Abstract
Objective
Patient navigators are a promising mechanism to link patients with primary care. While navigators have been used in population health promotion and prevention programmes, their impact on access to primary care is not clear. The aim of this scoping review was to examine the use of patient navigators to facilitate access to primary care and how they were defined and described, their components and the extent to which they were patient centred.
Setting and participants
We used the Arksey and O’Malley scoping review method. Searches were conducted in MEDLINE, Embase, ProQuest Medical, other key databases and grey literature for studies reported in English from January 2000 to April 2016. We defined a patient navigator as a person or process creating a connection or link between a person needing primary care and a primary care provider. Our target population was people without a regular source of, affiliation or connection with primary care. Studies were included if they reported on participants who were connected to primary care by patient navigation and attended or made an appointment with a primary care provider. Data analysis involved descriptive numerical summaries and content analysis.
Results
Twenty studies were included in the final scoping review. Most studies referred to ‘patient navigator’ or ‘navigation’ as the mechanism of connection to primary care. As such, we grouped the components according to Freeman’s nine-principle framework of patient navigation. Seventeen studies included elements of patient-centred care: informed and involved patient, receptive and responsive health professionals and a coordinated, supportive healthcare environment.
Conclusions
Patient navigators may assist to connect people requiring primary care to appropriate providers and extend the concept of patient-centred care across different healthcare settings. Navigation requires further study to determine impact and cost-effectiveness and explore the experience of patients and their families.
Keywords: access to health care, patient navigation, patient-centred care, primary care
Strengths and limitations of this study.
This is the first scoping review to explore how patient navigators are defined, described and used to facilitate access to primary care for people without an affiliation to a primary care provider.
It is a comprehensive overview of sources covering peer-reviewed and grey literature.
Sources were included only if the outcome of the navigation was reported; sources describing patient navigation without reporting of outcomes were excluded.
The inclusion of a description of the patient centredness of the sources is a unique addition to this review of patient navigators.
Introduction
Primary care is the first level of access to healthcare, delivered in the community most often by family physicians or general medical practitioners. However, not all people access primary care that best meets their healthcare needs, where and when they need it. Some people, such as those living in poverty, with a long-term disability, from a culturally and linguistically diverse background or located in rural and remote areas, have difficulty accessing primary care services and resources.1–4
Access to healthcare is the opportunity to reach and obtain appropriate healthcare in situations of perceived need.5 Access to primary care is important to reduce healthcare disparities, mortality, morbidity, hospitalisation rates and healthcare costs.6–9 Recent reforms to primary care have focused on trialling new processes and models of care to improve access.10 These include integrated care models, after-hours telephone consultations, walk-in centres and nurse-led initiatives. However, disparities in care remain for many, such as people having low literacy and numeracy, cognitive deficits, being a member of a marginalised group or not understanding the need for primary care.11
A new approach to improve access to primary care is patient navigation, a process where a person (navigator) engages with a patient to determine barriers to care and provides information to improve access to components of the health system, not just primary care.12 A patient navigator has been described as a type of ‘broker’ who uses a biopsychosocial approach to provide a range of instrumental and relational functions and processes13 14 to support patients to access primary care and directly identify providers willing to treat vulnerable people requiring care.15 Patient navigator tasks can include educating patients about early symptoms of cancer (in preventive care) or facilitating and coordinating appointments with providers to improve access to a regular primary care provider. Originating in the 1990s, Freeman developed patient navigation as a strategy to reduce barriers to breast cancer care in Harlem, New York.16 Since then, patient navigators have been used for the screening of various cancers and through the cancer care continuum, with mixed success.17–27 In primary care, navigators may have a role in improving access and coordination of care, especially for vulnerable populations whose access to care may be compromised by a range of geographic, demographic, socioeconomic or cultural characteristics.28
Patient-centred care is a core element of high-quality primary care, facilitates access to appropriate care11 and has been identified as one of six areas of focus for improving healthcare systems.29 In primary care, patient-centred care consists of interactions and relationships between providers and patients to share information, explore values and preferences, facilitate access to appropriate care, and address healthcare disparities.30 31 While numerous frameworks of patient-centred care have been described,32 Epstein’s11 succinct model of patient-centred care comprising an informed and involved patient, receptive and responsive health professionals and a coordinated, supportive healthcare environment, sits well within the context of patient navigation and its extension beyond the patient–clinician relationship to the setting in which care is delivered.
While navigators have been used in population health promotion and prevention programs,33 34 there has been recent interest in their use in facilitating access to primary care for vulnerable people without a regular primary care provider.28 Understanding the components of these programmes can assist those interested in designing or implementing similar programmes. Therefore, we performed a scoping review of the use of patient navigation to facilitate access to primary care. Given its importance and relevance to navigation, we included an additional focus on the extent to which identified patient navigation interventions were patient centred.
Methods
We chose the scoping review method to map the extent, range and nature of published research on the use of patient navigation to further understand how it links people to primary care.35 When compared with systematic reviews, scoping reviews address broader topics and are less reliant on detailed research questions or quality assessments.35 The work was structured around the five stages of the Arksey and O’Malley framework: (1) identify the research question, (2) identify relevant studies, (3) study selection, (4) chart the data and (5) collate, summarise and report the results. The review was also informed by Levac et al’s36 refinements to Arksey and O’Malley’s framework.
Stage 1: identify the research question
Patient navigation has been defined as a ‘process, by which an individual, a patient navigator, guides patients in overcoming barriers to healthcare services access to facilitate timely access to care’.37 We expanded this definition to include a patient navigator as a person or process creating a connection or link between a person needing primary care and a primary care provider.
