Abstract
Background:
Laparoscopic total gastrectomy (LTG) is increasingly performed in patients with gastric cancer. However, the usage of intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy (IEJ) following LTG is limited, as the safety and efficacy remain unclear. The present meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the feasibility and safety of IEJ following LTG.
Methods:
Studies published from January 1994 to January 2017 comparing the outcomes of IEJ and extracorporeal esophagojejunostomy (EEJ) following LTG were reviewed and collected from the PubMed, EBSCO, Cochrane Library, Embase, and China National Knowledge Internet (CNKI). Operative results, postoperative recovery, and postoperative complications were compared and analyzed. The weighted mean difference (WMD) and odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated using the Review Manager 5.3.
Results:
Seven nonrandomized studies with 785 patients were included. Compared with EEJ, IEJ has less blood loss (WMD: −13.52 ml; 95% CI: −24.82–−2.22; P = 0.02), earlier time to first oral intake (WMD: −0.49 day; 95% CI: −0.83–−0.14; P < 0.01), and shorter length of hospitalization (WMD: −0.62 day; 95% CI: −1.08–−0.16; P < 0.01). There was no significant difference between IEJ and EEJ regarding the operation time, anastomotic time, number of retrieved lymph nodes, time to first flatus, anastomosis leakage rate, anastomosis stenosis rate, and proximal resections (all P > 0.05).
Conclusions:
Compared with EEJ, IEJ has better cosmesis, milder surgical trauma, and a faster postoperative recovery. IEJ can be performed as safely as EEJ. IEJ should be encouraged to surgeons with sufficient expertise.
Keywords: Gastric Neoplasms, Intracorporeal Esophagojejunostomy, Laparoscopy, Total Gastrectomy
摘要
背景:
腹腔镜全胃切除术在胃癌治疗中应用日益增加。然而, 腹腔镜全胃切除术后采用腹腔内食管空肠吻合术却很有限, 因其安全性和疗效尚不明确。本篇荟萃分析旨在评估腹腔镜全胃切除术后采用腹腔内食管空肠吻合术的可行性和安全性。
方法:
在PubMed、EBSCO、Cochrane Library、Embase、中国知网数据库中查阅从1994年1月至2017年1月发表的腹腔镜全胃切除术行腹腔内和腹腔外食管空肠吻合术的对比研究。比较并分析两组手术结果, 术后恢复, 和术后并发症情况。用Review Manager 5.3软件计算加权平均差(WMD)和比值比(OR)以它们的95%置信区间(CI)。
结果:
7篇非随机研究文献纳入研究,共包含785名患者。相比于腹腔外食管空肠吻合术,腹腔内食管空肠吻合术术中出血更少(WMD: -13.52 ml; 95 % CI: -24.82 – -2.22; P = 0.02),术后进食时间更早(WMD: -0.49 day; 95 % CI: -0.83 – -0.14; P <0.01),住院时间更短(WMD: -0.62 day; 95 % CI: -1.08 – -0.16; P <0.01)。在手术时间、吻合时间、淋巴结切除数目、术后排气、吻合口漏、吻合口狭窄和近端切缘这些指标上,两组间无明显差异(P>0.05)。
结论:
与腹腔外食管空肠吻合术相比,腹腔内食管空肠吻合术具有更好的美观性,更轻的手术创伤,更快术后恢复等优势,同时可以做到一样安全。因此,应该鼓励具有足够手术经验的外科医生尝试腹腔内食管空肠吻合。
INTRODUCTION
Laparoscopic gastrectomy (LG) has gained widespread global popularity, especially in Eastern Asia. LG has notable advantages including smaller incisions, milder pain, and faster recovery[1,2,3] and is already a standard procedure in some hospitals. Several randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and large-scale studies have confirmed the feasibility and oncological safety of LG in the treatment of early gastric cancer (GC).[4,5,6,7] Preliminary outcomes of some ongoing RCTs demonstrated LG has acceptable efficacy in locally advanced GC.[8,9,10]
Although LG is frequently performed, laparoscopic distal gastrectomy (LDG) accounts for most procedures and laparoscopic total gastrectomy (LTG) and is not commonly performed because of its technical difficulty. In recent years, LTG has been increasingly performed with good results compared with its open counterparts.[11,12,13] A meta-analysis by Wang et al.[14] had revealed surgical outcomes of LTG were even better than those of open total gastrectomy (OTG), especially with comparable oncological outcomes. Extracorporeal esophagojejunostomy (EEJ) in LTG is similar to conventional esophagojejunostomy in OTG. Surgeons usually extend the trocar incision after completing total stomach and lymph node resection, the esophageal stump and jejunum are pulled out and the esophagojejunostomy is performed extracorporeally. However, EEJ also partially impedes the minimally invasiveness benefit of LTG due to the enlarged incision. In addition, surrounding structures might be injured due to high tension in performing EEJ, and the potential risk of anastomosis leakage is increased. Intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy (IEJ) avoids the mini-laparotomy and provides better operative view than does EEJ, but it requires greater skill. To date, the results of randomized studies and reviews focusing on IEJ following LTG have rarely been reported. To evaluate the feasibility and safety of IEJ, we conducted this meta-analysis by reviewing and analyzing the previous studies.
