Abstract
Effector molecules translocated by the Salmonella pathogenicity island (SPI)1-encoded type 3 secretion system (T3SS) critically contribute to the pathogenesis of human Salmonella infection. They facilitate internalization by non-phagocytic enterocytes rendering the intestinal epithelium an entry site for infection. Their function in vivo has remained ill-defined due to the lack of a suitable animal model that allows visualization of intraepithelial Salmonella. Here, we took advantage of our novel neonatal mouse model and analyzed various bacterial mutants and reporter strains as well as gene deficient mice. Our results demonstrate the critical but redundant role of SopE2 and SipA for enterocyte invasion, prerequisite for transcriptional stimulation and mucosal translocation in vivo. In contrast, the generation of a replicative intraepithelial endosomal compartment required the cooperative action of SipA and SopE2 or SipA and SopB but was independent of SopA or host MyD88 signaling. Intraepithelial growth had no critical influence on systemic spread. Our results define the role of SPI1-T3SS effector molecules during enterocyte invasion and intraepithelial proliferation in vivo providing novel insight in the early course of Salmonella infection.
Author summary
Non-typhoidal Salmonella represent a major causative agent of gastroenteritis worldwide. Hallmark of the pathogenesis is their ability to actively invade the intestinal epithelium by virtue of their type 3 secretion system that delivers bacterial virulence factors directly into the host cell cytosol. The role of these virulence factors during enterocyte entry and intraepithelial growth has only been investigated in vitro since the previously established in vivo models in small animals did not allow visualization of intraepithelial Salmonella. However, immortalized cell lines lack the overlaying mucus layer, final cell lineage differentiation, apical-basolateral polarization as well as continuous migration along the crypt villus axis and thus the role of virulence factors during the Salmonella infection in vivo has remained largely undefined. Here, we took advantage of our novel neonatal mouse infection model and for the first time systematically analyzed the importance of Salmonella virulence factors for enterocyte invasion and intraepithelial growth.
Introduction
Non-typhoidal Salmonella like Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica sv. Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium) represent a major causative agent of gastroenteritis in humans worldwide [1, 2]. Infection usually occurs through the ingestion of contaminated food or drinking water. Salmonella colonizes the distal small intestine, penetrates the intestinal epithelium and induces a strong inflammatory tissue response provoking the main clinical symptoms such as abdominal pain and diarrhea. In the healthy human host, non-typhoidal Salmonella remain restricted to the intestinal tissue. In contrast, spread to systemic organs associated with high mortality is observed in immunosuppressed individuals and newborns. This renders Salmonella one of the most important causative agents of neonatal sepsis and meningitis in parts of Asia and sub-Saharan Africa [3, 4]
Salmonella employs a multitude of virulence factors to overcome the mucosal barrier and evade the cellular and humoral host defence [5]. Effector molecules secreted by the Salmonella pathogenicity island (SPI)1-type 3 secretion system (T3SS) act during the early phase of infection and enable Salmonella to penetrate the intact intestinal epithelial barrier and reach the subepithelial tissue [6, 7]. SPI1-T3SS effector molecules such as SipA, SopA, SopB, and SopE2 intimately interact with host cell processes and manipulate cellular functions such as F-actin dynamics, signal transduction, chemokine secretion, fluid homeostasis, membrane trafficking and tight junction formation [6, 8–24]. Thereby, they facilitate enterocyte invasion followed by intraepithelial proliferation, histological hallmark of Salmonella pathogenesis [7, 25–29]. An intact SPI1-T3SS has been strongly associated with mucosal inflammation and diarrhea and thus the clinical symptoms of Salmonella gastrointestinal infection in different models [30–36]. The presence in all Salmonella subspecies and clinical isolates indicates a critical and non-redundant function of SPI1 also during human infection [37, 38].
The functional relevance of the SPI1-T3SS for tissue infiltration, mucosal inflammation and enhanced fluid secretion in vivo has first been characterized using the bovine ileal loop or oral calf infection model [13, 32–34, 39–42]. Infection of calves mimics the disease in humans, characterized by small intestinal mucosal inflammation with chemokine secretion and leukocyte infiltration as well as enhanced fluid secretion [43–45]. Epithelial invasion has also been observed in guinea pig, swine and rabbit intestinal tissue [25–27, 46, 47]. In the most widely used animal model of adult mice, however, oral administration of Salmonella does not lead to detectable epithelial invasion and mucosal inflammation but causes a typhoid fever-like systemic infection following a largely SPI1-independent M cell-mediated mucosal translocation [48–50]. Streptomycin administration prior to infection facilitates bacterial expansion and leads to mucosal inflammation [35]. Salmonella-induced tissue pathology, however, is largely restricted to the caecum and colon and SPI1-dependent epithelial invasion is observed at low frequency due to rapid enterocyte exfoliation [28, 29, 35, 51, 52]. Although enterocyte invasion and intracellular proliferation has been observed in epithelial cells of the caecum of S. Typhimurium infected adult animals and mechanisms of host defence have been investigated [29, 53], the role of individual SPI1-T3SS mediated effector molecules during the early steps of Salmonella infection in vivo has remained ill-defined.
We have recently introduced a novel oral Salmonella infection model using neonate mice [50]. In this model, Salmonella invades the neonatal small intestinal epithelium, forms intraepithelial microcolonies and spreads to systemic organs in a strongly SPI1-T3SS dependent manner. Here, we used this model and employed wild type Salmonella, sopABE2sipA quadruple mutants complemented with individual effector molecules, the respective triple mutants, sopE2sipA, sopAE2, and sopBE2 double mutants as well as sipA, sopB, and sopE2 single mutants in combination with wild type and myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 (MyD88)-/- mice to investigate the contribution of individual SPI1-T3SS effector molecules and host factors during epithelial cell invasion and intraepithelial microcolony formation in vivo.
Results
Comparative analysis of individual SPI1-T3SS effector molecules by complementation
We initially employed a previously established approach using a sopABE2sipA quadruple mutant S. Typhimurium strain complemented in trans by an expression plasmid encoding the respective SPI1 virulence factors SipA, SopA, SopB or SopE2 [42]. Consistent with our previous results obtained using the SPI1-T3SS defective S. Typhimurium invC mutant, the sopABE2sipA quadruple mutant was unable to invade murine enterocytes, failed to induce a significant transcriptional epithelial response and remained restricted to the gut lumen (S1A–S1F Fig) [50]. Complementation with SipA alone significantly enhanced S. Typhimurium viable counts in isolated enterocytes, spleen, liver and mesenteric lymph node (MLN) tissue and induced transcriptional epithelial activation (S1A–S1F Fig). Consistently, immunostaining visualized sipA complemented ΔsopABE2sipA Salmonella within intestinal epithelial cells (S1G Fig). Also sopE2 complemented quadruple mutant Salmonella were observed intracellularly (S1G Fig). In contrast, no enterocyte invasion could be observed for sopA or sopB complemented ΔsopABE2sipA Salmonella (S1G Fig). Whereas SopE2 is conserved in all pathogenic strains of Salmonella, some strains additionally harbor a homologue broad-spectrum guanine nucleotide exchange factor, SopE [54–56]. Also SopE enhanced the invasive behavior leading to a significant increase in enterocyte invasion, transcriptional stimulation as well as spread to systemic tissues (S2A–S2F Fig) [57]. Importantly, albeit able to invade the epithelium, sipA, sopE2 and sopE complemented ΔsopABE2sipA Salmonella were unable to proliferate and generate intraepithelial microcolonies (S1G Fig, S2G Fig).
Analysis of enterocyte invasion using triple mutants
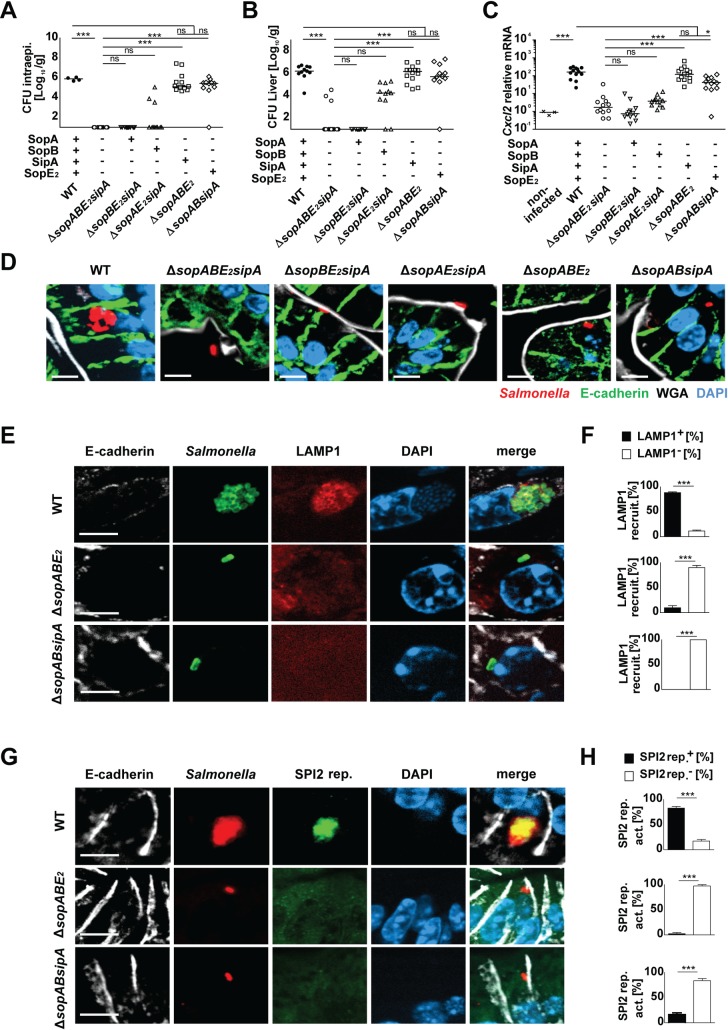
To overcome the technical obstacles associated with trans-complementation such as plasmid loss, multiple effector gene copies or an impaired access of regulatory elements we next employed triple mutants leaving the fourth SPI1-T3SS effector gene under the native regulatory control. In accordance with our previous results, sopABE2 and sopABsipA mutant Salmonella expressing solely a functional SipA and SopE2 effector, respectively, displayed the ability to invade primary enterocytes and enhance Cxcl2 and Cxcl5 mRNA expression in the intestinal epithelium (Fig 1A and 1C, S3C Fig). Both mutants also penetrated the mucosal barrier reaching liver, MLN, and spleen tissue at numbers comparable to wild type bacteria (Fig 1B, S3A and S3B Fig). In contrast, sopBE2sipA and sopAE2sipA mutant bacteria expressing sopA or sopB alone failed to significantly invade and penetrate the epithelium, stimulate a transcriptional response and spread to systemic organs (Fig 1A–1C). Consistently, immunostaining identified intraepithelial Salmonella in the presence of SipA or SopE2 but not SopA or SopB (Fig 1D). Again, despite the intraepithelial localization, SipA expressing ΔsopABE2 or SopE2 expressing ΔsopABsipA Samonella failed to proliferate intracellularly.
Fig 1. Comparative analysis of the role of SPI1-T3SS effector molecules SopA, SopB, SipA, and SopE2 using triple mutants.
1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU wild type (WT) (filled circles), isogenic quadruple sopABE2sipA mutant (open circles), or ΔsopBE2sipA (open inverted triangles), ΔsopAE2sipA (open triangles), ΔsopABE2 (open squares), or ΔsopABsipA (open diamonds) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) isolated gentamicin-treated enterocytes and (B) total liver tissue homogenate at 4 days post infection (p.i.). (C) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl2 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 4–6 animals per group). (D) Immunostaining for Salmonella (red) in small intestinal tissue sections at 4 days p.i. with 100 CFU WT S. Typhimurium (WT), ΔsopABE2sipA quadruple mutant, or ΔsopBE2sipA, ΔsopAE2sipA, ΔsopABE2, or ΔsopABsipA triple mutant bacteria. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (green), WGA (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (E) Co-immunostaining for Salmonella WT, ΔsopABE2, or ΔsopABsipA (green) and LAMP1 (red) in small intestinal tissue sections at day 4 p.i.. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (F) Quantitative evaluation of the percentage of intraepithelial S. Typhimurium associated with LAMP1 staining. Three tissue sections per infected neonate (n = 3) were analyzed at day 4 p.i.. Results represent the mean ± SD. (G) Co-immumostaining for Salmonella WT, ΔsopABE2 or ΔsopABsipA (red) and the GFP-expressing SPI2 reporter (pM973; green) in small intestinal tissue sections at day 4 p.i.. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5μm. (H) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of intraepithelial S. Typhimurium expressing the SPI2 reporter. All microcolonies from three tissue sections per infected neonate were analyzed (n = 3) at day 4 p.i.. Results represent the mean ± SD.
Following internalization, Salmonella manipulates maturation of the endosomal compartment. This recruits the lysosomal-associated membrane protein (LAMP)1 from Golgi-derived vesicles [58] and provides the environmental signals that coordinate the expression of SPI2-T3SS effector genes and the development of a replicative compartment [59, 60]. LAMP1 recruitment to intraepithelial bacteria was observed following infection with wild type but not ΔsopABE2 or ΔsopABsipA Salmonella (Fig 1E and 1F). Additionally, we used a previously described SPI2 reporter construct expressing gfp under the control of the ssaG promoter to analyze the induction of SPI2-encoded genes [52]. SPI2 reporter activity was detected in intraepithelial wild type but not SipA expressing ΔsopABE2 or SopE2 expressing ΔsopABsipA Salmonella (Fig 1G and 1H).
