Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this study was to review previously published meta-analyses on the effectiveness of dietary fiber on type 2 diabetes.
Methods
An umbrella review of all published meta-analyses was performed. A PubMed search from January 1, 1980, to April 30, 2017, was conducted using the following search strategy: (fiber OR glucan OR psyllium) AND (meta-analysis OR systematic review). Only English-language publications that provided quantitative statistical analysis on type 2 diabetes, fasting blood glucose concentrations, or glycosylated hemoglobin were retrieved.
Results
Sixteen meta-analyses were retrieved for inclusion in this umbrella review. In the meta-analyses comparing highest versus lowest dietary fiber intake, there was a statistically significant reduction in the relative risk (RR) of type 2 diabetes (RR = 0.81-0.85), with the greatest benefit coming from cereal fibers (RR = 0.67-0.87). However, statistically significant heterogeneity was observed in all of these meta-analyses. In the meta-analyses of supplementation studies using β-glucan or psyllium fibers on type 2 diabetic participants, statistically significant reductions were identified in both fasting blood glucose concentrations and glycosylated hemoglobin percentages.
Conclusion
This review suggests that those consuming the highest amounts of dietary fiber, especially cereal fiber, may benefit from a reduction in the incidence of developing type 2 diabetes. There also appears to be a small reduction in fasting blood glucose concentration, as well as a small reduction in glycosylated hemoglobin percentage for individuals with type 2 diabetes who add β-glucan or psyllium to their daily dietary intake.
Key Indexing Terms: Blood Glucose; Dietary Fiber; Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2; Hemoglobin A, Glycosylated
Introduction
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates there are 30 million people with type 2 diabetes in the United States, and most will, at some point in their life, develop some form of vascular complication.1 These vascular complications can present in the form of microvascular disease (retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy) and/or macrovascular disease (coronary heart disease, stroke, or peripheral artery disease).2, 3 These serious complications of diabetes confer substantial morbidity and impair patient quality of life. It has been estimated that diabetes costs the United States more than $174 billion per year when taking into account medical costs and loss of productivity.4
Both microvascular and macrovascular complications are thought to be due to prolonged hyperglycemia, which promotes an increase in oxidative stress, inflammation, and vascular damage.2, 3 Evidence indicates that medical interventions designed to lower blood glucose concentrations can reduce the risk of developing microvascular and macrovascular complications.5 One of these interventions includes a low glycemic index diet. Because increased fiber content decreases the glycemic index of foods, the American Diabetes Association encourages diabetics to consume a variety of fiber-containing foods.6 Unfortunately the blood glucose–lowering effects of fiber intake have not been consistently reported in the literature, with some clinical intervention studies reporting improvements in fasting blood glucose control and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) percentages,7, 8, 9, 10 but others reporting no improvement.11, 12, 13, 14, 15
Many of the clinical trials conducted to study the effects of dietary fiber intake on type 2 diabetes may have had sample sizes that did not provide sufficient statistical power to detect small, potentially meaningful changes in effect. Given the inconsistency of the existing literature and the insufficient statistical power as a result of small sample sizes, a pooling of information from individual trials could provide a more precise and accurate estimate of dietary fibers role in reducing the incidence of type 2 diabetes. To achieve this result, many investigators have turned to performing a powerful statistical method known as meta-analysis. Meta-analyses are fundamental in providing the highest level of evidence to best inform health care decision making. Therefore, the purpose and objective of this paper is to summarize the evidence from previously published meta-analyses regarding the effectiveness of dietary fiber as a therapeutic agent for type 2 diabetes.
Methods
An umbrella review was selected for this study. An umbrella review provides a summary of existing published meta-analyses and systematic reviews and determines whether authors addressing similar review questions independently observe similar results and arrive at similar conclusions.16
Because meta-analyses began appearing in medical literature in the early 1980s, a systematic literature search of PubMed and CINAHL from January 1, 1980, to April 30, 2017, was conducted using the following search strategy: “(fiber OR fibre OR chitosan OR fructan OR glucan OR gums OR inulin OR lignin OR pectin OR psyllium OR bran) AND (meta-analysis OR systematic review).” The titles and abstracts from the literature search were scanned, and only English-language publications that provided quantitative statistical analysis on type 2 diabetes, fasting blood glucose concentrations, and glycosylated hemoglobin were retrieved. Meta-analyses or systematic reviews that did not present study-specific summary data using a minimum of 4 randomized controlled trials were excluded.
For the published papers that were accepted into this review, the following information was extracted and entered into an Excel spreadsheet: number of publications included in the meta-analysis, number of total participants, fiber type and daily dose, pooled treatment effects for clinical endpoints (such as fasting blood glucose concentrations or glycosylated hemoglobin percentages), and/or summary relative risks. Although not always present, the meta-analyses were also analyzed for their disclosure of quality assessment, statistical heterogeneity (Cochrane Q test and I2 statistic) and publication bias (visual inspection of funnel plots and Egger or Begg regression test). A methodological quality appraisal was conducted for all meta-analyses using the Critical Appraisal Checklist for Systematic Reviews, which was developed by the Umbrella Review Methodology Working Group.17 This checklist consists of 10 items where each item within the instrument can receive 1 point for an overall quality score that could range from 0 to 10. Meta-analyses with quality scores ranging from 0 to 4 were labeled as low quality, those with scores between 5 and 7 as medium quality, and those with scores of 8 to 10 as high quality. Because this is a descriptive summary review of meta-analyses, no statistical analyses were performed.
