Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida51 |
aData are expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments; bPositive control.
n.d not determined.
*Significant p < 0.05 between positive control and tested compound.
In addition to its sensitivity towards the leukaemia cell line, polygonumins A exhibited cytotoxic activities against human breast cancer and colorectal cancer cells. This finding could well explain why polygonumins A has been widely used to treat digestive disorders. It is believed that the sugar moiety, a sucrose unit, in its structure plays an important role in determining its pharmacological and biological activities. Structure and activity relationship (SAR) analysis of several related compounds containing sugar moieties, such as CCL-34 and its natural analogues, revealed that the sugar moiety was essential to their anticancer activity23. In particular, the sugar moiety was recognized to be critical to the topoisomerase inhibition activity of anthracyclines as antitumour drugs. It has also been suggested that the sugar structure in daunorubicin plays a critical role in determining its anticancer activity24. To date, there is no report on the cytotoxicity activity of vanicoside A, except in an MCF cell line. However, vanicoside A has been classified as a member of the family of protein kinase C inhibitors18, which exhibit antitumour effects.
The equivalence between the therapeutic effect on cancer cell lines and the toxicological effect on target human organs is an important criterion of the applicability of an anticancer compound. Therefore, we conducted toxicological studies on the V79–4 cell line (lung fibroblast cell line derived from Chinese hamsters) to determine the safe concentration range of polygonumins A. This test has been widely used to evaluate general cytotoxicity and target organ toxicity25. In some cases, this test may also provide information about lethal dose in vivo26. The results indicated a loss of viability of V79–4 fibroblasts at concentrations above 50 µg/ml following approximately 24 hours of exposure. Thus, the compound is approximately 10 times as toxic towards cancer cells and normal cells at these concentrations, as it is at its therapeutic concentration.
Interestingly, vanicoside A also showed significant β-glucosidase inhibitory activity, indicating promising therapeutic potential in the treatment of metastatic cancer and human immunodeficiency virus infection (HIV)27. As polygonumins A possesses a structure similar to that of vanicoside A, we performed an HIV-1 protease inhibition test against the newly isolated compound. Based on our results (Table 3), polygonumins A showed potential activity as an HIV-1 protease inhibitor. A relative inhibition level of 56% towards HIV-1 protease was detected compared with pepstatin A as a positive control. This is the first report indicating that P. minus exhibits activity towards HIV-1 protease. Several Polygonum spp have been reported to possess anti-HIV properties, with compounds such as flavonoid glycoside, quercetin and phenolics playing an essential role in anti-HIV activity28–30. Based on the results of this study, we believe that the phenyl propanoid glycoside moiety in the structure of polygonumins A is associated with the activation of anti-HIV protease activity. Moreover, previous study have shown that the phenylpropanoid glycoside group acts as an inhibitor of HIV-1 integrase activity, thus supporting our findings31
Table 3.
Relative inhibition of polygonumins A against HIV-1 protease.
| % relative inhibitiona | |
|---|---|
| Pepstatin A (1 mM) | 81.48 ± 0.76 |
| 1% DMSO | 8.07 ± 0.13 |
| Polygonumins A | 56.51 ± 0.13 |
aData are expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.
Several techniques have been used to determine antioxidant capacity. One of the methods we used is based on scavenging activity, in which we measured the ability of polygonumins A to donate electrons to a free radical to scavenge potential damage. The antioxidant activity determined by the DPPH free radical-scavenging method (Table 2) was not consistent with our expectations. The measured IC50 value of 812 µg/ml indicated that polygonumins A is far less potent than gallic acid and ascorbic acid. It has been reported that ethanolic, methanolic, and aqueous extracts of P. minus exhibit antioxidant activity as remarkable as that of gallic acid and ascorbic acid13,32. This activity is due to the phenylpropane group of P. minus. The four units of the phenylpropanoid group in the structure have been show to produce lower scavenging activity33. However, the high antioxidant activity of P. minus extracts has been attributed to high contents of polyphenolic compounds16. Therefore, we measured the total phenolic content of polygonumins A by the Folin-Ciocalteu method. Phenols consist of hydroxyl groups that are able to destroy free radicals to form stable phenoxyl radicals34. Although the results of the DPPH assay showed a weak scavenging ability, the total phenolic content of this compound is relatively high at 124.0625 ± 0.88 mg GAE/g when compared with that of crude extract. In our previous studies, we found that the total phenolic content in crude P. minus ethanolic extract produced the highest scavenging activity, ranging from 100 to 140 mg GAE/g16. Perhaps the antioxidant activity of this compound is not due to DPPH scavenging activity alone. Because antioxidant activity can be realized by multiple mechanisms or a single mechanism, we analysed the reducing power capacity of polygonumins A. This assay determines a substance’s ability to reduce Fe3+ to Fe2+. The presence of antioxidants in the extracts result in the reduction of the ferric cyanide complex (Fe3+) to the ferrous cyanide form (Fe2+). We found that polygonumins A may act as an electron donor (a hydrogen electron donor), supporting its antioxidant activity, as the compound showed a comparatively high reducing capacity, with an EC50 of 89.3 µg/ml, near the value of its reference compound gallic acid (Table 2). The reducing power of this compound increased rapidly with its concentration. Based on this antioxidant activity, the compound’s high total phenolic content was correlated with its reducing power. Hence, It can be inferred that polygonumins A could act as a strong antioxidant agent.
It is well documented that the use of antioxidants may minimize neuronal degeneration and slow the progress of Alzheimer’s disease35. Anticholinesterase activity in compounds has also been reported to be related to radical-scavenging activity36. Moreover, based on our previous findings on crude extracts of polygonumins A, the compound showed promising anticholinesterase activity16. Therefore, we evaluated the anticholinesterase activity of polygonumins A relative to that of tacrine. However, the compound showed only weak anticholinesterase activity at concentrations of up to 2 mg/ml. (Table 2), and the compound did not show potential to serve as an anticholinesterase drug. The IC50 for this compound could not be determined due to its low activity; but we managed to determine the IC20 value for this compound (1980 µg/ml).
