Abstract
Background
Snail intermediate hosts play active roles in the transmission of snail-borne trematode infections in Africa. A good knowledge of snail-borne diseases epidemiology particularly snail intermediate host populations would provide the necessary impetus to complementing existing control strategy.
Main body
This review highlights the importance of molecular approaches in differentiating snail hosts population structure and the need to provide adequate information on snail host populations by updating snail hosts genome database for Africa, in order to equip different stakeholders with adequate information on the ecology of snail intermediate hosts and their roles in the transmission of different diseases. Also, we identify the gaps and areas where there is need for urgent intervention to facilitate effective integrated control of schistosomiasis and other snail-borne trematode infections.
Conclusions
Prioritizing snail studies, especially snail differentiation using molecular tools will boost disease surveillance and also enhance efficient schistosomaisis control programme in Africa.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s40249-018-0401-z) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Schistosomiasis, snail host, schistosoma spp., genome database, Africa
Multilingual abstracts
Please see Additional file 1 for translations of the abstract into the four official working languages of the United Nations.
Background
Snails are invertebrate animals, belonging to the Phylum Mollusca. This group of organisms (except slug) possess a unique feature, known as “shell” which is a major characteristic of the group [1]. The snails inhabits a wide range of habitats because they are found not only in freshwater environment but also in other ecological niches [2].
Some snails are medically important because they transmit disease-causing trematodes in humans and other animals [3]. Most of the diseases caused by snail-borne trematodes are prevalent in the tropic and sub-tropic regions of the world, and the medical and economic burden of these diseases are often neglected which is why they are called neglected tropical diseases (NTDs). The distribution of the diseases caused by snail-borne trematodes especially schistosomiasis is focal. Hence, the parasites distribution is strongly dependent on the intermediate snail hosts distribution [4, 5].
Firstly, the continued transmission of snail-borne trematode infections in most endemic areas is facilitated by the presence and distribution [6, 7] of these important snail intermediate hosts that provide suitable environment for the development of trematode parasites [8].
Secondly, poor access to basic infrastructure by most inhabitants living in endemic settings [9] and the limitation of chemotherapy (the main control strategy in Africa) to effectively control the burden of schistosomiasis led to the call for the implementation of integrated control strategies through the incorporation of snail control to achieve the goal of schistosomiasis elimination [3]. More so, the high risk population largely depend on water bodies domiciled by the snail hosts for their daily and economic activities.
Several studies have been done to unravel the identity of the “supposed enemy” whose influence is of great public health importance and with pronounced burden amongst people living in marginalized settings of the tropic and sub-tropic regions [10–12].
Therefore, it is important to develop the platform that will monitor and identify snail distribution and infected snails, to help improve control efforts of the diseases caused by snail-borne trematodes. Also, a lot of achievements have been recorded in the identification of some snail hosts of medical and veterinary importance using both morphological and molecular approaches [13–16] and these have provided information that helped improve schistosomiasis control efforts.
There are continued efforts at improving the development of biomarkers that are effective in differentiating schistosome parasites and also provide insights into factors influencing host-parasites compatibilities on local scales [17, 18].
Despite all the efforts, it is obvious that more reliable genomic information is required for snail intermediate hosts populations to help improve control programmes [19, 20] particularly in the schistosomiasis endemic regions of Africa. It is imperative to develop tools that will detect and quantify genetic differences and changes in snail populations and also closely monitor the spread of these genetic variants that have the potentials to affect control strategies [21].
Great tasks lie ahead and more commitment is required to ensuring the elimination of schistosomiasis from endemic regions of Africa.
Though, snail hosts studies are crucial especially in Africa as we prioritize NTDs elimination but only few studies have established snail hosts differentiation on local scales [15, 22, 23].
Therefore, it is imperative to provide adequate information on snail host population structure and diversity both on national and continental scales using molecular approaches in order to strengthen control programmes in Africa. Such information is important for reliable decision making and efficient control implementation. This should be a pre-requisite for setting up effective control programmes that will be supported by active surveillance response system in endemic areas especially in sub-Saharan Africa where the disease burden is enormous but control efforts are limited due to poor funding and lack of political will.
As suggested by Rollinson et al. [24] that a global awareness be raised to provide adequate support for the elimination of schistosomiasis in endemic countries, it is believed that the support will be more effective by updating the genomic status of snail hosts of trematode parasites where available and also establish reliable comprehensive genome identification database where information is lacking across Africa.
This paper summarize the available information on the progress made in controlling schistosomiasis transmission through snail intermediate hosts studies using molecular approaches and also identify areas where actions are required to be taken for effective integrated control efforts to be achieved in Africa.
The predominant snail intermediate hosts implicated for transmitting schistosome parasites in Africa is shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Predominant snail intermediate hosts found in Africa and the schistosome parasites harboured by them
| S/N | Snail intermediate hosts | Parasites transmitted |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bulinus globosus | Schistosoma haematobium |
| 2 | Bulinus truncatus | Schistosoma haematobium |
| 3 | Bulinus africanus | Schistosoma haematobium |
| 4 | Bulinus senegalensis | Schistosoma haematobium |
| 5 | Bulinus forskalii | Potential snail intermediate host |
| 6 | Bulinus camerunensis | Schistosoma haematobium |
| 7 | Biomphalaria pfeifferi | Schistosoma mansoni |
| 8 | Biomphalaria sudanica | Schistosoma mansoni |
| 9 | Biomphalaria choanomphala | Schistosoma mansoni |
| 10 | Bulinus alexandrina | Schistosoma mansoni |
The male and female adult schistosome worms dwell inside the blood stream of humans. Schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium are responsible for intestinal schistosomiasis and urinary schistosomiasis respectively [25] (Fig. 1). S. haematobium is located in the venous plexus and it drains the infected person’s urinary bladder while S. mansoni is located in the mesenteric veins and it drains both the large and small instestines.
Fig. 1.
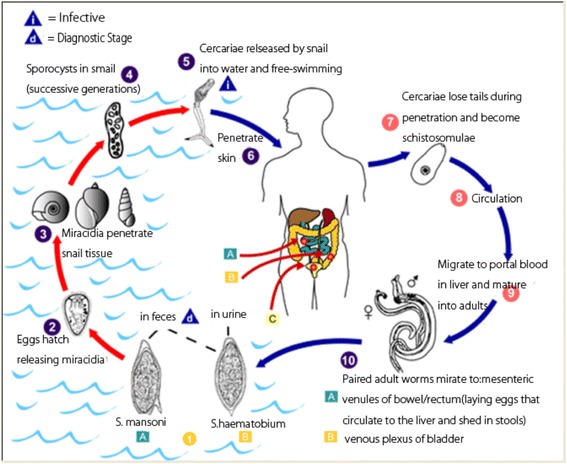
Typical life cycle of schistosome parasites [84]
Schistosome eggs equipped with spines are deposited by the female schistosome parasites into the small venules of the portal and perivesical systems. The eggs migrate towards the bladder and ureter (S. haematobium) and the lumen of the intestine (S. mansoni) and are released into the environment with urine or feces. The accumulation of eggs deposited in the venules cause its blockage and this burst the veins and allows eggs and blood to access the urinary bladder and the intestine and this leads to the characteristic symptom of blood in urine and feces. When the eggs are released into the freshwater bodies, they hatch into miracidia and penetrate a suitable snail intermediate host of the genus Bulinus (with species such as Bulinus truncatus, B. globosus, B. senegalensis, B. forskalii, B. camerunensis, B. africanus and B. tropicus) or Biomphalaria (with species such as Biomphalaria pfeifferi, Bi. Choanomphala, Bi. alexandrina, Bi. sudanica), both serve as snail hosts of S. haematobium and S. mansoni respectively. The schistosome parasites develop and multiply into the infective cercariae within the snail hosts and are released into the water bodies by the snails. Humans become infected when they have contact with waterbodies that are infested with active cercariae [25].
