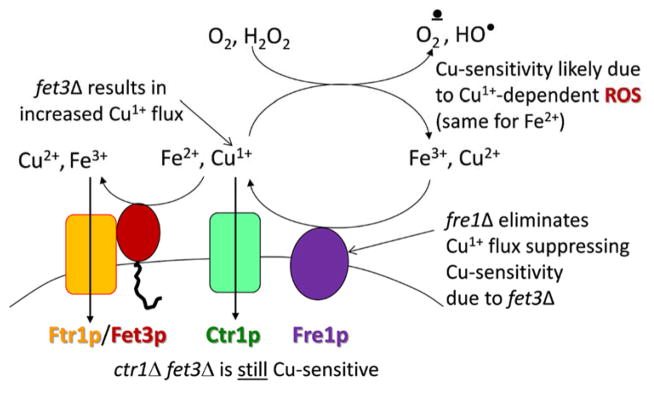
Fig. 4.
In yeast, deletion of FET3 leads to copper sensitivity. Common lab strains of S. cerevisiae exhibit normal growth up 10 mM copper. Growth of a fet3Δ strain is inhibited >0.5 mM copper, a sensitivity suppressed by deletion of FRE1. In contrast, the copper sensitivity of the fet3Δ strain is not suppressed by deletion of CTR1 indicating that the molecular trigger of the induced cytotoxicity is extracellular cuprous copper likely supporting redox cycling of dioxygen 1e− reduction products 16.