Screening a panel of Bordetella bronchiseptica–defined mutants lacking various “virulence factors” revealed one completely unable to transmit between animals. Surprisingly, mutation of a locus associated with extracellular polysaccharide affected both shedding from infected animals and colonization of exposed animals.
Keywords: polysaccharide, colonization, transmission
Abstract
Background
The lack of animal models to experimentally study how infectious agents transmit between hosts limits our understanding of what makes some pathogens so contagious.
Methods
We recently developed a Bordetella bronchiseptica mouse model to study transmission and have used it to assess, for the first time, which of several well-studied “virulence factors” common to classical Bordetella species contribute to transmission.
Results
Among 13 mutants screened, a mutant lacking an extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) locus consistently failed to transmit. The loss of EPS had no obvious effect on in vitro characteristics of growth, adherence, cytotoxicity, or serum resistance, though it profoundly reduced the ability of the mutant to colonize the lower respiratory tract of mice. While wild-type B. bronchiseptica was shed from colonized mice and efficiently transmitted to cage-mates, the mutant colonized less efficiently, shed at lower numbers, and consequently did not transmit to naive animals.
Conclusions
These results have important implications for potential roles of polysaccharides in the pathogenesis and transmission of Bordetella species as well as other respiratory pathogens. Cases of pertussis (whooping cough) caused by Bordetella pertussis are on the rise, and understanding factors that contribute to their spread is critical to its control.
The transmission of Bordetella pertussis, the primary etiological agent of pertussis (whooping cough) in humans, is becoming a matter of great concern [1]. Despite the widespread use of effective vaccines, reported cases have been growing in many countries [2–6]. Within the United States, a relatively well-vaccinated population, cases of pertussis have been increasing and are now at levels last seen in the 1950s [7, 8]. Experimental studies using animals also strongly indicate that current vaccines prevent symptoms and severe disease but do not effectively prevent the transmission of the bacterium from host to host [9–13]. In this respect, undetected transmission represents a clearly defined problem requiring focused attention to guide efforts to control pertussis.
Experimental studies using animals such as baboons and pigs have confirmed clinical observations that current acellular vaccines provide limited protections against subclinical infection and transmission between hosts. However, large animal models make experimentation expensive and logistically demanding and are therefore unsuited for the detailed studies needed to define the roles of each of many bacterial factors that may be involved in the complex process of transmission. Realizing that such studies would require an amenable model system, we have established a robust mouse-based transmission assay [14] and have used it to examine bacterial factors that contribute to transmission.
In our extensive comparisons of the classical bordetellae, we observed that the 2 species that have adapted to transmit very rapidly and efficiently have both altered their lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to avoid Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) stimulation. Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis are >10-fold and >100-fold less stimulatory of TLR4, compared to their common progenitor, Bordetella bronchiseptica [15]. These observations led us to hypothesize that poor stimulation of the TLR4 receptor allows for increased transmission, leading to the prediction that B. bronchiseptica, which strongly stimulates TLR4 and transmits at a low rate among mice, would transmit more efficiently among TLR4-deficient mice [15]. Consistent with our hypothesis, we recently demonstrated that B. bronchiseptica efficiently transmits among TLR4-deficient C3H/HeJ when housed with naive (secondary) mice, thereby serving as an efficient experimental model in which to examine the effect of specific bacterial factors in the transmission process [11, 14, 16].
