Abstract
The scientific community has reported several cases of microbes that exhibit elevated rates of antibiotic resistance in different regions of the planet. Due to this emergence of antimicrobial resistant microorganisms, the use of antibiotics as promoters of livestock animals’ growth is being banned in most countries around the world. One of the challenges of agricultural immunology therefore is to find alternatives by modulating the immune system of animals in drug-independent safe food production systems. In this regard, in an effort to supplant antibiotics from bovine feeds, several alternatives were proposed including the use of immunomodulatory probiotics (immunobiotics). The purpose of this review is to provide an update of the status of the modulation of intestinal antiviral innate immunity of the bovine host by immunobiotics, and the beneficial impact of immunobiotics on viral infections, focused on intestinal epithelial cells (IECs). The results of our group, which demonstrate the capacity of immunobiotic strains to beneficially modulate Toll-like receptor 3-triggered immune responses in bovine IECs and improve the resistance to viral infections, are highlighted. This review provides comprehensive information on the innate immune response of bovine IECs against virus, which can be further investigated for the development of strategies aimed to improve defenses in the bovine host.
Keywords: immunobiotics, antiviral immunity, beneficial microbes, bovine rotavirus, toll-like receptor 3 pathway, inflammation, agricultural immunology
Introduction
Over the past decades, the global bovine production has been subjected to intensification, in order to improve efficiency of production because of the demand from a growing human population. The intensification of bovine production involved the application of confinement methods characterized by the concentration of animals in large outdoor feedlots or in specialized indoor environments. In confinement, the potential for transfer of pathogens among animals is higher, as there are more animals in a smaller space (1–3).
Severe gastrointestinal infectious diseases causing malabsorption and diarrhea are important causes of discomfort and death in young calves, resulting in important economic losses to bovine producers. Gastrointestinal infectious diseases are able to cause significant economic losses to the cattle industry in big cattle-producing countries and can impair the development of cattle industry in small cattle-producing countries (1–3). In particular, the neonatal gastroenteritis in the bovine host is a multifactorial disease. This disorder can be caused by different bacterial or viral pathogens, including bovine coronavirus (BCV), bovine rotavirus (BRV), and bovine viral diarrhea viruses (BVDV) (4, 5). Although these viral pathogens belong to distinct families and possess different physical characteristics, they are all able to infect intestinal epithelial cells (IECs), generate villous atrophy, and cause inflammatory intestinal tissue damage and diarrhea.
Probiotics are defined as live microorganisms with the capacity to confer a health benefit on the host when administered in adequate amounts. Among them, those that are able to impact on human and animal health by modulating the mucosal and systemic immune systems have been called immunobiotics. It has been reported that immunobiotic lactic acid bacteria are able to generate protection against viral pathogens by differentially modulating antiviral immune responses in humans and livestock animals like pigs (6, 7). It is also believed that immunobiotics could be used in cattle feeds to improve bovine health and produce safe animals (8–10).
The purpose of this review is to provide an update of the status of the modulation of intestinal antiviral innate immunity in the bovine host by immunobiotics, and their beneficial impact on viral infections. The results of our group, which demonstrate the capacity of immunobiotic strains to advantageously modulate Toll-like receptor (TLR)-3-triggered immune responses in bovine IECs and improve the resistance to viral infections, are particularly highlighted.
The Use of Probiotics in the Bovine Host
Before weaning, dairy calves are highly susceptible to infectious diseases. For several years, antimicrobial compounds have been used to reduce the severity and mortality of infectious diseases and to improve economic benefits in terms of enhanced bovine performance and diminished medication expenses. However, the use of antibiotics in livestock animal management is in question because of the enhanced resistance of microbes to antimicrobial compounds. Therefore, there is an urgent need to reduce and finally eliminate the use of antibiotics in livestock and for this purpose many feed additives have been proposed including beneficial microbes (8–10). In fact, research from the past decade has provided evidence that probiotic bacteria and prebiotics can be effectively used to improve health and growth in calves and reduce the use of antibiotics (Table 1), although detailed mechanistic studies were not performed. The production of antimicrobial compounds, inhibition of adherence or aggregation with pathogens and the modulation of the microbiota were described as mechanisms of probiotics action in the bovine host [reviewed in Ref. (10)]. Immunomodulation was also proposed as a mechanism of bovine probiotics as mentioned later.
Table 1.
Probiotics for the bovine host.
