Abstract
Multiple signals control the balance between proliferation and differentiation of neural progenitor cells during corticogenesis. A key point of this regulation is the control of G1 phase length, which is regulated by the Cyclin/Cdks complexes. Using genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation assay and mouse genetics, we have explored the transcriptional regulation of Cyclin D1 (Ccnd1) during the early developmental stages of the mouse cerebral cortex. We found evidence that SP8 binds to the Ccnd1 locus on exon regions. In vitro experiments show SP8 binding activity on Ccnd1 gene 3′-end, and point to a putative role for SP8 in modulating PAX6-mediated repression of Ccnd1 along the dorso-ventral axis of the developing pallium, creating a medialLow-lateralHigh gradient of neuronal differentiation. Activation of Ccnd1 through the promoter/5′-end of the gene does not depend on SP8, but on βcatenin (CTNNB1). Importantly, alteration of the Sp8 level of expression in vivo affects Ccnd1 expression during early corticogenesis. Our results indicate that Ccnd1 regulation is the result of multiple signals and that SP8 is a player in this regulation, revealing an unexpected and potentially novel mechanism of transcriptional activation.
Keywords: corticogenesis, gene expression regulation, Cyclin D1, transcription factors, SP8, PAX6
Introduction
The cerebral cortex is the most complex structure of the mammalian brain. It is the site of numerous higher-order sensory, motor, and cognitive functions. Cortical function relies on the proper formation of specialized cortical areas as well as on their sophisticated interconnections (Glasser et al., 2016).
During development, regionalization of the embryonic brain is achieved through multi-step processes. Sources of diffusible signaling molecules act as organizing centers and pattern neighboring domains through regulation of specific transcription factors expression, thereby creating molecular compartments that lead to the generation of distinct cortical fields (Rubenstein et al., 1998; Sur and Rubenstein, 2005; O'Leary et al., 2007).
Cortical projection neurons are generated in the germinal zones (GZ) of the dorsal telencephalon and, following cell-cycle exit, migrate radially to the cortical plate. Previous work has shown that regional differences in the proliferative programs in the GZ have far reaching consequences for histogenesis of cortical areas (Dehay et al., 1993; Polleux et al., 1997; Lukaszewicz et al., 2005).
Neuron number and types specific of each cortical layer and area are defined by the fine-tuned balance between proliferation and differentiation of cortical progenitor cells. While cell biology mechanisms underlying the switch from proliferative to differentiative divisions have been identified (Fish et al., 2006; Delaunay et al., 2014, 2017; Mora-Bermudez et al., 2014; Paridaen and Huttner, 2014; Matsuzaki and Shitamukai, 2015), it has been shown that the increasing fraction of progenitor cells that quit the cell cycle to embark on neuronal differentiation correlate with a lengthening of the G1 phase of the cell cycle (Takahashi et al., 1995; Calegari et al., 2005; Salomoni and Calegari, 2010; Arai et al., 2011). G1 phase is considered as a time window of susceptibility to differentiation signals (Mummery et al., 1987) and G1 phase lengthening increases the competence of a proliferating cell to withdraw from the cell cycle and to differentiate (Zetterberg et al., 1995).
During corticogenesis, proliferative and differentiative divisions are characterized by short and long G1 phases respectively (Dehay et al., 2001; Lukaszewicz et al., 2002, 2005; Calegari and Huttner, 2003; Dehay and Kennedy, 2007; Pilaz et al., 2009). Progression through G1 phase is regulated mainly by the kinase activity of Cyclin D/CDK4 and Cyclin E/CDK2 (Sherr and Roberts, 2004), both of which have been shown to play a key role in determining neuron number during mouse mid-corticogenesis (Lange et al., 2009; Pilaz et al., 2009). In particular, Cyclin D1 (Ccnd1) dynamic expression levels have been shown to be at the heart of a regulatory network that control the balance between cortical progenitor proliferation and differentiation (Ghosh et al., 2014).
Here we have explored the transcriptional regulation of Ccnd1 expression during early corticogenesis. Numerous transcriptional factors binding to the Ccnd1 promoter have been identified (Klein and Assoian, 2008). It is targeted by TCF/βcatenin complex (Shtutman et al., 1999; Tetsu and McCormick, 1999), effector of the Wnt pathway, which plays a key role in regulating cortical expansion (Chenn and Walsh, 2003). More recently, it has been reported that the transcription factor PAX6, known to regulate proliferation and differentiation of cortical progenitors (Warren et al., 1999; Estivill-Torrus et al., 2002; Quinn et al., 2007; Sansom et al., 2009; Mi et al., 2013) binds to the Ccnd1 locus (Sun et al., 2015).
PAX6 plays a key role in forebrain patterning and cortex arealization (Stoykova et al., 1997; Bishop et al., 2000, 2002; Muzio et al., 2002; Englund et al., 2005). Interestingly, Pax6 shows a complementary expression pattern to the transcription factor Sp8 in the developing pallium with a rostro-ventralHigh gradient (Sahara et al., 2007; Borello et al., 2014). SP8 is a zinc finger transcription factor belonging to the Sp-family of transcription factors (Zhao and Meng, 2005). SP8 acts downstream of FGF8 signaling (Storm et al., 2006), regulates forebrain patterning and cortical arealization (Sahara et al., 2007; Zembrzycki et al., 2007; Borello et al., 2014), and regulates cortical progenitor cell differentiation (Borello et al., 2014). Interestingly, SP5/SP8 have been shown to act as co-activators of the Wnt pathway in mouse embryos and differentiating embryonic stem (ES) cells (Kennedy et al., 2016).
We have therefore sought to analyze the putative role of SP8, together with PAX6 and βcatenin, on the transcriptional control of Ccnd1. Our ChipSeq and mouse genetics analysis reveal that Ccnd1 is a target gene of SP8. We show that SP8 is a critical player in the regulation of Ccnd1 expression during in vivo mouse corticogenesis. SP8 is able to modulate the moderate repressive transcriptional activity exerted by PAX6 on the Ccnd1 exon 1 region in vitro. By contrast, we did not observe cooperation between SP8 and βcatenin on Ccnd1 activation from the promoter/5′end of the gene. Finally, we demonstrate that SP8 is able to specifically activate gene expression from the Ccnd1 exon 5 fragment, containing part of the 3′UTR, suggesting that the 3′-end of the Ccnd1 gene may be target of gene regulation at multiple levels, including transcription.
Materials and methods
Animals
Foxg1tTA+/− and tetO-Sp8-IE mice (Waclaw et al., 2009), Foxg1cre (Hebert and McConnell, 2000) and Sp8fl/fl (Waclaw et al., 2006) mice were maintained and genotyped as already described (Waclaw et al., 2006, 2009, 2010). Mouse colonies were maintained at the SBRI/INSERM U1208, in accordance with the European requirement for animal experimentation 2010/63/UE. The protocol APAFIS #4748 has been approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee CELYNE (C2EA #42).
Histology and in situ RNA hybridization (ISH)
Embryos were collected considering noon on the day of the vaginal plug as E0.5. The embryos were dissected and fixed overnight by immersion in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) at 4°C. The tissue was cryoprotected by immersion in 30% sucrose/PBS, embedded in OCT (Tissue-Tek), and cryostat sectioned at 20 μm.
In situ RNA hybridization on cryostat sections was performed as previously described (Borello et al., 2008). cRNA probes used were: Sp8 (K. Campbell, Cincinnati Children's Hospital, OH, USA), Ccnd1 (A. Mallamaci, SISSA, Trieste, IT), Axin2 (B. Cheyette, UCSF, USA), and Pax6 (D. Price, University of Edinburgh).
Gene expression patterns were compared between brains of different genotypes by matching the plane of section according to multiple anatomical features. Whenever possible, this was performed for multiple planes of sections for each gene, and from at least three brains for each genotype.
Foxg1tTA/+ and the tetO-Sp8-IE mice were used as control; differences in phenotype were not observed between these two lines or between Foxg1tTA/+ and the tetO-Sp8-IE mice and the wild type embryos.
ChipSeq
Dorsal telenchephalon (pallium) was dissected from E12.5 CD1 mouse embryos. The cells were crosslinked with 1% formaldehyde for 10 min. The formaldehyde reaction was quenched by adding glycine to a final concentration of 0.125 M for 10 min. Cells were then pelleted, rinsed once in cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) with 1 mM PMSF and once in cold lysis buffer (10 mM Tris pH 7.5, 10 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 0.5% NP-40, and Roche Complete Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) to obtain nuclear pellets. Nuclei were sonicated in RIPA buffer (1X PBS, 1% NP-40 Substitute, 0.5% Sodium Deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS, and Roche Complete Protease Inhibitor Cocktail) at a concentration of 5 × 107 nuclei/mL using a diagenode sonicator (Bioruptor Plus). The DNA fragments bound by SP8 were isolated using a goat polyclonal anti-SP8 antibody (C-18, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), a rabbit polyclonal anti-SP8 antibody (ab739494, abcam), or rabbit polyclonal H3K27ac (ab4729, abcam) coupled to magnetic beads (Dynabeads, ThermoFisher). The beads were washed 5 times with LiCl Wash Buffer (100 mM Tris pH 7.5, 500 mM LiCl, 1% NP-40, 1% sodium deoxycholate) and finally with TE buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 0.1 mM Na2EDTA).
The DNA was incubated o/n at 65°C in elution buffer (1% SDS, 0.1 M NaHCO3) to reverse the formaldehyde crosslink and was purified using a QIAquick PCR Purification Kit (Qiagen), following the manufacturer protocol. To check for fragment size distribution after sonication, a small fraction of the sample was reverse cross-linked for 2 h at 65°C, purified using DNA purification columns from Qiagen, then loaded onto a 2% agarose gel.