Here, we report the use of this experimental system to screen a panel of 13 deletion mutants of B. bronchiseptica to identify their contributions to transmission. Of the 13 strains screened, we have found that 12 well-studied virulence factors are not required for transmission, but a strain deleted for an extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) locus consistently failed to transmit from inoculated to naive mice. This is the first report of any screening for transmission factors among known virulence determinant of the bordetellae and is also the first time that a bacterial extracellular polysaccharide has been implicated in facilitating transmission. Furthermore, the ability of the mutant to colonize the lower respiratory tract was also found to be severely compromised, suggesting that the locus may have 2 roles in the interactions between B. bronchiseptica and its mammalian host. Because the absence of the locus displays such a dramatic effect on the ability of the bacterium to transmit, we refer to this locus as the transmission extracellular polysaccharide locus (tEPS).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Growth and Culture of Bacteria
Bordetella bronchiseptica liquid cultures were prepared using Stainer Scholte (SS) media supplemented with 0.5% (w/v) Heptakis (2,6-di-O-methyl)-β-cyclodextrin) (Sigma H0513). Plate cultures were grown on Bordet Gengou (BG) agar supplemented with 10% (v/v) defibrinated sheep blood (Hemstat, Hemostat Laboratories) and streptomycin (20 μg/mL). Comparative growth curves were generated from triplicate cultures of bacteria grown 48 hours in SS medium at 37°C and shaking at 200 rpm.
Generation of tEPS Mutant
The entire polysaccharide biosynthetic locus, except for the 5ʹ 137 bp of wcbR and the 3ʹ 193 bp of tviD, was deleted by allelic exchange (Figure 1). Two regions corresponding to coordinates 3088224–3089032 and 3117648–3118391 of the B. bronchiseptica RB50 genome sequence (nucleotide accession number BX470250) were amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). These amplicons were cloned flanking a kanamycin resistance cassette in the suicide plasmid pEX100T (Schweizer). This construct was transformed into the Escherichia coli donor strains SM10 (Simon) and introduced into B. bronchiseptica by conjugation as described previously [17]. Conjugants were selected on LB agar supplemented with 50 μg/mL kanamycin, 200 μg/mL streptomycin, and 15% w/v sucrose. The expected chromosomal deletion was confirmed by PCR on genomic DNA, transcript expression, and Southern blot (data not shown).
Figure 1.
The extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) locus in Bordetella bronchiseptica RB50. A, Table of EPS genes for biosynthesis, modification, and export of polysaccharide. B, Schematic representation of the orientation of 18 genes of the locus showing accession numbers for the first and last genes. The deletion in the B. bronchiseptica RB50Δteps mutant is indicated by arrows. Position numbers refer to the RB50 genome (accession number: BX470250). C, Polymerase chain reaction analysis B. bronchiseptica RB50Δteps mutant. Ethidium bromide stained 1% agarose gels showing kpsT and kpsM transporter gene amplification products of the EPS locus in wild-type (WT) genomic DNA but missing in the capsule locus deletion mutant. The recA gene was used as the control.
Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Real-time PCR analyses were performed on a QuantStudio (Applied Biosystems) using Power SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems). Complementary DNA (cDNA) transcript libraries were prepared from triplicate SS cultures of wild-type (WT) and mutant bacteria grown with or without 50 mM magnesium sulfate at 37°C. Mid-log cultures with OD600 (optical density at 600 nm) values of 0.7–1.0 were collected for RNA extraction using TRIzol Reagent (Ambion by Life Technologies) and PureLink TM RNA Mini Kit following manufacturer instructions and treated with PureLink DNase (Invitrogen). Primers (Supplementary Table 3) were manually designed and purchased from IDT. The cycling parameters were as follows: 5-minute preincubation at 95°C followed by 40 cycles of a 2-step PCR at 95°C and 60°C. Gene expression was calculated using the ΔΔCt method with recA expression used as reference. Data were analyzed using DataAssist version 3.0 (Applied Biosystems).
Adherence Assays
Adherence assays were conducted following protocols described earlier [18, 19]. In brief, mouse macrophage-like RAW 264.7 and human epithelial lung A459 cells were seeded in triplicate in 24-well plates at a density of 2.5 × 105 macrophages/well in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (with 10% fetal bovine serum, 10 mM glutamine, 25 mM sodium pyruvate, 10 mM HEPES). Log-phase bacteria were suspended in warm DMEM media and added to each well at a multiplicity of infection of 10:1 (bacteria:eukaryotic cells). The plate was centrifuged at 300g for 10 minutes to synchronize infection and the assay plates were incubated for 5 minutes at 37°C. Unattached bacteria were then removed by washing cells 4 times with 1 mL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Macrophages were lysed with 100 μL of 0.1% sodium deoxycholate for 5 minutes and released bacteria suspended in 900 μL of PBS. The bacteria were enumerated by dilution plating on BG agar plates. RB50 ΔfhaB [19], a mutant strain deleted of the filamentous hemagglutinin and known to be defective in adherence, was used as the negative control.