| Strain | Viability | Route | Host | Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus acidophilus LAC-300 | Viable | Oral | Holstein calves | Increase in body weight gain. Improvement in fecal scores | (11) |
| Bifidobacterium pseudolongum M-602 | Viable | Oral | Holstein calves | Increase in body weight gain. Improvement in fecal scores | (11) |
| Bifidobacterium thermophilum S-501, Lactobacillus acidophilus LAC-300, and Enterococcus faecium FA-5 | Viable | Oral | Holstein calves | No effect on body weight gain was observed. Reduction of diarrhea | (11) |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, Streptococcus termophilus, and Aspergillus niger | Viable | Oral | Holstein calves | Improvement in daily live weight gain and feed efficiency ratio. Reduction of diarrhea | (12) |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG | Viable | Oral | Holstein calves | The probiotic strain survived the gastrointestinal transit. No beneficial effect was recorded | (13, 14) |
| Saccharomyces boulardii | Viable | Oral | Holstein bull calves | Treated animals consumed more grain, had increased weight gain, and increased plasma glucose concentrations. Days with diarrhea were reduced | (15) |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus 15 | Viable | Oral | buffalo calve (1 day to 31 weeks) | Weight gain was improved and feed: gain ratio was reduced | (16) |
| Multispecies probiotic preparation: Lactobacillus acidophilus W55, Lactobacillus salivarius W57, Lactobacillus paracasei W56, Lactobacillus plantarum W59, Lactococcus lactis W58, and Enterococcus faecium W54 | Viable | Oral | Male Holstein-Friesian calves | Probiotics enhanced growth rate and average daily gain and feed efficiency were significantly improved. Modest effect on diarrhea | (17) |
| Calf-specific multistrain probiotic preparation (six lactobacilli strains) | Viable | Oral | Male Holstein-Friesian calves | Probiotics enhanced growth rate and average daily gain and feed efficiency were significantly improved. Treatment reduced the incidence of diarrhea and the fecal counts of coliforms | (17) |
| Lactobacillus casei subsp. casei JCM1134T and Dextran | Viable | Oral | Holstein dairy calves | Increase the milk production | (18) |
| Lactobacillus acidophillus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, and Enterococcus faecium | Viable | Oral | Holstein calves | Significant reduction of diarrhea but no effect on mastitis | (19) |
| Bacillus subtilis natto | Viable | Oral | Male Holstein calves | Increased average daily gain and feed efficiency. No difference in serum IgE, IgA, and IgM, whereas serum IgG and IFN-γ were higher in probiotic-treated than in the controls. | (20) |
| Lactobacillus plantarum 220, Enterococcus faecium 26, and Clostridium butyricum Miyari | Viable | Oral | Holstein bull calves | Increased the numbers of CD282+ monocytes, CD3+ T cells and CD4+, CD8+, and WC1+ γδ T cell in blood. Increment of production of IL-6, INF-γ, and TNF-α were also observed | (21) |
| Faecalibacterium prausnitzii 34, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii 35, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii 1S, and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii 2S | Viable | Oral | Preweaned dairy Holstein heifer calves | Decreased the incidence of severe diarrhea and related mortality rate, while increasing weight gain | (22) |
| Lactobacillus plantarum GF103 | Viable | Oral | Male Holstein calves | No significant differences were observed in dry matter intake or average daily gain, but the feed conversation ratio was improved. Treatment improved mitogen-induced lymphocyte proliferation | (23) |
| Kefir | Viable | Oral | Female Holstein calves calves | Kefir intake improved fecal scores and reduced days with diarrhea during the first 2 weeks of life. No effect on weight gain | (24) |
| Milk fortified with symbiotic complex containing prebiotics (mannan-oligossacharides) and probiotics (Lactobacillus acidophilus, Enterococcus faecium, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae) | Viable | Oral | Female Holstein heifer calves | Symbiotic did not affect weight gain or feed efficiency of calves but it improved fecal scores | (25) |
As described for other livestock animals, the most critical stage in the bovine life is the period from birth to weaning. During this stage factors like nutrition can directly affect the immune system development and function and impact later in bovine performance (26). However, nutritional interventions during this phase are often inappropriate due to the elevated costs of milk feeding. The administration of poor-quality milk or colostrum, and the additions of antibiotics are common practices. Poor nutrition during preweaning stage often conduces to low weaning weight and impaired immunity, thereby increasing losses related to disease. Therefore, the majority of research studying the influence of beneficial microbes in the bovine host has been performed during this period of life.
Early studies showed that orally administered Bifidobacterium pseudolongum M-602 or Lactobacillus acidophilus LAC-300 enhanced the gain of body weight and reduced diarrhea frequency in calves (11). Similarly, several subsequent studies reported that treatments with probiotic microorganisms beneficially influence body weight gain, body height, milk production, and the general health condition of calves (Table 1). Additionally, oral treatment with probiotics significantly reduced the incidence and the severity of gastrointestinal infections. Moreover, some studies have also shown that probiotic treatments are able to improve not only mucosal defenses in the bovine host but systemic immunity as well (20, 21).
Classical probiotic strains have been used to evaluate their beneficial effects on the bovine hosts including Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Enterococcus, Bacillus, and the yeast Saccharomyces (Table 1). More recently, new species of beneficial bacteria have been also tested as next-generation probiotics. In this regard, the obligate anaerobic, Gram-positive microorganism Faecalibacterium prausnitzii that belongs to the phylum Firmicutes has been tested as a potential probiotic for the bovine host (27). Oikonomou et al. (27) reported that the high relative abundance of this bacterium in the first week of life of Holstein calves was associated with improved weight gain and diminished occurrence of diarrhea. Recently, Foditsch et al. (22) confirmed the safety and efficacy of F. prausnitzii in young dairy heifers. Researchers reported that the oral administration of viable F. prausnitzii reduced severe diarrhea incidence and its related mortality rate. Moreover, F. prausnitzii treatment significantly enhanced the weight gain.
The anti-inflammatory properties of F. prausnitzii, including its ability to synthetize butyrate, were proposed as factors involved in the beneficial effects observed in calves. These works demonstrated that this intestinal bacterium could be a novel approach to enhance the intestinal health in calves and improve their body weight gain (22).
These studies indubitably show the potential of beneficial microbes to differentially modulate weight gain, intestinal hemostasis, and immunocompetence in young calves. However, the cellular and molecular interactions of probiotics with the cells of the bovine host have not been studied in depth. A better molecular understanding of how the selected beneficial microbes improve resistance against infections by antagonizing pathogens and/or modulating the immune system is needed.
Bovine IECs as a Model to Study Antiviral Immunity
It is considered that an important step forward toward the understanding of the cellular and molecular interactions of pathogenic or probiotic microorganisms with the bovine host is the establishment of appropriate in vitro systems models. Therefore, the development of suitable bovine cell cultures such as IECs would be of great value to advance in this field of research. Those cell cultures should be minutely characterized with regard to their permissiveness for bacterial and viral adhesion and invasion, and the ability to sense microbial-associated molecular patterns through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) (28).
Primary cultures of small or large IECs have been used to evaluate the effects of microbial virulence factors, toxic compounds, and antimicrobial factors in cattle. Moreover, those primary cultures have been also used for the study of innate immune responses through PRRs signaling (28–33). Soft mechanical agitation combined with enzymatic digestion using dispase and collagenase has been proved to successfully release viable intact bovine colonic cells. However, these cells suspensions contained contaminating non-epithelial cells (mostly fibroblasts) and therefore, a series of purification steps was required to obtain relatively pure bovine colonic cells. The development of primary bovine cell lines from rectum, colon and ileum was reported by Dibb-Fuller et al. (29). Those bovine primary cell cultures were successfully used to evaluate the interaction of several intestinal pathogenic bacteria with bovine IECs and to determine mechanisms of adherence and invasion. More recently, Zhan et al. (34) successfully cultured primary bovine IECs and established a novel clone cell method. Authors demonstrated the expression of E-cadherin and cytokeratin 18, as well as characteristics of epithelial-like morphology in this new cell line. However, the immunological characteristics of cells or viral infections have not been evaluated in those systems.