Sequence base calls were made using standard Illumina methods. Resulting 1 × 50 bp sequences were filtered to remove sequencing artifacts and adaptors and then mapped to the mouse genome (mm9) using the BWA algorithm (Li and Durbin, 2009). The resulting uniquely mapped reads were used for peak calling with MACS1.4 for SP8 and MACS2.1 for H3K27ac (Zhang et al., 2008; Feng et al., 2011), using recommended settings for transcriptional factor analysis and histone marks respectively. Called peaks were filtered to remove regions where a significant number of artifacts could originate (Consortium, 2012) (https://sites.google.com/site/anshulkundaje/projects/blacklists). Pearson's correlation on the two replicates calculated with a call to wigCorrelate (http://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/admin/exe/macOSX.x86_64/) or Wiggletools (Zerbino et al., 2014) gave a value of 0.9. Peaks were annotated based on nearest transcription start site (TSS) using the Bioconductor package ChiPpeakAnno (Zhu et al., 2010) and ChiPseeker (Yu et al., 2015) and visualized using the Gviz package (Hahne and Ivanek, 2016).
The SP8 ChipSeq data presented in the “Results” section were obtained using the goat polyclonal anti-Sp8 antibody. These results were confirmed with a SP8 ChipSeq performed on two other independent biological replicates with the rabbit polyclonal anti-Sp8 antibody (Table S1 and data not shown).
Cell transfection and luciferase assay
P19 cells (ATCC number: CRL-1825) were maintained in growth medium: Alpha Minimum Essential Medium with ribonucleosides and deoxyribonucleosides (ThermoFisher) completed with 7.5% bovine calf serum and 2.5% fetal calf serum (ThermoFisher) (McBurney and Rogers, 1982; McBurney et al., 1982). The cells were transfected with the expression vector for the full-length cDNA of human βcatenin (gifts of Dr Grosschedl, Max Planck Institute of Immunology, Germany), or Pax6 (D. Price, University of Edinburgh, UK), or Sp8 (gift of K. Campbell, Cincinnati Children's Hospital, OH, USA), along with the different Ccnd1 fragments identified by ChipSeq (Table S1), cloned in the pGL4.10[Luc2] vector (Promega) containing the human βglobin minimal promoter upstream of the luciferase gene (Luc2, Photinus pyralis). The fragment named Ccnd1 exon 2.3 contains Ccnd1 exons 2 and 3. The vector pG4.74[hRLuc/TK] (Promega), containing the Renilla luciferase gene, was co-transfected for normalization. The TK promoter of the pG4.74[hRLuc/TK] vector was substituted with the human βglobin minimal promoter (from vector BGZ40) (Yee and Rigby, 1993).
The cells were transfected with Lipofectamine 2000 (ThermoFisher) in OPTIMEM medium (ThermoFisher) following the manufacturer's instructions, and cultured after 6 h in growth medium. Twenty-four hours after the transfection the cells were harvested in lysis buffer (Promega), and the luciferase and renilla luciferase activities were measured using the Dual Luciferase Assay protocol (Promega). Each transfection experiment was performed in triplicate and repeated at least two times. Reporter gene activities shown in Figures 3–5 represent the average of the three replicates obtained in one representative transfection experiment. Statistical analysis was performed using the statistical package R and ANOVA analysis was performed using the “aov” R function and Tukey multiple comparison test. p < 0.05 were considered statistical significant.
Results
Cyclin D1 is expressed in the developing forebrain at E12.5 with a rostro-ventralHigh gradient
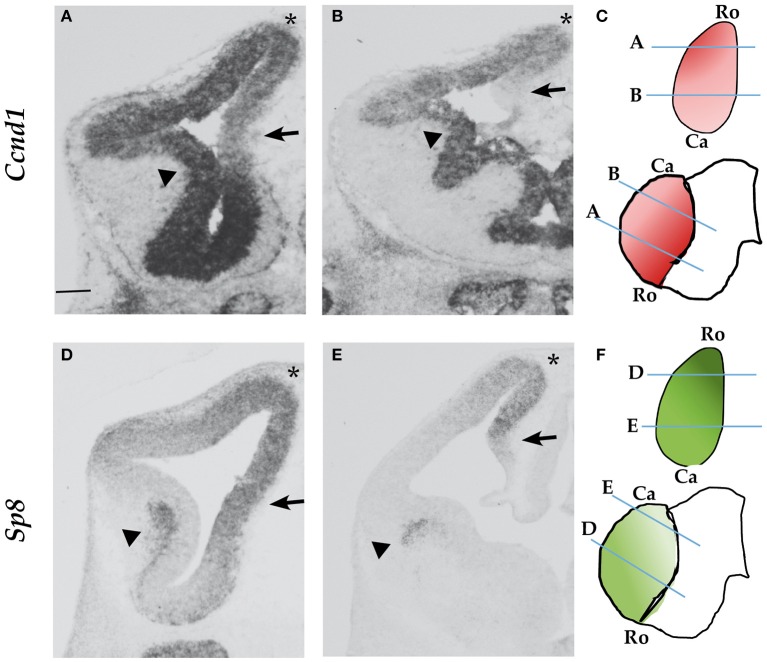
Cyclin D1 is a key regulator of G1 phase progression in neural progenitor cells. We analyzed the mRNA expression of Cyclin D1 in the embryonic forebrain at E12.5. We found that while Ccnd1 is strongly expressed in the ventricular zone (VZ) of the basal ganglia (Figures 1A,B, arrowheads), its expression in the pallial VZ follows a rostro-lateralHigh gradient (Figures 1A–C). In particular, Ccnd1 expression is low in the medial pallium compared to dorsal and lateral regions (Figure 1A, arrow), while it is not expressed caudally in the hem (Figure 1B, arrow). This shows that Ccnd1 is not expressed in all pallial progenitor cells at the same level, suggesting that the complex Ccnd1 expression pattern is regulated by different factors.
Figure 1.
Ccnd1 and Sp8 expression patterns at E12.5. ISH performed on E12.5 mouse forebrain coronal sections. Panels (A,B) show Ccnd1 mRNA expression; Panels (D,E) indicate Sp8 mRNA expression. Schematic of Ccnd1 (C) and Sp8 (F) gradients of expression are indicated along with the positions of sections shown in (A–D). Panels (A,D) represent sections at the rostral level, while Panels (B,E) represent sections at the caudal level. Arrows point to the medial pallium; arrowheads indicate the VZ (A,B) or the SVZ of the LGE (D,E). The asterisk indicates the dorsal pallium. Bar in panel (A) is 200 μm. Ro, rostral; Ca, Caudal.
Sp8 is expressed in the pallium with a rostro-medialHigh gradient (Figures 1D–F). Sp8 is expressed in the pallial VZ, as Ccnd1. In the subpallium Sp8 is expressed in the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ganglionic eminence (LGE) (Figures 1D,E, arrowheads), while Ccnd1 is expressed in the subpallial VZ (Figures 1A,B, arrowheads).
Ccnd1 appears to be highly expressed in the dorsal pallium were Sp8 expression is high (Figures 1A,B,D,E, asterisks); interestingly Ccnd1 expression is lower in the medial pallium, a region of strong Sp8 expression (Figures 1A,B,D,E, arrows).
In conclusion, the expression pattern of Sp8 is compatible with the possibility that it contributes to the transcriptional regulation of Ccnd1 in the dorso-medial pallium.
The zinc finger transcriptional factor SP8 binds to the Ccnd1 locus in cortical progenitor cells
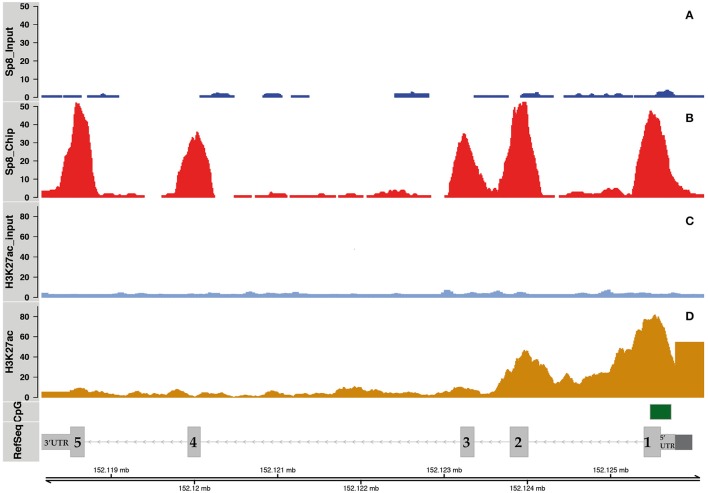
To test the hypothesis that SP8 regulates Ccnd1 at the transcriptional level, we performed SP8 ChipSeq experiments using E12.5 mouse embryos pallial cells (manuscript in preparation). We found that SP8 binds the Ccnd1 locus in vivo decorating Ccnd1 exons (Figures 2A,B), with higher values for exon 1 containing the 5′UTR, exon 2, and exon 5 containing part of the 3′UTR.
Figure 2.
SP8 binding regions on the Ccnd1 locus. Panels (A,B) show SP8 ChipSeq peaks in input and SP8 antibody (Ab) treated samples respectively. Panel (C) shows normalized H3K27ac ChipSeq peaks. Panel (D) shows Ccnd1 RefSeq gene model in light gray, the promoter (Eto, 2000) in dark gray, and the CpG islands in green. Sp8 exons are numbered and the UTRs are indicated.
The presence of acetylated histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27ac) on exons 1 and 2 indicated that these regions correspond to active chromatin domains (Figures 2C,D). The Ccnd1 exon 5 and exon 3 co-localize with the H3K27ac signal, even though it is of smaller intensity than in the exon 1 (Figures 2C,D). H3K27ac signals were obtained from ChipSeq experiments using, as for SP8, E12.5 mouse pallial cells (data not shown, manuscript in preparation).
