Abstract
In both excitable and non-excitable cells, calcium (Ca2+) signals are maintained by a highly integrated process involving store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE), namely the opening of plasma membrane (PM) Ca2+ channels following the release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores. Upon depletion of Ca2+ store, the stromal interaction molecule (STIM) senses Ca2+ level reduction and migrates from endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-like sites to the PM where it activates the channel proteins Orai and/or the transient receptor potential channels (TRPC) prompting Ca2+ refilling. Accumulating evidence suggests that SOCE dysregulation may trigger perturbation of intracellular Ca2+ signaling in neurons, glia or hematopoietic cells, thus participating to the pathogenesis of diverse neurodegenerative diseases. Under acute conditions, such as ischemic stroke, neuronal SOCE can either re-establish Ca2+ homeostasis or mediate Ca2+ overload, thus providing a non-excitotoxic mechanism of ischemic neuronal death. The dualistic role of SOCE in brain ischemia is further underscored by the evidence that it also participates to endothelial restoration and to the stabilization of intravascular thrombi. In Parkinson’s disease (PD) models, loss of SOCE triggers ER stress and dysfunction/degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. Disruption of neuronal SOCE also underlies Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathogenesis, since both in genetic mouse models and in human sporadic AD brain samples, reduced SOCE contributes to synaptic loss and cognitive decline. Unlike the AD setting, in the striatum from Huntington’s disease (HD) transgenic mice, an increased STIM2 expression causes elevated synaptic SOCE that was suggested to underlie synaptic loss in medium spiny neurons. Thus, pharmacological inhibition of SOCE is beneficial to synapse maintenance in HD models, whereas the same approach may be anticipated to be detrimental to cortical and hippocampal pyramidal neurons. On the other hand, up-regulation of SOCE may be beneficial during AD. These intriguing findings highlight the importance of further mechanistic studies to dissect the molecular pathways, and their corresponding targets, involved in synaptic dysfunction and neuronal loss during aging and neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, endoplasmic reticulum, Orai, Parkinson’s disease, SOCE, STIM, stroke, TRPC
Introduction
Calcium (Ca2+) is a ubiquitous second messenger involved in a number of cellular functions. Ca2+ ions are extruded from the cell or sequestered in intracellular compartments (stores) by energy-driven pumps that maintain cytosolic Ca2+ concentrations approximately 100,000-fold the extracellular space. As a consequence of this large concentration gradient, a rapid influx of Ca2+ occurs upon opening of ion channels located on the plasma membrane (PM) or on the membranes of intracellular stores, including the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) that is considered the major intracellular store. In both excitable and non-excitable cells, including those involved in the immune response, Ca2+ signals are generated by store-operated Ca2+entry (SOCE), namely the opening of PM Ca2+ channels following the release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores. Upon ER leak, SOCE determines ER Ca2+ refilling through the activation of two currents: the Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ current (ICRAC), a non-voltage activated and inwardly rectifying current, highly selective for Ca2+, and the store-operated Ca2+ current (ISOC), a non-selective outward current with different biophysical features (Golovina et al., 2001; Trepakova et al., 2001; Strübing et al., 2003; Ma et al., 2015; Lopez et al., 2016). Although the electrophysiological properties of ICRAC are known since decades (Hoth and Penner, 1993; Lewis and Cahalan, 1995), the molecular components underlying SOCE have been discovered more recently, with the identification of stromal interaction molecule (STIM) and Orai proteins (Liou et al., 2005; Roos et al., 2005; Zhang et al., 2005; Feske et al., 2006; Peinelt et al., 2006). In vertebrates, two different STIM-related genes have been described (Williams et al., 2001). STIM1 and STIM2 homologous are broadly and ubiquitously expressed in murine and human brain tissue, with a predominant expression of STIM2 (Kraft, 2015). More precisely, while STIM1 is most prominent in the cerebellum, STIM2 expression dominates in hippocampus and cortex (Lein et al., 2007; Uhlén et al., 2015). Upon depletion of Ca2+ store, STIM senses Ca2+ level reduction and migrates from ER-like sites to the PM where it activates Orai (Zhang et al., 2005), a tetraspanning protein forming a ion-conducting pore highly selective for Ca2+ (Feske et al., 2006; Peinelt et al., 2006; Prakriya et al., 2006). This PM channel exists in three different forms, Orai1, Orai2 and Orai3 exhibiting distinct inactivation and permeability properties (DeHaven et al., 2007; Lis et al., 2007). All three forms interact with STIM1 to produce SOCE, although Orai1 mediates a quantitatively much higher current than the other two forms (Putney, 2017). In particular, upon dissociation of Ca2+ from its EF-hand domains, STIM oligomerizes and translocates to ER-PM, where it forms large protein clusters referred to as puncta (Luik et al., 2006). Then, Orai1 is recruited to these puncta and promotes Ca2+ influx. Like its homolog, STIM2 mediates SOCE, although with slower activation kinetics and requiring a weaker depletion of ER Ca2+ stores to be activated (Brandman et al., 2007; Stathopulos et al., 2009). Despite the focus on STIM-regulated Orai channels for ICRAC-mediated SOCE, evidence is growing for STIM-operated transient receptor potential channel (TRPC)1 activity in mediating ISOC. Indeed, TRPC1 is recruited to the PM upon Orai/STIM complex formation from Rab4-vescicles (Liu et al., 2003; Ambudkar et al., 2007). Therefore, TRPC1-mediated outward current is subordinated to ICRAC. There are six TRPC proteins in humans (TRPC1, TRPC3–TRPC7), divided into two subfamilies, TRPC1/TRPC4/TRPC5 and TRPC3/TRPC6/TRPC7, based on biochemical and functional similarities. Search for SOCE partners led to the identification of several TRPCs, including TRPC1, TRPC3 and TRPC4 that are differently involved in this phenomenon. TRPC3 and TRPC4 can be activated by store depletion, while activation of TRPC5, TRPC6 and TRPC7 occurs via store-independent mechanisms (Ambudkar et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2007; Venkatachalam and Montell, 2007). Interestingly, TRPC form heteromeric structures involved in SOCE (Goel et al., 2002; Hofmann et al., 2002; Strübing et al., 2003), including endogenous TRPC1/TRPC3 in human parotid gland ductal cells (Liu et al., 2005) and rat hippocampal cell lines (Wu et al., 2004), TRPC1/TRPC5 in vascular smooth muscle (Wu et al., 2004), TRPC1/TRPC4 in endothelial cells (Sundivakkam et al., 2012) and TRPC1/TRPC3/TRPC7 in HEK293 cells (Zagranichnaya et al., 2005).
Both in vitro and in vivo studies, as well as evidence in human subjects with defects in SOCE have disclosed the pivotal involvement of Orai and STIM in several physiological and pathological conditions, including platelet function and hemeostasis (Varga-Szabo et al., 2008; Braun et al., 2009; Ahmad et al., 2011; Berna-Erro et al., 2016), neuronal excitability (Moccia et al., 2015), hypoxic/ischemic neuronal injury (Berna-Erro et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2014), cardiac hypetrophy (Hulot et al., 2011; Saliba et al., 2015; Bénard et al., 2016), proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (Potier et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2011; Jia et al., 2017), carcinogenesis (Yang et al., 2009; Chen et al., 2011; White, 2017). Of particular interest is the role of SOCE in the modulation of innate and adaptive immunity (Feske et al., 2006; Oh-Hora et al., 2008; Demaurex and Nunes, 2016; Vaeth et al., 2017). Indeed, store-operated Ca2+ current, ICRAC, was for the first time observed in mast cells and T lymphocytes (Parekh and Penner, 1997), whose activation is controlled by SOCE (Feske et al., 2001, 2005). In fact, recurrent infections take place in patients with mutations in Orai1 and Stim1 genes that abolish SOCE (Feske, 2011; Lacruz and Feske, 2015). Although immunodeficiency was mainly ascribed to T-cell dysregulation and the original initial work was focused on adaptive immunity, subsequent evidence demonstrated that SOCE also represents a major pathway for generating calcium signals in innate immune cells (Feske, 2011). Accordingly, calcium signaling has been implicated in numerous functions performed by phagocytes (e.g., macrophages, neutrophils and dendritic cells), including differentiation, maturation, migration, secretion and phagocytosis (Demaurex and Nunes, 2016). Although the present review mainly focusses on experimental data documenting the role of neuronal SOCE in neurodegenerative diseases, given the close interaction between the immune system and the brain during diverse pathological conditions (Amantea, 2016), the contribution of SOCE in immune cells could be envisaged and should deserve further investigation.
SOCE in Stroke
Stroke is a major cause of death and long-term disability worldwide. Occlusion of a cerebral artery is the most common cause of brain ischemia, characterized by reduced cerebral blood flow, oxygen deprivation and activation of a cascade of events that ultimately lead to tissue damage. Over the past three decades, crucial findings from animal models have improved our understanding of the pathobiological mechanisms contributing to ischemic brain damage (Dirnagl and Endres, 2014). The blockade of cerebral circulation leads within seconds to cessation of neuronal electrical activity and within few minutes to disruption of energy state and ion homeostasis. It is widely accepted that a critical factor in determining neuronal death in stroke is the progressive accumulation of intracellular Ca2+ that, together with Na+ ions, can precipitate necrosis and apoptosis of vulnerable neurons (Kumar et al., 2014).
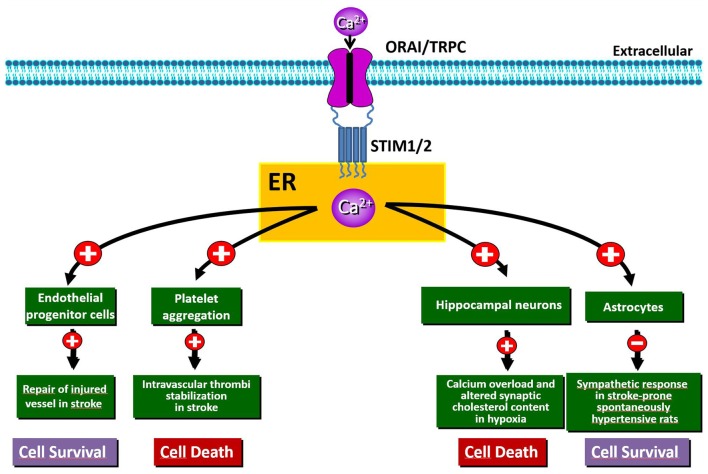
Despite this evidence, the mechanisms of Ca2+ cytotoxicity remain partially uncharacterized. In fact, Ca2+ seems to play a controversial role in this process since its increase or leak could assume different meanings. Accordingly, together with a detrimental role played by intracellular Ca2+ overload, it has been shown that Ca2+ leak from intracellular organelles can precipitate cell death (Pinton and Rizzuto, 2006). Thus, during brain ischemia, the complete depletion of Ca2+ from ER leads to neuronal death via ER stress (Ferri and Kroemer, 2001; Sirabella et al., 2009). Molecularly, the engagement of Gq-linked receptors results in a significant depletion of ER and in a robust influx of Ca2+ from the extracellular space that refills the organelle in order to reestablish Ca2+ homeostasis. This influx is specifically due to SOCE mediated by SOC channels and should protect neurons against ischemia-induced ER stress (Sirabella et al., 2009; Parekh, 2010). By contrast, in the hippocampus of rats exposed to global cerebral ischemia, the increased expression of STIM1 and Orai has been suggested to be the source of excessive calcium influx, whereby SOCE represents an important non-excitotoxic mechanism of ischemic neuronal death (Zhang et al., 2014). Thus, SOCE dysfunction is involved in stroke pathogenesis, but, to date, its exact role in brain ischemia is still controversial, since distinct mechanisms participating to either cell death or survival have been reported (Figure 1). Interestingly, SOCE has been widely investigated at the level of several components of the neurovascular unit, including astrocytes, endothelial cells and platelets, where it represents the major mechanism supporting agonist-induced Ca2+ signals (Rosado, 2016). By contrast, little is known about the functional importance of SOCE and its components at the neuronal level under both normoxic and hypoxic conditions.
