Abstract
Circadian rhythms are 24-h rhythms in physiology and behaviour generated by molecular clocks, which serve to coordinate internal time with the external world. The circadian system is a master regulator of nearly all physiology and its disruption has major consequences on health. Sleep and circadian rhythm disruption (SCRD) is a ubiquitous feature in today’s 24/7 society, and studies on shift-workers have shown that SCRD can lead not only to cognitive impairment, but also metabolic syndrome and psychiatric illness including depression (1,2). Mouse models of clock mutants recapitulate these deficits, implicating mechanistic and causal links between SCRD and disease pathophysiology (3–5). Importantly, treating clock disruption reverses and attenuates these adverse health states in animal models (6,7), thus establishing the circadian system as a novel therapeutic target. Significantly, circadian and clock-controlled gene mutations have recently been identified by Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) in the aetiology of sleep, mental health and metabolic disorders. This review will focus upon the genetics of circadian rhythms in sleep and health.
Introduction to the Circadian Clock
Life has evolved under a 24-h rhythm where environmental factors such as temperature and light fluctuate with a daily predictable sequence. As a consequence, most organisms have evolved circadian clocks that anticipate these regular environmental changes and establish endogenous 24-h rhythms to get the correct physiology and behaviour to the appropriate time window each day. The mechanisms underlying circadian regulation are cell autonomous transcription-translation feedback loops (TTFLs): In mammals, the transcription factors CLOCK and BMAL1 drive the expression of Period (Per1/2) and Cryptochrome (Cry1/2), whose protein products in turn feed-back to inhibit CLOCK and BMAL1 (8) (Fig. 1). Downstream of these four factors lie thousands of clock-controlled genes that orchestrate the oscillation of tissue-specific metabolic and physiological functions. Most cells in the body possess a molecular clock and are maintained in synchrony by a master pacemaker located in the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) of the hypothalamus (9).
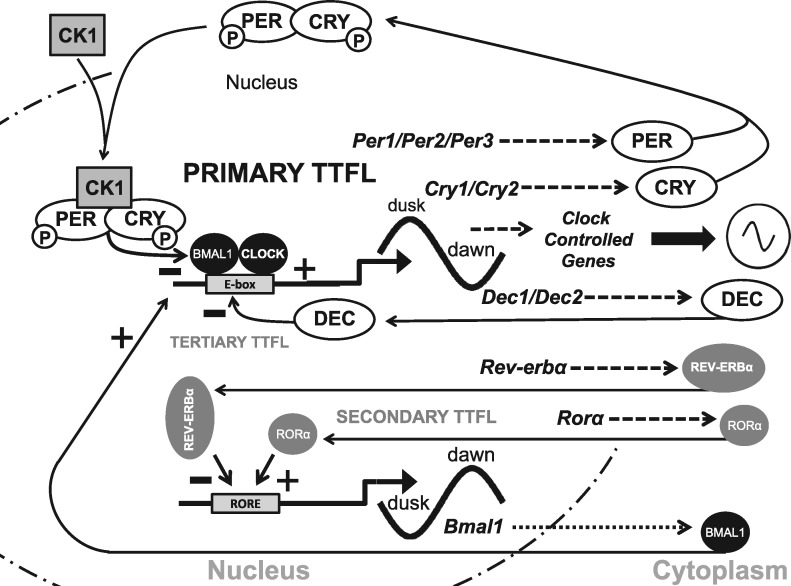
Figure 1.
