Abstract
Objectives
The primary objective of this systematic review was to evaluate the association between dental caries and preterm birth (PTB). The secondary objective was ascertaining the difference between women with dental caries who experienced PTB and those who did not with regard to decayed, missing and filled teeth (DMFT), and decayed, missing and filled surfaces (DMFS) indices.
Methods
MEDLINE, Embase, CINAHL and Cochrane databases were searched initially in November 2015 and repeated in December 2016. We included observational cohort and case–control studies. Only studies reporting the risk of PTB in women affected compared with those not affected by dental caries in pregnancy were included. Random-effect meta-analyses were used to compute the summary OR of PTB among women with caries versus women without caries, and the mean difference in either DMFT or DMFS indices between women experiencing PTB and those without PTB.
Results
Nine observational studies (4826 pregnancies) were included. Women affected by dental caries during pregnancy did not show a significantly higher risk of PTB (OR: 1.16, 95% CI 0.90 to 1.49, P=0.25, I2=35%). Also, the women with PTB did not show significantly higher DMFT or DMFS indices (summary mean differences: 1.56, P=0.10; I2=92% and −0.15, P=0.9, I2=89%, respectively).
Conclusion
Dental caries does not appear to be a substantial risk factor for PTB.
Trial registration number
NCT01675180; Pre-results.
Keywords: dental caries, pregnancy, pregnant woman, risk, preterm birth
Strengths and limitations of this study.
Strength of the study is its robust methodology. We tried to cover all available studies, access data quality and synthesise suitable data.
Small number of cases in some of the included studies, their design, different follow-up periods and dissimilarity of the population studies are the limitations.
Similarly, the lack of description or classification of dental caries stage is another limitation due to which the stratification of analysis according to the disease severity could not be performed.
Introduction
Preterm birth (PTB) is the major cause of perinatal mortality and morbidity in the developed countries, with an estimated incidence of 5%–13%.1–4 Although advances in neonatal care have led to a reduction in the neonatal mortality rate, infants born prematurely remain at a risk of developing a wide array of short-term and long-term complications such as respiratory, gastrointestinal and neurodevelopmental disabilities.4
Several risk factors have been associated with PTB1 5; among these, intrauterine infection has emerged as one of the most important factors. Despite this, PTB cannot be considered a unique disease but rather a syndrome characterised by multiple aetiology and in which different factors may play a peculiar role.5
Periodontal disease has been shown to carry an increased risk for PTB; the rationale for this association is based on the suggestion that periodontitis may lead to maternal and fetal inflammation, thus triggering the common pathway of preterm parturition syndrome including increased uterine contractility, cervical ripening and decidua/membrane activation.6–11 Although dental caries, defined as a localised destruction of the tooth and its structure by the acidic by-product produced by the bacteria during the dietary carbohydrate fermentation,12 is one of the major oral health problems in developed countries, the effects of dental caries on pregnancy outcome have not been consistently explored. Pregnant women are more susceptible to dental caries and gingivitis compared with their non-pregnant counterparts13 because of the change in their diet, frequent snacking due to food craving and oral health negligence.14 If left untreated, dental caries may result in further inflammatory complications,15 which could influence pregnancy outcomes. Several studies reported that dental caries causing bacteria may have some influence on the pregnancy outcome as PTB and/or low birth weight, while in contrary, the other showed no association between these two factors.16–27
The primary aim of this systematic review was to explore the association between dental caries and PTB; the secondary aim was to ascertain the differences in dental caries characteristics between women who deliver preterm and those who do not deliver preterm.
Methodology
Protocol, eligibility criteria, information sources and search
This review was performed according to an a priori designed protocol and recommended for systematic reviews and meta-analysis.28 29
We developed a search strategy, and a systematic literature search was performed in the following databases: Ovid MEDLINE (In-Process and Other Non-Indexed Citations, Ovid MEDLINE, Daily, Ovid MEDLINE and Ovid OLDMEDLINE, Embase Classic + EMBASE (Ovid), The Web of Science (Thomson Reuters), The Cochrane Library (Wiley) and CINAHL Plus (EBSCOhost).
