To the editor
Dyskeratosis congenita (DC) is a telomere biology disorder (TBD) associated with bone marrow failure (BMF) and the classic triad of reticulate skin pigmentation, nail dystrophy, and oral leukoplakia. Disease-causing variants in at least 11 telomere biology genes have been implicated in DC and exhibit autosomal dominant (AD), autosomal recessive (AR), and X-linked recessive (XLR) inheritance, as well as de novo occurrence (TINF2). Patients with XLR, AR or TINF2 DC tend to manifest more severe hematologic outcomes than patients with AD DC.1, 2 We sought to assess the sensitivity of the clinical triad for DC diagnosis, quantify additional mucocutaneous features, and examine the relationship between DC genotype and mucocutaneous phenotype.
This study included 60 patients with genetically-proven DC in an IRB-approved longitudinal cohort study, NCT-00027274 (Table 1).3 The prevalence of triad features and eight additional mucocutaneous findings (adermatoglyphia, palmoplantar hyperkeratosis, hyperhidrosis, premature graying, scalp or eyelash hair loss, epiphora, and lash irritation/blepharitis) were elicited from comprehensive medical photographs and dermatology evaluations. Hematologic and mortality outcomes data were gathered prospectively. Telomere length data were obtained for 58/60 patients as previously described.4 Patients with XLR/AR and AD DC were compared. Because TINF2 variants can be AD inherited or de novo and typically have severe phenotypes, patients with TINF2 DC were excluded from the AD group and analyzed separately.2
Table I.
Patient demographics and results
| Characteristics (%) |
Total (n=60) |
XLR/AR (n=23) |
TINF2 (n=14) |
Non-TINF2 AD (n=23) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yrs) | ||||
| Median | 23 | 32 | 17 | 15 |
| Range | 1–69 | 1–46 | 2–31 | 1–69 |
| Age group (yrs) | ||||
| 0–9 (n=14) | 14 (23) | 6 (26) | 6 (43) | 2 (9) |
| 10–19 (n=14) | 14 (23) | 10 (43) | 1 (7) | 3 (13) |
| 20–29 (n=14) | 14 (23) | 5 (22) | 6 (43) | 3 (13) |
| 30–39 (n=7) | 7 (12) | 1 (4) | 1 (7) | 5 (22) |
| 40–49 (n=6) | 6 (10) | 1 (4) | 0 | 5 (22) |
| 50+ (n=6) | 6 (10) | 0 | 0 | 5 (22) |
| DC gene | ||||
| TINF2 | 14 (23) | - | 14 (100) | - |
| RTEL1 | 12 (20) | 6 (26) | - | 6 (26) |
| DKC1 | 11 (18) | 11 (48) | - | - |
| TERT | 10 (17) | 1 (4) | - | 9 (39) |
| TERC | 8 (13) | - | - | 8 (35) |
| PARN | 3 (5) | 3 (13) | - | - |
| ACD | 1 (2) | 1 (4) | - | - |
| WRAP53 | 1 (2) | 1 (4) | - | - |
| CTC1 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| NHP2 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| NOP10 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 44 (73) | 20 (87) | 12 (86) | 12 (52) |
| Female | 16 (27) | 3 (13) | 2 (14) | 11 (48) |
| # Triad features | ||||
| 0/3 | 6 (10) | 0 | 0 | 6 (26) |
| 1/3 | 17 (28) | 6 (26) | 2 (14) | 9 (39) |
| 2/3 | 15 (25) | 6 (26) | 4 (29) | 5 (22) |
| 3/3 | 22 (37) | 11 (48) | 8 (57) | 3 (13) |
| # Total features | ||||
| 0–2 | 23 (38) | 7 (30) | 3 (21) | 13 (57) |
| 3–5 | 21 (35) | 7 (30) | 4 (29) | 10 (43) |
| 6–9 | 16 (27) | 9 (39) | 7 (50) | 0 |
XLR:X-linked recessive inheritance, pathogenic variants in DKC1. AR: autosomal recessive, pathogenic variants in RTEL1, PARN, ACD, TERT, and WRAP53. AD: autosomal dominant, pathogenic variants in TERT, TERC, and RTEL1. Parenthesis indicate percent of total with specified inheritance pattern (%).