Our target population was people without a regular source of or affiliation or connection with primary care. The outcome of interest was the person needing care attended an appointment or made contact with the referred primary care provider. These definitions helped us to clarify the focus of the review, confirm the inclusion criteria adopted and establish parameters for the search strategy.36 This review did not focus on the impact or effectiveness of patient navigation programmes in this context. We asked three questions to guide the scoping review:
How have patient navigators been defined and described in connecting people who are unattached to primary care to a primary care provider for regular care?
What are the components of these patient navigation programmes?
To what extent has patient centredness been incorporated into the design, implementation and analysis of patient navigation programmes?
Stage 2: identify relevant studies
We identified relevant studies through a search of electronic databases, grey literature and reference lists of key articles sourced (online supplementary file 1).
bmjopen-2017-019252supp001.pdf (358.4KB, pdf)
A three-step search strategy was used. First, we undertook an initial limited search of MEDLINE, Embase and Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) using terms and variants of ‘navigator’, ‘broker’, ‘link worker’ and ‘community health worker’. We analysed the text in the titles and abstracts of retrieved studies and index terms used to refine key terms. The terms most common were related to navigation, linkage and access to care. We completed a second search of the same databases and extended the search to include related medical and social science databases and grey literature using the key terms and variants (table 1) identified by the initial search strategy (online supplementary file 2).
Table 1.
Key search terms
| Concept, programme or intervention |
Setting |
| Navigator/navigation Patient navigator/navigation Peer navigator/navigation Broker Health broker Health services broker Community health worker Community navigator/navigation Lay health worker Linkage to care |
Community health Family practice/practitioner General practice/practitioner Primary care Primary healthcare |
bmjopen-2017-019252supp002.pdf (503KB, pdf)
Finally, we checked the reference lists of all identified studies (and their citations) for additional studies.
Stage 3: study selection
Inclusion criteria were applied as a basis for which studies were considered relevant to the review questions. Studies were included if they:
were published in English from January 2000 to May 2016. The start date of 2000 reflects the increasing interest in patient-centred care in the last two decades. Reforms of primary care commenced around this time29 along with the emergence of navigator-type approaches38;
reported on patients who did not have a regular source of primary care (provider or practice);
connected patients to primary care by a process (eg, navigation) or a person (eg, navigator);
reported an outcome of patients attending or making at least one appointment with primary care providers.
We excluded studies if they originated in countries who were not members of the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), as their primary care systems differ significantly from those of OECD countries. Other exclusion criteria were applied to studies where:
patients lived in residential care, or incarcerated with no imminent release date, as their primary care needs were assumed to be met by institutional providers;
a navigator was attached to a primary care provider or practice as this indicated the patient was already connected to primary care;
a navigator referred patients to health screening or assessment services only and not to a primary care provider.
AP reviewed titles and abstracts of studies, and GR independently reviewed abstracts where there was uncertainty for inclusion.
Stage 4: chart the data
Data extracted were entered into a template developed in Microsoft Excel specifically for this review. Information on authors, year of publication, study location and context, aims or purpose of the research, study type or design, population and sample size, methodology, conceptual model, intervention type and duration, measures used and key findings were recorded on this form. We also extracted data relevant to the research questions: definitions and descriptions of navigators, components of navigator programmes and elements of patient-centred care. Charting the data was an iterative process36 that we updated as studies revealed useful data categories. Studies were reviewed a number of times to ensure all relevant data was captured.
Stage 5: collate, summarise and report the results
We collated the data using a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. Excerpts of text were coded deductively by AP to identify concepts and themes related to the research questions. GR checked the coding scheme and the themes raised.
Results
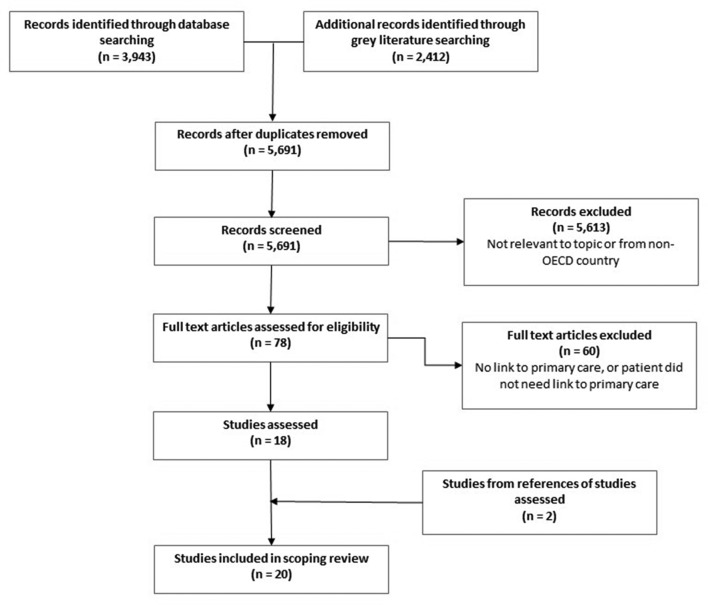
Our initial search terms generated 6355 records from electronic databases and grey literature (figure 1). We removed 664 duplicates, leaving 5691 records to be screened. Of these, 5613 records were excluded based on the title and/or abstract review, as they were not relevant to the question, did not meet inclusion criteria or originated in non-OECD countries. Of the remaining 78 records, full-text review excluded 44 where participants were not linked to primary care and 16 where participants already had a primary care provider or did not indicate a need for primary care. We searched references and citations of the remaining 18 records, adding two additional studies. This resulted in 20 selected for inclusion in the scoping review. The selection process is shown in the flow chart (figure 1).