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the beneficial and/or detrimental effects of store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) activation in different cell types involved in hypoxia/ischemia insult.
Role of STIM in Hypoxic/Ischemic Damage
Numerous in vitro studies have demonstrated that STIM2 is involved in ischemia-induced neuronal Ca2+ accumulation (Soboloff et al., 2006; Vig et al., 2006; Berna-Erro et al., 2009). In fact, hippocampal neurons both in culture and in acute hippocampal slices from Stim2−/− mice show significantly reduced Ca2+ accumulation into ER during hypoxia and increased survival under hypoxic conditions compared to wild-type neurons (Berna-Erro et al., 2009). Accordingly, deficiency of STIM2 confers protection against stroke in mice (Berna-Erro et al., 2009). This is possibly due to the stabilization of cholesterol content at the level of neuronal PM (Sodero et al., 2012). In fact, the lack of STIM2 abolishes variations in synaptic cholesterol content in neurons in response to high excitatory neurotransmission (Sodero et al., 2012), a conditions occurring in stroke as well as in epilepsy and brain trauma (Müller and Connor, 1991).
Interestingly, wild-type mice reconstituted with Stim2−/− bone marrow developed infarcts like those of control wild-type mice, whereas infarcts were smaller in Stim2−/− mice transplanted with wild-type bone marrow (Berna-Erro et al., 2009). This highlights that the neuroprotective effects exerted by STIM2 deficiency in mice are independent of functional alterations within the hematopoietic system. This is of interest since, in various immune cell types, such as T cells and phagocytes, SOCE controls a number of functions, including the release of cytokines, the production of reactive oxygen species, migration and polarization (Feske, 2007, 2011; Demaurex and Nunes, 2016). Regarding the immune cells of the brain, there is evidence that STIM1 and STIM2, modulating Orai1, regulate SOCE and purinergic activation of microglia (Ikeda et al., 2013; Michaelis et al., 2015). In fact, pharmacological inhibition of SOC channels reduces proinflammatory and neurotoxic responses of microglia (Lee et al., 2011). Given the crucial role of purinergic signaling in microglia activation following an ischemic insult (Pedata et al., 2016), it is intriguing to speculate that STIM and Orai may have a role in this process. Since activation of the innate and adaptive immune systems has been demonstrated to play a major role in the progression of cerebral damage (Amantea et al., 2014, 2015), investigating the relevance of SOCE in the modulation of immune cells following stroke is of pivotal importance.
Another component of the neurovascular unit that rapidly senses the reduction of blood flow is represented by astrocytes, whose function is critically affected by Ca2+ signaling. In these cells, hypoxia triggers Ca2+ release from ER stores, efficiently buffered by mitochondria (Smith et al., 2005). Such release of Ca2+ is sufficient to trigger capacitative Ca2+ entry. These findings indicate that the local O2 level is a key determinant of astrocyte Ca2+ signaling, likely modulating their Ca2+-dependent functions. Playing a pivotal role in neurovascular signaling in the brain (Haydon and Carmignoto, 2006; Viscomi et al., 2008; Mishra et al., 2016; Lu et al., 2017; Lind et al., 2018), astrocytes have also been implicated in the pathogenesis of hypertension in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHRSP) via a sympatho-excitation mechanism (Allen et al., 2006; Isegawa et al., 2014). In particular, the reduction of glial STIM1 in SHRSP has been identified as a candidate pathogenic mechanism responsible for this exaggerated sympathetic response leading to stroke. In fact, truncated STIM1 expressed in SHRSP astrocytes fails to interact with the PM Ca2+ channel TRPC1 and impairs SOCE function (Ohara and Nabika, 2016). Since the interaction with the C-terminus of STIM1 is required for TRPC1 activation (Huang et al., 2006), SOCE activity is decreased in astrocytes from SHRSP resulting in perturbation of downstream gene and neuronal network dysfunction. In the same direction are also the new strategies against the de-endothelialization of blood vessels, considered an early event of severe vascular disorders, including stroke. For instance, restoration of the endothelial lining may be accomplished by circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs). In this context, SOCE activation favoring EPCs homing to the injured vessel is now considered the most appropriate route to therapeutically induce the regrowth of denuded vessels (Moccia et al., 2014).
Role of Orai in Hypoxic/Ischemic Damage
It has been shown that the increased expression of ORAI1 and STIM1, occurring in the rat hippocampus after global ischemia, underlies detrimental intracellular Ca2+ accumulation, thus leading to neuronal death (Zhang et al., 2014). Moreover, deletion of Orai1 in platelets results in resistance to ischemic brain infarction of mice subjected to transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (Braun et al., 2009). Analysis of global neurological function and of motor function and coordination revealed that Orai1−/− mouse chimeras develop fewer neurological deficits compared with controls (Braun et al., 2009). This is consistent with the evidence that SOCE in platelets plays a crucial role in the stabilization of intravascular thrombi (Varga-Szabo et al., 2008). Besides, studies involving Orai1 gain-of-function mutants in platelets indicate that SOCE might play a prominent role in thrombus formation, thus suggesting that the inhibition of platelet activation through pharmacological modulation of SOCE may represent an important strategy to prevent or treat acute ischemic events (Bhatt and Topol, 2003; van Kruchten et al., 2012). However, the role of Orai and its relationship with the other partners contributing to SOCE in stroke pathogenesis remains obscure; therefore, further work should be undertaken to clarify their specific function at the level of neurons, glia and hematopoietic cells.
SOCE in Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that causes progressive memory loss, impairment of other cognitive functions and psychosis (Hort et al., 2010; McKhann et al., 2011). It represents the major cause of dementia worldwide and, in most cases, it appears sporadically after the age of 65 years (late-onset AD). The etiology of sporadic AD has not been clarified and its progression results from the combination of multiple factors (genetics, nutrition, lifestyle and chronic metabolic disorders), with aging being the major risk factor (Fjell et al., 2014; Scheltens et al., 2016). Less than 5% of cases correspond to early-onset AD, a familial form of the disease caused by genetic alterations, including mutations in genes encoding the amyloid-β precursor protein (APP), presenilin 1 (PSEN1) and presenilin 2 (PSEN2; Karch and Goate, 2015). PSEN1 and PSEN2 provide the catalytic subunit to the γ-secretase protease complex that, together with the β-secretase, catalyzes the sequential cleavage of APP to produce amyloid-β. The neuropathological features of both forms of AD comprise extraneuronal neuritic plaques mainly composed of insoluble amyloid-β(40,42), intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles consisting of hyperphosphorylated and misfolded tau, and synaptic/neuronal loss leading to brain atrophy (Serrano-Pozo et al., 2011). It was initially hypothesized that accumulation of insoluble amyloid-β in mature fibrils was an upstream contributor to the other pathological features; nevertheless, more recent findings have demonstrated that soluble amyloid-β(1–42) oligomers play a more important role in neurotoxicity (Wang et al., 2017). Thus, inhibiting amyloid-β generation, facilitating its clearance and blocking oligomerization might represent promising strategies to block AD progression (Selkoe and Hardy, 2016). Nevertheless, the majority of these strategies failed in recent Phase III clinical trials (Godyn et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2017), supporting a poor association between brain amyloid-β levels and cognitive function (Doody et al., 2013; Briggs et al., 2017). Therefore, several key issues need to be reconsidered, most notably the pivotal role of amyloid-β in the upstream events that lead to neurodegeneration and the opportunity to target alternative pathways for clinical success.
Intriguingly, the earliest disclosed abnormality in AD pathogenesis, namely dysfunctional calcium signaling, is attracting renewed interest on the basis of its pivotal role in driving the synaptic defects occurring during memory loss (Khachaturian, 1989; Alzheimer’s Association Calcium Hypothesis Workgroup, 2017; Briggs et al., 2017). Accordingly, there is evidence that PSEN mutations, identified in familial AD, correlate with neuronal dysfunction and apoptosis through early dysregulation of Ca2+ homeostasis, that may occur before the appearance of amyloid-β or tau aggregation (Zeiger et al., 2013; Del Prete et al., 2014; Duggan and McCarthy, 2016). Therefore, the “calcium hypothesis of AD” strongly supports the concept that restoration of calcium homeostasis represents a valid alternative to targeting amyloid-β for the successful development of novel therapies.
Both in experimental models of AD and in patients, an excess release of Ca2+ from intracellular stores such as the ER was described (Pannaccione et al., 2012). In fact, in addition to γ-secretase function, PSENs also display a low conductance ER Ca2+ leak function through their hydrophilic catalytic cavity, and many familial AD PSEN mutations impair this function (Nelson et al., 2007, 2011). Regulation of Ca2+ levels by PSENs also involves their ability to interact with and activate Ca2+ channels: sarco/ER Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) pump (Green et al., 2008), the inositol triphosphate receptor (IP3R; Cheung et al., 2008; Shilling et al., 2014) and the Ryanodine receptor (RyR; Stutzmann et al., 2007; Hayrapetyan et al., 2008). These effects of PSEN on Ca2+ may occur upstream of amyloid-β production and recent evidence also demonstrates that amyloid-β production is regulated by post-translational modifications of the RyR2 (Bussiere et al., 2017; Lacampagne et al., 2017). Accordingly, the RyR-mediated Ca2+ upregulation observed in synaptic compartments is associated with altered synaptic homeostasis and network depression at early, presymptomatic AD stages (Stutzmann et al., 2006; Chakroborty et al., 2009, 2012). Dysregulated RyR Ca2+ signaling disrupts synaptic function at both pre- and post-synaptic levels, thus affecting neuronal excitability and short and long term plasticity mechanisms implicated in learning and memory (Llano et al., 2000; Kuchibhotla et al., 2008; Chakroborty et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2015a; Briggs et al., 2017).
The magnitude of Ca2+ signaling through IP3R and RyR channels is affected by the concentration of Ca2+ in the ER. Accordingly, it has been suggested that familial AD PSEN mutations may increase IP3R and RyR Ca2+ signaling through elevated ER Ca2+ stores. Although this hypothesis has been disputed (Bezprozvanny et al., 2012; Shilling et al., 2012), there is evidence that knockdown of PSEN2 elevates ER Ca2+ stores corroborating the concept that unprocessed forms of PSEN function as ER Ca2+ leak channels (Nelson et al., 2007, 2011; Bandara et al., 2013). In addition, PSEN-1 M146V knockin (PSEN1KI) mutation disrupts ER Ca2+ leak functions of PSEN1, leading to ER Ca2+ elevation (Zhang et al., 2010; Sun et al., 2014), enhanced Ca2+-induced Ca2+-release from ER (Stutzmann et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2010), increased activation of Ca2+-activated potassium channels and supranormal afterhyperpolarization (Stutzmann et al., 2006; Zhang et al., 2015a). These latter mechanisms lead to reduced excitability, synaptic depotentiation and impaired plasticity in KI neurons and may underlie memory defects (Zhang et al., 2015a).