Figure 2 shows the distribution of schistosomiasis on the African continent [26].
Fig. 2.
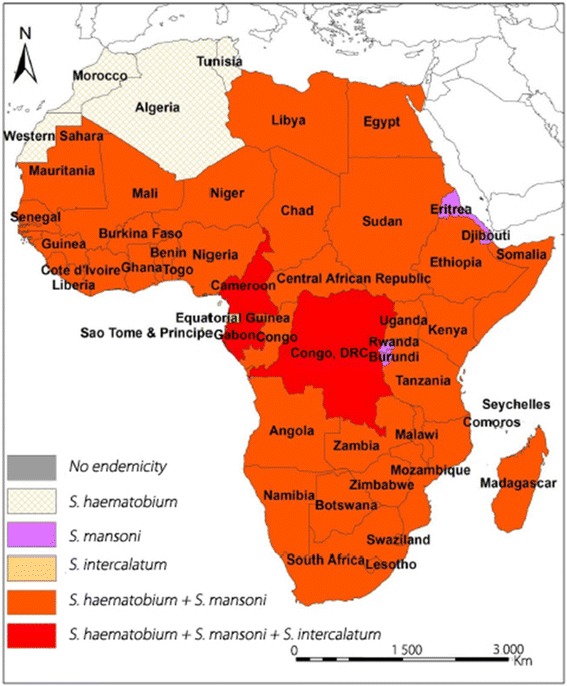
Distribution of schistosomiasis in Africa [26]
Tables 2 and 3 shows the identified Bulinus sp. and Biomphalaria sp. and their accession numbers selected from the GenBank. Source: [27]
Table 2.
Selected Bulinus sp. isolates with their accession numbers on GenBank
| S/N | Species | Locality | Country | Accession No | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | B. globosus | Ngwachani school, Pemba Island | Tanzania | AM 921827 | Kane et al., [12] |
| 2 | B. globosus | Kandaria dam, Kisumu, West Africa (via DBL)a | Kenya | AM 286286 | |
| 3 | B. globosus | Pemba Island | Tanzania | AM 921823 | Kane et al., [12] |
| 4 | B. globosus | Kimbuni, Pemba Island | Tanzania | AM 921830 | Kane et al., [12] |
| 5 | B. globosus | Tiengre stream, Kisumu (via DBL)a | Kenya | AM 286285 | |
| 6 | B. globosus | Pietermaritzburg (Prof. K.N. De Kock)a | South Africa | AM 286289 | |
| 7 | B. globosus | Kinyasini, Unguja Island | Tanzania | AM 286292 | |
| 8 | B. globosus | Lugufu (Dr E. Michel)a | Tanzania | AM 286287 | |
| 9 | B. globosus | Road to Mtagani, Pemba Island | Tanzania | AM 921820 | Kane et al., [12] |
| 10 | B. globosus | Ngwachani school, Pemba Island | Tanzania | AM 921826 | Kane et al., [12] |
| 11 | B. globosus | Tiengre stream, Kisumu (via DBL)a | Kenya | AM 286284 | |
| 12 | B. globosus | Road to Mtagani, Pemba Island | Tanzania | AM 921825 | Kane et al., [12] |
| 13 | B. globosus | Moyo | Uganda | AM 286291 | |
| 14 | B. globosus | Pietermaritzburg (Prof. K.N. De Kock)a | South Africa | AM 286290 | |
| 15 | B. globosus | Kinango | Kenya | AM 921844 | |
| 16 | B. globosus | Kinyasini, Unguja Island | Tanzania | AM 921840 | |
| 17 | B. globosus | Chan-jamjawiri, Pemba Island | Tanzania | AM 921828 | Kane et al., [12] |
| 18 | B. globosus | Thiekeene Hulle | Senegal | AM 921808 | |
| 19 | B. africanus | Isipingo, Durban (Prof. C. Appleton)a | South Africa | AM 286296 | |
| 20 | B. globosus | Machengwe, Pemba Island | Tanzania | AM 921829 | Kane et al., [12] |
| 21 | B. globosus | Ipogoro, Iringa | Tanzania | AM 286288 | |
| 22 | B. globosus | Mwaduli | Kenya | AM 921850 | |
| 23 | B. globosus | IRDC farm, Iringa (Dr. S. Walker)a | Tanzania | AM 921821 | |
| 24 | B. globosus | Mogtedo barrage | Burkina Faso | AM 286293 | |
| 25 | B. globosus | Kinyasini, Unguja Island | Tanzania | AM 921839 | |
| 26 | B. globosus | Moyo | Uganda | AM 921843 | |
| 27 | B. globosus | Kinango | Kenya | AM 921845 | |
| 28 | B. globosus | Tondia | Niger | AM 286294 | |
| 29 | B. globosus | Kachetu | Kenya | AM 921847 | |
| 30 | B. globosus | Moyo | Uganda | AM 921851 | |
| 31 | B. globosus | Imashayi, Ogun State | Nigeria | KJ361814 | Akinwale et al., [23] |
| 32 | B. globosus | Owode, Ogun State | Nigeria | KF989347 | Akinwale et al., [23] |
| 33 | B. truncatus | Mondego River, Coimbra (Prof. M. Gracio)a | Portugal | AM 286314 | |
| 34 | B. truncatus | Mogtedo barrage | Burkina Faso | AM 286315 | |
| 35 | B. truncatus | Mbane | Senegal | AM 921806 | |
| 36 | B. truncatus | Satoni | Niger | AM 286317 | |
| 37 | B. truncatus | Nyanguge | Tanzania | AM 286313 | |
| 38 | B. truncatus | Bouton Batt | Senegal | AM 921807 | |
| 39 | B. truncatus | Posada, Sardinia (Prof. Marco Curini Galletti and Dr. D.T.J Littlewood)a | Italy | AM 286312 | |
| 40 | B. truncatus | Satoni | Niger | AM 286316 | |
| 41 | B. camerunensis | Lake Barombi, Kotto | Cameroon | AM 286309 | |
| 42 | B. camerunensis | Owode, Ogun State | Nigeria | KF989354 | Akinwale et al., [23] |
| 43 | B. camerunensis | Ayetoro | Nigeria | KF989356 | Akinwale et al., [23] |
| 44 | B, senegalensis | Ayetoro | Nigeria | KJ361803 | Akinwale et al., [23] |
| 45 | B. forskalii | Ijale Ketu, Ogun State | Nigeria | KF989358 | Akinwale et al., [23] |
| 46 | B. forskalii | Owode, Ogun State | Nigeria | KF989359 | Akinwale et al., [23] |
| 47 | B. forskalii | Katosho swamp, Lake Tanganyika, Tanzania | Tanzania | HQ 121587 | Nalugwa, et al., [85] |
| 48 | B. forskalii | Lake Edward | Uganda | HQ 121583 | Nalugwa, et al., [85] |
| 49 | B. forskalii | Mogtedo barrage | Burkina Faso | AM 286310 | Kane, et al., [12] |
| 50 | B. forskalii | Sao Tome Island, Sao Tome City | Sao Tome & Principe | AM 286305 | Kane, et al., [12] |
| 51 | B. forskalii | Satoni | Niger | AM 286308 | Kane, et al., [12] |
| 52 | B. forskalii | Quifangondo | Angola | AM 286306 | Kane, et al., [12] |
| 53 | B. forskalii | Lake George | Uganda | HQ 121586 | Nalugwa, et al., [85] |
| 54 | B. cernicus | Mont Oreb | Mauritius | AM 286303 | |
| 55 | B. barthi | Kanga swamp, Mafia Island | Tanzania | AM 921817 | |
| 56 | B. tropicus | Njombe Kibena (Dr. S. Walker)a | Tanzania | AM 921842 | |
| 57 | B. nyassanus | Kasankha, Money Bay | Lake Malawi | AM 921838 | |
| 58 | B. nasutus productus | Nimbodze | Kenya | AM 921841 | |
| 69 | Bulinus sp. | ADC farm, Kisumu (via DBL)a | Kenya | AM 286297 |
aContributors Source: www.ncbi/BLAST/index/html
Table 3.