Figure 1.
Flow of study selection. OECD, Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development.
Of the 20 included studies, three reported on the same randomised controlled trial at different phases.39–41 These three studies were counted as unique studies as each reported on different elements of the same trial: preliminary findings, qualitative analysis of interviews and longitudinal findings.
Eleven studies were descriptions or evaluations of programmes, eight were intervention studies and one was a retrospective study. Thirteen were programmes based in emergency departments, six were community-based programmes and one was delivered in an inpatient setting. All studies were conducted in the USA. Table 2 outlines characteristics of the included studies.
Table 2.
Characteristics of included studies
| Authors | Context | Study type | Population and sampling | Primary outcome | Description |
| Bishop49 | Private, non-profit, community homeless shelter | Description of Charlottesville Health Access initiative to enhance access to care | Homeless and near-homeless people, without a healthcare provider, attending health fair at shelter or soup kitchen (no sample reported) | People connected to permanent healthcare provider | Volunteer navigator (student or community member) completed a training course, engaged person by building relationships, assessed needs, guided to providers, translated confusing information, coordinated follow-up and empowered people to understand health system and self-care. |
| Chan et al 42 | ED in low-income, urban area served by three community clinics | Non-randomised, non-blinded interventional trial to improve primary care access for underserved patients | Patients with no primary care provider assessed by ED physician to benefit from clinic follow-up (n=326) | Patients follow-up at community clinic within 14 days | Internet-based secure referral system between ED medical record and clinic appointment systems. System accessed clinic availability and allowed ED physicians to give patients follow-up appointments at clinics. |
| Doran et al 57 | Urban, public, safety-net hospital ED with primary care clinic in same building complex | Quasiexperimental trial to navigate willing patients from ED to clinic | Adults with no primary care provider, presenting with low-acuity problems, assigned to intervention or usual care based on where care expected to result in least delay (n=965) | Patients follow-up at primary care clinic within 1 year | Trained patient navigator escorted patients from ED waiting room to clinic. Patients assigned physician who addressed current problems, established care plan and gave card with name and clinic telephone number. |
| Elliott et al 43 | Urban ED, serving high proportion of vulnerable patients | Retrospective study using full electronic medical record abstraction, randomly sampled | Patients with no primary care provider, discharged and referred to transitional care clinic (n=660) | Patient completed follow-up visit in transitional care clinic as scheduled | Transitional care clinic staff worked with patients to determine preferences and locate convenient, appropriate provider and made new appointment with chosen provider. |
| Gany et al 51 | Unused parking lot adjacent to JFK International Airport’s taxi holding lot | Description of Step On It! workplace intervention to increase healthcare access | Convenience sample of taxi drivers waiting in airport holding lot (n=466) | Driver completed follow-up visit with linked provider within 6 months | Healthcare access and case management to link drivers to providers, including referrals to low-cost (or free) culturally appropriate clinics or hospitals. |
| Griswold et al 39–41 | Urban Comprehensive Psychiatric Emergency Program (psychiatric assessment and management, targeted therapeutic approaches, links to community mental health services) as usual care | Randomised controlled trial comparing linkage with primary care with usual care after psychiatric emergency visit | Adults presenting with psychiatric disorder, with no primary care provider or have not seen one within 6 months (n=101–175) | Patients connected to and visited primary care within 3 and 12 months | Care navigator trained in interviewing and case management provided information about low-cost care, facilitated access and reinforced patient education; information to providers about patient’s history, follow-up, peer connections to access community and social services. |
| Horwitz et al 58 | Level 1 urban trauma centre | Randomised study of intensive case management intervention to improve primary care use | Uninsured adults presenting to ED, excluding substance abuse or mental health issues only (n=230) | Patients visited one of four participating primary care clinics within 2 months | Health Promotion Advocates in ED assisted patients to choose provider, gave brochure, faxed information to case worker at selected clinic. Clinic case worker contacted patient to make appointment. |
| Kahn et al 61 | Medicaid managed care organisation for people with mental health and/or substance abuse diagnoses | Evaluation to assess effectiveness of case management in linking new members with primary care providers | New members with behavioural health diagnosis and no primary care provider completing mailed survey, referred to case management (n=368) | Member visited primary care provider within 12 months | Telephone case managers made at least three contact attempts to ensure linkage to provider. |
| Kangovi et al 45 | Two urban, academically affiliated hospitals | Two-armed, single-blind, randomised clinical trial to improve primary care follow-up postdischarge | Newly admitted low-income, uninsured or Medicaid adult inpatients randomly numbered, approached until three per day enrolled (n=446) | Patient completed follow-up visit with primary care provider within 14 days | Community health workers (trained lay people of similar backgrounds to patients, selected for personality traits patients identified as important) set goals, supported goal achievement, connected to provider. |
| Kim et al 53 | Five hospital EDs in an affluent area with large and poor immigrant population | Analysis of Emergency Department-Primary Care Connect initiative to link patients to four local primary care clinics | Merged data set (hospital discharge, clinic and navigator referral data) of low-income or uninsured patients with no primary care provider (n=10 761) | Patients completed two or more visits to same clinic across 33-month period | Patient navigators of various backgrounds (most unlicenced, selected for communication skills) based in clinics (three sites) or hospitals (two sites) spoke face to face or telephoned patients referred by ED providers. |
| Marr et al 50 | Urban ED with high rates of potentially avoidable hospitalisations and lack of community-based care | Evaluation of programme to connect patients with community-based, primary care providers | Patients with no primary care provider approached by navigator (n=7185) | Patients completed three or more visits to same clinic across 18-month period | Patient navigator (advocate) recruited from community, trained in ED, visited patients waiting for medical care or before discharge, offered referral within 18-clinic system. |