METHODS
Literature search and selection criteria
This review was performed according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis statement.[15] A search for primary studies was performed using the PubMed, EBSCO, Cochrane Library, Embase, and China National Knowledge Internet (CNKI) from January 1994 to January 2017. The search strategy format was as follows: ([(totally laparoscopic OR completely laparoscopic) OR Intracorporeal]) AND ([([gastric neoplasms OR gastric adenocarcinoma] OR gastric cancer)] AND laparoscopic total gastrectomy). The reference lists and related articles of the retrieved articles were also searched to identify the potential studies. The language was limited to English and Chinese.
Eligibility criteria included the following: (1) all patients were confirmed GC, (2) studies compared IEJ and EEJ in patients who underwent LTG, and (3) availability of data for anastomosis-related complications. The anastomosis-related complications included anastomotic leakage, structure (or stenosis), and bleeding. Exclusion criteria were the following: (1) hand-assisted LG or robotic gastrectomy, (2) abstracts presented at meetings, review articles, case reports or letters, and (3) duplicated studies.
Data extraction
Data extraction was conducted independently by two authors. Disagreements were discussed, and a consensus was reached. An evidence table was prepared including the following data: study name, study period, sample size, mean age, tumor size, mean body mass index, extent of lymph node dissection, anastomotic time, total operation time, intraoperative blood loss, number of harvested lymph nodes, time to first flatus, time to first oral intake, length of postoperative hospital stay, and anastomotic complications. To assess qualities of each study, the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS; http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp) was used. The total score was nine stars, and a study with at least six stars was graded as high quality.
Statistical analysis
All statistical calculations were performed using the Review Manager 5.3 (Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, UK). Estimated effect measures were weighted mean differences (WMDs) for continuous data and odds ratios (ORs) for dichotomous data. A value of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Heterogeneity between included studies was evaluated using the Chi-square test; A value of P < 0.1 was considered statistically significant for high heterogeneity.[16] A random-effect model was used for pooled effect with high heterogeneity.[17] Otherwise, a fixed-effect model was used.[18]
RESULTS
The initial search retrieved 179 hits. By screening title and abstract, irrelevant studies were excluded, leaving 13 articles for full-text assessment. Six studies were excluded due to overlapping data, statistical data unavailable, or noncomparative study. Finally, seven studies were included for meta-analysis.[19,20,21,22,23,24,25] The PRISMA flowchart of literature review is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
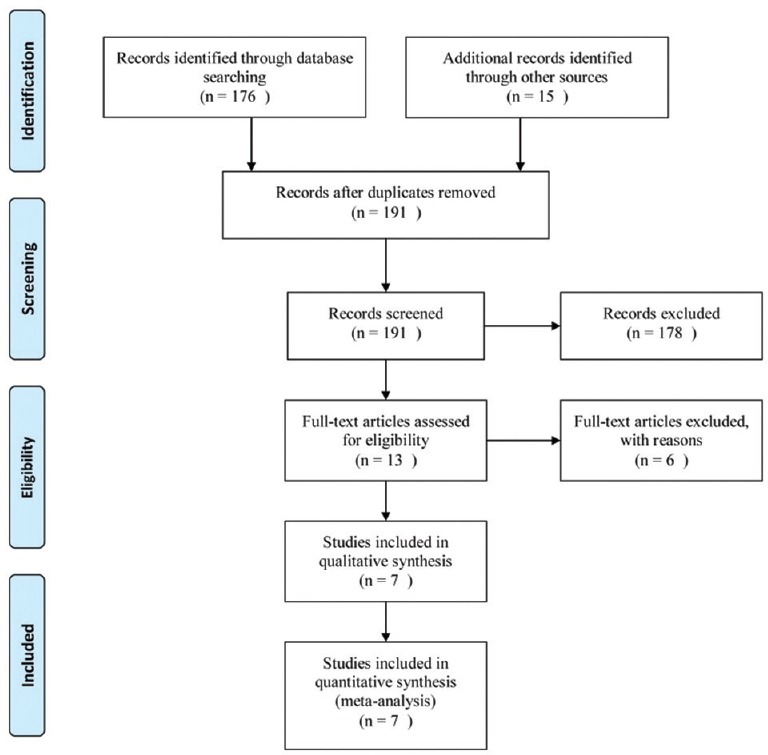
Flow chart of the studies included in the meta-analysis.
The characteristics of the included studies were summarized in Tables 1 and 2. Overall, there were 785 patients (423 underwent IEJ and 362 underwent EEJ) included in the meta-analysis. The patients were from China, Japan, and Korea. LTG were performed from 2001 to 2015. Most of the included patients underwent extended lymphadenectomy (D1+ or D2). Three studies reported IEJ using the Orvil™,[20,21,24] and three studied reported IEJ using linear staple.[22,23,25] and Chen et al.[19] reported IEJ using multiple technique including linear stapler and conventional circular stapler. All the seven studies achieved no less than six stars [Table 3].