The mammalian molecular clock. The driving force of the mammalian molecular clockwork is the transcriptional drive provided by two proteins named ‘Circadian Locomotor Output Cycles Kaput’, CLOCK (CLOCK), which heterodimerises with ‘Brain muscle arnt-like 1’ (BMAL1). Bmal1 gene transcription produces a rhythmically produced BMAL1 protein that heterodimerises with a constitutively expressed CLOCK. The CLOCK-BMAL1 complex binds to E-box promoters driving rhythmic transcription of the Per1-3 and two Cryptochrome genes (Cry1, Cry2). The various PER and CRY proteins can complex (dimerise) with themselves to form PER-PER homo- or PER-CRY heterodimers. PER is phosphorylated by the kinase CK1 (Casein kinase 1 family of kinases) and other kinases earmarking it for degradation. However, the PER-CK1 complex allows the CRYs to bind to form a CRY-PER-CK1 complex which prevents further phosphorylation and degradation of PER in the cytoplasm. Within the complex of CRY-PER-CK1, CRY and PER are phosphorylated by other kinases which then allows the CRY-PER-CK1 complex to move into the nucleus and inhibit CLOCK-BMAL1 transcription of the Per and Cry genes forming the core negative limb of the transcriptional/translational feedback loop (TTFL). The CRY-PER-CK1 protein complex levels rise throughout the day, peak at dusk and decline to their lowest level the following dawn. The stability/degradation rate of the CRY-PER-CK1 complex in the nucleus and the resumption of CLOCK-BMAL1 mediated transcription is a key process in setting the period of the clock. It seems that CK1 and other kinases phosphorylate PER and target it for degradation, whilst at least two F-Box protein (FBXL3 and 11) target CRY proteins for degradation. The net result is that CRY and PER proteins fall to their lowest levels just before dawn. Light acts to up-regulate Per1 and Per2 transcription and this allows the entrainment of the molecular clockwork to the dawn/dusk cycle. An interlocked secondary TTFL directs alternating activation and repression of BMAL1 expression. This occurs via the nuclear receptors RORα (RAR-related orphan receptor alpha) and REV-ERBα, respectively, via binding at ROR elements (retinoic acid-related orphan receptor response elements/ROREs) in the Bmal1 promoter. Both Rorα and Rev-erbα have an E-box and are driven rhythmically via CLOCK-BMAL1 transcription. The rates of transcription and translation of these genes differ so that ROR peaks at dawn and REV-ERBα peaks at dusk and this action on the Bmal1 promoter ensures that BMAL1 levels rise at dusk, peak at dawn and then fall throughout the day to their low point just before dusk. In this way BMAL1 levels cycle in antiphase to those of CRY and PER. The Dec1 and Dec2 genes give rise to DEC1 and DEC2 proteins which inhibit CLOCK-BMAL1 transcription and constitute the tertiary TTFL, which reinforces the action of CRY-PER-CK1 inhibition on CLOCK-BMAL1 transcription. Finally, the presence of an E-box in the promoter of downstream clock target genes gives rise to overt circadian rhythms in physiology and behaviour. However, it is also known that many clock controlled genes do not possess an E-Box. As a result the nature of the circadian regulation in these genes remains uncertain.
In order for the circadian network to have adaptive value, it must receive and respond to signals that provide temporal cues (zeitgebers). Zeitgebers modulate the temporal expression patterns of clock genes such as Per1/2 (10), to set the phase, amplitude and period of the molecular clockwork. Light, which signals the dawn-dusk cycle, is the best-characterised zeitgeber, and this light input from the photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (pRGCs) of the retina (11) is transmitted directly to the ventral SCN through synaptic connections, where glutamate signalling then drives cAMP response element binding factor (CREB-CRTC)-mediated transcription of Per genes in the SCN (12) (Fig. 2). Peripheral circadian clocks throughout the body receive inputs from the SCN and numerous additional signals, including feeding (13); glucocorticoids (14); temperature (15); and indicators of physiological condition such as metabolic state (16) and sleep history (17,18). The mechanisms by which many of these these zeitgebers interact with the molecular clockwork of the peripheral clocks remains unclear.
