Abstract
Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1) is a selective and potent allosteric inhibitor of necroptosis by specifically inhibiting the activity of receptor-interacting protein (RIP) 1 kinase. The aim of the present study was to determine the effect of Nec-1 on an anoxia model comprising mouse skeletal C2C12 myotubes. In the present study, a hypoxic mimetic reagent, cobalt chloride (CoCl2), was used to induce hypoxia in C2C12 myotubes. The cytotoxic effects of CoCl2-induced hypoxia were determined by a Cell Counting kit-8 assay and flow cytometry. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was used to characterize the morphological characteristics of dead cells at the ultrastructural level. To clarify the signaling pathways in CoCl2-mediated cell death, the expression levels of RIP1, RIP3, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and B cell lymphoma-2 adenovirus E1B 19-kDa interacting protein 3 (BNIP3) were investigated by western blotting. Oxidative stress was determined using 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate to measure intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the fluorescent dye JC-1 was used to measure mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm). The results showed that the ratios of apoptotic and necrotic C2C12 cells were increased following CoCl2 treatment, typical necroptotic morphological characteristics were able to observe by TEM, whereas Nec-1 exhibited a protective effect against CoCl2-induced oxidative stress. Treatment with Nec-1 significantly decreased the levels of RIP1, p-ERK1/2, HIF-1α, BNIP3 and ROS induced by CoCl2, and promoted C2C12 differentiation. Nec-1 reversed the CoCl2-induced decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential. Together, these findings suggested that Nec-1 protected C2C12 myotubes under conditions of CoCl2-induced hypoxia.
Keywords: C2C12, necrostatin-1, cobalt chloride, hypoxia, extracellular-signal regulated kinase 1/2, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/Bcl-2 adenovirus E1B 19-kDa interacting protein 3, reactive oxygen species
Introduction
Oxygen is central to cellular respiration and energy metabolism. However, hypoxia is common in the tissues of the majority of individuals. Hypoxia-induced muscle wasting is a condition frequently reported in several environmental and pathological conditions, including exposure to high altitudes, prolonged immobilization, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, exercise, and anemia (1–4). However, the mechanism underlying the effects of hypoxia in skeletal muscle remains to be elucidated.
Cobalt chloride (CoCl2) is a well-known hypoxia mimetic, which competes with the activity of bivalent ions and suppresses the formation of oxygenated hemoglobin (5). In cell culture systems, CoCl2 inhibits the catalysis of prolyl hydroxylases, leading to an intracellular hypoxia-like state (6,7). Therefore, CoCl2 was applied in the present study to simulate a hypoxic condition.
In the mid-19th century, necrosis was the first identified form of cell death. Necrosis is unregulated and is considered to be a cause or consequence of disease; by contrast, apoptosis is a highly regulated and programmed process, which is manipulated by defined molecular pathways (8). However, in 1988, a pioneering publication reported a type of necrotic cell death driven by specific genes, which was defined as 'necroptosis' (9,10). Necroptosis is initiated by tumor necrosis factor (TNF)/Fas ligand under apoptosis-deficient conditions. Molecules that regulate necroptosis include those involved in receptor-interacting protein kinase (RIP)1, RIP3, and mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein signaling. Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1) is a small molecule inhibitor, which allosterically inhibits RIP1 by interacting with the T-loop, which is essential for death domain receptor engagement (11). Accumulating evidence has indicated that Nec-1 inhibits RIP1 but does not affect RIP3 (11,12).
Hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1α is a transcription factor, which acts in response to hypoxia. The hypoxia- or CoCl2-induced increase in HIF-1α is due to increased protein stability, which is mediated by activation of the JNK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways (13). The Raf/MAPK kinase (MEK)/ERK cascade couples signals which regulate the activity of several proteins involved in cell death (14). The activation of RIP1 results in phosphorylation of the ERK signaling pathway through the activation of MEK1/2. Nec-1 can inhibit the interaction between MEK and ERK1/2 (15). Another report showed that the inhibitory effect on ERK1/2 was significantly augmented by Nec-1 in K562 and HL60 cells.
HIF-1α also affects pro-death genes, including Bcl-2 adenovirus E1B 19-kDa interacting protein 3 (BNIP3) (16,17). Early reports suggested that BNIP3 is pivotal in the loss of skeletal muscle mass, and provides a potential therapeutic target in muscle wasting disorders and other diseases (18). BNIP3 readily inserts into the mitochondrial membrane following a hypoxic stimulus or reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Nec-1 effectively suppresses BNIP3-induced caspase-independent necrosis, including cell death and lactate dehydrogenase leakage (19). However, the role of Nec-1 in the response of HIF-1α to hypoxia remains to be fully elucidated. Based on these findings, the present study hypothesized that HIF-1α/BNIP3 is involved in CoCl2-induced necroptosis.
