Abstract
Brain metastasis is very rare in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). We retrospectively analyzed 4494 patients diagnosed with ESCC between 2010 and 2015 at a single institute; 15 of these patients developed brain metastases. All 15 patients had neurologic symptoms and were diagnosed by imaging or biology. Of the 15 patients, 67% had a solitary brain lesion and 73% had lesions larger than 3 cm. After treatment of the brain lesions, including surgery (53%) or stereotactic radiotherapy with or without whole brain radiation (20%), the median progression free survival time and the 2-year overall survival rate calculated from diagnosis of brain metastasis were 14.4 months and 36%, respectively. A graded prognostic assessment (GPA) score > 2.0 was associated with significantly better overall survival. Patients with brain metastases from ESCC achieve good overall survival after appropriate treatment of the brain lesion(s); GPA score may represent a prognostic factor for treatment decision-making.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, bran metastases, survival, treatment
Background
Esophageal cancer was the eighth most common cancer worldwide in 2012 1. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is distinct to the other major histological subtype, esophageal adenocarcinoma, and is more common in eastern and south-east Asia 2. Esophageal cancer frequently metastasizes to the liver, lungs, regional lymph nodes, bone and adrenal glands 3.
Brain metastases are exceedingly rare in esophageal cancer, with rates of 2% in both ESCC and esophageal adenocarcinoma reported by previous studies 3-5. Increased use of neuroimaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the clinic to diagnose early central nerve system disease, coupled with increased survival rates, have led to more frequent detection of brain metastases in patients with esophageal cancer. However, there are no treatment guidelines for patients with these rare brain metastases due to a lack of data on treatment and outcomes.
The graded prognostic assessment (GPA) is a prognostic index for patients with brain metastases and is a useful tool for treatment decision-making 10. The GPA was validated against diagnosis-specific prognostic indices in retrospective analysis of patients with brain metastases from other types of cancer, including breast cancer, lung cancer and melanoma. The prognostic factors for patients with brain metastases vary depending on the primary tumor 11,12.
There is no index of patients with brain metastases from ESCC. An index of patients with gastrointestinal cancer is used as a surrogate; however, it is not known if the prognostic factors for patients with brain metastases from gastrointestinal cancer accurately reflect those of patients with brain metastases from ESCC. The aim of this study was to define the incidence and treatment outcomes of brain metastases from ESCC and validate the association between the GPA score and survival for patients with brain metastases from ESCC.
Materials and Methods
Patients
The institution database at the Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University was used to identify patients diagnosed with primary ESCC between January 1, 2010 and December 31, 2015. The characteristics of these 4494 patients are listed in Table 1. Of this cohort, 15 patients (0.3%) were diagnosed with brain metastases. All brain metastases were diagnosed by contrast-enhanced MRI or CT. The brain tumor imaging reports describing the lesion numbers, sizes and location were collected for all 15 patients. Eight of the 15 patients (53%) had histologic confirmation of brain metastases after undergoing surgical resection of the brain lesions. One patient with carcinomatous meningitis and two patients with brain metastases from esophageal adenocarcinoma were excluded from this study. Treatments for brain metastases were determined by the treating oncologists. Treatment effects were noted if serial images collected over time were available for review. Radiation therapy was administered to the brain lesions using a 4-6 MV linear accelerator with hypofrationated radiotherapy or stereotactic radiosurgery. The vital status of patients at the time of review and/or cause of death were noted.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the 4494 patients with ESCC.
| Characteristic | No. of patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Age at hospital registration (years) | |
| Median | 60 |
| Range | 28-80 |
| Gender | |
| Male | 3606 |
| Female | 889 |
| Histology | |
| Well-differentiated squamous carcinoma | 252 |
| Moderately differentiated squamous carcinoma | 1754 |
| Poorly differentiated squamous carcinoma | 1093 |
| Grade unknown | 1395 |
| Stage of primary tumor | |
| In situ | 15 |
| Extension/lymph node involvement | 2513 |
| Distant involvement | 1966 |
| Treatment of primary tumor | |
| Surgery ± adjuvant radiotherapy/chemotherapy | 2269 |
| Chemoradiotherapy/chemotherapy/radiotherapy | 2225 |
Overall survival and progression free survival was calculated from the date of diagnosis of brain metastases until the date of last follow-up or death or the date of disease progression including cranial and extracranial lesions respectively, and plotted using the Kaplan-Meier method and compared using the log-rank test. The multivariate Cox proportional hazard model was used to provide estimates of hazard ratios (HR) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs); factors with P values <0.15 were included in the model. P-values < 0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance. Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS software package (version 13.0; SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA).