Complement Killing Assay
Blood from 2 naive mice was collected by cardiac puncture and incubated on ice for 30 minutes. The blood was then centrifuged in a cold microfuge at 1200g for 15 minutes and serum collected. Actively growing mid-log RB50 and RB50Δteps bacteria (approximately 2 × 106 colony-forming units [CFU]) were incubated in PBS with or without 20% serum at 37°C for 45 minutes and survival of bacteria was enumerated by dilution plating. The RB50Δwbm strain known to be susceptible to complement [20] was used as a negative control. Percentage survival of the capsule mutant was compared to that of the WT.
Cytotoxicity Assay
Cytotoxicity assays were conducted on RAW 264.7 cells, using the CytoTox 96 Nonradioactive Cytotoxicity Assay Kit (Promega) following manufacturer’s protocols. In brief, 100 μL of 2.5 × 104 macrophages were seeded in triplicate in a 96-well plate followed by adding bacteria at an multiplicity of infection of 10:1 and 1:1. The assay plate was centrifuged at 300g for 10 minutes. Bacteria were incubated with the macrophages for 4 hours, following which the plate was centrifuged for 5 minutes (300g). Fifty microliters of the supernatant was taken into a fresh flat-bottomed 96-well plate and colorimetrically assayed for lactate dehydrogenase. RB50ΔclpV, a mutant of the type 6 secretory system [21], was used as a negative control.
Mouse Infections
All work with mice was conducted following institutional guidelines. Six-week-old female C57/BL6 or C3H/HeJ mice (Jackson Laboratories, Bar Harbor, Maine) were used for assessing the colonization and the progress of infection of the respiratory tract. As required, 5–150 CFU of bacteria was delivered in 5 μL of PBS to the nares of mice anesthetized with isoflurane/oxygen. For the growth curves, groups of 4 mice were infected with WT or mutant bacteria, and at the indicated days 4 mice each of WT and mutant were euthanized with carbon dioxide (CO2) and the nasal cavity, trachea, and lungs were collected in PBS and homogenized using a bead tissue disruptor. Bacterial load was enumerated by dilution plating.
Transmission and Shedding Assay
Transmission assays were conducted using the transmission permissive C3H/HeJ (TLR4 deficient) strain of mice (Jackson Laboratory) whereby infected (index) with uninfected (naive) mice were co-housed [14]. In brief, mice were lightly anaesthetized with isoflurane/oxygen and infected with 150 CFU of bacteria delivered in 5 μL of PBS onto the nares. Inoculated (index) mice were then placed in cages with 2 uninfected (naive) mice. Transmission of B. bronchiseptica was assessed after 3 weeks of co-housing by enumerating the bacterial load in the nasal cavities of the naive mice. To monitor shedding, the external nares of the index mice were swabbed (30 swipes) with a Dacron polyester swab at the indicated times. The swab was vortexed vigorously in 1 mL PBS for 30 seconds and bacteria enumerated on BG agar plates.
Ethics Statement
Mice experiments used in this study were performed in strict accordance to recommendations outlined in the Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institute of Health. Protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the Pennsylvania State University at University Park, PA (number 46284, Bordetella-Host Interactions) and the University of Georgia (A2016 02-010-Y2-A3, Bordetella-Host Interactions). Mice were closely monitored during experiments and any mouse found moribund was killed using CO2 inhalation to prevent unnecessary suffering.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis of differences between the WT and mutant groups was performed using the paired Student 2-tailed t test of significance with a P value <.05 considered to be statistically significant.