Molecular docking of polygonumins A, vanicoside A and pepstatin in HIV-1 protease (pdb ID: 3OXC)
Polygonumins A appeared to possess high binding affinity towards HIV protease (pdb ID: 3OXC), as indicated by low binding free energy range of −10.5 to −11.3 kcal/mol (Table 4) recorded in 3 independent runs. The low binding free energies are comparable to those of vanicoside A (−10.5 to −11.7 kcal/mol) docked to the same protein, as illustrated in Fig. 3. Moreover, pepstatin (positive control) exhibited low binding free energies of −8.9 to −9.5 kcal/mol in 3 independent runs. Pepstatin has been used as positive control drug that exhibits anti-HIV properties through enzymatic assay37,38, and thus, pepstatin was included as a reference in a comparative analysis of molecular docking to determine the compound’s activity as an anti-HIV protease based on its potential binding affinity. The structures possessing the lowest binding free energy were visualized, and hydrogen bond analysis was conducted using the surface/binding analysis tool in UCSF Chimera version 1.11. The residues involved in hydrogen bond interactions are summarized in Table 5. Moreover, superimposition of the structures showed that polygonumins A, vanicoside A and pepstatin were docked in a similar binding domain (Fig. 4).
Table 4.
Affinity of polygonumins A, vanicoside A and pepstatin to HIV-1 protease.
| Affinity (kcal/mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| run #1 | run #2 | run #3 | |
| Polygonumins A | −11.3 | −10.5 | −10.5 |
| Vanicoside A | −10.5 | −11.1 | −11.7 |
| Pepstatin | −9.5 | −9.4 | −8.9 |
Figure 3.
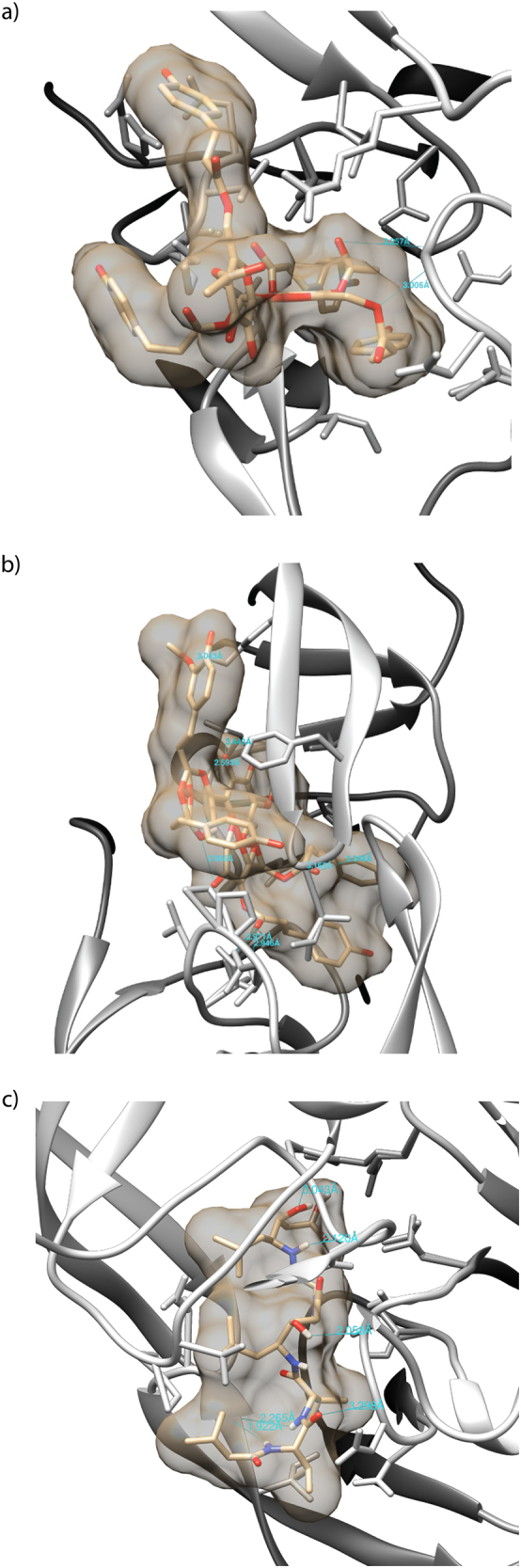
Hydrogen bond interaction of polygonumins A (a), vanicoside A (b) and pepstatin (c) with HIV-1 protease at respective lower binding energy.
Table 5.
Residues of HIV-1 protease involved in hydrogen bond interactions.
| Residue | Position | |
|---|---|---|
| Polygonumins A | ASP GLY |
29 27 |
| Vanicoside A | ASP LYS ILE ILE THR |
30 45 50 150 180 |
| Pepstatin | ASP ASP GLY GLY GLY |
29 129 48 127 27 |
Figure 4.
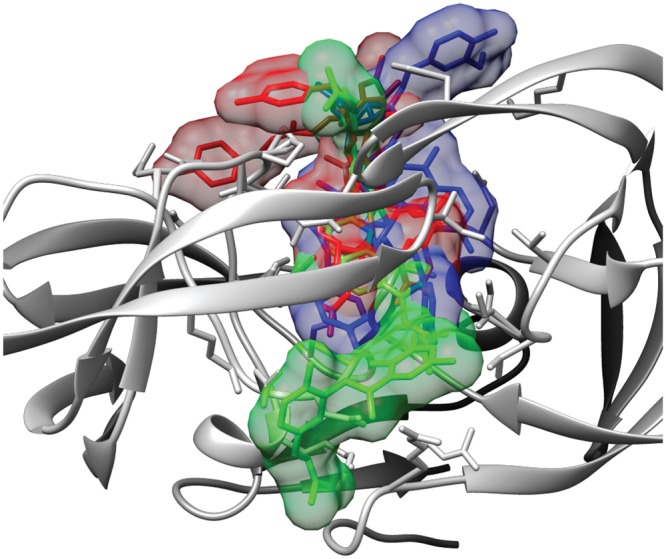
Superimposition of the structures revealed polygonumins A (red), vanicoside A (blue), and pepstatin (green) were docked in a similar binding domain.