Selected Biomphalaria sp. isolates with their accession numbers on genbank
| S/N | Species | Locality | Country | Accession No | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Biomphalaria pfeifferi | Lake Albert | Uganda | EU 141219 | Plam et al., [86] |
| 2. | Biomphalaria pfeifferi | Ngamilajojo | Uganda | DQ 084834 | Plam et al., [86] |
| 3. | Biomphalaria sudanica | Ntoroko | Uganda | DQ 084843 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 4. | Biomphalaria pfeifferi | Kibwezi | Kenya | DQ 084830 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 5. | Biomphalaria glabrata | Imbaba | Egypt | DQ 084823 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 6. | Biomphalaria pfeifferi | Lake De Guirs | Senegal | DQ 084831 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 7. | Biomphalaria pfeifferi | Chiweshe | Zimbabwe | DQ 084829 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 8. | Biomphalaria pfeifferi | Lwampanga, Lake Kyoga | Uganda | DQ 084833 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 9. | Biomphalaria alexandrina | Egypt | Egypt | DQ 084825 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 10. | Biomphalaria pfeifferi | Lwampanga, Lake Kyoga | Uganda | DQ 084833 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 11. | Biomphalaria pfeifferi | Mansidi port, Lake Kyoga | Uganda | DQ 084841 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 12. | Biomphalaria pfeifferi | Muzizi | Uganda | DQ 084842 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 13. | Biomphalaria stanleyi | Lake Albert | Uganda | EU 141215 | Plam et al., [86] |
| 14. | Biomphalaria sudanica | Lake Albert | Uganda | EU 141227 | Plam et al., [86] |
| 15. | Biomphalaria stanleyi | Lake Albert | Uganda | EU 141225 | Plam et al., [86] |
| 16. | Biomphalaria sudanica | Butiaba, Lake Albert | Uganda | DQ 084838 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 17. | Biomphalaria stanleyi | Butiaba, Lake Albert | Uganda | DQ 084837 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 18. | Biomphalaria sudanica | Mahyoro | Uganda | DQ 084840 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 19. | Biomphalaria sudanica | Rutoto | Uganda | DQ 084844 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 20. | Biomphalaria sudanica | Ntoroko | Uganda | DQ 084843 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 21. | Biomphalaria smithi | Kwensliama, Lake Edward | Uganda | DQ 084836 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 22. | Biomphalaria camerunensis | Lake Bakassi | Cameroon | DQ 084827 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 23. | Biomphalaria choanomphala | Lake Victoria | Uganda | EU 141235 | Plam et al., [86] |
| 24. | Biomphalaria angulosa | Ruaha River | Tanzania | DQ 084826 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 25. | Biomphalaria smithi | Rwenshama, Lake Edward | Uganda | DQ 084836 | Jorgensen et al., [87] |
| 26. | Biomphalaria sudanica | Lake Albert | Uganda | EU 141230 | Plam et al., [86] |
| 27. | Biomphalaria choanomphala | Lake Albert | Uganda | EU 141226 | Plam et al., [86] |
Source: www.ncbi/BLAST/index/html
Snail molecular studies: identification of snail taxa
The use of molecular tools in species identification and exploring host-parasite compatibilities has provided answers to complex evolutionary questions over the years. Though, before the advent of molecular methods in differentiating snail hosts, intermediate snail hosts identification were largely done using morphological descriptions such as shell shape, shell size, nature of aperture, observations on the radula and reproductive system to assess taxonomic variations [28, 29]. However, its applications have enhanced the establishment of database platforms to deepen our understanding on snail hosts diversity and population structure [5, 30]. More importantly, its’ usage in differentiating the complex Bulinus group [31] which is the major snail intermediate hosts of S. haematobium, a prominent schistosome parasites causing serious morbidity across Africa especially in sub-Saharan Africa.
Advances in the production of effective genetic markers such as random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPDs) ribosomal gene (rRNA), and the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I (COI) have created robust and reliable taxonomy [31] which has improve our knowledge on the epidemiology of schistosomiasis [12].
Though the use of molecular approaches in differentiating snail hosts population structure have been applied on local scales across Africa but it is yet to be fully explored. For instance, [14] identified B. forskalii, Bi. pfeifferi and B. truncatus using molecular methods in N’Djamena, Chad [22]. Comprehensively identified five snail hosts (B. globosus, B. forskalii, Bi. pfeifferi, Lymnaea natalensis and Indoplanorbis exutus) of trematode parasites in Nasarawa State, north central, Nigeria using mitochondrial gene cytochrome oxidase I (cox1). The study assessed the phylogenetic relationship of these snails and established that B. globosus from Nasarawa State, Nigeria clusters with B. globosus sequence data from other West African countries such as Burkina Faso, Senegal and Niger when BLAST, using nucleotide blast homology on genbank forming a monophyletic lineage but forms paraphyletic relationship with B. globosus species from East Africa. B. forskalii also followed similar pattern, as it cluster to form a monophyletic relationship with species from Burkina Faso (Mogtedo barrage), Niger (Tondia) and Senegal (Thiekeene Hulle) while Bi. pfeifferi from Nigeria clustered with Bi. pfeifferi species from Senegal (Lake De Guirs), Kenya (Kibwezi), Uganda (Lake Albert) and Zimbabwe (Chiweshe) to form a monophyletic relationship. Indoplanorbis exutus formed a paraphyletic relationship with species from Asia. Information is lacking on the phylogenic status of Indoplanorbis exutus and Lymnaea natalensis from Africa, there is need to prioritize the establishment of reliable genome database for these snails across Africa considering their veterinary importance. Similarly, [32] characterized Bulinus truncatus using PCR-RFLP technique and assessed their infection status with Dra I gene repeat in Southwest Nigeria while [23] established the population structure of B. globosus, B. forskalii, B. camerunensis and B. senegalensis in schistosomiasis endemic communities of Ogun state, Southwestern Nigeria through the application of PCR-RFLP on the snails ribosomal ITS region.