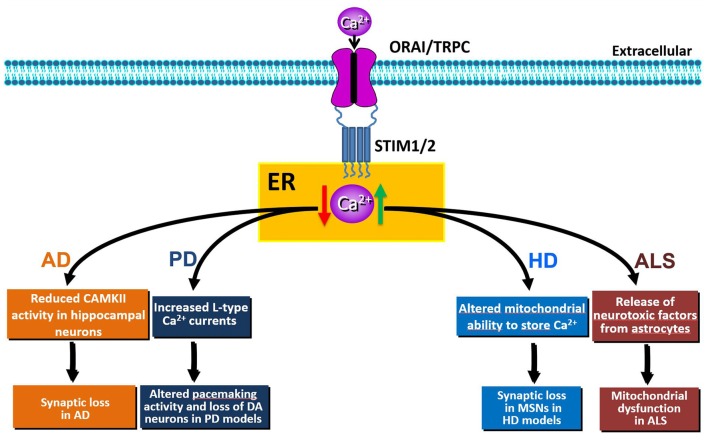
The movement of Ca2+ from the cytosol to the ER is controlled by SOCE and by SERCA pumps. In mice, both STIM1 and STIM2 are key regulators of synaptic plasticity in neural circuits encoding spatial learning and memory (Garcia-Alvarez et al., 2015). Moreover, a recent study has demonstrated that the maturation of dendritic spines and the formation of functional synapses in immature hippocampal neurons is facilitated by the influx of calcium through Orai1 (Korkotian et al., 2017). In hippocampal neurons from the PSEN1KI or the APP-knockin (APPKI) mouse models of AD and in human sporadic AD cortical samples, downregulation of STIM2 protein disrupts neuronal SOCE thus inhibiting the continuous Ca2+ influx necessary for sustained calmodulin kinase II (CaMKII) activation that is, in turn, essential for the stability of mushroom spines (Sun et al., 2014). In APPKI hippocampal neurons, extracellular amyloid-β42 over-activates mGluR5 receptor leading to elevated ER Ca2+ levels, compensatory downregulation of STIM2 expression, impairment of synaptic SOCE, and reduced CaMKII activity (Zhang et al., 2015b). Conversely, overexpression of STIM2 rescues neuronal SOCE and mushroom spine defects in hippocampal neurons from PS1KI and APPKI mouse models of familial AD (Sun et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2015b) and protects mushroom spines from synaptotoxic effects of amyloid-β42 oligomers (Popugaeva et al., 2015). Thus, disturbance of STIM2-SOCE-CaMKII pathway contributes to synaptic loss and cognitive decline; conversely, upregulation of STIM2 expression levels or activation of synaptic neuronal SOCE pathway may yield therapeutic benefits for the treatment of AD and other age-related memory disorders (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the effects of SOCE dysfunction (elevation: green arrow or reduction: red arrow) in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Huntington’s disease (HD), Parkinson’s disease (PD) or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) pathobiology.
Although in these latter studies the expression of STIM1 was not affected by aging or AD (Sun et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2015b), recent studies identified STIM1 as a target of PSEN1-containing γ–secretase activity. In particular, PSEN1 mutations, associated with familial AD, enhanced γ–secretase cleavage of STIM1, reducing activation of Orai1 and attenuating SOCE (Tong et al., 2016). As a consequence of the inhibition of SOCE in hippocampal neurons, dendritic spine deformity was observed (Tong et al., 2016). Thus, PSEN-mediated cleavage of STIM1 may contribute to memory loss through SOCE dysregulation, and it has been hypothesized that STIM2 could also represent a target for γ-secretase, given the sequence similarities of the transmembrane domains of STIM1 and STIM2 (Tong et al., 2016). It is therefore intriguing to speculate that cleavage of STIM2 may account for the previously reported reduction of protein expression in AD (Sun et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2015b).
The molecular identity of STIM-regulated neuronal SOCE in the spines is under investigation and recent findings have suggested that TRPCs may play a role. In fact, in addition to their classical individual effects, TRPC can complex with STIM or STIM/Orai to form SOCE (Ong et al., 2016). Of the seven members of the TRPC family, TRPC1 is the most extensively studied and has been involved in SOCE. However, in the settings where downregulation of STIM2 was detected, expression of TRPC1 was unaffected as no difference was found when comparing protein levels in brain samples from AD mice models or patients with controls (Sun et al., 2014). However, downregulation of TRPC1 and Orai1 proteins was suggested to underlie the reduction of SOCE in astrocytes from APP knockout mice (Linde et al., 2011; but also see, Ronco et al., 2014). Another member of the family that may also contribute to neuronal SOCE (Alkhani et al., 2014; Ong et al., 2016), TRPC3, was found to be negatively correlated with memory performance in mice (Neuner et al., 2015, 2017). By contrast, TRPC6 displays memory-preserving functions by promoting excitatory synapse formation through Ca2+-dependent pathways (Zhou et al., 2008) and/or by specifically interacting with APP thus leading to inhibition of its cleavage by γ-secretase and reduced amyloid-β production independently from its ion channel activity (Wang et al., 2015). Conversely, familial AD PSEN2 mutations abolish agonist-induced TRPC6 activation and thus its Ca2+ entry function (Lessard et al., 2005). TRPC6 physically interacts with Orai (Liao et al., 2007) and TRPC6 and Orai2 channels form a STIM2-regulated neuronal SOCE channel complex in hippocampal mushroom spines (Zhang et al., 2016). Pharmacological activation of TRPC6 stimulates the activity of neuronal SOCE pathway in the spines and rescues mushroom spine loss and long-term potentiation impairment in the APP knockin mouse model of AD (Zhang et al., 2016). Thus, STIM2-regulated TRPC6/Orai2 SOCE channel complex in dendritic mushroom spines represents a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of memory loss in aging and AD.
An important point that needs to be addressed regards the evidence that downregulation of SOCE does not exclusively occur in neurons from different models of familial AD, but is also observed in astrocytes (Linde et al., 2011; Ronco et al., 2014), human microglia (Ronco et al., 2014) and in lymphoblasts obtained from familial AD patients (Bojarski et al., 2009). FAD mutations in endogenous PSEN1 in human B lymphocytes resulted in a decreased expression of STIM2 in parallel to an attenuation of capacitative Ca2+ entry (Bojarski et al., 2009). Thus, PSENs mutations may disrupt calcium homeostasis in various cell types and this may contribute to the multifactorial cascade that leads to neuronal dysfunction. Moreover, calcium signaling is also modified in peripheral cells obtained from sporadic AD patients (Ito et al., 1994; Gibson et al., 1996; Sulger et al., 1999). Lymphocytes from patients with mild cognitive impairment or sporadic AD exhibit an enhanced magnitude of calcium influx during SOCE, whereas, only the former were characterized by higher basal cellular calcium levels as compared to cells from non-demented subjects (Jaworska et al., 2013). Therefore, peripheral cells can be considered useful material for diagnosis and for drug screening.
The current treatment for AD relies on acetylcholinesterase inhibition (with donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine) or blockade of NMDA receptor overstimulation (with memantine) that provide some symptomatic benefits for a limited period of time, followed by a steep cognitive decline due to the fact that these are not disease modifying drugs and do not prevent cell death. The current drug development pipeline is largely based on the amyloid hypothesis; however, despite efficacy at reducing amyloid levels in patients, all the clinical trials to date have generated disappointing results with respect to cognition function. Given the compelling evidence that aberrant calcium signaling, particularly in the ER, is associated with familial AD mutations and sporadic AD risk factors, modulation of calcium channels or calcium regulating proteins is in varying stages of therapeutic validation (Chakroborty and Stutzmann, 2014). In addition to targeting voltage-gated calcium channels, inhibition of RyR or restoration of SOCE have been suggested to represent promising approaches for drug development. Short-term treatment with the RyR inhibitor dantrolene stabilizes Ca2+ signals, ameliorates cognitive decline and reduces neuropathology, amyloid load and memory impairments in various AD mouse models (Chakroborty et al., 2012; Oulès et al., 2012; Peng et al., 2012). Regarding SOCE, its positive modulator NSN21778 rescues mushroom spine loss in both PSENKI and APPKI mouse models of AD (Zhang et al., 2016); while, its induction through overexpression of STIM2 or following pharmacological stimulation of TRPC6 is beneficial in AD animal models (Sun et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2015b, 2016). Moreover, it is also noteworthy to highlight that, in addition to block NMDA receptor overstimulation, memantine increases SOCE in HEK cells (Blanchard et al., 2008). Thus, either through repositioned drugs or originally developed new molecular entities, therapeutic strategies aimed at promoting SOCE may represent promising ways for the development of effective AD therapies.
Soce in Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the selective loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. PD is mostly sporadic, but approximately 10–15% of cases are familial (Fleming, 2017). The major symptoms of PD involve motor dysfunctions, such as asymmetric bradykinesia, resting tremor, rigidity and postural instability (Ali and Morris, 2015). Pathogenic mechanisms of sporadic and familial PD are still elusive. However, the dysregulation of ER Ca2+ homeostasis is one of the mechanisms affecting the selective loss of DA neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (Stefani et al., 2012; Calì et al., 2014). Unlike other neurons, rhythmic activity of DA neurons depends on L-type Cav1.3 channels. Pharmacological inhibition of these currents by izradipine restores Ca2+−independent “juvenile” pacemaking activity and protects DA neurons in animal models of the disease (Chan et al., 2007). In normal conditions, the pacemaking activity of DA neurons is inhibited by the TRPC1-STIM1 complex. Accordingly, increased L-type Cav1.3 currents were observed upon Stim1 or TRPC1 silencing. Interestingly, the neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+)—that mimics PD—decreases the level of TRPC1 and its interaction with STIM1, thus increasing neuronal death both in vitro and in vivo (Bollimuntha et al., 2005; Selvaraj et al., 2012). Molecularly, the decrease of TRPC1 expression leads to an abnormal increase in Cav1.3 activity, thereby causing degeneration of DA neurons (Sun et al., 2017; Figure 2). Despite the abnormal increase in L-type activity, downregulation of TRPC1 also leads to the loss of SOCE, thus triggering ER stress and initiation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) in DA neurons (Selvaraj et al., 2012). Conversely, in PC12 cell lines, Stim1 knockdown significantly attenuated 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)- and MPP+-induced toxicity through inhibition of SOCE-mediated Ca2+-overload (Li et al., 2013, 2014); while, pharmacological inhibition of SOCE by SKF-96365 was protective against MPP+ cytotoxicity (Chen et al., 2013). The effect on SOCE was related to Orai1 and L-type Ca2+ channels, but not to TRPC1 (Li et al., 2014). Moreover, Stim1 knockdown attenuated 6-OHDA- and MMP+-induced mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake and dysfunction in PC12 cells (Li et al., 2013, 2014). This further underscores that STIM1, through SOCE, may be responsible for neuronal oxidative stress induced by ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in PD.