| Overholser et al 52 | Specialist outpatient clinics of urban tertiary teaching hospital | Description of patient navigation programme to overcome barriers to finding primary care | Adults with sickle cell disease with no primary care provider or not seen regularly by provider, referred by specialist physicians (n=21) | Patients attended initial visit with new primary care provider | Patient navigators of various backgrounds trained in navigation proactively sought local providers and established network through outreach, made appointments with patients, sent reminders and educated on importance of primary care. |
| Treadwell et al 54 | African-American community centre | Evaluation of Save Our Sons group health education and intervention model to reduce incidence of diabetes and obesity, improve regular access to care and build community networks | African-American men at risk for or diagnosed with diabetes and/or in poor health related to obesity and/or other health concerns; recruited at community event (n=42) | Participants connected to medical home | Six-week community-based, culturally responsive, gender-specific health prevention programme delivered by community health workers, and trusted community members provided links between health system and community. |
| Wang et al 37 | Community health centre providing comprehensive services to ethnically diverse population with low incomes or uninsured | Evaluation of patient navigation programme to optimise healthcare utilisation | Patients with diabetes and/or hypertension not seen by provider in last 6 months (n=215) | Patient visited primary care provider and/or chronic disease nurse within 6 months | Patient navigator trained in chronic illness education, motivational interviewing and appointment scheduling. Telephoned patients, built rapport, educated patients, made appointment with provider, assessed need for specialist referrals, identified barriers to access and assisted to overcome barriers. |
| Wexler et al 44 | ED within urban academic medical centre and affiliated primary care practices | Randomised controlled trial comparing health information technology intervention to improve access to primary care, with usual care | Medicaid enrollees who did not have usual source of care, ED physician confirmed visit non-urgent, completed baseline survey, randomly assigned (n=148) | Patients attend primary care provider office after discharge at 3, 6 and 12 months | ED electronic medical record to make appointment at clinic based on patient location and preference. Patient given appointment reminder card and directions to clinic. Electronic message to clinic with information about patient and appointment. |
| Emergency department navigators connect patients to better venues of care55 | EDs of eight-hospital system | News article on use of ED navigators to redirect patients with non-emergency issues to most appropriate care setting | Health plan members with non-urgent problems (no sample reported) | Patient scheduled to be seen by another provider | Navigator with customer service background assigned members to provider and made appointments. |
| Navigator reduces readmissions, inappropriate ED visits56 | Urban ED | News article on community health outreach worker helping patients find a primary care provider | Patients with non-urgent problems who are uninsured and do not have a primary care provider, insured but do not have a provider or have a provider but cannot access him or her (n=1500) | Self-pay patients find medical home; other patients identify primary care provider and set up follow-up appointment | Community health outreach coordinator/navigator of varying cultures representing patients served. Met patient in ED, coordinated appointments and set patients up in medical homes. |
| ED navigators help patients find a PCP59 | Urban ED | News article on a pilot project to reduce 30-day readmissions and number of self-pay patients who visit ED for non-emergent care | Patients without insurance and primary care provider admitted to hospital through ED and/or not admitted (no sample reported) | Patients directed to primary care provider and set up in medical home | Navigator worked with patients to discuss discharge and help facilitate follow-up appointments. |
ED, emergency department; PCP, primary care provider.
Patient navigators: definition and descriptions
One study defined patient navigation as a ‘process, by which an individual, a Patient Navigator, guides patients in overcoming barriers to health care services access to facilitate timely access to care’.37 The studies provided either a description of a navigator (person) or, for three of the studies, navigation process.42–44 Descriptions varied in detail and often consisted of the type of person recruited as a navigator, the tasks they performed and the training provided (table 2).
Patient navigation programme components
All of the studies outlined components of their programmes; four provided detailed descriptions.39–41 45 We grouped programme components according to Freeman’s consensus-based nine-principle framework of patient navigation, originally developed in response to the expansion of patient navigation as a community-based intervention.16 46 47 These principles have been widely used in patient navigation programmes. Each of these principles is outlined below with examples from the studies selected that included sufficient information to inform each principle in the framework.
Principle 1: patient-centred healthcare service delivery model
Seventeen of the studies outlined aspects of patient-centred care. This will be discussed further in the section addressing research question three.
Principle 2: integration of a fragmented healthcare system
This principle relates to a patient experiencing a seamless, timely flow through the continuum of care.16 We grouped another principle (principle 8: connect disconnected healthcare systems) here with principle 2, as the two are similar concepts, and this has been done previously.48 All studies in our scoping review reported on these principles grouped together. Two examples of integration in our scoping review were assisting patients to understand the entire health system,49 and linking the emergency department with a primary care provider, as well as to community dental, mental health, substance abuse and other social services.50
Principle 3: elimination of barriers
This principle is most effectively carried out through relationships with patients.16 While removing barriers to accessing primary care appears implicit in a navigator programme, not all studies provided detail of what the barriers were and how they were addressed. One exception of note is the Step on It! intervention at JFK International Airport, which focused on the barriers taxi drivers faced. This intervention went to the airport holding lot, assisted drivers to locate providers with flexible hours, culturally and linguistically appropriate models of care and at low-cost.51 Another study described a programme that helped adults with sickle cell disease find primary care.52 The barriers addressed included patients not understanding why they needed a primary care provider when they already had a specialist, low literacy, difficulty filling out forms and forgetting appointments. These navigators used motivational interviewing to identify further barriers and help patients set priorities beyond accessing primary care.52
Principle 4: clear scope of practice
Three studies provided detail about the role and responsibilities of the navigator.37 45 52 The most detailed of these was a randomised clinical trial by Kangovi et al,45 providing a website link (http://chw.upenn.edu) containing protocols for recruitment, training and standardised work practices for navigators, organisational directors and managers.