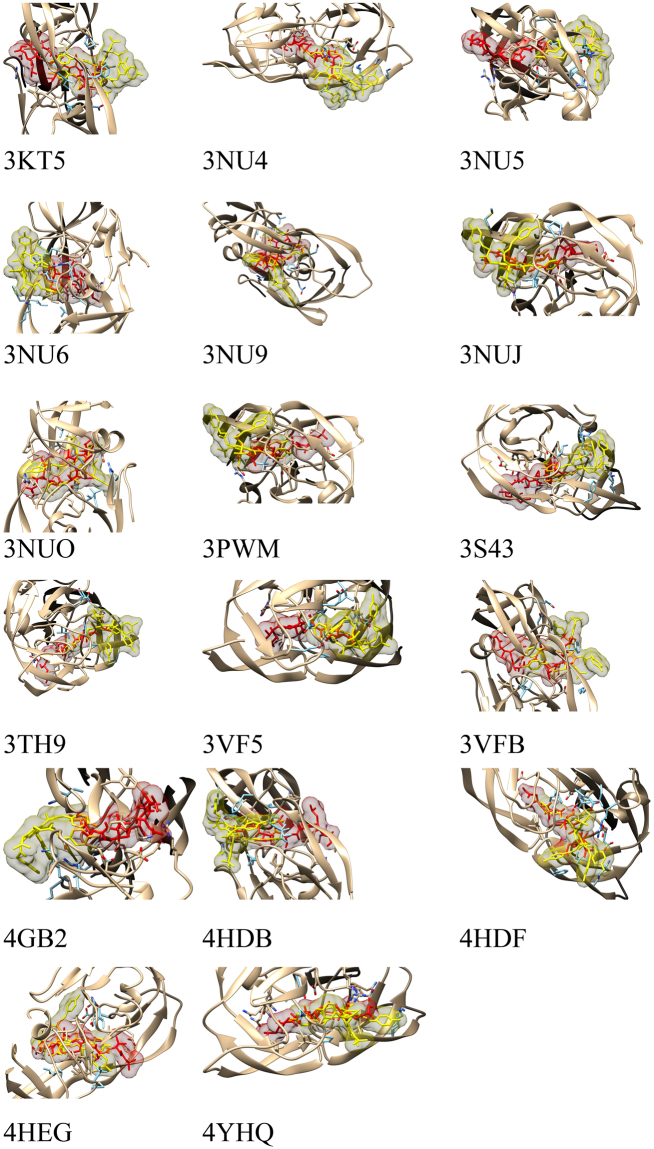
Recent studies have reported the anti-HIV activity of several bioactive compounds derived from plant extracts37,38 and mushroom39. The current study examined the anti-HIV activity of polygonumins A, and the compound’s potential activity was further evaluated to identify the potential interactions of the compound with mutant HIV-1 proteases through molecular docking simulation. Mutant HIV-1 proteases available in the protein databank were downloaded and submitted to docking analysis using VinaAutodock. Polygonumins A was found to engage in potential interactions with mutant HIV-1 proteases with the following PDB IDs: 3PWM, 4HDB, 4HDF, 4HEG, and 4YHQ; the affinities recorded were lower than −10 kcal/mol. The potential interaction was found to be particularly significant for the mutant 4YHQ, for which the affinity was as low as −13.8 kcal/mol. These results are comparable to those obtained for the positive control drug pepstatin, which showed a significant binding affinity towards the mutant HIV-1 proteases. The results are summarized in Table 6. The docked positions of pepstatin and polygonumins A are depicted in Fig. 5. This analysis indicated that polygonumins A possesses the potential to inhibit a range of HIV-1 protease mutants that are currently known to resist available antiretroviral drugs. The potential anti-HIV activities against different protease mutants were predicted based on a complementary fit of polygonumins A with the target HIV protease mutants relative to the positive control drug pepstatin. This approach is well established for identifying potent HIV protease inhibitors40, which can be used for drug development in the future.
Table 6.
Affinities of polygonumins A and pepstatin docked in HIV-1 protease mutants. Residues of HIV-1 protease mutants involved in hydrogen bond interactions with polygonumins A and pepstatin.