Previous studies have shown that necroptosis can be induced by CoCl2 and identified mitochondrion-generated ROS as essential mediators of this process (5,20). Several lines of evidence have shown that excessive ROS can directly trigger mitochondrial dysfunction or activated tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, which subsequently induces caspase-dependent classical apoptosis or caspase-independent necrosis (21,22). However, the mechanism underlying the effects of CoCl2-induced necroptosis in skeletal muscle remains to be elucidated.
Nec-1 has been used as evidence of the role of necroptosis in different disorders (8,23,24). Nec-1 exhibits protective effects against Parkinson's disease, cerebral ischemia injury, cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, Alzheimer's disease, stroke, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, in which oxidative stress or free radical injury is considered a potent inducer (23–25). However, the effect of Nec-1 on hypoxia-induced muscle wasting remains to be fully elucidated. In the present study, it was shown that RIP1-dependent necroptosis induced by CoCl2 was mediated through the ERK1/2 and HIF-1α/BNIP3 pathways. Nec-1 may exert protective effects on C2C12 cell viability and differentiation under conditions of CoCl2-induced hypoxia, which may provide a novel insight into protecting against hypoxia-induced muscle wasting.
Materials and methods
C2C12 culture and drug administration
The C2C12 mouse myoblast cell line (Stem Cell Bank, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China) was cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) high glucose (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (HyClone; GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Logan, UT, USA), 100 U/ml of penicillin, and 100 µg/ml of streptomycin in 5% CO2 at 37°C. When the cells reached 80–90% confluence, they were differentiated by incubation in DMEM containing 2% horse serum (HyClone; GE Healthcare Life Sciences). A stock solution of Nec-1 (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck Millipore, Munich, Germany) was prepared in DMSO at a concentration of 150 mM and the working solution was diluted into 0.1% with DMEM. CoCl2 (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck Millipore) was dissolved in DMEM as a 2,000 × concentrate and diluted to 200 µM for actual use. Subsequently, 150 µM Nec-1 was added to cells for treatment in the absence or presence of 200 µM CoCl2 for 48 h prior to cell collection.
Cell viability assays
Cell viability was assessed using CCK8 assays (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Jiangsu, China). Briefly, the C2C12 cells were seeded onto 96-well plates at a density of 0.2×104 cells/well. Following drug treatment for 48 h, the cells were treated with CCK8 solution. Quantification was performed 1 h later by measuring the absorbance at 450 nm on a microplate reader (BioTek Instruments, Inc., Midland, ON, Canada). Data are presented as the percentage of the control.
Detection of necrosis and apoptosis
An Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate apoptosis detection kit (Sony Biotechnology Inc., San Jose, CA, USA) was used in accordance with the manufacturer's protocol. The C2C12 myotubes were incubated with CoCl2 or Nec-1 for 48 h. The cells were then digested with trypsin and washed twice with cold phosphate-buffered saline. The cells were subsequently resuspended in 500 µl of binding buffer. Subsequently, 5 µl of Annexin V and 5 µl of 7-aminoactinomycin D were added to the cells and incubated in the dark for 15 min.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
The specimens were fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde and post-fixed in 1% osmium tetroxide, dehydrated through a graded ethanol series, and embedded in epoxy resin. Serial ultrathin sections were cut to 70 µm on an LKB-III ultratome (Leica Microsystems GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany), stained with uranyl acetate (Ted Pella, Inc., Redding, CA, USA) and lead citrate (Ted Pella, Inc.), and examined on an electron microscope (H7600; Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) at an acceleration voltage of 100 kV.
Western blot analysis
The C2C12 myotubes were lysed in RIPA buffer containing protease inhibitor (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) and phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride to extract total proteins. An equal quantity of protein (20 µg) was separated by 10–12% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. The membranes were blocked with 5% non-fat milk and incubated with primary antibodies targeting RIP1 (1:1,000; MAB3585, R&D Systems, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA), RIP3 (1:1,000; ab16090, Abcam, Cambridge, UK), myogenin (1:500; MAB3876, EMD Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA), myosin heavy chain (MyHC; 1:1,000; MAB4470, R&D Systems, Inc.), atrogin-1 (1:1,000; ab168372, Abcam), phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2, 1:1,000; 4370, Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA, USA), ERK1/2 (1:1,000; 4695, Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.), HIF-1α (1:1,000; ab179483, Abcam), or BNIP3 (1:1,500; ab109362, Abcam) overnight at 4°C. The membranes were then incubated with goat anti-mouse (1:10,000; AS003, ABclonal Biotech, Co., Ltd., Woburn, MA USA) or anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (1:10,000; AS014, ABclonal Biotech, Co., Ltd.) for 1 h at room temperature. Band intensity was determined using a chemiluminescent imaging system (Tanon Sciences and Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Tubulin (1:5,000; AC021, ABclonal Biotech, Co., Ltd.) was used as a control for protein quantification. Band intensity was quantified using ImageJ software (v1.4.3.67, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Determination of intracellular ROS
The level of intracellular ROS was measured by BD Accuri C6 (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) using a DCFDA-Cellular Reactive Oxygen Species Detection Assay kit (Abcam) according to the manufacturer's protocol. The cells were incubated with 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate (DCFH-DA) at a final concentration of 10 µM in 1X buffer for 30 min at 37°C, and detected by fluorescence spectroscopy with maximum excitation and emission spectra of 485 and 535 nm, respectively. For each analysis, 10,000 events were recorded. Data were exported by Accuri CFlow software (v1.0.227.4, BD Biosciences), and the intracellular ROS levels were expressed as the average DCF fluorescence intensity.
Measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm)
The Δψm of the C2C12 cells was determined by CytoFLEX (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA) with the fluorescent dye JC-1 (Nanjing KeyGEN Biotech Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China). The cells were incubated with 1 µl JC-1 solution for 20 min at 37°C. Fluorescence was measured on a flow cytometer with excitation and emission spectra of 488 and 530 nm, respectively. Data were exported by CyExpert (v1.2.11.0, Beckman Coulter).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using Prism 5 software (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA). Data are reported as the mean ± standard error of the mean. Statistical significance was assessed by a one-way analysis of variance between groups. When significant variations were found, Tukey's multiple comparison test was performed. In all analyses, P<0.05 was considered to indicate statistically significant difference.
Results
Nec-1 treatment increases cell viability and reduces cell death in C2C12 cells under conditions of CoCl2-induced hypoxia
In the present study, the well-known hypoxia mimetic CoCl2 was used to induce hypoxia, and C2C12 cell viability was measured. As evidenced by the CCK8 assay, CoCl2 produced toxic effects on the C2C12 cells in a time-dependent manner. Cell viability was decreased by ~40% following CoCl2 treatment for 48 h and had decreased to ~50% at 72 h. To determine the protective effects of Nec-1 on hypoxia-induced cell viability, the C2C12 cells were cultured with CoCl2 and Nec-1 for 72 h. The CoCl2-induced cytotoxicity towards the C2C12 cells was significantly reversed by Nec-1 treatment. This suggested that Nec-1 protected against hypoxia-induced cell death in C2C12 myotubes (Fig. 1A).
Figure 1.

Nec-1 treatment increases cell viability and reduces cell death in C2C12 cells under conditions of CoCl2-induced hypoxia. (A) Cell viability was assessed using a CCK8 assay and is expressed as the percentage of the control, *P<0.05, compared with the control group. (B) Cells stained with Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate on the x-axis and 7-AAD on the y-axis. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean from three independent experiments. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001, compared with the control group; ##P<0.01, compared with the CoCl2 group. CoCl2, cobalt chloride; 7-AAD, 7-amino-actinomycin D.
The cytotoxic effects of CoCl2-induced hypoxia were also analyzed by flow cytometry, which revealed that the percentage of cells undergoing apoptosis and necrosis in response to CoCl2 treatment was 22.52% (Fig. 1B). Nec-1 inhibited CoCl2-induced cell death, suggesting that CoCl2-induced cell death was RIP1-dependent.
Nec-1 treatment promotes C2C12 differentiation under conditions of CoCl2-induced hypoxia
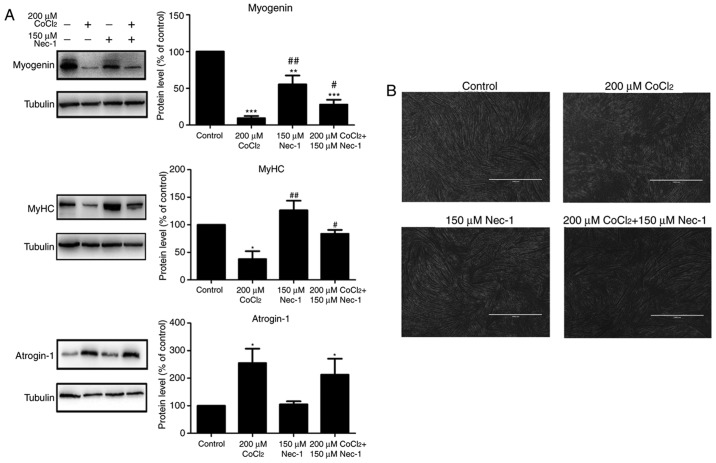
Myogenin and MyHC are specific differentiation markers required for the fusion of myoblasts to form myotubes. As shown in Fig. 2A, the expression of myogenin and MyHC was inhibited by CoCl2 treatment for 48 h. Nec-1 reversed the changes in the expression of myogenin and MyHC under conditions of hypoxia. Spindled ring-shaped myotubes were formed in all groups with the exception of the CoCl2 group (Fig. 2B). The level of atrogin-1, a muscle-specific protein that mediates muscle degradation, was also detected. No significant decrease in the protein level of atrogin-1 was found in the Nec-1+CoCl2 group, compared with that in the CoCl2 group, suggesting that Nec-1 did not reverse CoCl2-induced muscular atrophy (Fig. 2A).
Figure 2.