The full search was performed in November 2015 and repeated in December 2016. The online supplementary material 1 shows the complete search string as it was performed in MEDLINE. The controlled vocabulary of Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) from MEDLINE and the Emtree thesaurus from Embase, including subheadings, were used when applicable. In addition, the search fields, title, abstract and keywords, were searched when applicable. In The Web of Science, the search fields, title and topic were used. All references were exported to Endnote (X7.4, Thompson Reuters), where duplicates were removed. There were no restrictions regarding languages or publication year for the searches.
bmjopen-2017-018556supp001.pdf (99.4KB, pdf)
Reference lists of relevant articles and reviews were hand searched for additional reports. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines were followed.30
The study was registered with the PROSPERO database (registration number: CRD42017062573).
Study selection, data collection and data items
We aimed to compare the incidence of PTB among the pregnant women population with dental caries with those who do not have dental caries.
The primary outcome was the occurrence of PTB, defined as birth <37 weeks of gestation. We aimed to categorise the analysis according to the type of PTB (spontaneous vs iatrogenic vs term) and according to the gestational age at birth moderate to late preterm (32 to <37 weeks), very preterm (28 to <32 weeks) and extremely preterm <28 weeks31.
The secondary objective was to ascertain the difference between women with dental caries who experienced PTB and those who did not experience PTB in either decayed, missing and filled teeth (DMFT) or decayed, missing and filled surfaces (DMFS) indices.32
DMFT and DMFS indices are numerical expressions of the caries prevalence of an individual or groups and are widely used in epidemiological surveys of oral health. DMFT/DMFS is calculated by adding up permanent teeth that are caries affected wherein D is for decay, M is missing due to caries and F is filled teeth (T) or surfaces (S). If one tooth has filling as well as a caries lesion, then it is counted as D for the DMFT index, whereas the filling+caries surface is counted as D but if there is F on one and D in other surface, then they are counted differently for the DMFS index. The anterior teeth up to canine have four and premolars and molars teeth have five surfaces, respectively, in the DMFS index. D+M+F=caries prevalence of an individual [maximum of 28 for DMFT and 128 for DMFS, if 28 permanent teeth are included (excluding 4 wisdom molar teeth)].32 33
Studies were assessed according to the following criteria: population, outcome, gestational age at birth and clinical characteristics of the caries during pregnancy. Observational cohort and case–control studies were included. Similarly, studies reporting the occurrence of PTB in women affected compared with those not affected by dental caries in pregnancies and the full-text articles were considered suitable for the inclusion in the present systematic review. Case reports, conference abstracts and case series with fewer than three cases were also excluded to avoid publication bias.
Two authors (MW and FD) reviewed all abstracts independently. Agreement regarding potential relevance was reached by consensus; full-text copies of those papers were obtained and the same two reviewers independently extracted relevant data regarding study characteristics and pregnancy outcome. Inconsistencies were discussed among the reviewers and consensus reached. Any dispute was resolved by discussion with a third author. If more than one study was published for the same cohort with identical endpoints, the report containing the most comprehensive information on the population was included to avoid overlapping populations. For those articles in which information was not reported but the methodology was such that this information would have been recorded initially, the authors were contacted.
Quality assessment of the included studies was performed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS)34; according to NOS, each study is judged on three broad perspectives: the selection of the study groups, the comparability of the groups and ascertainment outcome of interest. An assessment of the selection of a study includes the evaluation of the representativeness of the exposed cohort, selection of the non-exposed cohort, ascertainment of exposure and the demonstration that outcome of interest was not present at the start of study. The NOS tool for the quality assessment of the studies is provided in the online supplementary material 2. According to the tool, a study can be awarded a maximum of one star for each numbered item within the selection and outcome categories. A maximum of two stars can be given for comparability.34
bmjopen-2017-018556supp002.pdf (22KB, pdf)
Statistical analysis
A first random-effect meta-analysis of binary outcomes was used to compute the summary OR (and relative 95% CI) of PTB among women with caries versus women without caries (controls).