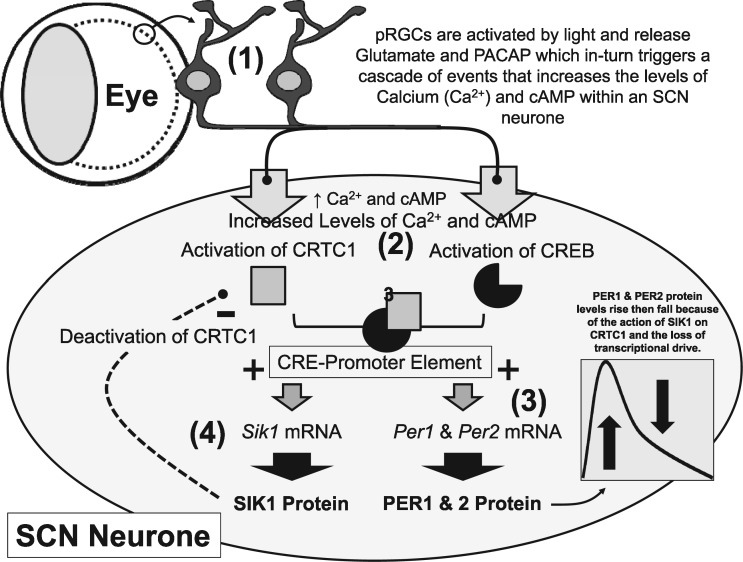
Figure 2.
Light regulation of the molecular clockwork in mammals. The sequence of events that entrains the molecular clockwork of a SCN neurone to the solar day are summarised here and involve the following steps: (1) Light is detected by the photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (pRGCs) within the eye. This induces the release of neurotransmitters (glutamate and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide/PACAP) from the pRGC terminals which synapse with neurones in the ventral SCN. These neurotransmitters trigger a sequence of events that increase the levels of Calcium (Ca2+) and 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) within an SCN neurone. Calcium levels rise as a result of influx from the extracellular medium or release from internal stores. (2) Raised intracellular Ca2+ and cAMP activate two proteins: CREB-binding protein (CREB) through phosphorylation by Protein Kinase A (PKA) and CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 1 (CRTC1) by dephosphorylation, these work together and bind to a cAMP response element (CRE element) in the promoter of Per1, Per2 and Sik1. (3) CRE activation of the Per genes (+), leads to elevated Per mRNA and increased levels of PER1 and PER2 protein. Changed levels of PER 1 and 2 act to shift the molecular clockwork, advancing the clock at dawn and delaying the clock at dusk. However, Per mRNA and PER protein levels fall rapidly even if the animal remains exposed to light. As a result, the effects of light on the molecular clock are limited and entrainment is a gradual process requiring repeated shifting stimuli over multiple days. This phenomenon explains why we get jet-lag, the clock cannot move immediately to a new dawn/dusk cycle because there is a ‘brake’ on the effects of light on the clock. (4) The mechanism that provides this molecular brake is the production of SIK1 protein. SIK1 deactivates CRTC (-) by phosphorylation, so that it can no longer provide the co-transcriptional drive with CREB on the CRE promoter, and transcription largely stops. This negative feedback turns off Per1 and Per2 transcription and translation, limiting the effects of light on the clock. Sik1 mRNA and SIK1 protein levels also decline but more slowly than PER 1 and 2. The system then re-sets itself for possible light detection several hours later. Experiments on mice in which SIK1 has been suppressed show very rapid entrainment to simulated jet-lag. By limiting the shifting effects of light on the SCN, the circadian system of the animal is protected from abnormal light exposure at the wrong time of day. In addition, it may be important to buffer the effects of light on the SCN clock so that it is not pulled rapidly to a new phase, and in the process uncouple the SCN from the peripheral circadian network, resulting in internal desynchrony.
Circadian clock outputs have a profound impact upon the biology of a cell, with anywhere between 2 and 30% of each tissue’s transcriptome displaying a circadian rhythm (19–21). Interaction between clock transcription factors and tissue specific transcription factors overlay a circadian rhythm onto tissue specific gene expression patterns (22), resulting in the appropriate circadian transcriptome and in turn, appropriately timed physiology and behaviour. As a result, sleep and circadian rhythm disruption resulting from either social/health reasons or mutations in circadian and clock-controlled genes contributes to the development of a range of disorders. The evidence for these genetic links is discussed below with three examples: mental illness, metabolic disorders and sleep timing disruption. There is also compelling evidence for many other links between circadian disruption and conditions such as cancer (23) and immune system disorders (24), which are not discussed here.