RESULTS
Transmission Is Facilitated by an tEPS Locus
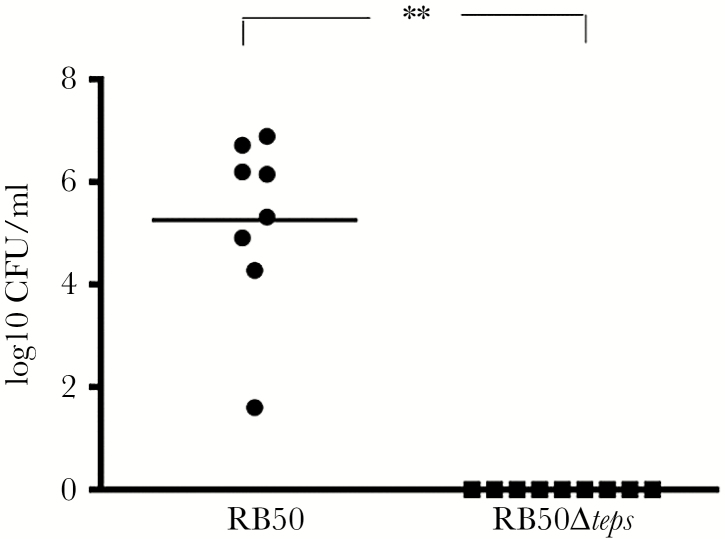
We recently established a robust mouse transmission assay [14] and proceeded to search for bacterial factors that could be facilitating transmission. We screened a panel of B. bronchiseptica RB50 mutants deleted for various genes associated with virulence to assess their contributions to transmission (Supplementary Tables 1 and 2). For our primary screen, C3H/HeJ mice were inoculated with 150 CFU of either WT or mutant strains and co-housed with uninfected (naive) mice. After 21 days, WT B. bronchiseptica was detected in both inoculated and co-housed animals, indicating that it had transmitted. Similarly, mutants ΔclpV (type 6 secretory system), ΔcyaA (adenylate cyclase), ΔbrkA (serum complement resistance), ΔpagP (lipid A modification), ΔsigE (Sigma factor), ΔslyA (putative transcriptional regulator), and Δaqp (putative aquaporin) transmitted to cage-mates, indicating that these factors are not required for transmission. Mutants lacking ΔfhaB (filamentous hemagglutinin), ΔfimBCD (fimbriae), ΔbscN (type 3 secretory system), ΔlpxO (LPS), and Δeps (EPS) failed to transmit in this first screen. To more rigorously test whether these mutants could transmit, we used 2 inoculated and 2 naive mice. There was at least 1 transmission event in this second assay for the mutants ΔfhaB, ΔfimBCD, ΔbscN, and ΔlpxO, suggesting that these genes may contribute but are not necessary for transmission between hosts. Only a single mutant, Δteps, was not detected in any of the co-housed naive mice (P = .001), indicating that of all the 13 mutants, only the EPS locus (Figure 1) is required for transmission (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Transmission of Bordetella bronchiseptica RB50 and RB50Δteps in C3H/HeJ mice. Graph represents the bacteria recovered from the nasal cavities of naive C3H/HeJ mice co-housed for 21 days with mice infected with either RB50 (black circle) or the RB50Δteps mutant (black square). The results represent observations from several independent assays and the asterisks indicate significant differences (**P ≤ .001)
Because this locus could have a variety of effects, we assessed various measures of growth and interactions with host cells in vitro. We failed to detect any differences in growth, adherence to host cells, resistance to serum complement, or cytotoxicity, eliminating several trivial explanations for the failure to transmit (Supplementary Figure 1). Although this locus was reported to be preferentially expressed under Bvg– (avirulent phase) conditions [22] that are believed to represent those experienced outside the host [23], we observed expression under both Bvg+ (virulent phase) and Bvg– conditions (Supplementary Figure 2), suggesting the tEPS it synthesizes might have a variety of roles in different environments.