Other two meta-analyses evaluated continuous outcomes: DMFT and DMFS. As the included studies did not differ in their outcome definitions, we used a random-effect approach to compute the mean difference in either DMFT or DMFS between PTB and non-PTB. In one study by Martinez-Martinez et al,35 the SD were not available, and we thus conservatively used the largest values recorded in the other included studies.
For all meta-analyses, the heterogeneity across studies was quantified using I2 statistic, and all computations were made using Review Manager (RevMan), V.5.3 (Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014).
Results
General characteristics
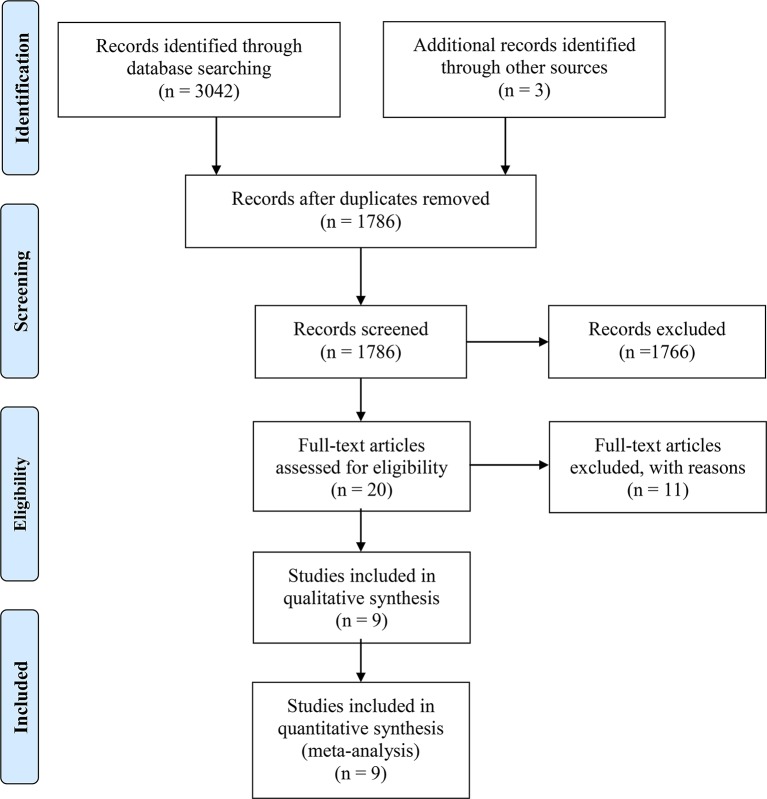
A total of 1786 articles were identified, 20 were assessed with respect to their eligibility for inclusion (online supplementary material 3) and 9 studies were included in the systematic review (table 1, figure 1). These nine studies included 4826 pregnancies.
Table 1.
General characteristics of the included studies
| Author | Year | Country | Period analysed (year) | Study design | Gestational age at dental examination | Number of subject (n) | Definition of PTB |
| Martinez-Martinez et al35 | 2016 | Mexico | 2013–2014 | Retrospective | From the first trimester of pregnancy until 8 weeks postpartum | 70 | <37 weeks |
| Harjunmaa et al24 | 2015 | Malawi | 2011–2013 | Prospective | Within 6 weeks after delivery | 1024 | <37 weeks |
| Acharya et al23 | 2013 | India | 2009 | Retrospective | Within 1 day after delivery | 316 | <37 weeks |
| Vergnes et al22 | 2011 | France | 2003–2006 | Retrospective | Within 2–4 days post partum | 2201 | <37 weeks |
| Ryalat et al21 | 2011 | Jordan | 2009 | Prospective | Within 1 week post partum | 200 | <37 weeks |
| Durand et al17 | 2009 | France | 2005–2006 | Prospective | Within 8 weeks after delivery | 107 | <37 weeks |
| Heimonen et al20 | 2008 | Finland | 2002–2004 | Retrospective | Within 2 days post partum | 328 | <37 weeks |
| Mumghamba and Manji19 | 2007 | Tanzania | NS | Retrospective | Within 40 days from delivery | 373 | <37 weeks |
| Meurman et al18 | 2006 | Finland | 1998–2000 | Retrospective | From the first trimester of pregnancy | 207 | <37 weeks |
PTB, preterm birth.