Together, these results identifed the critical but redundant role of SopE2 and SipA for enterocyte invasion in vivo and highlighted the requirement of enterocyte invasion for transcriptional stimulation. Notably, invasion per se appeared not to be sufficient to generate an appropriate intracellular niche allowing intraepithelial bacterial proliferation. On the other hand, the formation of intraepithelial microcolonies did not significantly promote systemic spread. The ability and degree of individual SPI1-T3SS effector molecules to confer an enterocyte-invasive phenotype differed markedly between the situation in vivo and a classical in vitro cell culture-based invasion assay (S1H Fig, S2H Fig, S3D Fig) illustrating the need for a detailed investigation of the bacteria-epithelial cell interaction in vivo [61].
Infection-induced innate stimulation and intraepithelial proliferation
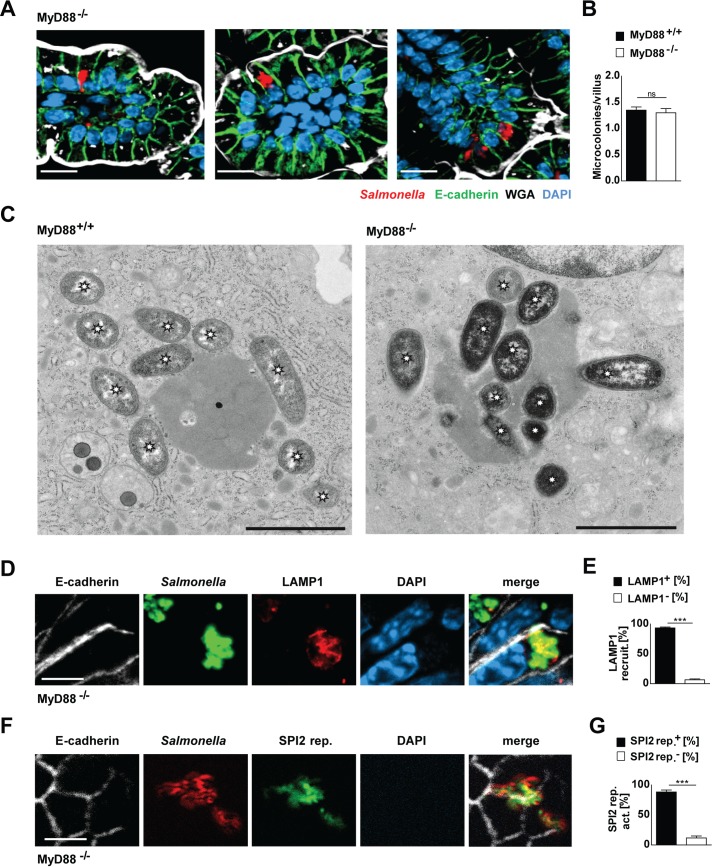
Host innate immune recognition through Toll-like receptor (TLR)2, 4 and 9 and signaling through the common adapter molecule MyD88 has previously been shown to provide the stimulatory signal for SPI2 effector gene expression and represent a prerequisite for the expression of SPI2-encoded effector genes, intracellular growth and microcolony formation in myeloid cells [60]. Interestingly, innate immune stimulation in Salmonella-infected neonate mice was also induced by TLR stimulation and mediated by the common adapter molecule MyD88 [50]. We therefore tested the requirement of intact MyD88-dependent signaling for intraepithelial Salmonella proliferation in vivo. As expected, MyD88-deficient mice exhibited significantly reduced epithelial Cxcl2 and Cxcl5 mRNA expression (S4A and S4B Fig). However, in contrast to the situation in myeloid cells, Salmonella maintained its ability to generate intraepithelial microcolonies with similar numbers of microcolonies per villus also in the absence of MyD88 signaling as illustrated by immunostaining and transmission electron microscopy (Fig 2A–2C). Also, LAMP1 was recruited to the majority of Salmonella-containing vacuole (SCV) in enterocytes and the SPI2 reporter was induced in the absence of MyD88-dependent signal transduction (Fig 2D–2G). The disease course was significantly accelerated rather than delayed, most probably as a result of an impaired MyD88-mediated antimicrobial host defence (S4C Fig). Thus, intraepithelial Salmonella proliferation and microcolony formation occurred independently of MyD88-mediated host innate immune signaling in vivo.
Fig 2. The influence of MyD88-dependent innate immune signaling on intraepithelial microcolony formation.
1-day-old MyD88+/+ and MyD88-/- mice were orally infected with 100 CFU S. Typhimurium WT. (A) 4 days after infection, small intestinal tissues were collected and analyzed by immunostaining. Three representative images showing S. Typhimurium (red) forming intraepithelial microcolonies in MyD88-/- mice. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (green), WGA (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 10 μm. For wild type controls see Fig 1D. (B) Quantitative evaluation of the number of intraepithelial microcolonies per villus in MyD88+/+ and MyD88-/- mice at 4 days p.i.. S. Typhimurium microcolonies were quantified in 20–30 villi per animal (n = 6–8). Results represent the mean ± SD. (C) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of intraepithelial Salmonella in MyD88+/+ (left panel) and MyD88-/- mice (right panel). Asterisks highlight bacteria. Bar, 2 μm. (D) Co-immunostaining for Salmonella (green) and LAMP1 (red) in small intestinal tissue sections at day 4 p.i.. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (E) Quantitative evaluation of the percentage of intraepithelial S. Typhimurium associated with LAMP1 staining. Four neonates were analyzed at day 4 p.i.. Results represent the mean ± SD. (F) Co-immumostaining for Salmonella (red) and the GFP expressing SPI2 reporter (pM973, green) in small intestinal tissue sections at day 4 p.i.. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (G) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of intraepithelial S. Typhimurium expressing the SPI2 reporter. Microcolonies from tissue sections from four neonates were analyzed at day 4 p.i.. Results represent the mean ± SD.
Requirement of SPI1-T3SS effector molecules for intraepithelial microcolony formation
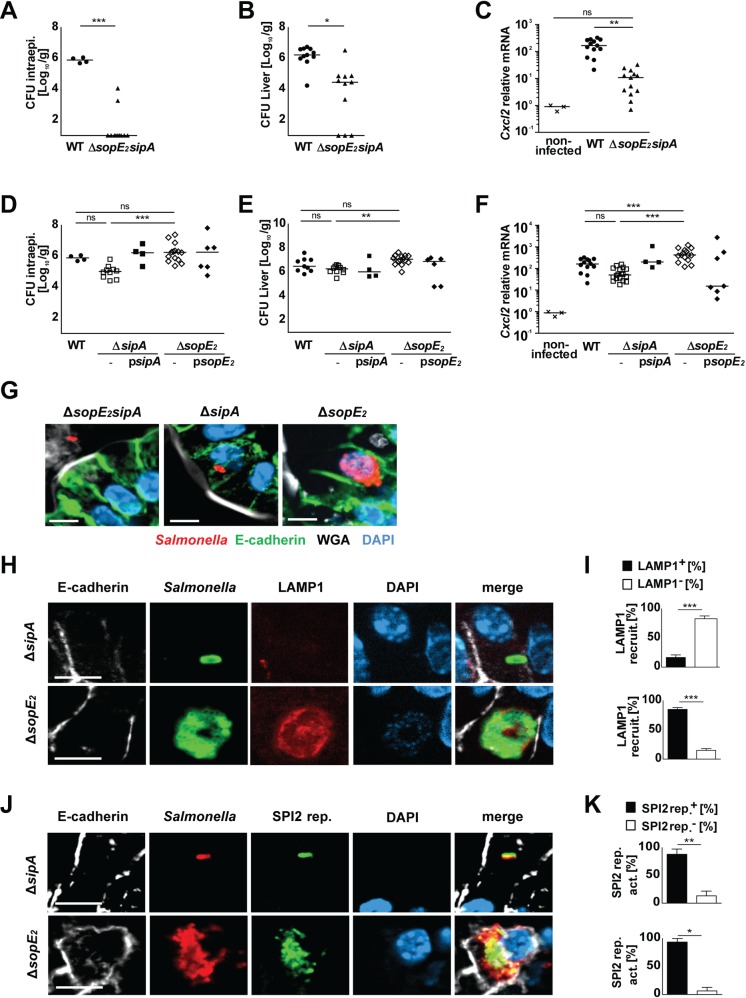
Although SipA or SopE2 were sufficient to facilitate enterocyte invasion, Salmonella failed to induce intraepithelial microcolony formation. This suggested that intracellular proliferation required the contribution of SPI1-T3SS effector proteins beyond their invasion-promoting function. We first investigated the requirement of SipA and/or SopE2 for intraepithelial proliferation. As expected, ΔsopE2sipA Salmonella exhibited severely impaired enterocyte invasion, transcriptional stimulation and organ spread (Fig 3A–3C, S5A–S5C Fig). In contrast, sipA or sopE2 mutant bacteria displayed only a minor phenotype with intact enterocyte invasion, transcriptional stimulation and spread to systemic organs (Fig 3D–3F, S5D–S5F Fig). Strikingly, however, sopE2 mutant bacteria similar to wild type Salmonella generated LAMP1-positive intraepithelial microcolonies, whereas ΔsipA Salmonella failed to do so (Fig 3G, 3H and 3I). In contrast, both ΔsopE2 and ΔsipA Salmonella exhibited detectable intraepithelial SPI2 reporter activity (Fig 3J and 3K). Consistent with intracellular proliferation of ΔsopE2 Salmonella, the presence of SipA as compared to SopE2 resulted in significantly higher intraepithelial viable counts (Fig 3D). The enhanced number of intraepithelial bacteria was in turn associated with increased Cxcl2 mRNA expression as well as augmented spread to spleen, MLN and liver tissue (Fig 3E and 3F, S5D and S5E Fig).
Fig 3. The redundant role of SipA and SopE2 for enterocyte invasion.
(A-C) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU wild type (WT) (filled circles) or isogenic sopE2sipA mutant S. Typhimurium (filled triangles). Viable counts in (A) isolated gentamicin-treated enterocytes and (B) total liver tissue homogenate at 4 days p.i.. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl2 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 4–6 animals per group). The data for uninfected control animals and WT Salmonella infected mice are identical to Fig 1A–1C. (D-F) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (filled circles), isogenic sipA mutant (open squares), complemented ΔsipA psipA (filled squares), isogenic sopE2 mutant (open diamonds), or complemented ΔsopE2 psopE2 (filled diamonds) Salmonella. Viable counts in (D) isolated gentamicin-treated enterocytes and (E) total liver tissue homogenate at 4 days p.i.. (F) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl2 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 3–5 animals per group). The data for uninfected control animals and Salmonella WT infected mice are identical to Fig 1A–1C. (G) Immunostaining for S. Typhimurium (red) in small intestinal tissue sections at 4 days p.i. with 100 CFU ΔsopE2sipA, ΔsipA, or ΔsopE2 S. Typhimurium Salmonella. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (green), WGA (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (H) Co-immunostaining for Salmonella ΔsipA, ΔsopE2 (green) and LAMP1 (red) in small intestinal tissue sections at day 4 p.i.. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (I) Quantitative evaluation of the percentage of intraepithelial S. Typhimurium associated with LAMP1 staining. All microcolonies from three tissue sections per infected neonate were analyzed (n = 5) at day 4 p.i.. Results represent the mean ± SD. (J) Co-immunostaining for Salmonella ΔsipA or ΔsopE2 (red) and the GFP-expressing SPI2 reporter (pM973; green) in small intestinal tissue sections at day 4 p.i.. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5μm. (K) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of intraepithelial S. Typhimurium expressing the SPI2 reporter. All microcolonies from three tissue sections per infected neonate were analyzed (n = 3) at day 4 p.i.. Results represent the mean ± SD.
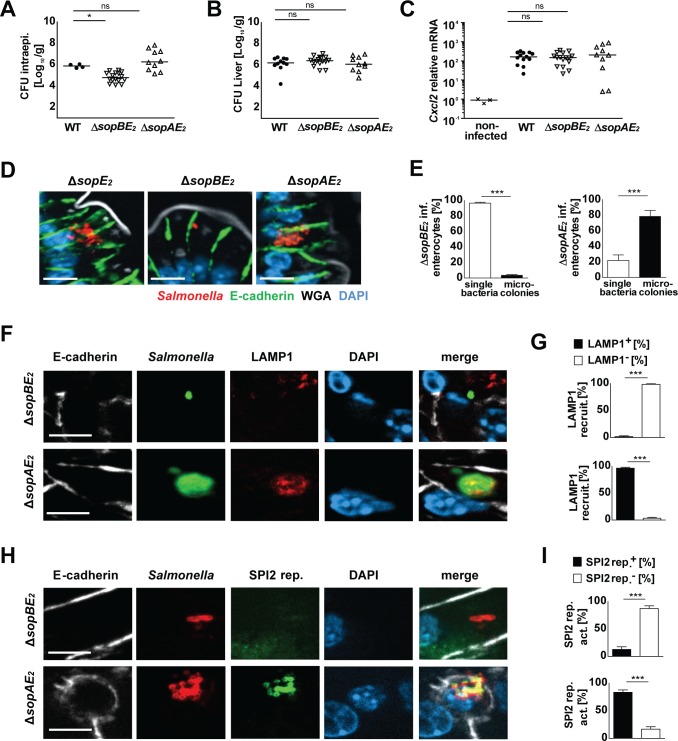
We next defined the role of SopA and/or SopB during microcolony formation, analyzing the phenotype of sopAE2 and sopBE2 double mutant Salmonella in vivo. Both SipA expressing sopAE2 and sopBE2 mutants gained access to the intracellular compartment of epithelial cells, spread to systemic anatomical sites and stimulated a potent transcriptional response (Fig 4A–4C, S6A–S6C Fig). Interestingly, sopBE2 mutant Salmonella failed to generate microcolonies, whereas the majority of sopAE2 mutant-infected epithelial cells exhibited intraepithelial growth (Fig 4D and 4E). Consistently, significantly lower intraepithelial bacterial numbers were found for ΔsopBE2 but not ΔsopAE2 Salmonella as compared to wild type bacteria (Fig 4A). Also, sopAE2 mutant but not sopBE2 mutant Salmonella recruited LAMP1 (Fig 4F and 4G) and upregulated SPI2 gene expression (Fig 4H and 4I). These results highlighted the role of SipA and SopB for intraepithelial proliferation and excluded SopA as critical SPI1 component for intraepithelial microcolony formation.