Results
Patients
All 4494 patients had histologically confirmed primary ESCC. The clinical characteristics of the 15 patients with brain metastases are listed in Table 2. The median time from diagnosis of ESCC to diagnosis of brain metastases was 13 months (range, 0 to 47 months). All 15 patients had clinical symptoms of brain metastases including dizziness, headaches, limb weakness, seizures and visual-field defects. A single brain lesion was found in 10 patients (67%), two or three lesions in four patients (27%), and > 3 lesions in one patient (7%). The median maximal diameter for all brain lesions was 4.6 cm (range, 0.8 to 8.0 cm); 11 patients (73%) had at least one brain lesion larger than 3.0 cm.
Table 2.
Characteristics of the 15 patients with brain metastasis from ESCC.
| Characteristic | No. of patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis of primary ESCC | |
| Median (range) | 60 (43-73) years |
| Gender | |
| Male | 14 |
| Female | 1 |
| Treatment of primary tumor | |
| Surgery with or without chemo/radiotherapy | 4 |
| Chemoradiotherapy | 11 |
| Time from diagnosis of primary ESCC to brain metastases | |
| Median (range) | 13 (0-47) months |
| No treatment | 0 |
| Neurological symptoms of brain metastases | |
| Dizziness/headaches | 15 |
| Limb weakness | 6 |
| Seizures | 3 |
| Visual-field defects | 2 |
| Systemic metastases | |
| Yes | 9 |
| Diagnosed before brain metastases | 3 |
| Diagnosed after brain metastases | 6 |
| KPS at diagnosis of brain metastases | |
| 90 | 9 |
| 80 | 5 |
| ≤ 70 | 1 |
| No. of brain metastases | |
| 1 | 10 |
| 2-3 | 4 |
| > 3 | 1 |
| Diameter of all brain lesions | |
| Median (range) | 4.6 (0.8-8.0)cm |
| Maximum diameter ≥ 3.0 cm | 11 |
| Maximum diameter < 3.0 cm | 4 |
| GPA score | |
| 0-2.0 | 4 |
| 2.5-3.0 | 11 |
| Histology of brain lesions | 8 |
| Poorly differentiated squamous carcinoma | 6 |
| Well-differentiated squamous carcinoma | 1 |
| Grade unknown | 1 |
Brain metastases treatment response and survival
Of the 14 patients with three or fewer brain lesions, eight underwent surgery (seven underwent surgery followed by whole brain radiation or brain tumor bed local radiation, one underwent surgery alone), three underwent stereotactic radiotherapy (SRS) with or without whole brain radiation (WBRT), one underwent hyperfractionated radiotherapy (54 Gy in 18 fractions to the brain lesion), one underwent whole brain irradiation alone, and one discontinued treatment due to simultaneous serious cerebral infarction.
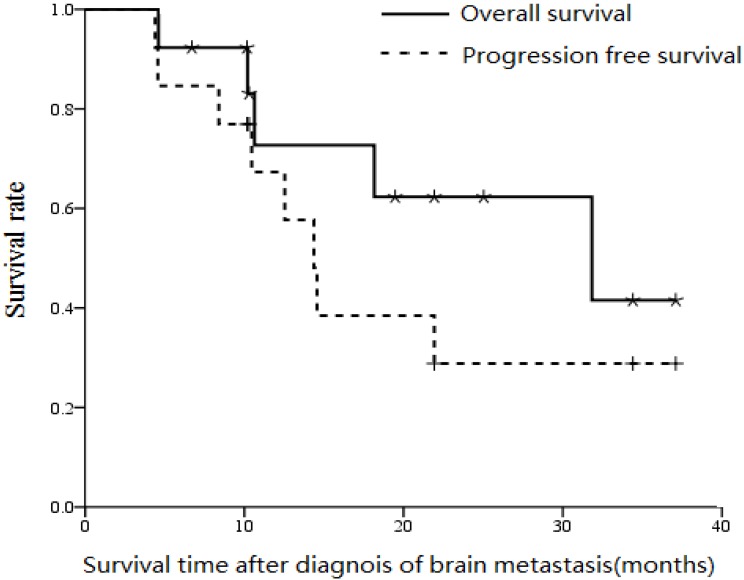
After median follow-up of 19.5 months (range, 4.6 to 37.1 months), median progression free survival, overall survival and the 2-year overall survival rate were 14.4 months, 30.1 months and 36% respectively (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Overall survival and progression free survival curves (from diagnosis of metastases) for the 15 patients with ESCC who developed brain metastases.