The fact that Ccnd1 5′UTR showed H3K27ac signal and it contains a CpG island suggests a role for this region in the transcriptional regulation of Ccnd1 in E12.5 cortical progenitor cells (Figures 2C,D). Moreover, Ccnd1 promoter and the 3′UTR represent important regulative regions for the transcriptional regulation of this gene (Klein and Assoian, 2008; Deshpande et al., 2009; Guo et al., 2011). Together these data indicate that SP8 binds transcriptionally active regions in the Ccnd1 locus in vivo in pallial progenitor cells.
SP8 regulates gene expression through Ccnd1 exon 5 fragment in vitro
The observation that SP8 binds mainly on Ccnd1 exons is intriguing. It is generally assumed that the coding genome is physically distinct from the regulatory genome. Consequently, the binding of transcription factors to gene exons is considered generally non-functional (Li et al., 2008). Therefore, we evaluated the relevance of SP8 binding on Ccnd1 exons observed in our ChipSeq experiments.
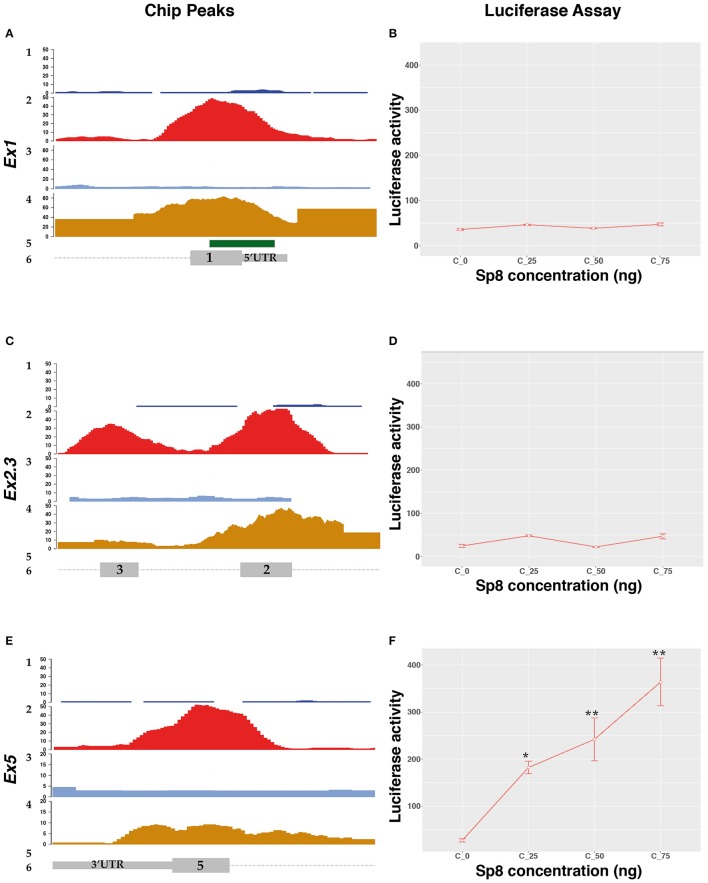
To test the transcriptional activity of SP8 on the different Ccnd1 exons we performed a luciferase assay in vitro. We focused on the Ccnd1 exons showing both SP8 ChipSeq peaks and active chromatin signature (i.e., H3K27ac signal) (Figure 2). The exon 1 (Ex1) fragment contained the last 293 bp of the Ccnd1 promoter (Eto, 2000), the entire exon 1 (containing the 5′UTR) and the first 526 bp of intron 1 (Figure 2 and Figure S1). The exon 5 (Ex5) fragment spanned from intron 4 (last 425 bp) to the coding region up to the first 299 bp of the 3′UTR (Figure 2 and Figure S2).
The DNA region corresponding to the SP8 ChipSeq peaks were cloned upstream of the luciferase gene and tested in P19 cells in the presence of increasing levels of SP8. Surprisingly, we found that SP8 had no activity on the Ccnd1 Ex1 fragment (Figures 3A,B), nor on exons 2 and 3 (Ex2.3) fragment (Figures 3C,D). However, increasing amounts of SP8 activated the luciferase gene through the Ccnd1 Ex5 fragment (Figures 3E,F).
Figure 3.
SP8 transcriptional regulation of Ccnd1 genomic regions bound by Sp8. Panels (A,C,E) show details of the Ccnd1 locus where the SP8 ChipSeq peak have been detected: (A) SP8 peak at the Ccnd1 Ex1 fragment; (C) SP8 peak at the Ccnd1 Ex5 fragment; (E) Sp8 peak at the Ccnd1 Ex2.3 fragment. 1: SP8 Chip input peaks, 2: SP8 Chip peaks, 3: H3K27ac Chip Input peaks, 4: H3K27ac Chip peaks, 5: CpG island, 6: Ccnd1 RefSeq gene model. For details refer to the legend of Figure 2. Panels (B,D,F) show the results of the luciferase assays performed with Ccnd1 Ex1 (B), Ccnd1 Ex2.3 (F), and Ccnd1 Ex5 (D) fragments. Statistical significance, ANOVA: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
Bioinformatic analysis using the Jaspar software, indicated 7 putative SP8 binding sites located in the Ex5 fragment (Table S2); specifically, a cluster of 6 sites is located in the exon 5 ORF (Figure S2). This region contains the SP8 peak summit identified in our ChipSeq results (Figure 5 and Figure S2). This unexpected result indicates that SP8 binds to the exonic region 5 of Ccnd1, thereby modulating its transcription.
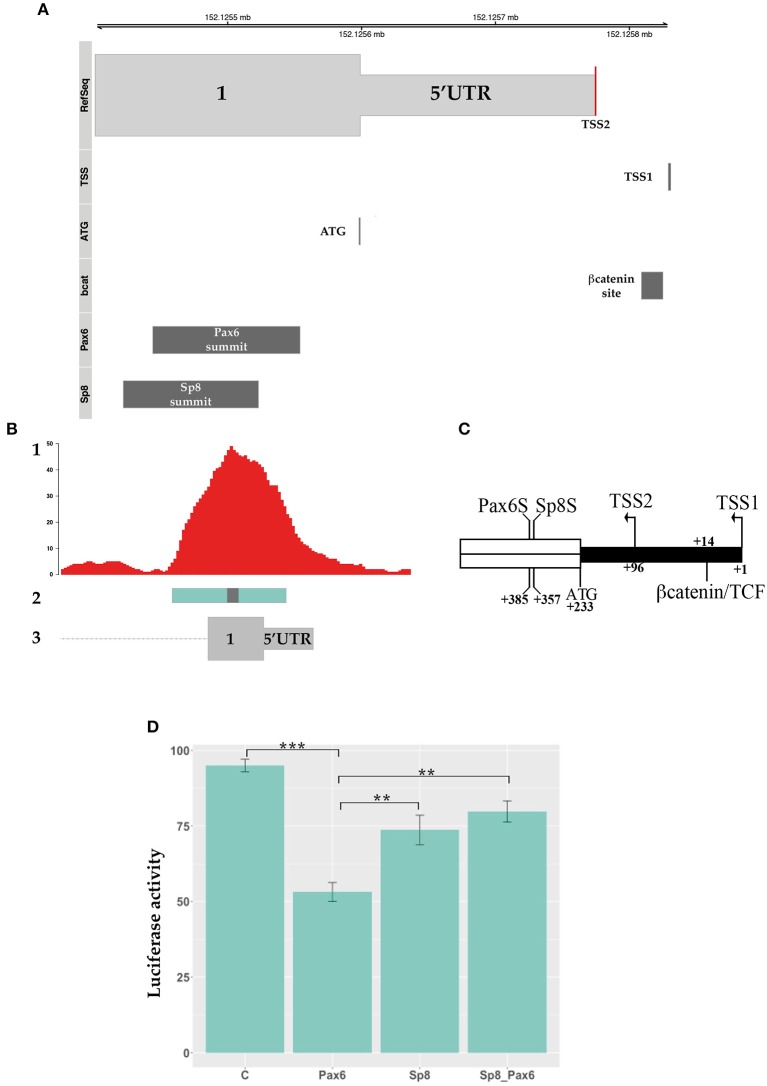
Figure 5.
PAX6 transcriptional regulation of Ccnd1 regulative regions. Panel (A) shows the schema of Ccnd1 locus. PAX6 [Chip peak fragment indicated in Sun et al. (2015)], SP8 (Chip peak summit ±50 bp), βcatenin binding sites, and the TSS (named TSS1) described in Eto (2000) are depicted together with Ccnd1 exon 1 first codon (ATG) and the TSS reported by the RefSeq gene model (TSS2, red line on the RefSeq track). Panel (B) represents the schema of the SP8 and PAX6 peaks positions on the Ccnd1 locus, showing the overlap between the SP8 (this work) and PAX6 ChipSeq peaks (Sun et al., 2015) on Ccnd1 Ex1 fragment. 1: SP8 Chip peaks, 2: PAX6 chipped fragment, 3: Ccnd1 RefSeq gene model. The gray box on the Pax6 fragment is the PAX6 binding summit shown in (A). Panel (C) shows a schematic of βcatenin, SP8 and PAX6 sites position on the 5′ portion of the exon 1 fragment. The PAX6 (PAX6S) and SP8 (SP8S) summit positions [indicated as the central nt of the Chip-qPCR fragment indicated in Sun et al. (2015) and the calculated ChipSeq summit respectively] are indicated. The TSS described in Eto (2000) (TSS1), the Ccnd1 first codon (ATG), and the TSS reported by the RefSeq gene model (TSS2) are also shown. The 5′UTR is depicted in black. Panel (D) shows the luciferase assay results obtained from one representative experiment. Ccnd1 exon 1 was transfected in P19 cells alone or in combination with PAX6, SP8, and PAX6 together with SP8 (SP8_PAX6). Statistical significance, ANOVA: ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01.