Fig 4. Analysis of sopBE2 and sopAE2 double mutant S. Typhimurium.
(A-C) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU wild type (WT) (filled circles), isogenic ΔsopBE2 (inverted open triangles), or ΔsopAE2 (open triangles) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) isolated gentamicin-treated enterocytes and (B) total liver tissue homogenate at 4 days p.i.. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl2 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 3–6 animals per group). The data for uninfected control animals and Salmonella WT infected mice are identical to Fig 1A–1C. (D) Immunostaining for Salmonella (red) in small intestinal tissue sections at 4 days p.i. with 100 CFU ΔsopE2, ΔsopBE2, or ΔsopAE2 S. Typhimurium. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (green), WGA (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (E) Percentage of epithelial cells positive for single bacteria or microcolonies (>1 intraepithelial bacterium) at 4 days p.i. with ΔsopBE2 or ΔsopAE2 S. Typhimurium. 30 Salmonella-positive epithelial cells per infected neonate (n = 8–13) were analyzed. Results represent the mean ± SD. (F) Co-immunostaining for Salmonella ΔsopBE2 and ΔsopAE2 (green) and LAMP1 (red) in small intestinal tissue sections at day 4 p.i.. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (G) Quantitative evaluation of the percentage of intraepithelial ΔsopBE2 and ΔsopAE2 S. Typhimurium associated with LAMP1 staining. All microcolonies from three tissue sections per infected neonate were analyzed (n = 3–4) at day 4 p.i.. Results represent the mean ± SD. (H) Co-immunostaining for ΔsopBE2 and ΔsopAE2 Salmonella (red) and the GFP-expressing SPI2 reporter (pM973; green) in small intestinal tissue sections at day 4 p.i.. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (I) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of intraepithelial S. Typhimurium expressing the SPI2 reporter. All microcolonies from three tissue sections per infected neonate were analyzed (n = 3–4) at day 4 p.i.. Results represent the mean ± SD.
The role of SopB during the interaction of Salmonella with the epithelium in vivo
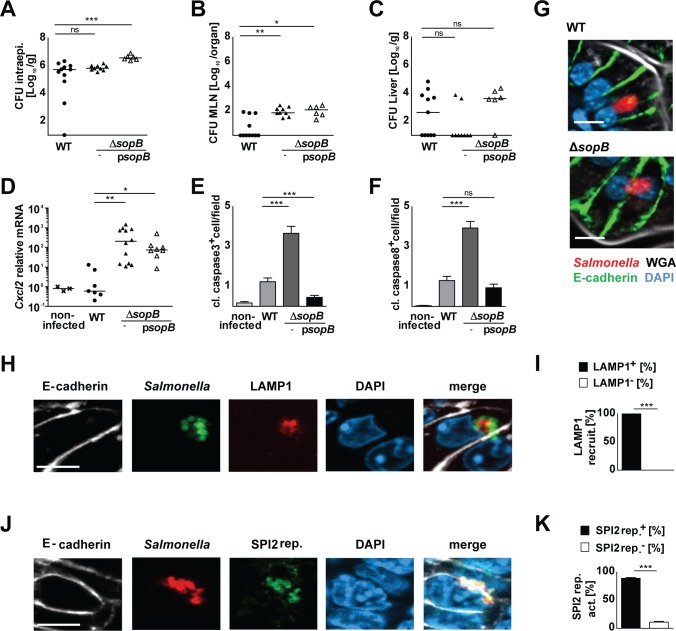
To further evaluate SopB as a potential essential effector for intraepithelial proliferation, we next tested single sopB mutant Salmonella in vivo. Unexpectedly, sopB mutant Salmonella induced a more severe clinical phenotype with accelerated disease progression. Due to the accelerated disease course induced by ΔsopB Salmonella, the following analyses were performed at day 2 and 3 postinfection (p.i.) (Fig 5, S7 Fig). Enterocyte invasion of both wild type and ΔsopB Salmonella already occurred at this early time point, but spread to spleen and liver tissue remained low (Fig 5A and 5C, S7A Fig). Infection with ΔsopB Salmonella was accompanied by significantly enhanced Cxcl2 and Cxcl5 mRNA expression that was not observed during infection with wild type Salmonella (Fig 5D, S7B Fig). This increase in epithelial immunostimulation was associated with a significantly accelerated bacterial spread to the MLN (Fig 5B) and enhanced numbers of caspase 3- and caspase 8-positive enterocytes (Fig 5E and 5F, S7C Fig). Since a similar phenotype was not observed after infection with sopBE2 mutant Salmonella (Fig 4), these results suggested that SopB by a hitherto unidentified mechanism counteracts the proapoptotic activity induced by SopE2 [62, 63].
Fig 5. The role of SopB in the interaction between Salmonella and the epithelium.
1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU wild type (WT) (filled circles), isogenic sopB mutant (filled triangles), or psopB-complemented ΔsopB (open triangles) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) isolated gentamicin-treated enterocytes, (B) total MLN and (C) total liver tissue homogenate at 2 days p.i.. (D) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl2 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 2 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 3–5 animals per group). (E) Quantitative analysis of the number of cleaved caspase 3- and (F) cleaved caspase 8 positive cells per 200 times magnification image field. Positive cells from 20 image fields from one section were analyzed per infected neonate (n = 3–6) at day 3 p.i.. Results represent the mean ± SD. (G) Immunostaining for S. Typhimurium (red) in small intestinal tissue sections at 3 days p.i. with 100 CFU WT and ΔsopB S. Typhimurium. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (green), WGA (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (H) Co-immunostaining for ΔsopB S. Typhimurium (green) and LAMP1 (red) in small intestinal tissue sections at day 3 p.i.. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (I) Quantitative evaluation of the percentage of intraepithelial S. Typhimurium associated with LAMP1 staining. All microcolonies from three tissue sections per infected neonate were analyzed (n = 3) at day 3 p.i.. Results represent the mean ± SD. (J) Co-immumostaining for ΔsopB S. Typhimurium (red) and the GFP expressing SPI2 reporter (pM973; green) in small intestinal tissue sections at day 3 p.i.. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (K) Quantitative analysis of the percentage of intraepithelial S. Typhimurium expressing the SPI2 reporter. All microcolonies from three tissue sections per infected neonate were analyzed (n = 3) at day 3 p.i.. Results represent the mean ± SD.
Strikingly, immunostaining revealed that Salmonella deficient solely for sopB were still able to proliferate intraepithelially demonstrating that SopB is not essential for intraepithelial microcolony formation (Fig 5G). Consistently, ΔsopB Salmonella generated LAMP1-positive intraepithelial endosomal compartments (Fig 5H and 5I) and showed induction of SPI2 reporter gene activity (Fig 5J and 5K). The fact that both sopE2 and sopB single mutant Salmonella were able to grow intraepithelially (Figs 3G and 5G), whereas sopBE2 double mutant Salmonella failed to form intraepithelial microcolonies (Fig 4D and 4E) suggests that SopE2 and SopB exert a critical but redundant role during intraepithelial proliferation and microcolony formation.
The contribution of SipA to mucosal inflammation and intraepithelial proliferation
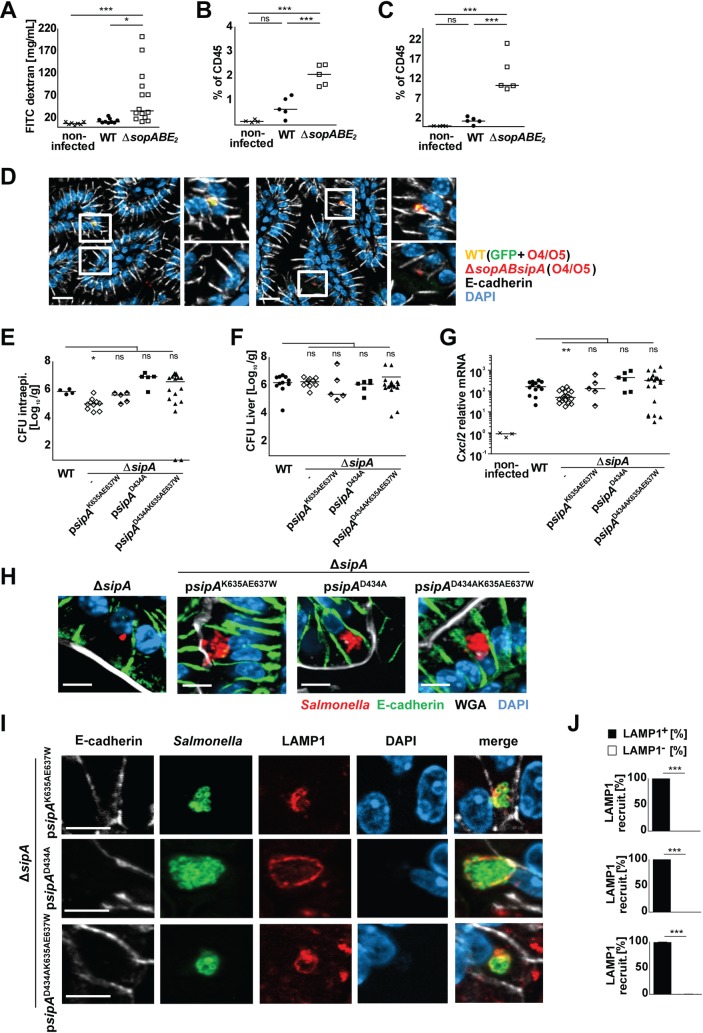
Neonate mice infected with the SipA-expressing sopABE2 triple mutant Salmonella exhibited a more severe disease phenotype. Whereas mice infected with wild type Salmonella showed low but still significant weight gain during the first days after infection, mice infected with sopABE2 mutant Salmonella failed to increase their body weight and exhibited an aggravated course of the disease (S8A and S8B Fig). We therefore infected 4-day-old mice in some experiments to facilitate the analysis. The accelerated disease course of ΔsopABE2 Salmonella was associated with an increased tissue inflammation and epithelial barrier impairment illustrated by an enhanced translocation of labelled 4 kDa dextran at day 3 p.i. and a reduced length of the small intestine (Fig 6A, S8C and S8D Fig). Flow cytometric analysis of lamina propria immune cells confirmed a significantly stronger recruitment of monocytes and polymorphonuclear cells (PMN) 3 days after infection with ΔsopABE2 Salmonella as compared to wild type Salmonella (Fig 6B and 6C, S8E and S8F Fig). Immunohistological detection of infiltrating PMNs corroborated the role of SipA in tissue inflammation. Salmonella infection enhanced the number of lamina propria PMNs and this effect was significantly reduced after infection with ΔsipA S. Typhimurium (S8G and S8H Fig). Notably, genetic complementation with wild type sipA (ΔsipA psipA) as well as a form of SipA with a point mutation at position 434 (ΔsipA psipAD434A) previously described to harbor reduced inflammatory activity reversed this phenotype (S8G and S8H Fig). These results demonstrate an intrinsic proinflammatory activity of SipA. They are consistent with previous studies showing that SipA inhibits the phospholipid glutathione peroxidase (GPX4) and leads to enhanced secretion of the proinflammatory chemotactic eicosanoid hepoxillin A3 (HXA3)[64, 65]. However, our results fail to confirm a significant importance of the caspase 3 cleavage site in SipA for this activity [12, 66].
Fig 6. The role of SipA for intraepithelial microcolony formation.
(A) Mucosal barrier integrity tested by serum quantification 4 hours after oral administration of FITC labeled-4kDa dextran. 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were left untreated (crosses) or infected with WT (filled circles) or ΔsopABE2 (open squares) S. Typhimurium. FITC labeled-4 kDa dextran was quantified in serum at day 3 p.i. as indicated. (B and C) Flow cytometric analysis of lamina propria immune cells. 4-day-old mice were left untreated or orally infected with 100 CFU WT or ΔsopABE2 S. Typhimurium and total small intestinal leukocytes were analyzed by flow cytometry at day 3 p.i.. (B) Monocytes (Ly6ChiLy6G-CD11b+ MHCIIlo/-CD45+DAPI-) and (C) neutrophils (Ly6G+Ly6CintCD11b+ MHCIIlo/-CD45+DAPI-) are depicted as percentage of CD45+ cells in non-infected (crosses), WT (filled circles) and ΔsopABE2 Salmonella (open squares). The results represent the mean values from at least two independent experiments (n = 4–6 per group). (D) Immunostaining for Salmonella in small intestinal tissue sections at 4 days after co-infection with 100 CFU GFP-expressing WT (yellow) and ΔsopABsipA (red) S. Typhimurium. WT Salmonella appear in yellow due to simultaneous staining for O4/O5 antigen (red) and GFP (green). ΔsopABsipA Salmonella appear in red due to simultaneous staining for O4/O5 antigen (red). Counterstaining with E-cadherin (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 10 μm. (E-J) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (filled circles), ΔsipA (open diamonds), ΔsipA complemented with psipAK635A E637W (half-filled diamonds), ΔsipA complemented with psipAD434A (filled squares), or ΔsipA complemented with psipAD434A K635A E637W (filled triangles) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (E) isolated gentamicin-treated enterocytes and (F) total liver tissue homogenate at 4 days p.i.. (G) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl2 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 4–7 animals per group). The data for WT Salmonella infected mice and uninfected control animals are identical to Fig 1A–1C. (H) Immunostaining for Salmonella (red) in small intestinal tissue sections at 4 days p.i. with 100 CFU ΔsipA, ΔsipA complemented with psipAK635A E637W, ΔsipA complemented with psipAD434A, or ΔsipA complemented with psipAD434A K635A E637W S. Typhimurium. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (green), WGA (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (I) Co-immunostaining for LAMP1 (red) and ΔsipA complemented with psipAK635A E637W, ΔsipA complemented with psipAD434A, or ΔsipA complemented with psipAD434A K635A E637W S. Typhimurium (green) in small intestinal tissue sections at day 4 p.i.. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (J) Quantitative evaluation of the percentage of intraepithelial S. Typhimurium associated with LAMP1 staining. All microcolonies from three tissue sections per infected neonate were analyzed (n = 3) at day 4 p.i.. Results represent the mean ± SD.