Results
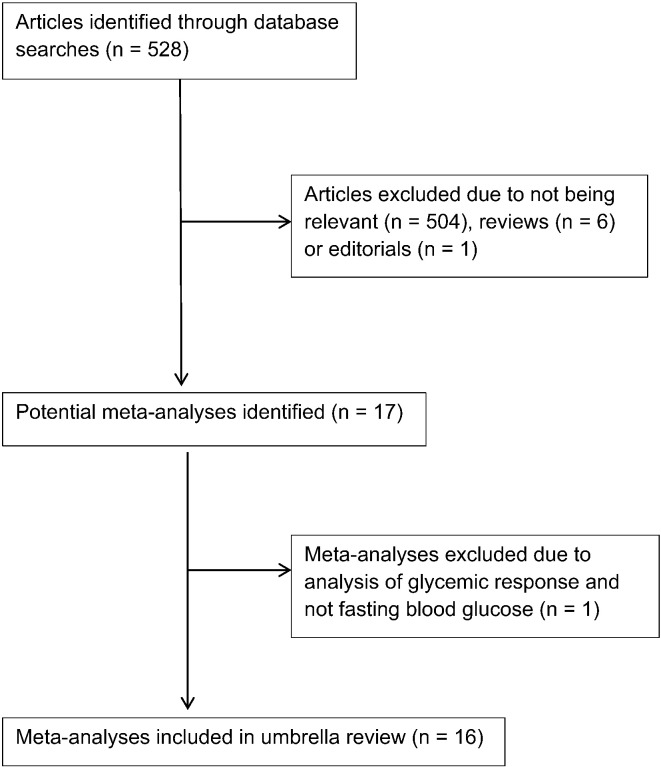
The initial search strategy identified 528 articles and, after careful review, 17 meta-analyses were retrieved for inclusion into this umbrella review.17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33 One meta-analysis was excluded because it analyzed studies that administered a soluble fiber (resistant maltodextrin) for acutely reducing glycemic response with participants on a high-carbohydrate diet.20 A flow chart of the meta-analyses selection process is provided in Figure 1.
Fig 1.
Flow chart of meta-analysis selection.
In regard to the methodological quality of the remaining 16 meta-analyses in this umbrella review, the mean quality appraisal score was 8/10, where 12 (75%) meta-analyses satisfied high-quality scoring between 8 and 10; 3 (19%) satisfied medium-quality scoring between 5 and 7; and 1 (6%) satisfied low-quality scoring with a score of 4 out of 10. Although the meta-analysis by Post et al23 had been deemed lower quality, it was still included in this umbrella review because it provided useful information regarding the effectiveness of dietary fiber as a therapeutic agent for people with type 2 diabetes.
The meta-analyses presented in Table 1 are based on dietary surveys that compare the highest versus lowest daily dietary fiber consumption on the incidence of developing type 2 diabetes. For populations that consumed the highest dietary fiber intake, the incidence of type 2 diabetes was significantly reduced in all 3 meta-analyses, with the relative risk ranging between 0.81 and 0.85 (Table 1). However, for all 3 meta-analyses, statistically significant heterogeneity was noted. For populations that consumed the highest cereal fiber intake, the incidence of type 2 diabetes was significantly reduced in all 4 meta-analyses, with the relative risk ranging between 0.67 and 0.87. But again, statistically significant heterogeneity was noted in all 4 meta-analyses, as well as statistically significant publication bias being identified in 2 of the 4 meta-analyses. In the 4 meta-analyses that compared populations consuming either the highest intakes of fruit or vegetable fiber, there was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of developing type 2 diabetes when compared with those consuming the lowest intakes. The relative risks ranged between 0.94 and 1.04 in both the fruit and vegetable fiber categories.
Table 1.
High vs Low Dietary Fiber Intake on the Incidence of Developing Type 2 Diabetes
| Meta-analysis Authors and Date | No. of Studies in Meta-analysis | No. of Participants in Meta-analysis | Total Dietary Fiber Relative Rate; P Value; Q-Test P Value; I2 Statistic; Publication Bias P Value |
Cereal Fiber Relative Rate; P Value; Q-Test P Value; I2 Statistic; Publication Bias P Value |
Fruit Fiber Relative Rate; P Value; Q-Test P Value; I2 Statistic; Publication Bias P Value |
Vegetable Fiber Relative Rate; P Value; Q-Test P Value; I2 Statistic; Publication Bias P Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schulze et al, 200718 | 9 | 432 730 | 0.67, P < .05 0.04, NR NR |
0.96, NS NS, NR NR |
1.04, NS NS, NR NR |
|
| Ye et al, 201219 | 10 | 350 241 | 0.84, P < .05 0.04, 44% NS |
0.87, P < .05 0.001, 74% NS |
||
| Yao et al, 201417 | 11 | 359 167 | 0.81, P < .05 0.014, 54% NS |
0.77, P < .05 0.011, 56% 0.004 |
0.94, NS NS, 29% NS |
0.95, NS 0.008, 60% NS |
| InterAct Consortium, 201521 | 14 | 414 711 | 0.85, P < .05 0.002, 61% NS |
0.77, P < .05 0.001, 78% 0.004 |
0.95, NS NS, 17% 0.04 |
0.96, NS 0.04, 48% 0.000 |
| Wang et al, 201522 | 11 | 448 287 | 1.00, NS NS, 1.5% NS |
0.94, NS 0.005, 53% NS |
NR, not reported; NS, not significant.