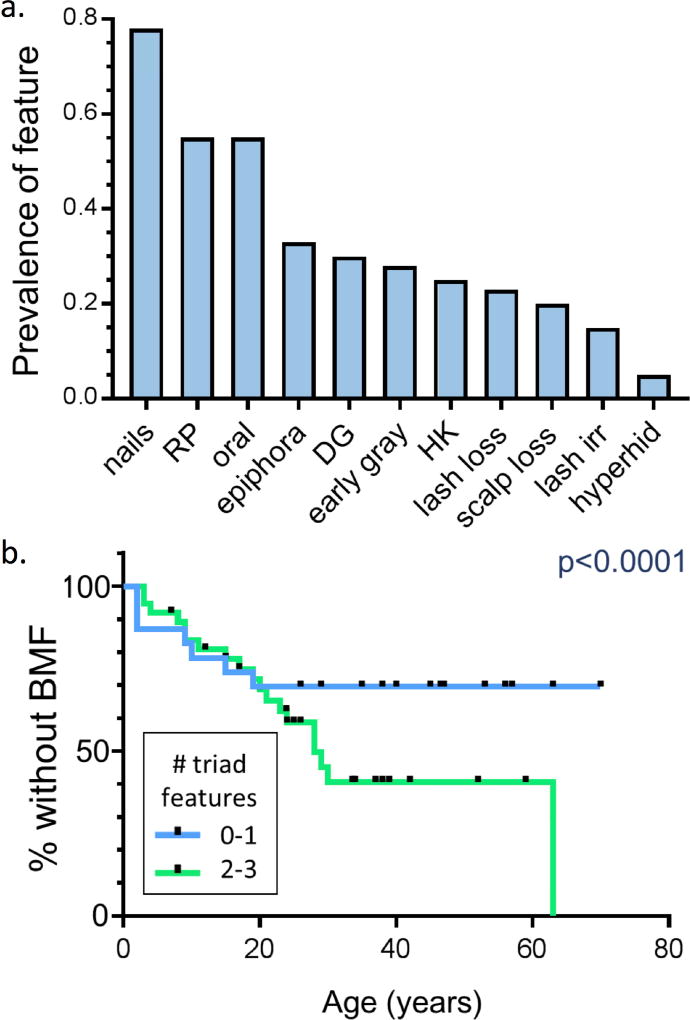
Patients displayed a wide spectrum of clinical findings (range 0–9 features out of a possible 11; median 3 features: 2 triad, 1 non-triad). While triad features were most common, six non-triad features were present in more than 20% of the cohort: epiphora, adermatoglyphia, early graying, palmoplantar hyperkeratosis, eyelash loss, and hair loss from scalp (Figure 1a). The complete clinical triad manifested in only 37% (22/60) of patients, while 10% (6/60) lacked all triad features. Patients with higher numbers of triad and total mucocutaneous features were more likely to have AR DC or heterozygous TINF2 mutations (p < 0.01, chi squared test). All 6 patients lacking any triad features had AD DC. The number of triad features was strongly inversely associated with telomere length (p=0.002). Patients with 2–3 triad features had a greater cumulative incidence of BMF compared with patients with 0–1 triad features (Figure 1b, p < 0.0001). A higher number of total features was also associated with cumulative incidence of BMF and overall mortality (p < 0.0001).
Figure 1. Dyskeratosis Congenita.
a: Prevalence of mucocutaneous findings in 60 patients. Nails= nail dystrophy, RP= reticulate pigmentation, oral= leukoplakia or oral SCC, early gray= graying of the hair before age 30, HK= hyperkeratosis of the palms and/or soles, lash loss= thinning or sparseness of the eyelashes, DG= dermatoglyphic changes, scalp loss= premature hair thinning or balding of the scalp, lash irr= blepharitis or irritation due to lash regrowth, hyperhid= hyperhidrosis. b: The number of DC clinical triad features is associated with moderate to severe bone marrow failure. Kaplan Meier curves for development of moderate to severe BMF among patients with 0–1 (blue) or 2–3 (green) DC clinical triad features. BMF was defined as peripheral blood counts below the normal for age. Black notches indicate time points at which patients were censored. P values for Kaplan Meier curves were calculated with Cox regressions. Statistical analysis was performed with Stata Statistical Software (Release 14, StataCorp LP)
This study specifically focused on mucocutaneous phenotypes in a large cohort of patients with DC. Severe mucocutaneous phenotypes, as defined by number of triad features and additional findings, are associated with higher risk genotypes and poorer prognosis compared with milder mucocutaneous phenotypes. We believe careful detection of all mucocutaneous features of DC is important for early referral, confirmatory testing and appropriate clinical management.
Acknowledgments
This research was made possible through the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Medical Research Scholars Program, a public-private partnership supported jointly by the NIH and generous contributions to the Foundation for the NIH from the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation, The American Association for Dental Research, the Colgate-Palmolive Company, Genentech and alumni of student research programs and other individual supporters via contributions to the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health.
We thank the patients and their families for their valuable contributions to this study. Lisa Leathwood, RN, Maureen Risch, RN, and Ann Carr, MS of Westat, Inc. provided excellent study support. The work of NG, BPA, PSR, and SAS was supported by the intramural research program of the Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics, National Cancer Institute.
Patients are enrolled in an IRB approved longitudinal cohort study, Etiologic Investigation of Cancer Susceptibility in Inherited Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes (NCT-00027274)
Funding sources: This research was made possible through the Intramural Research Program of the Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Medical Research Scholars Program, a public-private partnership supported jointly by the NIH and generous contributions to the Foundation for the NIH from the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation, The American Association for Dental Research, the Colgate- Palmolive Company, Genentech and alumni of student research programs and other individual supporters via contributions to the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors state no conflict of interest
Prior presentation: This research has not been published elsewhere, nor is it under consideration by any other journal.
References
- 1.Bertuch AA. The molecular genetics of the telomere biology disorders. RNA Biol. 2016;13(8):696–706. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1094596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Alter BP, Rosenberg PS, Giri N, Baerlocher GM, Lansdorp PM, Savage SA. Telomere length is associated with disease severity and declines with age in dyskeratosis congenita. Haematologica. 2012;97(3):353–359. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2011.055269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Alter BP, Giri N, Savage SA, et al. Malignancies and survival patterns in the National Cancer Institute inherited bone marrow failure syndromes cohort study. Br J Haematol. 2010;150(2):179–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Alter BP, Baerlocher GM, Savage SA, Chanock SJ, Weksler BB, Willner JP, Peters JA, Giri N, Lansdorn PM. Very short telomere length by flow fluorescence in situ hybridization identifies patients with dyskeratosis congenita. Blood. 2007;110(5):1439–1437. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-02-075598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]