Molecular tools application is not limited to elucidating relationships across snail hosts taxa. The application of PCR DraI and sm17 in the early detection of S. haematobium and S. mansoni in infected snail intermediate hosts of the Bulinus sp. and Bi. pfeifferi respectively have helped strengthen snail surveillance and boost schistosomiasis control efforts [33, 34]. Also, the simultaneous usage of PCR, DraI PCR and Sh110 SmSl PCR were effective in differentiating schistosome parasites that infected snails within the Bulinus group in Morocco [35]. Table 4 shows the summary of intermediate snail host studies carried out in different parts of Africa.
Table 4.
Summary of snail intermediate hosts studies in different parts of Africa
| S/N | Country | Snail species | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nigeria | Bulinus globosus | [13, 22] |
| Bulinus forskalii | |||
| Biomphalaria pfeifferi | |||
| Lymnaea natalensis | [16] | ||
| Indoplanorbis exutus | |||
| Bulinus sp. | [23] | ||
| 2. | Chad | Bulinus truncatus | [14] |
| Bulinus forskalii | |||
| Biomphalaria pfeifferi | |||
| 3. | Angola | B. globosus | [77] |
| B. canescens | |||
| B. angolensis | |||
| B. crystallinus | |||
| Bi, salinarium | |||
| B. globosus | |||
| B. canescens | |||
| 4. | Egypt | Biomphalaria alexandrina | [37] |
| [38] | |||
| Lymnaea natalensis | [88] | ||
| Bulinus truncatus | |||
| Bulinus truncatus | [39] | ||
| 5. | Cameroon | Bulinus truncatus | [39] |
| B. globosus | |||
| B. senegalensis | |||
| B. tropicus | |||
| B. forskalii | |||
| B. camerunensis | |||
| B. globosus | [15] | ||
| B. forskalii | [11] | ||
| 6. | Senegal | Bulinus truncatus | [39] |
| B. senegalensis | |||
| B. umbilicatus | |||
| 7. | Lake Victoria (across Tanzania, Kenya and Uganda) | Biomphalaria choanomphala | [40] |
| 8. | Tanzania | B. globosus | [89] |
| 9. | Madagascar | Biomphalaria pfeifferi | [44] |
| 10. | Malawi | B. globosus | [90] |
| B. nyassanus | |||
| 11. | Cote D’ voire | B. forskalii | [11] |
| B. globosus | |||
| 12. | Equitorial Guinea | B. forskalii | [11] |
| 13. | Niger | B. umbilicatus | [11] |
Snail genome studies: implication for effective control programme
The need to meet the goals of schistosomiasis elimination prompted the pursuit of an integrated control approach [3, 36] and contributions from different stakeholders [31] have provided baseline information and vigor for the pursuit of efficient implementation of control efforts in Africa [15, 37–40].
It is observed that environmental factors play significant role in the population size of snail host’s natural populations. The effects of these environmental conditions greatly affect gene flow between populations and induces important variations in population size [29]. Their hermaphroditic capabilities enable self or cross fertilization and allows for different genetic consequences [41]. Also, the fitness impact of parasites on the snail mating systems affects the genetic structure of the snail hosts population [42, 43]. Good understanding of local fluctuation in geographic origin, population size and snail hosts’ reproductive potentials are fundamental to improving our knowledge on the demographic stochasticity of natural population’s genetic structure [43].
The investigation of snail genetics role in trematode parasite infections variation using molecular approaches is vital to understanding their epidemiology. The assessment of the genetic differentiation of Bulinus snails from different ecological zones across Cameroon, Egypt and Senegal revealed high genetic diversity within Bulinus populations sampled from the three countries with the highest diversity observed within populations of B. forskalii and B. senegalensis [39], but this is contrary to findings on Biomphalaria pfeifferi in Madagascar which was reported to have high level of inter-population variation [44]. Utilizing the use of molecular markers[45], showed that there was high intra-population diversity with high levels of population structure but low level gene flow among populations of Biomphalaria choanomphala along Lake Victoria covering Tanzania, Kenya and Uganda. The study identified consistent parasitism as the major influencing factor [46] indicated that Biomphalaria species of African origin were derived from the neotropical natives and that proto-Biomphalaria glabrata is the progenitor of the African species through the trans-Atlantic colonization of Africa.
Findings have shown that schistosome parasites development inside the snail host is influenced by both the host and parasite genes [17, 47]. This has increase stakeholders consciousness to unsnarl the schistosome parasites and snail genes that influence this intrinsic association [48, 49]. This led to the development of genetic markers for the identification of resistant genes within the snail hosts. Detailed elucidation of snail hosts population structure and the identification of genetic markers for parasite resistance will further boost the resolve of effective integrated control approach for schistosomiasis elimination in Africa [37]. Observed from investigation on identified refractory strains to S. mansoni in Bi. alexandrina population from Egypt that refractory character within the snail hosts population is hereditary and therefore advised that snails that are actively resistant to schistosome parasites should be cultured to encourage biological control of snail intermediate hosts in a natural population.
Furthermore, it was established that snail hosts infection with schistosome parasites is species specific and often localized [50], efforts should be made to identify and document snail hosts that have refractory characters across regions. The introduction of snail hosts with parasite resistant genes into the natural population to replace the susceptible snail species in endemic areas will discourage schistosomiasis transmission and also reduce damage to the natural ecosystem through the use of molluscicides.
More importantly, it is necessary to encourage the extensive study of snail genome differentiation on a large scale due to the current global changes that have led to changes in the modification of the geographical distribution of species prompting hybridization, such hybridization is already known to occur in schistosomes and offspring have been shown to have superior virulence and invasive capacities [51]. This is an emerging public health concern particularly because of the changing geographic distribution of humans, domestic animals and wildlife [52]. Prioritizing snail studies is essential and there is need to update the snail hosts genome library for Africa in order to boost the realization of schistosomiasis elimination through active integrated control mechanisms. This is important because of the dynamic changes in climatic and environmental conditions which play key roles in the distribution of the snail intermediate hosts and the development of schistosome parasites.
Large-scale assessment of snail intermediate hosts genome will create the platform to determine the degree of variability among and within snail populations across the continent and give an overview of schistosomiasis distribution in Africa with current realities.
Determination of snail intermediate hosts population genetics and diversity using biomarkers is shown in Fig. 3
Fig. 3.
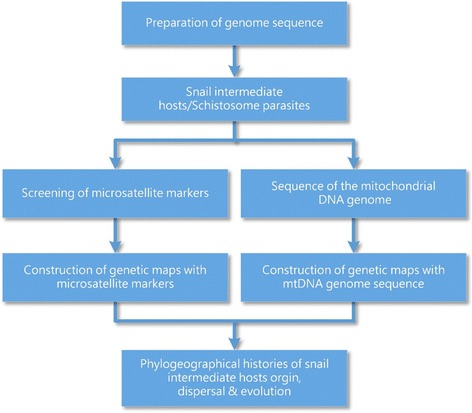
Determination of snail intermediate hosts population genetics and diversity using biomarkers
Gaps analysis: three research priorities identified
Though, molecular approaches to differentiating snail intermediate hosts are key to combating the menace of this debilitating disease in Africa [17]. However, studies on snail biology should not be limited to the application of molecular methods because there are other aspects of snail studies that are essential and should be taken seriously.