As mentioned earlier, viral infections in livestock animals could cause a fatal disease that implicate serious economic loses. Therefore, the effective and non-costly control of this type of infections is a key factor for improving animal production. It is believed that the clear and detailed understanding of viral pathogenicity as well as host immune response in the bovine host is necessary to develop strategies capable of reducing infectious disease caused by these viruses. In this sense, a deeper understanding of the molecular interactions of virus with bovine IECs is necessary for the development of better prevention strategies to improve protection in animals.
Bovine virus pathology and immune response have been studied mainly in heterologous systems including mouse models (35) and human cell lines (36). Taking into consideration the differences in viral strains, the specific receptors for virus uptake, the factors required for viral replication and pathogenesis as well as the specific species variations in innate immune responses; the information generated in those heterologous models may not be fully applicable to cattle. Therefore, scientists have tried to establish bovine systems for the study of viral infections. One of the earliest works able to confirm that cultured bovine IECs were susceptible to BRV infection was reported by Kaushik et al. (37). Epithelial cultures obtained from jejunal and ileal tissues were incubated with BRV and both cell types were similarly infected with the viral pathogen. Long incubation times of BRV with the epithelial cultures coming from jejunal and ileal tissues resulted in extensive cellular damage and reduced cell viability, which is in line with the knowledge that BRV is a lytic virus. Furthermore, BRV particles were recovered from the culture supernatants confirming that viral replication occurred in bovine IECs (37). However, the immune response was not studied. In addition, those epithelial cell cultures contained fibroblasts, and therefore if the immune response is evaluated in this system it cannot be discriminated whether the response (cytokine production, for example) is mediated by one or both cells, especially considering that the authors also demonstrated that BRV infected and replicated in fibroblasts (37).
Bovine primary IEC cultures have been of value to study the molecular mechanisms involved in diseases caused by pathogens. However, the cellular and molecular interactions of beneficial or commensal microorganisms with bovine IECs cells have been less examined. In addition, the intestinal cell lines established from adult cattle may have limitations in the study of infections with BRV, BVDV, or BCV, since these viruses infect IECs in the gut of young calves (4, 5).
In order to understand: (i) the pathogenesis of bovine viral infections and the subsequent gastrointestinal diseases, (ii) the role of bovine IECs in the generation of mucosal immune responses, and (iii) the effect of beneficial microbes that may be used to advantageously modulate the antiviral immune response in bovine IECs; we have developed an immortalized bovine IEC line from young calves: bovine intestinal epithelial (BIE) cells (38).
Bovine intestinal epithelial cells have an epithelial-like morphology and they grow forming a monolayer with cells that establish close contact between them (38). Scanning electron microscopy analysis revealed that 3-day-old BIE cells have microvilli-like structures on their surface that are irregular and slender. These cellular structures increase in complexity as the cells grow as observed in 10-day-old BIE cells (38). The evaluations of the expression of cytokeratin and specific villin protein, which are known as markers of epithelial cells, have demonstrated that BIE cells are strongly positive for both proteins. In contrast, vimentin and desmin that are markers for mesenchymal cells and muscle cells, respectively, were not found in BIE cells.
Bovine intestinal epithelial cells also expressed the cell-to-cell adhesion molecules ZO-1 and beta-catenin (39). Both proteins were strongly positive in the cell-to-cell contact region when cells reached confluence. Moreover, the functional integrity of BIE cells gradually increased with time as indicated by studies of TEER and paracellular permeability (38). These results provide clear evidence of the intestinal epithelial nature of BIE cells.
Immunobiology of Bovine Epithelial Cells
Significant progress has been made in the understanding of both the beneficial and detrimental roles of TLR3 in innate antiviral immune responses in mucosal tissues (6, 40). Therefore, to decipher the exact role of TLR3 in antiviral defenses in IECs is of value to understand the mechanisms that activate and regulate the intestinal immune system of the host. Few studies have been conducted on cattle. Those studies are of importance since the determination of the mechanisms involved in the activation and regulation of TLR3 in bovine IECs could give the scientific basis for the development of efficient preventive or therapeutic strategies for reducing severity and mortality of viral diseases, including oral vaccines and functional feeds. Then, the expression of mRNAs of TLRs was evaluated in BIE cells and it was reported that all the genes for these receptors were expressed in this cell line (41). TLR1, TLR3, TLR4, and TLR6 were strongly expressed while TLR5, TLR9, TLR2, and TLR7 were expressed modestly. We were especially interested in expression of TLR3 as the most important receptor detecting double-stranded genomic RNA (dsRNA) from viruses.
Therefore, to confirm these findings, we further examined the expression of TLR3 protein in BIE cells by immunohistochemical analysis and demonstrated that this PRRs is strongly expressed in the cytoplasm of BIE cells (42). Of note, no TLR3expression was detected at the BIE cell surface. Therefore, BIE cells, in addition to displaying characteristics of epithelial cells like those mentioned earlier such as microvilli-like structures, and strong expression of cell-to-cell junctional proteins (38), they also express TLR3 and thus are similar to the IECs of other species.
The innate immune response induced by TLR3 activation in BIE cells was also studied. BIE cells were treated with the TLR3 agonist poly(I:C) and an upregulation of type I interferon (IFN), and proinflammatory cytokines expression was detected. The changes in the expression of inflammatory factors induced by poly(I:C) in BIE cells correlate with the changes reported in various intestinal viral infections of cattle and other hosts. For instance, enhanced gene expression of CCL5 (RANTES), CXCL10 (IP-10), CXCL8 (IL-8), and CCL2 (MCP-1) were observed in rotavirus-infected HT-29 cells (43, 44). In addition, in vitro studies showed that the challenge of bovine intestinal tissues with BRV or BCV activated TLR3, upregulated nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and increase IL-6 production (4). These findings indicate that BIE cells are valuable tools for the in vitro study of immune responses mediated by TLR3 in bovine IECs.