| Protease Mutant (PDB ID) | Affinity (kcal/mol) | Residues involved in hydrogen bond interaction with ligand : hydrogen bond distance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polygonumins A | Pepstatin | Polygonumins A | Pepstatin | |
| 3KT5 | −7.3 | −8.5 | ASP 1029: 3.038 LYS 1045: 2.937 ASP 1030: 3.459 |
ASP 29: 3.103 GLY 1027: 3.315 GLY 48: 3.244 |
| 3NU4 | −8.3 | −8.6 | ASP 29: 3.346 LYS 45: 2.912 LYS 45: 3.176 |
ASP 29: 2.761 GLY 27: 3.139 GLY 27: 2.985 GLY 127: 3.243 |
| 3NU5 | −9.1 | −8.3 | LYS 145: 3.386 LYS 145: 2.800 GLY 148: 3.285 GLU 21: 3.345 |
VAL 50: 3.225 VAL 150: 3.171 GLY 48: 2.972 ASP 29: 2.859 |
| 3NU6 | −8.3 | −8.3 | LYS 45: 3.126 ARG 87: 3.111 ARG 87: 3.039 ARG 8: 2.982 ARG 8: 3.257 ARG 8: 3.335 ARG 8: 3.211 |
ARG 8: 3.099 ARG 8: 3.006 ASP 29: 3.269 GLY 27: 2.957 GLY 48: 3.089 GLY 27: 2.779 |
| 3NU9 | −9.3 | −8.3 | ILE 50: 3.012 GLU 121: 3.158 ASP 130: 3.269 PRO 181: 3.491 |
ASP 29: 3.087 ILE 150: 3.024 GLY 48: 3.195 GLY 48: 3.166 GLY 48: 2.920 |
| 3NUJ | −8.6 | −8.1 | ASP 30: 3.004 LYS 45: 2.965 ARG 8: 3.222 ILE 50: 3.280 MET 46: 3.620 |
ASP 29: 3.077 GLY 48: 3.091 ILE 50: 3.078 ASP 30: 2.861 GLY 48: 3.074 GLY 48: 3.084 ASP 25: 3.244 |
| 3NUO | −9.3 | −8.6 | ARG 8: 3.381 ARG 8: 2.944 |
ASP 29: 2.965 ILE 50: 3.063 GLY 27: 3.018 GLY 48: 3.276 GLY 48: 2.780 GLY 48: 2.892 |
| 3PWM | −10.2 | −9.8 | ASP 30: 2.895 ILE 150: 3.098 ASP 30: 3.371 PRO 181: 3.317 |
ASP 29: 2.930 GLY 48: 2.880 GLY 48: 3.237 ASP 29: 2.936 |
| 3S43 | −8.3 | −8.4 | ARG 8: 2.807 ASP 130: 2.982 LYS 145: 3.279 LYS 145: 3.094 ARG 187: 2.994 MET 146: 3.573 |
ILE 50: 3.285 GLY 48: 3.113 GLY 48: 3.271 ASP 29: 2.817 GLY 48: 3.283 GLY 48: 2.794 |
| 3TH9 | −7.5 | −8.4 | ARG 8: 2.937 GLU 21: 3.160 GLY 48: 3.249 |
ASP 29: 2.936 ASP 30: 3.356 ASP 29: 3.327 GLY 48: 3.200 |
| 3VF5 | −9.5 | −9.7 | ARG 8: 2.962 ARG 8: 3.185 GLY 48: 3.153 |
ASP 29: 2.991 ASP 29: 3.370 GLY 27: 3.066 GLY 48: 2.894 ASP 25: 3.097 |
| 3VFB | −9.4 | −9.7 | ASP 29: 2.917 ASP 30: 3.371 LYS 45: 2.939 ASN 83: 3.022 ASP 30: 3.335 PRO 81: 3.522 |
ARG 8: 2.792 ASP 30: 3.031 GLY 27: 3.015 GLY 27: 3.157 ASP 25: 2.967 GLY 48: 2.602 ASP 25: 2.962 ASP 25: 3.130 |
| 4GB2 | −7.5 | −8.3 | LYS 45: 3.352 LYS 45: 3.389 ARG 87: 3.383 ARG 87: 2.878 THR 91: 3.220 ASP 29: 3.216 |
LYS 45: 3.121 GLY 48: 3.035 ARG 8: 3.365 ARG 8: 2.941 GLY 27: 3.034 GLY 48: 2.945 GLY 27: 3.289 |
| 4HDB | −11.4 | −11.2 | ASP 129: 3.175 ASN 130: 2.964 ASN 130: 3.386 LYS 145: 3.088 ASN 130: 3.073 |
LYS 45: 3.400 GLY 48: 3.100 GLY 48: 3.110 GLY 48: 2.802 GLY 148: 3.261 |
| 4HDF | −10.8 | −11.2 | GLY 48: 3.356 GLY 48: 3.298 ARG 8: 3.335 ARG 8: 3.296 ASP 25: 3.295 GLU 21: 3.436 |
GLY 27: 3.223 GLY 48: 3.146 GLY 27: 3.341 ASP 25: 3.124 GLY 48: 2.759 ASP 25: 3.462 GLY 48: 2.996 GLY 48: 2.989 ASP 30: 3.165 |
| 4HEG | −11.4 | −11.3 | GLY 48: 3.381 GLY 48: 3.243 ASP 30: 3.125 GLY 49: 3.551 |
ASP 29: 2.882 GLY 48: 3.135 GLY 48: 3.037 GLY 48: 3.141 GLY 48: 3.166 GLY 48: 3.175 |
| 4YHQ | −13.8 | −12.2 | ARG 8: 3.193 ARG 8: 2.931 VAL 82: 3.170 ASP 29: 3.268 ASN 30: 3.325 ASN 30: 3.184 LYS 45: 3.258 LYS 45: 2.836 GLY 48: 3.261 GLY 48: 2.964 ASN 30: 3.208 ASN 30: 3.478 ASN 30: 3.384 |
ASP 29: 2.803 GLY 48: 3.098 GLY 48: 2.935 GLY 48: 2.955 GLY 48: 3.178 GLY 48: 2.946 GLY 27: 2.629 GLY 48: 3.292 ASN 30: 2.953 |
Figure 5.
polygonumins A (yellow chain), and pepstatin (red chain) docked in HIV-1 protease mutants (labelled with PDB ID).
Experimental procedures
Plant material
The stem of P. minus was originally collected from Ulu Yam, Malaysia, and a voucher specimen was deposited in the UKMB Herbarium, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia. Specimens were identified by a taxonomist and further confirmed by ITS sequencing41. Samples were washed and stored at −80 °C prior to use.