The 2 meta-analyses that analyzed clinical studies administering soluble fiber supplementation in participants with type 2 diabetes reported statistically significant reductions in fasting blood glucose concentrations of 15.3 and 10.0 mg/dL (Table 2). It appears that a higher average daily dose of 18 g/day of soluble fiber resulted in a greater reduction in fasting blood glucose concentrations compared with the lesser dose of 11 g/day. In the 7 meta-analyses that analyzed clinical studies that exclusively used β-glucan supplementation, there were mixed results; only 4 of the 7 meta-analyses reported statistically significant reductions in fasting blood glucose concentrations. With the 4 meta-analyses that reported statistically significant reductions in blood glucose concentrations, the changes noted included 2.3, 7.0, 9.4, and 44.6 mg/dL. However, statistically significant heterogeneity was identified in 2 of the 4 of these meta-analyses. There is considerable heterogeneity in the individual clinical studies selected and used by these 7 meta-analyses on β-glucan supplementation: 62% of the 47 individual citations were used only once (Table 3).11, 12, 14, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 42, 43, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56
Table 2.
Effects of Increased Fiber Intake on Changes in Fasting Blood Glucose Concentrations
| Meta-analysis Authors and Date | No. of Studies in Meta-analysis | No. of Participants in Meta-analysis | Fiber Type and Dose/Day | Mean Duration in Weeks | Reduction in Fasting Blood Glucose Concentration in mg/dL | Q Test P Value and I2 Statistic |
Egger or Begg Test P Value | Quality Assessment and Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post et al, 201223a | 13 T2D | 400 | Soluble 18 g | 8 | ↓ 15.3, P < .001 | NS, 5% | GRADE 9/13 high quality |
|
| Silva et al, 201324 | 8 T2D | 496 | Soluble 11 g | 12 | ↓ 10.0, P < .05 | P < .001, 96% | NS | GRADE NR |
| Tiwari and Cummins, 201125 | 22 | 487 | β-Glucan 6 g | 6 | ↓ 44.6, P < .001 | P < .001, 97% | NS | |
| Bao et al, 201426 | 12 | 630 | β-Glucan 5.5 g | 8 | ↓ 0.7, NS | P < .001, 68% | NS | Jadad scale 7/12 high quality |
| Zhu et al, 201527 | 8 | 378 | β-Glucan 5 g | 6.5 | ↓ 0.4, NS | NS, 0% | NS | Jadad scale 4/8 high quality |
| Zou et al, 201528 | 12 | 603 | β-Glucan 5 g | 6 | ↓ 0.9, NS | NS, 0% | NS | Jadad scale 7/12 high quality |
| Hou et al, 201529 | 6 T2D | 437 | β-Glucan NR | 4.5 | ↓ 7.0, P < .001 | NS, 0% | NOS 5/6 high quality |
|
| Shen et al, 201630 | 4 T2D | 239 | β-Glucan 3g | 4.5 | ↓ 9.4, P < .01 | NS, 0% | NS | Cochrane 3/4 high quality |
| He et al, 201631 | 16 | 933 | β-Glucan 5.5g | 7.5 | ↓ 2.3, P < .01 | P < .001, 99% | ||
| Gibb et al, 201532 | 4 T2D 14 |
245 1267 |
Psyllium 12g Psyllium 10 g |
8.5 9.5 |
↓ 37.0, P < .05 ↓ 1.6, NS |
P < .05, 61% P < .05, 68% |
||
| Liu et al, 201633 | 15 | 579 | Fructans 12.5 g | 7.5 | ↓ 0.9, NS | NS, 26% | P < .05 | Cochrane 4/15 high quality |
NOS, Newcastle-Ottawa Scale; NR, not reported; NS, not significant; T2D, participants with type 2 diabetes only.
Low-quality score on the Critical Appraisal Checklist for Systematic Reviews.
Table 3.
Citation Matrix for Meta-analyses on β-glucan Supplementation Studies
| Studies | He et al, 201631 16 citations |
Shen et al, 201630 4 T2D citations |
Hou et al, 201529 6 T2D citations |
Zou et al, 201528 12 citations |
Zhu et al, 201527 8 citations |
Bao et al, 201426 12 citations |
Tiwari and Cummins 2011,25a 22 citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ballesteros et al, 201534 | Yes | ||||||
| Beck et al, 201035 | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Biorklund et al, 200536 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Biorklund et al, 200814 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Charlton et al, 201237 | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Cugnet-Anceau et al, 201012 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| Davy et al, 200238 | Yes | Yes | |||||
| DeNatale et al, 201239 | Yes | ||||||
| Granfeldt et al, 200840 | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Johansson et al, 201441 | Yes | ||||||
| Kabir et al, 200242 | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Keogh et al, 200343 | Yes | ||||||
| Li et al, 201144 | Yes | ||||||
| Liatis et al, 200945 | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Lovegrove et al, 200046 | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Ma et al, 201347 | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Maki et al, 200748 | Yes | ||||||
| McGeoch et al, 201311 | Yes | ||||||
| McIntosh et al, 199149 | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Onning et al, 199950 | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Queenan et al, 200751 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| Reyna et al, 200352 | Yes | ||||||
| Reyna-Villasmil et al, 200753 | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Rondanelli et al, 201154 | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Saltzman et al, 200155 | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Stevens et al, 198556 | Yes | ||||||
| Tighe et al, 201057 | Yes | ||||||
| Uusitupa et al, 199258 | Yes | ||||||
| Zhang et al, 201259 | Yes | Yes |
T2D, participants with type 2 diabetes only.
In the meta-analysis by Tiwari and Cummins,25 only 4 of the 22 citations were common to those listed here. The total number of individual citations combined for all 7 meta-analyses is 47, and 29 are cited only once (62%).
The meta-analysis on psyllium supplementation was only statistically significant for the participants with type 2 diabetes with a fasting blood glucose reduction of 37.0 mg/dL, but again there was statistically significant heterogeneity. The meta-analysis on fructan supplementation studies identified no statistical significant reduction in fasting blood glucose concentrations.