Bovine rotavirus is able to induce a potent inflammatory response mediated by IFN and IFN-induced genes as well as inflammatory cytokines. In this regard, studies performed in HT29 cells infected with BRV (A5-13 strain) demonstrated that viral infection significantly upregulated most of the IFN-inducible genes including IL-18, IFN-α-inducible protein 6, IFN-induced transmembrane protein 3, TAP1, DDX58 [retinoic acid inducible gene-I (RIG-I)], and 2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthetase (OAS) 1 as well as several cytokines such as IL-8, CCL5, CXCL10, and CXCL11 (36). Few studies evaluated the BRV infection and its immune responses by using in vivo or in vitro bovine systems. By performing an intestinal loop surgical technique, Aich et al. (4) investigated the innate immune responses against bovine BRV in newborn calves. BRV (field isolate BRV85) challenge was able to induce accumulation of fluid and visible histological alterations in the gut of infected animals. Moreover, transcriptional profile of gene expression analysis and qPCR revealed that BRV enhanced TLR3, NF-κB p65, and IL-6. In addition, IRF1, a transcriptional regulator involved in the activation of IFN responses, was activated after rotaviral challenge (4).
We demonstrated that 10-days old BIE cells have developed microvilli-like structures on their surface (45). These characteristics of BIE cells together with their capacity to respond to TLR3 activation allowed us to hypothesize that this cell line could be a valuable in vitro tool for studying the interactions between BRV and bovine IECs. Therefore, we compared the infection capacity of four rotavirus strains in BIE cells including human (Wa), murine (EW), porcine (OSU), and bovine (UK), and we found that BIE cells can be effectively infected with the four rotavirus strains (45). Our results showed that 3-day-old BIE cells were more resistant to rotavirus infection than 10-day cultured cells, which probably related to the differences in the length and number of microvilli present on their surfaces. As we mentioned previously, the presence of these cellular structures is important for rotaviral infection since it was suggested that differentiated non-dividing mature enterocytes express the factors that are essential for the efficient rotavirus infection and replication (46, 47). In addition, we found significant differences regarding the viral titers when rotaviruses of different origins were compared. BIE cells were highly infected by bovine and porcine strains, whereas human and murine rotavirus showed a lower capacity to infect this bovine cell line (45). We also observed that viral titers were higher in BIE cells infected with UK than OSU strains, confirming that BRV strain isolated from cattle has a higher capacity to infect these cells. This is in line with previous studies that reported that the infection of porcine small intestinal epithelial (IPEC-J2) cells with OSU rotavirus induced a higher cytopathic effect and significantly reduced cell survival when compared with Wa strain (48). Moreover, our results in BIE cells are also in agreement with our results in porcine IECs (PIE cells) that showed a higher capacity of OSU rotavirus to infect those cells when compared to UK, Wa, or EW strains (49).
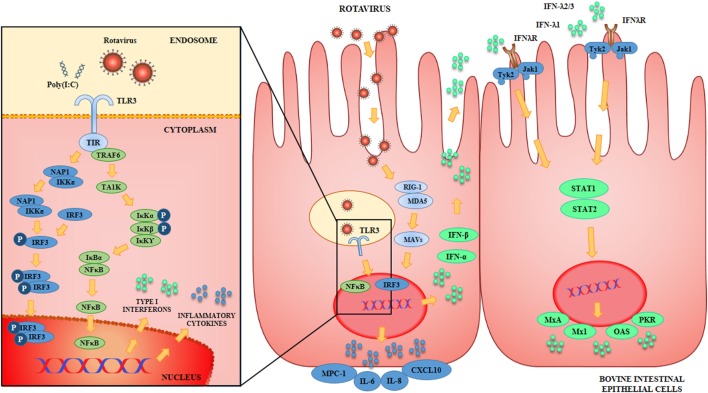
The innate immune response triggered by BRV infection in BIE cells was also characterized (Figure 1). We observed that BRV challenge activated antiviral PRRs in BIE cells and induced immune responses characterized by IFN regulatory factor-3 (IRF3) and NF-κB activation, with the subsequent upregulation of IFN-β and inflammatory chemokines and cytokines. Those results are in agreement with the innate immune mechanisms described for BRV infection in several experimental models as mentioned previously (4, 35, 36). Of interest, we also observed that UK rotavirus was able to induce a stronger innate immune response in BIE cells than OSU strain as demonstrated by the higher levels of expression of inflammatory factors IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, and IFN-β.
Figure 1.
Antiviral Innate immune response against rotavirus in bovine intestinal epithelial (BIE) cells. Rotavirus double-stranded genomic RNA activates toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), retinoic acid inducible gene-I (RIG-I), and melanoma differentiation-associated gene-5 (MDA-5), which are pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) expressed in BIE cells. Cellular signaling cascades are activated and converge at the level of interferon (IFN) regulatory factor-3 (IRF3) that upregulate the expression of type I (IFN-α, IFN-β) and type III (IFNλ1, IFNλ2/3) IFN, which in turn induces the synthesis of IFN-stimulated genes with antiviral activities including: myxovirus resistance 1 IFN-inducible protein (Mx1), MxA, ribonuclease L (RNaseL), 2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthetase (OAS), and protein kinase R (PKR). Antiviral PRRs also activate nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway and induce the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines including: interleukin 6 (IL-6), IL-8, monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1/CCL2), and IFN gamma-induced protein 10 (IP-10/CXCL10).
The, BIE cells have several characteristics that make them extremely interesting for the study of BRV pathogenesis, and the molecular mechanisms involved in the generation of innate immune responses. In addition, this cell line could be of value for the evaluation of treatments aimed to beneficially modulate antiviral defenses and reduce inflammatory-mediated damage.