Nec-1 treatment promotes C2C12 differentiation under conditions of CoCl2-induced hypoxia. (A) Western blot analysis showed the relative expression of myogenin, MyHC and atrogin-1 in C2C12 cells treated in the absence or presence of CoCl2 and Nec-1. Band intensity was quantified using ImageJ software. Tubulin was used as an internal control. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001, compared with the control group; #P<0.05 and ##P<0.01, compared with the CoCl2 group. (B) Optical micrographs of C2C12 cells treated in the absence or presence of CoCl2 and Nec-1. Scale bar=1 µm. MyHC, myosin heavy chain; Nec-1, necrostatin-1; CoCl2, cobalt chloride.
Nec-1 treatment inhibits necroptosis induced by CoCl2 in C2C12 cells
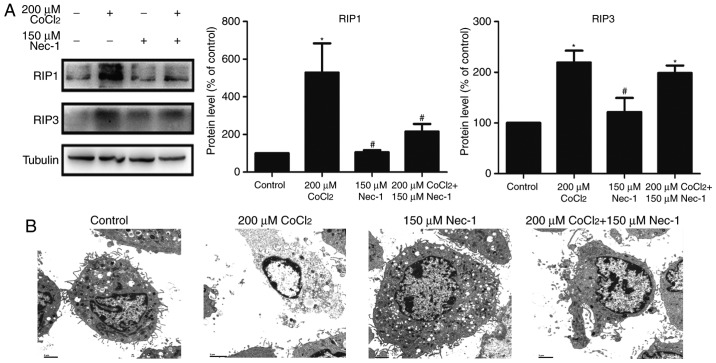
RIP1 and RIP3 are key factors in triggering necroptosis. The expression of RIP1 was upregulated following treatment with CoCl2 and inhibited by Nec-1. However, Nec-1 had minimal effect on RIP3 in the CoCl2-treated cells (Fig. 3A). TEM was also used to characterize the morphological characteristics of dead cells at the ultrastructural level. CoCl2 induced typical necroptotic morphological characteristics, including mitochondrial swelling, membranolysis, organelle disappearance, and mitochondrial damage (Fig. 3B). Consistent with the results of the flow cytometric analysis, Nec-1 lessened the morphological damage to the C2C12 cells induced by CoCl2. Collectively, these results indicated that CoCl2 induced necroptosis in the C2C12 myotubes, and that it was reversed by Nec-1 treatment.
Figure 3.
Nec-1 treatment inhibits necroptosis induced by CoCl2 in C2C12 cells. (A) Western blot analysis revealed the protein levels in C2C12 myotubes treated in the absence or presence of CoCl2 and Nec-1. Band intensity was quantified using ImageJ software. Tubulin was used as an internal control. *P<0.05, compared with the control group; #P<0.05, compared to the CoCl2 group. (B) Transmission electron microscopic images of C2C12 cells. Scale bar=2 µm. CoCl2, cobalt chloride; RIP1, receptor-interacting protein 1; RIP3, receptor-interacting protein 3.
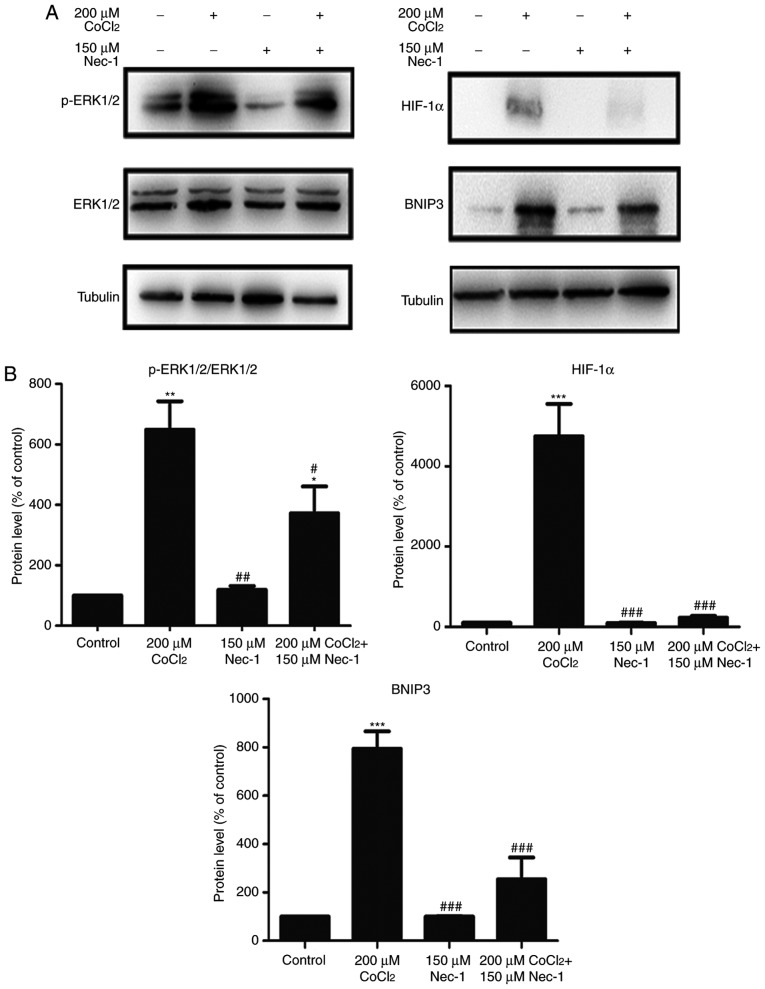
Nec-1 treatment prevents the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, and expression of HIF-1α and BNIP3 under CoCl2-induced hypoxic conditions
To understand the protective mechanisms underlying the effect of Nec-1 on C2C12 cells under hypoxic conditions, the present study detected the levels of total and p-ERK1/2, which regulate the activity of several proteins involved in cell death. The increase in p-ERK1/2 induced by CoCl2 was inhibited by Nec-1 (Fig. 4A). The expression of HIF-1α and its downstream target, BNIP3, was also evaluated. HIF-1α and BNIP3 were upregulated following CoCl2 treatment, consistent with the results from our previous study (26), whereas culture with Nec-1 and CoCl2 reduced the expression of HIF-1α and BNIP3, suggesting the involvement of the HIF-1α/BNIP3 signaling pathway in CoCl2-induced hypoxia in C2C12 cells (Fig. 4B).