Firstly, snail identification using shell morphology and bionomics studies are essential to understanding the distribution pattern of snail hosts and transmission dynamics of schistosomiasis and other disease causing snail-borne trematodes at local scales across the continent [53, 54]. We observed that there is dearth of knowledge and lack of expertise in the area of malacology in Africa, this might be due to lack of interest from individuals as it is believed that the application of molecular methods is more acceptable and efforts are geared towards establishing collaborations that will help access such platforms. However, the knowledge and expertise of snail identification using shell morphology requires highly trained professionals to enhance capacity building due to its importance in disease surveillance and should be prioritized in order to achieve the goal of schistosomiasis elimination in Africa.
Secondly, the application of Geographical Information System (GIS) and remote sensing technologies to map and define the spatial limits of snail hosts distribution is an important area that requires utmost attention. Though it has been applied in some parts of Africa on local scales [55–57], but information on the geospatial distribution of important snail intermediate hosts is lacking in most African countries. Mapping and predicting snail hosts distribution on national and continental scales to establish comprehensive GIS database will help characterize the different eco-zones with relevance to the prevalent diseases, thus provide information that will enhance optimizing the use of available resources [58], and also strengthen the drive for effective schistosomiasis control on the continent.
Thirdly, there is urgent need to aggresively create awareness by educating the larger society especially people in the endemic areas through the mass media and other communication platforms on the importance of these planorbid snail hosts in schistosomiasis epidemiology. Experience in the field have shown that most locals who live around waterbodies in most endemic settings have little or no knowledge of the snails and are not aware of the danger their presence poses to their well-being. Hence, it is important to consistently create awareness on snail hosts control. The locals should be equipped with information that will spur them to ensuring that the snails does not thrive in their environment and also be mandated to urgently report snail hosts presence in any waterbody around their domain to the relevant health authorities promptly.
In addition to the aforementioned three gaps on snail biology, there are other areas that requires attention. This includes effort to put infrastructure in place or consistently modify the environment to discourage the continued presence and distribution of snail hosts and schistosomiasis transmission in most endemic countries. The environment in most endemic countries are characterized by factors that influence the distribution of snail hosts of schistosome parasites as a result of poor environmental management [59–62]. The presence of aquatic plants such as Eichhornia crassipes within and around waterbodies enhance the occurrence, distribution and abundance of snail hosts because it serves as a good source of food, provide shelter and oviposition sites for the snails [63–65]. Environmental modification through active removal of aquatic plants and silts from waterbodies renders the habitat unfriendly to the snail hosts [66, 67]. The indiscriminate disposal of human wastes due to lack of sanitary facilities and poor access to potable water sources for domestic purposes also add to the sources of infection in the environment, this facilitates easy access of schistosome parasites in feces or urine from infected persons to waterbodies and snail intermediate hosts.
Despite the public health significance of schistosomiasis globally especially in Africa where about 95% of global schistosomiasis is concentrated [68, 69], the use of micro-array platforms to decipher the intricate interplay between the parasites and the snail hosts is scarce. There is need for drastic improvement in the application of immunomic and next-generation sequencing platforms regarding schistosomiasis and other NTDs [70–75]. Efforts should be geared towards identifying genes that are actively involved in snail’s immune responses in order to initiate defence mechanisms that will block schistosome parasites survival in the snails [76]. Molecular tools application is vital for efficient snail surveillance and has great potential, as it is important for snail hosts and trematode parasites identification and also useful in defining the level of species biodiversity [5, 22, 31, 77]; these are pre-requisite to blocking schistosomiasis transmission effectively [78]. The lack of reference laboratories to carry out early diagnosis of schistosomiasis cases on infected people is a big challenge to the pursuit of schistosomiasis elimination in Africa. This debacle also extends to poor or absence of platform for researchers to execute evidence-based research on snail hosts. Such platforms, if available would help strengthen schistosomiasis surveillance and capacity building within the continent.
The challenge of insufficient supply of praziquantel due to scarcity of funds and the resistance of schistosome parasites to the drug of choice [79] led to the increasing call for the use of molluscicide to curtail snail distribution, but molluscicide application is yet to be substantially utilized in many countries endemic for schistosomiasis in Africa. This is partly due to reliance on prioritized chemotherapy treatment of school-aged children with praziquantel, which is not very effective due to the high re-infection rate few weeks after treatment or due to insensitivity or poor knowledge about snail hosts’ role in schistosomiasis transmission.
This might also be attributed to the perceived negative impact that niclosamide, the molluscicide of choice have on fishes, an important protein source and means of generating income for people living in rural settings. Therefore, it is advised that the molluscicide formulation be improved to ensure that it has less negative impact on the environment and biodiversity [80], but retain its potency against snail hosts [81].
The exploration of the molluscicidal properties of plants such as Phytolacca dodencandra and Millettia thonningii and some other plants with similar properties [82] should be considered. The distribution of these molluscicidal plants in areas identified as schistosomiasis hotspots in endemic areas will help curtail the distribution of snail hosts. However, it is important to effectively monitor the plants when cultivated in large scale because of their toxic properties.
The use of biological techniques for snail hosts control is long overdue in Africa, measures should be taken to effectively apply natural predators or encourage biotechnological methods to induce infecundity in the snails [83]. Figure 4 shows the mechanism for efficient schistosomiasis transmission interruption.
Fig. 4.
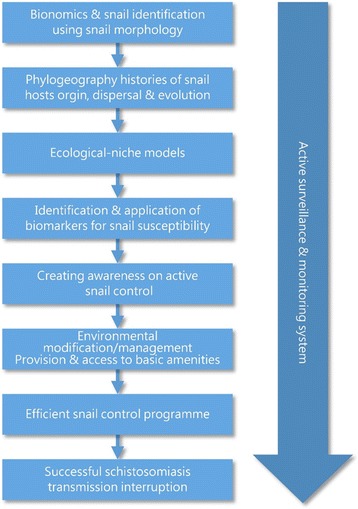
Mechanism for efficient schistosomiasis transmission interruption
Conclusions
The elimination of schistosomiasis and other trematode parasite infections will receive a great boost when snail hosts studies and effective snail control programme are prioritized. There is urgent need to set-up reference laboratories and other platforms that will encourage qualitative snail intermediate hosts and schistosomiasis researches and also facilitate early diagnosis of schistosomiasis cases. It is imperative to encourage capacity building through training and re-training of scholars, health workers and different stakeholders in Africa on snail hosts identification using both morphological and molecular approaches.
Additional file
Multilingual abstracts in the four official working languages of the United Nations. (PDF 514 kb)
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
The study is supported by Chinese National Science and Technology Major Program (grant no. 2016ZX10004222-004). The funders played no role in the study design, data collection, and data analysis or interpretation.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable
Declarations
E. M. Abe is supported by postdoctoral fellowships from the National Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Chinese Centre for Disease Control and Prevention. The study is supported by the Chinese National Science and Technology Major Program (grant no. 2016ZX10004222, no. 2012ZX10004 220) The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
Abbreviations
- DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- RAPD
Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA
- rRNA
ribosomal ribonucleic acid
- COI
Cytochrome oxidase I
- PCR-RFLP
Polymerase Chain Reaction- Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
- ITS
Internal Transcribed Spacer
- GIS
Geographical Information System
Authors’ contributions
EMA and XNZ conceived the study, EMA and XNZ wrote the manuscript, SZL, UFE, XJ, GYH, GW,QZ, KK and CJH revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript published.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
XNZ is the Editor-in-Chief of Infectious Diseases of Poverty. Other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s40249-018-0401-z) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Contributor Information
Eniola Michael Abe, Email: abeeniola11@126.com.