In support of the important role of SOCE for DA neurons survival, the mutant dominant-negative form of Orai1 channel leads to tyrosine hydroxylase downregulation in Drosophila thus affecting dopamine synthesis and release (Pathak et al., 2015). Furthermore, skin fibroblasts from idiopathic PD patients and patients bearing familial R747W mutation in PLA2g6 gene, that encodes for a Ca2+- independent phospholipase A2, exhibit depleted stores and reduced SOCE (Zhou et al., 2016). Overall, these findings indicate that SOCE pathway in DA neurons represents an attractive target for PD drug discovery (Pchitskaya et al., 2018).
Soce in Huntington’s Disease
HD is a fully penetrant neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by cognitive, motor and psychiatric disturbances, and caused by a dominantly inherited CAG trinucleotide repeat expansion in the huntingtin gene on chromosome 4 (McColgan and Tabrizi, 2018). Mutant huntingtin (mHtt) causes defective striatal neuron function, reduction of synaptic contacts, disruption of immune cell function and eventual neurodegeneration through a number of mechanisms (Kim and Fung, 2014; Andre et al., 2016).
Accumulating evidence indicates that dysregulation of intracellular neuronal Ca2+ signaling by mHTT plays a role in HD progression (Pchitskaya et al., 2018; Raymond, 2017). Unlike the AD setting, in the striatum from HD transgenic mice, an increased STIM2 expression causes elevated synaptic SOCE, that was suggested to underlie synaptic loss in medium spiny neurons (MSNs; Wu et al., 2011, 2016). After binding IP3R1, mHtt increases its sensitivity to activation by IP3, thus producing a reduction of ER Ca2+ levels that, in turn, promotes sustained and synaptotoxic SOCE in the spines of MSNs from YAC128 transgenic HD mice (Tang et al., 2005, 2009; Wu et al., 2016). In this context, STIM2 expression is elevated, as documented both in aged YAC128 striatal cultures and in YAC128 mouse striatum. In human neuroblastoma cells, the expression of the N-terminal fragment of mHtt (Htt138Q-1exon) is sufficient to cause a HD pathological phenotype, as it induces an increase of SOCE that requires STIM1 in this in vitro model (Vigont et al., 2014). Similar findings were obtained in mouse neuroblastoma cells and in primary culture of mouse MSNs, where lentiviral expression of Htt138Q-1exon results in enhanced SOCE through the involvement of the sensor STIM1 and of both TRPC1- and Orai1 subunits forming a heteromeric channel (Vigont et al., 2015). A key role of TRPC1 channels in supporting SOCE was also demonstrated in YAC128 MSNs primary cultures, where TRPC1 suppression by a short interfering RNA has a significant protective effect against glutamate-induced apoptosis (Wu et al., 2011).
Notably, pharmacological inhibition of neuronal SOCE by EVP4593 rescues striatal spine loss in both in vitro and in vivo transgenic HD models (Vigont et al., 2015; Wu et al., 2016); analogously, stabilization of SOCE by tetrahydrocarbazoles was associated with beneficial effects on the function of mitochondria from YAC128 MSNs (Czeredys et al., 2017).
Another mechanism that contributes to the dysregulation of SOCE during HD progression involves the sigma-1 receptor (S1R), an ER resident transmembrane protein that is regulated by ER Ca2+ homeostasis. Consistent with ER calcium dysregulation in HD, striatal upregulation of S1R occurs in aged YAC128 transgenic HD mice and in patients. Pharmacological activation of S1R with pridopidine prevents MSN spine loss in aging YAC128 co-cultures through suppression of supranormal ER Ca2+ release, restored ER calcium levels and reduced excessive SOCE in spines (Ryskamp et al., 2017).
Thus, pharmacological inhibition of SOCE is beneficial to synapse maintenance in HD models, whereas the same approach may be anticipated to be detrimental to cortical and hippocampal pyramidal neurons (Figure 2). Conversely, while up-regulation of SOCE may be beneficial for pyramidal neurons during AD, it may be detrimental for other CNS synapses. These intriguing findings highlight the importance of further mechanistic studies to dissect the molecular pathways, and their corresponding targets, involved in synaptic loss during aging and neurodegenerative diseases.
Soce in Motor and Sensory Peripheral Nerve Degeneration
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a severe human progressive neurodegenerative disease affecting lower and upper motor neurons whose specific etiology is incompletely understood. Familial ALS (fALS) patients with known genetic mutations are relatively rare, and over 90% of cases occur sporadically. However, mutations in superoxide dismutase-1 (SOD1), TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TARDBP/TDP-43) and C9orf72 have been identified in subsets of familial and sporadic patients (Rosen et al., 1993; DeJesus-Hernandez et al., 2011; Renton et al., 2011). In these ALS forms, dysregulation of calcium homeostasis, oxidative stress, ER stress and UPR have been identified as molecular and neuropathological features (Kaus and Sareen, 2015). Beside the evidence that perturbations in ER Ca2+ homeostasis are implicated in ALS pathology, data on the involvement of SOCE and its molecular components are currently limited. Some evidence on SOCE dysregulation in ALS was provided only in glial cells that actively participate to the neurodegenerative process of the disease. In particular, astrocytes obtained from animal models of ALS or from human familial or sporadic ALS patients are able to release toxic factors that induce cell death in primary motor neurons (Di Giorgio et al., 2007; Nagai et al., 2007; Haidet-Phillips et al., 2011). However, the mechanisms underlying this pathological release remain unclear. In this respect, it has been reported that mutant SOD1G93A astrocytes display aberrant ER calcium filling that involves enhanced S-glutathionylation of STIM1. This reversible posttranslational modification occurs in response to oxidative stress in a number of neurodegenerative diseases (Mieyal et al., 2008), including ALS (Poon et al., 2005; Cassina et al., 2008). STIM1 glutathionylation in the ER promotes its interaction with PM Orai1 in a calcium-independent manner thus inducing constitutive calcium entry (Hawkins et al., 2010). Increased STIM1 glutathionylation may, indeed, underlie continuous SOCE and ER calcium overload in SOD1G93A astrocytes (Kawamata et al., 2014).
SOCE dysfunction is also implicated in Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease, one of the most frequent inherited neurological disorders characterized by either demyelinating or axonal neuropathy of motor and sensory peripheral nerves (Pareyson et al., 2013). Mutations in ganglioside-induced differentiation-associated protein-1 (GDAP1), which maps at human chromosome 8q21.1, are causative for autosomal recessive demyelinating CMT4A (Baxter et al., 2002). The severe recessive form of GDAP1-related CMT starts early in infancy or childhood with weakness and wasting of the feet followed by involvement of the hands leading to pronounced disability. In the animal models of CMT, mutations in the GDAP1 gene recapitulates pathological features of the disease causing a peripheral neuropathy with a loss of motor neurons and abnormal neuromuscular junctions. GDAP1 is located in the mitochondrial outer membrane where it participates in the mitochondrial network dynamics and in the mitochondria/ER coupling. Importantly, GDAP1 silencing significantly reduces Ca2+ inflow through SOCE upon mobilization of ER Ca2+. This causes a partial depletion of intracellular Ca2+ stores and/or release defects (Barneo-Muñoz et al., 2015). This suggests that GDAP1-related CMT neuropathy may be associated with a decrease in SOCE activity and impaired SOCE-driven Ca2+ uptake in intracellular storing organelles with a consequent abnormal distribution and movement of mitochondria throughout cytoskeleton towards the ER and subplasmalemmal microdomains (Pla-Martín et al., 2013).
Conclusion
The experimental evidence reviewed in the present work clearly demonstrates that Ca2+ homeostasis and, most notably, SOCE components are dysregulated in both acute and chronic neurodegenerative diseases. Thus, SOCE is not only involved in Ca2+ refilling of ER, but also provides an influx of Ca2+ that performs signaling functions and may (positively or negatively) contribute to the progression of neurodegenerative diseases (Majewski and Kuznicki, 2015). In fact, SOCE and its components, namely STIM, Orai and TRPC, have a well-established significance in both excitable and non-excitable cells, including neurons, glial cells and leukocytes. Dysregulation of SOCE in these cells may play specific roles in neuronal demise or protection, depending on the nature of the insult (Figures 1, 2). SOCE seems to be neuroprotective in PD and AD, while in other situations, such as for instance HD, neuroprotection is achieved by blocking SOCE. The role of SOCE in stroke is instead still controversial. Dissection of the molecular components sustaining SOCE should be performed at the level of each specific cell type in order to identify the exact role played by SOCE in each of them. The dualistic role of SOCE in the different forms of neurodegeneration should be carefully considered when its elements are regarded as potential targets for the development of new drugs. Promising pharmacological targets for the modulation of SOCE are: the Ca2+ sensors (e.g., STIMs), the Ca2+ channels (e.g., Orais and TRPCs) or the proteins that sense Ca2+ entry through SOCE and then activate the cellular response. Although some compounds that modulate SOCE have been developed and tested in pre-clinical models of neurodegenerative diseases, the validation of new drugs that specifically target SOCE components would result in successful treatment strategies for currently incurable neurodegenerative diseases, including AD, PD, HD and stroke.
Author Contributions
AS, GB and DA participated in the collection, review and analysis of the relevant literature, as well as in drafting and revising the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Funding. This work was supported by the Italian Ministry of Health (Progetto Giovani Ricercatori GR-2010-2318138 to AS) and by the Italian Ministry of Education, University of Research (PRIN2015–Prot. 2015KRYSJN to AS and DA).