Figure 4.
Nec-1 treatment prevents ERK1/2 phosphorylation and decreases the expression of HIF-1α and BNIP3 in hypoxia induced by CoCl2. Western blot analysis was used to examine the expression of (A) p-ERK1/2, ERK1/2, (B) HIF-1α and its downstream target, BNIP, in C2C12 cells in the absence or presence of CoCl2 and Nec-1. Band intensity was quantified using ImageJ software. Tubulin was used as an internal control. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001, compared with the control group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 and ###P<0.01, compared with the CoCl2 group. ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; p-, phosphorylated; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; BNIP3, Bcl-2 adenovirus E1B 19-kDa interacting protein 3; Nec-1, necrostatin-1; CoCl2, cobalt chloride.
Nec-1 treatment decreases intracellular ROS in C2C12 cells under CoCl2-induced hypoxic conditions
Intracellular ROS production was measured by flow cytometric analysis following DCFH-DA staining. DCFH-DA diffuses into cells and is deacetylated by cellular esterase to non-permeable and non-fluorescent DCFH, which is rapidly oxidized to the fluorescent compound DCF and can be detected by fluorescence spectroscopy. Compared with the control group, CoCl2 produced more ROS; however, this effect was inhibited by Nec-1 administration (Fig. 5A and B).
Figure 5.

Nec-1 treatment decreases intracellular ROS in C2C12 cells under hypoxia induced by CoCl2. (A) Flow cytometry images and (B) statistical analysis of ROS-positive cells. The x-axis represents DCF intensity, whereas the y-axis indicates the cell count corresponding to fluorescence intensity. ***P<0.001, compared with the control group; ##P<0.01 compared with the CoCl2 group. ROS, reactive oxygen species; CoCl2, cobalt chloride.
Nec-1 treatment decreases the Δψm of C2C12 cells under CoCl2-induced hypoxic conditions
Δψm is an indicator of cell health, and the dissipation of Δψm suggests a loss of mitochondrial membrane integrity, reflecting the initiation of a pro-apoptotic signal. A red fluorescent aggregate and monomer fluorescence were detected in the control group. Following the administration of CoCl2, the ratio of JC-1 aggregate/monomer fluorescence intensity decreased, suggesting the earliest event in the process of apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction. There was a significant increase in aggregate fluorescence in the CoCl2+Nec-1 group, compared with that in the CoCl2 group (Fig. 6A and B).
Figure 6.