Two of the 3 meta-analyses that investigated β-glucan supplementation on changes in fasting insulin concentrations reported statistically significant reductions, with both of these meta-analyses reporting reductions of 6.3 pmol/L (Table 4). However, 1 of the 2 meta-analyses had statistically significant heterogeneity. The meta-analysis on fructan supplementation studies reported no statistically significant reduction in fasting insulin concentrations.
Table 4.
Effects of Increased Fiber Intake on Changes in Fasting Insulin Concentrations
| Meta-analysis Authors and Date | No. of Studies in Meta-analysis | No. of Participants in Meta-analysis | Fiber Type and Dose/Day | Mean Duration in Weeks | Reduction in Insulin Concentrations in pmol/L | Q Test P Value and I2 Statistic |
Egger or Begg Test P Value | Quality Assessment and Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bao et al, 201426 | 9 | 496 | β-Glucan 5.5 g | 8 | ↓ 6.3, P < .05 | NS, 0% | NS | Jadad scale 6/9 high quality |
| Zou et al, 201528 | 6 | 283 | β-Glucan 3.5 g | 6 | ↓ 0.8, NS | NS, 0% | NS | Jadad scale 4/6 high quality |
| He et al, 201631 | 10 | 597 | β-Glucan 5 g | 8 | ↓ 6.3, P < .05 | P < .001, 98% | ||
| Liu et al, 201633 | 13 | 432 | Fructans 13 g | 7 | ↓ 0.7, NS | P < .001, 88% | P < .05 | Cochrane 4/13 high quality |
NS, not significant.
Five meta-analyses examined the effects of fiber supplementation on HbA1c, and all 5 assessed clinical studies that involved participants with type 2 diabetes (Table 5). The observed reductions in HbA1c for all 5 meta-analyses ranged between 0.21% and 0.52%, and 4 of the 5 meta-analyses reported that their differences were statistically significant. Only 1 of these 4 meta-analyses presenting with statistically significant changes in HbA1c had statistically significant heterogeneity.
Table 5.
Effects of Increased Fiber Intake on Changes in HbA1c%
| Meta-analysis Authors and Date | No. of Studies in Meta-analysis | No. of Participants in Meta-analysis | Fiber Type and Dose/Day | Mean Duration in Weeks | Reduction in HbA1c% | Q Test P Value and I2 Statistic |
Egger or Begg Test P Value | Quality Assessment and Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post et al, 201223a | 10 T2D | 324 | Soluble 16 g | 8 | ↓ 0.26, P < .05 | NS, 21% | GRADE 9/10 high quality |
|
| Silva et al, 201324 | 11 T2D | 605 | Soluble 15 g | 11 | ↓ 0.52, P < .05 | P < .001, 94% | NS | GRADE NR |
| Hou et al, 201529 | 6 T2D | 437 | β-Glucan NR | 4.5 | ↓ 0.42, P < .001 | NS, 18% | NOS 5/6 high quality |
|
| Shen et al, 201630 | 4 T2D | 139 | β-Glucan 3 g | 4.5 | ↓ 0.21, P < .05 | NS, 0% | NS | Cochrane 3/4 high quality |
| He et al, 201631 | 4 T2D | 229 | β-Glucan 3.5 g | 5.5 | ↓ 0.22, NS | P < .001, 92% |
HbA1c%, glycosylated hemoglobin percentage; NOS, Newcastle-Ottawa Scale; NR, not reported; NS, not significant; T2D, participants with type 2 diabetes only.
Low-quality score on the Critical Appraisal Checklist for Systematic Review.
Discussion
In this umbrella review, 3 meta-analyses presented with statistically significant findings ranging between a 15% to 19% reduction in the incidence of developing type 2 diabetes when comparing participants with the highest intakes of total dietary fiber to those with the lowest intakes (see Table 1).17, 19, 21 Moreover, when total dietary fiber was separated into cereal, fruit, and vegetable fiber groups, it appeared that only cereal fiber significantly reduced the incidence of developing type 2 diabetes because a 17% to 33% statistically significant reduction was observed with all 4 meta-analyses that compared participants with the highest intakes of total cereal fiber to those with the lowest intakes.17, 18, 19, 21 However, we must appreciate these positive results with some caution because statistically significant heterogeneity was noted in all 3 meta-analyses on total dietary fiber, as well as all 4 meta-analyses on cereal fiber. Heterogeneity may be due to the wide variation in study design with differences in the number and characteristics of participants surveyed (such as age, sex, body mass index, total energy intake, and overall health status), as well as differences in the amounts and compositions of dietary fibers consumed and study duration.