Kangovi et al 45 created a community health worker model and tested its effect on posthospital outcomes among general medical inpatients. This was based on qualitative participatory action research and had detailed protocols including standardised work practices in three stages: goal setting, goal support and connection with primary care. A substantial component was to build relationships with patients to help set goals for recovery, develop an individualised action plan and liaise between the patient and inpatient care team. The worker provided tailored support based on the patient goals. Patients were connected to primary care and coached to make and attend appointments independently. Provider resources included a discharge summary and the patient’s action plan taken to the appointment.
Principle 5: cost-effective
None of the studies evaluated the cost-effectiveness of their programme.
Principle 6: defined level of skill
Nine studies provided information on the skill level required of the navigators.39 45 49 50 52–55 This ranged from volunteers with inhouse training, staff with customer service backgrounds, to college-accredited navigators. They were trained on topics such as navigation processes, disease-specific content such as diabetes education or motivational interviewing. Similarly, seven studies presented strategies intentionally used to inform the development of resources to support the navigation intervention, including a needs assessment,49 56 software development,42 community-based participatory action research45 51 54 and provider collaboration to develop and test navigation mechanisms.50
Principle 7: defined beginning and end
Eleven studies outlined definite points at which navigation began and ended.37 42–45 50 51 56–59 Entry usually involved meeting a patient (eg, in the emergency department or on a hospital ward) to schedule an appointment. End points of the interventions included ‘patient has an appointment made’ or ‘patient sees provider’.
Principle 8: connect disconnected healthcare systems
This principle was combined with a similar principle (principle 2: integration of a fragmented healthcare system) for the purposes of this review.
Principle 9: coordinated system
This principle relates to having an assigned coordinator to oversee all aspects of the intervention.16 This was evident in two studies: where navigators served as executive officers on a governing board49 and were supervised by a social worker as well as having weekly team meetings.45
Patient navigation: patient centredness
Our third question for this review was, ‘To what extent has patient-centredness been incorporated into the design, implementation and analysis of patient navigation programs?’ We focused on the three factors on which patient-centred care depends: informed and involved patient, receptive and responsive health professionals and a coordinated, supportive healthcare environment.11 Seventeen studies included at least one of the three factors. Table 3 indicates the number of studies and some examples of approaches to patient-centred care for each of the three factors. The columns of the table indicate whether patient centredness was included in the design, implementation or analysis phase of patient navigation programmes.
Table 3.
Examples of patient centredness
| Patient-centred care factor | Design phase examples | Implementation phase examples | Analysis phase examples | Total studies* |
| Patients informed and involved in their care | Two studies: user-friendly and culturally sensitive health materials; bilingual, bicultural community members | 17 studies: provided information to patient on difference between emergency and primary care; identified barriers to access and help to overcome barriers | No studies | 19 |
| Receptive and responsive health professionals | Three studies: clinics added capacity for walk-in appointments, navigator visited clinics to provide information and establish working relationship | Six studies: after connection, navigator worked with provider to schedule other visits as per care plan; assisted with patient education and follow-up | Two studies: providers wanted to continue in programme; information to providers more complete and accessible than previously | 11 |
| Coordinated, supportive healthcare environment | Four studies: collaborative organisation linked emergency department with 18 clinics; each hospital adopted unique provider arrangement and approach | One study: emergency physicians encouraged to establish relationships with clinics | One study: community mobilised around population health issues through increased local media attention | 6 |
*Some studies included more than one instance of the patient-centred factor in more than one phase of the intervention.
The Kangovi et al 45 study had an explicit patient-centred focus. The intervention prioritised relationship building with patients through goal setting and development of action plans, liaising with inpatient staff to ensure the patient’s goals were at the forefront and giving the action plan to a provider the patient chose based on needs and preferences.
Similarly, in the three studies reporting the same randomised controlled trial, Griswold et al 39–41 used a care navigator to connect patients with a history of psychiatric crisis to primary care. The navigator built relationships by meeting with patients routinely while admitted and also at primary care appointments and maintaining regular contact via phone or in person. The navigator would take the patient to the appointment and reinforce any education provided. Patients were informed of low-cost clinics, and further assistance was provided through coordinating follow-up and connecting patients to peer and social services. Provider resources included information to clinics on discharge diagnosis, medications and mental health treatment site referral.
Other studies included the three factors yet did not explicitly state patient centredness as a driver.
Discussion
Our scoping review identified 20 studies that used patient navigation to facilitate access, and connect vulnerable patients without regular primary care, to a primary care provider. All except three studies used a person to connect the patient to a provider; the remaining three used a navigation process. Most programmes described components that could be included in a framework of patient navigation, and 17 of the 20 studies included factors inherent to patient-centred care in their design, implementation or analysis.
