Abstract
Formic acid is corrosive and a sensitive and selective sensor could be useful in industrial, medical, and environmental settings. We present a chemiresistor for detection of formic acid comprised of single-walled carbon nanotubes and nickel bis(ortho-diiminosemiquinonate) (1)—a planar metal complex that can act as a ditopic hydrogen-bonding selector. Formic acid is detected in concentrations as low as 83 ppb. The resistance of the material decreases on exposure to formic acid, but slightly increases on exposure to acetic acid. We propose that 1 assists in partial protonation of the CNT by formic acid, but the response toward acetic acid is dominated by inter-CNT swelling. This technology establishes CNT-based chemiresistive discrimination between formic and acetic acid vapors.
Keywords: formic acid, carbon nanotubes, chemiresistor, nickel, gas sensor
Graphical abstract
Authors are required to submit a graphic entry for the Table of Contents (TOC) that, in conjunction with the manuscript title, should give the reader a representative idea of one of the following: A key structure, reaction, equation, concept, or theorem, etc., that is discussed in the manuscript. Consult the journal’s Instructions for Authors for TOC graphic specifications. (3.33 × 1.88 inches)
Formic acid, the simplest organic acid, is highly pungent and corrosive with a Permissible Exposure Limit (U.S. OSHA PEL) of 5 ppm. An inexpensive, real-time, electronic sensor for formic acid vapors can protect worker health and limit formicary corrosion of metal components.1 Formic acid sensors can also be useful in diagnosing health conditions,2–4 monitoring air quality,5–7 tracking the spread of invasive formicine ant species such as Nylanderia fulva (“tawny crazy ant”),8 and enabling automated pest control. Sensors would facilitate the adoption of formic acid as a hydrogen carrier for energy storage.9 While much work has been done on low-power aqueous-phase pH sensors,10–13 volatile acidity detectors have been less explored. A selective formic acid detector should be able to discriminate it from other polar compounds. For example, formic and acetic acid are present in similar quantities in environmental and human breath samples and their discrimination has utility.2,14
Carbon nanotube (CNT)-based chemiresistors are an attractive platform for developing gas sensors. Although colormetric15–17 and metal-oxide and -nitride chemiresistors18 for formic acid detection exist, CNT chemiresistors are cost-effective, low-power, and operational at room temperature.19–21 CNT chemiresistors can be straightforwardly integrated with electronic devices, making them ideal candidates for distributed sensor networks.22,23 While strong acids have been shown to protonate and p-dope CNTs (Figure 1a),22,24–27 there have been few reports of the chemiresistive response of CNTs to carboxylic acids. Specifically, vertically aligned CNT arrays have a chemicapacitive response to formic acid.28 Chemical-vapor-deposition-grown graphene becomes more conductive upon exposure to acetic acid vapor.29 A single-CNT field effect transistor (FET) responds to propanoic acid vapors upon functionalization with guanine-rich single-stranded DNA.30 However, these device architectures require greater manufacturing and operating complexity than chemiresistors based on solution-processed networks of CNTs. Networks of covalently-modified CNTs have been reported to increase in resistance, non-selectively, on exposure to acetic acid or other volatile organics via a swelling mechanism.31,32 Studies on CNT-based vapor sensors discriminating between formic and other carboxylic acids are lacking.
Figure 1.
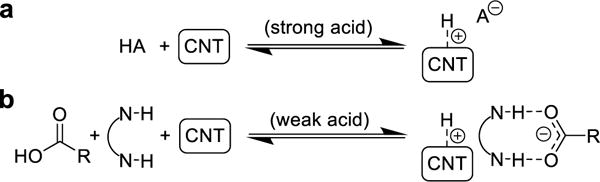
Carbon nanotube protonation and p-doping by (a) strong acid or (b) carboxylic acid assisted by anion receptor.