If an increase in the consumption of cereal fibers can truly reduce the incidence of type 2 diabetes, the mechanism of action may be achieved through a reduction in both fasting blood glucose and insulin concentrations. This occurs because cereals made from oats and barley possess water-soluble gel-forming fibers such as β-glucan. These dietary fibers form a viscous solution in the small intestine, which reduces the contact and mixing of macronutrients with digestive enzymes, and this delays the absorption of glucose, which consequently reduces the postprandial plasma glucose and insulin levels.60
However, only 6 of the 11 meta-analyses on interventional fiber supplementation studies reported that increased dietary fiber was associated with a reduction in fasting blood glucose concentrations (see Table 2), and only 2 of the 4 meta-analyses on fasting insulin concentrations was associated with significant reductions (see Table 4).23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33 Moreover, only 4 of the 7 meta-analyses analyzing interventional studies on β-glucan supplementation reported statistically significant reductions in fasting blood glucose, with reductions ranging widely between 2.3 to 44.6 mg/dL. It should be noted that 2 of these 4 meta-analyses used participants who had type 2 diabetes, whereas 3 of the 5 meta-analyses on participants without diabetes reported only small nonsignificant reductions in blood glucose concentrations. A similar finding was also noted with the only meta-analysis that looked at psyllium supplementation studies, which separated their studies by type 2 diabetic and nondiabetic participants.32 Just as noted in the β-glucan meta-analyses, the psyllium supplementation meta-analysis on participants with type 2 diabetes reported significant reductions in fasting blood glucose concentrations of 37 mg/dL, but the participants without diabetes had nonsignificant reductions of only 1.6 mg/dL. Also, 1 of the 2 meta-analyses identifying significant reductions in fasting insulin concentrations analyzed studies that used only participants with type 2 diabetes.26, 31
Based on these meta-analyses created from the dietary fiber interventional studies, it does not appear that the significant reductions in the incidence of type 2 diabetes noted with increased cereal fiber consumption are due to reductions in fasting blood glucose and insulin concentrations. Apart from soluble fibers like β-glucan, foods containing dietary fibers are also a rich source of magnesium. Magnesium is a co-factor for enzymes involved in glucose metabolism, such as tyrosine kinase, and it has been previously reported that there is an inverse association between dietary magnesium and the incidence of type 2 diabetes.61 Also, dietary fiber intake has been reported to be inversely associated with inflammatory markers such as interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor α that are central in the initiation and progression of type 2 diabetes.62
Although the changes in fasting blood glucose concentrations may not explain the reductions reported in the incidence of type 2 diabetes in participants who increase their dietary fiber intake, these reductions may have significant benefits on reducing the negative consequences brought on by both microvascular and macrovascular changes in participants with type 2 diabetes. Measuring a patient’s HbA1c is a good proxy measurement for assessing microvascular and macrovascular changes.63, 64, 65 In this umbrella review, 4 of the 5 meta-analyses reported statistically significant reductions in HbA1c ranging between 0.21% and 0.52%, and more promising is the observation that only 1 of these 4 meta-analyses had statistically significant heterogeneity (see Table 5).23, 24, 29, 30, 31 Although the percentage change in HbA1c is modest, it has potential to be clinically significant in light of the fact that the average change attributed to metformin ranges between 0.2% to 2%.23 It must be recognized that this positive effect on HbA1c is modest compared with some of the changes noted in fasting blood glucose concentrations, and this may simply be attributed to the fact that the duration of these studies averaged only 4.5 to 8 weeks, which is less than the customary 12 week retesting period for HbA1c. HbA1c represents a weighted average of the blood glucose concentration because 50% of glycation occurs in days 90 to 120 of the red blood cell’s 120-day average lifespan.66 Although HbA1c is considered the standard measurement of long-term glycemic control, HbA1c tests may not be clinically reliable, especially for short-term outcomes, and should therefore be interpreted with caution.67
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans state that the adequate intake value of dietary fiber consumption is 25 to 38 g/day, but the 2009-2010 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey indicated that the daily intake of fiber in the United States is only 17 g/day.68 Therefore, emphasizing fiber consumption for health promotion and disease prevention is a critical public health goal, and by aggressively promoting the Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommendations of at least 25 to 38 g/day of total dietary fiber, this may prevent a significant number of new cases of type 2 diabetes. Although the evidence in this umbrella review supports the beneficial association of dietary fiber on reducing the incidence of type 2 diabetes, there are still too few long-term, large population, randomized controlled trials that have undertaken the goal to analyze this potential causal relationship between dietary fiber and type 2 diabetes. Also, evidence is lacking to recommend a higher dietary fiber intake for patients with diabetes than for the population as a whole. Finally, although no tolerable upper limit has been established for total fiber intake, it should be noted that minor side effects have been reported, such as flatulence, abdominal bloating, loose stools or diarrhea and abdominal cramping.69
Limitations
This umbrella review has several limitations that should be acknowledged. First, confounding factors are always a potential threat to the validity of any meta-analysis. For instance, people who consume high dietary fiber intakes tend to have other healthy behaviors such as being physically active and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol intake. Fortunately, the majority of studies included in the meta-analyses that were involved in this umbrella review did adjust for potential confounding factors, but the possibility of residual confounders cannot be excluded. Second, self-reported dietary fiber intake is most often assessed using food frequency questionnaires, and because these dietary assessment tools were not specifically developed for dietary fiber intake, misclassifications and measurement errors regarding fiber doses and types are quite likely. This problem may also be compounded by the fact that dietary fiber may be defined differently by the various food frequency questionnaire databases in use.69 A third limitation is that the meta-analyses reviewed here represent a heterogeneous group of clinical studies composed from a diverse group of participants of different ages, sexes, races, and ethnic groups, and therefore readers are cautioned against specifying these results to any one specific sociodemographic group. Finally, as in all literature reviews, the quality of this umbrella review is directly related to the quality of the included meta-analyses, which are dependent on the design and reporting quality of the individual meta-analysis itself, as well as on the quality of the individual studies used to conduct the meta-analysis. Fortunately, the majority (94%) of the meta-analyses in this umbrella review were appraised as having moderate to high methodological quality.
Conclusion
This umbrella review suggests that there may be some evidence for dietary fiber intake, especially from cereal fibers, to be beneficial in the prevention of type 2 diabetes; however, these results should be considered with caution because of the statistically significant heterogeneity. There also appears to be a small reduction in fasting blood glucose concentration, as well as a small reduction in HbA1c percentage, for individuals with type 2 diabetes who add β-glucan or psyllium to their daily dietary intake. Therefore, people with type 2 diabetes should be encouraged to increase their dietary intake of foods that are rich in fiber, such as high-fiber cereals, or to use fiber supplements. Further studies using large multicenter randomized controlled trials are required to confirm these findings, and more studies evaluating HbA1c for durations of longer than 12 weeks are warranted. Moreover, future studies are required to explore the underlying mechanisms responsible for the relationship between dietary fiber intake and the reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes.
