Abstract
Background
Non-digestible carbohydrates present in cereals such as fructans and arabinoxylans represent promising prebiotic nutrients to prevent the development of obesity and related metabolic disorders. OBJECTIVE AND DESIGN: The aim of this study was to determine the corrective effects of wheat bran-derived arabinoxylan oligosaccharides in obese mice fed a western diet (WD). WD was given for 4 weeks before wheat bran extract (WBE) supplementation (5%) for an additional 4 weeks, whereas a control group received the standard diet.
Results
Bifidogenic effect of WBE was evidenced by an induction of both Bifidobacterium animalis and Bifidobacterium pseudolongum in the caecal content. WBE supplementation normalised WD-induced fat-mass expansion, steatosis, hypercholesterolemia, hyperleptinemia, hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia reaching the values of control mice. The reduced glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) release observed in WD + WBE mice may be a protective mechanism in terms of reducing adipose tissue storage, hepatic steatosis and glucose homoeostasis.
Conclusion
We found that WBE completely abolished WD-induced metabolic disorders. Those results might be useful to take into account nutritional advices to treat obesity and related metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes, hypercholesterolaemia and fatty liver diseases when obesity was already established.
Introduction
Obesity and related metabolic disorders such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases become major health problems in Western countries, while the consumption of cereals has decreased markedly over the last century1. Dietary fibres are the most important constituents in cereal grains related to positive health effects, and the consumption of the whole grain products help to reach the recommended dietary fibre intake2–4. Wheat bran is a low-cost byproduct of conventional wheat milling. Hydrolysis products of arabinoxylan—named arabinoxylan oligosaccharides (AXOS)—are characterised by their average degree of arabinose substitution and their lower average degree of polymerisation5.
Gut microbiota is an important factor involved in the control of body weight and metabolic alterations occurring in obesity6,7. Several mechanisms are proposed, linking events occurring in the gut upon carbohydrate fermentation and the control of metabolic disorders8. We have previously shown that oligosaccharides issued from inulin-type fructans counteracted obesity and metabolic alteration development upon high-fat feeding including dyslipidemia and diabetes, by modulating the gut microbiota9,10. The glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), a satietogenic gut-derived peptide, contributes largely to explain those effects9,11. However, to date, no study has evaluated the potential effect of AXOS on metabolic disorders in a model of obesity pre-established upon western diet feeding, in relationship with gut microbiota modulation.
METHODS
Animals and diets
Twenty seven male C57BL6 mice (9 weeks old, Janvier laboratories, France) were housed in specific pathogen-free (SPF) conditions in groups of 3 mice per cage in a controlled environment (12-hour daylight cycle) with free access to food and water. After 1 week of acclimatisation, mice were divided into two groups: a control group (CT) fed with a control diet (low fat, no sucrose, matched, purified ingredient diet corresponding to D12450K, Ssniff, Germany; n = 9) and a group fed with a WD (high-fat diet corresponding to D12451, Ssniff, Germany; n = 18). The composition of the diets is presented in supplementary information. After 4 weeks of dietary treatment, WD-treated mice were divided into two subgroups fed a WD with or without 5% wheat bran-derived arabinoxylan oligosaccharides (WBE group). WBE contained 72% of AXOS with an average degree of polymerisation of 5 and a degree of substitution arabinose/xylose of 0.24 (Cargill R&D centre Europe BVBA, Belgium). Mice body weight, food intake and water intake were recorded twice a week. Total fat mass was determined using a 7.5 MHz Time domain-Nuclear magnetic resonance (LF50 minispec, Bruker, Germany). After a total of 8 weeks of dietary treatment and a 6-h period of fasting, mice were anesthetised with isoflurane (Forene®, Abbott, Queenborough, Kent, England) and blood samples were harvested. Mice were killed by cervical dislocation. Portal blood was taken in <30 s and directly flushed within tubes containing dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor (Millipore, St Charles, MO, USA). Plasma was immediately collected after centrifugation and stored at −80°C. Liver, colon and caecum were carefully dissected, weighted and immersed in liquid nitrogen before storage at −80 °C; pieces of liver were embedded in OCT compound and frozen in nitrogen-cooled isopentane for histology. Mouse experiment was approved by and performed in accordance with the guidelines of the local ethics committee under the specific agreement numbers 2014/UCL/MD/022. Housing conditions were as specified by the Belgian Law of 29 May 2013, on the protection of laboratory animals (Agreement LA 1230314).
Biochemical analysis
Hepatic content of lipids and plasma insulin, triglycerides, cholesterol and non-esterified fatty acid concentrations were measured as described in supplementary information. Portal concentrations of glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP), glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), ghrelin and leptin were determined in 2 × 15 µl of plasma using a multiplex immunoassay kit (Bioplex, Bio-Rad) and measured using Luminex technology (Bioplex, Bio-Rad).