The tEPS Mutant Has Reduced Efficiency in Colonizing the Lungs
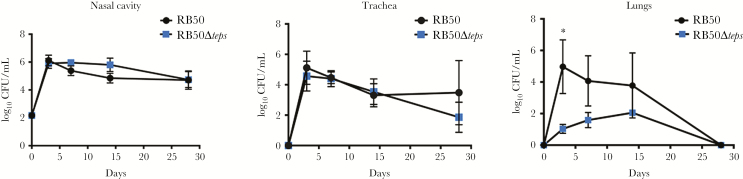
To examine the role of tEPS in vivo, we inoculated C57Bl/6 mice with 150 CFU of either the WT or Δteps mutant. Both strains grew in numbers in the nasal cavity during the first 3 days and persisted over the course of 28 days (Figure 3). Bacterial numbers of both strains recovered from the trachea were similar, with nominally lower levels of mutant compared to WT at 28 days. Interestingly, the mutant was recovered at significantly lower numbers from the lungs by day 3 (P = .012), and decreased thereafter until clearance on day 28, indicating that the tEPS-deficient strain was severely defective in the ability to colonize, grow, and/or persist in the lungs. The technical barriers for complementing large multigene deletions in B. bronchiseptica did not allow for conducting experiments to restore the phenotype and assess polar effects of the deletion. However, 3 independently generated Δteps mutants showed similar transmission and defects in lung colonization (Supplementary Figure 3), supporting the dependence of both transmission and lung persistence on this locus.
Figure 3.
Comparative colonization profiles of Bordetella bronchiseptica RB50 and RB50Δteps. Number of colony-forming units (CFU) recovered on days 3,7, 14, and 28 from the nasal cavities, trachea, and lungs of C57Bl/6 mice infected with either wild-type (black circle) or mutant (blue square). Dashed gray lines indicate the limit of detection. Asterisk indicates significant differences (*P ≤ .05).
tEPS Facilitates Shedding
The ability to transmit depends upon bacteria being shed from inoculated mice. To measure bacterial shedding, swabs from the external nares of infected mice were collected over the course of the 21-day transmission assay and the bacteria enumerated by plating on BG agar plates. The mutant was consistently shed in much lower numbers than WT over time. From as early as day 4 up to day 10, hundreds to tens of thousands of bacteria were recovered per mouse from swabs of the WT during its peak shedding phase. In contrast, during this period the mutant was shed at numbers approximately 90% lower, or was not detected at all. Over the 21-day period of the assay, the number of bacteria shed was >10 times higher for the WT strain than for the mutant (Supplementary Figure 4).
tEPS Facilitates Efficient Colonization
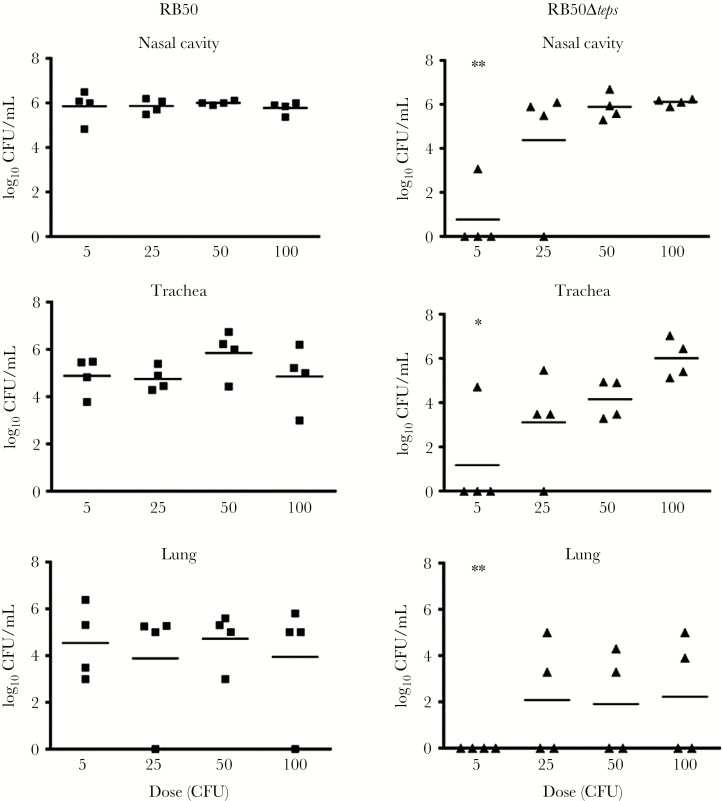
Bordetella bronchiseptica can efficiently colonize the nasal cavities of mice with an experimental dose as low as 5 CFU. To examine the contribution of tEPS to colonization, we incrementally increased the inoculation dose of bacteria from 5 CFU to 100 CFU and monitored the colonization of the nasal cavity of C57Bl/6 mice. WT bacteria efficiently colonized all mice given an inoculation dose of 5 CFU (Figure 4). In contrast, the Δteps mutant only colonized 1 of 4 mice at this dose (P = .001) and even at 25 CFU not all mice were colonized. Based on these observations, the ID50 (median infective dose) of the WT strain is <5 CFU, while that of the Δteps mutant is estimated to be between 5 and 25 CFU. Furthermore, while WT colonized the lungs of most mice at every inoculation dose, the mutant never colonized more than half of the mouse lungs, even at the highest inoculation dose, confirming that the Δteps mutant was deficient in colonizing the lungs. Similar defect of the RB50Δteps mutant was also observed in C3H/HeJ mice (Supplementary Figure 5).