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of included studies comparing IEJ and EEJ after laparoscopic total gastrectomy for gastric cancer
| Study | Country | Period | Surgical type | Sample size, n | Mean age (years) | Gender (male/female, n) | Mean BMI (kg/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al.[19] | China | 2006–2015 | TLTG | 108 | 59.4 | 73/35 | 23.5 |
| LATG | 145 | 57.3 | 98/47 | 23.1 | |||
| Cui et al.[25] | China | 2013–2014 | TLTG | 16 | 61.3 | 10/6 | 22.8 |
| LATG | 47 | 67.6 | 34/16 | 23.2 | |||
| Ito et al.[20] | Japan | 2001–2012 | TLTG | 117 | NA | NA | NA |
| LATG | 46 | NA | NA | NA | |||
| Jung et al.[21] | Korea | 2004–2012 | TLTG | 40 | 63.4 | 31/9 | 24.0 |
| LATG | 47 | 61.2 | 37/10 | 23.4 | |||
| Kim EY et al.[22] | Korea | 2009–2014 | TLTG | 27 | 60.8 | 22/5 | 24.0 |
| LATG | 29 | 59.3 | 20/9 | 23.3 | |||
| Kim HS et al.[23] | Korea | 2010–2011 | TLTG | 90 | 58.0 | 61/29 | 23.2 |
| LATG | 23 | 56.8 | 19/6 | 22.2 | |||
| Lu et al.[24] | China | 2011–2014 | TLTG | 25 | 59.0 | 22/3 | 22.5 |
| LATG | 25 | 58.4 | 21/4 | 22.9 |
BMI: Body mass index; TLTG: Totally laparoscopic total gastrectomy; LATG: Laparoscopy-assisted laparoscopic gastrectomy; NA: Not available; EEJ: Extracorporeal esophagojejunostomy; IEJ: Intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy.
Table 2.
Surgical techniques of included studies comparing IEJ and EEJ after laparoscopic total gastrectomy for gastric cancer
| Study | Surgical type | Tumor stage (I/II/III/IV, n) | Extent of LND (D1+/D2, n) | EEJ incision length (cm) | IEJ technique |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al.[19] | TLTG | 53/27/28/0 | 0/108 | NA | Multiple |
| LATG | 82/27/36/0 | 0/145 | |||
| Cui et al.[25] | TLTG | NA | 0/16 | 10 | Linear staple side to side |
| LATG | NA | 0/47 | |||
| Ito et al.[20] | TLTG | 79/24/12/2 | 89/28 | NA | OrVil™ |
| LATG | 35/5/5/1 | 35/9 | |||
| Jung et al.[21] | TLTG | 25/6/9/0 | 18/22 | 5–7 | OrVil™ |
| LATG | 19/11/17/0 | 1/46 | |||
| Kim EY et al.[22] | TLTG | 25/1/1/0 | 25/2 | 7 | Linear staple side-to-side |
| LATG | 12/6/10/1 | 21/8 | |||
| Kim HS et al.[23] | TLTG | NA | NA | 4–5 | Linear staple side-to-side |
| LATG | NA | NA | |||
| Lu et al.[24] | TLTG | 0/5/17/3 | 8/17 | 4–6 | OrVil™ |
| LATG | 4/5/15/1 | 10/15 |
LND: Lymph node dissection; EEJ: Extracorporeal esophagojejunostomy; IEJ: Intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy; TLTG: Totally laparoscopic total gastrectomy; LATG: Laparoscopy-assisted laparoscopic gastrectomy; NA: Not available.
Table 3.
Qualities of included studies evaluated by NOS (score)
| Study | *Selection | Comparability | †Outcomes | Total scores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al.[19] | 4 | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| Cui et al.[25] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Ito et al.[20] | 4 | 1 | 1 | 6 |
| Jung et al.[21] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 8 |
| Kim EY et al.[22] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Kim HS et al.[23] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Lu et al.[24] | 4 | 2 | 2 | 8 |
*:1. Representativeness of exposed cohort; 2. Selection of non-exposed cohort; 3. Ascertainment of exposure; 4. Outcome not present at the start of the study; †:1. Assessment of outcomes, 2. Length of follow-up, 3. Adequacy of follow-up. NOS: the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale
Intraoperative outcomes
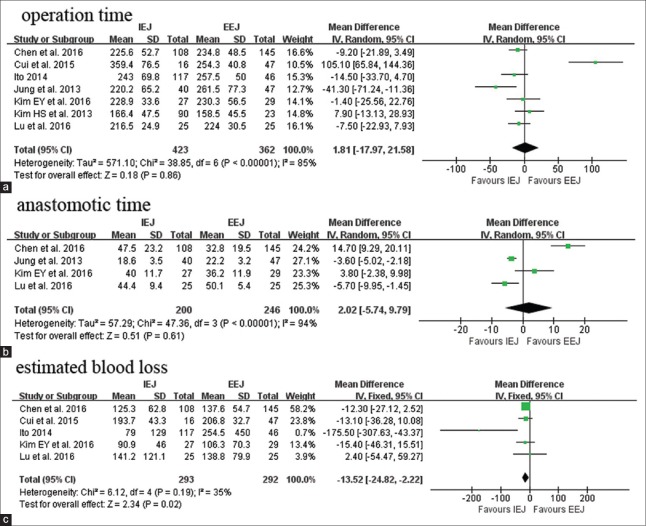
All seven pooled studies reported the operation time. The mean operation time of IEJ ranged from 166.4 min to 259.4 min. Compared with EEJ, IEJ had similar operation time (WMD: 1.81 min; 95% CI: −17.97–21.58; P = 0.86; Figure 2a). According to four studies reporting anastomotic time,[19,21,22,24] the meta-analysis found that there was no difference between IEJ and EEJ patients (WMD: 2.02 min; 95% CI: −5.74–9.79; P = 0.61; Figure 2b). IEJ had less blood loss compared with EEJ as reported by five studies (WMD: −13.52 ml; 95% CI: −24.82–−2.22; P = 0.02; Figure 2c).