Bovine IECs as a Model to Select and Characterize Immunobiotics with Antiviral Activity
The capacity of beneficial microbes to differentially modulate the response of BIE cells to TLR3 stimulation was evaluated by using several lactobacilli and bifidobacteria strains (42, 45) (Figure 2). Some strains such as L. rhamnosus LA-2, S. thermophilus TMC1543 (42), B. infantis MCC12, and B. breve MCC1274 (45) were able to enhance IFN-β levels after poly(I:C) challenge. The improved production of IFN-β by BIE cells after TLR3 activation induced by those probiotic strains may have significant in vivo effects in the protection against enteric viruses. It is well known that IFN-α and IFN-β are important factors of the innate immune response against viral infections. Type I IFNs, after their interaction with the IFN-α/β receptor (IFNAR), upregulate the expression of hundred of antiviral proteins capable to reduce or inhibit viral replication and promote viral clearance. In this regard, transcriptomic analyses of bovine intestinal tissues after the challenge with BRV or BCV have shown that the expression of several IFN-regulated genes is reduced, supporting the conclusion that both viruses have developed mechanism(s) to inhibit immune responses mediated by IFNs (4). Moreover, it has been reported that BVDV is able to impair the induction of type I IFN, which not only affect innate immunity, but in addition interferes with the appropriate development of adaptive immune defenses (5, 50). Based on these findings, immunobiotics that enhance IFN-β production in BIE cells could have a prominent role in the reinforcement of innate and adaptive immune responses against bovine intestinal virus.
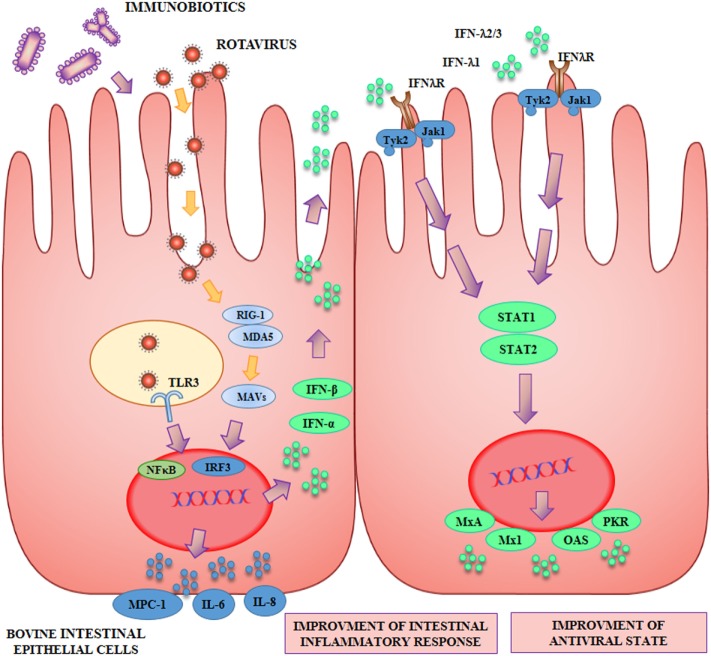
Figure 2.
Beneficial effects of immunobiotics on the antiviral innate immune response against rotavirus in bovine intestinal epithelial (BIE) cells. Rotavirus doublestranded genomic RNA activates toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), retinoic acid inducible gene-I (RIG-I), and melanoma differentiation-associated gene-5 (MDA-5), which are pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) expressed in IECs. Cellular signaling cascades mediated by interferon (IFN) regulatory factor-3 (IRF3) upregulate the expression of type I (IFN-α, IFN-β), and type III (IFNλ1, IFNλ2/3) IFN, which in turn induces the synthesis of IFN-stimulated genes with antiviral activities including: myxovirus resistance 1 IFN-inducible protein (Mx1), MxA, ribonuclease L (RNaseL), 2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthetase (OAS), and protein kinase R (PKR). Antiviral PRRs also activate nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway and induce the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines including: interleukin 6 (IL-6), IL-8, monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1/CCL2), and IFN gamma-induced protein 10 (IP-10/CXCL10). Preventive treatment of BIE cells with immunobiotics increase the activation of IRF3, improve the production of the antiviral factors and differentially regulate the expression of inflammatory mediators.
As the duration and intensity of proinflammatory factors secretion after TLR3 activation by viral dsRNA can become harmful to the host (51), we also evaluated the levels of key inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in BIE cells including IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1. Our results indicated that BIE cells pretreated with the probiotic strain L. casei TMC0409 (42) produced lower levels of MCP-1, IL-6, and IL-8 when compared with control cells after stimulation with poly(I:C). It has been well established that the unregulated activation of TLR3 is capable to mediate detrimental inflammatory responses in the intestine, thus contributing to the tissue damage induced by viral infections (6, 52). Therefore, the diminished production of proinflammatory factors after the exposure to immunobiotics may allow a better control of the inflammatory responses and reduce the tissue injury mediated by this mechanism. In this way, beneficial bacteria like the TMC0409 strain may offer a different protection mechanism against bovine viral infection.
In conclusion, the BIE cells in vitro system was of value for the efficient screening of two types of immunomodulatory probiotic strains capable to improve protection against viral intestinal diseases in the bovine host: (i) strains with the ability to increase antiviral defenses like L. rhamnosus LA-2, B. infantis MCC12 and B. breve MCC1274 and (ii) strains with anti-inflammatory capacities like L. casei TMC0409.
Considering the mentioned results and that some recent research indicated that the presence of bifidobacteria in the gut of young calf is associated with a good health status (53), we next aimed to evaluate the capacity of the selected immunobiotic bifidobacteria strains to improve resistance of BIE cells to viral challenge.
Studies with the porcine IPEC-J2 cell line, demonstrated that L. rhamnosus GG reduced the mucin and IL-6 secretion response triggered by porcine rotavirus, diminishing the inflammatory damage (48). Our own studies in PIE cells also demonstrated that selected immunobiotic strains were capable to upregulate IFN-β expression in response to poly(I:C) stimulation (54, 55). Moreover, we recently demonstrated that B. infantis MCC12 and B. breve MCC1274 were capable to significantly improve the resistance of PIE cells to porcine rotavirus infection (49). Both immunobiotic bifidobacteria strains significantly enhanced the expression of IFN-β, MxA and ribonuclease L (RNaseL) in infected PIE cells, reducing viral replication. Therefore, we aimed to determine whether the studies performed in our laboratory using porcine IECs could be reproduced in BIE cells. Then, we evaluated whether immunobiotic B. infantis MCC12 and B. breve MCC1274 were able to protect BIE cells against BRV infection.