Figure 1.
Systematic review flow chart.
bmjopen-2017-018556supp003.pdf (16.9KB, pdf)
Results of quality assessment of the included studies using NOS for cohort studies are presented in table 2. Most of the included studies scored at least one star in each of the three categories: the selection and comparability of the study groups, and ascertainment of the outcome of interest. The main weaknesses of these studies were their retrospective design, small sample size with even smaller number of events (PTB) and different gestational ages at assessment.
Table 2.
Quality assessment of the included studies according to Newcastle-Ottawa Scale, a study can be awarded a maximum of one star for each numbered item within the selection and outcome categories
| Author | Year | Selection | Comparability | Outcome |
| Martinez-Martinez et al35 | 2016 | ★★ | ★ | ★ |
| Harjunmaa et al24 | 2015 | ★★ | ★ | ★ |
| Acharya et al23 | 2013 | ★★ | ★ | ★★ |
| Vergnes et al22 | 2011 | ★★★ | ★★ | ★ |
| Ryalat et al21 | 2011 | ★★★ | ★ | ★★ |
| Durand et al17 | 2009 | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ |
| Heimonen et al20 | 2008 | ★★ | ★ | ★ |
| Mumghamba and Manji19 | 2007 | ★★ | ★ | ★ |
| Meurman et al18 | 2006 | ★★ | ★ | ★ |
A maximum of two stars can be given for comparability.
Synthesis of the results
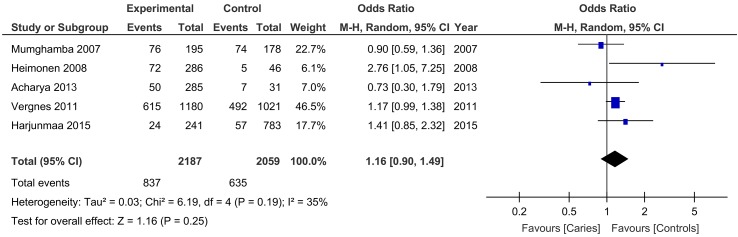
Five studies explored the risk of PTB in women who had caries compared with those who did not have caries during pregnancy and reported that women affected by caries in pregnancy did not have an increased risk of delivering <37 weeks of gestation (OR: 1.16, 95% CI 0.90 to 1.49, P=0.25; I2: 35%) (figure 2).
Figure 2.
Pooled OR for the risk of preterm birth in women compared with those without dental caries.
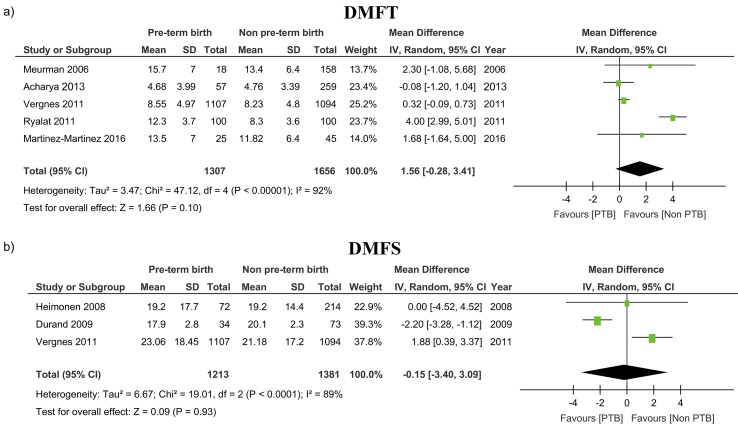
Stratification according to DMFT and DMFS indices to evaluate the association between caries and PTB was performed only by five and three studies, respectively. There was no difference in either DMFT (1.56, 95% CI −0.28 to 3.41, P=0.10) and DMFS (−0.15, 95% CI −3.40 to 3.09, P=0.9) (table 3 and figure 3).
