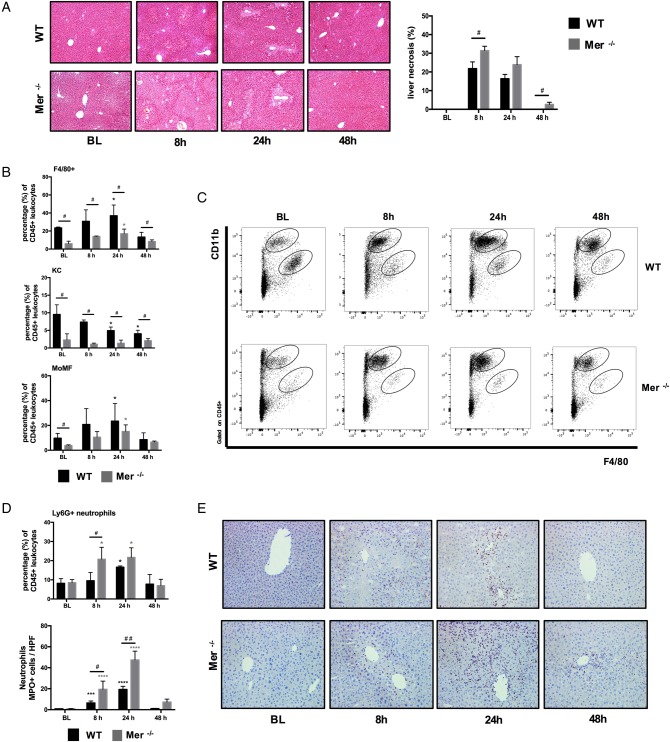
Figure 4.
Mer tyrosine kinase (MerTK)-deficient mice are characterised by increased hepatic inflammation and reduced macrophages following APAP-induced liver injury. Wild-type (WT) (black bars) and Mer−/− (grey bars) mice dosed with APAP were studied at 8, 24 and 48 hours, and untreated mice served as baseline controls (n=4/group). (A) Representative images of H&E stained liver tissue and quantification of necrotic area (%). (B) F4/80+ hepatic macrophages, Kupffer cells (KC) and monocyte-derived macrophages (MoMF) as percentage of total liver CD45+ leucocytes, as determined by flow cytometry. (C) Representative flow cytometric analysis from liver CD45+ leucocytes showing detection of (CD11bhighF4/80low) MoMF and (CD11blowF4/80high) KC. (D) Ly6G+ hepatic neutrophils as percentage of total liver CD45+ leucocytes and enumeration of MPO+ neutrophils using flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry, respectively. (E) Representative images of liver tissue stained for MPO+ (purple) cells (200×). Non-parametric (Mann-Whitney) statistical analysis was used. Data are presented as median values with IQR. * or #p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.