We showed that BIE cells treated with bifidobacteria were more resistant to BRVs infection, and that MCC12 and MCC1274 treatments significantly increased IFN-β in BRV-infected BIE cells. This is in line with the observation that BRV replication is restricted in susceptible cells by preventive treatment with recombinant IFN-β (56). Likewise, administration of recombinant IFN-β to newborn calves prior to BRV challenge suppresses virus replication and diminishes disease severity (57). A recent study reported the antiviral activity of bacterial strains in mice and Caco-2 cells, in which the probiotic B. longum SPM1206 and L. ruminis SPM0211 induced the expression of IFN-β in response to human rotavirus (58). Moreover, these probiotic strains had the capacity to inhibit RVs infection through the increase IFN signaling component (STAT1), and IFN-inducible antiviral effectors MXA, protein kinase R (PKR), and OAS in mice. In line with these findings, our recent immunotranscriptomic analysis showed that both B. infantis MCC12 and B. breve MCC1274 are able to improve the expression of several antiviral factors through their capacity to improve IFN-β production. Both bifidobacteria improved the expression of IFN-α and IFN-β as well as the antiviral factors RNASEL, MX1, and MX2 when compared to controls. In addition, bifidobacteria increased the expression of NLRP3 [Albarracin et al. (59), in preparation]. In agreement with the central role of IFN-β in the protection of BIE cells against BRV, we also observed that B. breve MCC1274 induced an earlier and higher activation of TRAF3, higher levels of IFN-β and significantly lower titers of BRV in infected BIE cells when compared with B. infantis MCC12. The mechanism(s) (probiotic molecules and host receptors and signaling pathways) by which these immunobiotic bifidobacteria induce higher expression of IFN-β in BRV-infected BIE cells is an interesting topic for future research.
Conclusion
Prophylactic administration of low doses of antibiotics has been historically used to promote the growth and avoid infectious diseases in livestock animals. However, due to the emergence of antibiotic resistant microbes, several governments in countries around the world have prohibited the use of antibiotics as growth promoters for animals.
One of the most important challenges of agricultural immunology therefore is to find alternatives for developing drug-independent safe food production systems by modulating the immune system of animals. The work reviewed here encourages the research of probiotics to beneficially modulate the immune system of the bovine host. This review provides comprehensive information on the innate antiviral immune response of bovine IECs against virus, which can be further studied for the development of strategies aimed to improve antiviral defenses. The analyzed data also suggest that beneficial microbes have a great potential to be used as antiviral alternatives able to reduce severity of infections in the bovine host.
The development of specific in vitro study systems for cattle such as BIE cells as well as the selection and characterization of microbes that exert beneficial functions specifically and efficiently in the bovine host are key points for the successful development of immunomodulatory feeds aimed to protect against infections and reduce or avoid the use of antibiotics.
Author Contributions
All the authors contributed equally to the design, writing, and editing of the review article.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Funding. This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B)(2) (24380146, 16H05019), Challenging Exploratory Research (23658216, 26660216, 16K15028), and Open Partnership Joint Projects of JSPS Bilateral Joint Research Projects from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) to HK and by an ANPCyT–FONCyT Grant PICT-2013 (No. 3219) to JV. This work was also supported by JSPS Core-to-Core Program A (Advanced Research Networks) entitled: “Establishment of international agricultural immunology research-core for a quantum improvement in food safety.” This study was also supported by grants for “Scientific Research on Innovative Areas” from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Science, Sports and Technology (MEXT) of Japan (grant numbers: 16H06429, 16K21723, and 16H06435).
References
- 1.Cappellini OR. Dairy Development in Argentina. Rome: FAO; (2011). [Google Scholar]
- 2.Greiser-Wilke I, Grummer B, Moennig V. Bovine viral diarrhoea eradication and control programmes in Europe. Biologicals (2003) 31(2):113–8. 10.1016/S1045-1056(03)00025-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Richter V, Lebl K, Baumgartner W, Obritzhauser W, Käsbohrer A, Pinior B. A systematic worldwide review of the direct monetary losses in cattle due to bovine viral diarrhoea virus infection. Vet J (2017) 220:80–7. 10.1016/j.tvjl.2017.01.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Aich P, Wilson HL, Kaushik RS, Potter AA, Babiuk LA, Griebel P. Comparative analysis of innate immune responses following infection of newborn calves with bovine rotavirus and bovine coronavirus. J Gen Virol (2007) 88:2749–61. 10.1099/vir.0.82861-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lee SR, Pharr GT, Boyd BL, Pinchuk LM. Bovine viral diarrhea viruses modulate toll-like receptors, cytokines and co-stimulatory molecules genes expression in bovine peripheral blood monocytes. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis (2008) 31:403–18. 10.1016/j.cimid.2007.06.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Villena J, Vizoso-Pinto MG, Kitazawa H. Intestinal innate antiviral immunity and immunobiotics: beneficial effects against rotavirus infection. Front Immunol (2016) 7:563. 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00563 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kandasamy S, Vlasova AN, Fischer DD, Chattha KS, Shao L, Kumar A, et al. Unraveling the differences between Gram-positive and Gram-negative probiotics in modulating protective immunity to enteric infections. Front Immunol (2017) 8:334. 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00334 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nader-Macías ME, Otero MC, Espeche MC, Maldonado NC. Advances in the design of probiotic products for the prevention of major diseases in dairy cattle. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol (2008) 35:1387–95. 10.1007/s10295-008-0438-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Maldonado NC, de Ruiz CS, Otero MC, Sesma F, Nader-Macías ME. Lactic acid bacteria isolated from young calves-characterization and potential as probiotics. Res Vet Sci (2012) 92:342–9. 10.1016/j.rvsc.2011.03.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Uyeno Y, Shigemori S, Shimosato T. Effect of probiotics/prebiotics on cattle health and productivity. Microbes Environ (2015) 30(2):126–32. 