The level of detail in descriptions of the studies varied; this variation has been reported elsewhere.60 In the studies included in this review, different terms were used for the same role: patient or care navigator, advocate, case manager or community health worker, for example. This presents challenges in clearly characterising navigators and understanding what they do. Similarly, while there is no generally accepted definition of patient navigation, there is a call for descriptions of the tasks navigators do and the networks of contacts they use to support their actions.60 Valaitis et al 28 described the specific activities undertaken by patient navigators: facilitating access to health-related programmes, promoting and facilitating continuity of care, identifying and removing barriers to care and effective and efficient use of the health system. Our findings add to these activities: a key feature of patient navigation to facilitate access to primary care is a relationship-based approach, informing and involving patients in connecting them to care.
The studies in this scoping review included elements that seemed to match the components of Freeman’s patient navigation framework. This indicates the framework may be generalisable to the tasks of connecting vulnerable people without a primary care provider to regular care. An evaluation of these principles used in 10 self-identified breast cancer navigation programmes using observation of patient navigator activities found the programmes were consistent with individual-level principles (eg, eliminating barriers, patient-centred care and integration of care); however, programme-level principles (eg, skill level, scope of practice and coordinated system) were not consistent across the programmes. We did not examine this level of detail for our scoping review, however, can see a role for this type of observation-based study to further contribute to this field.48 Generally, programmes adhered to published criteria for patient-centred care.11 Although not overtly stated as an aim, almost all studies incorporated at least one of the three patient-centred care factors: an informed and involved patient, receptive and responsive health professionals and a coordinated, supportive healthcare environment. We found these mostly in the implementation of the programmes to a lesser degree in the design phase and mentioned in only three studies in the analysis. Our assertion that a navigator working with patients unattached to primary care is patient centred, with a focus on connections and relationships, has some merit.
This scoping review has several limitations. Although a scoping review is iterative and involves revisiting the research question and key terms during searches, our search strategy may have missed studies that reported on interventions not designed to connect people to primary care but where this connection may have been a secondary outcome of the intervention (eg, access to information on cancer screening may have prompted participants to link in with a primary care provider). Additionally, information in the title and abstracts of such studies may not have referred to primary care. This approach, however, allowed us to undertake a more targeted review. Similarly, while our search strategy sought to include all terms we determined could be synonymous with patient navigation, we may have missed studies where different names were used for the same function.
Studies where there was no indication patients attended a primary care appointment were not included in our review. While this strategy contributed to a more focused search, studies that reported the implementation of programmes but not outcomes are missing. All of our included studies originated in the USA, which we acknowledge would impact on generalisability. These limitations highlight the need for consistent documentation of processes to improve access to care and the outcomes measured.
We did not look for or report on the effectiveness of the interventions or programmes in our included studies. While we are unable to report on the impact, we consider our approach to looking at descriptions and uses of patient navigation in this specific context of connection to primary care, with a focus on patient-centred care, is consistent with the current focus on patient-reported outcome measures and acknowledging the patient experience of care.
This paper contributes to the discussion of access to primary care by considering patient navigation to connect vulnerable populations to providers in three ways. First, we aligned components of the patient navigation studies reviewed to an existing generic navigation framework. This framework appears to be appropriate for considering navigators facilitating access for people without a primary care provider to regular care. Second, a relational approach acts as the backdrop to connecting vulnerable people to care, based on principles of patient-centred care. Finally, in the absence of a consistent definition of patient navigation in facilitating access to primary care, we have added to an existing description of patient navigation activities, which will assist clinicians and researchers to design and implement similar programmes.
Implications for practice
The studies included in the review used navigators in a range of settings, from emergency departments, inpatient wards, outpatient services and in the community. Most of these studies demonstrate established principles of patient navigation and use a patient-centred approach, particularly when using a navigator (person) rather than a process, such as an electronic system. For providers and organisations wanting to link vulnerable people to primary care in a patient-centred way, navigators may assist in this process.
Future research
Analysis of cost effectiveness, while not a focus of this review, was nevertheless absent in the cited studies. As the concept of navigator continues to show promise, further research is required to measure impact and give direction to settings interested in using this intervention. For example, the link between patient navigation principles and outcomes of interest require further exploration.
Conclusion
Patient navigators may be used across healthcare settings to improve access to primary care. Navigators are inherently patient-centred due to their relational approach and ability to connect people to primary care. Interventions to improve access to primary care require further study to determine their impact and cost-effectiveness.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We wish to acknowledge the peer reviewers of the original version of this paper who provided valued and insightful suggestions to improve the structure, flow and clarity of this paper.
Footnotes
Contributors: AP involved in writing protocol, searches, screening, extraction, drafting of results and writing of manuscripts. VL and TB involved in content expert input (methodology) and editing manuscripts. GR oversaw the project, assisted with screening, content expert input, drafting of results and editing of manuscripts.
Funding: This work was supported by the Professor Leon Piterman AM PhD scholarship, Southern Academic Primary Care Research Group, Monash university.
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent: Not required.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: Further details on studies included in this scoping review can be retrieved by contacting the corresponding author at annette.peart@monash.edu.
References
- 1. Schamess A, Foraker R, Kretovics M, et al. Reduced emergency room and hospital utilization in persons with multiple chronic conditions and disability receiving home-based primary care. Disabil Health J 2017;10:326–33. 10.1016/j.dhjo.2016.10.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Loignon C, Hudon C, Goulet É, et al. Perceived barriers to healthcare for persons living in poverty in Quebec, Canada: the EQUIhealThY project. Int J Equity Health 2015;14:4 10.1186/s12939-015-0135-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Ford JA, Wong G, Jones AP, et al. Access to primary care for socioeconomically disadvantaged older people in rural areas: a realist review. BMJ Open 2016;6:e010652 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010652 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Davy C, Harfield S, McArthur A, et al. Access to primary health care services for Indigenous peoples: A framework synthesis. Int J Equity Health 2016;15:163 10.1186/s12939-016-0450-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Levesque JF, Harris MF, Russell G. Patient-centred access to health care: conceptualising access at the interface of health systems and populations. Int J Equity Health 2013;12:18–19. 10.1186/1475-9276-12-18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. McColl MA, Aiken A, Schaub M. Do people with disabilities have difficulty finding a family physician? Int J Environ Res Public Health 2015;12:4638–51. 10.3390/ijerph120504638 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Shi L, Lebrun-Harris LA, Daly CA, et al. Reducing disparities in access to primary care and patient satisfaction with care: the role of health centers. J Health Care Poor Underserved 2013;24:56–66. 10.1353/hpu.2013.0022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Starfield B. Primary care: balancing health needs, services, and technology. New York: Oxford University Press, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 9. Starfield B. Primary care: an increasingly important contributor to effectiveness, equity, and efficiency of health services. SESPAS report 2012. Gac Sanit 2012;26:20–6. 10.1016/j.gaceta.2011.10.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Janamian T, Jackson CL, Glasson N, et al. A systematic review of the challenges to implementation of the patient-centred medical home: lessons for Australia. Med J Aust 2014;201:69–73. 10.5694/mja14.00295 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Epstein RM, Fiscella K, Lesser CS, et al. Why the nation needs a policy push on patient-centered health care. Health Aff 2010;29:1489–95. 10.1377/hlthaff.2009.0888 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Kelly E, Ivers N, Zawi R, et al. Patient navigators for people with chronic disease: protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev 2015;4:28 10.1186/s13643-015-0019-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Natale-Pereira A, Enard KR, Nevarez L, et al. The role of patient navigators in eliminating health disparities. Cancer 2011;117:3541–50. 10.1002/cncr.26264 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Jean-Pierre P, Hendren S, Fiscella K, et al. Understanding the processes of patient navigation to reduce disparities in cancer care: perspectives of trained navigators from the field. J Cancer Educ 2011;26:111–20. 10.1007/s13187-010-0122-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Dennis S, Hasan I, Jackson Pulver L, et al. Experiences and views of a brokerage model for primary care for Aboriginal people. Aust Health Rev 2015;39:26–32. 10.1071/AH13205 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Freeman HP. The origin, evolution, and principles of patient navigation. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2012;21:1614–7. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-12-0982 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Manderson B, McMurray J, Piraino E, et al. Navigation roles support chronically ill older adults through healthcare transitions: a systematic review of the literature. Health Soc Care Community 2012;20:113–27. 10.1111/j.1365-2524.2011.01032.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Glick SB, Clarke AR, Blanchard A, et al. Cervical cancer screening, diagnosis and treatment interventions for racial and ethnic minorities: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med 2012;27:1016–32. 10.1007/s11606-012-2052-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Tho PC, Ang E. The effectiveness of patient navigation programs for adult cancer patients undergoing treatment: a systematic review. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep 2016;14:295–321. 10.11124/jbisrir-2016-2324 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Chh T, Wilson S, McConigley R. Experiences of cancer patients in a patient navigation program: a qualitative systematic review. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep 2015;13:136–68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Robinson-White S, Conroy B, Slavish KH, et al. Patient navigation in breast cancer: a systematic review. Cancer Nurs 2010;33:127–40. 10.1097/NCC.0b013e3181c40401 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Naylor K, Ward J, Polite BN. Interventions to improve care related to colorectal cancer among racial and ethnic minorities: a systematic review. J Gen Intern Med 2012;27:1033–46. 10.1007/s11606-012-2044-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Genoff MC, Zaballa A, Gany F, et al. Navigating language barriers: a systematic review of patient navigators' impact on cancer screening for limited english proficient patients. J Gen Intern Med 2016;31:426–34. 10.1007/s11606-015-3572-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Eschiti V, Burhansstipanov L, Watanabe-Galloway S. Native cancer navigation: the state of the science. Clin J Oncol Nurs 2012;16:73–82. 10.1188/12.CJON.73-82 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Ranaghan C, Boyle K, Meehan M, et al. Effectiveness of a patient navigator on patient satisfaction in adult patients in an ambulatory care setting: a systematic review. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep 2016;14:172–218. 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-003049 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Meredith SM. Disparities in breast cancer and the role of patient navigator programs. Clin J Oncol Nurs 2013;17:54–9. 10.1188/13.CJON.54-59 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Krok-Schoen JL, Oliveri JM, Paskett ED. Cancer Care Delivery and Women’s Health: The Role of Patient Navigation. Front Oncol 2016;6:2 10.3389/fonc.2016.00002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Valaitis RK, Carter N, Lam A, et al. Implementation and maintenance of patient navigation programs linking primary care with community-based health and social services: a scoping literature review. BMC Health Serv Res 2017;17:116 10.1186/s12913-017-2046-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Institute of Medicine. Crossing the quality chasm: a new health system for the 21st century. Washington, DC: National Academies Press, 2001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Epstein RM, Street RL. The values and value of patient-centered care. Ann Fam Med 2011;9:100–3. 