Figure 2.
Forest plots of operative outcomes: Operation time (a), anastomotic time (b), estimated blood loss (c). IEJ: Intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy; EEJ: Extracorporeal esophagojejunostomy; SD: Standard deviation; CI: Confidence interval.
Postoperative outcomes
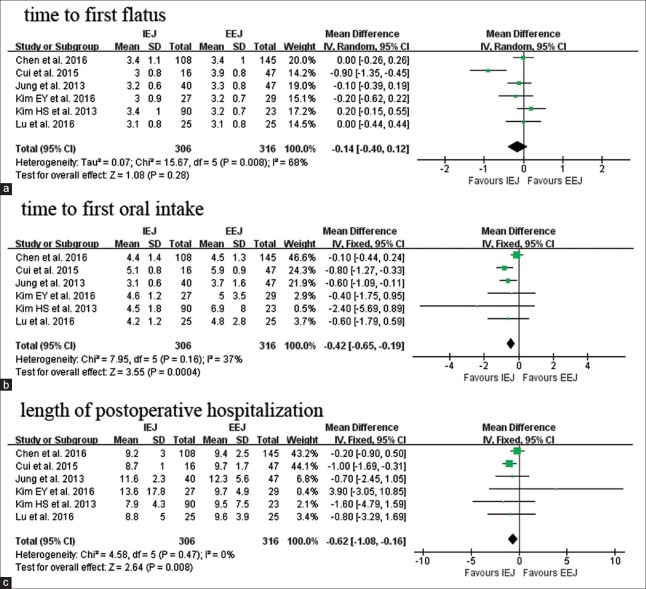
As for postoperative recovery, we mainly evaluate three parameters, including time to first flatus and to first oral intake and length of hospitalization (LOH). IEJ and EEJ had equivalent time to first flatus (WMD: −0.14 day; 95% CI: −0.40–0.12; P = 0.28; Figure 3a). Earlier first oral intake (WMD: −0.42 day; 95% CI: −0.65–−0.19; P < 0.01;Figure 3b) and shorter postoperative LOH was observed in IEJ (WMD: −0.62 day; 95% CI: −1.08–−0.16; P < 0.01; Figure 3c).
Figure 3.
Forest plots of postoperative recovery: Time to first flatus (a), time to first oral intake (b), length of postoperative hospitalization (c). IEJ: Intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy; EEJ: Extracorporeal esophagojejunostomy; SD: Standard deviation; CI: Confidence interval.
IEJ and EEJ had equivalent risk for esophagojejunostomy leakage (OR: 0.70; 95% CI: 0.27–1.82; P = 0.47). Similar to esophagojejunostomy stenosis, there was no significant difference between two groups (OR: 0.93; 95% CI: 0.35–2.45; P = 0.88).
Oncological outcomes
For the oncological outcomes, we evaluated retrieved lymph nodes and proximal resection. IEJ retrieved similar lymph nodes as EEJ (WMD: 1.45; 95% CI: −0.41–3.30; P = 0.13). The proximal resection in IEJ and EEJ was comparable (WMD: 0.03 cm; 95% CI: −0.19–0.25; P = 0.79).
Sensitivity analysis and publication bias
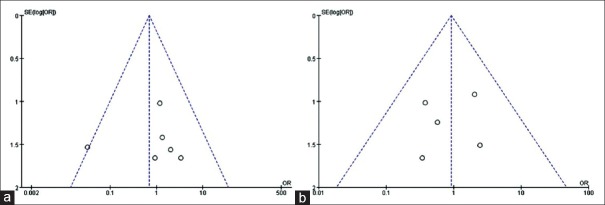
Sensitivity analyses were conducted by exclusion of the highest weighted study in each pooled analysis. These exclusions did not alter the results obtained in cumulative analyses. Funnel plots based on the esophagojejunostomy leakage and stenosis were performed to assess publication bias. No significant publication bias was detected by visual inspection of the funnel plot in which the pooled studies were almost symmetry and none of them was outside the 95% CI [Figure 4].
Figure 4.
Funnel plots of esophagojejunostomy-related complications: leakage (a), stenosis (b). SE: Standard error; OR: Odds ratio.
