Abstract
Background:
Weakness of curriculum development in nursing education results in lack of professional skills in graduates. This study was done on master's students in nursing to evaluate challenges of neonatal intensive care nursing curriculum based on context, input, process, and product (CIPP) evaluation model.
Materials and Methods:
This study was conducted with qualitative approach, which was completed according to the CIPP evaluation model. The study was conducted from May 2014 to April 2015. The research community included neonatal intensive care nursing master's students, the graduates, faculty members, neonatologists, nurses working in neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), and mothers of infants who were hospitalized in such wards. Purposeful sampling was applied.
Results:
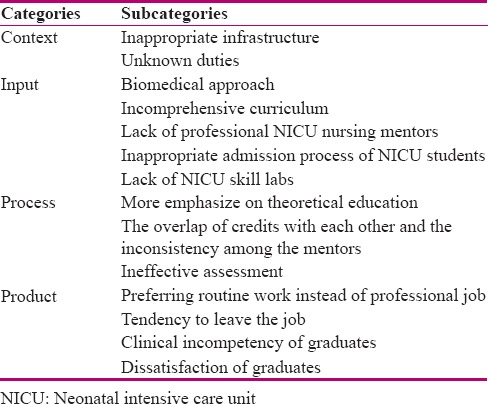
The data analysis showed that there were two main categories: “inappropriate infrastructure” and “unknown duties,” which influenced the context formation of NICU master's curriculum. The input was formed by five categories, including “biomedical approach,” “incomprehensive curriculum,” “lack of professional NICU nursing mentors,” “inappropriate admission process of NICU students,” and “lack of NICU skill labs.” Three categories were extracted in the process, including “more emphasize on theoretical education,” “the overlap of credits with each other and the inconsistency among the mentors,” and “ineffective assessment.” Finally, five categories were extracted in the product, including “preferring routine work instead of professional job,” “tendency to leave the job,” “clinical incompetency of graduates,” “the conflict between graduates and nursing staff expectations,” and “dissatisfaction of graduates.”
Conclusions:
Some changes are needed in NICU master's curriculum by considering the nursing experts' comments and evaluating the consequences of such program by them.
Keywords: Curriculum, educational models, evaluation, intensive care, neonatal, nursing, nursing program, qualitative research
Introduction
Neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) nursing is one of the nursing specialties which reduce death toll or disease side effects in neonatal wards by optimizing care of unwell or premature newborn infants and their families. The role of NICU nurses was established first in 1970s.[1] Later, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) presented a precise definition for NICU nursing in 2001 and introduced this topic to the education system and assessment of this unit.[2] It was first accepted as an educational specialty of nursing sciences for enrolling students in 2009 academic year.[3]
Medical sciences education system has significant duties, such as education, research, providing health services to the society, professional evaluation of different courses, and cultural development.[4] Nursing education explaining their duty should always match the needs of the society. One of the solutions to reach this goal is to make changes in nursing curriculum to maintain a balance between health system needs and educational and economic policies in society.[5] Curriculums are among the most important and the most fundamental factors of higher education system; thus, systematic design and actions are needed to make them effective.[6]
However, there is a shortage of experienced and skilled NICU nurses in Iran; thus, any change in society needs and professional duties of experts should be accompanied with a change in curriculum by reviewing the whole program to make it inclusive of all duties. This goal can be achieved by matching the contents and scopes of education system with the duties of graduates. To find strengths and weaknesses of a curriculum, numerous studies are needed.[7]
Each curriculum is designed to train professional and experienced personnel [8] so that they can fill job vacancies in the society. Moreover, education unit policymakers should also be able to review their activities and policies to decide whether to keep or stop them.[9] In Iran, enrolling NICU students started from 2009, and presently there are five groups of graduates who have availed professional jobs. Thus to improve educational program, assessment of its effectiveness should be done by beneficiaries, including students, graduates, professors, nurses, and nursing managers. However, there is no record available on evaluating NICU nurse practitioner curriculum or using the experience of those who have had a role in applying the curriculum. Taken together, it is of prime importance to conduct research to review or rebuild the program. Changes in health care systems, technologies, expectations, and needs are also demanding studies to review and implement changes in nursing curriculums as some of them do need some major changes.[10]
Khodaveisi et al. have shown that partial evaluation by nursing education managers via considering the input, process, and output can improve the effectiveness of the whole evaluation process in nursing education system; however, further studies are needed to design an efficient and applicable evaluation system in nursing education.[11] The aim of the present study was to evaluate challenges in neonatal intensive care nursing curriculum based on context, input, process and product (CIPP) evaluation model in nursing master's students.