Isolation of polygonumins A
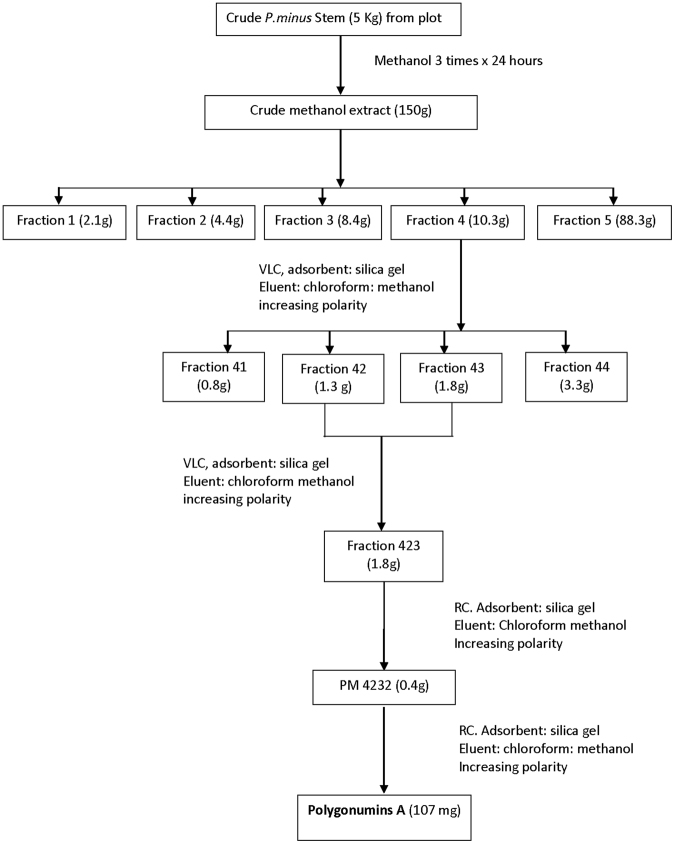
A total of 5 kg of P. minus stem bark powder (230–250 mesh) was extracted using methanol 3 times for 24 hours each time at room temperature. The extracts were concentrated by a vacuum rotary evaporator at low pressure to yield a dark-green gum (260 g). A total of 150 g of methanol extract was fractionated by vacuum liquid chromatography (VLC) using a column (Φ 10 cm) with silica gel 60PF254 (0.063–0.200 mm) as an adsorbent and a chloroform:methanol mixture with increasing polarity (100% chloroform, 90–10%, 80–20%, and MeOH 100%) to yield 5 fractions i.e., F1 (2.1 g), F2 (4.4 g), F3 (8.4 g), F4 (10.3 g), and F5 (88.3 g), respectively. Based on the spot size produced by thin layer chromatography (TLC), F4 was refractionated by the VLC method using a column (Φ 5 cm) with silica gel 60PF254 (0.063–0.200 mm) as an adsorbent and a chloroform:methanol mixture (100% chloroform, 90–10%, 80–20%, and MeOH 100%) as an eluent to produce 4 fractions: F41 (0.8 g), F42 (1.3 g), F43 (1.8 g) and F44 (3.3 g), respectively. The selected fractions, F43 and F42 (1.8 g), were combined and further purified by radial chromatography (RC) with silica gel 60PF254 containing gypsum as an adsorbent with a chloroform:methanol mixture as an eluent with increasing polarity (95:5% 100% MeOH) to yield Fraction 4232 (0.4 g). Radial chromatography was then performed iteratively using the same eluent mixture to obtain polygonumins A (107 mg) as a white amorphous compound with a melting point of 150.2–152.0 °C. The schematic representation of polygonumins A isolation is summarized in Fig. 6.
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of polygonumins A isolation.
Compound identification
The structure of the purified compound was determined based on spectral data recorded on a Frontier Perkin-Elmer FTIR/NIR (Perkin-Elmer Inc., Norwalk, CT, USA) spectrophotometer and a Bruker NMR 600 MHz Cryo-Probe instrument that could perform 1-D and 2-D NMR measurements (Bruker, Germany). ESIMSs were recorded on a Bruker Daltonics micrOTOF-Q 86 (direct infuse + ve.m). Isolation was carried out by radial chromatography using round glass plates on a Merck Kieselgel 60 PF254 (art. no. 7749), and the profile was analysed using aluminium sheets measuring 20 × 20 cm on a Merck TLC silica gel 60 F254 with a thickness of 0.25 mm (art. no. 5554) with UV light detection (254 nm) or CeSO4 spraying followed by heating.
Anticholinesterase activity
Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) was assessed using the spectrophotometric method developed by Ellman42 with slight modifications. Electric eel AchE (electric eel acetyl-cholinesterase, type-VI-S, EC 3.1.1.7, Sigma–Aldrich, St. Louis, USA) and acetylthiocholine iodide (Sigma–Aldrich, Steinheim, Germany) were used as the enzyme and substrate, respectively. Briefly, 125 μl of DTNB (Sigma–Aldrich, Steinheim, Germany) (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8, 0.1 M NaCl, 0.02 M MgCl2.6H2O), 25 μl of AChE (0.2 U/ml), 25 μl of test compound solution in DMSO, and 50 μl of buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8, 0.1% BSA) were mixed and incubated at 25 °C for 30 min. DMSO or buffer (25 μl) was added instead of the test compound solution in control experiments. The reaction was then initiated by the addition of 25 μl of acetylthiocholine iodide (0.25 mmol/l), which brought the final volume to 250 μl. The formation of 5-thio-2-nitrobenzoate anion from the enzymatic hydrolysis of acetylthiocholine iodide was monitored based on the absorbance at 412 nm on a 96-well microplate reader (Model 680, Biorad Inc., and Hercules, CA, USA). The reaction rates were calculated from data collected at specific time points over the first 180 s in 20 s increments. Percent inhibition of AChE was determined by the ratio of the reaction rate with the test sample to that with the blank control (DMSO in Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.0) using the formula (E − S)/E × 100, where E is the activity of enzyme with DMSO and S is the activity of enzyme with the test sample. The experiments were carried out in triplicate. Tacrine was used as a reference compound.
Antioxidant activity
Free radical-scavenging assay
Radical-scavenging activities were determined by the DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) assay. Various concentrations of the experimental samples were obtained, and the volume was adjusted to 200 μl with ethanol. Approximately 100 μl of 0.5 mM DPPH in methanol was added to the samples or standard (ascorbic acid and gallic acid) in a 96-well plate. After incubation for 30 min in the dark, changes in absorbance at 600 nm were measured on a 96-well plate reader. IC50 was calculated as the sample concentration required for a 50% decrease in the absorbance of a control solution of DPPH.