Table 3.
Selected outcomes evaluating the association between dental caries and PTB
| Outcomes | N studies (n/N) | OR (95% CI) | P | I2 %* |
| PTB, women with dental caries versus controls | 5 (1472/4246) | 1.16 (0.90 to 1.49) | 0.25 | 35 |
| DMFT (PTB vs non-PTB) | 5 (2963) | 1.56 (−0.28 to 3.41) | 0.10 | 92 |
| DMFS (PTB vs non-PTB) | 3 (2594) | −0.15 (−3.40 to 3.09) | 0.9 | 89 |
*I2 is a measure of the heterogeneity among the included studies. a value ≥50% indicates high while <50% low heterogeneity.
DMFT, decayed, missed and filled teeth; DMFS, decayed, missed and filled surface; n, number of events; N, total number of participants; PTB, preterm birth.
Figure 3.
Mean differences in DMFT and DMFS indices in women with dental caries compared with those who did not experience PTB. DMFS, decayed, missing and filled surface; DMFT, decayed, missing and filled teeth; PTB, preterm birth.
Due to very small number of included cases and lack of information from the original study, it was not possible to perform any subanalysis according to different gestational age at birth and type of PTB (spontaneous vs iatrogenic vs term).
Discussions
Summary of evidence
The findings from this systematic review showed that pregnant women with dental caries are not at increased risk for PTB. Furthermore, there was no difference in the mean DMFT and DMFS indices between women with dental caries who experienced PTB and those who did not.
Strength and limitations
This is, to our knowledge, the first systematic review exploring the strength of association between dental caries and PTB. The strength of this meta-analysis is its robust methodology. We tried to cover all available studies, access the quality of the data and synthesise all suitable data.
The small number of cases in some of the included studies, their retrospective non-randomised design, different periods of follow-up, dissimilarity of the populations studies (due to various inclusion criteria) and lack of standardised criteria for the antenatal management of pregnancies with dental caries represent the major limitations of this systematic review. Lack of data on early PTB, which is typically associated with infection and inflammation, was another major limitation of the present systematic review. Furthermore, we could not stratify the analysis according to maternal characteristics and caries stage at diagnosis in view of the lack of such information in the large majority of included studies. Assessment of the potential publication bias was also problematic because of the nature of the outcome evaluated (outcome rates with the left side limited to a value of zero), which limits the reliability of funnel plots, and because of the small number of individual studies, which strongly limits the reliability of formal tests. Finally, statistical heterogeneity among the included studies was another major limitation of the present review which may potentially bias the study findings. In view of these limitations, the findings from this systematic review should be interpreted with cautions.
Implication for clinical practice
The consequences of overall oral health including the oral health in pregnant women is of a great concern.36 Dental caries and periodontal disease are the most common oral diseases worldwide. The higher prevalence of gingival alterations during pregnancy, especially bleeding during brushing, is a problem that is commonly encountered by pregnant women. Properly maintained oral hygiene care is known to have an impact on the oral health of pregnant women37 38 and availability of free dental care also appears to influence this.39 Whereas in contrast, if proper oral hygiene is not maintained during pregnancy, the chances to develop oral health problems such as enamel erosions, dental caries40 and gingivitis increase.
There are no reports indicating that the incidence of dental caries increases during pregnancy, but the chances of getting dental caries could increase14 and the prevalence of dental caries seemed to be higher in older pregnant women.41 Despite the high dental caries prevalence in most developed countries, very few studies have explored the potential association between oral health and adverse pregnancy outcome.