The GPA classification includes age, KPS score and number of central nervous system and extracranial metastases 10. Patients with GPA scores over 2.0 was found to be a predictor of overall survival by both univarate and multivariate analysis, and patients with GPA score of 0-2.0 achieved median overall survival of 4.6 months compared to 31.5 months for patients with GPA scores of 2.5-3.0 (P < 0.01). Of the 15 patients, four experienced cranial tumor progression and six experienced extracranial tumor progression. All four patients with cranial tumor progression died within one month.
Discussion
Metastasis to the brain is very rare in ESCC. In this study, we found 15 of 4494 (0.3%) patients diagnosed with ESCC between 2010 and 2015 at our institution experienced brain metastases. Brain metastases were mainly diagnosed more than 1 year after definitive treatment for ESCC and were not always simultaneously accompanied by metastasis to other organs. Patients achieved median progression-free survival of 14.4 months after local treatment of the brain lesions, longer than patients with other organ recurrence without brain metastases. GPA score was significantly associated with overall survival, and patients with GPA scores of 2.5-3.0 achieved median overall survival of 31.5 months. We suggest local treatment of brain lesions should be actively considered for patients with brain metastases from ESCC, especially patients with a GPA score over 2.
Previous studies reported the frequency of brain metastases from esophageal cancer was about 0.4-5% 3-8; this variation may be due to a higher incidence of brain metastases in esophageal adenocarcinoma than ESCC. In retrospective studies, the crude incidence of brain metastases in patients with esophageal cancer (with no further classification) was approximately 1.4-1.5% 4,6,13. In patients with newly diagnosed esophageal cancer, the incidence of brain metastasis was only 0.4% overall and 2% in patients with metastatic disease 3. A summary published by authors from M. D. Anderson Cancer Center showed 22 of 1085 (2.0%) patients with esophageal adenocarcinoma but only 2 of 405 (0.4%) patients with ESCC experienced brain metastasis 13, in agreement with a report from University of Michigan Hospital (3.9% vs. 0.9%) 14. In our study, 15 of 4494 (0.3%) patients with ESCC experienced brain metastasis, confirming the incidence of brain metastases is extremely low in ESCC. However, in the absence of routine neuroimaging recommendations or neurological consultations for patients without neurological symptoms, the true incidence could be higher. Metastasis to the brain from ESCC seems unpredictable. In this study, the median time from diagnosis of ESCC to diagnosis of brain metastases was 13 months and no patients experienced local and/or regional recurrence, although 40% experienced other organ metastases. This interval is similar to previous reports of 10.2 to 12.3 months 6,7. In this cohort, the majority of brain lesions were solitary (60%), large (73% with a greatest dimension > 3 cm), and not necessarily accompanied by metastasis to other organs (40% of patients only had brain metastasis at death). Similarly, Ogawa et al. 4 reported that of 36 patients with brain metastases from esophageal carcinoma, 47% had single brain metastases and 53% had a greatest lesion dimension > 3 cm. Song et al. 7 and Yashida et al. 8 reported 46% and 65% of patients had single lesions, respectively (Table 3).
Table 3.
Summary of published data on the treatment and survival of patients with brain metastases from esophageal cancer
| Author/year | Cases | Pathology of primary esophageal carcinoma | Median survival after diagnosis of brain metastases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ogawa et al., 2002 4 | 35 | 32 ESSC, 2 EUC, 1 EAC | Resection + WBRT: 9.6 months WBRT alone (30 Gy): 1.8 months |
| Yoshida et al., 2007 8 | 17 | 12 ESSC, 3 EAC, 2 other | Resection alone: 17.7 months Resection + WBRT: 65.5 months Radiosurgery: 9.5 months |
| Song et al., 2014 7 | 26 | 22 ESSC, 4 EAC | Resection alone: 7.0 months RT alone: 4.0 months Chemotherapy alone: 1.8 months |
| Our study | 15 | All ESCC | Resection with or without WBRT: 31.5 months |
ESSC, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; EUC, esophageal undifferentiated carcinoma; EAC, esophageal adenocarcinoma; WBRT, whole brain radiotherapy.