βcatenin and PAX6 regulate Ccnd1 exon1 fragment activity in vitro
The Wnt/βcatenin pathway was demonstrated to be a major regulator of Ccnd1 gene expression (Shtutman et al., 1999; Tetsu and McCormick, 1999). The Wnt pathway regulates gene expression by binding of the cofactor βcatenin to genomic regulative regions specifically recognized by TCF/LEF, the effectors of the Wnt pathway (Clevers, 2006; van Amerongen and Nusse, 2009).
Interestingly, the SP8 ChipSeq peak corresponding to exon 1 and containing the last 293 nucleotides of the mouse Ccnd1 promoter (Eto, 2000), contains a highly conserved consensus for TCF/LEF transcriptional factors (Klein and Assoian, 2008) (Figure 4A). As in human, mouse Ccnd1 promoter has no TATA or TATA-like sequence, and the TSS is determined by the Initiator sequence (Inr) (Eto, 2000). However, two possible Inr sequences are present in the mouse Ccnd1 promoter, the second one located at nt +90 from the first Inr sequence, determining a TSS at nt +96 (Eto, 2000) (Figure 4A). According to the Inr site described by Eto (2000), the conserved TCF/LEF site is located downstream to the first TSS, starting at nt + 14, in the Ccnd1 5′UTR (Figure 4A).
Figure 4.
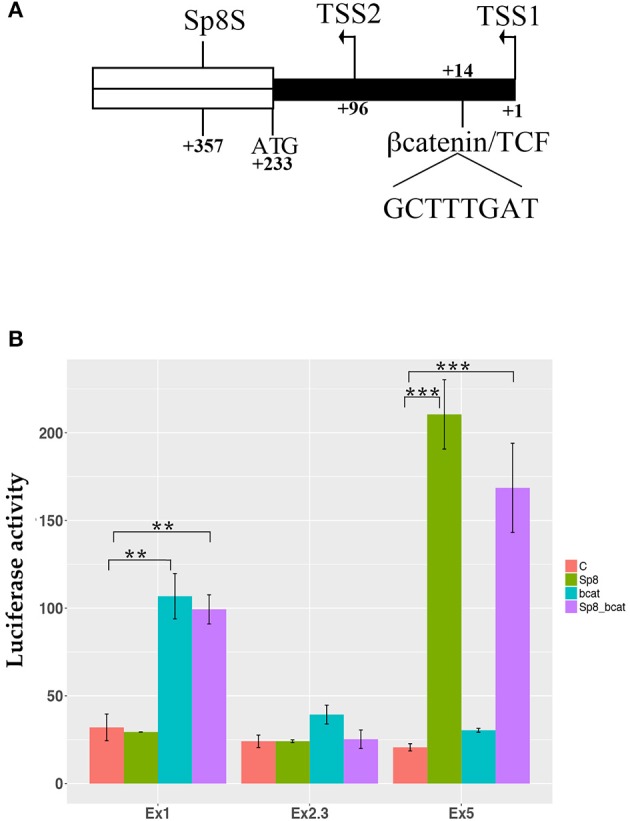
βcatenin and PAX6 transcriptional regulation of Ccnd1 regulative regions identified by SP8 ChipSeq. (A) represents the schema of the 5′ portion of the exon 1 fragment. The transcriptional start sites, TSS1 and TSS2, the first codon ATG, and the conserved βcatenin binding site (Klein and Assoian, 2008), and the SP8 summit (SP8S) positions are indicated. The 5′UTR region is depicted in black; the ORF of exon 1 is indicated in white. Panel (B) shows the results of the luciferase assay obtained from one representative experiment. P19 cells were transfected with the Ccnd1 exon fragments identified by SP8 ChipSeq alone or in combination with βcatenin, SP8, or βcatenin together with SP8. Statistical significance, ANOVA: **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
We tested βcatenin transcriptional activity in combination with SP8 on the above described Ccnd1 fragments. We used a constitutively active form of βcatenin that is not degraded by the proteasome and accumulates into the nucleus (Hsu et al., 1998) in a luciferase assay in vitro. Our results showed that βcatenin activates luciferase transcription specifically through the Ccnd1 Ex1 fragment, and that SP8 does not modulate this effect (Figure 4B). No effect was observed on Ccnd1 Ex2.3 or Ex5 fragments (Figure 4B).
PAX6 is a transcription factor which regulates forebrain patterning and growth. It is expressed with a complementary gradient to that of Sp8 (Figures S3A,B). PAX6 binds to the Ccnd1 locus (Sun et al., 2015). When we compared the position of the PAX6 ChipSeq peak with that of SP8, we found that the two transcription factors bind to an overlapping region in the Ex1 fragment and that the SP8 peak summit was located near the PAX6 binding region (Figures 5A,B and Figure S1). Bioinformatics analysis using the Jaspar database showed a potential PAX6 binding site in the Ex1 fragment at position + 392 from the first TSS (Figure 5C and Figure S1); this predicted consensus sequence is near the summit of the PAX6 ChipSeq peak (Figure S1) (Sun et al., 2015).
We tested the effect of PAX6 on Ccnd1 Ex1 fragment transcriptional activity and the effect of SP8 upon co-expression. Our results showed that PAX6 exerts a moderate repressive transcriptional activity on the Ccnd1 exon 1 region, and that SP8 counteracts this repression when co-transfected with PAX6 (Figure 5D).
SP8 regulates Ccnd1 during in vivo corticogenesis
To further test the role of SP8 on Ccnd1 gene regulation we analyzed the relevance of our in vitro results by altering the level of Sp8 expression in vivo during corticogenesis. For this purpose, we took advantage of genetic systems in which Sp8 was either overexpressed or absent. In the Sp8 gain-of-function (GOF) transgenic mouse system, Sp8 is over-expressed during forebrain development (Waclaw et al., 2009; Borello et al., 2014), while in the loss-of-function (LOF) transgenic mouse system (Waclaw et al., 2006; Borello et al., 2014), Sp8 expression is eliminated (Figure S4).
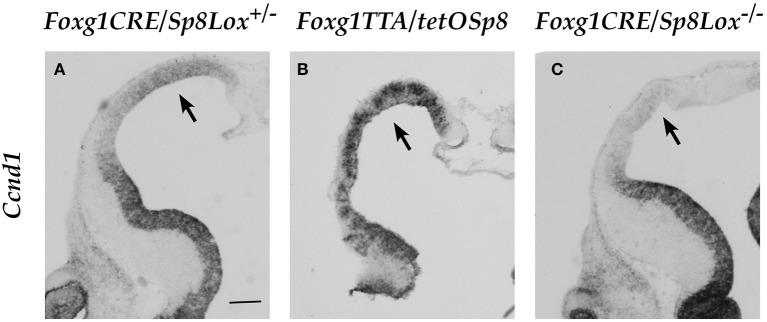
When we analyzed Ccnd1 expression during early corticogenesis using these genetic tools we found that Ccnd1 expression was strongly increased after Sp8 over-expression in the GOF mutant mice (Figures 6A,B), while it was strongly reduced in the LOF mutant mice in regions corresponding to the higher Sp8 expression domain, i.e. the rostral dorso-medial pallium (Figures 6A–C).
Figure 6.
Expression of Ccnd1 in embryonic forebrain after Sp8 misexpression in vivo. ISH on E12.5 mouse forebrain coronal sections. Arrow in Panel (A) shows Ccnd1 expression in the control pallial VZ. Arrows in Panels (B,C) show Ccnd1 expression in the Sp8 GOF and Sp8 LOF pallial VZ respectively. Bar in (A): 200 μm.
These data were further confirmed by RNASeq experiments (data not shown) performed on E12.5 mouse pallial cells showing an increase of Ccnd1 expression in the Sp8 GOF mutants of 3 folds (FDR adjusted p < 0.001) and a reduction of 0.8 folds in the Sp8 LOF mutants (FDR adjusted p-value 0.09) (Table S3).
These findings indicate that SP8 is a critical player in the regulation of Ccnd1 expression during mouse corticogenesis in vivo.
Discussion
Cyclin D1 is a major cell-cycle regulator (Ekholm and Reed, 2000; Sherr and Roberts, 2004) and has been shown to be at the heart of a regulatory network controlling the balance between proliferation and differentiation in the cerebral cortex (Ghosh et al., 2014).
βcatenin is one of the main regulators of Ccnd1 expression (Shtutman et al., 1999; Tetsu and McCormick, 1999; Klein and Assoian, 2008). Our observations that Ccnd1 expression signal does not necessarily correlate to regions of high Wnt/βcatenin activity during early in vivo corticogenesis is consistent with the idea that activation of the Ccnd1 gene might be modulated by cooperation with other transcription factors. Indeed, Axin2, a direct target and recognized proxy of the Wnt/βcatenin pathway activity (Yan et al., 2001; Jho et al., 2002; Lustig et al., 2002; Kim et al., 2007; Al Alam et al., 2011; van Amerongen et al., 2012; Bowman et al., 2013), is strongly localized in the medial pallium where Ccnd1 expression is low or absent and weakly expressed in the dorsal pallium where Ccnd1 is highly expressed (Figures 1A,B and Figures S3C,D). Altogether these data suggest that while βcatenin regulates Ccnd1 expression during corticogenesis in vivo, other transcription factors are also at work to produce the observed Ccnd1 expression pattern in the dorso-medial pallium.
Sp8 and Ccnd1 expression patterns in the early mouse corticogenesis in vivo are consistent with a potential role of SP8 on Ccnd1 gene regulation. The present data confirm this hypothesis and show the identification of Ccnd1 as the first SP8 target gene.