Funding Sources and Conflicts of Interest
No funding sources or conflicts of interest were reported for this study.
Contributorship Information
Concept development (provided idea for the research): M.P.M.
Design (planned the methods to generate the results): M.P.M.
Supervision (provided oversight, responsible for organization and implementation, writing of the manuscript): M.P.M.
Data collection/processing (responsible for experiments, patient management, organization, or reporting data): M.P.M.
Analysis/interpretation (responsible for statistical analysis, evaluation, and presentation of the results): M.P.M.
Literature search (performed the literature search): M.P.M.
Writing (responsible for writing a substantive part of the manuscript): M.P.M.
Critical review (revised manuscript for intellectual content, this does not relate to spelling and grammar checking): M.P.M.
Practical Applications
-
•
Dietary fiber consumption has been postulated to reduce the incidence of type 2 diabetes and the risk of microvascular and macrovascular complications in those with type 2 diabetes.
-
•
There is much discrepancy when it comes to randomized controlled studies on dietary fiber’s effects on these important clinical conditions.
-
•
By combining the meta-analyses on these clinical outcomes as an umbrella review, we can determine that increased dietary fiber intake may help reduce the incidence of type 2 diabetes, as well as reduce both fasting blood glucose concentrations and glycosylated hemoglobin percentages in people with type 2 diabetes.
Alt-text: Image 1
References
- 1.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Diabetes Surveillance System . US Department of Health and Human Services; Atlanta, GA: 2017. National Diabetes Statistics Report.http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/data/statistics/national-diabetes-statistics-report.pdf Available at: [Google Scholar]
- 2.Seaquist ER. Microvascular complications of diabetes. Strategies for managing retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy. Postgrad Med. 1998;103(1):61–63. doi: 10.3810/pgm.1998.01.273. 66-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stancoven A, McGuire DK. Preventing macrovascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus: glucose control and beyond. Am J Cardiol. 2007;99(11A):5H–11H. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ariza MA, Vimalananda VG, Rosenzweig JL. The economic consequences of diabetes and cardiovascular disease in the United States. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2010;11(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/s11154-010-9128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Woolf SH, Davidson MB, Greenfield S. Controlling blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. An evidence-based policy statement by the American Academy of Family Physicians and American Diabetes Association. J Fam Pract. 2000;49(5):453–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.American Diabetes Association Nutrition recommendations and interventions for diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(suppl 1):S61–S78. doi: 10.2337/dc08-S061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Karhunen LJ, Juvonen KR, Flander SM. A psyllium fiber-enriched meal strongly attenuates postprandial gastrointestinal peptide release in healthy young adults. J Nutr. 2010;140(4):737–744. doi: 10.3945/jn.109.115436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ziai SA, Larijani B, Akhoondzadeh S. Psyllium decreased serum glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin significantly in diabetic outpatients. J Ethnopharmacol. 2005;102(2):202–207. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2005.06.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Anderson JW, Allgood LD, Turner J, Oeltgen PR, Daggy BP. Effects of psyllium on glucose and serum lipid responses in men with type 2 diabetes and hypercholesterolemia. Am J Clin Nutr. 1999;70(4):466–473. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/70.4.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pacy PJ, Dodson PM, Kubicki AJ, Fletcher RF, Taylor KG. Effect of a high fibre, high carbohydrate dietary regimen on serum lipids and lipoproteins in type II hypertensive diabetic patients. Diabetes Res. 1984;1(3):159–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.McGeoch SC, Johnstone AM, Lobley GE. A randomized crossover study to assess the effect of an oat-rich diet on glycaemic control, plasma lipids and postprandial glycaemia, inflammation and oxidative stress in Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2013;30(11):1314–1323. doi: 10.1111/dme.12228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cugnet-Anceau C, Nazare JA, Biorklund M. A controlled study of consumption of beta-glucan-enriched soups for 2 months by type 2 diabetic free-living subjects. Br J Nutr. 2010;103(3):422–428. doi: 10.1017/S0007114509991875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, McKeown-Eyssen G. Effect of a low-glycemic index or a high-cereal fiber diet on type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2008;300(23):2742–2753. doi: 10.1001/jama.2008.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Biörklund M, Holm J, Onning G. Serum lipids and postprandial glucose and insulin levels in hyperlipidemic subjects after consumption of an oat beta-glucan-containing ready meal. Ann Nutr Metab. 2008;52(2):83–90. doi: 10.1159/000121281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, Augustin LS. Effect of wheat bran on glycemic control and risk factors for cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002;25(9):1522–1528. doi: 10.2337/diacare.25.9.1522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Aromataris E, Fernandez R, Godfrey CM, Holly C, Khalil H, Tungpunkom P. Summarizing systematic reviews: methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2015;13(3):132–140. doi: 10.1097/XEB.0000000000000055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yao B, Fang H, Xu W. Dietary fiber intake and risk of type 2 diabetes: A dose-response analysis of prospective studies. Eur J Epidemiol. 2014;29(2):79–88. doi: 10.1007/s10654-013-9876-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schulze MB, Schulz M, Heidemann C, Schienkiewitz A, Hoffmann K, Boeing H. Fiber and magnesium intake and incidence of type 2 diabetes: a prospective study and meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(9):956–965. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.9.956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ye EQ, Chacko SA, Chou EL, Kugizaki M, Liu S. Greater whole-grain intake is associated with lower risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and weight gain. J Nutr. 2012;142(7):1304–1313. doi: 10.3945/jn.111.155325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Livesey G, Tagami H. Interventions to lower the glycemic response to carbohydrate foods with a low-viscosity fiber (resistant maltodextrin): meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;89(1):114–125. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.26842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.InterAct Consortium Dietary fibre and incidence of type 2 diabetes in eight European countries: the EPIC-InterAct Study and a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Diabetologia. 