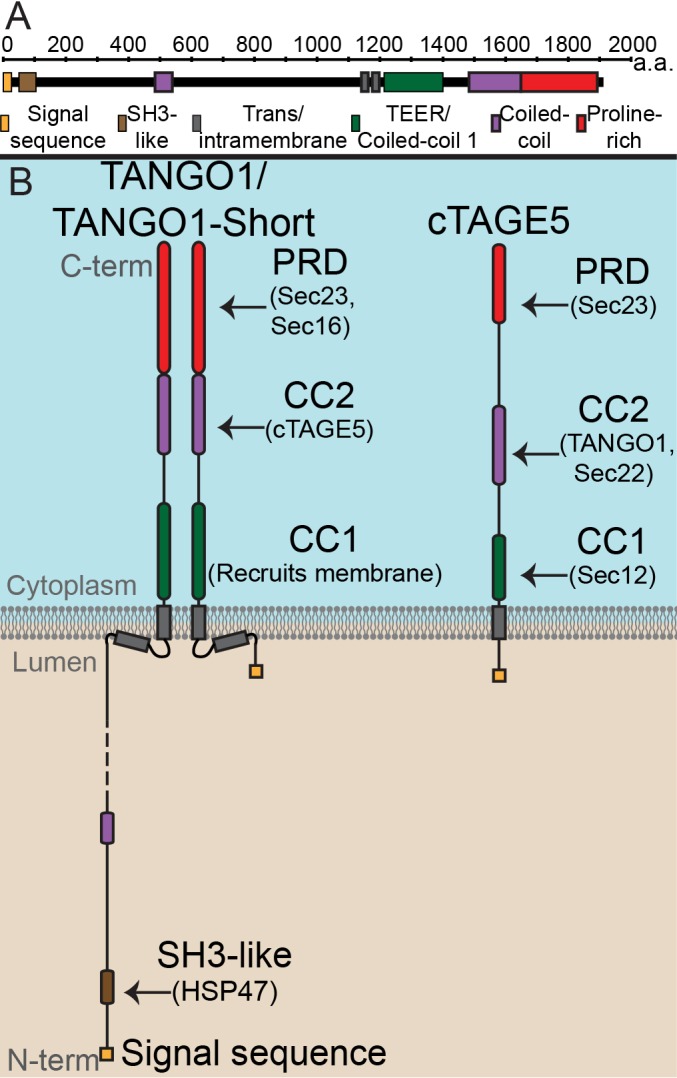
Figure 1. The domain architecture and topology of TANGO1 and cTAGE5.
(A) A schematic depiction of full length TANGO1, showing the extent of each domain in amino acids. (B) Three TANGO1-family proteins (TANGO1, TANGO1-short and cTAGE5) that form a stable complex at the ERES (Maeda et al., 2016). TANGO1 is a type one single-pass transmembrane protein of 1907 amino acids, localised to ER exit sites. TANGO1 has an N-terminal lumenal SH3-like domain that interacts with collagen (Saito et al., 2009) via the chaperone, HSP47 (Ishikawa et al., 2016). There is a transmembrane helix and, in close proximity, a membrane insertion helix. On the cytoplasmic side of the ER membrane, TANGO1 has two coiled-coil (CC) domains (CC1 and CC2). CC1 is used by TANGO1 to recruit ERGIC membranes for producing a collagen carrier (Santos et al., 2015). CC2 binds to a similar coiled-coil domain in cTAGE5 (18). The proline-rich domain (PRD) binds ER exit site machinery Sec23 (Saito et al., 2009; Ma and Goldberg, 2016) and Sec16 (Maeda et al., 2017). Alternative splicing of TANGO1 results in a short isoform, TANGO1-short (Wilson et al., 2011), lacking the lumenal domain. The closely related protein cTAGE5 has a similar cytoplasmic domain organisation with two coiled-coil domains (CC1 and CC2) and a proline-rich domain (PRD). Via its CC1 it recruits Sec12 (Saito et al., 2014). cTAGE5 and TANGO1/TANGO1-short interact through their respective CC2 domains. In addition, the cTAGE5 CC2 also interacts with the retrograde v-SNARE Sec22 (Fan et al., 2017). Like the TANGO1/TANGO1-short PRDs, the cTAGE5 PRD also interacts with Sec23 (Ma and Goldberg, 2016; Saito et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2016).