Based on these characteristics, surgery or SRS seem most appropriate for treating brain metastases in ESCC. In our cohort, 92% of patients underwent surgery or SRS to treat the brain lesions and achieved median progression free survival of 14.4 months. Moreover, 61% of patients whose lesions were treated survived for more than 1 year after diagnosis of brain metastases. Analysis of the data of preview and our studies revealed patients who underwent brain surgery plus radiotherapy achieved better overall survival than those who underwent conventional 30-40 Gy whole brain irradiation. In these studies, surgery alone resulted in overall survival of 7.0-17.7 months, compared to 9.6-65.5 months for surgery followed by radiation and only 1.8-9.5 months for 30 Gy whole brain radiation (Table 3). Similarly, Depypere et al. 9 recently reported patients with esophageal cancer and solitary solid organ metastases achieved good median overall survival of 54 months after surgery, which was superior to chemotherapy alone. Guttmann et al. found definitive dose radiotherapy was associated with improved survival compared to conventional palliative dose radiotherapy based on analysis of 12683 patients with esophageal cancer 15. These studies indicate that-similarly to brain metastases-patients with solitary solid organ metastases may achieve better treatment outcomes after definitive local treatment of recurrent lesions. However, identification of which patients with brain metastases should undergo brain lesion surgery, SRS or definitive radiotherapy is critical.
The GPA is a validated prognostic index for patients with brain metastasis from all tumor types 10. Patients with brain metastases are heterogonous; the prognostic factors are not the same for all patients with brain metastases. No prognostic factors have yet been validated for patients with brain metastases from esophageal cancer due to its extremely low incidence. In this study, we used the GPA scoring system, which incorporates age, KPS and number of brain metastases. Median overall survival for patients with a GPA score ≤ 2.0 was only 4.6 months, which was significantly shorter than that of patients with a GPA score > 2 (over 2 years). Therefore, the GPA scoring system may represent a good guide for treatment decision-making for patients with brain metastases from ESCC; patients with GPA scores over 2 should consider aggressive treatment such as surgery or SRS and can achieve encouraging survival outcomes.
The true incidence of brain metastasis from ESCC could be higher as this study was a retrospective analysis at one institution and some data could be missing if patients chose to attend another hospital for follow-up or obtain treatment for brain lesions. Additionally, there is an inherent bias towards symptomatic brain lesions as the entire cohort did not undergo routine neurological imaging follow-up. Overall, this study indicates the patients experiencing brain metastases with ESCC is extremely low and is easy to be ignored. But patients with brain metastases achieved unexpectedly encouraging overall survival after treatment such as surgery or SRS. Moreover, GPA score may represent a useful prognostic tool for evaluating patients and assisting treatment decision-making for patients with brain metastases from ESCC. Furtherly for some patients with high risk of metastasis, like the patients with high fibrinogen/albumin ratio 16, the routine brain screening after definitive treatment may be needed.
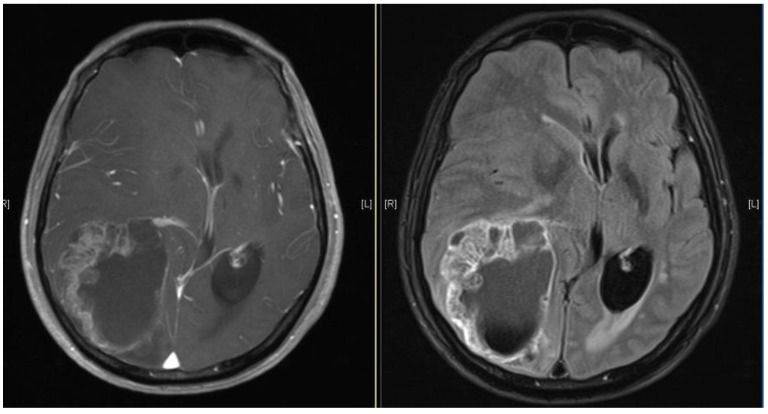
Figure 1.