2015;58(7):1394–1408. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3585-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wang PY, Fang JC, Gao ZH, Zhang C, Xie SY. Higher intake of fruits, vegetables or their fiber reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. J Diabetes Investig. 2016;7(1):56–69. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Post RE, Mainous AG, III, King DE, Simpson KN. Dietary fiber for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. J Am Board Fam Med. 2012;25(1):16–23. doi: 10.3122/jabfm.2012.01.110148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Silva FM, Kramer CK, de Almeida JC, Steemburgo T, Gross JL, Azevedo MJ. Fiber intake and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr Rev. 2013;71(12):790–801. doi: 10.1111/nure.12076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tiwari U, Cummins E. Meta-analysis of the effect of β-glucan intake on blood cholesterol and glucose levels. Nutrition. 2011;27(10):1008–1016. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2010.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bao L, Cai X, Xu M, Li Y. Effect of oat intake on glycaemic control and insulin sensitivity: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. 2014;112(3):457–466. doi: 10.1017/S0007114514000889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhu X, Sun X, Wang M. Quantitative assessment of the effects of beta-glucan consumption on serum lipid profile and glucoselevel in hypercholesterolemic subjects. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015;25(8):714–723. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2015.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zou Y, Liao D, Huang H, Li T, Chi H. A systematic review and meta-analysis of beta-glucan consumption on glycemic control in hypercholesterolemic individuals. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2015;66(4):355–362. doi: 10.3109/09637486.2015.1034250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hou Q, Li Y, Li L. The metabolic effects of oats intake in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2015;7(12):10369–10387. doi: 10.3390/nu7125536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Shen XL, Zhao T, Zhou Y, Shi X, Zou Y, Zhao G. Effect of oat β-glucan intake on glycaemic control and insulin sensitivity of diabetic patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrients. 2016;8(1) doi: 10.3390/nu8010039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.He LX, Zhao J, Huang YS, Li Y. The difference between oats and beta-glucan extract intake in the management of HbA1c, fasting glucose and insulin sensitivity: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Food Funct. 2016;7(3):1413–1428. doi: 10.1039/c5fo01364j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gibb RD, McRorie JW, Jr., Russell DA, Hasselblad V, D’Alessio DA. Psyllium fiber improves glycemic control proportional to loss of glycemic control: a meta-analysis of data in euglycemic subjects, patients at risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus, and patients being treated for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015;102(6):1604–1614. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.115.106989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Liu F, Prabhakar M, Ju J, Long H, Zhou HW. Effect of inulin-type fructans on blood lipid profile and glucose level: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2017;71(1):9–20. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2016.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ballesteros MN, Valenzuela F, Robles AE. One egg per day improves inflammation when compared to an oatmeal-based breakfast without increasing other cardiometabolic risk factors in diabetic patients. Nutrients. 2015;7(5):3449–3463. doi: 10.3390/nu7053449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Beck EJ, Tapsell LC, Batterham MJ, Tosh SM, Huang XF. Oat beta-glucan supplementation does not enhance the effectiveness of an energy-restricted diet in overweight women. Br J Nutr. 2010;103(8):1212–1222. doi: 10.1017/S0007114509992856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Biörklund M, van Rees A, Mensink RP, Onning G. Changes in serum lipids and postprandial glucose and insulin concentrations after consumption of beverages with beta-glucans from oats or barley: a randomized dose-controlled trial. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2005;59(11):1272–1281. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Charlton KE, Tapsell LC, Batterham MJ. Effect of 6 weeks' consumption of β-glucan-rich oat products on cholesterol levels in mildly hypercholesterolaemic overweight adults. Br J Nutr. 2012;107(7):1037–1047. doi: 10.1017/S0007114511003850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Davy BM, Davy KP, Ho RC, Beske SD, Davrath LR, Melby CL. High-fiber oat cereal compared with wheat cereal consumption favorably alters LDL-cholesterol subclass and particle numbers in middle-aged and older men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;76(2):351–358. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/76.2.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.De Natale C, Minerva V, Patti L. Effects of baked products enriched with n-3 fatty acids, folates, β-glucans, and tocopherol in patients with mild mixed hyperlipidemia. J Am Coll Nutr. 2012;31(5):311–319. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2012.10720427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Granfeldt Y, Nyberg L, Björck I. Muesli with 4 g oat beta-glucans lowers glucose and insulin responses after a bread meal in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2008;62(5):600–607. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Johansson-Persson A, Ulmius M, Cloetens L, Karhu T, Herzig KH, Onning G. A high intake of dietary fiber influences C-reactive protein and fibrinogen, but not glucose and lipid metabolism, in mildly hypercholesterolemic subjects. Eur J Nutr. 2014;53(1):39–48. doi: 10.1007/s00394-013-0496-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kabir M, Oppert JM, Vidal H. Four-week low-glycemic index breakfast with a modest amount of soluble fibers in type 2 diabetic men. Metabolism. 2002;51(7):819–826. doi: 10.1053/meta.2002.33345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Keogh GF, Cooper GJ, Mulvey TB. Randomized controlled crossover study of the effect of a highly beta-glucan-enriched barley on cardiovascular disease risk factors in mildly hypercholesterolemic men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003;78(4):711–718. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/78.4.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Li L, Zhang J, Song P, Wang C, Man Q, Meng L. Effect of oat on blood lipids level of middle-aged and elderly men with hypercholesterolemia. J Chin Inst Food Sci Technol. 2011;11(4):102–107. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Liatis S, Tsapogas P, Chala E. The consumption of bread enriched with betaglucan reduces LDL-cholesterol and improves insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2009;35(2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2008.