Identification of women at higher risk of PTB is fundamental to prevent the likelihood of delivering preterm. Several risk factors have been associated with PTB, such as prior history of PTB, cervical disease and infection. Despite this, finding an association between a given risk factor and the occurrence of PTB is challenging.
Dental caries is a frequently encountered oral health problem in pregnancy as pregnant women are more susceptible to caries compared with non-pregnant women.13 Being caused by an infectious process, dental caries can theoretically lead to inflammation and thus increase the risk of PTB.12 Despite this, we could not find any significant association between dental caries and PTB; furthermore, we did not find any significant difference in the severity of caries assessed by DMFT and DMFS indices between women who experienced PTB compared with those who did not. In addition to this, since most of these studies have evaluated women after delivery, this may also have influenced the results.
The lack of association between dental caries and PTB is difficult to explain. The initiation and progression of the caries lesion is very slow and the destruction caused by caries in initial stage can be reversible.12 In addition to this, pregnancy itself does not cause dental caries but it may exacerbate the existing condition. Dental caries is symptomless until there is severe and irreversible destruction of teeth.42 It might be possible that bacterial spreading during caries formation and the subsequent production of proinflammatory mediators induced by oral pathogens may not be of the magnitude to cause production of proinflammatory mediators enough to initiate PTB.
Even though we found no significant relationship between the dental caries and PTB, it is still important for the health professionals to promote oral health among the pregnant women. This is because pregnant women are susceptible to dental problems and have very limited knowledge and awareness about the importance of oral health and its potential impact on pregnancy outcomes.39 43 Furthermore, the risk of transmitting the oral cariogenic flora from the mother to her infant through feeding practices and predisposing the infant to early childhood caries in the future should not be neglected.44–47 Therefore, large prospective studies aiming at ascertaining the association between dental caries and spontaneous PTB, according to the gestational age at occurrence, severity of the disease and presence of other co-morbidities are needed in order to elucidate the role, if any, of dental caries in increasing the risk of PTB.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors would sincerely like to thank Professor S Acharya, Professor S Abati, Professor I Cetin, Professor GG Campus, Professor A Villa, Professor R Martinez, Professor S Ryalat, Professor J H Meurman, Professor Y Khader, Professor A Heimonen, Professor U Harjunmaa, Professor R Durand, Professor N Buduneli and Professor A P Dasanayake for their co-operation and contribution by providing additional data and necessary information for this systematic review.
Footnotes
Contributors: MW, GA, FD’A and ER: study concept, design and methodology. ER: data collection and entry. MW and FD’A: abstracts and articles review. F’DA, MW, GO and LM: analysis and interpretation of data. FD’A, GA, PB and TAT: involved in supervision. MW, FD’A, ER, TAT, PB, GO, LM and GA: writing, review, critique, comments and revision of manuscript.
Funding: No funding was received for the conduction of this review. The publication charges for this article have been funded by a grant from the publication fund of UiT - The Arctic University of Norway.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent: Not required.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: No additional data are available.