Wei Guan, Email: sg690287@sina.cn.
Yun-Hai Guo, Email: guoyunhaigy@163.com.
Kokouvi Kassegne, Email: ephremk@hotmail.fr.
Zhi-Qiang Qin, Email: qinzq1008@hotmail.com.
Jing Xu, Email: xfmjing@163.com.
Jun-Hu Chen, Email: junhuchen@hotmail.com.
Uwem Friday Ekpo, Email: ufekpo@hotmail.com.
Shi-Zhu Li, Email: stoneli1130@126.com.
Xiao-Nong Zhou, Email: zhouxn1@chinacdc.cn.
References
- 1.Boundless Biology. “Classification of Phylum Mollusca.” Boundless Biology. Boundless. https://www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/invertebrates-28/superphylum-lophotrochozoa-168/classification-of-phylum-mollusca-653-11874/20 May. 2016. Accessed 27 May 2016.
- 2.Okafor FC, Ngang I. Freshwater snails of Niger-Cem, Nkalagu, Eastern Nigeria: Observations on some demographic aspects of the schistosome-transmitting bulinids. Animal Res Inter. 2004;1(2):120–124. [Google Scholar]
- 3.WHO. The control of schistosomiasis. WHO Tech Rep Ser. 1993; 830, 1–85 [PubMed]
- 4.Hanington PC, Forys MA, Loker ES. A somatically diversified defense factor, FREP3, is a determinant of snail resistance to schistosome infection. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012; 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.Gordy, MA, Kish, L, Tarrabain, M, Hanington, PC. A comprehensive survey of larval digenean trematodes and their snail hosts in central Alberta, Canada. Parasitol Res. 2016; doi: 10.1007/s0043601651529 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 6.Loker ES. Research on the Molluscan Intermediate Hosts for Schistosomiasis: What are the Priorities? Presented to the Scientific Working Group on Schistosomiasis14–16 November. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Torgerson PR, Devleesschauwer B, Praet N, Speybroeck N, Willingham AL, Kasuga F, et al. World Health Organization. Estimates of the Global and Regional Disease Burden of 11 Foodborne Parasitic Diseases, 2010: A Data Synthesis. PLoS Med. 2015; 12(12):e1001920 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8.Centres for Disease Control and Prevention: Schistosomiasis Fact Sheet. 2010. https://www.cdc.gov/globalhealth/ntd/diseases/schisto_burden.htmlWeblink. Accessed 17 August, 2016.
- 9.Lardans V, Dissous C. Snail control strategies for reduction of schistosomiasis transmission. Parasitol Today. 1998;14:10. doi: 10.1016/S0169-4758(98)01320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jones CS, Noble LR, Ouma J, Kariuki HC, Mimpfoundi R, Brown DS, et al. Molecular identification of schistosome intermediate hosts: case studies of Bulinus forskalii group species (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) from Central and East Africa. Biol J Linn Soc. 1999;68:215–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8312.1999.tb01167.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Langand J, Barral V, Delay B, Jourdane J. Detection of genetic diversity with snail intermediate hosts of the genus Bulinus using random amplified polymorphic DNA markers (RAPDs) Acta Trop. 1993;55:205–215. doi: 10.1016/0001-706X(93)90078-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kane RA, Stothard JR, Emery AM, Rollinson D. Molecular characterization of freshwater snails in the genus Bulinus: a role for barcodes? Parasit Vectors. 2008;1:15. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-1-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Abe EM, Oluwole AS, Ojo DA, Idowu OA, Mafiana CF, Braide EI, et al. Predicting the geospatial distribution of Bulinus snail vector of urinary schistosomiasis in Abeokuta, South-Western. Nigeria. The Zool. 2012;10:53–60.
- 14.Moser W, Greter H, Schindler C, Allan F, Ngandolo BNR, Moto DD, et al. The spatial and seasonal distribution of Bulinus truncatus, Bulinus forskaliiand Biomphalaria pfeifferi, the intermediate host snails of schistosomiasis, in N’Djamena. Chad. Geo Health. 2014;9(1):109–18. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 15.Djuikwo-Teukenga FF, Da Silva A, Njiokou F, Kamgang B, Same Ekobo A, Dreyfuss G. Significant population genetic structure of the Cameroonian freshwater snail, Bulinus globosus, (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) revealed by nuclear microsatellite loci analysis. Acta Trop. 2014;137:111–117. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2014.04.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Abe EM, Oluwole AS, Ahmed HO, Ekpo UF. Malacological survey and geospatial distribution of Indoplanorbis exutus (Deshayes, 1934) and Lymnaea natalensis (Krauss 1848) snail vectors of trematode parasites, in Abeokuta, south-western, Nigeria. Nig. J. Parasitol. 2016; 37(1) ISSN 1117 4145
- 17.Rollinson D, Stothard JR, Jones CS, Lockyer AE, de Souza CP, Noble LR. Molecular Characterisation of Intermediate Snail Hosts and the Search for Resistance Genes. Mem Inst Osw. Cruz. 1998;93(1):111–116. doi: 10.1590/S0074-02761998000700015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Webster JP, Shrivastava J, Johnson PJ, Blair L. Is host-schistosome coevolution going anywhere? BMC Evol Bio. 2007;7:9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lu DB, Wang TP, Rudge JW, Donnelly CA, Fang GR, Webster JP. Evolution in a multi-host parasite: chronobiological circadian rhythm and population genetics of Schistosoma japonicum cercariae indicates contrasting definitive host reservoirs by habitat. Int J Parasitol. 2009;39:1581–1588. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2009.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lu DB, Wang TP, Rudge JW, Donnelly CA, Fang GR, Webster JP. Contrasting reservoirs for Schistosoma japonicum between marshland and hilly regions in Anhui, China–a two-year longitudinal parasitological survey. Parasitol. 2010;137(1):99–110. doi: 10.1017/S003118200999103X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Campbell G, Jones CS, Lockyer AE, Hughes S, Brown D, Noble LR, et al. Molecular evidence supports an African affinity of the Neotropical freshwater gastropod, Biomphalaria glabrata, Say 1818, an intermediate host for Schistosoma mansoni. Proc R Soc Lond Ser B Biol. 2000;267:2351–2358. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2000.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Abe EM. Studies on diversity, molecular characterization and spatial distribution of vector snails in Nasarawa State, Nigeria. Ph.D. Thesis 2015. Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta, Nigeria.
- 23.Akinwale O, Oso O, Salawu O, Odaibo A, Tang P, Chen TW, et al. Molecular characterisation of Bulinus snails intermediate hosts of schistosomes in Ogun State, South-western Nigeria. Fol Malacol. 2015; 23;1-12. doi.10.12657/folmal.023.009
- 24.Rollinson D, Knopp S, Levitz S, Stothard RJ, TchuemTchuente L, Garba A, et al. Time to set the agenda for schistosomiasis elimination. Acta Trop. 2014;128:423–440. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2012.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.World Health Organization The control of schistosomiasis: report of a WHO expert committee. WHO Tech Rep Ser. 1985;728:1–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ren G, Liang Y. African schistosomiasis. People's Med: Publishing House, Beijing; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 27.http//:www.ncbi/BLAST/index/html. Accessed on 25 June, 2017.
