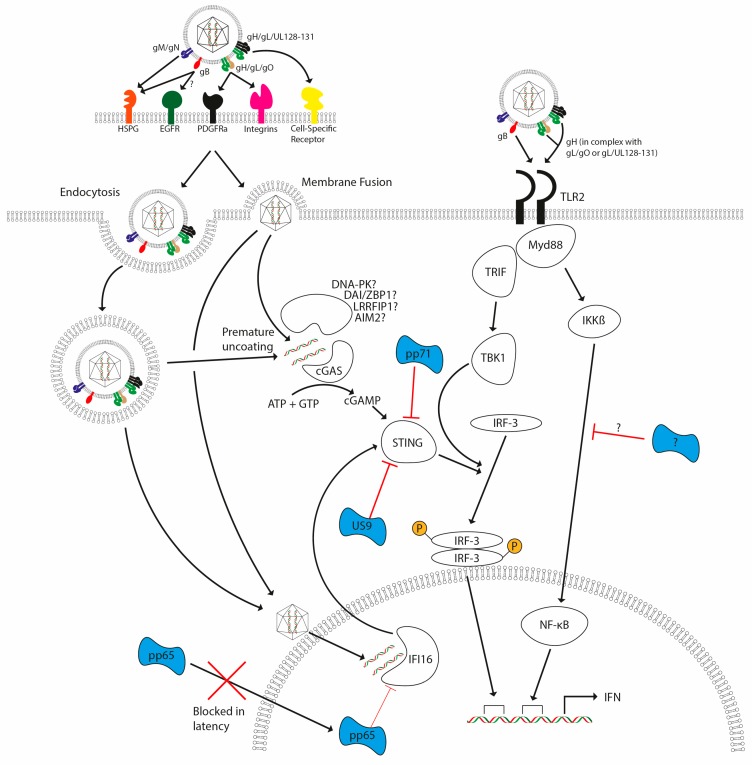
Figure 3.
HCMV detection by the host and subsequent evasion strategies. HCMV lytic infection (either via endocytosis or membrane fusion) triggers TLR- and DNA-sensing pathways upon infection, with these pathways leading to the induction of interferon (and other antiviral cytokines). TLR2 activation by HCMV glycoproteins gB and gH lead to activation of TRIF and MyD88 pathways. DNA-sensing pathways involving cGAS and possibly other documented sensors signal via STING and TBK-1, leading to the activation of IRF3. TLR signalling activates NF-κB and IRF3 via MyD88 and TRIF, respectively. Failure to antagonize these responses leads to activation of interferon responses. Antagonists are illustrated in blue and are delivered with the virion (pp65, pp71) as well as being encoded during infection (pp71 and US9) to inhibit host detection systems. A direct antagonist of IKK activation via TLRs has not yet been reported, but it is clear that multiple steps of the pathways are antagonised by CMV.