Materials and Methods
This study was conducted qualitatively with a directed content analysis approach, which was completed according to the CIPP evaluation model. The study was conducted from May 2014 to April 2015 in the nursing and midwifery schools of Tehran and Isfahan Universities of Medical Sciences, Iran, as well as their affiliated health centers. Participants were NICU master students, graduates, faculty members, neonatologists, and nurses working in NICU. Purposive sampling was done and continued up to data saturation, meaning that the researcher got repetitive data, and there were no other new concepts needed for code or available to expand the codes.
Data collection was done using semi-structured interviews with open questions related to the experience of participants in NICU nursing master's curriculum. Questions were according to the CIPP evaluation model about human resources, physical environment, facilities, competency of graduates, real educational needs, and their relationship with educational goals, educational policymaking, teaching and learning process, teaching method of the professors, updating and organizing aspects of concepts, learning chances, level of satisfaction of coworkers from graduates' function, etc. Single interviews were conducted in calm places in an appropriate time (with setting appointment before) in order to create a comfortable condition for participants. Interviews continued with probing questions such as “Would you please explain more?” Each interview continued up to data saturation and was recorded after obtaining consents from participants. Transcribing was also done during all 23 interviews that lasted between 30 and 60 minutes. Three participants (a student and two nurses) were interviewed twice.
Moreover, data collection was conducted through guided or theory-based content analysis. The goal of directed content analysis approach is to conceptually validate or extend a theoretical framework or theory. The theory can help focusing on the research question, and it can help researchers to start data collection by identifying key concepts or variables as initial coding categories.[12] In CIPP model, directed content analysis was used after collecting the data. After reviewing the literature, four categories (context, input, process, and product) were extracted that formed the basis for setting interview guide, and output codes resulted from the analysis were placed within the categories. The transcription of interviews was implemented at the end of each session, and the transcripts were read several times in order to achieve a correct understanding. Then, the text was divided into smallest meaningful units (codes), and codes were classified into four main categories, which were extracted from the literature.
Lincoln and Guba's evaluative criteria, including credibility, transferability, dependability, and conformability, were used for the rigor of study.[13] Due to prolonged (11 months) and continuous engagement of the researcher with the study data, participants, and member checking, the credibility of study increased. For this purpose, researcher gave typed summery of interviews to participants so that they can confirm their interpretations. In order to meet the confirmability of data, peer check was done. Researcher first coded and classified each interview, and then, presented these classifications and codes to other members of the research team for evaluation. The codes, which were not in agreement with other members and/or participants, were discussed until achieving clarification and consensus. To control the dependability of the data, researcher retained the preliminary data, codes, categories, and themes. To achieve transferability or stability of the results, sampling was carried out with great variety to improve credibility of the data.
Ethical considerations
All participants were aware of the aims of interview, and the interviews were recorded after obtaining written consent from them. Participants were assured about the confidentiality of the recorded data, and they were provided with sound track and results obtained from the study. Besides, they were notified about their right of leaving the process at any time they wanted.
The Ethics Review Board at Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran, approved the study. Prior to collecting the data, written informed consent was obtained from each participant. Lastly, students, nurses, and physician were informed that their participation in the study was voluntary.