Reducing power assay
Ferric reducing antioxidant power was determined by the direct reduction of Fe3+ (CN−)6 to Fe2+ (CN−)6 and by measuring the absorbance resulting from the formation of the Perls’ Prussian Blue complex following the addition of excess ferric ions (Fe3+). The reducing power method was performed as reported by Oyaizu43 with slight modifications. Different concentrations of samples (50 µg/ml to 500 µg/ml) were mixed with 2 ml of 0.2 M, pH 6.6 sodium phosphate buffer and 1.25 ml of potassium ferricyanide. The mixture was incubated at 50 °C for 20 minutes. After 20 minutes of incubation, 1.25 ml of trichlorocetic acid (10%) was added. Finally, 0.5 ml of FeCl3 (0.1%) was added to the mixture and incubated for 10 minutes. The intensity of the blue-green colour was measured at 700 nm. Increases in the absorbance of the reaction mixture indicated an increase in the reduction capability. The EC50 value (µg/mL) associated with the reducing power-the extract concentration at which the absorbance was 0.5 was calculated from a graph of absorbance at 700 nm against the extract concentration. Gallic acid was used as a positive control.
Total phenolic content
The total phenolic content was determined using the Folin-Ciocalteu method44. The reaction mixture was prepared by mixing 0.2 ml of sample (1 mg/mL) and 1.5 ml of 10% Folin-Ciocalteu reagent dissolved in water. The mixture was allowed to equilibrate for 5 minutes and then mixed with 1.5 ml 7.5% Na2CO3 solution. After incubation for 60 minutes at room temperature in the dark, the absorbance of the mixture was read at 725 nm against a blank using a spectrophotometer. The blank was prepared by using DMSO instead of a sample. The sample procedure was repeated for gallic acid at different concentrations, i.e., 0.00, 0.25, 0.50, 0.75 and 1 mg; the results were used to produce a calibration curve. Total phenolic content was calculated as the milligrams of gallic acid equivalent (GAE) per gram of sample (mg GAE/g) by using the gallic acid calibration curve, y = 0.0016× + 0.0295, R² = 0.9548.
In vitro cytotoxicity
Cell lines and cell culture
Cells of the lines K-562 (human leukaemia cell line), C33A (cervical cancer cell line), HCT116 (colorectal cancer cell line), and A549 (human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cell line) were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection. H1299 (human non-small cell lung cancer cell line) and MCF7 (human breast adenocarcinoma cell line) were provided as a courtesy by Prof. Masa-Ikeda of Tokyo Medical and Dental University. Cells were cultured in DMEM media supplemented with 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin and streptomycin. All cell lines were cultured at 37 °C with 5% CO2.
V79 fibroblast cultures
V79–4 cells were grown in tissue culture flasks using DMEM as the growth medium at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% carbon dioxide and 95% air. Cultures were examined daily to ensure they remained healthy. The confluent monolayer was removed by trypsinization, and the number of viable cells was calculated. Cells were seeded into a 96-well plate at a seeding density of 10 000 cells/well and incubated at 37 °C. The test substance was prepared by dilution with an appropriate volume of complete growth medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS) to obtain the highest working concentration of 100 µg/ml (weight/volume). Procedures were performed aseptically.
The test substance was tested in triplicate at concentrations of 3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50 and 100 µg/ml. Growth medium from each well of a 96-well plate containing healthy culture was replaced with 200 µl of the test substance and controls respectively. The cultures were then incubated for 24 hours at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% carbon dioxide and 95% air.
In vitro cytotoxicity assay
Cells were plated in 96-well microplates and cultured for 24 h. The test compounds were dissolved in DMSO and added at different concentrations (100, 50, 25, 12.5, 6.25, 3.13 µg/ml) to the plate in triplicate. The cytotoxicities against K-562 and H1299 cell lines were measured using a colorimetric MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)−2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay. Exponentially growing cells were harvested and suspended in DMEM, and a 100 µl cell suspension was added to a 96-well plate. After 24 h incubation at 37 °C with 5% CO2, the cells were treated with varying concentrations of the test compounds (100 µl). The medium was removed, and cells in each well were incubated with PBS containing 1 mg/ml MTT for 24 h at 37 °C with 5% CO2. DMSO (100 µl) was added to each well to dissolve the insoluble formazan crystal, and plates were incubated for 4 h at 37 °C for complete solubilization of formazan. The level of coloured formazan derivative was analysed on a microplate reader using the results at wavelengths of 570 nm and 630 nm as references45. The percent viability of cells was calculated using the following equation:
Percent viability was plotted versus compound concentration, and IC50 values at which the compound showed 50% inhibition of tumour cell proliferation were calculated using Microsoft Excel. The compound was tested at each concentration in triplicate.
HIV-1 protease fluorogenic assay
The HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor Screening Kit (Fluorometric) from Biovision Incorporated (Milpitas, CA, USA) was used to measure the inhibitory effect of each sample on HIV-1 protease activity. Pepstatin A (1 mM) was used as a known standard for HIV-1 protease inhibition, and 1% DMSO was used as a solvent control. The assay was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, each sample (1 mg/ml) was incubated with HIV-1 protease enzyme at room temperature for 15 minutes. Then, the HIV-1 protease fluorescent substrate was added. The fluorescence (excitation/emission = 330/450 nm) in kinetic mode over a period of 90 minutes at 37 °C was determined using a PerkinElmer EnSpire plate reader.
Statistical analysis
One-way ANOVA at 95% confidence level was used for statistical analysis followed by Dunnett’s test in relation to control and standard.
Molecular docking
The structure of wild-type HIV-1 protease (PDB ID: 3OXC) was downloaded from the protein databank for molecular docking. The protein model was prepared by removing all non-standard residues that included antiviral drug saquinavir, sulfate ion and formic acid in their structure. Water molecules were removed from the structure and hydrogen atoms added using AutoDockTools-1.5.6 prior to conversion of the file format to PDBQT for docking analysis. A grid box with dimensions of 50 × 40 × 40 A3 was generated with HIV-1 protease as the centroid using AutoDockTools-1.5.6. Vanicoside, pepstatin, and polygonuminss were docked in the HIV-1 protease using AutoDockVina 1.1.246. Docking of the molecules was repeated in three independent runs. Structures were visualized and hydrogen bond interactions were further analysed using UCSF Chimera version 1.1147.