The proinflammatory activity of SipA was reported to occur independently of enterocyte invasion, following secretion and binding of SipA to the epithelial surface molecule p53-effector related to PMP-22 (PERP) [12, 65, 67, 68]. Consistently, the aggravated disease phenotype was also observed after infection with Salmonella that lack SopA, SopB and SopE2 and carry two point mutations in SipA (SipAK635A E637W) previously shown to impair the actin-modulating activity and reduce the invasion-promoting effect of SipA (S8B Fig). The reduced invasion-promoting activity of SipAK635A E637W as compared to wild type SipA was confirmed by quantification of the number of intraepithelial bacteria 2 days after infection with ΔsipA S. Typhimurium complemented with either psipA or psipAK635A E637W (S8I Fig). The invasion-independent activity of SipA suggested that it might act in trans and stimulate the epithelium at anatomical locations distant to the site of enterocyte invasion.
To test whether the SipA-mediated immune stimulation contributes to the intraepithelial growth and microcolony formation, we next infected mice with a 1:1 mixture of SipA-sufficient wild type Salmonella and SipA-deficient ΔsopABsipA Salmonella. As shown in previous experiments (Fig 1A and 1D), ΔsopABsipA Salmonella were able to invade epithelial cells through the activity of SopE2 but failed to proliferate intraepithelially. Following double infection, wild type Salmonella readily formed microcolonies in intestinal epithelial cells (Fig 6D, double stained appearing in yellow). In contrast, ΔsopABsipA Salmonella invaded but failed to proliferate intracellularly (Fig 6D, in red). Thus, the induction of a proinflammatory signal by SipA-expressing wild type Salmonella was not sufficient to induce a replicative endosomal environment in distant enterocytes and rescue the intraepithelial proliferation defect of SipA-deficient ΔsopABsipA Salmonella.
Next, we investigated the intrinsic activity of SipA in vivo. We therefore analyzed ΔsipA Salmonella complemented in trans with the gene for (i) wild type SipA (ΔsipA psipA) (ii) SipA with two point mutations at position 635 and 637 previously shown to impair its actin stabilization and reduce the invasion-promoting activity (ΔsipA psipAK635A E637W) [67] (S8I Fig), (iii) SipA that lacks the caspase 3 cleavage site reported to be critical for the proinflammatory activity [66] (ΔsipA psipAD434A) and (iv) SipA that lacks both, the actin-stabilizing and proinflammatory activity (ΔsipA psipAD434A K635A E637W). Expression of these constructs was tested in the presence of SopE2 to ensure enterocyte invasion and allow the comparative analysis of the different SipA variants in respect to intraepithelial growth and microcolony formation. As expected, ΔsipA, ΔsipA psipAK635A E637W, ΔsipA psipAD434A and ΔsipA psipAD434A K635A E637W Salmonella were able to invade the epithelium (Fig 6E), cause systemic infection (Fig 6F, S9A and S9B Fig) and induce transcriptional stimulation (Fig 6G, S9C Fig). As observed before, ΔsipA Salmonella exhibited significantly reduced intraepithelial bacterial numbers and Cxcl2 mRNA expression, and failed to proliferate and form intraepithelial microcolonies (Fig 6E, 6G and 6H). Infection with ΔsipA Salmonella was also associated with a moderately reduced mortality (S9D Fig). In contrast, ΔsipA Salmonella complemented with psipAK635A E637W, psipAD434A, psipAD434A K635A E637W behaved indistinguishably from wild type Salmonella and readily formed LAMP1-positive intraepithelial microcolonies (Fig 6I and 6J). Together, these results demonstrate the critical importance of SipA. However, in the presence of SopE2, neither the actin-stabilizing activity nor the reported caspase 3-dependent proinflammatory activity were required for intraepithelial proliferation and microcolony formation.
Discussion
Salmonella expressing SopE, SopE2 or SipA but not ΔsopE2sipA Salmonella were able to invade the epithelium indicating that the production of SopE, SopE2 or SipA is necessary and sufficient to facilitate enterocyte invasion in vivo. SopE or SopE2 activate the Rho GTPases Rac-1 and Cdc42 or only Cdc42, respectively, leading to actin assembly, membrane ruffling and bacterial internalization [22–24, 54, 56]. SipA with its C-terminal domain stabilizes actin filaments, promoting bacterial invasion in the absence of prominent membrane ruffling [9–12, 42, 69]. Their potent activity was illustrated by the finding that the presence of only one of the two effector molecules facilitated enterocyte invasion at levels indistinguishable from wild type bacteria. Notably, also the ubiquitin E3 ligase SopA was previously shown to contribute to invasion of polarized epithelial cells in vitro [15, 16, 42]. Also SopB was shown to promote membrane fission and bacterial invasion [18, 19, 70, 71]. It was suggested that SopB supports SopE-mediated actin filament polymerization by recruiting ARNO (Cytohesin2) to the site of invasion [72]. Our in vivo results do not support a significant role for SopA or SopB in enterocyte entry. However, although unlikely, we cannot exclude that enterocyte invasion by strains expressing effectors other than sipA or sopE2 occurred but remained undetected due to rapid enterocyte apoptosis or exfoliation as observed in adult mice [29].
Consistent with previous in vitro results, enterocyte invasion was not sufficient to allow proliferation and microcolony formation despite the presence of a fully functional SPI2 locus [73]. ΔsopB, ΔsopE2 and ΔsopAE2 but not ΔsipA Salmonella were able to generate intraepithelial microcolonies assigning SipA a critical non-redundant role for intracellular growth. ΔsipA Salmonella failed to recruit LAMP1 to the endosomal epithelial compartment, confirming a recent report on the contribution of the NH2-terminal domain of SipA (aa1-458) to endosomal maturation and intracellular replication [74]. SipA was recently also shown to promote intracellular proliferation via interaction with the actin nucleator family member Spire2 [69]. In our study, the SipA activity required for intraepithelial microcolony formation was independent of its actin stabilizing function or proinflammatory activity reported to depend on caspase 3 processing [66, 67]. This might be explained by the recently described cooperative action of SipA with the SPI2 effector SifA to promote phagosome maturation and the generation of a replicative intraepithelial compartment [74]. Interestingly, intraepithelial ΔsipA Salmonella exhibited expression of the SPI2 reporter indicating that SPI2 effector expression can occur independently of SipA.
Whereas both ΔsopE2 and ΔsopB Salmonella readily proliferated in enterocytes, sopBE2 mutant Salmonella were unable to form intraepithelial microcolonies. Consistently, ΔsopBE2 and ΔsopABE2 (in contrast to ΔsopE2 or ΔsopB) Salmonella failed to recruit LAMP1 to the endosomal compartment and to turn on SPI2 gene expression. Thus, SopB and SopE2 contributed in a redundant fashion to the generation of a replicative endosomal compartment in enterocytes. Both, SopE2 and SopB activate Rho GTPases and mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPK), which might contribute to endosomal modification [22–24, 72]. Alternatively, SopB was described to directly or indirectly lead to the accumulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate on the outer leaflet of the SCV, altering the recruitment of host cell endocytic trafficking molecules and thereby preventing SCV-lysosomal fusion [17, 18, 75, 76]. Although SopE2 was shown to influence endosomal maturation and intracellular proliferation, it is currently unknown how it could compensate for the lack of SopB [77].
Enterocyte invasion was consistently associated with a transcriptional stimulation of the intestinal epithelium. In contrast, non-invasive ΔsopABE2sipA Salmonella failed to evoke a significant epithelial response despite the presence of high numbers of bacteria in the intestinal lumen. Also, the presence of a functional T3SS system in the absence of invasion in sopAE2sipA, sopBE2sipA or sopE2sipA mutant bacteria was unable to induce a significant epithelial transcriptional response. Whereas invasion led to a more than 100-fold increase in Cxcl2 and Cxcl5 mRNA expression, intraepithelial proliferation only moderately contributed to this response. Our results therefore suggest that the presence of intraepithelial Salmonella per se or, alternatively, downstream events such as stimulation of lamina propria immune cells as a consequence of penetration of the epithelial barrier drive epithelial transcriptional stimulation [67]. This is consistent with the previously reported requirement of a functional SPI1 system to evoke PMN transmigration and fluid secretion in calves and the bovine ligated loop model [32–34]. It is also in accordance with the presence of a functional SPI1 locus among all isolates from symptomatic human patients [37, 38].
In addition to the stimulation of pattern recognition receptors the activation of host cell signaling pathways by Salmonella virulence factors has been described. For example, SopA was reported to contribute to tissue inflammation by targeting two host E3 ubiquitin ligases, TRIM56 and TRIM65 [13, 15, 78]. Also SopB was shown to indirectly stimulate Rho family GTPases and nuclear responses [56]. However, no significant influence of SopA or SopB on chemokine expression was observed in our study. Instead, our results suggest that SopA together with SopB and/or SopE2 may contribute to balance the adverse effects of the inflammatory activity of SipA. Additionally, T3SS-mediated translocation of SipA and SopE2 was reported to directly induce host cell activation [23, 79]. SopE-mediated activation of the Rho family of small molecular weight GTPase Cdc42 and activation of p21-activated kinase was reported to induce mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase and NF-κB stimulation [23, 80, 81]. However, invasive ΔsopABsipA and ΔsopABE2 Salmonella (in the absence of SipA and SopE2, respectively) still provoked potent transcriptional enterocyte stimulation in vivo.
SipA (SipA294-424) was additionally shown to induce PMN transmigration and tissue inflammation via PKCα-dependent secretion of the chemotactic eicosanoid hepoxillin A3 (HXA3) [12, 65, 82]. Notably, this pro-inflammatory activity was demonstrated to be independent of actin filament stabilization and enterocyte invasion and thus differed from the invasion-mediated immune stimulation discussed above [52, 65, 67, 82]. Binding of SipA to the epithelial surface molecule p53-effector related to PMP-22 (PERP) was shown to inhibit the phospholipid glutathione peroxidase (GPX4) [12, 65, 67, 68]. This effect was also observed in vivo with major influence on epithelial barrier integrity, immune cell infiltration and the outcome of the disease. Consistent with previous reports, immune stimulation was still observed in sipAK635A E637W ΔsopABE2 Salmonella despite a reduced invasiveness, supporting the idea that SipA acts extracellularly to stimulate the mucosal immune system [65, 68]. However, no influence of this SipA-mediated immune stimulation was observed on intraepithelial proliferation. The fact that ΔsopABE2 Salmonella exhibited a more severe proinflammatory effect as compared to SipA-competent wild type bacteria suggests that SopA, SopB or SopE2 might counteract this SipA effect in vivo.
Enhanced epithelial apoptosis and increased mortality were noted in the absence of SopB, consistent with a recent report that demonstrated protection from Nlrc4/ASC-mediated apoptosis by SopB in vitro [20, 83]. SopB might additionally prevent apoptosis by other mechanisms [21, 84]. Epithelial barrier damage after infection with ΔsopB Salmonella explains the higher bacterial load in the mesenteric lymph node. Intriguingly, enhanced disease progression following infection with ΔsopB Salmonella was absent using ΔsipAsopBE2 and ΔsopBE2 Salmonella. This suggests that the apoptosis-promoting effect is SopE2-mediated. Indeed, SopE2 has long been described to activate the c-jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) [23, 80] and JNK signaling is known to drive ROS-induced caspase 3-dependent apoptosis [85]. Alternatively, SopE2 was recently shown to activate caspase 1 [63]. Thus, our results identify a previously undescribed role for SopB: to protect from SopE2-mediated epithelial cell damage.
Despite the lack of intraepithelial microcolonies, ΔsopABsipA, ΔsopABE2, ΔsopBE2 or ΔsipA Salmonella efficiently penetrated the epithelial barrier and spread to systemic organs, reaching levels in spleen and liver tissue comparable to wild type Salmonella. This suggests that intraepithelial replication, although considered a hallmark of Salmonella pathogenesis, does not represent a prerequisite for efficient penetration of the epithelial barrier. This is consistent with the observation by Müller et al., who described SPI1-T3SS dependent penetration of the colon epithelium in the absence of detectable intraepithelial growth [28]. We even cannot exclude that two different bacterial populations simultaneously drive mucosal translocation and systemic spread. These results indicate that the functional relevance of intraepithelial replication and SCV formation has not been fully established and warrants further investigation.
Together, we validate the new neonatal infection model and present the first detailed in vivo analysis of the host and bacterial factors required for enterocyte invasion and intraepithelial microcolony formation, hallmark of Salmonella pathogenesis (Fig 7, S3 Table). We define the redundant and cooperative function of the SPI1-T3SS effectors SopA, SopB, SopE2 and SipA for invasion of the intestinal epithelium and intraepithelial growth and characterize their influence on innate immune stimulation, mucosal translocation and spread to systemic organs. Our results thereby significantly extend our insight in the early steps of the microbial-host interplay in vivo and might reveal new targets for future preventive and therapeutic measures.
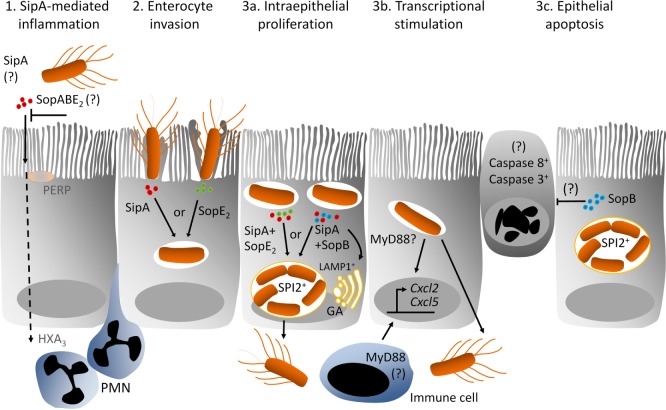
Fig 7. Graphical illustration of the role of the SPI1-T3SS effectors SopA, SopB, SopE2 and SipA during enterocyte invasion and intraepithelial proliferation in vivo.