DISCUSSION
Esophagojejunostomy is the most important part of reconstruction after total gastrectomy. LG with intracorporeal anastomosis has frequently performed based on the strength of accumulated experiences and improved laparoscopic instruments. IEJ and EEJ after LTG have some differences. First, esophagojejunostomy is usually completed in deep and narrow surgical space. IEJ provides a more tension-free anastomosis and avoids injuring to the surrounding structures. Second, IEJ requires smaller incision and decreases manipulation and exposure of the operating field. Third, IEJ is performed more meticulously in a magnified surgical vision. These characteristics of IEJ contribute to reduce the surgical trauma and accelerate the postoperative recovery. This meta-analysis showed IEJ has better cosmesis, less blood loss, faster bowel function recovery, and shorter LOH as compared with EEJ.
Concerning the high techniques demanding in laparoscopic hand-sewn,[26,27] intracorporeal gastrointestinal reconstruction was rarely performed in a quite long period until the introduction of liner or circular staplers.[28,29] In previous retrospective studies and meta-analyses, LDG with intracorporeal anastomosis was reported to be safer, more technically feasible, and less invasive compared to that with extracorporeal anastomosis.[30,31] However, LTG with IEJ was rarely performed and was limited to a few centers. Unlike intracorporeal gastroduodenostomy or gastrojejunostomy, the surgical space for IEJ is deeper and narrower. Referring to our experience, the manipulations of the surgeon or assistant who stands on the right side of the patient might be hindered. When to conjoint to the jejunum, the esophageal stump tends to retract to the thoracic cavity and is more difficult to hold than the remnant stomach. Several innovative methods were proposed to facilitate IEJ, including end-to-side anastomosis with Orvil™,[32] side-to-side anastomosis with liner stapler,[33] functional end-to-end anastomosis with liner stapler[34] and so on. In this meta-analysis, we found IEJ and EEJ could performed in comparable time similar to that historically reported for.[35,36] We also collected several studies reported IEJ techniques in large scales and summarized them in Table 4.[37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45] The surgical outcomes including operation time, blood loss, bowel recovery, and LOH were in accordance with the study.
Table 4.
Summary reported IEJ techniques of studies comparing IEJ and EEJ after laparoscopic total gastrectomy for gastric cancer
| Study | Year | Country | Sample size, n | IEJ technique | Mean operation time (min) | Mean EBL (ml) | Mean LOH (d) | Leakage rate (%) | Stenosis rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Miura et al.[45] | 2017 | Japan | 120 | FEEA | 350.8 | 0 | 13.0 | 1.7 | 0.8 |
| 48 | Overlap | 402.5 | 6.5 | 16.0 | 6.3 | 0 | |||
| Sugiyama et al.[44] | 2017 | Japan | 147 | FEEA | 342.0 | 128.0 | 19.4 | 2.0 | NA |
| Shida et al.[37] | 2016 | Japan | 100 | OrVil | 338.7 | 146.4 | 14.6 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| Kim JH et al.[38] | 2015 | Korea | 58 | DST | 251.8 | 204.6 | 9.6 | 0 | 1.7 |
| Kosuga et al.[39] | 2015 | Japan | 71 | HDST | 307.4 | 111.1 | 17.0 | 9.9 | 18.3 |
| 65 | SST | 325.4 | 72.8 | 14.9 | 3.1 | 6.2 | |||
| Yamamoto et al.[40] | 2014 | Japan | 53 | Overlap | 380.0 | 31.5 | 18.0 | 1.9 | 0 |
| Kim HS et al.[41] | 2013 | Korea | 139 | Linear side to side | 151.8 | NA | 7.8 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Nagai et al.[42] | 2013 | Japan | 57 | T shape | 368.0 | 80.4 | 14.2 | 0 | 0 |
| Inaba et al.[43] | 2010 | Japan | 53 | Overlap | 373.4 | 146.5 | 14.4 | 3.8 | 3.8 |
IEJ: Intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy; EEJ: Extracorporeal esophagojejunostomy; EBL: Estimated blood loss; LOH: Length of hospitalization; FEEA: Functional end-to-end anastomosis; DST: Double-staple technique; HDST: Hemi-double staple technique; SST: Single-staple technique; NA: Not available.
The complexity of IEJ raises concerns for surgical safety. In the meta-analysis, we used two fatal anastomosis-related complications, leakage and stenosis, to evaluate the safety of IEJ. This study demonstrated no statistical differences between IEJ and EEJ neither in leakage nor stenosis. IEJ appeared to have a slightly lower risk of leakage. We attribute this result to the inclusion of the study by Kim et al.[23] They compared IEJ and EEJ in patients with GC near the gastroesophageal junction. To achieve adequate surgical margins, the esophageal stumps were short to complete the EEJ. Hypothesis is also proposed that IEJ is accomplished in a tense-free circumstance, which avoids injuring the surrounding structure and preserves the blood supply of the anastomosis. One of our studies aimed to further evaluate this issue is ongoing. Stenosis is another uncommon but thorny complication relating to esophagojejunostomy. IEJ was reported to reduce the risk of stenosis by creating a side-to-side anastomosis stoma using liner stapler. Circular staple appears to have slightly higher risk of stenosis, particularly in cases using small anvils. Zuiki et al.[46] reported IEJ using double-stapled anastomosis had higher risk of stenosis. In the meta-analysis, the majority of IEJ styles were liner staple and Orvil™ and the risks of stenosis following IEJ and EEJ were similar.
