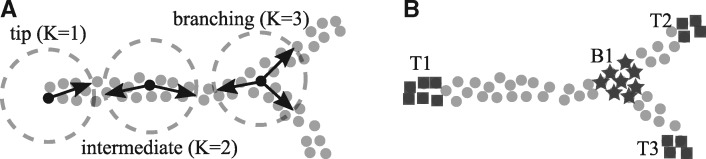
Fig. 1.
Local application of K-Branches clustering reveals tip, intermediate and branching regions in single-cell trajectories. (A) Each cell is used as the center of the branches (halflines) and local clustering is performed in its neighborhood. Then, by using model selection the center cell is either characterized as a tip cell, a cell belonging to an intermediate region or a cell belonging to a branching region depending on which of the three models ( branches) best describes the structure of the neighborhood. (B) After local clustering is performed on the dataset, cells belonging to three tips (T1, T2, T3) and one branching region (B1) have been identified, while the rest of the cells are considered to belong to intermediate regions. The exact number of tip and branching regions is inferred from the data and does not need to be specified by the user