10.1370/afm.1239 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Sidani S, Fox M. Patient-centered care: clarification of its specific elements to facilitate interprofessional care. J Interprof Care 2014;28:134–41. 10.3109/13561820.2013.862519 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Constand MK, MacDermid JC, Dal Bello-Haas V, et al. Scoping review of patient-centered care approaches in healthcare. BMC Health Serv Res 2014;14:1–9. 10.1186/1472-6963-14-271 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Cadzow RB, Craig M, Rowe J, et al. Transforming community members into diabetes cultural health brokers: the Neighborhood Health Talker project. Diabetes Educ 2013;39:100–8. 10.1177/0145721712465342 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Torres S, Spitzer DL, Labonté R, et al. Community health workers in Canada: innovative approaches to health promotion outreach and community development among immigrant and refugee populations. J Ambul Care Manage 2013;36:305–18. 10.1097/JAC.0b013e3182a5480f [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol 2005;8:19–32. 10.1080/1364557032000119616 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Levac D, Colquhoun H, O’Brien KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci 2010;5:1–9. 10.1186/1748-5908-5-69 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Wang ML, Gallivan L, Lemon SC, et al. Navigating to health: Evaluation of a community health center patient navigation program. Prev Med Rep 2015;2:664–8. 10.1016/j.pmedr.2015.08.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Parker VA, Lemak CH. Navigating patient navigation: crossing health services research and clinical boundaries. Adv Health Care Manag 2011;11:149–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Griswold KS, Homish GG, Pastore PA, et al. A randomized trial: are care navigators effective in connecting patients to primary care after psychiatric crisis? Community Ment Health J 2010;46:398–402. 10.1007/s10597-010-9300-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Griswold KS, Servoss TJ, Leonard KE, et al. Connections to primary medical care after psychiatric crisis. J Am Board Fam Pract 2005;18:166–72. 10.3122/jabfm.18.3.166 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Griswold KS, Zayas LE, Pastore PA, et al. Primary care after psychiatric crisis: a qualitative analysis. Ann Fam Med 2008;6:38–43. 10.1370/afm.760 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Chan TC, Killeen JP, Castillo EM, et al. Impact of an internet-based emergency department appointment system to access primary care at safety net community clinics. Ann Emerg Med 2009;54:279–84. 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2008.10.030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Elliott K, W Klein J, Basu A, et al. Transitional care clinics for follow-up and primary care linkage for patients discharged from the ED. Am J Emerg Med 2016;34:1230–5. 10.1016/j.ajem.2016.03.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Wexler R, Hefner JL, Sieck C, et al. Connecting emergency department patients to primary care. J Am Board Fam Med 2015;28:722–32. 10.3122/jabfm.2015.06.150044 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Kangovi S, Mitra N, Grande D, et al. Patient-centered community health worker intervention to improve posthospital outcomes: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 2014;174:535–43. 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.14327 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Freeman HP. The history, principles, and future of patient navigation: commentary. Semin Oncol Nurs 2013;29:72–5. 10.1016/j.soncn.2013.02.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Freeman HP, Rodriguez RL. History and principles of patient navigation. Cancer 2011;117:3537–40. 10.1002/cncr.26262 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Gunn CM, Clark JA, Battaglia TA, et al. An assessment of patient navigator activities in breast cancer patient navigation programs using a nine-principle framework. Health Serv Res 2014;49:1555–77. 10.1111/1475-6773.12184 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Bishop SE, Edwards JM, Nadkarni M. Charlottesville Health Access: a locality-based model of health care navigation for the homeless. J Health Care Poor Underserved 2009;20:958–63. 10.1353/hpu.0.0219 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Marr AL, Pillow T, Brown S. Southside medical homes network: linking emergency department patients to community care. Prehosp Disaster Med 2008;23:282–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Gany F, Bari S, Gill P, et al. Step on it! Impact of a workplace New York City taxi driver health intervention to increase necessary health care access. Am J Public Health 2015;105:786–92. 10.2105/AJPH.2014.302122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Overholser LS, Hassell K, Nuss R, et al. Using patient navigators to help adults with sickle cell disease obtain a primary care home. J Clin Outcomes Manage 2014;21:304–7. [Google Scholar]
- 53. Kim TY, Mortensen K, Eldridge B. Linking uninsured patients treated in the emergency department to primary care shows some promise in Maryland. Health Aff 2015;34:796–804. 10.1377/hlthaff.2014.1102 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Treadwell H, Holden K, Hubbard R, et al. Addressing obesity and diabetes among African American men: examination of a community-based model of prevention. J Natl Med Assoc 2010;102:794–802. 10.1016/S0027-9684(15)30676-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. ED navigators connect patients to better venues of care. ED Manag 2011;23:53–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Aantjes C, Quinlan T, Bunders J. Integration of community home based care programmes within national primary health care revitalisation strategies in Ethiopia, Malawi, South-Africa and Zambia: a comparative assessment. Global Health 2014;10:851 10.1186/s12992-014-0085-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Doran KM, Colucci AC, Hessler RA, et al. An intervention connecting low-acuity emergency department patients with primary care: effect on future primary care linkage. Ann Emerg Med 2013;61:312–21. 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2012.10.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Horwitz SM, Busch SH, Balestracci KM, et al. Intensive intervention improves primary care follow-up for uninsured emergency department patients. Acad Emerg Med 2005;12:647–52. 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2005.tb00922.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. ED navigators help patients find a PCP. Hosp Case Manag 2014;22:9–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Parker VA, Clark JA, Leyson J, et al. Patient navigation: development of a protocol for describing what navigators do. Health Serv Res 2010;514+. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Kahn LS, Aiello J, Berdine DE, et al. The use of telephonic case management to link a special-needs population with a primary care physician. J Am Board Fam Med 2009;22:585–7. 10.3122/jabfm.2009.05.080230 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
bmjopen-2017-019252supp001.pdf (358.4KB, pdf)
bmjopen-2017-019252supp002.pdf (503KB, pdf)