Figure 4.
Dose-dependent colonization of Bordetella bronchiseptica RB50 and RB50Δcap. Graphs showing the colonization levels of nasal cavities, trachea, and lungs from C57BL/6 mice infected for 7 days with either B. bronchiseptica RB50 (black square) or RB50Δteps (black triangle). Mice were inoculated with 5, 25, 50, and 100 colony-forming units (CFU). Asterisks denote significant differences between wild-type and mutant at an inoculum dose of 5 CFU (*P ≤ .05 and **P ≤ .001).
DISCUSSION
The study of transmission has been limited by the lack of tractable assay systems. We have utilized our mouse-based transmission assay which has enabled, for the first time, the large-scale screening of various mutant strains of B. bronchiseptica for possible contributions to transmission among animals. All 13 screened mutants had earlier been shown to have some defect in the context of established within-host virulence assays. Here we show for the first time that some of those might also contribute to transmission, an aspect of the infectious process that is critical to their biology but not previously examined. This is likely to reveal novel aspects of the functions of these factors that will be the focus of future studies. Interestingly, only 1 mutant, RB50Δteps, was completely unable to transmit between animals.
In vitro experiments indicated that the lack of the tEPS locus had no effect on growth, cell adherence, complement resistance or cytotoxicity, though the ΔtEPS mutant was defective in its ability to colonize the lungs of mice. Hoo et al [24] noted that a B. pertussis strain with a deletion in kpsT, the transporter component of the apparently orthologous EPS locus of this species, colonized and persisted in the lungs of mice less efficiently than the WT parental strain. Although the loci are not identical, our data demonstrate that the role of the tEPS locus in mediating colonization and persistence in the lungs is of similar importance in B. bronchiseptica and in B. pertussis, consistent with the substantial similarities observed between these 2 closely related subspecies. Prior transmission of B. pertussis has only been demonstrated in baboons in 1 laboratory and in an extremely difficult and cumbersome experimental system that is unlikely to be widely used. Our observation that this locus is involved in transmission of B. bronchiseptica identifies an important novel function for the locus as well as defines an experimental system in which the mechanistic basis for this function can be efficiently examined. As the locus had a similar impact on both B. bronchiseptica and B. pertussis lung infections, the effects we observe on transmission are likely to be relevant to both organisms. Thus, both the molecular mechanisms involved, and the potential therapeutic interventions they might suggest, can be established in the B. bronchiseptica mouse system, confirmed in the difficult B. pertussis baboon system and then applied to the pressing human health problem of the ongoing transmission of B. pertussis.