SP8 binds on the Ccnd1 locus on regions of active chromatin, as indicated by the H3K27ac ChipSeq results. Interestingly, peaks with higher intensity were positioned at the promoter/exon1 region, and in exon 5, containing also the first 299 bp of the 3′UTR. Our findings were further confirmed by results from SP8 ChipSeq experiments using a second SP8 antibody (Table S1 and data not shown). When we tested the responsiveness of these regions to SP8 we found that SP8 was able to activate gene expression from the Ccnd1 Ex5 but not from the Ex1 fragment, containing the last 293 nucleotides of the Ccnd1 promoter.
These results are unexpected. The regulatory regions of the genome are generally considered to localize outside of the coding sequences to keep the regulatory and the coding codes separated. However, a theoretical study predicts that the human genome, compared to a synthetic string of DNA letters, could accommodate short functional regulatory motifs in the protein coding regions (Itzkovitz and Alon, 2007). In addition, different studies aimed at identifying regulatory regions in the genome found that a small percentage of these regulatory domains are located in the coding sequences (Cawley et al., 2004; Visel et al., 2009) and that they are functional (Ritter et al., 2012). Recently, a comprehensive study mapping transcription factor binding on human genome exons in many cells lines found that ~15% of human codons specify both amino acids and transcription factor binding sites (Stergachis et al., 2013). Stergachis and colleagues suggest the fascinating hypothesis that the transcription factors binding to conserved sequences inside a gene exons have a role in codon choice and protein evolution. Numerous studies report that intergenic regulative regions like enhancers are sites of active transcription (De Santa et al., 2010; Kim et al., 2010; Natoli and Andrau, 2012; Shlyueva et al., 2014; Kim and Shiekhattar, 2015; Li et al., 2016), blurring the distinction between transcribed gene regions and regulative domains.
The Sp-family transcription factors bind preferentially GC and/or GT-reach regions in TATA-containing and TATA-less promoters and stimulate transcription by associating with the basal transcription complex and other transcription factors (Lania et al., 1997; Philipsen and Suske, 1999; Zhao and Meng, 2005). Consistently, the SP8 ChipSeq experiments showed that 78% of SP8 peaks correspond to gene promoters while genome wide SP8 binds only ~2% of gene exons and UTRs (see Figure S5 for details on the genome-wide SP8 binding localization). Interestingly, while our bioinformatics analysis identified several SP8 binding sites in the Ccnd1 promoter contained in the Ex1 fragment (Table S4 and Figure S1), the ChipSeq experiment indicates that the SP8 summit is located in the coding region. We hypothesize that SP8 binding on Ccnd1 exons is related to the fine-tuned regulation of Ccnd1 transcription, probably through a precise chromatin 3D structure, as well as to Ccnd1 mRNA maturation. There is also the possibility that SP8 is part of an epigenetic complex regulation of Ccnd1 locus replication and transcription. These questions will require further investigations.
Of interest, PAX6, which generally colocalizes with enhancers, binds Ccnd1 exon 1 (Sun et al., 2015). The predicted PAX6 binding site starts at position + 392 from the TSS (166 nucleotides downstream to the ATG), (Figures 2, 5A–C and Figure S1). Interestingly, while SP8 failed to directly regulate Ccnd1 Ex1 fragment expression, we show that SP8 was able to counteract the repressive activity exerted by PAX6 on the Ccnd1 Ex1 fragment in vitro. Moreover, the repressive activity we observed with PAX6 is consistent with the moderate increase of Ccnd1 mRNA observed in the Pax6 LOF E12.5 mutant forebrain (Mi et al., 2013; Sun et al., 2015).
SP8 could, therefore, interfere with PAX6 effect on Ccnd1 expression. It is possible that, due to the close proximity of the SP8 and PAX6 consensus, the two transcription factors compete for the binding on Ccnd1 exon 1. As mentioned above, Sp8 and Pax6 show opposite gradient of expression during early corticogenesis. At mid-gestation when Pax6 expression becomes homogeneous in the pallium, Sp8 expression is expressed at low levels. These data suggest that Ccnd1 is activated differentially by Sp8 and Pax6 in opposite domains of the pallium and is modulated by PAX6 and SP8 dosages along the neurogenic gradient.
SOX2 activates Ccnd1 in a dose-dependent manner during corticogenesis (Hagey and Muhr, 2014). SOX2, binding on different sites on the Ccnd1 locus and interacting with the TCF/βcatenin complex, regulates Ccnd1 expression and cortical progenitor cell mode of division and rate of differentiation (Hagey and Muhr, 2014). Considering the Sp8 graded expression in the pallial VZ and the strong Sp8 expression in the subpallial SVZ (Waclaw et al., 2006; Borello et al., 2014), one can hypothesize that a dose-dependent differential transcriptional regulation is also operant for SP8 (Figure 7).
Figure 7.
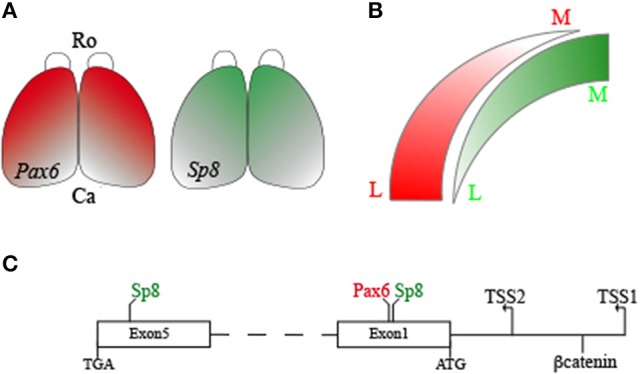
Schema of the SP8, PAX6, and βcatenin interactions on the mouse Ccnd1 gene. Panel (A) shows Sp8 and Pax6 expression gradients in the developing mouse cortex. Panel (B) summarizes differences in Sp8 and Pax6 expression levels along the medio-lateral axis of the pallium. Panel (C) is a graphical representation of SP8, PAX6, and βcatenin binding positions on Ccnd1 locus. R, Rostral; C, Caudal; M, Medial; L, Lateral.
In contrast to PAX6, βcatenin was able to activate transcription from the Ccnd1 5′UTR, and this activation was not dependent or modulated by SP8. The mouse Ccnd1 Ex1 fragment described here contains a TCF/LEF consensus that is conserved among different species, including human (Klein and Assoian, 2008), suggesting a critical and fundamental role for this site in Ccnd1 regulation. In addition, Tetsu and colleagues showed that activation of the CCND1 human minimal promoter,−962CD1 (Albanese et al., 1995), by βcatenin depends on the presence of TCF binding sites but not of other transcription factors (Tetsu and McCormick, 1999). These observations are in agreement with our results showing that the exon 1 fragment, containing only the last 293 nucleotides of the mouse Ccnd1 promoter, was sufficient to support βcatenin activity. The fact that βcatenin activity was independent of SP8 indicates that these two transcription factors do not cooperate by binding the Ccnd1 exon 1 region. However, a potential cooperation between βcatenin and SP8 binding to different Ccnd1 exon fragments (i.e., exon 5) needs further investigation.
Our results show that SP8 is able to specifically activate gene expression from the Ccnd1 Ex5 fragment. Consistently with our luciferase results, we found a cluster of putative SP8 binding sites at the end of the ORF in Ex5 fragment; this cluster overlapped with the SP8 summit identified in our ChipSeq experiments (Table S1 and Figure S2). These findings are very interesting as they rise the possibility that SP8 might control gene expression from binding to regions located at the 3′ end of the Ccnd1 gene in addition to the classical enhancer/promoter regulative domains located upstream of the target genes.
Human CCND1 3′UTR region has been shown to act as a critical regulatory element. Different miRNAs are predicted to bind human and mouse Ccnd1 3′UTR and regulate the level of Cyclin D1 expression (Deshpande et al., 2009; Ghosh et al., 2014); truncation or mutation of human CCND1 3′UTR alter the stability of the CCND1 transcript activating its oncogenic potential (Lebwohl et al., 1994; Molenaar et al., 2003; Wiestner et al., 2007; Deshpande et al., 2009; Ghosh et al., 2014). In addition, different Snps are present in the 3′UTR of mouse and human CCND1: Snp rs7178, localized on CCND1 3′UTR, is involved in neuroblastoma (Wang et al., 2011), and Snp rs7177, localized on CCND1 3′UTR, is involved in cognitive behavior (Rietveld et al., 2013). Considering that there is a 78.1% identity between human and mouse Ccnd1 3′UTR (as revealed using the ECR Browser Ovcharenko et al., 2004), these observations suggest a similar role in gene regulation and neurogenesis for the mouse Ccnd1 3′UTR.
Our data, showing that SP8 binds and specifically regulates Ccnd1 transcription from a region located at the end of the ORF in exon 5 and close to the 3′UTR, suggest that the 3′-end of the Ccnd1 gene may be a target of gene regulation at multiple levels, including the transcriptional one. The in vitro validation of the activity of SP8, as well as the interaction with PAX6 and βcatenin on the Ccnd1 locus, is based on an assay commonly used to screen the activity of genomic regulative regions. In addition, we provide further evidence based on manipulation of SP8 levels of expression in vivo in GOF and LOF transgenic mice as well as on RNAseq data that both clearly show a role for SP8 for Ccnd1 expression regulation at early stages of pallium development.
In summary, multiple signals regulate Ccnd1 transcription in mouse pallium during corticogenesis, resulting in a complex pattern of Ccnd1 expression. SP8 appears as a major player in this regulation, uncovering a potential novel role of the Sp-transcription factor family in transcription regulation, which awaits further analysis.
Author contributions
UB: Conceived the work; UB, BB, and ED: Collected and analyzed the data; UB, BB, DP, and CD: Wrote the paper.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We thank Xavier Bolchini, Marco Valdebenito, Murielle Seon, and Brigitte Beneyton for animal care. We acknowledge the precious help of Heather Wild, Veronique Cortay, and Pascale Giroud.