References
- 1.Goldenberg RL, Culhane JF, Iams JD, et al. Epidemiology and causes of preterm birth. Lancet 2008;371:75–84. 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60074-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Slattery MM, Morrison JJ. Preterm delivery. Lancet 2002;360:1489–97. 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11476-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McCormick MC. The contribution of low birth weight to infant mortality and childhood morbidity. N Engl J Med 1985;312:82–90. 10.1056/NEJM198501103120204 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Saigal S, Doyle LW. An overview of mortality and sequelae of preterm birth from infancy to adulthood. Lancet 2008;371:261–9. 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60136-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Romero R, Espinoza J, Kusanovic JP, et al. The preterm parturition syndrome. BJOG 2006;113(Suppl 3):17–42. 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2006.01120.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jeffcoat MK, Geurs NC, Reddy MS, et al. Current evidence regarding periodontal disease as a risk factor in preterm birth. Ann Periodontol 2001;6:183–8. 10.1902/annals.2001.6.1.183 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Offenbacher S. Maternal periodontal infections, prematurity, and growth restriction. Clin Obstet Gynecol 2004;47:808–21. 10.1097/01.grf.0000141894.85221.f7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Offenbacher S, Boggess KA, Murtha AP, et al. Progressive periodontal disease and risk of very preterm delivery. Obstet Gynecol 2006;107:29–36. 10.1097/01.AOG.0000190212.87012.96 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jarjoura K, Devine PC, Perez-Delboy A, et al. Markers of periodontal infection and preterm birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2005;192:513–9. 10.1016/j.ajog.2004.07.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Goepfert AR, Jeffcoat MK, Andrews WW, et al. Periodontal disease and upper genital tract inflammation in early spontaneous preterm birth. Obstet Gynecol 2004;104:777–83. 10.1097/01.AOG.0000139836.47777.6d [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Xiong X, Buekens P, Fraser WD, et al. Periodontal disease and adverse pregnancy outcomes: a systematic review. BJOG 2006;113:135–43. 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2005.00827.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Selwitz RH, Ismail AI, Pitts NB, et al. Dental caries. Lancet 2007;369:51–9. 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60031-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Martínez-Beneyto Y, Vera-Delgado MV, Pérez L, et al. Self-reported oral health and hygiene habits, dental decay, and periodontal condition among pregnant European women. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2011;114:18–22. 10.1016/j.ijgo.2011.03.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gajendra S, Kumar JV. Oral health and pregnancy: a review. N Y State Dent J 2004;70:40–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Silk H, Douglass AB, Douglass JM, et al. Oral health during pregnancy. Am Fam Physician 2008;77:1139–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dasanayake AP, Li Y, Wiener H, et al. Salivary Actinomyces naeslundii genospecies 2 and Lactobacillus casei levels predict pregnancy outcomes. J Periodontol 2005;76:171–7. 10.1902/jop.2005.76.2.171 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Durand R, Gunselman EL, Hodges JS, et al. A pilot study of the association between cariogenic oral bacteria and preterm birth. Oral Dis 2009;15:400–6. 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2009.01559.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Meurman JH, Furuholm J, Kaaja R, et al. Oral health in women with pregnancy and delivery complications. Clin Oral Investig 2006;10:96–101. 10.1007/s00784-006-0037-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mumghamba EG, Manji KP. Maternal oral health status and preterm low birth weight at Muhimbili National Hospital, Tanzania: a case-control study. BMC Oral Health 2007;7:8 10.1186/1472-6831-7-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Heimonen A, Rintamäki H, Furuholm J, et al. Postpartum oral health parameters in women with preterm birth. Acta Odontol Scand 2008;66:334–41. 10.1080/00016350802307620 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ryalat S, Sawair F, Baqain Z, et al. Effect of oral diseases on mothers giving birth to preterm infants. Med Princ Pract 2011;20:556–61. 10.1159/000329887 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vergnes JN, Kaminski M, Lelong N, et al. Maternal dental caries and pre-term birth: results from the EPIPAP study. Acta Odontol Scand 2011;69:248–56. 10.3109/00016357.2011.563242 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Acharya S, Pentapati KC, Bhat PV. Dental neglect and adverse birth outcomes: a validation and observational study. Int J Dent Hyg 2013;11:91–8. 10.1111/idh.12001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Harjunmaa U, Järnstedt J, Alho L, et al. Association between maternal dental periapical infections and pregnancy outcomes: results from a cross-sectional study in Malawi. Trop Med Int Health 2015;20:1549–58. 10.1111/tmi.12579 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Saraiva MC, Bettiol H, Barbieri MA, et al. Are intrauterine growth restriction and preterm birth associated with dental caries? Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2007;35:364–76. 10.1111/j.1600-0528.2006.00345.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Abati S, Villa A, Cetin I, et al. Lack of association between maternal periodontal status and adverse pregnancy outcomes: a multicentric epidemiologic study. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2013;26:369–72. 10.3109/14767058.2012.733776 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Buduneli N, Baylas H, Buduneli E, et al. Periodontal infections and pre-term low birth weight: a case-control study. J Clin Periodontol 2005;32:174–81. 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2005.00670.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Henderson LK, Craig JC, Willis NS, et al. How to write a Cochrane systematic review. Nephrology 2010;15:617–24. 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2010.01380.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.NHS Centre for Reviews and Dissemination. Systematic reviews: CRD’s guidance for undertaking reviews in health care. York (UK): University of York, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000;283:2008–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.World Health Organization. Preterm birth. 2017. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs363/en/ (accessed 3 May 2017).