Although the tEPS locus of B. bronchiseptica resembles those that generate capsules in other bacteria, and Hoo et al associated the B. pertussis locus with an elusive capsule, we were not able to observe either a clear capsule structure or a consistent effect of deletion of the tEPS locus on a discreet cell-associated structure we could observe by microscopy, confocal microscopy, or electron microscopy. Even a complete deletion of the entire locus, removing the potential caveat that the partial locus remaining in the B. pertussis ΔkpsT strain produced a disruptive intermediate [25], did not affect an observable cell-associated structure. Therefore, in the interest of caution, we refrain from referring to a “capsule”, as this term has very clear and important implications. However, the substantial within-host and between-host effects that we show are dependent on this locus clearly establish that it is important to the critical ability of this organism to transmit to new hosts and efficiently colonize the lower respiratory tract. We hope that our use of the more general term “extracellular polysaccharide” encourages broader consideration of many different possible forms and functions of likely complex secreted molecules.
To our knowledge, this is the first time a locus associated with any EPS has been demonstrated to play a role in transmission. Because bacterial shedding is a prerequisite for transmission, the defect in shedding of the mutant could explain the failure of the mutant to transmit. However, in addition to reduced shedding, we observed that higher numbers of the mutants were necessary to successfully colonize 2 different mouse strains, suggesting it also may be defective in its first encounter with a host. Understanding how tEPS contributes to both colonization of, and subsequent shedding from, the host will further explain the defect of the mutant and allow the specifics of this process to be studied in molecular detail.
It is worth considering the significance of these findings to the broader group of classical Bordetella species. Bordetella pertussis and B. parapertussis appear to have evolved from a B. bronchiseptica–like progenitor to emerge as the human pathogens that cause whooping cough, which the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recognizes as an important and reemerging infectious disease. These bacteria continue to circulate even in highly vaccinated populations, making understanding their transmission a critical concern. Unfortunately, the lack of experimental systems to study transmission has until now limited our ability to study this process. In both B. pertussis and B. parapertussis, the evolutionary adaptation to humans was accompanied by changes in the LPS that reduced the stimulation of the TLR4 receptor, compared to the progenitor B. bronchiseptica, by 10- and 100-fold, respectively [15]. This observation enabled our recent development of an efficient experimental system to study transmission in TLR4-deficient mice. Here we demonstrate that the B. bronchiseptica mouse experimental system can successfully identify bacterial factors that contribute to transmission and that one such factor appears to be an EPS. Experiments to further define the structures and functions of this tEPS, and its role in the transmission of B. pertussis, are likely to identify new vaccine and therapeutic targets and, perhaps, suggest novel strategies to control the ongoing spread of these important and highly infectious pathogens.
Supplementary Data
Supplementary materials are available at The Journal of Infectious Diseases online. Consisting of data provided by the authors to benefit the reader, the posted materials are not copyedited and are the sole responsibility of the authors, so questions or comments should be addressed to the corresponding author.
Supplementary Material
Notes
Acknowledgments. We acknowledge the staff of the mouse facilities at the College of Veterinary Sciences, Pennsylvania State University and the Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Georgia for help in facilitating the work. We also thank members of the Harvill laboratory for helpful discussions and editing of the manuscript.
Disclaimer. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Financial support. This work was supported by the Center for Diseases Control (grant number 200-2015-88062), the National Institute of Health (grant numbers GM083113, A1107016, AI116186, GM113681) and in part by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (contract number HHSN272200900007C) to E. T. H.
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors: No reported conflicts of interest. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
References
- 1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Pertussis (whooping cough) in other countries. 2016. www.cdc.gov/pertussis/countries/index.html. Accessed 14 April 2017.