We thank A. Mallamaci, B. Cheyette, and R. Grosschedl for kindly sharing reagents, and Kenneth Campbell for sharing mouse lines and reagents and for fruitful discussions and advices.
This work was supported by LABEX CORTEX (ANR-11-LABX-0042), LABEX DEVWECAN (ANR-10-LABX-0061) of Université de Lyon (ANR-11-IDEX-0007) operated by the French National Research Agency (ANR) (CD), ANR-10-IBHU-0003(IHU CESAME) (CD), ANR-14-CE13-0036 (Primacor) (CD), Fondation Neurodis (UB), and Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (ING20130526653, Equipe DEQ20160334943) (CD).
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2018.00119/full#supplementary-material
Predicted SP8 binding sites on Ccnd1 Ex1 fragment. The predicted SP8 sites from Table S4 (A–G), the SP8 summit (SP8S), the PAX6 summit (PAX6S), the predicted PAX6 binding site, and the ATG are indicated. The nt positions refer to the Ccnd1 TSS1; SP8 (G) site position is indicated as 164 nt downstream of the exon 1 ORF. The SP8 A-E sites are located in the promoter region; SP8 (F,G) sites are the closest to the SP8 summit. Positions of the SP8S and PAX6S are indicated in bold and underlined.
Predicted SP8 binding sites on Ccnd1 Ex5 fragment. The 7 predicted SP8 sites from Table S2 (A–G), the SP8 summit (SP8S), and the stop codon (TGA) are indicated. The nt positions refer to the Ccnd1 TSS1; SP8 (A,B) position is indicated as 125 nt upstream of the exon 5 ORF. Position of the SP8S is indicated in bold and underlined.
Pax6 and Axin2 expression at E12.5. ISH on E12.5 mouse forebrain coronal sections. Panel (A) shows Pax6 expression in the rostral forebrain and panel (B) shows Pax6 expression in a more caudal section, panel (C) shows Axin2 expression, as proxy of the Wnt pathway activity, in the rostral forebrain and panel (D) shows Axin2 expression in a more caudal section. Bar in (A): 200 μm.
Sp8 expression analysis in the Sp8 LOF and GOF mutants at E12.5. E12.5 mouse forebrain coronal sections. Sp8 mRNA expression levels are shown in the control (A) and Sp8 LOF mutant (C), immunofluorescence of EGFP (B) is shown as a proxy of Sp8 overexpression in the GOF mutant (Borello et al., 2014). Bar in (A): 200 μm.
Genome-wide distribution of the SP8 binding sites on gene features. Plot showing the percentage of the SP8 binding sites distributed genome-wide on gene features.
SP8 and H3K27ac ChipSeq fragments identified on the Ccnd1 locus. MACS results of the SP8 and H3K27ac ChipSeq peak calling. Position of the peaks summits is indicated. The column “name” indicates the genomic fragment names used in this study. The fragment named Ex1.2.3 in the H3K27ac ChipSeq dataset contains Ccnd1 promoter, 5′UTR, and exons 1–3; fragment Ex5 contains Ccnd1 exon 5 and 3′U TR.
Bioinformatic analysis using the Jaspar software (Mathelier et al., 2016) of the Ccnd1 Ex5 fragment. Position of the predicted SP8 sites refers to the Ex5 fragment full sequence, nt 1-889.
Ccnd1 expression levels in the Sp8 GOF and LOF mutants. Results of RNASeq analysis on Sp8 mutants obtained with DESeq2 (Love et al., 2014).
Bioinformatic analysis of the Ccnd1 Ex1 fragment using the Jaspar software (Mathelier et al., 2016). Position of the predicted SP8 sites refers to the Ex1 fragment full sequence, nt 1-1249. In bold are indicated the SP8 predicted sites in the Ccnd1 promoter (SP8 A–E) showing the highest score values, and the two SP8 sites (F,G) close to the position of the SP8 summit. The position of the predicted PAX6 site is indicated.
References
- Al Alam D., Green M., Tabatabai Irani R., Parsa S., Danopoulos S., Sala F. G., et al. (2011). Contrasting expression of canonical Wnt signaling reporters TOPGAL, BATGAL and Axin2(LacZ) during murine lung development and repair. PLoS ONE 6:e23139. 10.1371/journal.pone.0023139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albanese C., Johnson J., Watanabe G., Eklund N., Vu D., Arnold A., et al. (1995). Transforming p21ras mutants and c-Ets-2 activate the cyclin D1 promoter through distinguishable regions. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 23589–23597. 10.1074/jbc.270.40.23589 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai Y., Pulvers J. N., Haffner C., Schilling B., Nüsslein I., Calegari F., et al. (2011). Neural stem and progenitor cells shorten S-phase on commitment to neuron production. Nat. Commun. 2:154. 10.1038/ncomms1155 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop K. M., Goudreau G., O'Leary D. D. (2000). Regulation of area identity in the mammalian neocortex by Emx2 and Pax6. Science 288, 344–349. 10.1126/science.288.5464.344 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop K. M., Rubenstein J. L., O'Leary D. D. (2002). Distinct actions of Emx1, Emx2, and Pax6 in regulating the specification of areas in the developing neocortex. J. Neurosci. 22, 7627–7638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borello U., Cobos I., Long J. E., McWhirter J. R., Murre C., Rubenstein J. L. (2008). FGF15 promotes neurogenesis and opposes FGF8 function during neocortical development. Neural Dev. 3:17. 10.1186/1749-8104-3-17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borello U., Madhavan M., Vilinsky I., Faedo A., Pierani A., Rubenstein J., et al. (2014). Sp8 and COUP-TF1 reciprocally regulate patterning and Fgf signaling in cortical progenitors. Cereb. Cortex 24, 1409–1421. 10.1093/cercor/bhs412 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman A. N., van Amerongen R., Palmer T. D., Nusse R. (2013). Lineage tracing with Axin2 reveals distinct developmental and adult populations of Wnt/beta-catenin-responsive neural stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 7324–7329. 10.1073/pnas.1305411110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calegari F., Haubensak W., Haffner C., Huttner W. B. (2005). Selective lengthening of the cell cycle in the neurogenic subpopulation of neural progenitor cells during mouse brain development. J. Neurosci. 25, 6533–6538. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0778-05.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calegari F., Huttner W. B. (2003). An inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases that lengthens, but does not arrest, neuroepithelial cell cycle induces premature neurogenesis. J. Cell. Sci. 116(Pt 24), 4947–4955. 10.1242/jcs.00825 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawley S., Bekiranov S., Ng H. H., Kapranov P., Sekinger E. A., Kampa D., et al. (2004). Unbiased mapping of transcription factor binding sites along human chromosomes 21 and 22 points to widespread regulation of noncoding RNAs. Cell 116, 499–509. 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00127-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenn A., Walsh C. A. (2003). Increased neuronal production, enlarged forebrains and cytoarchitectural distortions in beta-catenin overexpressing transgenic mice. Cereb. Cortex 13, 599–606. 10.1093/cercor/13.6.599 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevers H. (2006). Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 127, 469–480. 10.1016/j.cell.2006.10.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consortium E. P. (2012). An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 489, 57–74. 10.1038/nature11247 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehay C., Giroud P., Berland M., Smart I., Kennedy H. (1993). Modulation of the cell cycle contributes to the parcellation of the primate visual cortex. Nature 366, 464–466. 10.1038/366464a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehay C., Kennedy H. (2007). Cell-cycle control and cortical development. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8, 438–450. 10.1038/nrn2097 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehay C., Savatier P., Cortay V., Kennedy H. (2001). Cell-cycle kinetics of neocortical precursors are influenced by embryonic thalamic axons. J. Neurosci. 21, 201–214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaunay D., Cortay V., Patti D., Knoblauch K., Dehay C. (2014). Mitotic spindle asymmetry: a Wnt/PCP-regulated mechanism generating asymmetrical division in cortical precursors. Cell Rep. 6, 400–414. 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.12.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaunay D., Kawaguchi A., Dehay C., Matsuzaki F. (2017). Division modes and physical asymmetry in cerebral cortex progenitors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 42, 75–83. 10.1016/j.conb.2016.11.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Santa F., Barozzi I., Mietton F., Ghisletti S., Polletti S., Tusi B. K., et al. (2010). A large fraction of extragenic RNA pol II transcription sites overlap enhancers. PLoS Biol 8:e1000384. 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000384 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande A., Pastore A., Deshpande A. J., Zimmermann Y., Hutter G., Weinkauf M., et al. (2009). 3'UTR mediated regulation of the cyclin D1 proto-oncogene. Cell Cycle 8, 3592–3600. 10.4161/cc.8.21.9993 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekholm S. V., Reed S. I. (2000). Regulation of G cyclin-dependent kinases in the mammalian cell cycle. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12, 676–684. 10.1016/S0955-0674(00)00151-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englund C., Fink A., Lau C., Pham D., Daza R. A., Bulfone A., et al. (2005). Pax6, Tbr2, and Tbr1 are expressed sequentially by radial glia, intermediate progenitor cells, and postmitotic neurons in developing neocortex. J. Neurosci. 25, 247–251. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2899-04.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estivill-Torrus G., Pearson H., van Heyningen V., Price D. J., Rashbass P. (2002). Pax6 is required to regulate the cell cycle and the rate of progression from symmetrical to asymmetrical division in mammalian cortical progenitors. Development 129, 455–466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eto I. (2000). Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the promoter region of mouse cyclin D1 gene: implication in phorbol ester-induced tumour promotion. Cell Prolif. 33, 167–187. 10.1046/j.1365-2184.2000.00176.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng J., Liu T., Zhang Y. (2011). Using MACS to identify peaks from ChIP-Seq data. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics Chapter 2, Unit 2.14. 10.1002/0471250953.bi0214s34 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish J. L., Kosodo Y., Enard W., Pääbo S., Huttner W. B. (2006). Aspm specifically maintains symmetric proliferative divisions of neuroepithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 10438–10443. 10.1073/pnas.0604066103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh T., Aprea J., Nardelli J., Engel H., Selinger C., Mombereau C., et al. (2014). MicroRNAs establish robustness and adaptability of a critical gene network to regulate progenitor fate decisions during cortical neurogenesis. Cell Rep. 7, 1779–1788. 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.05.