- 32.World Health Organization. Oral health surveys: basic methods. 4th edn Geneva: World Health Organization, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Malmo University. Caries prevalence and calculation. 2010. https://www.mah.se/CAPP/Methods-and-Indices/for-Caries-prevalence/ (accessed 11 April 2017).
- 34.Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Ottawa, Canada: The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Martínez-Martínez RE, Moreno-Castillo DF, Loyola-Rodríguez JP, et al. Association between periodontitis, periodontopathogens and preterm birth: is it real? Arch Gynecol Obstet 2016;294:47–54. 10.1007/s00404-015-3945-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Achtari MD, Georgakopoulou EA, Afentoulide N. Dental care throughout pregnancy: what a dentist must know. Oral Health Dent Manag 2012;11:169–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Huebner CE, Milgrom P, Conrad D, et al. Providing dental care to pregnant patients: a survey of Oregon general dentists. J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140:211–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Boggess KA, Urlaub DM, Massey KE, et al. Oral hygiene practices and dental service utilization among pregnant women. J Am Dent Assoc 2010;141:553–61. 10.14219/jada.archive.2010.0228 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hullah E, Turok Y, Nauta M, et al. Self-reported oral hygiene habits, dental attendance and attitudes to dentistry during pregnancy in a sample of immigrant women in North London. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2008;277:405–9. 10.1007/s00404-007-0480-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Merglova V, Hecova H, Stehlikova J, et al. Oral health status of women with high-risk pregnancies. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 2012;156:337–41. 10.5507/bp.2012.045 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Shamsi M, Hidarnia A, Niknami S, et al. The Status of Dental Caries and Some Acting Factors in a Sample of Iranian Women with Pregnancy. World J Med Sci 2013;9:190–7. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kloetzel MK, Huebner CE, Milgrom P. Referrals for dental care during pregnancy. J Midwifery Womens Health 2011;56:110–7. 10.1111/j.1542-2011.2010.00022.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Keirse MJ, Plutzer K. Women’s attitudes to and perceptions of oral health and dental care during pregnancy. J Perinat Med 2010;38:3–8. 10.1515/jpm.2010.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zanata RL, Navarro MF, Pereira JC, et al. Effect of caries preventive measures directed to expectant mothers on caries experience in their children. Braz Dent J 2003;14:75–81. 10.1590/S0103-64402003000200001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Goldie MP. Oral health care for pregnant and postpartum women. Int J Dent Hyg 2003;1:174–6. 10.1034/j.1601-5037.2003.00039.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Boggess KA, Edelstein BL. Oral health in women during preconception and pregnancy: implications for birth outcomes and infant oral health. Matern Child Health J 2006;10(5 Suppl):169–74. 10.1007/s10995-006-0095-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Boggess KA. Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine Publications Committee. Maternal oral health in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 2008;111:976–86. 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31816a49d3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
bmjopen-2017-018556supp001.pdf (99.4KB, pdf)
bmjopen-2017-018556supp002.pdf (22KB, pdf)
bmjopen-2017-018556supp003.pdf (16.9KB, pdf)