10.1264/jsme2.ME14176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Abe F, Ishibashi N, Shimamura S. Effect of administration of bifidobacteria and lactic acid bacteria to newborn calves and piglets. J Dairy Sci (1995) 78(12):2838–46. 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(95)76914-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Işik M, Ekimler F, Ozen N, Firat MZ. Effects of using probiotics on the growth performance and health of dairy calves. Turk J Vet Anim Sci (2004) 28(1):63–9. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ewaschuk JB, Naylor JM, Chirino-Trejo M, Zello GA. Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG is a potential probiotic for calves. Can J Vet Res (2004) 68(4):249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ewaschuk JB, Zello GA, Naylor JM. Lactobacillus GG does not affect D-lactic acidosis in diarrheic calves, in a clinical setting. J Vet Intern Med (2006) 20(3):614–9. 10.1892/0891-6640(2006)20[614:LGDNAD]2.0.CO;2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Galvão KN, Santos JE, Coscioni A, Villaseñor M, Sischo WM, Berge ACB. Effect of feeding live yeast products to calves with failure of passive transfer on performance and patterns of antibiotic resistance in fecal Escherichia coli. Reprod Nutr Dev (2005) 45(4):427–40. 10.1051/rnd:2005040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ramaswami N, Chaudhary LC, Agarwal N, Kamra DN. Effect of lactic acid producing bacteria on the performance of male crossbred calves fed roughage based diet. Asian-australas J Anim Sci (2005) 18(8):1110. 10.5713/ajas.2005.1110 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Timmerman HM, Mulder L, Everts H, Van Espen DC, Van Der Wal E, Klaassen G, et al. Health and growth of veal calves fed milk replacers with or without probiotics. J Dairy Sci (2005) 88(6):2154–65. 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(05)72891-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yasuda K, Hashikawa S, Sakamoto H, Tomita Y, Shibata S, Fukata T. A new synbiotic consisting of Lactobacillus casei subsp. casei and dextran improves milk production in Holstein dairy cows. J Vet Med Sci (2007) 69(2):205–8. 10.1292/jvms.69.205 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Batista CG, Coelho SG, Rabelo E, Lana AMQ, Carvalho AU, Reis RB, et al. Performance and health of calves fed milk without antimicrobials residue or milk from mastitis treated cows with or without probiotic. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootech (2008) 60(1):185–91. 10.1590/S0102-09352008000100026 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sun P, Wang JQ, Zhang HT. Effects of Bacillus subtilis natto on performance and immune function of preweaning calves. J Dairy Sci (2010) 93(12):5851–5. 10.3168/jds.2010-3263 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Qadis AQ, Goya S, Yatsu M, Yoshida YU, Ichijo T, Sato S. Effects of a bacteria-based probiotic on subpopulations of peripheral leukocytes and their cytokine mRNA expression in calves. J Vet Med Sci (2014) 76(2):189–95. 10.1292/jvms.13-0534 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Foditsch C, Pereira RVV, Ganda EK, Gomez MS, Marques EC, Santin T, et al. Oral administration of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii decreased the incidence of severe diarrhea and related mortality rate and increased weight gain in preweaned dairy heifers. PLoS One (2015) 10(12):e0145485. 10.1371/journal.pone.0145485 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhang R, Zhou M, Tu Y, Zhang NF, Deng KD, Ma T, et al. Effect of oral administration of probiotics on growth performance, apparent nutrient digestibility and stress-related indicators in Holstein calves. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (2016) 100(1):33–8. 10.1111/jpn.12338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fouladgar S, Shahraki AD, Ghalamkari GR, Khani M, Ahmadi F, Erickson PS. Performance of Holstein calves fed whole milk with or without kefir. J Dairy Sci (2016) 99(10):8081–9. 10.3168/jds.2016-10921 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Marcondes MI, Pereira TR, Chagas JC, Filgueiras EA, Castro MM, Costa GP, et al. Performance and health of Holstein calves fed different levels of milk fortified with symbiotic complex containing pre- and probiotics. Trop Anim Health Prod (2016) 48(8):1555–60. 10.1007/s11250-016-1127-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Drackley JK. Calf nutrition from birth to breeding. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract (2008) 24(1):55–86. 10.1016/j.cvfa.2008.01.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Oikonomou G, Teixeira AG, Foditsch C, Bicalho ML, Machado VS, Bicalho RC. Fecal microbial diversity in pre-weaned dairy calves as described by pyrosequencing of metagenomic 16S rDNA. Associations of Faecalibacterium species with health and growth. PLoS One (2013) 8:e63157. 10.1371/journal.pone.0063157 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bridger PS, Mohr M, Stamm I, Fröhlich J, Föllmann W, Birkner S, et al. Primary bovine colonic cells: a model to study strain-specific responses to Escherichia coli. Vet Immunol Immunopathol (2010) 137(1–2):54–63. 10.1016/j.vetimm.2010.04.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dibb-Fuller MP, Best A, Stagg DA, Cooley WA, Woodward MJ. An in-vitro model for studying the interaction of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and other enteropathogens with bovine primary cell cultures. J Med Microbiol (2001) 50(9):759–69. 10.1099/0022-1317-50-9-759 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Follmann W, Weber S, Birkner S. Primary cell cultures of bovine colon epithelium: isolation and cell culture of colonocytes. Toxicol In Vitro (2000) 14:435–45. 10.1016/S0887-2333(00)00033-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hoey DEE, Sharp L, Currie C, Lingwood CA, Gally DL, Smith DGE. Verotoxin 1 binding to intestinal crypt epithelial cells results in localization to lysosomes and abrogation of toxicity. Cell Microbiol (2003) 5(2):85–97. 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2003.00254.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rusu D, Loret S, Peulen O, Mainil J, Dandrifosse G. Immunochemical, biomolecular and biochemical characterization of bovine epithelial intestinal primocultures. BMC Cell Biol (2005) 6:42. 10.1186/1471-2121-6-42 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Baskaran S, Venkitanarayanan A. Plant-derived antimicrobials reduce E. coli O157:H7 virulence factors critical for colonization in cattle gastrointestinal tract in vitro. Biomed Res Int (2014) 2014:212395. 10.1155/2014/212395 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhan K, Lin M, Liu MM, Sui YN, Zhao GQ. Establishment of primary bovine intestinal epithelial cell culture and clone method. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim (2017) 53(1):54–7. 