Oncological outcomes are critical for patients with GC. In the meta-analysis, we evaluated the number of retrieved lymph nodes and proximal resection because limited studies included reported the detail of long-term outcomes. We found IEJ and EEJ harvested equivalent numbers of lymph nodes, which was reasonable as two approach were follow similar LTG and lymphadenectomy in theory. The study also showed the proximal resections for IEJ and EEJ had no significant differences, indicating IEJ could achieve both technical feasibility and oncological safety. However, in this meta-analysis, we could not evaluate the long-term outcomes directly using overall survival rates or disease-free survival rates, since there was no study reporting these outcomes with appropriate follow-up. On the basis of the indirect evidence in the meta-analysis, the IEJ is oncologically safe; however, further studies with long-term outcomes are needed for validation.
The present meta-analysis had several limitations as following. First, the majority of IEJ styles in pooled studies were liner staple and Orvil™. Several single-arm studies reporting other IEJ styles were excluded. Most of these styles were reported in case reports or case series and attempted in few surgeons. It is a fact that the style of IEJ is still unsettled currently. Modified styles and novel styles continue arising. In turn, using liner staple and Orvil™ are the top two prevailing styles. We also believe that they are the most promising two prevailing styles. This study reveals IEJ is as feasible and safe as EEJ, with some advantages additionally. We hope this study would encourage more experienced surgeons to attempt and perfect the techniques. Second, all included studies are retrospective, nonrandomized studies, with inevitable biases. These lead to some flaws in the plausibility of the study. Third, though we collected all the studies on this issue as we know, the sample size is still not large enough. We will continue following the studies on this issue and conducting our ongoing research. Fourth, there was no study include from Western countries, which might defect the utility of our standpoints in Western countries.
Compared with EEJ, IEJ following LTG is a feasible and safe procedure. IEJ has better cosmesis, milder surgical trauma, and faster postoperative recovery. More high-quality studies are awaited to confirm the benefit of IEJ and determine the appropriate anastomosis method. Surgeons with sufficient expertise are encouraged to attempt IEJ.
Financial support and sponsorship
This work was supported by the grants from the Medical and health technology project of Zhejiang Province (No. 2014KYB138, and No. 2016RCB008).
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Footnotes
Edited by: Ning-Ning Wang
REFERENCES
- 1.Chen K, Mou YP, Xu XW, Pan Y, Zhou YC, Cai JQ, et al. Comparison of short-term surgical outcomes between totally laparoscopic and laparoscopic-assisted distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A 10-y single-center experience with meta-analysis. J Surg Res. 2015;194:367–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.10.020. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.10.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cianchi F, Qirici E, Trallori G, Macrì G, Indennitate G, Ortolani M, et al. Totally laparoscopic versus open gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A matched cohort study. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2013;23:117–22. doi: 10.1089/lap.2012.0310. doi: 10.1089/lap.2012.0310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Aoyama T, Yoshikawa T, Hayashi T, Hasegawa S, Tsuchida K, Yamada T, et al. Randomized comparison of surgical stress and the nutritional status between laparoscopy-assisted and open distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21:1983–90. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-3509-9. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-3509-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Haverkamp L, Brenkman HJ, Seesing MF, Gisbertz SS, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Luyer MD, et al. Laparoscopic versus open gastrectomy for gastric cancer, a multicenter prospectively randomized controlled trial (LOGICA-trial) BMC Cancer. 2015;15:556. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1551-z. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1551-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kim HH, Han SU, Kim MC, Hyung WJ, Kim W, Lee HJ, et al. Long-term results of laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A large-scale case-control and case-matched korean multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:627–33. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.48.8551. doi: 10.1200/jco.2013.48.8551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lee JH, Lee CM, Son SY, Ahn SH, Park DJ, Kim HH, et al. Laparoscopic versus open gastrectomy for gastric cancer: Long-term oncologic results. Surgery. 2014;155:154–64. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2013.06.015. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2013.06.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Deng Y, Zhang Y, Guo TK. Laparoscopy-assisted versus open distal gastrectomy for early gastric cancer: A meta-analysis based on seven randomized controlled trials. Surg Oncol. 2015;24:71–7. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2015.02.003. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2015.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cui M, Li Z, Xing J, Yao Z, Liu M, Chen L, et al. A prospective randomized clinical trial comparing D2 dissection in laparoscopic and open gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 2015;32:241. doi: 10.1007/s12032-015-0680-1. doi: 10.1007/s12032-015-0680-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hu Y, Huang C, Sun Y, Su X, Cao H, Hu J, et al. Morbidity and mortality of laparoscopic versus open D2 distal gastrectomy for advanced gastric cancer: A Randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:1350–7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.63.7215. doi: 10.1200/jco.2015.63.7215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hur H, Lee HY, Lee HJ, Kim MC, Hyung WJ, Park YK, et al. Efficacy of laparoscopic subtotal gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy for locally advanced gastric cancer: the protocol of the KLASS-02 multicenter randomized controlled clinical trial. BMC cancer. 