References
- Ahmad F., Boulaftali Y., Greene T. K., Ouellette T. D., Poncz M., Feske S., et al. (2011). Relative contributions of stromal interaction molecule 1 and CalDAG-GEFI to calcium-dependent platelet activation and thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 9, 2077–2086. 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04474.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali K., Morris H. R. (2015). Parkinson’s disease: chameleons and mimics. Pract. Neurol. 15, 14–25. 10.1136/practneurol-2014-000849 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkhani H., Ase A. R., Grant R., O’Donnell D., Groschner K., Séguéla P. (2014). Contribution of TRPC3 to store-operated calcium entry and inflammatory transductions in primary nociceptors. Mol. Pain 10, 1744–8069 -10–43. 10.1186/1744-8069-10-43 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen A. M., Dosanjh J. K., Erac M., Dassanayake S., Hannan R. D., Thomas W. G. (2006). Expression of constitutively active angiotensin receptors in the rostral ventrolateral medulla increases blood pressure. Hypertension 47, 1054–1061. 10.1161/01.HYP.0000218576.36574.54 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alzheimer’s Association Calcium Hypothesis Workgroup . (2017). Calcium hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease and brain aging: a framework for integrating new evidence into a comprehensive theory of pathogenesis. Alzheimers Dement. 13, 178.e17–182.e17. 10.1016/j.jalz.2016.12.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amantea D. (2016). Editorial overview: neurosciences: brain and immunity: new targets for neuroprotection. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 26, v–viii. 10.1016/j.coph.2015.12.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amantea D., Micieli G., Tassorelli C., Cuartero M. I., Ballesteros I., Certo M., et al. (2015). Rational modulation of the innate immune system for neuroprotection in ischemic stroke. Front. Neurosci. 9:147. 10.3389/fnins.2015.00147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amantea D., Tassorelli C., Petrelli F., Certo M., Bezzi P., Micieli G., et al. (2014). Understanding the multifaceted role of inflammatory mediators in ischemic stroke. Curr. Med. Chem. 21, 2098–2117. 10.2174/0929867321666131227162634 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambudkar I. S., Ong H. L., Liu X., Bandyopadhyay B., Cheng K. T., Cheng K. T. (2007). TRPC1: the link between functionally distinct store-operated calcium channels. Cell Calcium 42, 213–223. 10.1016/j.ceca.2007.01.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andre R., Carty L., Tabrizi S. J. (2016). Disruption of immune cell function by mutant huntingtin in Huntington’s disease pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 26, 33–38. 10.1016/j.coph.2015.09.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara S., Malmersjö S., Meyer T. (2013). Regulators of calcium homeostasis identified by inference of kinetic model parameters from live single cells perturbed by siRNA. Sci. Signal. 6:ra56. 10.1126/scisignal.2003649 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barneo-Muñoz M., Juárez P., Civera-Tregón A., Yndriago L., Pla-Martin D., Zenker J., et al. (2015). Lack of GDAP1 induces neuronal calcium and mitochondrial defects in a knockout mouse model of charcot-marie-tooth neuropathy. PLoS Genet. 11:e1005115. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005115 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. V., Ben Othmane K., Rochelle J. M., Stajich J. E., Hulette C., Dew-Knight S., et al. (2002). Ganglioside-induced differentiation-associated protein-1 is mutant in charcot-marie-tooth disease type 4A/8q21. Nat. Genet. 30, 21–22. 10.1038/ng796 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bénard L., Oh J. G., Cacheux M., Lee A., Nonnenmacher M., Matasic D. S., et al. (2016). Cardiac Stim1 silencing impairs adaptive hypertrophy and promotes heart failure through inactivation of mTORC2/Akt signaling. Circulation 133, 1458–1471; discussion 1471. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.020678 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berna-Erro A., Braun A., Kraft R., Kleinschnitz C., Schuhmann M. K., Stegner D., et al. (2009). STIM2 regulates capacitive Ca2+ entry in neurons and plays a key role in hypoxic neuronal cell death. Sci. Signal. 2:ra67. 10.1126/scisignal.2000522 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berna-Erro A., Jardín I., Smani T., Rosado J. A. (2016). Regulation of platelet function by Orai, STIM and TRP. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 898, 157–181. 10.1007/978-3-319-26974-0_8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Supnet C., Sun S., Zhang H., De Strooper B. (2012). Response to Shilling et al. (10.1074/jbc.M111.300491). J. Biol. Chem. 287:20469, author reply 20470. 10.1074/jbc.L112.356790 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt D. L., Topol E. J. (2003). Scientific and therapeutic advances in antiplatelet therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2, 15–28. 10.1038/nrd985 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard A. P., Guillemette G., Boulay G. (2008). Memantine potentiates agonist-induced Ca2+ responses in HEK 293 cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 22, 205–214. 10.1159/000149798 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bojarski L., Pomorski P., Szybinska A., Drab M., Skibinska-Kijek A., Gruszczynska-Biegala J., et al. (2009). Presenilin-dependent expression of STIM proteins and dysregulation of capacitative Ca2+ entry in familial Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1793, 1050–1057. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.11.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollimuntha S., Singh B. B., Shavali S., Sharma S. K., Ebadi M. (2005). TRPC1-mediated inhibition of 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion neurotoxicity in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 2132–2140. 10.1074/jbc.M407384200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandman O., Liou J., Park W. S., Meyer T. (2007). STIM2 is a feedback regulator that stabilizes basal cytosolic and endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ levels. Cell 131, 1327–1339. 10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun A., Varga-Szabo D., Kleinschnitz C., Pleines I., Bender M., Austinat M., et al. (2009). Orai1 (CRACM1) is the platelet SOC channel and essential for pathological thrombus formation. Blood 113, 2056–2063. 10.1182/blood-2008-07-171611 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs C. A., Chakroborty S., Stutzmann G. E. (2017). Emerging pathways driving early synaptic pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 483, 988–997. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.09.088 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussiere R., Lacampagne A., Reiken S., Liu X., Scheuerman V., Zalk R., et al. (2017). Amyloid β production is regulated by β2-adrenergic signaling-mediated post-translational modifications of the ryanodine receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 292, 10153–10168. 10.1074/jbc.M116.743070 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calì T., Ottolini D., Brini M. (2014). Calcium signaling in Parkinson’s disease. Cell Tissue Res. 357, 439–454. 10.1007/s00441-014-1866-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassina P., Cassina A., Pehar M., Castellanos R., Gandelman M., de Leon A., et al. (2008). Mitochondrial dysfunction in SOD1G93A-bearing astrocytes promotes motor neuron degeneration: prevention by mitochondrial-targeted antioxidants. J. Neurosci. 28, 4115–4122. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5308-07.2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakroborty S., Briggs C., Miller M. B., Goussakov I., Schneider C., Kim J., et al. (2012). Stabilizing ER Ca2+ channel function as an early preventative strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 7:e52056. 10.1371/journal.pone.0052056 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakroborty S., Goussakov I., Miller M. B., Stutzmann G. E. (2009). Deviant ryanodine receptor-mediated calcium release resets synaptic homeostasis in presymptomatic 3xTg-AD mice. J. Neurosci. 29, 9458–9470. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2047-09.2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakroborty S., Stutzmann G. E. (2014). Calcium channelopathies and Alzheimer’s disease: insight into therapeutic success and failures. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 739, 83–95. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.11.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. S., Guzman J. N., Ilijic E., Mercer J. N., Rick C., Tkatch T., et al. (2007). “Rejuvenation” protects neurons in mouse models of Parkinson’s disease. Nature 447, 1081–1086. 10.1038/nature05865 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y.-F., Chiu W.-T., Chen Y.-T., Lin P.-Y., Huang H.-J., Chou C.-Y., et al. (2011). Calcium store sensor stromal-interaction molecule 1-dependent signaling plays an important role in cervical cancer growth, migration and angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 108, 15225–15230. 10.1073/pnas.1103315108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G., Xu T., Yan Y., Zhou Y., Jiang Y., Melcher K., et al. (2017). Amyloid β: structure, biology and structure-based therapeutic development. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 38, 1205–1235. 10.1038/aps.2017.28 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T., Zhu J., Zhang C., Huo K., Fei Z., Jiang X. (2013). Protective effects of SKF-96365, a non-specific inhibitor of SOCE, against MPP+-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells: potential role of Homer1. PLoS One 8:e55601. 10.1371/journal.pone.0055601 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung K.-H., Shineman D., Müller M., Cárdenas C., Mei L., Yang J., et al. (2008). Mechanism of Ca2+ disruption in Alzheimer’s disease by presenilin regulation of InsP3 receptor channel gating. Neuron 58, 871–883. 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.04.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czeredys M., Maciag F., Methner A., Kuznicki J. (2017). Tetrahydrocarbazoles decrease elevated SOCE in medium spiny neurons from transgenic YAC128 mice, a model of Huntington’s disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 483, 1194–1205. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.106 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeHaven W. I., Smyth J. T., Boyles R. R., Putney J. W. (2007). Calcium inhibition and calcium potentiation of Orai1, Orai2 and Orai3 calcium release-activated calcium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 17548–17556. 10.1074/jbc.m611374200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeJesus-Hernandez M., Mackenzie I. R., Boeve B. F., Boxer A. L., Baker M., Rutherford N. J., et al. (2011). Expanded GGGGCC hexanucleotide repeat in noncoding region of C9ORF72 causes chromosome 9p-linked FTD and ALS. Neuron 72, 245–256. 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.09.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete D., Checler F., Chami M. (2014). Ryanodine receptors: physiological function and deregulation in Alzheimer disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 9:21. 10.1186/1750-1326-9-21 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaurex N., Nunes P. (2016). The role of STIM and ORAI proteins in phagocytic immune cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 310, C496–C508. 10.1152/ajpcell.00360.2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Giorgio F. P., Carrasco M. A., Siao M. C., Maniatis T., Eggan K. (2007). Non-cell autonomous effect of glia on motor neurons in an embryonic stem cell-based ALS model. Nat. Neurosci. 10, 608–614. 10.1038/nn1885 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirnagl U., Endres M. (2014). Found in translation: preclinical stroke research predicts human pathophysiology, clinical phenotypes and therapeutic outcomes. Stroke 45, 1510–1518. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.004075 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doody R. S., Raman R., Farlow M., Iwatsubo T., Vellas B., Joffe S., et al. (2013). A phase 3 trial of semagacestat for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 369, 341–350. 10.1056/NEJMoa1210951 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan S. P., McCarthy J. V. (2016). Beyond γ-secretase activity: the multifunctional nature of presenilins in cell signalling pathways. Cell. Signal. 28, 1–11. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.10.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferri K. F., Kroemer G. (2001). Organelle-specific initiation of cell death pathways. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, E255–E263. 10.1038/ncb1101-e255 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feske S. (2007). Calcium signalling in lymphocyte activation and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7, 690–702. 10.1038/nri2152 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feske S. (2011). Immunodeficiency due to defects in store-operated calcium entry. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 1238, 74–90. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06240.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feske S., Giltnane J., Dolmetsch R., Staudt L. M., Rao A. (2001). Gene regulation mediated by calcium signals in T lymphocytes. Nat. Immunol. 2, 316–324. 10.1038/86318 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feske S., Gwack Y., Prakriya M., Srikanth S., Puppel S.-H., Tanasa B., et al. (2006). A mutation in Orai1 causes immune deficiency by abrogating CRAC channel function. Nature 441, 179–185. 