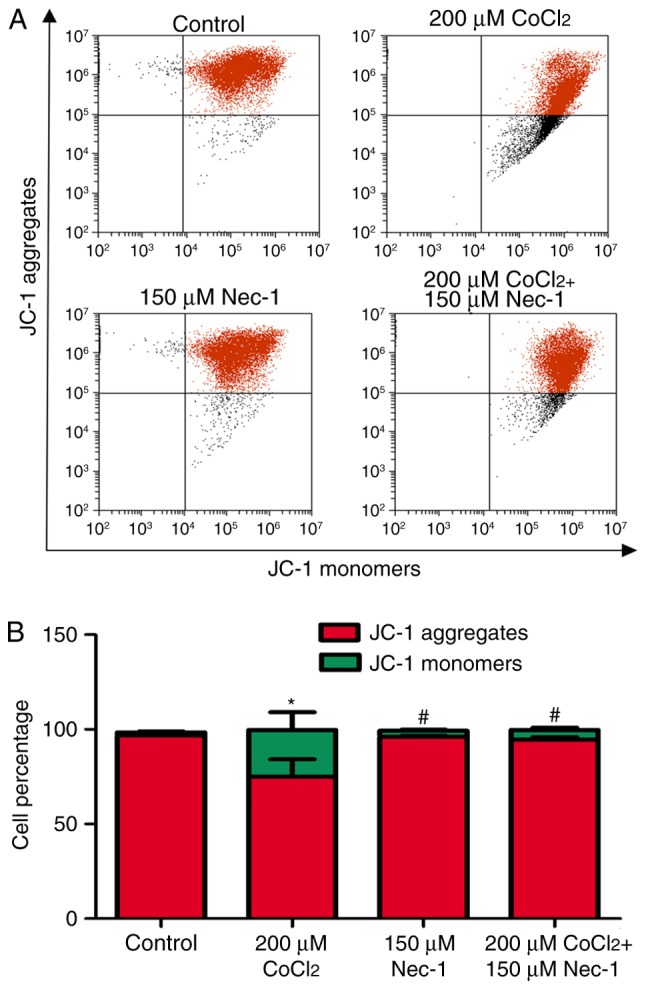
Nec-1 treatment decreases the Δψm of C2C12 cells under hypoxic conditions. (A) Flow cytometry images and (B) statistical analysis of JC-1. The x-axis represents monomer intensity, whereas the y-axis indicates the aggregate intensity. *P<0.05, compared with the control group; #P<0.05, compared with the CoCl2 group. Δψm, mitochondrial membrane potential; CoCl2, cobalt chloride.
Discussion
In the present study, it was shown that necroptosis elicited by CoCl2 was mediated through the ERK1/2 and HIF-1α/BNIP3 pathways, and that this was associated with an increase in ROS. The production of ROS in the mitochondria of C2C12 cells resulted in a decreased Δψm, which led to cell death and inhibited differentiation. Nec-1 decreased the expression of RIP1, HIF-1α and BNIP3, and the phosphorylation of ERK1/2. The inhibition of CoCl2-induced necroptosis by Nec-1 promoted myogenic differentiation.
Necroptosis has been demonstrated in a variety of disease models, particularly neurological disorders and cancer (27–29). The present study aimed to investigate the effects of CoCl2 on C2C12 myotubes, which may be associated with necroptosis; additionally, it has been reported that the viability of C2C12 myotubes was affected by CoCl2, which may be attenuated by Nec-1 (5). In the present study, it was demonstrated that CoCl2 treatment upregulated the expression of RIP1 and RIP3, members of the RIP family, which are key factors in triggering necroptosis. In addition, TEM revealed necroptotic characteristics in dead cells, including mitochondrial swelling, membranolysis and organelle disappearance. Nec-1 is an allosteric inhibitor, which interacts with the RIP1-RIP3 complex. The results also showed that Nec-1 markedly inhibited the expression of RIP1 but only marginally decreased that of RIP3, whereas Nec-1 increased cell viability and reversed morphological damage in the cells treated with CoCl2. Together, these results suggested that Nec-1 exerted a protective effect against CoCl2-induced cytotoxicity. In our previous study, it was demonstrated that CoCl2-induced hypoxia downregulated the expression of myogenin and impaired myoblast fusion (26). To further examine the protective effect of Nec-1 on skeletal C2C12 cells, the present study examined the specific differentiation markers, myogenin and MyHC, which are required for the fusion of myoblasts to form myotubes. The expression levels of myogenin and MyHC were increased following Nec-1 treatment. However, no significant difference in the muscle degradation-mediated protein, atrogin-1 was found, indicating that Nec-1 facilitated muscle differentiation but did not attenuate CoCl2-induced hypoxia-induced myofibrillar degradation.
Several lines of evidence have shown that the MEK/ERK pathway regulates cell survival and death (30-32). Xie et al (32) investigated the effects of dimethyl fumarate on different gastrointestinal cancer cell lines and found that it induced necroptosis in colon cancer cells; the mechanism involved glutathione depletion, an increase in ROS, and activation of MAPK-mediated signaling. Locatelli et al (31) reported that the PI3K/AKT and RAF/MEK/ERK pathways were constitutively activated in patients with Hodgkin's lymphoma. AEZS-136, a PI3K/ERK dual inhibitor, markedly promoted the dephosphorylation of MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathway components, leading to caspase-independent necroptosis with ROS generation (31). Hypoxia or CoCl2 increased HIF-1α due to increased protein stability, which was mediated by activation of the ERK pathway; the inhibition of RIP1 kinase activity by Nec-1 or the knockdown of RIP1 using small interfering RNA significantly inhibited the activation of ERK (11). The results of the present study indicated that the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 induced by CoCl2-induced hypoxia was inhibited by Nec-1.