Histochemical detection of liver lipids
Frozen liver sections were sliced at 5 µm, treated with oil red O and scanned as previously described12. The lipid area were determined on whole sections using the imaging software TissueIA (v 2.0.3, Leica Biosystems, Dublin, Ireland). Pixels corresponding to the oil red O staining were selected to create a colour profile. Total tissue area was defined by setting the tissue intensity threshold at 210 (grey value). Results were expressed as stained area (below threshold)/tissue area (below threshold). Two representative tissue pieces were analysed for each mice.
Analysis of the gut bacteria
At the end of the experiment, the total caecum content was collected and weighed before storage at −80°C. Genomic DNA was extracted from the caecal content using a QIAamp DNA Stool Mini Kit (Qiagen, Germany). Absolute quantification of bacteria was performed as described in supplementary information.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance between groups was assessed by one-way ANOVA (two-way ANOVA for body weight evolution). The ANOVA tests were followed by post-hoc Tukey’s multiple comparison tests (post-hoc Bonferroni for body weight evolution) using GraphPad Prism software (San Diego, CA, USA).
Results
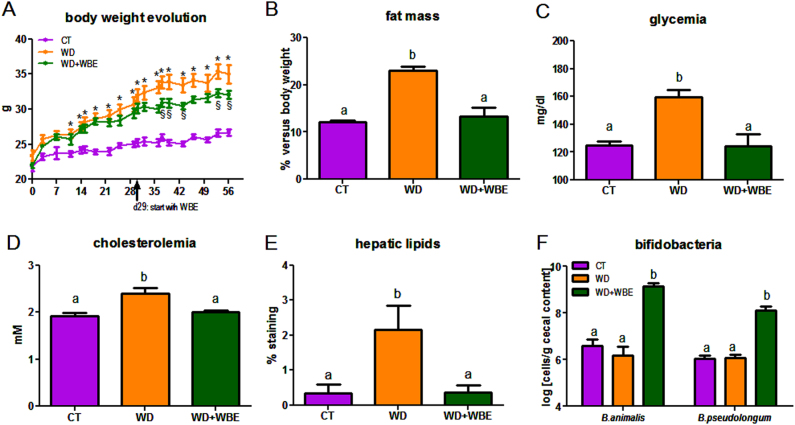
The WD consumption induced obesity after 4 weeks of dietary treatment (the body weight gain (d29-d0) was 2.91 ± 0.56 g and 6.97 ± 0.31 g for CT and WD groups, respectively; p < 0.05 Student t-test). WBE supplementation in the WD diet from d29 until d56 slowed down the body weight gain compared to the WD group (Fig. 1a) independently of the food intake (total food intake from d29 to d56: 70 ± 3, 64 ± 1, 70 ± 2 g for CT, WD and WD + WBE, respectively; p > 0.05, one-way ANOVA). Furthermore, WBE treatment blunted fat-mass expansion reaching the control value at the end of the treatment (Fig. 1b). The portal level of leptin, an adipokine produced proportionally to fat mass, was markedly increased in WD, whereas it decreased in WBE group (Table 1). In contrast, the plasma ghrelin was not significantly affected by the dietary treatments. Interestingly, WBE treatment counteracted the higher release of GIP induced by the WD. WBE supplementation upregulated proglucagon expression in the colon (1.00 ± 0.05 a, 1.05 ± 0.08 a and 1.33 ± 0.08 b for CT, WD and WD + WBE group, respectively; one-way ANOVA), whereas the plasma level of GLP-1 was not significantly affected (data not shown). WD-induced hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, insulin resistance (HOMA-IR index) and hypercholesterolemia were decreased upon WBE supplementation, reaching the control values after 4 weeks of supplementation (Fig. 1c, d; Table 1). In contrast, plasma levels of triglycerides and free fatty acids were not significantly modified by the dietary treatments (Table 1). It is worth noting that higher hepatic content of lipids (mostly triglyceride content) observed upon WD was completely blunted by the WBE treatment (Fig. 1e). Finally, we determined the levels of several bacteria known to be affected by wheat bran product supplementation such as Lactobacillus spp., Roseburia spp., Bacteroides spp.13,14 but none of these bacteria was changed by the WBE supplementation (Table 1). We analysed two specific bifidobacteria species known to be present in mice and in humans: Bifidobacterium animalis and Bifidobacterium pseudolongum15. After only 4 weeks of WBE supplementation, we observed a marked bifidogenic effect for both species (Fig. 1f).