- 2. Gabutti G, Rota MC. Pertussis: a review of disease epidemiology worldwide and in Italy. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2012; 9:4626–38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Choi YH, Campbell H, Amirthalingam G, van Hoek AJ, Miller E. Investigating the pertussis resurgence in England and Wales, and options for future control. BMC Med 2016; 14:121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Hallander HO, Advani A, Donnelly D, Gustafsson L, Carlsson RM. Shifts of Bordetella pertussis variants in Sweden from 1970 to 2003, during three periods marked by different vaccination programs. J Clin Microbiol 2005; 43:2856–65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Hozbor D, Mooi F, Flores D et al. Pertussis epidemiology in Argentina: trends over 2004–2007. J Infect 2009; 59:225–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Australian vaccine preventable disease epidemiological review series: pertussis, 2006–2012 Australian Government Department of Health, 2014. http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/content/cda-cdi3803b.htm. Accessed 15 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 7. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC provisional 2015 surveillance reports of notifiable diseases 2016. www.cdc.gov/pertussis/downloads/pertuss-surv-report-2015-provisional.pdf. Accessed 14 April 2017.
- 8. Clark TA. Changing pertussis epidemiology: everything old is new again. J Infect Dis 2014; 209:978–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Warfel JM, Zimmerman LI, Merkel TJ. Acellular pertussis vaccines protect against disease but fail to prevent infection and transmission in a nonhuman primate model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014; 111:787–92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Warfel JM, Zimmerman LI, Merkel TJ. Comparison of three whole-cell pertussis vaccines in the baboon model of pertussis. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2016; 23:47–54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Smallridge WE, Rolin OY, Jacobs NT, Harvill ET. Different effects of whole-cell and acellular vaccines on Bordetella transmission. J Infect Dis 2014; 209:1981–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Althouse BM, Scarpino SV. Asymptomatic transmission and the resurgence of Bordetella pertussis. BMC Med 2015; 13:146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Trainor EA, Nicholson TL, Merkel TJ. Bordetella pertussis transmission. Pathog Dis 2015; 73:ftv068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Rolin O, Smallridge W, Henry M, Goodfield L, Place D, Harvill ET. Toll-like receptor 4 limits transmission of Bordetella bronchiseptica. PLoS One 2014; 9:e85229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Mann PB, Wolfe D, Latz E, Golenbock D, Preston A, Harvill ET. Comparative Toll-like receptor 4-mediated innate host defense to Bordetella infection. Infect Immun 2005; 73:8144–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Rolin O, Muse SJ, Safi C et al. Enzymatic modification of lipid A by ArnT protects Bordetella bronchiseptica against cationic peptides and is required for transmission. Infect Immun 2014; 82:491–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Allen A, Maskell D. The identification, cloning and mutagenesis of a genetic locus required for lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Bordetella pertussis. Mol Microbiol 1996; 19:37–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Letourneau J, Levesque C, Berthiaume F, Jacques M, Mourez M. In vitro assay of bacterial adhesion onto mammalian epithelial cells. J Vis Exp 2011; 51. pii:2783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Nicholson TL, Brockmeier SL, Loving CL. Contribution of Bordetella bronchiseptica filamentous hemagglutinin and pertactin to respiratory disease in swine. Infect Immun 2009; 77:2136–46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Burns VC, Pishko EJ, Preston A, Maskell DJ, Harvill ET. Role of Bordetella O antigen in respiratory tract infection. Infect Immun 2003; 71:86–94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Weyrich LS, Rolin OY, Muse SJ et al. A Type VI secretion system encoding locus is required for Bordetella bronchiseptica immunomodulation and persistence in vivo. PLoS One 2012; 7:e45892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. de Gouw D, Hermans PW, Bootsma HJ et al. Differentially expressed genes in Bordetella pertussis strains belonging to a lineage which recently spread globally. PLoS One 2014; 9:e84523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Mattoo S, Cherry JD. Molecular pathogenesis, epidemiology, and clinical manifestations of respiratory infections due to Bordetella pertussis and other Bordetella subspecies. Clin Microbiol Rev 2005; 18:326–82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Hoo R, Lam JH, Huot L et al. Evidence for a role of the polysaccharide capsule transport proteins in pertussis pathogenesis. PLoS One 2004; 9:e0115243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Pavelka MS Jr, Hayes SF, Silver RP. Characterization of KpsT, the ATP-binding component of the ABC-transporter involved with the export of capsular polysialic acid in Escherichia coli K1. J Biol Chem 1994; 269:20149–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.