ROS are also required for TNF-induced necroptosis (33). In the present study, a lower Δψm and a simultaneous increase in ROS production was observed in the CoCl2 group, suggesting dysfunction and decreased activity of the respiratory chain. Nec-1 decreased ROS accumulation and prevented the execution of programmed necrosis. The present study also investigated the expression of BNIP3, which integrates into the mitochondrial membrane under conditions triggering ROS accumulation, resulting in necroptosis associated with energy failure (19,28). Kim et al (19) reported that BNIP3 induced caspase-independent necrosis-like cell death, which was significantly inhibited by Nec-1, whereas the pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD-FMK did not. BNIP3 contains a hypoxia response element and appears to be a direct target of transcriptional activation by HIF-1α. Of note, HIF-1α was downregulated following Nec-1 treatment, suggesting that the molecular mechanism of Nec-1 in C2C12 cells under CoCl2-induced hypoxia involved the HIF-1α/BNIP3 pathway.
In conclusion, the findings of the present study revealed that necroptosis was initiated by CoCl2, which was mainly associated with the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, upregulation of HIF-1α/BNIP3, and mitochondrion-generated ROS. Therefore, Nec-1 may protect C2C12 cells under conditions of CoCl2-induced hypoxia.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Footnotes
Funding
The study was supported by grants from the Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (grant no. A2016612), the Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Guangdong Province (grant no. 20172004), the Science Foundation of Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital (grant nos. YQ2015-017 and YN2017-003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81101866) and the Sci-tech Development Program of Guangdong Province (grant no. 2014A020212581).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors' contributions
RC, JX and YS conceived and designed the experiments. RC, JX, YS, TJ, SZ and HS performed the experiments. TJ and CL analyzed the data. RC and YS wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Kawamura I, Takemura G, Kanamori H, Takeyama T, Kawaguchi T, Tsujimoto A, Goto K, Maruyama R, Watanabe T, Shiraki T, et al. Repeated phlebotomy augments angiogenesis to improve blood flow in murine ischemic legs. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010;299:H372–H378. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00035.2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Masschelein E, Van Thienen R, D'Hulst G, Hespel P, Thomis M, Deldicque L. Acute environmental hypoxia induces LC3 lipidation in a genotype-dependent manner. FASEB J. 2014;28:1022–1034. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-239863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Samaras N, Samaras D, Chambellan A, Pichard C, Thibault R. Pulmonary rehabilitation: The reference therapy for undernourished patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:248420. doi: 10.1155/2014/248420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Saxena S, Shukla D, Saxena S, Khan YA, Singh M, Bansal A, Sairam M, Jain SK. Hypoxia preconditioning by cobalt chloride enhances endurance performance and protects skeletal muscles from exercise-induced oxidative damage in rats. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2010;200:249–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2010.02136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rovetta F, Stacchiotti A, Faggi F, Catalani S, Apostoli P, Fanzani A, Aleo MF. Cobalt triggers necrotic cell death and atrophy in skeletal C2C12 myotubes. Toxicol Appl Pharm. 2013;271:196–205. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cervellati F, Cervellati C, Romani A, Cremonini E, Sticozzi C, Belmonte G, Pessina F, Valacchi G. Hypoxia induces cell damage via oxidative stress in retinal epithelial cells. Free Radical Res. 2014;48:303–312. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2013.867484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yuan Y, Hilliard G, Ferguson T, Millhorn DE. Cobalt inhibits the interaction between hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha and von Hippel-Lindau protein by direct binding to hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:15911–15916. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M300463200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Linkermann A, Green DR. Necroptosis. New Engl J Med. 2014;370:455–465. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1310050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Laster SM, Wood JG, Gooding LR. Tumor necrosis factor can induce both apoptic and necrotic forms of cell lysis. J Immunol. 1988;141:2629–2634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Degterev A, Huang Z, Boyce M, Li Y, Jagtap P, Mizushima N, Cuny GD, Mitchison TJ, Moskowitz MA, Yuan J. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol. 2005;1:112–119. doi: 10.1038/nchembio711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Han W, Xie J, Fang Y, Wang Z, Pan H. Nec-1 enhances shikonin-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells by inhibition of RIP-1 and ERK1/2. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:7212–7225. doi: 10.3390/ijms13067212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D, Genga R, Ray TD, Guildford M, Chan FK. Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation. Cell. 2009;137:1112–1123. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen JK, Zhan YJ, Yang CS, Tzeng SF. Oxidative stress-induced attenuation of thrombospondin-1 expression in primary rat astrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112:59–70. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Locatelli SL, Cleris L, Stirparo GG, Tartari S, Saba E, Pierdominici M, Malorni W, Carbone A, Anichini A, Carlo-Stella C. BIM upregulation and ROS-dependent necroptosis mediate the antitumor effects of the HDACi Givinostat and Sorafenib in Hodgkin lymphoma cell line xenografts. Leukemia. 