2015;15:355. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1365-z. doi: 101186/s12885-015-1365-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lee SR, Kim HO, Son BH, Shin JH, Yoo CH. Laparoscopic-assisted total gastrectomy versus open total gastrectomy for upper and middle gastric cancer in short-term and long-term outcomes. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2014;24:277–82. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0b013e3182901290. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0b013e3182901290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lu J, Huang CM, Zheng CH, Li P, Xie JW, Wang JB, et al. Short- and long-term outcomes after laparoscopic versus open total gastrectomy for elderly gastric cancer patients: A Propensity score-matched analysis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2015;19:1949–57. doi: 10.1007/s11605-015-2912-2. doi: 10.1007/s11605-015-2912-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lee JH, Nam BH, Ryu KW, Ryu SY, Park YK, Kim S, et al. Comparison of outcomes after laparoscopy-assisted and open total gastrectomy for early gastric cancer. Br J Surg. 2015;102:1500–5. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9902. doi: 10.1002/bjs.9902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang W, Zhang X, Shen C, Zhi X, Wang B, Xu Z, et al. Laparoscopic versus open total gastrectomy for gastric cancer: An updated meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014;9:e88753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol. 2009;62:1006–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.005. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–60. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–88. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mantel N, Haenszel W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959;22:719–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chen K, Pan Y, Cai JQ, Wu D, Yan JF, Chen DW, et al. Totally laparoscopic versus laparoscopic-assisted total gastrectomy for upper and middle gastric cancer: A single-unit experience of 253 cases with meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 2016;14:96. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0860-2. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0860-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ito H, Inoue H, Odaka N, Satodate H, Onimaru M, Ikeda H, et al. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of esophagojejunostomy after totally laparoscopic total gastrectomy using a trans-orally inserted anvil: A single-center comparative study. Surg Endosc. 2014;28:1929–35. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-3417-x. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-3417-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jung YJ, Kim DJ, Lee JH, Kim W. Safety of intracorporeal circular stapling esophagojejunostomy using trans-orally inserted anvil (OrVil) following laparoscopic total or proximal gastrectomy – Comparison with extracorporeal anastomosis. World J Surg Oncol. 2013;11:209. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-11-209. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-11- [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kim EY, Choi HJ, Cho JB, Lee J. Totally laparoscopic total gastrectomy versus laparoscopically assisted total gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016;36:1999–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kim HS, Kim MG, Kim BS, Lee IS, Lee S, Yook JH, et al. Comparison of totally laparoscopic total gastrectomy and laparoscopic-assisted total gastrectomy methods for the surgical treatment of early gastric cancer near the gastroesophageal junction. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2013;23:204–10. doi: 10.1089/lap.2012.0393. doi: 10.1089/lap.2012.0393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lu X, Hu Y, Liu H, Mou T, Deng Z, Wang D, et al. Short-term outcomes of intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy using the transorally inserted anvil versus extracorporeal circular anastomosis during laparoscopic total gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A propensity score matching analysis. J Surg Res. 2016;200:435–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.08.013. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2015.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cui C, Liang W, Zhu Z, Yao H, Wu Y, Liu L. Feasibility, safety and short-term efficacy of totally laparoscopic total gastrectomy for upper stomach cancer (In Chinese) Chin J Gen Surg. 2015;24:1377–82. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.1005-6947.2015.10.007. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Puntambekar S, Badran R, Parikh H, Bansal A, Sharma V, Chitale M, et al. Technical feasibility and short-term outcome of intracorporeal hand-sewn esophagojejunostomy after laparoscopic total gastrectomy: Our experience. Indian J Surg. 2017;79:497–503. doi: 10.1007/s12262-016-1509-7. doi: 10.1007/s12262-016-1509-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Norero E, Muñoz R, Ceroni M, Manzor M, Crovari F, Gabrielli M, et al. Two-layer hand-sewn esophagojejunostomy in totally laparoscopic total gastrectomy for gastric cancer. J Gastric Cancer. 2017;17:267–76. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2017.17.e26. doi: 10.5230/jgc.2017.17.e26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kanaya S, Kawamura Y, Kawada H, Iwasaki H, Gomi T, Satoh S, et al. The delta-shaped anastomosis in laparoscopic distal gastrectomy: Analysis of the initial 100 consecutive procedures of intracorporeal gastroduodenostomy. Gastric Cancer. 2011;14:365–71. doi: 10.1007/s10120-011-0054-0. doi: 10.1007/s10120-011-0054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kim HI, Cho I, Jang DS, Hyung WJ. Intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy using a circular stapler with a new purse-string suture technique during laparoscopic total gastrectomy. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;216:e11–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.10.008. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2012.