Brain MRI images of a patient diagnosed with ESCC who experienced brain metastasis 22 months after surgical resection of the esophagus. The maximal brain lesion diameter was 6.8 cm. The patient underwent surgery followed by local irradiation of the lesion and survived for 34 months after diagnosis of brain metastases.
References
- 1.Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Melina Arnold, Isabelle Soerjomataram, Jacques Ferlay, David Forman. Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological subtype in 2012. Gut. 2015;64:381–387. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Quint LE, Hepburn LM, Francis IR, Whyte RI, Orringer MB. Incidence and distribution of distant metastases from newly diagnosedesophageal carcinoma. Cancer. 1995;76(7):1120–5. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19951001)76:7<1120::aid-cncr2820760704>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ogawa K, Toita T, Sueyama H, Fuwa N, Kakinohana Y, Kamata M, Adachi G, Saito A, Yoshii Y, Murayama S. Brain metastases from esophageal carcinoma: natural history, prognostic factors, and outcome. Cancer. 2002;94(3):759–64. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Go PH, Klaassen Z, Meadows MC, Chamberlain RS. Gastrointestinal cancer and brain metastasis: a rare and ominous sign. Cancer. 2011;117(16):3630–40. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yoshida S. Brain metastasis in patients with esophageal carcinoma. Surg Neurol. 2007;67(3):288–90. doi: 10.1016/j.surneu.2006.05.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Song Z, Lin B, Shao L, Zhang Y. Brain metastases from esophageal cancer: clinical review of 26 cases. World Neurosurg. 2014;81(1):131–5. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2013.02.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Yoshida S. Brain metastasis in patients with esophageal carcinoma. Surg Neurol. 2007 Mar;67(3):288–90. doi: 10.1016/j.surneu.2006.05.065. Epub 2006 Nov 3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Depypere L, Lerut T, Moons J, Coosemans W, Decker G, Van Veer H, De Leyn P, Nafteux P. Isolated local recurrence or solitary solid organ metastasis after esophagectomy for cancer is not the end of the road. Dis Esophagus. 2016 doi: 10.1111/dote.12508. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sperduto CM, Watanabe Y, Mullan J, Hood T, Dyste G, Watts C, Bender GP, Sperduto P. A validation study of a new prognostic index for patients with brain metastases: the Graded Prognostic Assessment. J eurosurg. 2008;109:S87–9. doi: 10.3171/JNS/2008/109/12/S14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sperduto PW1, Chao ST, Sneed PK, Luo X, Suh J, Roberge D, Bhatt A, Jensen AW, Brown PD, Shih H, Kirkpatrick J, Schwer A, Gaspar LE, Fiveash JB, Chiang V, Knisely J, Sperduto CM, Mehta M. Diagnosis-specific prognostic factors, indexes, and treatment outcomes for patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis of 4,259 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;77(3):655–61. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.08.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Chao ST, Weil RJ, Suh J, Bhatt A, Jensen AW, Brown PD, Shih HA, Kirkpatrick J, Gaspar LE, Fiveash JB, Chiang V, Knisely JP, Sperduto CM, Lin N, Mehta M. Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(4):419–25. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.0527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Weinberg JS, Suki D, Hanbali F, Cohen ZR, Lenzi R, Sawaya R. Metastasis of esophageal carcinoma to the brain. Cancer. 2003;98(9):1925–33. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gabrielsen TO, Eldevik OP, Orringer MB, Marshall BL. Esophageal carcinoma metastatic to the brain: clinical value and cost-effectiveness of routine enhanced head CT before esophagectomy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1995;16(9):1915–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Guttmann DM, Mitra N, Bekelman J, Metz JM, Plastaras J, Feng W, Swisher-McClure S. Improved overall survival with aggressive primary tumor radiotherapy for patients with metastatic esophageal cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2017 doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.03.026. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tan Z, Zhang M, Han Q. et al. A novel blood tool of cancer prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: the Fibrinogen/Albumin Ratio. J Cancer. 2017;8(6):1025–1029. doi: 10.7150/jca.16491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]