2014;28:1861–1871. doi: 10.1038/leu.2014.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Obitsu S, Sakata K, Teshima R, Kondo K. Eleostearic acid induces RIP1-mediated atypical apoptosis in a kinase-independent manner via ERK phosphorylation, ROS generation and mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e674. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Choi H, Merceron C, Mangiavini L, Seifert EL, Schipani E, Shapiro IM, Risbud MV. Hypoxia promotes noncanonical autophagy in nucleus pulposus cells independent of MTOR and HIF1A signaling. Autophagy. 2016;12:1631–1646. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1192753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Feng CC, Lin CC, Lai YP, Chen TS, Marthandam Asokan S, Lin JY, Lin KH, Viswanadha VP, Kuo WW, Huang CY. Hypoxia suppresses myocardial survival pathway through HIF-1α-IGFBP-3-dependent signaling and enhances cardiomyocyte autophagic and apoptotic effects mainly via FoxO3a-induced BNIP3 expression. Growth Factors. 2016;34:73–86. doi: 10.1080/08977194.2016.1191480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mammucari C, Milan G, Romanello V, Masiero E, Rudolf R, Del Piccolo P, Burden SJ, Di Lisi R, Sandri C, Zhao J, et al. FoxO3 controls autophagy in skeletal muscle in vivo. Cell Metab. 2007;6:458–471. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kim JY, Kim YJ, Lee S, Park JH. BNip3 is a mediator of TNF-induced necrotic cell death. Apoptosis. 2011;16:114–126. doi: 10.1007/s10495-010-0550-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang H, Zhang B. Cobalt chloride induces necroptosis in human colon cancer HT-29 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16:2569–2574. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.6.2569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Huang YC, Tsai MS, Hsieh PC, Shih JH, Wang TS, Wang YC, Lin TH, Wang SH. Galangin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammation and cell death in mice through inhibition of ERK and NF-kappaB signaling. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017;329:128–139. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.05.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Liu S, Ai Q, Feng K, Li Y, Liu X. The cardioprotective effect of dihydromyricetin prevents ischemia–reperfusion-induced apoptosis in vivo and in vitro via the PI3K/Akt and HIF-1α signaling pathways. Apoptosis. 2016;21:1366–1385. doi: 10.1007/s10495-016-1306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhang M, Li J, Geng R, Ge W, Zhou Y, Zhang C, Cheng Y, Geng D. The inhibition of ERK activation mediates the protection of necrostatin-1 on glutamate toxicity in HT-22 cells. Neurotox Res. 2013;24:64–70. doi: 10.1007/s12640-012-9361-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gao S, Andreeva K, Cooper NG. Ischemia-reperfusion injury of the retina is linked to necroptosis via the ERK1/2-RIP3 pathway. Mol Vis. 2014;20:1374–1387. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhao M, Lu L, Lei S, Chai H, Wu S, Tang X, Bao Q, Chen L, Wu W, Liu X. Inhibition of receptor interacting protein kinases attenuates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy induced by palmitic acid. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:1451676. doi: 10.1155/2016/1451676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chen R, Jiang T, She Y, Xu J, Li C, Zhou S, Shen H, Shi H, Liu S. Effects of cobalt chloride, a hypoxia-mimetic agent, on autophagy and atrophy in skeletal C2C12 myotubes. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7097580. doi: 10.1155/2017/7097580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chen G, Cheng X, Zhao M, Lin S, Lu J, Kang J, Yu X. RIP1-dependent Bid cleavage mediates TNFα-induced but Caspase-3-independent cell death in L929 fibroblastoma cells. Apoptosis. 2015;20:92–109. doi: 10.1007/s10495-014-1058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Das A, McDonald DG, Dixon-Mah YN, Jacqmin DJ, Samant VN, Vandergrift WA, III, Lindhorst SM, Cachia D, Varma AK, Vanek KN, et al. RIP1 and RIP3 complex regulates radiation-induced programmed necrosis in glioblastoma. Tumor Biol. 2016;37:7525–7534. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4621-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Chavez-Valdez R, Martin LJ, Flock DL, Northington FJ. Necrostatin-1 attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction in neurons and astrocytes following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Neuroscience. 2012;219:192–203. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Festjens N, Vanden Berghe T, Cornelis S, Vandenabeele P. RIP1, a kinase on the crossroads of a cell's decision to live or die. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14:400–410. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Locatelli SL, Careddu G, Stirparo GG, Castagna L, Santoro A, Carlo-Stella C. Dual PI3K/ERK inhibition induces necroptotic cell death of Hodgkin Lymphoma cells through IER3 downregulation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:35745. doi: 10.1038/srep35745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Xie X, Zhao Y, Ma CY, Xu XM, Zhang YQ, Wang CG, Jin J, Shen X, Gao JL, Li N, et al. Dimethyl fumarate induces necroptosis in colon cancer cells through GSH depletion/ROS increase/MAPKs activation pathway. Brit J Pharmacol. 2015;172:3929–3943. doi: 10.1111/bph.13184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhao W, Feng H, Sun W, Liu K, Lu JJ, Chen X. Tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BHP) induced apoptosis and necroptosis in endothelial cells: Roles of NOX4 and mitochondrion. Redox Biol. 2017;11:524–534. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2016.12.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]