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhang YX, Wu YJ, Lu GW, Xia MM. Systematic review and meta-analysis of totally laparoscopic versus laparoscopic assisted distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:116. doi: 10.1186/s12957-015-0532-7. doi: 10.1186/s12957-015-0532-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Woo J, Lee JH, Shim KN, Jung HK, Lee HM, Lee HK, et al. Does the difference of invasiveness between totally laparoscopic distal gastrectomy and laparoscopy-assisted distal gastrectomy lead to a difference in early surgical outcomes? A Prospective randomized trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:1836–43. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-4229-x. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-4229-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Jeong O, Park YK. Intracorporeal circular stapling esophagojejunostomy using the transorally inserted anvil (OrVil) after laparoscopic total gastrectomy. Surg Endosc. 2009;23:2624–30. doi: 10.1007/s00464-009-0461-z. doi: 10.1007/s00464-009-0461-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Matsui H, Okamoto Y, Nabeshima K, Nakamura K, Kondoh Y, Makuuchi H, et al. Endoscopy-assisted anastomosis: A modified technique for laparoscopic side-to-side esophagojejunostomy following a total gastrectomy. Asian J Endosc Surg. 2011;4:107–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1758-5910.2011.00088.x. doi: 10.1111/j.1758-5910.2011.00088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ebihara Y, Okushiba S, Kawarada Y, Kitashiro S, Katoh H. Outcome of functional end-to-end esophagojejunostomy in totally laparoscopic total gastrectomy. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2013;398:475–9. doi: 10.1007/s00423-013-1051-z. doi: 10.1007/s00423-013-1051-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bo T, Peiwu Y, Feng Q, Yongliang Z, Yan S, Yingxue H, et al. Laparoscopy-assisted vs.Open total gastrectomy for advanced gastric cancer: Long-term outcomes and technical aspects of a case-control study. J Gastrointest Surg. 2013;17:1202–8. doi: 10.1007/s11605-013-2218-1. doi: 10.1007/s11605-013-2218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shim JH, Oh SI, Yoo HM, Jeon HM, Park CH, Song KY, et al. Short-term outcomes of laparoscopic versus open total gastrectomy: A matched-cohort study. Am J Surg. 2013;206:346–51. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2012.11.011. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2012.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Shida A, Mitsumori N, Fujioka S, Takano Y, Iwasaki T, Takahashi N, et al. Comparison of short-term and long-term clinical outcomes between laparoscopic and open total gastrectomy for patients with gastric cancer. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2016;26:319–23. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000000285. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000000285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kim JH, Choi CI, Kim DI, Kim DH, Jeon TY, Kim DH, et al. Intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy using the double stapling technique after laparoscopic total gastrectomy: A retrospective case-series study. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:2973–81. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2973. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kosuga T, Hiki N, Nunobe S, Ohashi M, Kubota T, Kamiya S, et al. Does the single-stapling technique for circular-stapled esophagojejunostomy reduce anastomotic complications after laparoscopic total gastrectomy? Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:3606–12. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4417-3. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4417-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yamamoto M, Zaima M, Yamamoto H, Harada H, Kawamura J, Yamaguchi T, et al. A modified overlap method using a linear stapler for intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy after laparoscopic total gastrectomy. Hepatogastroenterology. 2014;61:543–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kim HS, Kim BS, Lee S, Lee IS, Yook JH, Kim BS, et al. Reconstruction of esophagojejunostomies using endoscopic linear staplers in totally laparoscopic total gastrectomy: Report of 139 cases in a large-volume center. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2013;23:e209–16. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0b013e31828e3b79. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0b013e31828e3b79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nagai E, Ohuchida K, Nakata K, Miyasaka Y, Maeyama R, Toma H, et al. Feasibility and safety of intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy after laparoscopic total gastrectomy: Inverted T-shaped anastomosis using linear staplers. Surgery. 2013;153:732–8. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2012.10.012. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2012.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Inaba K, Satoh S, Ishida Y, Taniguchi K, Isogaki J, Kanaya S, et al. Overlap method: Novel intracorporeal esophagojejunostomy after laparoscopic total gastrectomy. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;211:e25–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2010.09.005. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2010.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sugiyama M, Oki E, Ogaki K, Morita M, Sakaguchi Y, Koga S, et al. Clinical outcomes of esophagojejunostomy in totally laparoscopic total gastrectomy: A Multicenter study. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2017;27:e87–91. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000000435. doi: 10.1097/sle.0000000000000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Miura S, Kanaya S, Hosogi H, Kawada H, Akagawa S, Shimoike N, et al. Esophagojejunostomy with linear staplers in laparoscopic total gastrectomy: Experience with 168 cases in 5 consecutive years. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2017;27:e101–7. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0000000000000464. doi: 10.1097/sle.0000000000000464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zuiki T, Hosoya Y, Kaneda Y, Kurashina K, Saito S, Ui T, et al. Stenosis after use of the double-stapling technique for reconstruction after laparoscopy-assisted total gastrectomy. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:3683–9. doi: 10.1007/s00464-013-2945-0. doi: 10.1007/s00464-013-2945-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]