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasser M. F., Coalson T. S., Robinson E. C., Hacker C. D., Harwell J., Yacoub E., et al. (2016). A multi-modal parcellation of human cerebral cortex. Nature 536, 171–178. 10.1038/nature18933 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Z. Y., Hao X. H., Tan F. F., Pei X., Shang L. M., Jiang X. L., et al. (2011). The elements of human cyclin D1 promoter and regulation involved. Clin. Epigenetics 2, 63–76. 10.1007/s13148-010-0018-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagey D. W., Muhr J. (2014). Sox2 acts in a dose-dependent fashion to regulate proliferation of cortical progenitors. Cell Rep. 9, 1908–1920. 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.11.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahne F., Ivanek R. (2016). Visualizing genomic data using gviz and bioconductor, in Statistical Genomics: Methods and Protocols, eds Mathé E., Davis S. (New York, NY: Springer; ), 335–351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert J. M., McConnell S. K. (2000). Targeting of cre to the Foxg1 (BF-1) locus mediates loxP recombination in the telencephalon and other developing head structures. Dev. Biol. 222, 296–306. 10.1006/dbio.2000.9732 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. C., Galceran J., Grosschedl R. (1998). Modulation of transcriptional regulation by LEF-1 in response to Wnt-1 signaling and association with beta-catenin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 4807–4818. 10.1128/MCB.18.8.4807 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itzkovitz S., Alon U. (2007). The genetic code is nearly optimal for allowing additional information within protein-coding sequences. Genome Res. 17, 405–412. 10.1101/gr.5987307 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jho E. H., Zhang T., Domon C., Joo C. K., Freund J. N., Costantini F. (2002). Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling induces the transcription of Axin2, a negative regulator of the signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 1172–1183. 10.1128/MCB.22.4.1172-1183.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. W., Chalamalasetty R. B., Thomas S., Garriock R. J., Jailwala P., Yamaguchi T. P. (2016). Sp5 and Sp8 recruit beta-catenin and Tcf1-Lef1 to select enhancers to activate Wnt target gene transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, 3545–3550. 10.1073/pnas.1519994113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim B. M., Mao J., Taketo M. M., Shivdasani R. A. (2007). Phases of canonical Wnt signaling during the development of mouse intestinal epithelium. Gastroenterology 133, 529–538. 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.04.072 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim T. K., Hemberg M., Gray J. M., Costa A. M., Bear D. M., Wu J., et al. (2010). Widespread transcription at neuronal activity-regulated enhancers. Nature 465, 182–187. 10.1038/nature09033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim T. K., Shiekhattar R. (2015). Architectural and functional commonalities between enhancers and promoters. Cell 162, 948–959. 10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E. A., Assoian R. K. (2008). Transcriptional regulation of the cyclin D1 gene at a glance. J. Cell. Sci. 121(Pt 23), 3853–3857. 10.1242/jcs.039131 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange C., Huttner W. B., Calegari F. (2009). Cdk4/cyclinD1 overexpression in neural stem cells shortens G1, delays neurogenesis, and promotes the generation and expansion of basal progenitors. Cell Stem Cell 5, 320–331. 10.1016/j.stem.2009.05.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lania L., Majello B., De Luca P. (1997). Transcriptional regulation by the Sp family proteins. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 29, 1313–1323. 10.1016/S1357-2725(97)00094-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebwohl D. E., Muise-Helmericks R., Sepp-Lorenzino L., Serve S., Timaul M., Bol R., et al. (1994). A truncated cyclin D1 gene encodes a stable mRNA in a human breast cancer cell line. Oncogene 9, 1925–1929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Durbin R. (2009). Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25, 1754–1760. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W., Notani D., Rosenfeld M. G. (2016). Enhancers as non-coding RNA transcription units: recent insights and future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Genet. 17, 207–223. 10.1038/nrg.2016.4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. Y., MacArthur S., Bourgon R., Nix D., Pollard D. A., Iyer V. N., et al. (2008). Transcription factors bind thousands of active and inactive regions in the Drosophila blastoderm. PLoS Biol. 6:e27. 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love M. I., Huber W., Anders S. (2014). Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:550. 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukaszewicz A., Savatier P., Cortay V., Giroud P., Huissoud C., Berland M., et al. (2005). G1 phase regulation, area-specific cell cycle control, and cytoarchitectonics in the primate cortex. Neuron 47, 353–364. 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.06.032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukaszewicz A., Savatier P., Cortay V., Kennedy H., Dehay C. (2002). Contrasting effects of basic fibroblast growth factor and neurotrophin 3 on cell cycle kinetics of mouse cortical stem cells. J. Neurosci. 22, 6610–6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig B., Jerchow B., Sachs M., Weiler S., Pietsch T., Karsten U., et al. (2002). Negative feedback loop of Wnt signaling through upregulation of conductin/axin2 in colorectal and liver tumors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 1184–1193. 10.1128/MCB.22.4.1184-1193.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathelier A., Fornes O., Arenillas D. J., Chen C. Y., Denay G., Lee J., et al. (2016). JASPAR 2016: a major expansion and update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, D110–D115. 10.1093/nar/gkv1176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki F., Shitamukai A. (2015). Cell division modes and cleavage planes of neural progenitors during mammalian cortical development. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 7:a015719. 10.1101/cshperspect.a015719 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Jones-Villeneuve E. M., Edwards M. K., Anderson P. J. (1982). Control of muscle and neuronal differentiation in a cultured embryonal carcinoma cell line. Nature 299, 165–167. 10.1038/299165a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Rogers B. J. (1982). Isolation of male embryonal carcinoma cells and their chromosome replication patterns. Dev. Biol. 89, 503–508. 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90338-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mi D., Carr C. B., Georgala P. A., Huang Y. T., Manuel M. N., Jeanes E., et al. (2013). Pax6 exerts regional control of cortical progenitor proliferation via direct repression of Cdk6 and hypophosphorylation of pRb. Neuron 78, 269–284. 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.02.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar J. J., van Sluis P., Boon K., Versteeg R., Caron H. N. (2003). Rearrangements and increased expression of cyclin D1 (CCND1) in neuroblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 36, 242–249. 10.1002/gcc.10166 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mora-Bermúdez F., Matsuzaki F., Huttner W. B. (2014). Specific polar subpopulations of astral microtubules control spindle orientation and symmetric neural stem cell division. Elife 3:e02875. 10.7554/eLife.02875 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mummery C. L., van den Brink C. E., de Laat S. W. (1987). Commitment to differentiation induced by retinoic acid in P19 embryonal carcinoma cells is cell cycle dependent. Dev. Biol. 121, 10–19. 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90133-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzio L., DiBenedetto B., Stoykova A., Boncinelli E., Gruss P., Mallamaci A. (2002). Emx2 and Pax6 control regionalization of the pre-neuronogenic cortical primordium. Cereb. Cortex 12, 129–139. 10.1093/cercor/12.2.129 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natoli G., Andrau J. C. (2012). Noncoding transcription at enhancers: general principles and functional models. Annu. Rev. Genet. 46, 1–19. 10.1146/annurev-genet-110711-155459 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary D. D., Chou S. J., Sahara S. (2007). Area patterning of the mammalian cortex. Neuron 56, 252–269. 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.10.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovcharenko I., Nobrega M. A., Loots G. G., Stubbs L. (2004). ECR Browser: a tool for visualizing and accessing data from comparisons of multiple vertebrate genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, W280–W286. 10.1093/nar/gkh355 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paridaen J. T., Huttner W. B. (2014). Neurogenesis during development of the vertebrate central nervous system. EMBO Rep. 15, 351–364. 10.1002/embr.201438447 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipsen S., Suske G. (1999). A tale of three fingers: the family of mammalian Sp/XKLF transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 27, 2991–3000. 10.1093/nar/27.15.2991 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilaz L. J., Patti D., Marcy G., Ollier E., Pfister S., Douglas R. J., et al. (2009). Forced G1-phase reduction alters mode of division, neuron number, and laminar phenotype in the cerebral cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 21924–21929. 10.1073/pnas.0909894106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polleux F., Dehay C., Moraillon B., Kennedy H. (1997). Regulation of neuroblast cell-cycle kinetics plays a crucial role in the generation of unique features of neocortical areas. J. Neurosci. 17, 7763–7783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. C., Molinek M., Martynoga B. S., Zaki P. A., Faedo A., Bulfone A., et al. (2007). Pax6 controls cerebral cortical cell number by regulating exit from the cell cycle and specifies cortical cell identity by a cell autonomous mechanism. Dev. Biol. 302, 50–65. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.08.035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietveld C. A., Medland S. E., Derringer J., Yang J., Esko T., Martin N. W., et al. (2013). GWAS of 126,559 individuals identifies genetic variants associated with educational attainment. Science 340, 1467–1471. 10.1126/science.1235488 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter D. I., Dong Z., Guo S., Chuang J. H. (2012). Transcriptional enhancers in protein-coding exons of vertebrate developmental genes. PLoS ONE 7:e35202. 10.1371/journal.pone.0035202 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein J. L., Shimamura K., Martinez S., Puelles L. (1998). Regionalization of the prosencephalic neural plate. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 21, 445–477. 