Fig. 2.
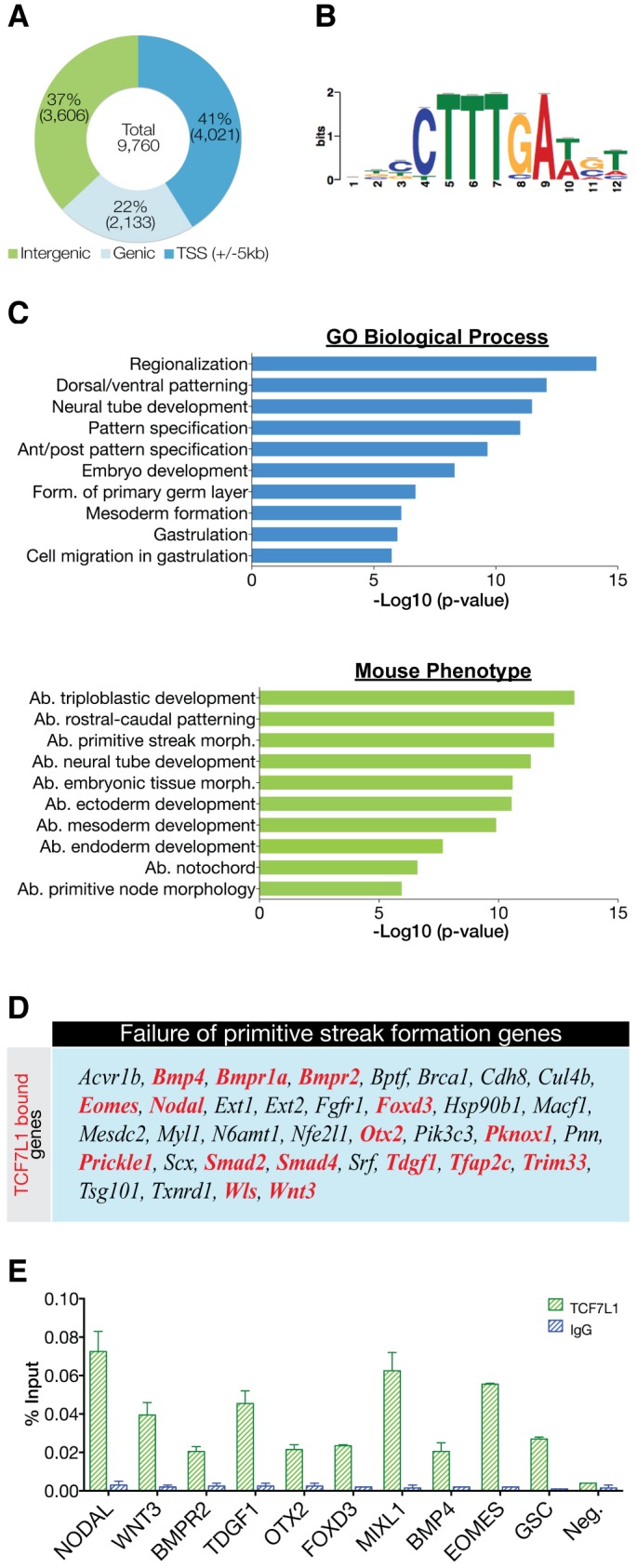
Characterization of TCF7L1 binding sites in hESCs. (A) Location of the top 9760 peaks (IDR<0.01325) relative to the nearest gene as determined by HOMER annotation. (B) De novo motif detected in TCF7L1/β-catenin-shared binding sites. The TCF7L1 site observed is a canonical WNT-response element (WRE). (C) GREAT analysis of underlying GO themes among TCF71 target genes. The top 1000 peaks were analyzed using ‘basal plus extension’ default settings. Data are presented as the –log10 of their respective P-values for convenience. Ab., abnormal; form., formation; morph., morphology. (D) TCF7L1-bound genes (red) represented in the mammalian phenotype category ‘failure of primitive streak formation’. Genes with TCF7L1 binding within ±5 kb of the TSS were used for this comparison. (E) ChIP-qPCR analysis (n=2) of TCF7L1 binding to crucial PS genes shown as percentage input recovery. Error bars indicate s.e.m.