Conclusion
Polygonumins A, a new compound isolated from P. minus, showed promising anticancer and HIV protease inhibition activities. This compound has been filed for a Malaysian patent (PI 2014700594). In summary, our investigation provided promising results supporting the potential use of P. minus in the treatment of cancers such as leukaemia and colorectal and breast cancer and as an anti-HIV agent. Hopefully, these leads can be taken up for the further development of anticancer and anti-HIV drugs.
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia grants (UKM-AP-BPB-14–2009) awarded to Normah Mohd Noor and Research University Grants from Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM-GUP-2013–028 and DLP 2013-024) awarded to Syarul Nataqain Baharum. We acknowledge Chulalongkorn University for the Visiting Lecturer Fellowship 2017 awarded to Syarul Nataqain Baharum. We thank Emelda R. Rohani for her significant contribution to the isolation of polygonumins A. We also acknowledge Bimo A. Tejo for his contribution in molecular docking analysis. The HIV-1 test assay was funded by the 90th Anniversary of Chulalongkorn University, Rachadapisek Sompote Fund awarded to Siriporn Chuchawankul and Chanin Sillapachaiyaporn. We also acknowledge the Centre for Research and Instrumentation Management (CRIM), UKM for Research Instrumentation Development Grants awarded in 2010 and 2013 (PIP-CRIM).
Author Contributions
S.N.B. and N.M.N. conceived and designed the whole experiments; R.A., I.S., M.T., C.F.L. and C.S. performed the experiments and analysed the data; S.N.B., N.M.N. and S.C. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; F.I. and N.F.R. performed the cytotoxicity test; R.A., I.S., C.F.L. C.S, S.C., T.S., T.T. and S.N.B. wrote and edited the paper. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Poonthananiwatkul B, Lim RHM, Howard RL, Pibanpaknitee P, Williamson EM. Traditional medicine use by cancer patients in Thailand. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2015;168:100–107. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.03.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Li X-Z, Zhang S-N, Liu S-M, Lu F. Recent advances in herbal medicines treating Parkinson’s disease. Fitoterapia. 2013;84:273–285. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2012.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hassan, W. W. Healing Herbs of Malaysia. Federal Land Development Authority (FELDA), Kuala Lumpur (2007).
- 4.Hunter M. Australian kesom oil - A new essential oil for the flavour and fragrance industry. Agro Food Industry Hi-Tech. 1996;7:26–28. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Miyazawa M, Tamura N. Components of the essential oil from sprouts of Polygonum hydropiper L. (‘Benitade’) Flavour and Fragrance Journal. 2007;22:188–190. doi: 10.1002/ffj.1779. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Vimala, S., Adenan, M. I., Ahmad, A. R. & Shahdan, R. Nature’s choice to wellness, antioxidant vegetables/ulam. (Forest Research Institute Malaysia, 2003).
- 7.Burkill, H., Vol. 2 (Kuala Lumpur: Ministry of Agriculture & Cooperatives, 1966).
- 8.Hassim N, et al. Antioxidant and Antibacterial Assays on Polygonum minus Extracts: Different ExtractionMethods. International Journal of Chemical Engineering. 2015;2015:10. doi: 10.1155/2015/826709. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.George A, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Polygonum minus (Huds) extract (LineminusTM) in in-vitro enzyme assays and carrageenan induced paw edema. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2014;14:355. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ali AM, et al. Antiviral and Cytotoxic Activities of Some Plants Used in Malaysian Indigenous Medicine. Pertanika Journal of Tropical Agricultural Science. 1996;19(2/3):129–136. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Qader S, Abdulla M, Chua L, Sirat H, Hamdan S. Pharmacological mechanisms underlying gastroprotective activities of the fractions obtained from Polygonum minus in sprague dawley rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:1481–1496. doi: 10.3390/ijms13021481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Azlim Almey, A. et al. Total phenolic content and primary antioxidant activity of methanolic and ethanolic extracts of aromatic plants’ leaves. International Food Research Journal17 (2010).
- 13.Huda-Faujan, N., Noriham, A., Norrakiah, A. & Babji, A. Antioxidant activity of plants methanolic extracts containing phenolic compounds. African Journal of Biotechnology8 (2009).
- 14.Maizura, M., Aminah, A. & Aida, W. M. W. Total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of kesum (Polygonum minus), ginger (Zingiber officinale) and turmeric (Curcuma longa) extract. International Food Research Journal18 (2011).
- 15.Baharum SN, Bunawan H, Ghani MA, Mustapha WA, Noor NM. Analysis of the chemical composition of the essential oil of polygonum minus huds. Using two-dimensional gas chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC-TOF MS) Molecules. 2010;15:7006–7015. doi: 10.3390/molecules15107006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ahmad R, et al. Volatile Profiling of Aromatic Traditional Medicinal Plant, Polygonum minus in Different Tissues and Its Biological Activities. Molecules. 2014;19:19220–19242. doi: 10.3390/molecules191119220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ahmad R, Bunawan H, Normah MN, Baharum SN. Chemical composition in different tissues of Polygonum minus by using GC X GC-TOF MS and direct discrimination by multivariate analysis of fourier transform infrared spectroscopy data. International Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemical Research. 2016;8:1986–1992. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zimmermann ML, Sneden AT. Vanicosides A and B, Protein Kinase C Inhibitors from Polygonum pensylvanicum. Journal of Natural Products. 1994;57:236–242. doi: 10.1021/np50104a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cordell GA, Beecher CWW, Pezzuto JM. Can ethnopharmacology contribute to the development of new anticancer drugs? Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 1991;32:117–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-8741(91)90110-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Boik, J. (Oregon Medical Press, Princeton, MN, USA, 2001).