- 28.Brown DS, Kristensen TK. A fish guide to freshwater snails. 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Brown DS. Freshwater snails of Africa and their medical importance. 2nd ed. Taylor and Francis; 1994.
- 30.Raghavan N, Knight M. The snail (Biomphalaria glabrata) genome project. TRENDS in Parasitol. 2006;22(4):148–151. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2006.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rollinson D, Stothard JR, Southgate VR. Interactions between intermediate snail hosts of the genus Bulinus and schistosomes of the Schistosoma haematobium group. Parasitol. 2001;123:S245–S260. doi: 10.1017/s0031182001008046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hassan AO, Amoo AOJ, Akinwale OP, Adeleke MA, Gyang PV. Molecular characterization and detection of infection in vector snails of urinary schistosomiasis around Erinle and Eko Ende Dams in South West. Nigeria. Brit Micro Res J. 2016;14(1):1–10.
- 33.Hamburger J. He-Na, Xu YS, Reda MR, Jourdane J, Ruppei A. A polymerase chain reaction assay for detecting snails infected with Bilharzia parasites (Schistosoma mansoni) from very early prepatency. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1998;59(6):872–876. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1998.59.872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hamburger J, Hoffman O, Kariuki C, Muchiri E, Ouma JH, Koech DK, et al. Large scale chain reaction-based surveillance of Schistosoma haematobium DNA in snails from transmission sites in coastal Kenya: a new tool for studying the dynamics of snail infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;71:765–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Amarir F, Sebti F, Abbasi I, Sadak A, Fellah H, Nhammi H, et al. Schistosoma haematobium detection in snails by DraI PCR and Sh110/Sm-Sl PCR: further evidence of the interruption of schistosomiasis transmission in Morocco. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:288. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-7-288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhang LJ, Li SZ, Wen LY, Lin DD, Abe EM, Zhu R, et al. The establishment and function of schistosomiasis surveillance system towards elimination in the People’s Republic of China. Adv Parasitol. 2016;92:117–137. doi: 10.1016/bs.apar.2016.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Abdel-Hamid ZA, Rawi SM, Arafa AF. Identification of a genetic marker associated with the resistance to Schistosoma mansoni infection using random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2006;101(8):863–868. doi: 10.1590/S0074-02762006000800007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mohamed AH, Sharaf El-Din AT, Mohamed AM, Habib MR. The relationship between genetic variability and the susceptibility of Biomphalaria alexandrina snails to Schistosoma mansoni infection. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2012;107(3):326–337. doi: 10.1590/S0074-02762012000300006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zein-Eddine R, Djuikwo-Teukeng FF, Al-Jawhari M, Senghor B, Huyse T, Dreyfuss G. Phylogeny of seven Bulinus species originating from endemic areas in three African countries, in relation to the human blood fluke Schistosoma haematobium. BMC Evol Biol. 2014;14:271. doi: 10.1186/s12862-014-0271-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Standley CJ, Goodacre SL, Wade CM, Stothard JR. The population genetic structure of Biomphalaria choanomphala in Lake Victoria. East Africa: implications for schistosomiasis transmission. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 41.Jarne P, Charlesworth D. The evolution of the selfing rate in functionally hermaphrodite plants and animals. Ann Rev Ecol Syst. 1993; 24, 441–466.
- 42.Hamilton WD, Axelrod R, Tanesse R. Sexual reproduction as an adaptation to resist parasites. Proc Nat Acad Sci. 1990;87:3566–3573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jarne P, Vianey-Liaud M, Delay B. Selfing and outcrossing in hermaphrodite freshwater gastropods (Basommatophora): where, when and why. Biol J Linn Soc. 1993;49:99–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8312.1993.tb00893.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Charbonnel N, Angers B, Rasatavonjizay R, Bremond P, Debain C, Jarne P. The influence of mating system, demography, parasites and colonization on the population structure of Biomphalaria pfeifferi in Madagascar. Mol Ecol. 2002;11:2213–2228. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294X.2002.01586.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Standley CJ, Goodacre S, Wade CM, Stothard JR. The population genetic structure of Biomphalaria choanomphala in Lake Victoria. East Africa: implications for schistosomiasis transmission. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 46.DeJong RJ, Morgan JAT, Lobato Paraense W, Pointier JP, Amarista M, Ayeh-Kumi PFK, et al. Evolutionary relationships and biogeography of Biomphalaria (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) with implications regarding its role as host of the human bloodfluke. Schistosoma mansoni. Mol Biol Evol. 2001;18:2225–2239. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a003769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Has W, Haberl B. Host recognition by trematode miracidaia and cercariae. In: Fried B, Graczyk TK, editors. Adv. in trem. biol. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 1997. pp. 196–227. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Spada RG, Silva D, Abdel-Hamid AZ, Sobral-Hamaguchi S, Zuim NR, Zanotti-Magalhaes EM, et al. Genetic markers between Biomphalaria glabrata snails susceptible and resistant to Schistosoma mansoni infection. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2002;97:53–58. doi: 10.1590/S0074-02762002000900012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lotfy WM, DeJong RJ, Black BS, Loker ES. Specific identification of Egyptian Biomphalaria species and possible hybrids using the polymerase chain reaction based on nuclear and mitochondrial loci. Mol Cell Prob. 2005;19:21–25. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2004.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sapp KK, Loker ES. Mechanisms underlying digenean-snail specificity: role of miracidial attachment and host plasma factors. J Parasitol. 2000;86:1012–1019. doi: 10.1645/0022-3395(2000)086[1012:MUDSSR]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.King KC, Stelkens RB, Webster JP, Smith DF, Brockhurst MA. Hybridization in parasites: consequences for adaptive evolution, pathogenesis, and public health in a changing world. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:e1005098. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nichols GL, Anderson Y, Lindgren E, Devaux I, Semenza JC. European monitoring systems and data for assessing environmental and climate impacts on human infectious diseases. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014;11(4):3894–3936. doi: 10.3390/ijerph110403894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Salawu OT, Odaibo AB. The bionomics and diversity of freshwater snails species in Yewa North, Ogun State. Southwestern Nigeria. Helminthol. 2014;51(4):337–44.
- 54.Abe EM, Ombugadu A, Oluwole AS, Njila HL, Mogaji HO, Adeniran AA, et al. Population abundance and bionomics of snail intermediate hosts of trematode parasites in Nasarawa State. Nigeria. Res J Parasitol. 2017:1–11. 10.3923/jp.2017.