Results
Specific details of participant are listed in Table 1. The data analysis was done according to the CIPP evaluation model [Table 2].
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of the study participants
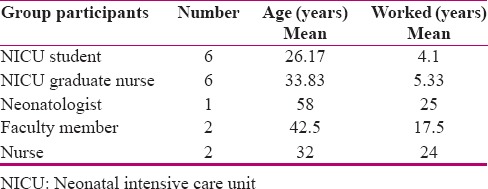
Table 2.
Categories and subcategories
Context
This section contained two categories: “inappropriate infrastructure” and “unknown duties.”
Inappropriate infrastructure
NICU students mentioned that they experience rejection from health care team members who often refuse to do job duties and providing infant professional care. They actually did not get opportunity to show their professional skills.
“The problem is that such subject is not accepted yet. All the nurses working in NICU are those who have learned something about infant care some years ago and are still applying them. I want to help them and teach them what I have learned but they say: take your certificate for yourself. It is 7 or 8 months I have graduated but I have not used the knowledge I have learned yet (NICU graduate nurse).”
NICU students need to have an appropriate atmosphere for learning and gaining skills; however, they experience problems such as not having permission of using ward facilities and not having the opportunity of experiencing and doing diagnostic/treatment procedures or doing professional care. Thus, an effective education is not possible unless clinical centers feel the need for using NICU students or understand the importance of educating and training them. Both mentor and student are considered as extra people and annoying in most of the clinical centers, which makes the cooperation level minimum. Most of the mentors are forced to lecture theoretical education due to not receiving enough support from education systems or colleagues.
“Nurses did not let us work with the infants directly. We were actually some observers in placements (NICU student).”
Unknown duties
NICU codification curriculums are not matched with the clinical duties and real society needs, causing waste of sources and facilities allocated for their education. Moreover, there is no fundamental endeavor on resolving problems and meeting patient needs by training professional people. NICU nurses do not have adequate duties matching their expertise, and their annual assessment is not generally reliable.
“The prophecy of training NICU nurses is something beyond the duties regular nurses apply. We are trained for more principled and more scientific handling of premature infants and so there should be better defined duties which the assessment would be valid by them (NICU graduate nurse).”
Input
This section included the categories of “biomedical approach,” “incomprehensive curriculum,” “lack of professional NICU nursing mentors,” “inappropriate admission process of NICU students,” and “lack of NICU skill labs.”
Biomedical approach
The aim of training NICU students is to provide professional nursing cares for infants; however, factors such as boldness of medical aspects compared to nursing aspects in the curriculum, which is formed because of doctor's intervention in writing it, has made it more inclined toward biomedical approach.
“Without situational assessment in clinics, the necessity of presenting the subject by a nurse is forgotten. The curriculum is written by doctor, our comments are ignored by nursing managers and the curriculum is presented with the same defects it had (faculty member).”
On the contrary, biomedical approach has increased the engagement of doctors in teaching both theoretical and clinical lessons. This fact mostly prevents students from learning professional infant cares.
“Some universities select all the mentors from doctors which is wrong in my opinion. There should be both doctors and nurses teaching together. Doctor mentors just come and talk about illnesses but not about the nursing care so that we can learn (NICU student).”
Incomprehensive curriculum
Curriculum should be written according to future job needs, different aspects of professional and developmental care, and prevention standpoint. However, different aspects of infant care are not mentioned in the curriculum. As a result, graduates experience conditions that they had never thought of before.
“I think the Newborn Individualized Developmental Care and Assessment Program (NIDCAP) should be taught in workshops or as a theoretical lesson. If there was more emphasize on NIDCAP, we could have made a revolution in NICU nursing! The other thing is family-centered care which is not favored in the curriculum and should be reinforced. Now they call NICU as “neuroprotection” meaning that we should discharge a healthy human not only physically, but also mentally. It is essential to teach the students in clinics since most of the developmental problems happen after the discharge (faculty member).”