Fig. 1. Prebiotic effect of wheat bran extract in the model of western diet-induced obesity and related metabolic alterations.
Body weight evolution (a), fat mass measured by NMR at days 50 (b), glycemia (c), cholesterolemia (d), histological analysis of liver lipids (e) and bifidobacteria (f). Mice were fed a control diet (CT), a western diet (WD) or a WD supplemented with 5% of WBE (WD + WBE) for 4 weeks. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 WD versus CT, §p < 0.05 WD + WBE versus WD, data with different superscript letters are significantly different at p < 0.05 (ANOVA)
Table 1.
Plasma parameters, liver lipids and caecal bacteria
| CT | WD | WD + WBE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum parameters | |||
| –Triglycerides (mM) | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 0.40 ± 0.02 | 0.40 ± 0.03 |
| –Free fatty acids (mM) | 0.40 ± 0.03 | 0.46 ± 0.03 | 0.48 ± 0.04 |
| –Insulin (pg/ml) | 0.15 ± 0.04a | 0.75 ± 0.29b | 0.13 ± 0.06a |
| –Leptin (pg/ml) | 989 ± 112a | 13967 ± 1583b | 4647 ± 1370a |
| –Ghrelin (pg/ml) | 122 ± 20 | 112 ± 26 | 76 ± 12 |
| –GIP (pg/ml) | 44 ± 5a | 93 ± 12b | 56 ± 8a |
| –HOMA-IR | 9 ± 2a | 60 ± 18b | 15 ± 4a |
| Liver lipid content | |||
| –Total lipids (mg/g tissue) | 48 ± 2a | 62 ± 4b | 48 ± 4a |
| –Triglycerides (nmol/mg protein) | 11.4 ± 0.9a | 18.2 ± 2.5b | 14.8 ± 1.4ab |
| –Cholesterol (nmol/mg protein) | 8.5 ± 0.3a | 11.9 ± 0.5b | 11.3 ± 0.4b |
| Gut bacteria, log (cells/g caecal content) | |||
| Total bacteria | 11.71 ± 0.08 | 11.70 ± 0.06 | 11.60 ± 0.09 |
| Lactobacillus spp. | 8.46 ± 0.11 | 8.17 ± 0.17 | 8.41 ± 0.15 |
| Roseburia spp. | 8.97 ± 0.08 | 8.95 ± 0.08 | 8.91 ± 0.07 |
| Bacteroides spp. | 10.51 ± 0.12 | 10.33 ± 0.06 | 10.31 ± 0.13 |
Mice were fed a control diet (CT), a western diet (WD) or a WD supplemented with 5% of WBE (WD + WBE) for 4 weeks. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. Data with different superscript letters are significantly different at p < 0.05 (ANOVA)
GIP glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide, HOMA-IR homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance
Discussion and conclusion
We confirmed the prebiotic effect of AXOS produced from wheat bran in a model of WD-induced obesity. Indeed, WBE feeding for 4 weeks improved host physiology and this was associated with an increase in bifidobacteria demonstrated by an induction of two representative species in mice: B. animalis and B. pseudolongum. Previous studies reported that B. animalis is a specific gut bacterial strain negatively correlated with the body mass index that was able to reduce fat mass and glucose intolerance in both obese and diabetic mice when used a probiotic16,17.
This bifidogenic effect of WBE was associated with a normalisation of fat mass and plasma leptin due to a 8-week WD feeding supporting results obtained in our previous studies12,14. Interestingly, in our study this effect is independent of the caloric intake or the modulation of peptides regulating appetite such as ghrelin or GLP-1.
WD-induced type 2 diabetes, steatosis and hypercholesterolemia after 8 weeks of dietary treatment. Plasma levels of cholesterolemia, glycemia, insulinemia, the insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR) as well as the hepatic level of lipids returned to the levels obtained in control mice after only 4 weeks of WBE supplementation when obesity is already established. Therefore, this is the first study suggesting that wheat bran-derived AXOS is effective to counteract obesity instead of preventing it as previously shown elsewhere12,14. The lack of effect on triglyceridemia is not surprising as the serum triglycerides is dependent not only on VLDL secretion by the liver, but also on the lipoprotein lipase in other tissues. Importantly, the reduced GIP release observed in WD + WBE mice may be a protective mechanism in terms of reducing adipose tissue storage, hepatic steatosis and improving insulin sensitivity18,19.
In conclusion, this study reinforces the promising beneficial aspects of wheat bran-derived AXOS as prebiotic nutrient as it improved obesity-related metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes, hypercholesterolemia and fatty liver disease when obesity was already established.