10.1146/annurev.neuro.21.1.445 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahara S., Kawakami Y., Izpisua Belmonte J. C., O'Leary D. D. (2007). Sp8 exhibits reciprocal induction with Fgf8 but has an opposing effect on anterior-posterior cortical area patterning. Neural Dev. 2:10. 10.1186/1749-8104-2-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomoni P., Calegari F. (2010). Cell cycle control of mammalian neural stem cells: putting a speed limit on G1. Trends Cell Biol. 20, 233–243. 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.01.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom S. N., Griffiths D. S., Faedo A., Kleinjan D. J., Ruan Y., Smith J., et al. (2009). The level of the transcription factor Pax6 is essential for controlling the balance between neural stem cell self-renewal and neurogenesis. PLoS Genet. 5:e1000511. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000511 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Roberts J. M. (2004). Living with or without cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev. 18, 2699–2711. 10.1101/gad.1256504 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlyueva D., Stampfel G., Stark A. (2014). Transcriptional enhancers: from properties to genome-wide predictions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 15, 272–286. 10.1038/nrg3682 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shtutman M., Zhurinsky J., Simcha I., Albanese C., D'Amico M., Pestell R., et al. (1999). The cyclin D1 gene is a target of the beta-catenin/LEF-1 pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96, 5522–5527. 10.1073/pnas.96.10.5522 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stergachis A. B., Haugen E., Shafer A., Fu W., Vernot B., Reynolds A., et al. (2013). Exonic transcription factor binding directs codon choice and affects protein evolution. Science 342, 1367–1372. 10.1126/science.1243490 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storm E. E., Garel S., Borello U., Hebert J. M., Martinez S., McConnell S. K., et al. (2006). Dose-dependent functions of Fgf8 in regulating telencephalic patterning centers. Development 133, 1831–1844. 10.1242/dev.02324 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoykova A., Götz M., Gruss P., Price J. (1997). Pax6-dependent regulation of adhesive patterning, R-cadherin expression and boundary formation in developing forebrain. Development 124, 3765–3777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J., Rockowitz S., Xie Q., Ashery-Padan R., Zheng D., Cvekl A. (2015). Identification of in vivo DNA-binding mechanisms of Pax6 and reconstruction of Pax6-dependent gene regulatory networks during forebrain and lens development. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, 6827–6846. 10.1093/nar/gkv589 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sur M., Rubenstein J. L. (2005). Patterning and plasticity of the cerebral cortex. Science 310, 805–810. 10.1126/science.1112070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Nowakowski R. S., Caviness V. S., Jr. (1995). The cell cycle of the pseudostratified ventricular epithelium of the embryonic murine cerebral wall. J. Neurosci. 15, 6046–6057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tetsu O., McCormick F. (1999). Beta-catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature 398, 422–426. 10.1038/18884 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Amerongen R., Bowman A. N., Nusse R. (2012). Developmental stage and time dictate the fate of Wnt/beta-catenin-responsive stem cells in the mammary gland. Cell Stem Cell 11, 387–400. 10.1016/j.stem.2012.05.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Amerongen R., Nusse R. (2009). Towards an integrated view of Wnt signaling in development. Development 136, 3205–3214. 10.1242/dev.033910 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visel A., Blow M. J., Li Z., Zhang T., Akiyama J. A., Holt A., et al. (2009). ChIP-seq accurately predicts tissue-specific activity of enhancers. Nature 457, 854–858. 10.1038/nature07730 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waclaw R. R., Allen Z. J., II., Bell S. M., Erdélyi F., Szabó G., Potter S. S., et al. (2006). The zinc finger transcription factor Sp8 regulates the generation and diversity of olfactory bulb interneurons. Neuron 49, 503–516. 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.01.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waclaw R. R., Ehrman L. A., Pierani A., Campbell K. (2010). Developmental origin of the neuronal subtypes that comprise the amygdalar fear circuit in the mouse. J. Neurosci. 30, 6944–6953. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5772-09.2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waclaw R. R., Wang B., Pei Z., Ehrman L. A., Campbell K. (2009). Distinct temporal requirements for the homeobox gene Gsx2 in specifying striatal and olfactory bulb neuronal fates. Neuron 63, 451–465. 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.07.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Diskin S. J., Zhang H., Attiyeh E. F., Winter C., Hou C., et al. (2011). Integrative genomics identifies LMO1 as a neuroblastoma oncogene. Nature 469, 216–220. 10.1038/nature09609 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren N., Caric D., Pratt T., Clausen J. A., Asavaritikrai P., Mason J. O., et al. (1999). The transcription factor, Pax6, is required for cell proliferation and differentiation in the developing cerebral cortex. Cereb. Cortex 9, 627–635. 10.1093/cercor/9.6.627 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiestner A., Tehrani M., Chiorazzi M., Wright G., Gibellini F., Nakayama K., et al. (2007). Point mutations and genomic deletions in CCND1 create stable truncated cyclin D1 mRNAs that are associated with increased proliferation rate and shorter survival. Blood 109, 4599–4606. 10.1182/blood-2006-08-039859 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan D., Wiesmann M., Rohan M., Chan V., Jefferson A. B., Guo L., et al. (2001). Elevated expression of axin2 and hnkd mRNA provides evidence that Wnt/beta -catenin signaling is activated in human colon tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98, 14973–14978. 10.1073/pnas.261574498 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee S. P., Rigby P. W. (1993). The regulation of myogenin gene expression during the embryonic development of the mouse. Genes Dev. 7, 1277–1289. 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1277 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu G., Wang L. G., He Q. Y. (2015). ChIPseeker: an R/Bioconductor package for ChIP peak annotation, comparison and visualization. Bioinformatics 31, 2382–2383. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv145 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zembrzycki A., Griesel G., Stoykova A., Mansouri A. (2007). Genetic interplay between the transcription factors Sp8 and Emx2 in the patterning of the forebrain. Neural Dev. 2:8. 10.1186/1749-8104-2-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerbino D. R., Johnson N., Juettemann T., Wilder S. P., Flicek P. (2014). WiggleTools: parallel processing of large collections of genome-wide datasets for visualization and statistical analysis. Bioinformatics 30, 1008–1009. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt737 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterberg A., Larsson O., Wiman K. G. (1995). What is the restriction point? Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 7, 835–842. 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80067-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Liu T., Meyer C. A., Eeckhoute J., Johnson D. S., Bernstein B. E., et al. (2008). Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol. 9:R137. 10.1186/gb-2008-9-9-r137 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao C., Meng A. (2005). Sp1-like transcription factors are regulators of embryonic development in vertebrates. Dev. Growth Differ. 47, 201–211. 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2005.00797.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L. J., Gazin C., Lawson N. D., Pagès H., Lin S. M., Lapointe D. S., et al. (2010). ChIPpeakAnno: a Bioconductor package to annotate ChIP-seq and ChIP-chip data. BMC Bioinformatics 11:237. 10.1186/1471-2105-11-237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Predicted SP8 binding sites on Ccnd1 Ex1 fragment. The predicted SP8 sites from Table S4 (A–G), the SP8 summit (SP8S), the PAX6 summit (PAX6S), the predicted PAX6 binding site, and the ATG are indicated. The nt positions refer to the Ccnd1 TSS1; SP8 (G) site position is indicated as 164 nt downstream of the exon 1 ORF. The SP8 A-E sites are located in the promoter region; SP8 (F,G) sites are the closest to the SP8 summit. Positions of the SP8S and PAX6S are indicated in bold and underlined.
Predicted SP8 binding sites on Ccnd1 Ex5 fragment. The 7 predicted SP8 sites from Table S2 (A–G), the SP8 summit (SP8S), and the stop codon (TGA) are indicated. The nt positions refer to the Ccnd1 TSS1; SP8 (A,B) position is indicated as 125 nt upstream of the exon 5 ORF. Position of the SP8S is indicated in bold and underlined.
Pax6 and Axin2 expression at E12.5. ISH on E12.5 mouse forebrain coronal sections. Panel (A) shows Pax6 expression in the rostral forebrain and panel (B) shows Pax6 expression in a more caudal section, panel (C) shows Axin2 expression, as proxy of the Wnt pathway activity, in the rostral forebrain and panel (D) shows Axin2 expression in a more caudal section. Bar in (A): 200 μm.
Sp8 expression analysis in the Sp8 LOF and GOF mutants at E12.5. E12.5 mouse forebrain coronal sections. Sp8 mRNA expression levels are shown in the control (A) and Sp8 LOF mutant (C), immunofluorescence of EGFP (B) is shown as a proxy of Sp8 overexpression in the GOF mutant (Borello et al., 2014). Bar in (A): 200 μm.
Genome-wide distribution of the SP8 binding sites on gene features. Plot showing the percentage of the SP8 binding sites distributed genome-wide on gene features.
SP8 and H3K27ac ChipSeq fragments identified on the Ccnd1 locus. MACS results of the SP8 and H3K27ac ChipSeq peak calling. Position of the peaks summits is indicated. The column “name” indicates the genomic fragment names used in this study. The fragment named Ex1.2.3 in the H3K27ac ChipSeq dataset contains Ccnd1 promoter, 5′UTR, and exons 1–3; fragment Ex5 contains Ccnd1 exon 5 and 3′U TR.
Bioinformatic analysis using the Jaspar software (Mathelier et al., 2016) of the Ccnd1 Ex5 fragment. Position of the predicted SP8 sites refers to the Ex5 fragment full sequence, nt 1-889.
Ccnd1 expression levels in the Sp8 GOF and LOF mutants. Results of RNASeq analysis on Sp8 mutants obtained with DESeq2 (Love et al., 2014).
Bioinformatic analysis of the Ccnd1 Ex1 fragment using the Jaspar software (Mathelier et al., 2016). Position of the predicted SP8 sites refers to the Ex1 fragment full sequence, nt 1-1249. In bold are indicated the SP8 predicted sites in the Ccnd1 promoter (SP8 A–E) showing the highest score values, and the two SP8 sites (F,G) close to the position of the SP8 summit. The position of the predicted PAX6 site is indicated.