- 21.Efferth T, Miyachi H, Bartsch H. Pharmacogenomics of a traditional Japanese herbal medicine (Kampo) for cancer therapy. Cancer Genomics and Proteomics. 2007;4:81–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dzoyem JP, et al. Cytotoxicity and antimicrobial activity of the methanol extract and compounds from Polygonum limbatum. Planta Medica. 2012;78:787–792. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1298431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lin, Y.-S. et al. In vitro and in vivo anticancer activity of a synthetic glycolipid as TLR4 activator. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 10.1074/jbc.M111.285171 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.Zhu L, et al. Syntheses and biological activities of daunorubicin analogs with uncommon sugars. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 2005;13:6381–6387. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2005.06.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cingi MR, et al. Choice and standardization of test protocols in cytotoxicology: A multicentre approach. Toxicology in Vitro. 1991;5:119–125. doi: 10.1016/0887-2333(91)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shrivastava RJ, Rispat GW, Chevalier G, Massingham A, Can R. the in vivo maximum tolerated dose be predicted using in vitro techniques? A working hypothesis. ATLA. 1991;19:393–402. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Borges de Melo, E., Gomes, A. S. & Carvalho, I. α- and β-Glucosidase inhibitors: chemical structure and biological activity. Tetrahedron62, 10277–10302, 10.1016/j.tet.2006.08.055 (2006).
- 28.Datta BK, et al. Anti-cholinergic, cytotoxic and anti-HIV-1 activities of sesquiterpenes and a flavonoid glycoside from the aerial parts of Polygonum viscosum. Pharmaceutical Biology. 2004;42:18–23. doi: 10.1080/13880200490504943. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lin HW, et al. Anti-HIV activities of the compounds isolated from polygonum cuspidatum and polygonum multiflorum. Planta Medica. 2010;76:889–892. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1240796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhong Y, et al. Highly potent anti-HIV-1 activity isolated from fermented Polygonum tinctorium Aiton. Antiviral Research. 2005;66:119–128. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2005.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kim HJ, et al. HIV-1 integrase inhibitory phenylpropanoid glycosides from Clerodendron trichotomum. Archives of pharmacal research. 2001;24:286–291. doi: 10.1007/BF02975093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Qader SW, et al. Antioxidant, total phenolic content and cytotoxicity evaluation of selected Malaysian plants. Molecules. 2011;16:3433–3443. doi: 10.3390/molecules16043433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Fan P, Terrier L, Hay AE, Marston A, Hostettmann K. Antioxidant and enzyme inhibition activities and chemical profiles of Polygonum sachalinensis F.Schmidt ex Maxim (Polygonaceae) Fitoterapia. 2010;81:124–131. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2009.08.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.De Gaulejac NS-C, Glories Y, Vivas N. Free radical scavenging effect of anthocyanins in red wines. Food Res Int. 1999;32:327–333. doi: 10.1016/S0963-9969(99)00093-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Atta ur R, Choudhary MI. Bioactive natural products as a potential source of new pharmacophores. A theory of memory. Pure and Applied Chemistry. 2001;73:555–560. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Papandreou MA, et al. Effect of a polyphenol-rich wild blueberry extract on cognitive performance of mice, brain antioxidant markers and acetylcholinesterase activity. Behavioural Brain Research. 2009;198:352–358. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kapewangolo P, Tawha T, Nawinda T, Knott M, Hans R. Sceletium tortuosum demonstrates in vitro anti-HIV and free radical scavenging activity. South African Journal of Botany. 2016;106:140–143. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2016.06.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Thayil SM, Thyagarajan SP. PA-9: A Flavonoid Extracted from Plectranthus amboinicus Inhibits HIV-1 Protease. International Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemical Research. 2016;8:1020–1024. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wang CR, et al. First report on isolation of methyl gallate with antioxidant, anti-HIV-1 and HIV-1 enzyme inhibitory activities from a mushroom (Pholiota adiposa) Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2014;37:626–637. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2014.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Razzaghi-Asl N, Sepehri S, Ebadi A, Miri R, Shahabipour S. Effect of Biomolecular Conformation on Docking Simulation: A Case Study on a Potent HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research: IJPR. 2015;14:785–802. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bunawan H, Choong C, Md-Zain B, Baharum S, Noor N. Molecular systematics of Polygonum minus Huds. based on ITS sequences. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12:7626–7634. doi: 10.3390/ijms12117626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ellman GL, Courtney KD. Andres jr, V. & Featherstone, R. M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochemical Pharmacology. 1961;7:88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Oyaizu, M. Studies on products of browning reaction prepared from glucoseamine. Japanese JNutr44 (1986).
- 44.Wootton-Beard PC, Moran A, Ryan L. Stability of the total antioxidant capacity and total polyphenol content of 23 commercially available vegetable juices before and after in vitro digestion measured by FRAP, DPPH, ABTS and Folin–Ciocalteu methods. Food Research International. 2011;44:217–224. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2010.10.033. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Abe K, Matsuki N. Measurement of cellular 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction activity and lactate dehydrogenase release using MTT. Neuroscience Research. 2000;38:325–329. doi: 10.1016/S0168-0102(00)00188-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Trott O, Olson AJ. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. Journal of computational chemistry. 2010;31:455–461. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Pettersen EF, et al. UCSF Chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem. 2004;25:1605–1612. doi: 10.1002/jcc.20084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Takasaki M, Konoshima T, Kuroki S, Tokuda H, Nishino H. Cancer chemopreventive activity of phenylpropanoid esters of sucrose, vanicoside B and lapathoside A, from Polygonum lapathifolium. Cancer letters. 2001;173:133–138. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3835(01)00670-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kiem PV, et al. New phenylpropanoid esters of sucrose from Polygonum hydropiper and their antioxidant activity. Archives of pharmacal research. 2008;31:1477–1482. doi: 10.1007/s12272-001-2133-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kawai Y, et al. beta-Glucosidase inhibitory activities of phenylpropanoid glycosides, vanicoside A and B from Polygonum sachalinense rhizome. Fitoterapia. 2006;77:456–459. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2006.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kumagai H, et al. Antimicrobial substances from rhizomes of the giant knotweed Polygonum sachalinense against the fish pathogen Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida. Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung. C, Journal of biosciences. 2005;60:39–44. doi: 10.1515/znc-2005-1-208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]