10.1007/s11626-016-0082-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rathi R, Kadian SK, Khurana B, Grover YP, Gulati BR. Evaluation of immune response to bovine rotavirus following oral and intraperitoneal inoculation in mice. Indian J Exp Biol (2007) 45:212–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bagchi P, Nandi S, Chattopadhyay S, Bhowmick R, Halder UC, Nayak MK, et al. Identification of common human host genes involved in pathogenesis of different rotavirus strains: an attempt to recognize probable antiviral targets. Virus Res (2012) 169(1):144–53. 10.1016/j.virusres.2012.07.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kaushik RS, Begg AA, Wilson HL, Aich P, Abrahamsen MS, Potter A, et al. Establishment of fetal bovine intestinal epithelial cell cultures susceptible to bovine rotavirus infection. J Virol Methods (2008) 148(1–2):182–96. 10.1016/j.jviromet.2007.11.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Miyazawa K, Hondo T, Kanaya T, Tanaka S, Takakura I, Itani W, et al. Characterization of newly established bovine intestinal epithelial cell line. Histochem Cell Biol (2010) 133(1):125–34. 10.1007/s00418-009-0648-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hollande F, Lee DJ, Choquet A, Roche S, Baldwin GS. Adherens junctions and tight junctions are regulated via different pathways by progastrin in epithelial cells. J Cell Sci (2003) 116:1187–97. 10.1242/jcs.00321 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kitazawa H, Villena J. Modulation of respiratory TLR3-anti-viral response by probiotic microorganisms: lessons learned from Lactobacillus rhamnosus CRL1505. Front Immunol (2014) 5:201. 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00201 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Takanashi N, Tomosada Y, Villena J, Murata K, Takahashi T, Chiba E, et al. Advanced application of bovine intestinal epithelial cell line for evaluating regulatory effect of lactobacilli against heat-killed enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-mediated inflammation. BMC Microbiol (2013) 13:54. 10.1186/1471-2180-13-54 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chiba E, Villena J, Hosoya S, Takanashi N, Simazu T, Aso H, et al. A newly established bovine intestinal epithelial cell line is effective for in vitro screening of potential antiviral immunobiotic microorganisms for cattle. Res Vet Sci (2012) 93:688–94. 10.1016/j.rvsc.2011.10.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Rollo EE, Kumar KP, Reich NC, Cohen J, Angel J, Greenberg HB, et al. The epithelial cell response to rotavirus infection. J Immunol (1999) 163(8):4442–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Xu J, Yang Y, Wang C, Jiang B. Rotavirus and coxsackievirus infection activated different profiles of toll-like receptors and chemokines in intestinal epithelial cells. Inflamm Res (2009) 58(9):585–92. 10.1007/s00011-009-0022-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kobayashi H, Kanmani P, Ishizuka T, Miyazaki A, Soma J, Albarracin L, et al. Development of an in vitro immunobiotic evaluation system against rotavirus infection in bovine intestinal epitheliocytes. Benef Microbes (2017) 8(2):309–21. 10.3920/BM2016.0155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lin CL, Chen SC, Liu SY, Chen KT. Disease caused by rotavirus infection. Open Virol J (2014) 8:14–9. 10.2174/1874357901408010014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chang K, Kim Y, Saif LJ. Rotavirus and reovirus. 10th ed In: Zimmerman JJ, Karriker LA, Ramirez A, Schwartz KJ, Stevenson GW, editors. Diseases of Swine. West Sussex, UK: Wiley-Blackwell; (2012). p. 621–34. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Liu F, Li G, Wen K, Bui T, Cao D, Zhang Y, et al. Porcine small intestinal epithelial cell line (IPEC-J2) of rotavirus infection as a new model for the study of innate immune responses to rotaviruses and probiotics. Viral Immunol (2010) 23:135–49. 10.1089/vim.2009.0088 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ishizuka T, Kanmani P, Kobayashi K, Miyazaki A, Soma J, Suda Y, et al. Immunobiotic bifidobacteria strains modulate rotavirus immune response in porcine intestinal epitheliocytes via pattern recognition receptor signaling. PLoS One (2016) 11:e0152416. 10.1371/journal.pone.0152416 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Peterhans E, Jungi TW, Schweizer M. BVDV and innate immunity. Biologicals (2003) 31(2):107–12. 10.1016/S1045-1056(03)00024-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Vercammen E, Staal J, Beyaert R. Sensing of viral infection and activation of innate immunity by toll-like receptor 3. Clin Microbiol Rev (2008) 21(1):13–25. 10.1128/CMR.00022-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zhou R, Wei H, Sun R, Zhang J, Tian Z. NKG2D recognition mediates toll-like receptor 3 signaling-induced breakdown of epithelial homeostasis in the small intestines of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2007) 104(18):7512–5. 10.1073/pnas.0700822104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bunešová V, Domig KJ, Killer J, Vlková E, Kopečný J, Mrázek J, et al. Characterization of bifidobacteria suitable for probiotic use in calves. Anaerobe (2012) 18(1):166–8. 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2011.09.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hosoya S, Villena J, Shimazu T, Tohno M, Fujie H, Chiba E, et al. Immunobiotic lactic acid bacteria beneficially regulate immune response triggered by poly(I:C) in porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Vet Res (2011) 42:111. 10.1186/1297-9716-42-111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Villena J, Kitazawa H. Modulation of intestinal TLR4-inflammatory signalling pathways by probiotic microorganisms: lessons learned from Lactobacillus jensenii TL2937. Front Immunol (2014) 4:512. 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00512 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Papp H, Laszlo B, Jakab F, Ganesh B, De Grazia S, Matthijnssens J, et al. Review of group A rotavirus strains reported in swine and cattle. Vet Microbiol (2013) 165:190–9. 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.03.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Arnold MM, Sen A, Greenberg HB, Patton JH. The battle between rotavirus and its host for control of the interferon signaling pathway. PLoS Pathog (2013) 9:e1003064. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003064 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kang JY, Lee DK, Ha NJ, Shin HS. Antiviral effects of Lactobacillus ruminis SPM0211 and Bifidobacterium longum SPM1205 and SPM1206 on rotavirus-infected Caco-2 cells and a neonatal mouse model. J Microbiol (2015) 53:796–803. 10.1007/s12275-015-5302-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Albarracin L, Kobayashi H, Iida H, Sato N, Nochi T, Aso H, et al. Transcriptomic analysis of the innate antiviral immune response in porcine intestinal epithelial cells: influence of immunobiotic lactobacilli. Front Immunol (2017) 8:57. 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]