Lack of professional NICU nursing mentors
One of the major challenges in the field of NICU is the lack or shortage of professional mentors and lecturers. Due to lack of expertise among mentors, the efficacy and self-confidence decrease. Such mentors behave warily with nurses and doctors working in NICU in order to hide their incompetency, and they are not able to defend the right of both students and themselves when they face disrespect.
“There is no professional mentor in NICU education, they are mostly graduated from pediatric nursing and they have not passed any NICU related course (NICU student).”
Lack of NICU skill labs
Given that infants are among the most vulnerable groups where it is difficult to apply most of the clinical procedures, labs with specialized skills and proper infrastructure are required for NICU students, which can help in acquiring relevant skills. However, most of the universities which enroll NICU master students offer general skill lab which is used for bachelor students and repeat what is taught during bachelor degree due to the lack of expert people or infants' specialized facilitations. Consequently, there would be no upgrade in students' skill level. Most of the clinical centers spend lots of money on facilitating their skill lab, but lack of professional technicians makes them useless.
“Skill labs we have in universities are designed for bachelor level and cover general nursing needs but not the NICU master ones. It is better to put NICU expert faculty or at least someone who knows how to work with facilities and someone who had worked with them before in skill lab section (Faculty member).”
Process
This section included the categories of “more emphasize on theoretical education,” “the overlap of credits with each other,” “the inconsistency among the mentors,” and “ineffective assessment.”
More emphasis on theoretical education
NICU nursing is a clinical subject, and the aim of the master course is to train nurses who work professionally in treatment centers; but, theoretical education is more emphasized compared to practical ones in educating students.
“The education should go on clinics. I mean the theoretical lesson should be taught next to the infant's bed; like the challenges of venipuncture or venesection of infants. I think teaching PICC (peripherally inserted central catheter) which is forgotten in the clinical education and is known as a nurse duty (faculty member and neonatologist).”
The overlap of credits with each other and the inconsistency among the mentors lessens overlap each other to a great extent. The topic of each lesson is expressed generally in the curriculum, which tends to repeat in some lessons. Non-nurse mentors and invited mentors are employed in most of the educational centers, which is one of the main reasons of disconformity among mentors and repeat of topics in some lessons.
“There were a lot of repeating lessons like seizure and asphyxia. I think the reason was that mostly the doctors taught the lessons and when they got to the nursing aspects, mentioned all the cares similarly, repeating the concepts because they had no expertise in this field (NICU student).”
Ineffective assessment
Designing questions up to the level of infants' fellowship makes barriers in getting to the real assessment aims in both theoretical and clinical placement among NICU students. The emphasis has been put on gaining clinical skills in clinical education assessing forms, but most of the students would not find the chance for a dedicated care. The assessment is ineffective in these situations.
“Most of our mentors and professors were doctors and taught the medical aspects of lessons instead of the nursing aspects. The questions of their exams were as hard as infants' fellowship ones! (NICU student).”
Product
This section included the categories of “preferring routine work instead of professional job,” “tendency to leave the job,” “clinical incompetency of graduates,” and “dissatisfaction of graduates.”
Preferring routine work instead of professional job
Preferring routines instead of professional job is a consequence of unknown duties.
“We are training a clinical expert nurse to upgrade the clinical job in order to make clinics cost-effective; meaning that a skillful routine job can be done by a graduated nurse cheaper than what a neonatologist does (faculty member).”
Tendency to leave the job
NICU graduates cannot feel any change after their graduation or they do not feel effective in upgrading the health system. So, they tend to leave their job as they know that master graduation is a time-consuming and costly process.
“Our duty is not clear in the hospital. There is no position determined for a master NICU nurse. It is three years I am working in the hospital but it has passed like thirty years. I greatly regret selecting this unit. Most of my colleagues are tending to leave their job (NICU graduate nurse).”
Clinical incompetency of graduates
NICU graduates are expected to apply their technical, communicational, scientific, logical, and emotional skills in caring of an infant or present nursing care according to professional standards; however, expert nurses are concerned and do not trust giving responsibility of premature infants to newly graduates due to their weaknesses in care and dysfunctions.
“A newly graduated nurse is not aware of not putting a necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) infant in a prone position. They do not know how to take the infant from the incubator out while he is under phototherapy. So what is their professional graduation used for? (nurse).”
The conflict between expectations
There are some conflicts between expectations of graduates and nursing staff. Nurses are not welcoming graduates in the ward and do not accept them as higher educated people with more updated knowledge. On the contrary, they believe that graduates do act weakly and tend to do managing and luxury jobs. Nurses who work as head nurses or supervisors do not accept NICU graduates easily since they fear from losing their position or formation of scientific differences between coworkers.
“NICU graduates like to work in managing positions with no night shift. Actually, they are full of improper expectations and just show off their certification while their turnover is weak. I expect to see a good consequence when a NICU graduated nurse takes care of an infant instead of making the situation worse and bring side effects for the kid (nurse).”
Dissatisfaction of graduates
Interactions between graduates and clinical nurses bring frustration due to a gap in education, which finally turns into dissatisfaction.
“I have not seen anyone satisfied with this subject. I see the students looking for the certificate instead of learning the NICU basics which is so bad and makes me sad (NICU graduate nurse).”
Discussion
The results of the study revealed that to meet NICU masters nursing curriculum goals and aims, clinical environments are not ready for accepting the students and do not provide a safe environment for learning and acquiring skills.
Obeidi et al.[14] believed that lack of learning chances in clinical centers is the main barrier in strengthening nursing students in experimental education units. However, nursing education policymakers know that clinical education is the main part and believe that students can increase their theoretical knowledge by working in clinical placement and facing different difficulties there. The intimate setting of ward and teamwork can increase the learning level of students.[15] Most of the graduates believe that present NICU curriculums do not match nurses' duties in clinical centers and real society needs. There is opportunity for using graduate's knowledge on infant care; however, students' duties should match with educational aims.[16]
Most of the participants believed that the required focus on nursing care is missing due to codification of NICU curriculum by doctors. Incompatibility of learnings with society needs, learners and the independent nursing science can substantially damage the nursing education.[17] Hanifi et al. believed that nurse mentors who believe in their profession can bring nursing spirit and interest for patient care in students by their words.[18] On the contrary, results of this study showed that the vast use of doctors for teaching both theoretical and clinical lessons prevents students from learning infant professional cares.[19]
According to participant's viewpoint, incomprehensive NICU nursing master's curriculum is among the main reasons behind ineffective theoretical and clinical education, and as the findings show, professional needs of graduates are not covered completely in the curriculum. Therefore, changes and reforms are necessary to meet professional aims as well as training creative and professional human resource.[4] Nikfarid and Ashk Torab have also mentioned inappropriate curriculum in their study.[19] Ajani has pointed out the necessity of preparing students for an immediate future.[20]
Reforming curriculum becomes more essential since nursing services and nursing education do not support fundamental needs in job conditions.[21]
Inadequacy of educational contents, unclearness of teaching/learning process, and indistinct assessment make the need for changing the curriculum even more important.[22] Results of this study showed that students tended to conduct their training by experienced and expert nurses. This finding matches with findings observed by Aghebati et al. on the expectations of participants from practice mentor. Limitations in expert human resources are among other main challenges, which our participants believed to be one of the main problems affecting NICU nursing masters' education.[23] Cheraghi et al. have mentioned the incompetency of nursing mentors in presenting nursing services in a new form, and that they do not have enough practical skills.[24] Differences in NICU nursing master's topics, lack of opportunity for retraining current mentors, and limitation for using experienced doctors and clinical preceptors are among the fundamental problems mentioned by our participants. Besides, it might be because of emphasizing on final certificate instead of gaining skills in nursing education. The shortage of clinical human resources in universities has made nursing mentors to work in different wards with different clinical conditions for which they are not trained for. These results are consistent with other researches.[25]
The results of this study showed that lack of expertise and abilities in mentors decreases their self-confidence and affects creation of safe and satisfying conditions for both students and mentors. Hanifi et al. believed that this kind of mentor's behavior comes from the fact that despite established position, mentors have no structural relationship with clinical centers and are known as outsiders and temporary part of the hospital. Hence there is no power and stability by which the students get more motivation. Decreasing the gap between education and practice with any method or approach can improve these situations.[18] There should be more stress on their theoretical knowledge and clinical skills before hiring them.[25]
In our study, participants tended to learn infant care in skilled labs before entering clinical wards, while they have no access to a NICU skilled lab. Morgan has also pointed to the continuity between what students learn and what they have to apply in patient's bedside acquired in skilled labs, which can resolve clinical learning problems widely.[26]
The concern of students in this study regarding transition from clinical to theoretical education is among the interesting findings of the research. Khosravi et al. showed that the inefficiency of apprenticeship tasks such as doing written assignments is overlaid by repeating theoretical unit subjects in lectures, while holding written exams in apprenticeships is a challenge for clinical education; whereas presenting practical tasks and generally those which apply the theoretical knowledge into clinical function such as case report, nursing rounds and totally leading both the tasks and exams toward practical and functional problems is emphasized.[27]
The majority of participants believed that lessons overlap each other a lot. A similar complaint is reported by students and masters in the study of Aghebati et al. that some lessons overlap in the curriculum, while students were eager to learn more professional skills. Therefore, reviewing current curriculum to decrease overlapping subjects and turning them into more professional ones such as the use of nursing theories in clinical centers can solve the problems to a great extent.[23]
Participants believed that their assessment in clinical units has not been educationally effective, while it is known as one of the important parts in clinical learning. Students deserve valid and stable assessment that follows their skills as a newcomer nurse.[27]
Preferring routines instead of professional job is another consequence of ineffective education for NICU master students, as believed by participants. Dehghan-Nayeri et al. have stated that routine-based spirit affects nurses.[28] Unadjusted relationship between theoretical education and nurses' clinical performance forces use of traditional and usual methods and, thereby, missing the scientific knowledge, which can stop expansion of theoretical sciences and decrease the quality of nursing services.[29] As stated by participants, they do not feel any change in their job position after their graduation and there is no support from the system; so, the tendency toward leaving job increases. Ashghali Farahani et al. believed that lack of specified job position, receiving no support from nursing managers, and inappropriate working atmosphere are among the main reasons for leaving job.[29]
Our study results showed that NICU graduates do not have clinical skills and mostly have problems with their duties; therefore, the cooperation between educational and clinical groups for designing the curriculum can fill the gap between theoretical and clinical practice. The accessibility to advanced atmosphere to employ learned skills and knowledge is known as an important factor contributing to the performance of graduates.[19] Masoudi has recommended examining clinical skills of students before graduation by using objective structured clinical examination method.[30]
The conflict between graduates and nursing staff expectations has made an unsafe atmosphere for learning, as stated by participants. In this context, the experience of new nurses is very important in role transition process. Therefore, the experience of newly graduated nurses from their earliest job position would influence their decision on whether they remain or leave.[31] Newly graduated nurses are more eager to keep values and standards, but they lose their motivation after sometime. Receiving full support from nursing managers can increase capabilities, skills, and clinical competency among newcomer nurses and is known as one of their fundamental needs.[29,32] The current study shows that if there is no effective facilities and factors for increasing both educational and job satisfaction among NICU nursing master graduates, performance level of nurses and graduates can decrease, which may in turn bring job dissatisfaction, morality decrease, more absence, more requests for relocation, tendency to leave job, and mental health damages. The probability of forgetting some memories or unwillingness of participants for sharing their experiences and feelings are among the research limitations, which are expected due to qualitative nature of the study. Therefore, further similar researches in other universities that involve different populations can promote the efficiency of conclusions.
Conclusion
There are some problems in codification and implementation of NICU master's curriculum considering experts' comments. It is necessary to make some changes in the curriculum according to the society needs and the comments of experts' in nursing as well as assessing the consequences in order to have more success in NICU nursing master program. Besides preparing learning environment for students, more interaction is needed between professors and clinical nurses to prevent any discontent and waste of money, dropout or turnover among students and graduates, and to apply the curriculum properly in order to meet its aims. Teaching according to the clinical needs and using expert NICU mentors can be effective in optimizing the education quality. Our study results focus on the necessity to create an appropriate initial infrastructure in order to design new curriculums. This study is a qualitative research. Therefore, one of the basic limitations is inability to generalize the findings to a target population. Accordingly, maximum effort has been made to improve rigor of data. This study is conducted in four major universities of the country and their affiliated hospitals, and the results are concluded by using a qualitative approach, deep data, and real experiences of people being involved in applying the NICU masters nursing curriculum, which are all known as the strengths of the study.
Financial support and sponsorship
Isfahan University of Medical Sciences.
Conflicts of interest
Nothing to declare.
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to acknowledge all those who cooperated to the research project; also, our thanks go to Iran University of Medical Sciences for their coordination and financial support and the Ethics Review Board at Iran University of Medical Sciences that approved the IR.IUMS.REC 1392.92-03-133-24171 study. We wish to thank all the nursing students, nurses, and physicians who gave their valuable time to participate in this study.
References
- 1.Dighe MP, Muckaden MA, Manerkar SA, Duraisamy BP. Is there a role of palliative care in the neonatal intensive care unit in India? Indian journal of palliative care. 2011;17:104. doi: 10.4103/0973-1075.84530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.LeFlore J, Thomas PE, Zielke MA, Buus-Frank ME, McFadden BE, Sansoucie DA. Educating neonatal nurse practitioners in the 21st century. J Perinat Neonatal Nurs. 2011;25:200–5. doi: 10.1097/JPN.0b013e318218137a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ebadi A, Tabanejad Z, Pazokian M. Clinical competence among MSc students of critical care nursing. Iranian J Med Educ. 2015;14:1036–46. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Safari M, Khodavisi M, Torkaman B. The viewpoints of nurses towards applicability of nursing curriculum in hospitals affiliated to Hamedan University of Medical Sciences. Iranian J Med Educ. 2009;8:205–11. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kermansaravi F, Navidian A, Imani M. Nursing students' views toward quality of theoretical and clinical nursing education: A qualitative study. J Med Educ Dev. 2013;7:28–40. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mohammadi F, Momennasab M, Yektatalab S, Kouchaki Z, Mozafari F. The effectiveness of doctoral program in nursing in Iran based on the Patrick model. Nursing and Midwifery Studies. 2016;5:e33726. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jahanpour F, Azodi P, Vahedparast H. Nursing students' perception of the learning experiences in neonatal intensive care units. Interdisciplinary Journal of Virtual Learning in Medical Sciences (IJVLMS) 2012;3:17–23. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Joolaee S, Jafarian Amiri SR, Ashghali Farahani M, Varaei S. Iranian nursing students' preparedness for clinical training: A qualitative study. Nurse Educ Today. 2015;35:e13–7. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2015.07.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Vajari TD, Sorkhabi MY, Arefi M, Fardanesh H. Conceptualization of curriculum development models in higher education. Journal of Shahid Beheshti University. 2011;8:48–62. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Iwasiw CL, Goldenberg D. Curriculum development in nursing education. Jones & Bartlett Publishers; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Khodaveisi M, Pazargadie M, Yaghmaei F, Bikmoradi A. Requirements for effective evaluation in nursing education: A qualitative study. J Res Med Sci. 2012;17:710–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Campos CJ, Turato ER. Content analysis in studies using the clinical-qualitative method: application and perspectives. Revista latino-americana de enfermagem. 2009;17:259–64. doi: 10.1590/s0104-11692009000200019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Polit DF. Essentials of nursing research: Appraising evidence for nursing practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott/Williams & Wilkins Health; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Obeidi N, Motamed N. Comparison of students' and teachers' viewpoints about clinical education environment: A study in paramedical and nursing and midwifery schools of Bushehr University of Medical Sciences. Strides in Development of Medical Education. 2011;8:88–93. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Delaram M, Reisi Z, Ali DM. Strengths and weaknesses of clinical education from the viewpoints of nursing and midwifery students in Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences, Shahrekord, Iran. 2012. QOM University of Medical Sciences Journal. 2012;6 [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rafiee G, Moattari M, Nikbakht AN, Kojuri J, Mousavinasab M. Problems and challenges of nursing students' clinical evaluation: A qualitative study. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2014;19:41–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ghorbani F, Rahkar Farshi M, Valizadeh L. Comparison of master's curriculum of pediatric nursing in Iran and United states. Journal of Nursing Education. 2015;4:41–7. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hanifi N, Parvizy S, Joolaee S. The role of clinical instructor in clinical training motivation of nursing students: A qualitative study. 2012;7:23–33. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nikfarid L, Ashktorab T. Understanding of neonatal intensive care nurse practitioner students of situation of their profession in Iran: A qualitative study. IJNR. 2013;8:37–46. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ajani K, Moez S. Gap between knowledge and practice in nursing. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences. 2011;15:3927–31. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cheraghi M, Salsali M. To understand the process of theory and practice gap in nursing education in Iran. Iranian Journal of Public Health. 2005;34:26–7. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Heydari A, Soudmand P, Hajiabadi F, Armat M, Rad M. The causes and solutions of the theory and practice gap from nursing education view point: A review article. Journal of Medical Education Development. 2014;7:72–85. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Aghebati N, Mohammadi E, Ahmadi F. The experiences of the lectures and nursing students in the implementation of the curriculum for master students in Critical Care Nursing: a qualitative research. Journal of Nursing Education. 2015;4:48–60. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cheraghi MA, Salasli M, Ahmadi F. Factors influencing the clinical preparation of BS nursing student interns in Iran. Int J Nurs Pract. 2008;14:26–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-172X.2007.00664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Khoshrang H, Salari A, Dadgaran I, Moaddab F, Rouh-Balasii L, Pourkazemi I. Quality of education provided at the clinical skills lab from medical students' viewpoints in Guilan University of Medical Sciences. Research in Medical Education. 2016;8:77–83. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Abdal M, Alavi NM, Adib-Hajbaghery M. Clinical self-efficacy in senior nursing students: A mixed-methods study. Nurs Midwifery Stud. 2015;4:e29143. doi: 10.17795/nmsjournal29143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Khosravi S, Pazargadi M, Ashktorab T. Nursing students viewpoints on challenges of student assessment in clinical settings: A qualitative study. Iranian Journal of Medical Education. 2012;11:735–49. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dehghan-Nayeri N, Ghaffari F, Shali M. Exploring Iranian nurses' experiences of missed nursing care: A qualitative study: A threat to patient and nurses' health. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2015;29:276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ashghaly Farahani M, Oskouie F, Ghaffari F. Factors affecting nurse turnover in Iran: A qualitative study. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2016;30:392–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Masoudi R. Prospective critical care master science graduated nurses of clinical competency: A content analysis. J Med Edu Dev. 2016;8:106–14. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ashghali Farahani M, Ghaffari F, Oskouie F, Tafreshi MZ. Attrition among Iranian nursing students: A qualitative study. Nurs Educ Pract. 2017;22:98–104. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2017.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Mohtashami J, Rahnam H, Farzinfard F, Talebi A, Shorideh FA, Ghalenoee M. A survey of correlation between professional identity and clinical competency of psychiatric nurses. Open Journal of Nursing. 2015;5:765. [Google Scholar]