10.1038/nature04702 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feske S., Prakriya M., Rao A., Lewis R. S. (2005). A severe defect in CRAC Ca2+ channel activation and altered K+ channel gating in T cells from immunodeficient patients. J. Exp. Med. 202, 651–662. 10.1084/jem.20050687 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fjell A. M., McEvoy L., Holland D., Dale A. M., Walhovd K. B., Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative . (2014). What is normal in normal aging? Effects of aging, amyloid and Alzheimer’s disease on the cerebral cortex and the hippocampus. Prog. Neurobiol. 117, 20–40. 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2014.02.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming S. M. (2017). Mechanisms of gene-environment interactions in Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 4, 192–199. 10.1007/s40572-017-0143-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Alvarez G., Shetty M. S., Lu B., Yap K. A. F., Oh-Hora M., Sajikumar S., et al. (2015). Impaired spatial memory and enhanced long-term potentiation in mice with forebrain-specific ablation of the Stim genes. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 9:180. 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00180 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson G. E., Zhang H., Toral-Barza L., Szolosi S., Tofel-Grehl B. (1996). Calcium stores in cultured fibroblasts and their changes with Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1316, 71–77. 10.1016/0925-4439(96)00002-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godyn J., Jonczyk J., Panek D., Malawska B. (2016). Therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease in clinical trials. Pharmacol. Rep. 68, 127–138. 10.1016/j.pharep.2015.07.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goel M., Sinkins W. G., Schilling W. P. (2002). Selective association of TRPC channel subunits in rat brain synaptosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 48303–48310. 10.1074/jbc.M207882200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golovina V. A., Platoshyn O., Bailey C. L., Wang J., Limsuwan A., Sweeney M., et al. (2001). Upregulated TRP and enhanced capacitative Ca2+ entry in human pulmonary artery myocytes during proliferation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 280, H746–H755. 10.1152/ajpheart.2001.280.2.h746 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. N., Demuro A., Akbari Y., Hitt B. D., Smith I. F., Parker I., et al. (2008). SERCA pump activity is physiologically regulated by presenilin and regulates amyloid β production. J. Cell Biol. 181, 1107–1116. 10.1083/jcb.200706171 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidet-Phillips A. M., Hester M. E., Miranda C. J., Meyer K., Braun L., Frakes A., et al. (2011). Astrocytes from familial and sporadic ALS patients are toxic to motor neurons. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 824–828. 10.1038/nbt.1957 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins B. J., Irrinki K. M., Mallilankaraman K., Lien Y.-C., Wang Y., Bhanumathy C. D., et al. (2010). S-glutathionylation activates STIM1 and alters mitochondrial homeostasis. J. Cell Biol. 190, 391–405. 10.1083/jcb.201004152 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon P. G., Carmignoto G. (2006). Astrocyte control of synaptic transmission and neurovascular coupling. Physiol. Rev. 86, 1009–1031. 10.1152/physrev.00049.2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayrapetyan V., Rybalchenko V., Rybalchenko N., Koulen P. (2008). The N-terminus of presenilin-2 increases single channel activity of brain ryanodine receptors through direct protein-protein interaction. Cell Calcium 44, 507–518. 10.1016/j.ceca.2008.03.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann T., Schaefer M., Schultz G., Gudermann T. (2002). Subunit composition of mammalian transient receptor potential channels in living cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 99, 7461–7466. 10.1073/pnas.102596199 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hort J., O’Brien J. T., Gainotti G., Pirttila T., Popescu B. O., Rektorova I., et al. (2010). EFNS guidelines for the diagnosis and management of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 17, 1236–1248. 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03040.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoth M., Penner R. (1993). Calcium release-activated calcium current in rat mast cells. J. Physiol. 465, 359–386. 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019681 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang G. N., Zeng W., Kim J. Y., Yuan J. P., Han L., Muallem S., et al. (2006). STIM1 carboxyl-terminus activates native SOC, I(crac) and TRPC1 channels. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 1003–1010. 10.1038/ncb1454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulot J.-S., Fauconnier J., Ramanujam D., Chaanine A., Aubart F., Sassi Y., et al. (2011). Critical role for stromal interaction molecule 1 in cardiac hypertrophy. Circulation 124, 796–805. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.031229 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda M., Tsuno S., Sugiyama T., Hashimoto A., Yamoto K., Takeuchi K., et al. (2013). Ca2+ spiking activity caused by the activation of store-operated Ca2+ channels mediates TNF-α release from microglial cells under chronic purinergic stimulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1833, 2573–2585. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.06.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isegawa K., Hirooka Y., Katsuki M., Kishi T., Sunagawa K. (2014). Angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression in astrocytes is upregulated leading to increased mortality in mice with myocardial infarction-induced heart failure. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 307, H1448–H1455. 10.1152/ajpheart.00462.2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito E., Oka K., Etcheberrigaray R., Nelson T. J., McPhie D. L., Tofel-Grehl B., et al. (1994). Internal Ca2+ mobilization is altered in fibroblasts from patients with Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 91, 534–538. 10.1073/pnas.91.2.534 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaworska A., Dzbek J., Styczynska M., Kuznicki J. (2013). Analysis of calcium homeostasis in fresh lymphocytes from patients with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1833, 1692–1699. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.01.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia S., Rodriguez M., Williams A. G., Yuan J. P. (2017). Homer binds to Orai1 and TRPC channels in the neointima and regulates vascular smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation. Sci. Rep. 7:5075. 10.1038/s41598-017-04747-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch C. M., Goate A. M. (2015). Alzheimer’s disease risk genes and mechanisms of disease pathogenesis. Biol. Psychiatry 77, 43–51. 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.05.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaus A., Sareen D. (2015). ALS Patient stem cells for unveiling disease signatures of motoneuron susceptibility: perspectives on the deadly mitochondria, ER stress and calcium triad. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 9:448. 10.3389/fncel.2015.00448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamata H., Ng S. K., Diaz N., Burstein S., Morel L., Osgood A., et al. (2014). Abnormal intracellular calcium signaling and SNARE-dependent exocytosis contributes to SOD1G93A astrocyte-mediated toxicity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurosci. 34, 2331–2348. 10.1523/jneurosci.2689-13.2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. (1989). Calcium, membranes, aging, and Alzheimer’s disease. Introduction and overview. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 568, 1–4. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb12485.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. D., Fung V. S. C. (2014). An update on Huntington’s disease. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 27, 477–483. 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000116 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korkotian E., Oni-Biton E., Segal M. (2017). The role of the store-operated calcium entry channel Orai1 in cultured rat hippocampal synapse formation and plasticity. J. Physiol. 595, 125–140. 10.1113/jp272645 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft R. (2015). STIM and ORAI proteins in the nervous system. Channels 9, 245–252. 10.1080/19336950.2015.1071747 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchibhotla K. V., Goldman S. T., Lattarulo C. R., Wu H.-Y., Hyman B. T., Bacskai B. J. (2008). Aβ plaques lead to aberrant regulation of calcium homeostasis in vivo resulting in structural and functional disruption of neuronal networks. Neuron 59, 214–225. 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.06.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V. S. S., Gopalakrishnan A., Naziroglu M., Rajanikant G. K. (2014). Calcium ion—the key player in cerebral ischemia. Curr. Med. Chem. 21, 2065–2275. 10.2174/0929867321666131228204246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacampagne A., Liu X., Reiken S., Bussiere R., Meli A. C., Lauritzen I., et al. (2017). Post-translational remodeling of ryanodine receptor induces calcium leak leading to Alzheimer’s disease-like pathologies and cognitive deficits. Acta Neuropathol. 134, 749–767. 10.1007/s00401-017-1733-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacruz R. S., Feske S. (2015). Diseases caused by mutations in ORAI1 and STIM1. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 1356, 45–79. 10.1111/nyas.12938 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M., Jantaratnotai N., McGeer E., McLarnon J. G., McGeer P. L. (2011). Mg2+ ions reduce microglial and THP-1 cell neurotoxicity by inhibiting Ca2+ entry through purinergic channels. Brain Res. 1369, 21–35. 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.10.084 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lein E. S., Hawrylycz M. J., Ao N., Ayres M., Bensinger A., Bernard A., et al. (2007). Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature 445, 168–176. 10.1038/nature05453 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessard C. B., Lussier M. P., Cayouette S., Bourque G., Boulay G. (2005). The overexpression of presenilin2 and Alzheimer’s-disease-linked presenilin2 variants influences TRPC6-enhanced Ca2+ entry into HEK293 cells. Cell. Signal. 17, 437–445. 10.1016/j.cellsig.2004.09.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. S., Cahalan M. D. (1995). Potassium and calcium channels in lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 13, 623–653. 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.003203 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Chen W., Zhang L., Liu W., Fei Z. (2013). Inhibition of store-operated calcium entry attenuates MPP+-induced oxidative stress via preservation of mitochondrial function in PC12 cells: involvement of homer1a. PLoS One 8:e83638. 10.1371/journal.pone.0083638 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li B., Xiao L., Wang Z. Y., Zheng P. S. (2014). Knockdown of STIM1 inhibits 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative stress through attenuating calcium-dependent ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in undifferentiated PC12 cells. Free Radic. Res. 48, 758–768. 10.3109/10715762.2014.905687 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao Y., Erxleben C., Yildirim E., Abramowitz J., Armstrong D. L., Birnbaumer L. (2007). Orai proteins interact with TRPC channels and confer responsiveness to store depletion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 104, 4682–4687. 10.1073/pnas.0611692104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind B. L., Jessen S. B., Lønstrup M., Joséphine C., Bonvento G., Lauritzen M. (2018). Fast Ca2+ responses in astrocyte end-feet and neurovascular coupling in mice. Glia 66, 348–358. 10.1002/glia.23246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linde C. I., Baryshnikov S. G., Mazzocco-Spezzia A., Golovina V. A. (2011). Dysregulation of Ca2+ signaling in astrocytes from mice lacking amyloid precursor protein. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 300, C1502–C1512. 10.1152/ajpcell.00379.2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou J., Kim M. L., Heo W. D., Jones J. T., Myers J. W., Ferrell J. E., et al. (2005). STIM is a Ca2+ sensor essential for Ca2+-store-depletion-triggered Ca2+ influx. Curr. Biol. 15, 1235–1241. 10.1016/j.cub.2005.05.055 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis A., Peinelt C., Beck A., Parvez S., Monteilh-Zoller M., Fleig A., et al. (2007). CRACM1, CRACM2 and CRACM3 are store-operated Ca2+ channels with distinct functional properties. Curr. Biol. 17, 794–800. 10.1016/j.cub.2007.03.065 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Bandyopadhyay B. C., Singh B. B., Groschner K., Ambudkar I. S. (2005). Molecular analysis of a store-operated and 2-acetyl-sn-glycerol-sensitive non-selective cation channel. Heteromeric assembly of TRPC1-TRPC3. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 21600–21606. 10.1074/jbc.c400492200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Singh B. B., Ambudkar I. S. (2003). TRPC1 is required for functional store-operated Ca 2+ channels. Role of acidic amino acid residues in the S5-S6 region. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 11337–11343. 10.1074/jbc.M213271200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D. Y., Thilo F., Scholze A., Wittstock A., Zhao Z. G., Harteneck C., et al. (2007). Increased store-operated and 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol-induced calcium influx in monocytes is mediated by transient receptor potential canonical channels in human essential hypertension. J. Hypertens. 25, 799–808. 