Electronic supplementary material
Acknowledgements
We thank Véronique Allaeys, Isabelle Blave, Remi Selleslagh and Bouazza Es Saadi for skilful technical assistance. L.B.B. is a recipient of FSR subsidies (UCL, Belgium). N.M.D. is a recipient of FRS-FNRS grants. P.D.C., a senior research associate at the FRS-FNRS (Belgium), is a recipient of an ERC Starting Grant 2013 (336452-ENIGMO), Baillet Latour grant for medical research 2015 and is supported by the FRS-FNRS via the FRFS-WELBIO under Grant number WELBIO-CGR-2017.
Conflict of interest
VGC is employed by Cargill R&D Europe, who provided partial support for this work. Cargill, Inc. is a producer of food ingredients. The remaining authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper at (10.1038/s41387-018-0019-z).
References
- 1.Adam A, et al. Whole wheat and triticale flours with differing viscosities stimulate cecal fermentations and lower plasma and hepatic lipids in rats. JNutr. 2001;131:1770–1776. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.6.1770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Neyrinck AM, Delzenne NM. Potential interest of gut microbial changes induced by non-digestible carbohydrates of wheat in the management of obesity and related disorders. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 2010;13:722–728. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32833ec3fb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Deehan EC, Walter J. The fiber gap and the disappearing gut microbiome: implications for human nutrition. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2016;27:239–242. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Delcour JA, Aman P, Courtin CM, Hamaker BR, Verbeke K. Prebiotics, fermentable dietary fiber, and health claims. Adv. Nutr. 2016;7:1–4. doi: 10.3945/an.115.010546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Broekaert WF, et al. Prebiotic and other health-related effects of cereal-derived arabinoxylans, arabinoxylan-oligosaccharides, and xylooligosaccharides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011;51:178–194. doi: 10.1080/10408390903044768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Delzenne NM, Cani PD. Interaction between obesity and the gut microbiota: relevance in nutrition. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2011;31:15–31. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-072610-145146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sonnenburg JL, Backhed F. Diet-microbiota interactions as moderators of human metabolism. Nature. 2016;535:56–64. doi: 10.1038/nature18846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Delzenne NM, Cani PD, Everard A, Neyrinck AM, Bindels LB. Gut microorganisms as promising targets for the management of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2015;58:2206–2217. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3712-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Delzenne NM, Neyrinck AM, Backhed F, Cani PD. Targeting gut microbiota in obesity: effects of prebiotics and probiotics. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011;7:639–646. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cani PD, et al. Selective increases of bifidobacteria in gut microflora improve high-fat-diet-induced diabetes in mice through a mechanism associated with endotoxaemia. Diabetologia. 2007;50:2374–2383. doi: 10.1007/s00125-007-0791-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cani PD, et al. Improvement of glucose tolerance and hepatic insulin sensitivity by oligofructose requires a functional glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. Diabetes. 2006;55:1484–1490. doi: 10.2337/db05-1360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Suriano F, et al. Fat binding capacity and modulation of the gut microbiota both determine the effect of wheat bran fractions on adiposity. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:5621. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05698-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Neyrinck A. M. et al. Prebiotic effects of wheat arabinoxylan related to the increase in bifidobacteria, roseburia and bacteroides/prevotella in diet-induced obese mice. PLoS ONE. 6, e20944 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 14.Neyrinck AM, et al. Wheat-derived arabinoxylan oligosaccharides with prebiotic effect increase satietogenic gut peptides and reduce metabolic endotoxemia in diet-induced obese mice. Nutr. Diabetes. 2012;2:e28. doi: 10.1038/nutd.2011.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Turroni F, et al. Exploring the diversity of the bifidobacterial population in the human intestinal tract. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009;75:1534–1545. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02216-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stenman LK, et al. Potential probiotic Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis 420 prevents weight gain and glucose intolerance in diet-induced obese mice. Benef. Microbes. 2014;5:437–445. doi: 10.3920/BM2014.0014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Million M, et al. Correlation between body mass index and gut concentrations of Lactobacillus reuteri, Bifidobacterium animalis, Methanobrevibacter smithii and Escherichia coli. Int. J. Obes. 2013;37:1460–1466. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2013.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 18.Moller CL, et al. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide is associated with lower low-density lipoprotein but unhealthy fat distribution, independent of insulin: The ADDITION-PRO Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016;101:485–493. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-3133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gault VA, McClean PL, Cassidy RS, Irwin N, Flatt PR. Chemical gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor antagonism protects against obesity, insulin resistance, glucose intolerance and associated disturbances in mice fed high-fat and cafeteria diets. Diabetologia. 2007;50:1752–1762. doi: 10.1007/s00125-007-0710-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.