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lovegrove JA, Clohessy A, Milon H, Williams CM. Modest doses of beta-glucan do not reduce concentrations of potentially atherogenic lipoproteins. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72(1):49–55. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/72.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ma X, Gu J, Zhang Z. Effects of Avena nuda L. on metabolic control and cardiovascular disease risk among Chinese patients with diabetes and meeting metabolic syndrome criteria: secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2013;67(12):1291–1297. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2013.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Maki KC, Galant R, Samuel P. Effects of consuming foods containing oat beta-glucan on blood pressure, carbohydrate metabolism and biomarkers of oxidative stress in men and women with elevated blood pressure. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2007;61(6):786–795. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.McIntosh GH, Whyte J, McArthur R, Nestel PJ. Barley and wheat foods: influence on plasma cholesterol concentrations in hypercholesterolemic men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991;53(5):1205–1209. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/53.5.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Onning G, Wallmark A, Persson M, Akesson B, Elmståhl S, Oste R. Consumption of oat milk for 5 weeks lowers serum cholesterol and LDL cholesterol in free-living men with moderate hypercholesterolemia. Ann Nutr Metab. 1999;43(5):301–309. doi: 10.1159/000012798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Queenan KM, Stewart ML, Smith KN, Thomas W, Fulcher RG, Slavin JL. Concentrated oat beta-glucan, a fermentable fiber, lowers serum cholesterol in hypercholesterolemic adults in a randomized controlled trial. Nutr J. 2007;6:6. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-6-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Reyna NY, Cano C, Bermúdez VJ. Sweeteners and beta-glucans improve metabolic and anthropometrics variables in well controlled type 2 diabetic patients. Am J Ther. 2003;10(6):438–443. doi: 10.1097/00045391-200311000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Reyna-Villasmil N, Bermúdez-Pirela V, Mengual-Moreno E. Oat-derived beta-glucan significantly improves HDLC and diminishes LDLC and non-HDL cholesterol in overweight individuals with mild hypercholesterolemia. Am J Ther. 2007;14(2):203–212. doi: 10.1097/01.pap.0000249917.96509.e7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Rondanelli M, Opizzi A, Monteferrario F, Klersy C, Cazzola R, Cestaro B. Beta-glucan- or rice bran-enriched foods: a comparative crossover clinical trial on lipidic pattern in mildly hypercholesterolemic men. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2011;65(7):864–871. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2011.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Saltzman E, Das SK, Lichtenstein AH. An oat-containing hypocaloric diet reduces systolic blood pressure and improves lipid profile beyond effects of weight loss in men and women. J Nutr. 2001;131(5):1465–1470. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.5.1465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Stevens J, Burgess MB, Kaiser DL, Sheppa CM. Outpatient management of diabetes mellitus with patient education to increase dietary carbohydrate and fiber. Diabetes Care. 1985;8(4):359–366. doi: 10.2337/diacare.8.4.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Tighe P, Duthie G, Vaughan N. Effect of increased consumption of whole-grain foods on blood pressure and other cardiovascular risk markers in healthy middle-aged persons: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;92(4):733–740. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2010.29417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Uusitupa MI, Ruuskanen E, Mäkinen E. A controlled study on the effect of beta-glucan-rich oat bran on serum lipids in hypercholesterolemic subjects: relation to apolipoprotein E phenotype. J Am Coll Nutr. 1992;11(6):651–659. doi: 10.1080/07315724.1992.10718264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhang J, Li L, Song P. Randomized controlled trial of oatmeal consumption versus noodle consumption on blood lipids of urban Chinese adults with hypercholesterolemia. Nutr J. 2012;11:54. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-11-54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Bernstein AM, Titgemeier B, Kirkpatrick K, Golubic M, Roizen MF. Major cereal grain fibers and psyllium in relation to cardiovascular health. Nutrients. 2013;5(5):1471–1487. doi: 10.3390/nu5051471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Dong JY, Xun P, He K, Qin LQ. Magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes: meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Care. 2011;34(9):2116–2122. doi: 10.2337/dc11-0518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Wannamethee SG, Whincup PH, Thomas MC, Sattar N. Associations between dietary fiber and inflammation, hepatic function, and risk of type 2 diabetes in older men: potential mechanisms for the benefits of fiber on diabetes risk. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(10):1823–1825. doi: 10.2337/dc09-0477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(14):977–986. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309303291401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Shankar A, Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE. Association between glycosylated hemoglobin level and 16-year incidence of chronic kidney disease in type 1 diabetes. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2007;115(3):203–206. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-956170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Shankar A, Klein R, Klein BE, Moss SE. Association between glycosylated hemoglobin level and cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in type 1 diabetes. Am J Epidemiol. 2007;166(4):393–402. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwm096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Reynolds TM, Smellie WS, Twomey PJ. Glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) monitoring. BMJ. 2006;333(7568):586–588. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38947.627847.AE. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bejan-Angoulvant T, Cornu C, Archambault P. Is HbA1c a valid surrogate for macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes? Diabetes Metab. 2015;41(3):195–201. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2015.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.McGill CR, Birkett A, Fulgonii Iii VL. Healthy Eating Index-2010 and food groups consumed by US adults who meet or exceed fiber intake recommendations NHANES 2001-2010. Food Nutr Res. 2016;60:29977. doi: 10.3402/fnr.v60.29977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Dahl WJ, Stewart ML. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: health implications of dietary fiber. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015;115(11):1861–1870. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2015.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]