10.1097/hjh.0b013e32803cae2b [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llano I., González J., Caputo C., Lai F. A., Blayney L. M., Tan Y. P., et al. (2000). Presynaptic calcium stores underlie large-amplitude miniature IPSCs and spontaneous calcium transients. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 1256–1265. 10.1038/81781 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. J., Albarran L., Gómez L. J., Smani T., Salido G. M., Rosado J. A. (2016). Molecular modulators of store-operated calcium entry. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1863, 2037–2043. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.04.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu L., Hogan-Cann A. D., Globa A. K., Lu P., Nagy J. I., Bamji S. X., et al. (2017). Astrocytes drive cortical vasodilatory signaling by activating endothelial NMDA receptors. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1177/0271678x17734100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luik R. M., Wu M. M., Buchanan J., Lewis R. S. (2006). The elementary unit of store-operated Ca2+ entry: local activation of CRAC channels by STIM1 at ER-plasma membrane junctions. J. Cell Biol. 174, 815–825. 10.1083/jcb.200604015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma G., Wei M., He L., Liu C., Wu B., Zhang S. L., et al. (2015). Inside-out Ca2+ signalling prompted by STIM1 conformational switch. Nat. Commun. 6:7826. 10.1038/ncomms8826 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewski L., Kuznicki J. (2015). SOCE in neurons: signaling or just refilling? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1853, 1940–1952. 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.01.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColgan P., Tabrizi S. J. (2018). Huntington’s disease: a clinical review. Eur. J. Neurol. 25, 24–34. 10.1111/ene.13413 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G. M., Knopman D. S., Chertkow H., Hyman B. T., Jack C. R., Kawas C. H., et al. (2011). The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 7, 263–269. 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis M., Nieswandt B., Stegner D., Eilers J., Kraft R. (2015). STIM1, STIM2 and Orai1 regulate store-operated calcium entry and purinergic activation of microglia. Glia 63, 652–663. 10.1002/glia.22775 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mieyal J. J., Gallogly M. M., Qanungo S., Sabens E. A., Shelton M. D. (2008). Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications of reversible protein S -glutathionylation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 10, 1941–1988. 10.1089/ars.2008.2089 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra A., Reynolds J. P., Chen Y., Gourine A. V., Rusakov D. A., Attwell D. (2016). Astrocytes mediate neurovascular signaling to capillary pericytes but not to arterioles. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 1619–1627. 10.1038/nn.4428 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moccia F., Tanzi F., Munaron L. (2014). Endothelial remodelling and intracellular calcium machinery. Curr. Mol. Med. 14, 457–480. 10.2174/1566524013666131118113410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moccia F., Zuccolo E., Soda T., Tanzi F., Guerra G., Mapelli L., et al. (2015). Stim and Orai proteins in neuronal Ca2+ signaling and excitability. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 9:153. 10.3389/fncel.2015.00153 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Connor J. A. (1991). Dendritic spines as individual neuronal compartments for synaptic Ca2+ responses. Nature 354, 73–76. 10.1038/354073a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai M., Re D. B., Nagata T., Chalazonitis A., Jessell T. M., Wichterle H., et al. (2007). Astrocytes expressing ALS-linked mutated SOD1 release factors selectively toxic to motor neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 10, 615–622. 10.1038/nn1876 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson O., Supnet C., Tolia A., Horré K., De Strooper B., Bezprozvanny I. (2011). Mutagenesis mapping of the presenilin 1 calcium leak conductance pore. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 22339–22347. 10.1074/jbc.m111.243063 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson O., Tu H., Lei T., Bentahir M., de Strooper B., Bezprozvanny I. (2007). Familial Alzheimer disease-linked mutations specifically disrupt Ca2+ leak function of presenilin 1. J. Clin. Invest. 117, 1230–1239. 10.1172/jci30447 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuner S. M., Wilmott L. A., Hoffmann B. R., Mozhui K., Kaczorowski C. C. (2017). Hippocampal proteomics defines pathways associated with memory decline and resilience in normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Behav. Brain Res. 322, 288–298. 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.06.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuner S. M., Wilmott L. A., Hope K. A., Hoffmann B., Chong J. A., Abramowitz J., et al. (2015). TRPC3 channels critically regulate hippocampal excitability and contextual fear memory. Behav. Brain Res. 281, 69–77. 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.12.018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara H., Nabika T. (2016). A nonsense mutation of Stim1 identified in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats decreased the store-operated calcium entry in astrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 476, 406–411. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.05.134 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh-Hora M., Yamashita M., Hogan P. G., Sharma S., Lamperti E., Chung W., et al. (2008). Dual functions for the endoplasmic reticulum calcium sensors STIM1 and STIM2 in T cell activation and tolerance. Nat. Immunol. 9, 432–443. 10.1038/ni1574 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong H. L., de Souza L. B., Ambudkar I. S. (2016). Role of TRPC channels in store-operated calcium entry. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 898, 87–109. 10.1007/978-3-319-26974-0_5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oulès B., Del Prete D., Greco B., Zhang X., Lauritzen I., Sevalle J., et al. (2012). Ryanodine receptor blockade reduces amyloid-β load and memory impairments in Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J. Neurosci. 32, 11820–11834. 10.1523/jneurosci.0875-12.2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannaccione A., Secondo A., Molinaro P., D’Avanzo C., Cantile M., Esposito A., et al. (2012). A new concept: A β1–42 generates a hyperfunctional proteolytic NCX3 fragment that delays caspase-12 activation and neuronal death. J. Neurosci. 32, 10609–10617. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6429-11.2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh A. B. (2010). Store-operated CRAC channels: function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 9, 399–410. 10.1038/nrd3136 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh A. B., Penner R. (1997). Store depletion and calcium influx. Physiol. Rev. 77, 901–930. 10.1152/physrev.1997.77.4.901 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pareyson D., Piscosquito G., Moroni I., Salsano E., Zeviani M. (2013). Peripheral neuropathy in mitochondrial disorders. Lancet Neurol. 12, 1011–1024. 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70158-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak T., Agrawal T., Richhariya S., Sadaf S., Hasan G. (2015). Store-operated calcium entry through orai is required for transcriptional maturation of the flight circuit in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 35, 13784–13799. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1680-15.2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pchitskaya E., Popugaeva E., Bezprozvanny I. (2018). Calcium signaling and molecular mechanisms underlying neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Calcium 70, 87–94. 10.1016/j.ceca.2017.06.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedata F., Dettori I., Coppi E., Melani A., Fusco I., Corradetti R., et al. (2016). Purinergic signalling in brain ischemia. Neuropharmacology 104, 105–130. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.11.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peinelt C., Vig M., Koomoa D. L., Beck A., Nadler M. J. S., Koblan-Huberson M., et al. (2006). Amplification of CRAC current by STIM1 and CRACM1 (Orai1). Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 771–773. 10.1038/ncb1435 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng J., Liang G., Inan S., Wu Z., Joseph D. J., Meng Q., et al. (2012). Dantrolene ameliorates cognitive decline and neuropathology in Alzheimer triple transgenic mice. Neurosci. Lett. 516, 274–279. 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.04.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinton P., Rizzuto R. (2006). Bcl-2 and Ca2+ homeostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Death Differ. 13, 1409–1418. 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401960 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pla-Martín D., Rueda C. B., Estela A., Sánchez-Piris M., González-Sánchez P., Traba J., et al. (2013). Silencing of the Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease-associated gene GDAP1 induces abnormal mitochondrial distribution and affects Ca2+ homeostasis by reducing store-operated Ca2+ entry. Neurobiol. Dis. 55, 140–151. 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.03.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon H. F., Hensley K., Thongboonkerd V., Merchant M. L., Lynn B. C., Pierce W. M., et al. (2005). Redox proteomics analysis of oxidatively modified proteins in G93A-SOD1 transgenic mice—a model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 39, 453–462. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.03.030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popugaeva E., Pchitskaya E., Speshilova A., Alexandrov S., Zhang H., Vlasova O., et al. (2015). STIM2 protects hippocampal mushroom spines from amyloid synaptotoxicity. Mol. Neurodegener. 10:37. 10.1186/s13024-015-0034-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potier M., Gonzalez J. C., Motiani R. K., Abdullaev I. F., Bisaillon J. M., Singer H. A., et al. (2009). Evidence for STIM1- and Orai1-dependent store-operated calcium influx through ICRAC in vascular smooth muscle cells: role in proliferation and migration. FASEB J. 23, 2425–2437. 10.1096/fj.09-131128 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakriya M., Feske S., Gwack Y., Srikanth S., Rao A., Hogan P. G. (2006). Orai1 is an essential pore subunit of the CRAC channel. Nature 443, 230–233. 10.1038/nature05122 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W. (2017). Forms and functions of store-operated calcium entry mediators, STIM and Orai. Adv. Biol. Regul. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1016/j.jbior.2017.11.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond L. A. (2017). Striatal synaptic dysfunction and altered calcium regulation in Huntington disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 483, 1051–1062. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.07.058 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renton A. E., Majounie E., Waite A., Simón-Sánchez J., Rollinson S., Gibbs J. R., et al. (2011). A hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72 is the cause of chromosome 9p21-linked ALS-FTD. Neuron 72, 257–268. 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.09.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco V., Grolla A. A., Glasnov T. N., Canonico P. L., Verkhratsky A., Genazzani A. A., et al. (2014). Differential deregulation of astrocytic calcium signalling by amyloid-β, TNFα, IL-1β and LPS. Cell Calcium 55, 219–229. 10.1016/j.ceca.2014.02.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos J., DiGregorio P. J., Yeromin A. V., Ohlsen K., Lioudyno M., Zhang S., et al. (2005). STIM1, an essential and conserved component of store-operated Ca2+ channel function. J. Cell Biol. 169, 435–445. 10.1083/jcb.200502019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosado J. A. (2016). Calcium entry pathways in non-excitable cells. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 898, vii–viii. 10.1007/978-3-319-26974-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen D. R., Siddique T., Patterson D., Figlewicz D. A., Sapp P., Hentati A., et al. (1993). Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 362, 59–62. 10.1136/jmg.30.6.532-b [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryskamp D., Wu J., Geva M., Kusko R., Grossman I., Hayden M., et al. (2017). The sigma-1 receptor mediates the beneficial effects of pridopidine in a mouse model of Huntington disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 97, 46–59. 10.1016/j.nbd.2016.10.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saliba Y., Keck M., Marchand A., Atassi F., Ouillé A., Cazorla O., et al. (2015). Emergence of Orai3 activity during cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc. Res. 105, 248–259. 10.1093/cvr/cvu207 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheltens P., Blennow K., Breteler M. M. B., de Strooper B., Frisoni G. B., Salloway S., et al. (2016). Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 388, 505–517. 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01124-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Hardy J. (2016). The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 8, 595–608. 10.15252/emmm.201606210 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj S., Sun Y., Watt J. A., Wang S., Lei S., Birnbaumer L., et al. (2012). Neurotoxin-induced ER stress in mouse dopaminergic neurons involves downregulation of TRPC1 and inhibition of AKT/mTOR signaling. J. Clin. Invest. 122, 1354–1367. 10.1172/JCI61332 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano-Pozo A., Frosch M. P., Masliah E., Hyman B. T. (2011). Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 1:a006189. 10.1101/cshperspect.a006189 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilling D., Mak D. O., Kang D. E., Foskett J. K. (2012). Lack of evidence for presenilins as endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ leak channels. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 10933–10944. 10.1074/jbc.M111.300491 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilling D., Müller M., Takano H., Mak D.-O., Abel T., Coulter D. A., et al. (2014). Suppression of InsP3 receptor-Mediated Ca2+ signaling alleviates mutant presenilin-linked familial Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. J. Neurosci. 34, 6910–6923. 10.1523/jneurosci.5441-13.2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirabella R., Secondo A., Pannaccione A., Scorziello A., Valsecchi V., Adornetto A., et al. (2009). Anoxia-induced NF-κB-dependent upregulation of NCX1 contributes to Ca2+ refilling into endoplasmic reticulum in cortical neurons. Stroke 40, 922–929. 10.1161/strokeaha.108.531962 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. F., Boyle J. P., Kang P., Rome S., Pearson H. A., Peers C. (2005). Hypoxic regulation of Ca2+ signaling in cultured rat astrocytes. Glia 49, 153–157. 10.1002/glia.20083 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soboloff J., Spassova M. A., Hewavitharana T., He L.-P., Xu W., Johnstone L. S., et al. (2006). STIM2 is an inhibitor of STIM1-Mediated store-operated Ca2+ entry. Curr. Biol. 16, 1465–1470. 10.1016/j.cub.2006.05.051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodero A. O., Vriens J., Ghosh D., Stegner D., Brachet A., Pallotto M., et al. (2012). Cholesterol loss during glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity. EMBO J. 31, 1764–1773. 10.1038/emboj.2012.31 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stathopulos P. B., Zheng L., Ikura M. (2009). Stromal interaction molecule (STIM) 1 and STIM2 calcium sensing regions exhibit distinct unfolding and oligomerization kinetics. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 728–732. 10.1074/jbc.c800178200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani I. C., Wright D., Polizzi K. M., Kontoravdi C. (2012). The role of ER stress-induced apoptosis in neurodegeneration. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 9, 373–387. 10.2174/156720512800107618 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strübing C., Krapivinsky G., Krapivinsky L., Clapham D. E. (2003). Formation of novel TRPC channels by complex subunit interactions in embryonic brain. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 39014–39019. 10.1074/jbc.m306705200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutzmann G. E., Smith I., Caccamo A., Oddo S., Laferla F. M., Parker I. (2006). Enhanced ryanodine receptor recruitment contributes to Ca2+ disruptions in young, adult and aged Alzheimer’s disease mice. J. Neurosci. 26, 5180–5189. 10.1523/jneurosci.0739-06.2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutzmann G. E., Smith I., Caccamo A., Oddo S., Parker I., Laferla F. (2007). Enhanced ryanodine-mediated calcium release in mutant PS1-expressing Alzheimer’s mouse models. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 1097, 265–277. 10.1196/annals.1379.025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulger J., Dumais-Huber C., Zerfass R., Henn F. A., Aldenhoff J. B. (1999). The calcium response of human T lymphocytes is decreased in aging but increased in Alzheimer’s dementia. Biol. Psychiatry 45, 737–742. 10.1016/s0006-3223(98)00218-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S., Zhang H., Liu J., Popugaeva E., Xu N.-J., Feske S., et al. (2014). Reduced synaptic STIM2 expression and impaired store-operated calcium entry cause destabilization of mature spines in mutant presenilin mice. Neuron 82, 79–93. 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.02.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y., Zhang H., Selvaraj S., Sukumaran P., Lei S., Birnbaumer L., et al. (2017). Inhibition of L-Type Ca2+ channels by TRPC1-STIM1 complex is essential for the protection of dopaminergic neurons. J. Neurosci. 37, 3364–3377. 10.1523/jneurosci.3010-16.2017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundivakkam P. C., Freichel M., Singh V., Yuan J. P., Vogel S. M., Flockerzi V., et al. (2012). The Ca2+ sensor stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) is necessary and sufficient for the store-operated Ca2+ entry function of transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) 1 and 4 channels in endothelial cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 81, 510–526. 10.1124/mol.111.074658 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang T.-S., Guo C., Wang H., Chen X., Bezprozvanny I. (2009). Neuroprotective effects of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor C-terminal fragment in a Huntington’s disease mouse model. J. Neurosci. 29, 1257–1266. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4411-08.2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang T.-S., Slow E., Lupu V., Stavrovskaya I. G., Sugimori M., Llinás R., et al. (2005). Disturbed Ca2+ signaling and apoptosis of medium spiny neurons in Huntington’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 102, 2602–2607. 10.1073/pnas.0409402102 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong B. C.-K., Lee C. S.-K., Cheng W.-H., Lai K.-O., Foskett J. K., Cheung K.-H. (2016). Familial Alzheimer’s disease-associated presenilin 1 mutants promote γ-secretase cleavage of STIM1 to impair store-operated Ca2+ entry. Sci. Signal. 9:ra89. 10.1126/scisignal.aaf1371 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepakova E. S., Gericke M., Hirakawa Y., Weisbrod R. M., Cohen R. A., Bolotina V. M. (2001). Properties of a native cation channel activated by Ca2+ store depletion in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 7782–7790. 10.1074/jbc.m010104200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén M., Fagerberg L., Hallstrom B. M., Lindskog C., Oksvold P., Mardinoglu A., et al. (2015). Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 347:1260419. 10.1126/science.1260419 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaeth M., Yang J., Yamashita M., Zee I., Eckstein M., Knosp C., et al. (2017). ORAI2 modulates store-operated calcium entry and T cell-mediated immunity. Nat. Commun. 8:14714. 10.1038/ncomms14714 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kruchten R., Braun A., Feijge M. A. H., Kuijpers M. J. E., Rivera-Galdos R., Kraft P., et al. (2012). Antithrombotic potential of blockers of store-operated calcium channels in platelets. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 32, 1717–1723. 10.1161/atvbaha.111.243907 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga-Szabo D., Braun A., Kleinschnitz C., Bender M., Pleines I., Pham M., et al. (2008). The calcium sensor STIM1 is an essential mediator of arterial thrombosis and ischemic brain infarction. J. Exp. Med. 205, 1583–1591. 10.1084/jem.20080302 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam K., Montell C. (2007). TRP channels. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 76, 387–417. 10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142819 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vig M., Peinelt C., Beck A., Koomoa D. L., Rabah D., Koblan-Huberson M., et al. (2006). CRACM1 is a plasma membrane protein essential for store-operated Ca2+ entry. Science 312, 1220–1223. 10.1126/science.1127883 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigont V., Kolobkova Y., Skopin A., Zimina O., Zenin V., Glushankova L., et al. (2015). Both Orai1 and TRPC1 are involved in excessive store-operated calcium entry in striatal neurons expressing mutant Huntingtin exon 1. Front. Physiol. 6:337. 10.3389/fphys.2015.00337 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigont V. A., Zimina O. A., Glushankova L. N., Kolobkova J. A., Ryazantseva M. A., Mozhayeva G. N., et al. (2014). STIM1 Protein activates store-operated calcium channels in cellular model of Huntington’s disease. Acta Naturae 6, 40–47. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscomi M. T., Florenzano F., Latini L., Amantea D., Bernardi G., Molinari M. (2008). Methylprednisolone treatment delays remote cell death after focal brain lesion. Neuroscience 154, 1267–1282. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.04.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Lu R., Yang J., Li H., He Z., Jing N., et al. (2015). TRPC6 specifically interacts with APP to inhibit its cleavage by γ-secretase and reduce Aβ production. Nat. Commun. 6:8876. 10.1038/ncomms9876 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Zhou X., Li G., Zhang Y., Wu Y., Song W. (2017). Modifications and trafficking of APP in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 10:294. 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00294 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. (2017). The Regulation of tumor cell invasion and metastasis by endoplasmic reticulum-to-mitochondrial Ca2+ transfer. Front. Oncol. 7:171. 10.3389/fonc.2017.00171 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. T., Manji S. S., Parker N. J., Hancock M. S., Van Stekelenburg L., Eid J. P., et al. (2001). Identification and characterization of the STIM (stromal interaction molecule) gene family: coding for a novel class of transmembrane proteins. Biochem. J. 357, 673–685. 10.1042/0264-6021:3570673 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Ryskamp D. A., Liang X., Egorova P., Zakharova O., Hung G., et al. (2016). Enhanced store-operated calcium entry leads to striatal synaptic loss in a Huntington’s disease mouse model. J. Neurosci. 36, 125–141. 10.1523/jneurosci.1038-15.2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Shih H.-P., Vigont V., Hrdlicka L., Diggins L., Singh C., et al. (2011). Neuronal store-operated calcium entry pathway as a novel therapeutic target for Huntington’s disease treatment. Chem. Biol. 18, 777–793. 10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.04.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X., Zagranichnaya T. K., Gurda G. T., Eves E. M., Villereal M. L. (2004). A TRPC1/TRPC3-mediated increase in store-operated calcium entry is required for differentiation of H19–7 hippocampal neuronal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 43392–43402. 10.1074/jbc.m408959200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S., Zhang J. J., Huang X.-Y. (2009). Orai1 and STIM1 are critical for breast tumor cell migration and metastasis. Cancer Cell 15, 124–134. 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.12.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagranichnaya T. K., Wu X., Villereal M. L. (2005). Endogenous TRPC1, TRPC3, and TRPC7 proteins combine to form native store-operated channels in HEK-293 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 29559–29569. 10.1074/jbc.M505842200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiger W., Vetrivel K. S., Buggia-Prévot V., Nguyen P. D., Wagner S. L., Villereal M. L., et al. (2013). Ca2+ influx through store-operated Ca2+ channels reduces Alzheimer disease β-amyloid peptide secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 26955–26966. 10.1074/jbc.m113.473355 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., Halligan K. E., Zhang X., Bisaillon J. M., Gonzalez-Cobos J. C., Motiani R. K., et al. (2011). Orai1-mediated I (CRAC) is essential for neointima formation after vascular injury. Circ. Res. 109, 534–542. 10.1161/circresaha.111.246777 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Liu J., Sun S., Pchitskaya E., Popugaeva E., Bezprozvanny I. (2015a). Calcium signaling, excitability and synaptic plasticity defects in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 45, 561–580. 10.3233/JAD-142427 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Wu L., Pchitskaya E., Zakharova O., Saito T., Saido T., et al. (2015b). Neuronal store-operated calcium entry and mushroom spine loss in amyloid precursor protein knock-in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 35, 13275–13286. 10.1523/jneurosci.1034-15.2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Sun S., Herreman A., De Strooper B., Bezprozvanny I. (2010). Role of presenilins in neuronal calcium homeostasis. J. Neurosci. 30, 8566–8580. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1554-10.2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Sun S., Wu L., Pchitskaya E., Zakharova O., Fon Tacer K., et al. (2016). Store-operated calcium channel complex in postsynaptic spines: a new therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. J. Neurosci. 36, 11837–11850. 10.1523/jneurosci.1188-16.2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang M., Song J.-N., Wu Y., Zhao Y.-L., Pang H.-G., Fu Z.-F., et al. (2014). Suppression of STIM1 in the early stage after global ischemia attenuates the injury of delayed neuronal death by inhibiting store-operated calcium entry-induced apoptosis in rats. Neuroreport 25, 507–513. 10.1097/wnr.0000000000000127 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. L., Yu Y., Roos J., Kozak J. A., Deerinck T. J., Ellisman M. H., et al. (2005). STIM1 is a Ca2+ sensor that activates CRAC channels and migrates from the Ca2+ store to the plasma membrane. Nature 437, 902–905. 10.1038/nature04147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J., Du W., Zhou K., Tai Y., Yao H., Jia Y., et al. (2008). Critical role of TRPC6 channels in the formation of excitatory synapses. Nat. Neurosci. 11, 741–743. 10.1038/nn.2127 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q., Yen A., Rymarczyk G., Asai H., Trengrove C., Aziz N., et al. (2016). Impairment of PARK14-dependent Ca2+ signalling is a novel determinant of Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Commun. 7:10332. 10.1038/ncomms10332 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]