- 55.Opisa S, Odiere MR, Jura WGZO, Kuranja DMS, Mwinzi PNM. Malacological survey and geographical distribution of vector snails for schistosomiasis within informal settlements of Kisumu City, western Kenya. Parasit Vectors. 2011;4:226. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-4-226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.de Kock KN, Wolmarans CT. Distribution and habitats of the Bulinus africanus species group, snail intermediate hosts of Schistosoma haematobium and S. mattheei in South Africa. Water SA. 2005;31:1. doi: 10.4314/wsa.v31i1.5128. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ibikounlé M, Mouahid G, Sakiti NG, Massougbodji A, Mone H. Freshwater snail diversity in Benin (West Africa) with a focus on human schistosomiasis. Acta Trop. 2009;111:29–34. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2009.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Elnaiem DE, Schorscher J, Bendall A, Obsomer V, Osman ME, Mekkawi AM, et al. Risk mapping of visceral leishmaniasis: the role of local variation in rainfall and altitude on the presence and incidence of kala-azar in eastern Sudan. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003, 68(1):10-7. [PubMed]
- 59.Senghor B, Diaw OT, Doucoure S, Seye M, Talla I, Diallo A, et al. Study of the snail intermediate hosts of urogenital schistosomiasis in Niakhar, region of Fatick. West central Senegal. Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 60.Lei ZL, Zheng H, Zhang LJ, Zhu R, Guo JG, Li SZ, et al. Schistosomiasis status in People’s Republic of China in 2004. Chin J Schisto Control. 2010;23(6):599–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Su ZM, He H, Tu ZW, Fan HP, Mao GX, Cao MM, et al. Surveillance of schistosomiasis in Hubei Province in 2010. Chin J Schisto Cont. 2010;23(4):438–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yang H, Xiao-Hua W, Zheng H, Wang LY, Guo JG, Xia G, et al. Schistosomiasis situation in People’s Republic of China in 2007. Chin J Schisto Cont. 2008;20(6):401–404. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Plummer M. l. Impact of invasive water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) on snail hosts of schistosomiasis in lake Victoria, East Africa. Ecol Health. 2005;2(1):81–86. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Holland BS. Chiaverano lM. Howard CK. Diminished fitness in an endemic Hawaiian snail in non-native host plants. Ethol Ecol Evol. 2016;12:1–12.
- 65.Boelee E, Laamrani H. Environmental control of schistosomiasis through community participation in a Moroccan oasis. Trop Med Int Health. 2004;9:997–1004. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2004.01301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Thomas JD, Tait AI. Control of snails hosts of schistosomiasis by environmental manipulation: a field and laboratory appraisal in the Ibadan area. Nigeria. Philosophical Trans Royal Soc Lond. 1984;B305:201–53. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 67.Oomen JMV, de Wolf J, Jobin WR. Health and Irrigation. Incorporation of Disease Control Measures in Irrigation, a Multi-faceted Task in Design, Construction, Operation. Intl Inst Land Reclam Improvement/ILRI Pub 45, Wageningen, 1990.
- 68.Steinmann P, Keiser J, Bos R, Tanner M, Utzinger J. Schistosomiasis and water resources development: systematic review, meta- analysis, and estimates of people at risk. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006;6:411–425. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70521-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Utzinger J, Raso G, Brooker S, De Savigny D, Tanner M, Ornbjerg N, et al. Schistosomiasis and neglected tropical diseases: towards integrated and sustainable control and a word of caution. Parasitol. 2009;136:1859–1874. doi: 10.1017/S0031182009991600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Driguez P, Doolan DL, Loukas A, Felgner PL, McManus DP. Schistosomiasis vaccine discovery using immunomics. Parasit Vectors. 2010;3:4. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-3-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Knight M, Arican-Goktas HD, Ittiprasert W, Odoemelam EC, Miller AN, Bridger JM. Schistosomes and snails: a molecular encounter. Front genet. 2014;5:230. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.McWilliam HE, Driguez P, Piedrafita D, McManus DP, Meeusen ENT. Discovery of novel Schistosoma japonicum antigens using a targeted protein microarray approach. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:290. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-7-290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Chen SB, Ai L, Hu W. New anti-schistosoma approaches in the People’s Republic of China: development of diagnostics, vaccines and other new techniques belonging to the ‘Omics’ group. Adv Parasitol. 2016;92:385–408. doi: 10.1016/bs.apar.2016.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kassegne K, Abe EM, Chen JH, Zhou XN. Immunomic approaches for antigen discovery of human parasites. Exp Rev Proteo. 2016:1–11. 10.1080/1478945020161252675. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 75.de Assis RR, Ludolf F, Nakajima R, Jasinskas A, Oliveira GC, Felgner PL, et al. A next-generation proteome array for Schistosoma mansoni. Intl J Parasitol. 2016;46(7):411–415. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2016.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Adema CM, Loker ES. Specificity and immunobiology of larval digenean-snail associations. In: Fried B, Graczyk TK, editors. Advances in trematode biology. Boca Raton and New York: CRC Press; 1997. pp. 229–263. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Allan F, Sousa-Figueiredo JC, Paulo R, Emery AM, Mirante C, Sebastiao A. Mapping freshwater snails in Angola: distribution, identity and molecular diversity of medically important taxa. Trop Med Intl Health. 2015;20:54–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 78.Adema CM, Bayne CJ, Bridger JM, Knight M, Loker ES, Yoshino TP, et al. Will all Scientists working on snails and the diseases they transmit please stand up? PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(12):e1835. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Fallon PG, Warren J, Behnke JM. Evaluation of immune-dependence of anthelmintic treatment of Heligmosomoides polygyrus in CBA/Ca mice. Intl J Parasitol. 1996;26(5):557–560. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(96)89383-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Sturrock RF. Schistosomiasis epidemiology and control: how did we get here and where should we go? Mem do Instit Oswaldo Cruz. 2001;96:17–27. doi: 10.1590/S0074-02762001000900003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Zheng Q, Vanderslott S, Jiang B, Xu LL, Liu CS, Huo LL, et al. Research gaps for three main tropical diseases in the People’s Republic of China. Infect Dis Poverty. 2013;2:15. doi: 10.1186/2049-9957-2-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Kloos H, McCullough FS. Plants with recognized molluscicidal activity. In: Mott KE, editor. Plant Molluscicides. New York: John Wiley; 1987. pp. 45–108. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Ding ZJ, Peng GY. Discussion of schistosomiasis infection source control. Chin J Schisto Cont. 2012;24(1):117–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Centre for Diseases Control. The life cycle of schistosomiasis. http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/schistosomiasis/biology.html 2013. Accessed 10 September, 2016.
- 85.Nalugwa A, Jørgensen A, Nyakaana S, Kristensen TK. Molecular phylogeny of Bulinus (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) reveals the presence of three species complexes in the Albertine Rift freshwater bodies. Int J Genet Mol Biol. 2010;2:130–139. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Plam M, Jorgensen A, Kristensen TK, Madsen H. Sympatric Biomphalaria species (Gastropoda: Planorbidae) in Lake Albert, Uganda, show homoplasies in shell morphology. African Zoology 2008; 43(1):34-44. doi.org/10.3377/1562-7020
- 87.Jorgensen A, Kristensen TK, Stothard JR. Phylogeny and biogeography of African Biomphalaria (Gastropoda: Planorbidae), with emphasis on endemic species of the great African lakes. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2007;151(2):337–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1096-3642.2007.00330.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Mohamed AH., Ahmad HO, Amal AM. Heba MF. Population dynamics of freshwater snails (Mollusca: Gastropoda) at Qena Governorate, Upper Egypt. Egypt Acad J Biol Sci. 2011; 3(1): 11 -22
- 89.Allan F, Rollinson D, Smith JE, Dunn AM. Host choice and penetration by Schistosoma haematobium miracidia. J Helminth. 2009;83:33–38. doi: 10.1017/S0022149X08073628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Stauffer JR, Jr, Madsen H, Webster B, Black K, Rollinson D, Konings A. Schistosoma haematobium in Lake Malawi: susceptibility and molecular diversity of the snail hosts Bulinus globosus and B. nyassanus. J Helminthol. 2008;82:377–382. doi: 10.1017/S0022149X08056290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Multilingual abstracts in the four official working languages of the United Nations. (PDF 514 kb)
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable