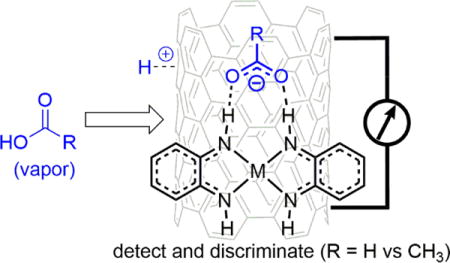
We have investigated planar ditopic complexes as selectors to improve the sensitivity and selectivity of CNT-based sensors toward formic acid. We hypothesized that selectors bearing ditopic hydrogen-bond donors could promote protonation of CNTs by carboxylic acids by stabilizing the carboxylate anion (Figure 1b). Looking to Nature’s formate dehydrogenase for selector inspiration, the highly conserved Arg587 residue is known to be crucial in formate binding as a ditopic hydrogen bond donor.33 Structurally related ureas/thioureas are receptors for carboxylates.34–36 For CNT-based chemiresistors, previous work has shown that thioureas can act as effective selectors for cyclohexanone, and the N-aryl substituents are key to tranducing a chemiresistive response to CNTs through non-covalent π-π interactions.37,38
In this study, we used square planar complexes 1 and 2 (Figure 2a)39 as selectors. The N-H moieties can participate in ditopic H-bonding with carboxylate,40 while the molecular planarity should enhance electronic communication though π-π interactions.41,42 Adding 0–4 equiv. of tetrabutylammonium acetate to 1 in d6-dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) results in a distinct shift of the N-H protons from 8.8 to 9.2 ppm (see Supporting Information, Figure S2). This behavior is consistent with competitive H-bonding to acetate and DMSO. UV-Vis-NIR absorption spectra of 1 in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) solution show a marked decrease in the LLCT band at 784 nm after exposure to CNTs, indicating strong CNT adsorption of 1 (Figure S7).
Figure 2.
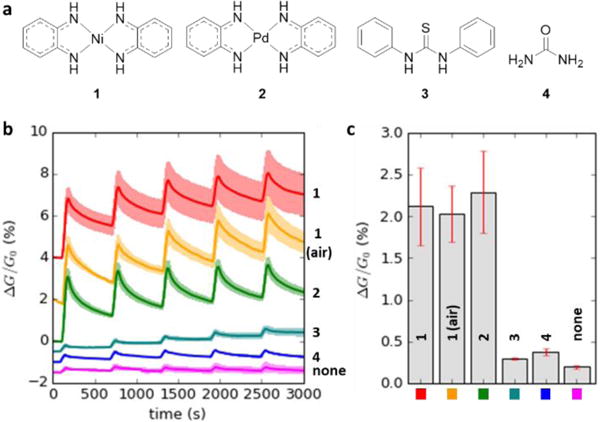
Formic acid vapor sensing (37 ppm) with CNT chemiresistors and (a) molecular selectors. (b) Each trace (vertically offset for clarity) is the average of four sensors with the standard deviation illustrated in a lighter shade; five cycles of one-minute exposure and nine-minute purge. The carrier gas is N2 unless otherwise noted. (c) Average conductivity change for each selector. Error bars represent one standard devation across 20 data points (five measurements each across four devices).
Chemiresistors made from CNT networks non-covalently functionalized with selector were exposed to formic acid at 37 ppm in N2 at room temperature (2% of its saturated vapor pressure from a calibrated oven held at 40°C). Analyte exposures were set at 1 minute followed by a 9 minute purge. Devices made with 1 or 2 exhibited semi-reversible 2% increases in conductivity, whereas devices made with N,N′-diphenylthiourea (3), urea (4), or no selector increased conductivity less than 0.4% (Figure 2b). Because benchtop DMF solutions of 1 remained stable for weeks while those of 2 formed brown particulate, further sensing experiments were conducted with 1 as the selector. An experiment using air (35% relative humidity) as the carrier gas instead of N2 for CNT/1 sensors gave a similar response.
We then demonstrated the sensitivity of CNT/1 chemiresistors to formic acid (Figure 3a). The response is linear for over nearly three orders of magnitude. This dynamic range includes the industrially relevant OSHA PEL of 5 ppm. The experimental limit of detection, 83 ppb, could conceivably be lowered by using longer exposure times.
Figure 3.
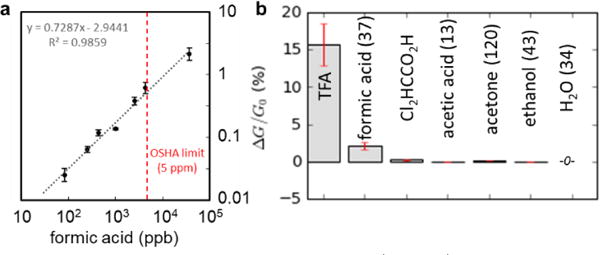
Average conductivity change (N = 20) of CNT/1 upon one-minute exposures to (a) a range of formic acid concentrations and (b) various analytes at 2% of their saturated vapor from 40°C analyte oven. For calibrated analytes, concentrations are listed parenthetically (ppm).
We established the selectivity of CNT/1 chemiresistors by exposure to a variety of other volatile organic compounds at 2% of their saturated vapor pressure from a 40°C analyte oven (Figure 3b). Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), dichloroacetic acid, and acetone induced increases in conductivity per exposure of 16%, 0.23%, and 0.15%. Acetic acid and ethanol resulted in small decreases in conductivity (−0.05% and −0.07%). Water did not cause any change in conductivity. The strong conductivity increase upon TFA exposure correlates with the high acidity of TFA (pKa = 0.0). Dichloroacetic acid, while a strong acid (pKa = 1.25), has lower volatility and thus a relatively low conductivity increase. Acetic acid is less acidic than formic acid (pKa = 4.75 vs 3.75), and the chemiresistive decrease in conductivity is consistent with swelling of inter-CNT gaps, similar to the responses observed for ethanol in this study. Acetic acid vapor also decreased conductivity in previous CNT network chemiresistive sensors.31,32 As a result, this sensor is selective for formic acid and stronger acids over acetic acid. This selectivity (and reversibility of the response) make CNT/1 chemiresistors unique from sensors based on strong Brønsted bases, which would be irreversible and not distinguish between various carboxylic acids.5,15
To interrogate the mechanism of this chemiresistive response, CNT/1 was examined with Raman spectroscopy (Figure S8). While the weak CNT D-band (~1340 cm−1) is obscured by overlapping signals from 1, the CNT G-band is distinct near 1590 cm−1 under ambient air. Under saturated formic acid vapor, however, the G-band shifts to higher energy by 0.5 cm−1 (Figure 4b). Other sharp Raman features of CNT/1 are not similarly shifted (Figure S9). Based on previous studies of CNTs in acidic solution,24,43 this shift corresponds to an introduction of approximately one hole per 640 carbon atoms in the CNT sample upon formic acid vapor exposure. Identical measurements of a sample of CNT without 1 showed no shift in the G-band (1589 cm−1) under ambient air or formic acid vapor (Figure 4a). These Raman observations are consistent with 1 facilitating protonation and p-doping of the CNTs.
Figure 4.
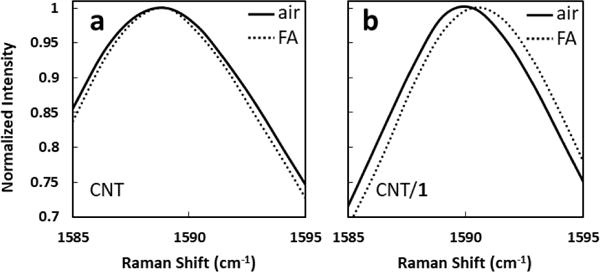
Raman G-band of (a) CNT and (b) CNT/1 under under ambient air or air saturated with formic acid vapor (FA).
To investigate the effect of π-stacking between the CNT and 1, we turned to computational models. Although 1 has nontrivial electronic structure as a result of ligand-based radical character, previous studies have shown accurate modeling using density function theory (DFT).44,45 Thus, a segment of (6,6)-CNT and 1 were geometry-optimized using a 2-layer ONIOM scheme in which 1 and the nearest C24 fragment (coronene) of the CNT were treated with restricted-spin, dispersion-corrected DFT while the remaining CNT atoms were modelled semiempirically. In the resulting structure, the metal complex adopts the curvature of the underlying CNT (Figure 5a). Furthermore, the short distance between the N atoms of the metal complex and the nearest CNT atoms (3.22 Å) supports a π-π interaction. The electronic structure was then examined via a single-point calculation, treating the whole model with DFT. The resulting density-of-states (DOS) plot shows a Fermi level of −5.94 eV compared to −5.99 eV for bare (6,6)-CNT (Figure 5c). Thus, 1 donates partial electron density to the CNT, activating the CNT toward protonation with mild acids. For comparison, an analogous model of (6,6)-CNT/3 also showed short non-bonded N-C contacts (Figure 5b), but the Fermi level shifts the opposite direction to −6.00 eV, indicating very slight withdrawal of electron density from the CNT. These results corroborate the experimental observation that CNT/1 chemiresistors respond to formic acid more readily than CNT or CNT/3 sensors.
Figure 5.
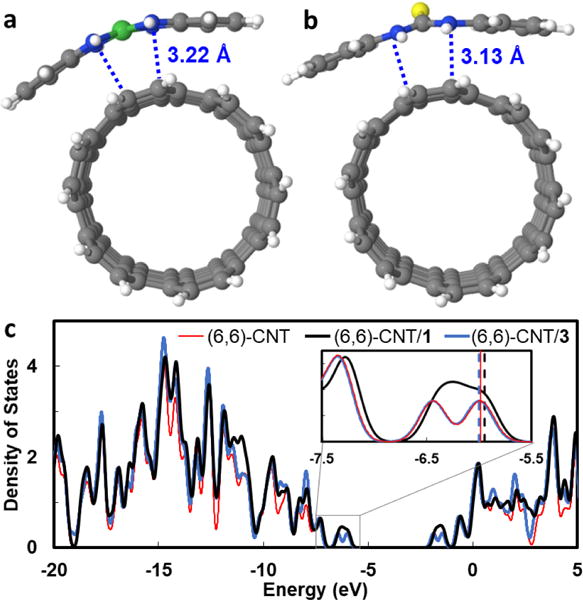
(a) Structural models of (6,6)-CNT/1 and (b) (6,6)-CNT/3. (c) DOS plots of (6,6)-CNT with and without 1 or 3. Inset: magnified view of frontier states with Fermi levels indicated by vertical lines.
In summary, square-planar metal complex selectors 1 and 2 leverage their chelating N-H moieties to facilitate protonation/p-doping of the CNT chemiresistor network by formic acid vapors. The resulting simple, low-power CNT/1 sensors can detect formic acid at concentrations relevant to industrial settings with short 1 minute exposure times. Although there is cross-reactivity with stronger acids, there is notably a smaller (and inverted) response to acetic acid, establishing the first CNT-based chemiresistive discrimination between formic and acetic acid vapors. Computational models also show that 1 can effectively π-stack and donate partial electron-density into the CNT network. We are interested in extending the use of 1, 2, and related metal complexes as selectors to detect and discriminate isosteres of carboxylate such as bicarbonate, phosphate, and arsenate in aqueous solution.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Army Research Office through the use of facilities at the Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies and National Science Foundation, DMR-1410718. S.L. was supported by NIH F32 NRSA (# GM110897).
Footnotes
Supporting Information
The Supporting Information is available free of charge on the ACS Publications website at DOI: 10.1021/xxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Experimental Details, Spectroscopic Characterization, Computational Details (PDF)
Notes
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- 1.Mikhailov AA. Effect of Low-Molecular Carbon Acids on Atmospheric Corrosion of Metals. Prot Met Phys Chem Surfaces. 2009;45(7):757–765. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Greenwald R, Johnson BA, Hoskins A, Dworski R. Exhaled Breath Condensate Formate after Inhaled Allergen Provocation in Atopic Asthmatics In Vivo. J Asthma. 2013;50(6):619–622. doi: 10.3109/02770903.2013.783065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Greenwald R, Fitzpatrick AM, Gaston B, Marozkina NV, Erzurum S, Teague WG. Breath Formate Is a Marker of Airway S-Nitrosothiol Depletion in Severe Asthma. PLoS One. 2010;5(7):e11919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McMartin KE, Ambre JJ, Tephly TR. Methanol Poisoning in Human Subjects. Role for Formic Acid Accumulation in the Metabolic Acidosis. Am J Med. 1980;68(3):414–418. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yan Y, Lu D, Zhou H, Hou H, Zhang T, Wu L, Cai L. Polyaniline-Modified Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor for Detection of Formic Acid Gas. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 2012;223(3):1275–1280. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nielsen GD, Hansen LF, Andersen B, Poulsen Nand OM. Indoor Air Guideline Levels for Formic, Acetic, Propionic and Butyric Acid. Indoor Air. 1998;8(S5):8–24. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Stavrakou T, Müller J-F, Peeters J, Razavi A, Clarisse L, Clerbaux C, Coheur P-F, Hurtmans D, De Mazière M, Vigouroux C, et al. Satellite Evidence for a Large Source of Formic Acid from Boreal and Tropical Forests. Nat Geosci. 2011;5(1):26–30. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wang Z, Moshman L, Kraus E, Wilson B, Acharya N, Diaz R. A Review of the Tawny Crazy Ant, Nylanderia Fulva, an Emergent Ant Invader in the Southern United States: Is Biological Control a Feasible Management Option? Insects. 2016;7(4):77. doi: 10.3390/insects7040077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sordakis K, Tang C, Vogt LK, Junge H, Dyson PJ, Beller M, Laurenczy G. Homogeneous Catalysis for Sustainable Hydrogen Storage in Formic Acid and Alcohols. Chem Rev. 2017 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00182. acs.chemrev.7b00182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Besteman K, Lee JO, Wiertz FGM, Heering HA, Dekker C. Enzyme-Coated Carbon Nanotubes as Single-Molecule Biosensors. Nano Lett. 2003;3(6):727–730. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fu Q, Liu J. Integrated Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube/microfluidic Devices for the Study of the Sensing Mechanism of Nanotube Sensors. J Phys Chem B. 2005;109(28):13406–13408. doi: 10.1021/jp0525686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Li CA, Han KN, Pham X-H, Seong GH. A Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Thin Film-Based pH-Sensing Microfluidic Chip. Analyst. 2014;139(8):2011. doi: 10.1039/c3an02195e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gou P, Kraut ND, Feigel IM, Bai H, Morgan GJ, Chen Y, Tang Y, Bocan K, Stachel J, Berger L, et al. Carbon Nanotube Chemiresistor for Wireless pH Sensing. Sci Rep. 2015;4(1):4468. doi: 10.1038/srep04468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Khare P, Kumar N, Kumari KM, Srivastava SS. Atmospheric Formic and Acetic Acids: An Overview. Rev Geophys. 1999;37(2):227–248. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sensidyne Industrial Health & Safety Information. Formic Acid 1–50 ppm Gas Detector Tube. http://www.sensidyne.com/colorimetric-gas-detector-tubes/detector-tubes/216s-formic-acid.php (accessed Nov 21, 2017)
- 16.Grant WM. Colorimetric Microdetermination of Formic Acid Based on Reduction to Formaldehyde. Anal Chem. 1948;20(3):267–269. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Genovese ME, Colusso E, Colombo M, Martucci A, Athanassiou A, Fragouli D. Acidochromic Fibrous Polymer Composites for Rapid Gas Detection. J Mater Chem A. 2017;5(1):339–348. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Eckshtain-Levi M, Capua E, Paltiel Y, Naaman R. Hybrid Sensor Based on AlGaN/GaN Molecular Controlled Device. ACS Sensors. 2016;1(2):185–189. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schnorr JM, Swager TM. Chemistry of Materials. American Chemical Society; Feb 8, 2011. Emerging Applications of Carbon Nanotubes; pp. 646–657. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Snow ES, Perkins FK, Robinson JA. Chemical Vapor Detection Using Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Chem Soc Rev. 2006;35(9):790. doi: 10.1039/b515473c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kauffman DR, Star A. Carbon Nanotube Gas and Vapor Sensors. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2008;47(35):6550–6570. doi: 10.1002/anie.200704488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ishihara S, Labuta J, Nakanishi T, Tanaka T, Kataura H. Amperometric Detection of Sub-Ppm Formaldehyde Using Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Hydroxylamines: A Referenced Chemiresistive System. ACS Sensors. 2017;2(10):1405–1409. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.7b00591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhu R, Azzarelli JM, Swager TM. Wireless Hazard Badges to Detect Nerve-Agent Simulants. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2016;55(33):9662–9666. doi: 10.1002/anie.201604431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Parra-Vasquez ANG, Behabtu N, Green MJ, Pint CL, Young CC, Schmidt J, Kesselman E, Goyal A, Ajayan PM, Cohen Y, et al. Spontaneous Dissolution of Ultralong Single- and Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. ACS Nano. 2010;4(7):3969–3978. doi: 10.1021/nn100864v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Davis VA, Parra-Vasquez ANG, Green MJ, Rai PK, Behabtu N, Prieto V, Booker RD, Schmidt J, Kesselman E, Zhou W, et al. True Solutions of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Assembly into Macroscopic Materials. Nat Nanotechnol. 2009;4(12):830–834. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2009.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Strano MS, Huffman CB, Moore VC, O’Connell MJ, Haroz EH, Hubbard J, Miller M, Rialon K, Kittrell C, Ramesh S, et al. Reversible, Band-Gap-Selective Protonation of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Solution. J Phys Chem B. 2003;107(29):6979–6985. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Puech P, Hu T, Sapelkin A, Gerber I, Tishkova V, Pavlenko E, Levine B, Flahaut E, Bacsa W. Charge Transfer between Carbon Nanotubes and Sulfuric Acid as Determined by Raman Spectroscopy. Phys Rev B. 2012;85(20):205412. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chen Y, Meng F, Li M, Liu J. Novel Capacitive Sensor: Fabrication from Carbon Nanotube Arrays and Sensing Property Characterization. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2009;140(2):396–401. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nallon EC, Schnee VP, Bright C, Polcha MP, Li Q. Chemical Discrimination with an Unmodified Graphene Chemical Sensor. ACS Sensors. 2016;1(1):26–31. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Staii C, Johnson Alan TJ, Chen M, Gelperin A. DNA-Decorated Carbon Nanotubes for Chemical Sensing. Nano Lett. 2005;5(9):1774–1778. doi: 10.1021/nl051261f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Niu L, Luo Y, Li Z. A Highly Selective Chemical Gas Sensor Based on Functionalization of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes with Poly(ethylene Glycol) Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2007;126(2):361–367. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hines D, Rümmeli MH, Adebimpe D, Akins DL. High-Yield Photolytic Generation of Brominated Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Their Application for Gas Sensing. Chem Commun. 2014;50(78):11568–11571. doi: 10.1039/c4cc03702b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hartmann T, Schrapers P, Utesch T, Nimtz M, Rippers Y, Dau H, Mroginski MA, Haumann M, Leimkühler S. The Molybdenum Active Site of Formate Dehydrogenase Is Capable of Catalyzing C–H Bond Cleavage and Oxygen Atom Transfer Reactions. Biochemistry. 2016;55(16):2381–2389. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kelly TR, Kim MH. Relative Binding Affinity of Carboxylate and Its Isosteres: Nitro, Phosphate, Phosphonate, Sulfonate, and δ-Lactone. J Am Chem Soc. 1994;116(16):7072–7080. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hughes MP, Shang M, Smith BD. High Affinity Carboxylate Binding Using Neutral Urea-Based Receptors with Internal Lewis Acid Coordination. J Org Chem. 1996;61(14):4510–4511. doi: 10.1021/jo9608026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fan E, Van Arman SA, Kincaid S, Hamilton AD. Molecular Recognition: Hydrogen-Bonding Receptors That Function in Highly Competitive Solvents. J Am Chem Soc. 1993;115(1):369–370. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schnorr JM, van der Zwaag D, Walish JJ, Weizmann Y, Swager TM. Sensory Arrays of Covalently Functionalized Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Explosive Detection. Adv Funct Mater. 2013;23(42):5285–5291. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Frazier KM, Swager TM. Robust Cyclohexanone Selective Chemiresistors Based on Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Anal Chem. 2013;85(15):7154–7158. doi: 10.1021/ac400808h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Balch AL, Holm RH. Complete Electron-Transfer Series of the [M-N 4 ] Type. J Am Chem Soc. 1966;88(22):5201–5209. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bill E, Bothe E, Chaudhuri P, Chlopek K, Herebian D, Kokatam S, Ray K, Weyhermüller T, Neese F, Wieghardt K. Molecular and Electronic Structure of Four- and Five-Coordinate Cobalt Complexes Containing Two O-Phenylenediamine- or Two O-Aminophenol-Type Ligands at Various Oxidation Levels: An Experimental, Density Functional, and Correlated Ab Initio Study. Chem - A Eur J. 2005;11(1):204–224. doi: 10.1002/chem.200400850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Georgakilas V, Tiwari JN, Kemp KC, Perman JA, Bourlinos AB, Kim KS, Zboril R. Noncovalent Functionalization of Graphene and Graphene Oxide for Energy Materials, Biosensing, Catalytic, and Biomedical Applications. Chem Rev. 2016;116(9):5464–5519. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Noro SI, Chang HC, Takenobu T, Murayama Y, Kanbara T, Aoyama T, Sassa T, Wada T, Tanaka D, Kitagawa S, et al. Metal-Organic Thin-Film Transistor (MOTFT) Based on a Bis(o-Diiminobenzosemiquinonate) nickel(II) Complex. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127(28):10012–10013. doi: 10.1021/ja052663s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sumanasekera GU, Allen JL, Fang SL, Loper AL, Rao AM, Eklund PC. Electrochemical Oxidation of Single Wall Carbon Nanotube Bundles in Sulfuric Acid. J Phys Chem B. 1999;103(21):4292–4297. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bachler V, Olbrich G, Neese F, Wieghardt K. Theoretical Evidence for the Singlet Diradical Character of Square Planar Nickel Complexes Containing Two O-Semiquinonato Type Ligands. Inorg Chem. 2002;41(16):4179–4193. doi: 10.1021/ic0113101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Herebian D, Wieghardt KE, Neese F. Analysis and Interpretation of Metal-Radical Coupling in a Series of Square Planar Nickel Complexes: Correlated Ab Initio and Density Functional Investigation of [Ni(LISQ)2] (LISQ=3,5-Di-Tert-Butyl-O-Diiminobenzosemiquinonate (1−)) J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125(36):10997–11005. doi: 10.1021/ja030124m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