(1) SipA (red dots) promotes the early recruitment of PMNs and causes barrier disruption and disease progression. This has been reported to occur via stimulation of the epithelial surface molecule p53-effector related to PMP-22 (PERP) and activation of the chemotactic eicosanoid hepoxillin A3 (HXA3) [68, 89]. This effect appears to be invasion-independent and strongly enhanced in the absence of SopA, SopB and SopE2 suggesting that these effectors exert regulatory functions. (2) Among the studied effector molecules, expression of SipA (red dots), SopE2 (green dots), or SopE (not shown here) alone is sufficient to facilitate enterocyte invasion. Intraepithelial Salmonella then reside within a LAMP1 negative endosomal compartment and fail to proliferate or express SPI2 encoded genes. (3a) SipA together with SopE2 or SipA together with SopB (blue dots) facilitate the recruitment of LAMP1 (yellow membrane) from the Golgi apparatus (GA) and the generation of a replicative compartment with intraepithelial bacterial proliferation and expression of SPI2 effector molecules. (3b) Enterocyte invasion or, alternatively, penetration of the epithelial barrier via innate stimulation and signaling through MyD88 induce expression of the chemokines Cxcl2 and Cxcl5 in the epithelium. (3c) SopB appears to directly or indirectly inhibit caspase 3 and caspase 8 mediated epithelial cell apoptosis. GA, golgi apparatus; HXA3, hepoxilin A3; LAMP1, lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1; PERP, p53-effector related to PMP-22; SPI2, Salmonella pathogenicity island 2.
Materials and methods
Bacterial strains and plasmids
All bacterial mutants and plasmids used in this study are listed in the S1 Table. Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium ATCC14028 were used as wild type bacteria. The sopABE2sipA quadruple mutant S. Typhimurium carrying the low copy number pWSK29 vector encoding sopA, sopB, sipA, SopE or sopE2, or the empty pWSK29 vector as control, as well as the respective isogenic S. Typhimurium triple, double or single mutants were used to analyze individual SPI1-T3SS effector molecules. Deletions of genes encoding effector proteins were generated by Red-mediated recombination basically as described before [86]. Strains with multiple deletions of effector genes were generated by P22-mediated transduction of mutant alleles containing the aph or CAT cassette. If required to generate multiple mutations by Red-mediated mutagenesis, antibiotic resistance genes were removed by FLP-mediated recombination between FRT sites. For the generation of a strain with point mutations in chromosomal sipA a two-step scarless mutagenesis approach according to Hoffmann et al. was applied [86]. A targeting cassette from pWRG717 was amplified using sipA633 In717 For and sipA939 In717 Rev (S2 Table). Salmonella WT harboring pWRG730 was induced for expression of redαβγ and transformed to kanamycin resistance. The resulting sipA mutant allele was transferred to other mutant strains using P22 transduction. The mutant allele sipA K635A E637W was amplified by PCR from plasmid p4758 target strains and the resulted DNA was used to transform MvP2511 haboring pWRG730. Resistance to I-SceI-mediated double strand breaks was used for selection of homologous recombination basically as described by Hoffmann et al. [86]. The point mutations in resulting strain MvP2520 were confirmed by DNA sequencing. Finally, the sopE2::aph mutation was introduced by P22 transduction to yield MvP2521.
For complementation of sipA, sopA, sopB, sopE or sopE2 deletions, the corresponding genes were amplified from S. enterica sv. Typhimurium genomic DNA introducing 3’ HA tag sequences for detection of the encoded proteins by immunoblotting. Oligonucleotides for amplification are listed in S2 Table. PCR products were cloned in low copy number vector pWSK29 and E. coli DH5α was used to propagate plasmids p4041, p4042, p4043 and p4044, SopA::HA, SopB::HA, SopE::HA, and SopE2::HA, respectively. Since sipA is the terminal gene of the sicAsipBCDA operon, the PsicA promoter was amplified and cloned upstream of sipA::HA to generate p4040. Mutant strains were transformed with complementation plasmids listed in S1 Table. Synthesis and translocation of the effector proteins by S. Typhimurium was confirmed by immunolabelling of the HA tag. Furthermore, the plasmids gradually complemented the invasion defect of a multi-effector mutant strain. The function of SipA was additionally analyzed using ΔsipA Salmonella carrying the sipA gene with point mutations at specific functional positions. Vector p4758 carrying two point mutations in the sipA gene at the actin binding site (amino acid position 635 and 637), vector p4890 carrying a point mutation in the sipA gene at the caspase 3 motif (amino acid position 434), and vector p4892 carrying all three point mutations in the sipA gene were generated by site-directed mutagenesis. Site-directed mutagenesis was performed using the Q5 SDM kit according to the manufacturers’ protocol (NEB). Multiple rounds of mutagenesis were performed if required for the generation of double or triple mutations using primers listed in the S2 Table. The plasmid with constitutive green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression (pGFP, AmpR) was kindly provided by Brendan Cormack, Stanford, USA. The reporter construct pM973 expressing gfp under the control of the SPI2 promoter pssaG (AmpR) kindly provided by Wolf D. Hardt, ETH Zürich, Switzerland was used to analyze the expression of SPI2 effector molecules by intraepithelial Salmonella.
In vitro infection experiments
Intestinal epithelial m-ICcl2 cells were cultured as previously described [87]. Bacteria were cultured in Luria Bertani (LB) broth at 37°C in the presence of 100 μg/mL ampicillin, 50 μg/mL kanamycin, or 100 μg/mL carbenicillin. Overnight cultures were diluted 1:10 and incubated at 37°C for approximately 80 min until reaching the logarithmic phase (OD600 approximately 0.5). Bacteria were then washed three times in PBS and the OD600 was adjusted to 0.55–0.60 corresponding to approximately 2.0×108 CFU bacteria per mL. The bacterial suspension was subsequently diluted to obtain the appropriate infection dose. Bacteria were added to the m-ICcl2 cells (2×105 cells per well) at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1:10. The cell culture plate was centrifuged at 300xg for 5 min and incubated at 37°C for 1 h. Cells were washed three times with PBS and cell culture medium supplemented with 100 μg/mL gentamicin (Sigma) was added. After incubation at 37°C for 1 h, cells were washed again three times in PBS and lyzed for 2 min at room temperature in 500 μL 0.1% Triton X-100 (Roth) in aqua dest. Viable bacteria were quantified by serial dilution and plating.
Ethics statement
All animal experiments were performed in compliance with the German animal protection law (TierSchG) and approved by the local animal welfare committee (Niedersachsische Landesamt für Verbraucherschutz und Lebensmittelsicherheit Oldenburg, Germany; Landesamt für Natur, Umwelt und Verbraucherschutz, North Rhine Westfalia) under the code 8402.04.2015A073, 84–02.042015.A067, 84–02.042015.A065 and 81–02.04.2017.A397 including all approved changes.
In vivo infection experiments
Adult C57BL/6J wild type and B6.129P2(SJL)-MyD88tm1.1Defr/J (MyD88-/-, stock no. 009088) were obtained from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbour, USA) and bred locally under SPF conditions. Bacteria were cultured as described above. 1- and 4-day-old animals were orally infected with 100 CFU of wild type S. Typhimurium or the indicated isogenic mutants in a volume of 1 μL PBS. At various time points post infection (p.i.), liver, mesenteric lymph mode (MLN) and spleen were collected and homogenized in sterile PBS. Viable counts were obtained by serial dilution and plating on LB agar plates supplemented with the appropriate antibiotics. Alternatively, small intestinal tissues were collected at the indicated time point p.i. and prepared for immunostaining or electron microscopy. For co-infection, 100 CFU of Salmonella wild type carrying pGFP and sopABsipA mutant Salmonella were administered orally to 1-day-old mice at a ratio of 1:1 in 2 μl.
Primary epithelial cell isolation
Primary small intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) from neonate mice were isolated as previously described [87]. Briefly, the small intestinal tissue was cut in small pieces and incubated in 30 mM EDTA/PBS at 37°C for 10 min. IEC were detached from the underlying tissue by shaking. Cells were then filtered through a 100 μm nylon cell strainer (BD Falcon) and harvested by centrifugation at 300xg for 10 min. The cell pellet was resuspended in 10% FCS/PBS and harvested by centrifugation at 300xg for 10 min. To obtain the intraepithelial bacterial count, IEC were treated with 100 μg/mL gentamicin for 1 h at room temperature as previously described and subsequently lyzed and plated in serial dilutions on selective LB agar plates [50].
Gene expression analysis
Total RNA was extracted from isolated IEC using TRIzol (Invitrogen) and the RNA concentration was determined on a NanoDrop 1000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific). First-strand complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized from 5 μg total RNA using Oligo-dT primers, RevertAid reverse transcriptase and RiboLock RNase inhibitor (ThermoFisher Scientific). RT-PCR was performed using the Taqman technology with an absolute QPCR ROX mix (Thermo Scientific), sample cDNA and the Taqman probes Hprt (Mm00446968-m1), Cxcl2 (Mm00436450_m1) and Cxcl5 (Mm00436451_g1) (Life Technologies). Results were calculated by the Δ2-CT method. For data analysis, values were normalized to the hprt housekeeping gene and were presented as fold induction over age-matched controls.
FITC dextran-mediated analysis of epithelial barrier function
Infected mice were orally administered 2 μL of a 0.6 mg/μL 4kDa FITC dextran solution (TdB Consultancy) at the indicated time point p.i.. After four hours, serum was collected and the serum concentration of FITC dextran was measured by fluorometry using a SpectraMax i3 at an excitation of 492nm (9 nm bandwidth) and an emission of 518nm (15 nm bandwidth) using a serially diluted FITC dextran solution as standard.
Immunofluorescence staining
4 μm paraformaldehyde-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections were deparaffinized in xylene and rehydrated followed by antigen retrieval in 10 mM sodium citrate and a blocking step with 10% normal donkey serum/5% BSA/PBS. Chicken anti-GFP (Abcam), rabbit anti-Salmonella O4 antigen (Abcam), rat anti-LAMP1 (Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank), rabbit anti-cleaved caspase-3 (Cell Signaling), rabbit anti-cleaved caspase-8 (Cell Signaling), rat anti-PMN (Ly6-6B2, SeroTec) and mouse anti-E-cadherin (BD Transduction Laboratories) antibodies as well as the indicated fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibodies (Jackson ImmunoResearch) were used. Fluorescein-conjugated (Vector) or AF647-conjugated (Invitrogen) Wheat Germ Agglutinin (WGA) was used to detect the mucus layer. Slides were subsequently mounted in DAPI mounting medium (Vector) and images were taken using a Zeiss ApoTome.2 system microscope connected to a Axiocam 506 digital camera. Images were formatted using the ZEN 2.3 imaging software.
Flow cytometry analysis
For immune cell isolation, the intestine was cut longitudinally and incubated 2x15min in 2mM EDTA/HBSS at 37°C to remove the epithelium. The lamina propria was digested in 30μg/ml Liberase/DNAse (Roche) for 45min at 37°C and filtered through a 100μm nylon cell strainer to obtain a single cell suspension. The following antibodies from Biolegend were used for the FACS analysis: CD45-BV510 (30-F11), Ly6C-PerCPCy5.5 (HK1.4), Ly6G-PE (1A8), CD11b-APCCy7 (M1/70), MHCII-AF488 (M5/115.14.2). Data were acquired with a BD FACS Canto II and analyzed with FlowJo X.
Transmission electron microscopy
1-day-old MyD88+/+ and MyD88-/- mice were infected with wild type S. Typhimurium and sacrificed at day 4 p.i.. Tissue samples were prepared for ultrastructural analysis as previously described [88]. After embedding, samples were post-fixed with 1% osmium tetroxide and contrasted with 2% uranyl acetate, both for 2 h. Samples were dehydrated with a graded ethanol series, followed by infiltration with epoxy resin and overnight heat polymerization. Thin, 70 nm sections were prepared using an ultramicrotome Ultracut UCT (Leica Microsystems) and contrasted with 0.2% lead citrate. Sections were analyzed with a JEM-1400 TEM microscope (Jeol) and images were recorded with TemCam-F216 camera using EM MENU software (both Tvips).
Statistical analysis
The One-way ANOVA Kruskal-Wallis test (with Dunn's posttest) and the Mann-Whitney test were employed for statistical analysis of bacterial counts in organ tissue and the comparative transcriptional analysis. Mortality was analyzed by log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. The GraphPad Prism Software 5.0 was used for statistical evaluation. p values are indicated as follows: ***p<0.001; **p<0.01, and *p<0.05.
Supporting information
1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU wild type (WT) pWSK (filled circles), quadruple mutant ΔsopABE2sipA pWSK (open circles), ΔsopABE2sipA psopA (inverted open triangles), ΔsopABE2sipA psopB (open triangles), ΔsopABE2sipA psipA (open squares), or ΔsopABE2sipA psopE2 (open diamonds) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) isolated gentamicin-treated enterocytes at 4 days post infection (p.i.).. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl2 and (C) Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Viable counts in (D) total MLN homogenate, (E) total liver tissue homogenate and (F) total spleen tissue homogenate at 4 days post infection (p.i.). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 5–8 animals per group). (G) Immunostaining for Salmonella (red) in small intestinal tissue sections at 4 days p.i. with 100 CFU WT pWSK, ΔsopABE2sipA pWSK, ΔsopABE2sipA psopA, ΔsopABE2sipA psopB, ΔsopABE2sipA psipA, or ΔsopABE2sipA psopE2 S. Typhimurium. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (green), WGA (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (H) A confluent monolayer of polarized murine intestinal epithelial m-ICcl2 cells were infected at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1:10 with WT pWSK, SPI1 mutant ΔinvC, ΔsopABE2sipA pWSK, ΔsopABE2sipA psopA, ΔsopABE2sipA psopB, ΔsopABE2sipA psipA, or ΔsopABE2sipA psopE2 S. Typhimurium for 1 h at 37°C. Cells were subsequently treated with 100 μg/mL gentamicin for 1 h at 37°C, washed three times, and lyzed in 0.1% Triton X-100. The number of viable bacteria in cell lysates and inoculi was determined by serial dilution and plating. The number of intracellular, gentamicin-protected bacteria relative to the inoculum is shown (%). Results represent the mean ± SD.
(TIF)
1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT pWSK (filled circles), ΔsopABE2sipA pWSK (open circles), ΔsopABE2sipA psopE2 (open diamonds), or ΔsopABE2sipA psopE (half-filled diamonds) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) isolated gentamicin-treated enterocytes at 4 days p.i.. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl2 and (C) Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Viable counts in (D) total MLN homogenate, (E) total liver tissue homogenate, and (F) total spleen tissue homogenate at 4 days p.i.. Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 5–8 animals per group). (G) Immunostaining for Salmonella (red) in small intestinal tissue sections at 4 days p.i. with 100 CFU WT pWSK or ΔsopABE2sipA psopE S. Typhimurium. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (green), WGA (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (H) Gentamicin protection assay (as described under (H)) was performed with WT pWSK, ΔsopABE2sipA pWSK, ΔsopABE2sipA psopE2, or ΔsopABE2sipA psopE. The number of intracellular, gentamicin-protected bacteria relative to the inoculum is shown (%). Results represent the mean ± SD.
(TIF)
(A-C) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (filled circles), sopABE2sipA quadruple mutant (open circles), sopBE2sipA (inverted open triangles), sopAE2sipA (open triangles), sopABE2 (open squares), or sopABsipA mutant (open diamonds) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) MLN and (B) total spleen tissue homogenate at 4 days post infection (p.i.). (C) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 5–8 animals per group). (D) Gentamicin protection assay (as described in S1H Fig) was performed using WTpWSK, ΔinvC, ΔsopABE2sipA, ΔsopBE2sipA, ΔsopAE2sipA, ΔsopABE2, or ΔsopABsipA S. Typhimurium. The number of intracellular, gentamicin-protected bacteria relative to the inoculum is shown (%). Results represent the mean ± SD.
(TIF)
(A and B) 1-day-old MyD88+/+ and MyD88-/- mice were left untreated or orally infected with 100 CFU wild type S. Typhimurium. Relative expression of (A) Cxcl2 and (B) Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated from non-infected and infected MyD88+/+ mice as well as non-infected and infected MyD88-/- mice at 4 days p.i. were measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Relative expression from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 2–6 animals per group). The data for MyD88+/+ animals infected with S. Typhimurium WT are identical to Fig 1C and S3C Fig. (C) Survival following S. Typhimurium infection. 1-day-old MyD88+/+ (n = 12; solid line) and MyD88-/- (n = 12; broken line) mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT S. Typhimurium (broken line). Animals that had to be euthanized due to a rise in the clinical score were included in the analysis (see material and methods).
(TIF)
(A-C) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (filled circles) or ΔsopE2sipA S. Typhimurium (filled triangels). Viable counts in (A) MLN and (B) total spleen tissue homogenate at 4 days p.i.. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 3–5 animals per group). (D-F) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (filled circles) ΔsipA (open squares), ΔsipA complemented with psipA (filled squares), ΔsopE2 (open diamonds), or ΔsopE2 complemented with psopE2 (filled diamonds) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (D) MLN and (E) total spleen tissue homogenate at 4 days p.i.. (F) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 3–7 animals per group). The data for uninfected control animals and Salmonella WT infected mice are identical to S3A–S3C Fig.
(TIF)
(A-C) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (filled circles), ΔsopBE2 (inverted open triangles), or ΔsopAE2 (open triangles) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) MLN and (B) total spleen tissue homogenate at 4 days p.i.. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 3–8 animals per group). The data for uninfected control animals and Salmonella WT infected mice are identical to S3A–S3C Fig.
(TIF)
(A and B) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU wild type (WT) (filled circles), ΔsopB (filled triangles), or ΔsopB psopB (open triangles) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) total spleen tissue homogenate at 2 days post infection (p.i.). (B) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 2 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 3–5 animals per group). (C) Immunostaining for cleaved caspase 3 (cl. caspase 3, upper panel, red) and cleaved caspase 8 (cl. caspase 8, lower panel, red) in small intestinal tissue sections from healthy age-matched control animals (non-infected) or at 3 days p.i. with WT, ΔsopB and ΔsopB psopB S. Typhimurium. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (green), and DAPI (blue). Bar, 50 μm.
(TIF)
(A) Postnatal body weight gain of healthy and infected animals. 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were left untreated (solid line) or orally infected with 100 CFU WT (broken line) or ΔsopABE2 S. Typhimurium (dotted line). (B) Survival following S. Typhimurium infection. 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (solid line), ΔsopABE2 (broken line), or sipAK635A E637W ΔsopABE2 S. Typhimurium (broken line). Animals that had to be euthanized due to a rise in the clinical score were included in the analysis (see material and methods). (C) Total length (in cm) of the small intestine at 4 days p.i. and of uninfected age-matched control animals. 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were infected with 100 CFU WT, ΔsopBE2sipA (inverted open triangles), ΔsopAE2sipA (open triangles) ΔsopABE2 (open squares) and or ΔsopABsipA (open diamonds) S. Typhimurium. Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 3–5 animals per group). (D) Mucosal barrier integrity tested by serum quantification 4 hours after oral administration of FITC labeled-4kDa dextran. 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were infected with WT (filled circles), ΔsopABsipA (open diamonds), or ΔsopAE2sipA (open triangles) S. Typhimurium. FITC labeled-4 kDa dextran was quantified in serum at day 4 p.i.. (E and F) Flow cytometric analysis of lamina propria immune cells. 1-day-old mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT, ΔsopAE2sipA, ΔsopABsipA, or ΔsopABE2 S. Typhimurium and total SI leukocytes were analyzed by flow cytometry at day 4 p.i.. (E) Monocytes (Ly6ChiLy6G-CD11b+MHCIIlo/-CD45+DAPI-) and (F) neutrophils (Ly6G+Ly6CintCD11b+MHCIIlo/-CD45+DAPI-) are depicted as % of CD45+ cells. The results represent the mean values from at least two independent experiments (n = 4–6 per group). (G and H) Quantitative analysis (G) and immunostaining (H) of PMN infiltrating the small intestinal tissue. PMN from 10–20 image fields obtained from neonates infected with wild type (WT), ΔsipA, ΔsipA psipA, ΔsipA psipAD434A S. Typhimurium (n = 3–9) and uninfected age-matched control animals (n = 5) were analyzed at day 4 p.i.. Values and mean are shown. Bar, 25 μm. (I) Viable counts in isolated gentamicin-treated enterocytes at 2 days p.i. of 1-day-old mice with 100 CFU WT (filled circle), ΔsopABE2 (open squares), or sipAK635A E637W ΔsopABE2 S. Typhimurium (filled squares). Values and mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 4–6 animals per group).
(TIF)
(A-C) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (filled circles), ΔsipA (open diamonds), ΔsipA complemented with psipAK635A E637W (half-filled diamonds), ΔsipA complemented with psipAD434A (filled squares), or ΔsipA complemented with psipAD434A K635A E637W (filled triangles) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) MLN and (B) total spleen tissue homogenate at 4 days p.i.. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 4–7 animals per group). The data for uninfected control animals and Salmonella WT infected mice are identical to S3A–S3C Fig. (D) Survival following S. Typhimurium infection. 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (solid line), ΔsipA (broken line), or ΔsipA complemented with sipAK635A E637W (broken line) S. Typhimurium. Animals that had to be euthanized due to a rise in the clinical score were included in the analysis (see Material and Methods).
(TIF)
Strain name, designation, genotype description and reference are listed for all strains and plasmids used in the study.
(DOCX)
Oligonucleotide name and sequence are listed for all oligonucleotides used in the study.
(DOC)
Summary of the results obtained in this study using all bacterial mutants indicating the genotype, the time point of the analysis and the phenotype, namely enterocyte invasion, LAMP1 recruitment to the Salmonella microcolony, SPI2 T3SS reporter activation, transcriptional stimulation of the intestinal epithelium, intraepithelial proliferation and spread to spleen and liver tissue.
(DOC)
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the technical support from Dominique Gütle, Thorben Albers, Regina Holland and Josephine Weber-Heynemann. We thank the Electron Microscopy Laboratory at the Department of Biosciences, University of Oslo.
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by: German Research Foundation (http://www.dfg.de/en/) Priority Program 1580 “Intracellular Compartments as Places of Pathogen - Host Interaction” to MWH and MH, the German Research Foundation Individual Grant Ho-2236/12-1, Ho-2236/8-1 and Ho-2236/14-1 to MHo. the German Research Foundation Individual Grant HE1964/18-2 and the Collaborative Research Center SFB 944 (P4) to MHe, and the German Research Foundation Individual Grant To-1052/1-1 to NT. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Coburn B, Grassl GA, Finlay BB. Salmonella, the host and disease: a brief review. Immunol Cell Biol. 2007;85(2):112–8. doi: 10.1038/sj.icb.7100007 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Majowicz SE, Musto J, Scallan E, Angulo FJ, Kirk M, O'Brien SJ, et al. The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clinical infectious diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2010;50(6):882–9. doi: 10.1086/650733 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Milledge J, Calis JC, Graham SM, Phiri A, Wilson LK, Soko D, et al. Aetiology of neonatal sepsis in Blantyre, Malawi: 1996–2001. Annals of tropical paediatrics. 2005;25(2):101–10. doi: 10.1179/146532805X45692 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Feasey NA, Dougan G, Kingsley RA, Heyderman RS, Gordon MA. Invasive non-typhoidal salmonella disease: an emerging and neglected tropical disease in Africa. Lancet. 2012;379(9835):2489–99. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61752-2 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3402672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.LaRock DL, Chaudhary A, Miller SI. Salmonellae interactions with host processes. Nature reviews Microbiology. 2015;13(4):191–205. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3420 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Que F, Wu S, Huang R. Salmonella pathogenicity island 1(SPI-1) at work. Current microbiology. 2013;66(6):582–7. doi: 10.1007/s00284-013-0307-8 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Laughlin RC, Knodler LA, Barhoumi R, Payne HR, Wu J, Gomez G, et al. Spatial segregation of virulence gene expression during acute enteric infection with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. mBio. 2014;5(1):e00946–13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00946-13 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3950517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Agbor TA, McCormick BA. Salmonella effectors: important players modulating host cell function during infection. Cellular microbiology. 2011;13(12):1858–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2011.01701.x ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3381885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhou D, Mooseker MS, Galan JE. Role of the S. typhimurium actin-binding protein SipA in bacterial internalization. Science. 1999;283(5410):2092–5. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhou D, Mooseker MS, Galan JE. An invasion-associated Salmonella protein modulates the actin-bundling activity of plastin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1999;96(18):10176–81. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC17862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lilic M, Galkin VE, Orlova A, VanLoock MS, Egelman EH, Stebbins CE. Salmonella SipA polymerizes actin by stapling filaments with nonglobular protein arms. Science. 2003;301(5641):1918–21. doi: 10.1126/science.1088433 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lee CA, Silva M, Siber AM, Kelly AJ, Galyov E, McCormick BA. A secreted Salmonella protein induces a proinflammatory response in epithelial cells, which promotes neutrophil migration. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2000;97(22):12283–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.22.12283 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC17333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wood MW, Jones MA, Watson PR, Siber AM, McCormick BA, Hedges S, et al. The secreted effector protein of Salmonella dublin, SopA, is translocated into eukaryotic cells and influences the induction of enteritis. Cellular microbiology. 2000;2(4):293–303. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Layton AN, Brown PJ, Galyov EE. The Salmonella translocated effector SopA is targeted to the mitochondria of infected cells. Journal of bacteriology. 2005;187(10):3565–71. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.10.3565-3571.2005 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC1112013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zhang Y, Higashide WM, McCormick BA, Chen J, Zhou D. The inflammation-associated Salmonella SopA is a HECT-like E3 ubiquitin ligase. Molecular microbiology. 2006;62(3):786–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05407.x . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Galyov EE, Wood MW, Rosqvist R, Mullan PB, Watson PR, Hedges S, et al. A secreted effector protein of Salmonella dublin is translocated into eukaryotic cells and mediates inflammation and fluid secretion in infected ileal mucosa. Molecular microbiology. 1997;25(5):903–12. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Norris FA, Wilson MP, Wallis TS, Galyov EE, Majerus PW. SopB, a protein required for virulence of Salmonella dublin, is an inositol phosphate phosphatase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1998;95(24):14057–9. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC24325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Terebiznik MR, Vieira OV, Marcus SL, Slade A, Yip CM, Trimble WS, et al. Elimination of host cell PtdIns(4,5)P(2) by bacterial SigD promotes membrane fission during invasion by Salmonella. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4(10):766–73. doi: 10.1038/ncb854 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhou D, Chen LM, Hernandez L, Shears SB, Galan JE. A Salmonella inositol polyphosphatase acts in conjunction with other bacterial effectors to promote host cell actin cytoskeleton rearrangements and bacterial internalization. Molecular microbiology. 2001;39(2):248–59. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Steele-Mortimer O, Knodler LA, Marcus SL, Scheid MP, Goh B, Pfeifer CG, et al. Activation of Akt/protein kinase B in epithelial cells by the Salmonella typhimurium effector sigD. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2000;275(48):37718–24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008187200 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Knodler LA, Finlay BB, Steele-Mortimer O. The Salmonella effector protein SopB protects epithelial cells from apoptosis by sustained activation of Akt. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2005;280(10):9058–64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M412588200 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wood MW, Rosqvist R, Mullan PB, Edwards MH, Galyov EE. SopE, a secreted protein of Salmonella dublin, is translocated into the target eukaryotic cell via a sip-dependent mechanism and promotes bacterial entry. Molecular microbiology. 1996;22(2):327–38. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hardt WD, Chen LM, Schuebel KE, Bustelo XR, Galan JE. S. typhimurium encodes an activator of Rho GTPases that induces membrane ruffling and nuclear responses in host cells. Cell. 1998;93(5):815–26. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Stender S, Friebel A, Linder S, Rohde M, Mirold S, Hardt WD. Identification of SopE2 from Salmonella typhimurium, a conserved guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Cdc42 of the host cell. Molecular microbiology. 2000;36(6):1206–21. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Takeuchi A. Electron microscope studies of experimental Salmonella infection. I. Penetration into the intestinal epithelium by Salmonella typhimurium. The American journal of pathology. 1967;50(1):109–36. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC1965174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Giannella RA, Formal SB, Dammin GJ, Collins H. Pathogenesis of salmonellosis. Studies of fluid secretion, mucosal invasion, and morphologic reaction in the rabbit ileum. The Journal of clinical investigation. 1973;52(2):441–53. doi: 10.1172/JCI107201 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC302274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Nietfeld JC, Tyler DE, Harrison LR, Cole JR, Latimer KS, Crowell WA. Invasion of enterocytes in cultured porcine small intestinal mucosal explants by Salmonella choleraesuis. American journal of veterinary research. 1992;53(9):1493–9. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Muller AJ, Kaiser P, Dittmar KE, Weber TC, Haueter S, Endt K, et al. Salmonella gut invasion involves TTSS-2-dependent epithelial traversal, basolateral exit, and uptake by epithelium-sampling lamina propria phagocytes. Cell host & microbe. 2012;11(1):19–32. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.11.013 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sellin ME, Muller AA, Felmy B, Dolowschiak T, Diard M, Tardivel A, et al. Epithelium-intrinsic NAIP/NLRC4 inflammasome drives infected enterocyte expulsion to restrict Salmonella replication in the intestinal mucosa. Cell host & microbe. 2014;16(2):237–48. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.07.001 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tsolis RM, Adams LG, Ficht TA, Baumler AJ. Contribution of Salmonella typhimurium virulence factors to diarrheal disease in calves. Infection and immunity. 1999;67(9):4879–85. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC96822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Tsolis RM, Adams LG, Hantman MJ, Scherer CA, Kimbrough T, Kingsley RA, et al. SspA is required for lethal Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infections in calves but is not essential for diarrhea. Infection and immunity. 2000;68(6):3158–63. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC97552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhang S, Santos RL, Tsolis RM, Stender S, Hardt WD, Baumler AJ, et al. The Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium effector proteins SipA, SopA, SopB, SopD, and SopE2 act in concert to induce diarrhea in calves. Infection and immunity. 2002;70(7):3843–55. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.7.3843-3855.2002 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC128071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhang S, Adams LG, Nunes J, Khare S, Tsolis RM, Baumler AJ. Secreted effector proteins of Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium elicit host-specific chemokine profiles in animal models of typhoid fever and enterocolitis. Infection and immunity. 2003;71(8):4795–803. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.8.4795-4803.2003 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC166006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhang S, Kingsley RA, Santos RL, Andrews-Polymenis H, Raffatellu M, Figueiredo J, et al. Molecular pathogenesis of Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium-induced diarrhea. Infection and immunity. 2003;71(1):1–12. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.1.1-12.2003 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC143292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Barthel M, Hapfelmeier S, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Kremer M, Rohde M, Hogardt M, et al. Pretreatment of mice with streptomycin provides a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium colitis model that allows analysis of both pathogen and host. Infection and immunity. 2003;71(5):2839–58. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.5.2839-2858.2003 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC153285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lawhon SD, Khare S, Rossetti CA, Everts RE, Galindo CL, Luciano SA, et al. Role of SPI-1 secreted effectors in acute bovine response to Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium: a systems biology analysis approach. PloS one. 2011;6(11):e26869 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026869 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3214023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Anjum MF, Marooney C, Fookes M, Baker S, Dougan G, Ivens A, et al. Identification of core and variable components of the Salmonella enterica subspecies I genome by microarray. Infection and immunity. 2005;73(12):7894–905. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.12.7894-7905.2005 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC1307019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ochman H, Groisman EA. Distribution of pathogenicity islands in Salmonella spp. Infection and immunity. 1996;64(12):5410–2. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC174539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hartmann H, Meyer H, Koch H, Steinbach G, Gunther H. [Salmonellosis in the calf. 1. development of an infection model and experiments on pathogenesis]. Arch Exp Veterinarmed. 1973;27(2):289–300. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Jones MA, Wood MW, Mullan PB, Watson PR, Wallis TS, Galyov EE. Secreted effector proteins of Salmonella dublin act in concert to induce enteritis. Infection and immunity. 1998;66(12):5799–804. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC108733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zhang S, Santos RL, Tsolis RM, Mirold S, Hardt WD, Adams LG, et al. Phage mediated horizontal transfer of the sopE1 gene increases enteropathogenicity of Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium for calves. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2002;217(2):243–7. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Raffatellu M, Wilson RP, Chessa D, Andrews-Polymenis H, Tran QT, Lawhon S, et al. SipA, SopA, SopB, SopD, and SopE2 contribute to Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium invasion of epithelial cells. Infection and immunity. 2005;73(1):146–54. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.1.146-154.2005 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC538951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Smith BP, Habasha F, Reina-Guerra M, Hardy AJ. Bovine salmonellosis: experimental production and characterization of the disease in calves, using oral challenge with Salmonella typhimurium. American journal of veterinary research. 1979;40(11):1510–3. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Frost AJ, Bland AP, Wallis TS. The early dynamic response of the calf ileal epithelium to Salmonella typhimurium. Veterinary pathology. 1997;34(5):369–86. doi: 10.1177/030098589703400501 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Santos RL, Zhang S, Tsolis RM, Baumler AJ, Adams LG. Morphologic and molecular characterization of Salmonella typhimurium infection in neonatal calves. Veterinary pathology. 2002;39(2):200–15. doi: 10.1354/vp.39-2-200 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bolton AJ, Martin GD, Osborne MP, Wallis TS, Stephen J. Invasiveness of Salmonella serotypes Typhimurium, Choleraesuis and Dublin for rabbit terminal ileum in vitro. Journal of medical microbiology. 1999;48(9):801–10. doi: 10.1099/00222615-48-9-801 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bolton AJ, Osborne MP, Wallis TS, Stephen J. Interaction of Salmonella choleraesuis, Salmonella dublin and Salmonella typhimurium with porcine and bovine terminal ileum in vivo. Microbiology. 1999;145 Pt 9):2431–41. doi: 10.1099/00221287-145-9-2431 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Jones BD, Ghori N, Falkow S. Salmonella typhimurium initiates murine infection by penetrating and destroying the specialized epithelial M cells of the Peyer's patches. The Journal of experimental medicine. 1994;180(1):15–23. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2191576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Martinez-Argudo I, Jepson MA. Salmonella translocates across an in vitro M cell model independently of SPI-1 and SPI-2. Microbiology. 2008;154(Pt 12):3887–94. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2008/021162-0 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhang K, Dupont A, Torow N, Gohde F, Leschner S, Lienenklaus S, et al. Age-dependent enterocyte invasion and microcolony formation by Salmonella. PLoS pathogens. 2014;10(9):e1004385 doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004385 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4161480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hapfelmeier S, Ehrbar K, Stecher B, Barthel M, Kremer M, Hardt WD. Role of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 effector proteins SipA, SopB, SopE, and SopE2 in Salmonella enterica subspecies 1 serovar Typhimurium colitis in streptomycin-pretreated mice. Infection and immunity. 2004;72(2):795–809. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.2.795-809.2004 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC321604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hapfelmeier S, Stecher B, Barthel M, Kremer M, Muller AJ, Heikenwalder M, et al. The Salmonella pathogenicity island (SPI)-2 and SPI-1 type III secretion systems allow Salmonella serovar typhimurium to trigger colitis via MyD88-dependent and MyD88-independent mechanisms. Journal of immunology. 2005;174(3):1675–85. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Knodler LA, Crowley SM, Sham HP, Yang H, Wrande M, Ma C, et al. Noncanonical inflammasome activation of caspase-4/caspase-11 mediates epithelial defenses against enteric bacterial pathogens. Cell host & microbe. 2014;16(2):249–56. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.07.002 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4157630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Mirold S, Rabsch W, Rohde M, Stender S, Tschape H, Russmann H, et al. Isolation of a temperate bacteriophage encoding the type III effector protein SopE from an epidemic Salmonella typhimurium strain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1999;96(17):9845–50. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC22298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bakshi CS, Singh VP, Wood MW, Jones PW, Wallis TS, Galyov EE. Identification of SopE2, a Salmonella secreted protein which is highly homologous to SopE and involved in bacterial invasion of epithelial cells. Journal of bacteriology. 2000;182(8):2341–4. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC111290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Patel JC, Galan JE. Differential activation and function of Rho GTPases during Salmonella-host cell interactions. The Journal of cell biology. 2006;175(3):453–63. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200605144 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2064522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Friebel A, Ilchmann H, Aepfelbacher M, Ehrbar K, Machleidt W, Hardt WD. SopE and SopE2 from Salmonella typhimurium activate different sets of RhoGTPases of the host cell. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2001;276(36):34035–40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100609200 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Madan R, Rastogi R, Parashuraman S, Mukhopadhyay A. Salmonella acquires lysosome-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP1) on phagosomes from Golgi via SipC protein-mediated recruitment of host Syntaxin6. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2012;287(8):5574–87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.286120 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3285332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Deiwick J, Nikolaus T, Erdogan S, Hensel M. Environmental regulation of Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 gene expression. Molecular microbiology. 1999;31(6):1759–73. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Arpaia N, Godec J, Lau L, Sivick KE, McLaughlin LM, Jones MB, et al. TLR signaling is required for Salmonella typhimurium virulence. Cell. 2011;144(5):675–88. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.01.031 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3063366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Bens M, Bogdanova A, Cluzeaud F, Miquerol L, Kerneis S, Kraehenbuhl JP, et al. Transimmortalized mouse intestinal cells (m-ICc12) that maintain a crypt phenotype. The American journal of physiology. 1996;270(6 Pt 1):C1666–74. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.270.6.C1666 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Chuang TH, Hahn KM, Lee JD, Danley DE, Bokoch GM. The small GTPase Cdc42 initiates an apoptotic signaling pathway in Jurkat T lymphocytes. Mol Biol Cell. 1997;8(9):1687–98. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC305729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Hoffmann C, Galle M, Dilling S, Kappeli R, Muller AJ, Songhet P, et al. In macrophages, caspase-1 activation by SopE and the type III secretion system-1 of S. typhimurium can proceed in the absence of flagellin. PloS one. 2010;5(8):e12477 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012477 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC2930008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Agbor TA, Demma Z, Mrsny RJ, Castillo A, Boll EJ, McCormick BA. The oxido-reductase enzyme glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) governs Salmonella Typhimurium-induced neutrophil transepithelial migration. Cellular microbiology. 2014;16(9):1339–53. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12290 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4146641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Wall DM, Nadeau WJ, Pazos MA, Shi HN, Galyov EE, McCormick BA. Identification of the Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium SipA domain responsible for inducing neutrophil recruitment across the intestinal epithelium. Cellular microbiology. 2007;9(9):2299–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00960.x . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Srikanth CV, Wall DM, Maldonado-Contreras A, Shi H, Zhou D, Demma Z, et al. Salmonella pathogenesis and processing of secreted effectors by caspase-3. Science. 2010;330(6002):390–3. doi: 10.1126/science.1194598 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4085780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Li D, Wang X, Wang L, Zhou D. The actin-polymerizing activity of SipA is not essential for Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium-induced mucosal inflammation. Infection and immunity. 2013;81(5):1541–9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00337-12 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3648018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Hallstrom KN, Srikanth CV, Agbor TA, Dumont CM, Peters KN, Paraoan L, et al. PERP, a host tetraspanning membrane protein, is required for Salmonella-induced inflammation. Cellular microbiology. 2015;17(6):843–59. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12406 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4915744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Andritschke D, Dilling S, Emmenlauer M, Welz T, Schmich F, Misselwitz B, et al. A Genome-Wide siRNA Screen Implicates Spire1/2 in SipA-Driven Salmonella Typhimurium Host Cell Invasion. PloS one. 2016;11(9):e0161965 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161965 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC5023170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Piscatelli HL, Li M, Zhou D. Dual 4- and 5-phosphatase activities regulate SopB-dependent phosphoinositide dynamics to promote bacterial entry. Cellular microbiology. 2016;18(5):705–19. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12542 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Hanisch J, Kolm R, Wozniczka M, Bumann D, Rottner K, Stradal TE. Activation of a RhoA/myosin II-dependent but Arp2/3 complex-independent pathway facilitates Salmonella invasion. Cell host & microbe. 2011;9(4):273–85. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.03.009 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Humphreys D, Davidson A, Hume PJ, Koronakis V. Salmonella virulence effector SopE and Host GEF ARNO cooperate to recruit and activate WAVE to trigger bacterial invasion. Cell host & microbe. 2012;11(2):129–39. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.01.006 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3314957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Steele-Mortimer O, Brumell JH, Knodler LA, Meresse S, Lopez A, Finlay BB. The invasion-associated type III secretion system of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is necessary for intracellular proliferation and vacuole biogenesis in epithelial cells. Cellular microbiology. 2002;4(1):43–54. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Brawn LC, Hayward RD, Koronakis V. Salmonella SPI1 effector SipA persists after entry and cooperates with a SPI2 effector to regulate phagosome maturation and intracellular replication. Cell host & microbe. 2007;1(1):63–75. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2007.02.001 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC1885946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Mallo GV, Espina M, Smith AC, Terebiznik MR, Aleman A, Finlay BB, et al. SopB promotes phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate formation on Salmonella vacuoles by recruiting Rab5 and Vps34. The Journal of cell biology. 2008;182(4):741–52. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200804131 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC2518712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bakowski MA, Braun V, Lam GY, Yeung T, Heo WD, Meyer T, et al. The phosphoinositide phosphatase SopB manipulates membrane surface charge and trafficking of the Salmonella-containing vacuole. Cell host & microbe. 2010;7(6):453–62. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2010.05.011 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Vonaesch P, Sellin ME, Cardini S, Singh V, Barthel M, Hardt WD. The Salmonella Typhimurium effector protein SopE transiently localizes to the early SCV and contributes to intracellular replication. Cellular microbiology. 2014;16(12):1723–35. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12333 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Kamanova J, Sun H, Lara-Tejero M, Galan JE. The Salmonella Effector Protein SopA Modulates Innate Immune Responses by Targeting TRIM E3 Ligase Family Members. PLoS pathogens. 2016;12(4):e1005552 doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005552 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4825927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Keestra AM, Winter MG, Klein-Douwel D, Xavier MN, Winter SE, Kim A, et al. A Salmonella virulence factor activates the NOD1/NOD2 signaling pathway. mBio. 2011;2(6). doi: 10.1128/mBio.00266-11 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3238304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Chen LM, Bagrodia S, Cerione RA, Galan JE. Requirement of p21-activated kinase (PAK) for Salmonella typhimurium-induced nuclear responses. The Journal of experimental medicine. 1999;189(9):1479–88. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC2193063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Bruno VM, Hannemann S, Lara-Tejero M, Flavell RA, Kleinstein SH, Galan JE. Salmonella Typhimurium type III secretion effectors stimulate innate immune responses in cultured epithelial cells. PLoS pathogens. 2009;5(8):e1000538 doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000538 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC2714975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Silva M, Song C, Nadeau WJ, Matthews JB, McCormick BA. Salmonella typhimurium SipA-induced neutrophil transepithelial migration: involvement of a PKC-alpha-dependent signal transduction pathway. American journal of physiology Gastrointestinal and liver physiology. 2004;286(6):G1024–31. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00299.2003 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Hu GQ, Song PX, Chen W, Qi S, Yu SX, Du CT, et al. Cirtical role for Salmonella effector SopB in regulating inflammasome activation. Mol Immunol. 2017;90:280–6. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.07.011 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Ruan H, Zhang Z, Tian L, Wang S, Hu S, Qiao JJ. The Salmonella effector SopB prevents ROS-induced apoptosis of epithelial cells by retarding TRAF6 recruitment to mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;478(2):618–23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.07.116 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Verheij M, Bose R, Lin XH, Yao B, Jarvis WD, Grant S, et al. Requirement for ceramide-initiated SAPK/JNK signalling in stress-induced apoptosis. Nature. 1996;380(6569):75–9. doi: 10.1038/380075a0 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Hoffmann S, Schmidt C, Walter S, Bender JK, Gerlach RG. Scarless deletion of up to seven methyl-accepting chemotaxis genes with an optimized method highlights key function of CheM in Salmonella Typhimurium. PloS one. 2017;12(2):e0172630 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172630 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC5315404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Lotz M, Gutle D, Walther S, Menard S, Bogdan C, Hornef MW. Postnatal acquisition of endotoxin tolerance in intestinal epithelial cells. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2006;203(4):973–84. doi: 10.1084/jem.20050625 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2118301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Dupont A, Sommer F, Zhang K, Repnik U, Basic M, Bleich A, et al. Age-Dependent Susceptibility to Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) Infection in Mice. PLoS pathogens. 2016;12(5):e1005616 doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005616 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4861285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Hurley BP, Sin A, McCormick BA. Adhesion molecules involved in hepoxilin A3-mediated neutrophil transepithelial migration. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008;151(2):297–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03551.x ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC2276941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU wild type (WT) pWSK (filled circles), quadruple mutant ΔsopABE2sipA pWSK (open circles), ΔsopABE2sipA psopA (inverted open triangles), ΔsopABE2sipA psopB (open triangles), ΔsopABE2sipA psipA (open squares), or ΔsopABE2sipA psopE2 (open diamonds) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) isolated gentamicin-treated enterocytes at 4 days post infection (p.i.).. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl2 and (C) Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Viable counts in (D) total MLN homogenate, (E) total liver tissue homogenate and (F) total spleen tissue homogenate at 4 days post infection (p.i.). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 5–8 animals per group). (G) Immunostaining for Salmonella (red) in small intestinal tissue sections at 4 days p.i. with 100 CFU WT pWSK, ΔsopABE2sipA pWSK, ΔsopABE2sipA psopA, ΔsopABE2sipA psopB, ΔsopABE2sipA psipA, or ΔsopABE2sipA psopE2 S. Typhimurium. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (green), WGA (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (H) A confluent monolayer of polarized murine intestinal epithelial m-ICcl2 cells were infected at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1:10 with WT pWSK, SPI1 mutant ΔinvC, ΔsopABE2sipA pWSK, ΔsopABE2sipA psopA, ΔsopABE2sipA psopB, ΔsopABE2sipA psipA, or ΔsopABE2sipA psopE2 S. Typhimurium for 1 h at 37°C. Cells were subsequently treated with 100 μg/mL gentamicin for 1 h at 37°C, washed three times, and lyzed in 0.1% Triton X-100. The number of viable bacteria in cell lysates and inoculi was determined by serial dilution and plating. The number of intracellular, gentamicin-protected bacteria relative to the inoculum is shown (%). Results represent the mean ± SD.
(TIF)
1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT pWSK (filled circles), ΔsopABE2sipA pWSK (open circles), ΔsopABE2sipA psopE2 (open diamonds), or ΔsopABE2sipA psopE (half-filled diamonds) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) isolated gentamicin-treated enterocytes at 4 days p.i.. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl2 and (C) Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Viable counts in (D) total MLN homogenate, (E) total liver tissue homogenate, and (F) total spleen tissue homogenate at 4 days p.i.. Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 5–8 animals per group). (G) Immunostaining for Salmonella (red) in small intestinal tissue sections at 4 days p.i. with 100 CFU WT pWSK or ΔsopABE2sipA psopE S. Typhimurium. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (green), WGA (white) and DAPI (blue). Bar, 5 μm. (H) Gentamicin protection assay (as described under (H)) was performed with WT pWSK, ΔsopABE2sipA pWSK, ΔsopABE2sipA psopE2, or ΔsopABE2sipA psopE. The number of intracellular, gentamicin-protected bacteria relative to the inoculum is shown (%). Results represent the mean ± SD.
(TIF)
(A-C) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (filled circles), sopABE2sipA quadruple mutant (open circles), sopBE2sipA (inverted open triangles), sopAE2sipA (open triangles), sopABE2 (open squares), or sopABsipA mutant (open diamonds) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) MLN and (B) total spleen tissue homogenate at 4 days post infection (p.i.). (C) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 5–8 animals per group). (D) Gentamicin protection assay (as described in S1H Fig) was performed using WTpWSK, ΔinvC, ΔsopABE2sipA, ΔsopBE2sipA, ΔsopAE2sipA, ΔsopABE2, or ΔsopABsipA S. Typhimurium. The number of intracellular, gentamicin-protected bacteria relative to the inoculum is shown (%). Results represent the mean ± SD.
(TIF)
(A and B) 1-day-old MyD88+/+ and MyD88-/- mice were left untreated or orally infected with 100 CFU wild type S. Typhimurium. Relative expression of (A) Cxcl2 and (B) Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated from non-infected and infected MyD88+/+ mice as well as non-infected and infected MyD88-/- mice at 4 days p.i. were measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Relative expression from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 2–6 animals per group). The data for MyD88+/+ animals infected with S. Typhimurium WT are identical to Fig 1C and S3C Fig. (C) Survival following S. Typhimurium infection. 1-day-old MyD88+/+ (n = 12; solid line) and MyD88-/- (n = 12; broken line) mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT S. Typhimurium (broken line). Animals that had to be euthanized due to a rise in the clinical score were included in the analysis (see material and methods).
(TIF)
(A-C) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (filled circles) or ΔsopE2sipA S. Typhimurium (filled triangels). Viable counts in (A) MLN and (B) total spleen tissue homogenate at 4 days p.i.. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 3–5 animals per group). (D-F) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (filled circles) ΔsipA (open squares), ΔsipA complemented with psipA (filled squares), ΔsopE2 (open diamonds), or ΔsopE2 complemented with psopE2 (filled diamonds) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (D) MLN and (E) total spleen tissue homogenate at 4 days p.i.. (F) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 3–7 animals per group). The data for uninfected control animals and Salmonella WT infected mice are identical to S3A–S3C Fig.
(TIF)
(A-C) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (filled circles), ΔsopBE2 (inverted open triangles), or ΔsopAE2 (open triangles) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) MLN and (B) total spleen tissue homogenate at 4 days p.i.. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 3–8 animals per group). The data for uninfected control animals and Salmonella WT infected mice are identical to S3A–S3C Fig.
(TIF)
(A and B) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU wild type (WT) (filled circles), ΔsopB (filled triangles), or ΔsopB psopB (open triangles) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) total spleen tissue homogenate at 2 days post infection (p.i.). (B) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 2 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 3–5 animals per group). (C) Immunostaining for cleaved caspase 3 (cl. caspase 3, upper panel, red) and cleaved caspase 8 (cl. caspase 8, lower panel, red) in small intestinal tissue sections from healthy age-matched control animals (non-infected) or at 3 days p.i. with WT, ΔsopB and ΔsopB psopB S. Typhimurium. Counterstaining with E-cadherin (green), and DAPI (blue). Bar, 50 μm.
(TIF)
(A) Postnatal body weight gain of healthy and infected animals. 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were left untreated (solid line) or orally infected with 100 CFU WT (broken line) or ΔsopABE2 S. Typhimurium (dotted line). (B) Survival following S. Typhimurium infection. 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (solid line), ΔsopABE2 (broken line), or sipAK635A E637W ΔsopABE2 S. Typhimurium (broken line). Animals that had to be euthanized due to a rise in the clinical score were included in the analysis (see material and methods). (C) Total length (in cm) of the small intestine at 4 days p.i. and of uninfected age-matched control animals. 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were infected with 100 CFU WT, ΔsopBE2sipA (inverted open triangles), ΔsopAE2sipA (open triangles) ΔsopABE2 (open squares) and or ΔsopABsipA (open diamonds) S. Typhimurium. Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 3–5 animals per group). (D) Mucosal barrier integrity tested by serum quantification 4 hours after oral administration of FITC labeled-4kDa dextran. 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were infected with WT (filled circles), ΔsopABsipA (open diamonds), or ΔsopAE2sipA (open triangles) S. Typhimurium. FITC labeled-4 kDa dextran was quantified in serum at day 4 p.i.. (E and F) Flow cytometric analysis of lamina propria immune cells. 1-day-old mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT, ΔsopAE2sipA, ΔsopABsipA, or ΔsopABE2 S. Typhimurium and total SI leukocytes were analyzed by flow cytometry at day 4 p.i.. (E) Monocytes (Ly6ChiLy6G-CD11b+MHCIIlo/-CD45+DAPI-) and (F) neutrophils (Ly6G+Ly6CintCD11b+MHCIIlo/-CD45+DAPI-) are depicted as % of CD45+ cells. The results represent the mean values from at least two independent experiments (n = 4–6 per group). (G and H) Quantitative analysis (G) and immunostaining (H) of PMN infiltrating the small intestinal tissue. PMN from 10–20 image fields obtained from neonates infected with wild type (WT), ΔsipA, ΔsipA psipA, ΔsipA psipAD434A S. Typhimurium (n = 3–9) and uninfected age-matched control animals (n = 5) were analyzed at day 4 p.i.. Values and mean are shown. Bar, 25 μm. (I) Viable counts in isolated gentamicin-treated enterocytes at 2 days p.i. of 1-day-old mice with 100 CFU WT (filled circle), ΔsopABE2 (open squares), or sipAK635A E637W ΔsopABE2 S. Typhimurium (filled squares). Values and mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 4–6 animals per group).
(TIF)
(A-C) 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (filled circles), ΔsipA (open diamonds), ΔsipA complemented with psipAK635A E637W (half-filled diamonds), ΔsipA complemented with psipAD434A (filled squares), or ΔsipA complemented with psipAD434A K635A E637W (filled triangles) S. Typhimurium. Viable counts in (A) MLN and (B) total spleen tissue homogenate at 4 days p.i.. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR for Cxcl5 mRNA in total RNA prepared from enterocytes isolated at 4 days p.i.. Values were normalized to uninfected age-matched control animals (crosses). Individual values and the mean from at least two independent experiments are shown (n = 4–7 animals per group). The data for uninfected control animals and Salmonella WT infected mice are identical to S3A–S3C Fig. (D) Survival following S. Typhimurium infection. 1-day-old C57BL/6 mice were orally infected with 100 CFU WT (solid line), ΔsipA (broken line), or ΔsipA complemented with sipAK635A E637W (broken line) S. Typhimurium. Animals that had to be euthanized due to a rise in the clinical score were included in the analysis (see Material and Methods).
(TIF)
Strain name, designation, genotype description and reference are listed for all strains and plasmids used in the study.
(DOCX)
Oligonucleotide name and sequence are listed for all oligonucleotides used in the study.
(DOC)
Summary of the results obtained in this study using all bacterial mutants indicating the genotype, the time point of the analysis and the phenotype, namely enterocyte invasion, LAMP1 recruitment to the Salmonella microcolony, SPI2 T3SS reporter activation, transcriptional stimulation of the intestinal epithelium, intraepithelial proliferation and spread to spleen and liver tissue.
(DOC)
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.