Circadian Rhythm Disruption in Mental Illness
There is considerable evidence that patients with neuropsychiatric diseases, such as bipolar disorder, schizophrenia and depression exhibit SCRD and this, alongside the evidence from mouse models has been extensively reviewed previously (2,25). This disruption encompasses a wide range of sleep perturbations, including fragmented sleep, reduced total sleep time and changes in normal sleep architecture (26). Furthermore, these patients show dysregulation of multiple circadian outputs and of the core molecular clock (Fig. 1). Remarkably, fibroblasts isolated from schizophrenic patients show a loss of rhythmicity in CRY1 and PER1 expression, and their peripheral blood leukocytes have decreased and/or disrupted diurnal expression of CLOCK, PER1/2/3, CRY1 and a functional CLOCK homologue NPAS2 in comparison to healthy controls (27). Fibroblasts isolated from bipolar patients display a larger variance in period and amplitude and deficits in the entrainment pathways. Lithium is used for the treatment of bipolar disorder, and lithium’s primary therapeutic target is postulated to be Rev-erba (28) (Fig. 1). Additionally, patients with major depressive disorder display a marked disruption in the circadian rhythmicity and phasing of core clock genes across multiple brain regions (29).
It is becoming increasingly clear that disruption of the molecular clock is not just a consequence of neuropsychiatric illness, but instead forms part of a bidirectional feedback loop with neuropsychiatric disease, whereby perturbations in one exacerbate dysfunction in the other (2,5). In this context, it is worth noting that, many disease relevant processes are under circadian control, such as sleep-wake timing and monoaminergic neurotransmitter synthesis, signalling and degradation (30–32). Furthermore, multiple single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the genes encoding the core components of the molecular clock have been demonstrated, albeit weakly, to be associated with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression, suggesting a causal role for clock dysfunction in neuropsychiatric disease (Table 1).
Table 1.
A list of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in core clock genes that are associated with neuropsychiatric or neurodegenerative diseases. Only P values highlighted in bold remain significant after multiple comparisons correction
| Gene | Disease | Sample size | Total SNPs tested | SNP | P value | Test used | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARNTL | BPD | 180 controls | 44 | rs1481892 | P = 0.018 | Cochran-Armitage trend test | (33) |
| 234 patients | rs4757142 | P = 0.0009 | |||||
| rs1982350 | P = 0.005 | ||||||
| rs7107287 | P = 0.033 | ||||||
| BPD | 477 controls | 268 | rs7126303 | P = 0.04 | Cochran-Armitage trend test | (34) | |
| 523 patients | |||||||
| SAD | 136 controls | 13 | rs2290035 | P = 0.02 | Logistic regression analysis | (35) | |
| 137 patients | |||||||
| MD | 926 controls | 115 | rs2290036 | P = 0.043 | Logistic regression analysis | (36) | |
| 459 patients | |||||||
| PS | 913 controls | 6 | rs2290036 | P = 0.005 | Logistic regression analysis | (37) | |
| 535 patients | |||||||
| BPD | 405 controls | 92 | rs3789327 | P = 0.0212 | Association testing using FBAT | (38) | |
| 465 patients | |||||||
| AD | 423 controls | 1 | rs2278749 | P < 0.0001 | Pearson’s chi-squared test | (39) | |
| 296 patients | |||||||
| PD | 1342 controls | 125 | rs7950226 | P = 0.0088 | Cochran-Armitage trend test | (40) | |
| 1394 patients | rs11605776 | P = 0.0049 | |||||
| rs10832022 | P = 0.0048 | ||||||
| rs11022765 | P = 0.0049 | ||||||
| rs7941761 | P = 0.0197 | ||||||
| rs1562437 | P = 0.0013 | ||||||
| rs3816358 | P = 0.0275 | ||||||
| rs900147 | P = 0.00423* | ||||||
| CLOCK | BPD | 101 patients | 1 | rs180260 | P = 0.026 | One-way ANOVA | (41) |
| BPD | 635 controls | 44 | rs180260 | P = 0.0138 | Association determined using the SNPassoc software package | (42) | |
| 515 patients | rs11932595 | P = 0.0319 | |||||
| SZ | 128 controls | 1 | rs180260 | P = 0.026 | Logistic regression analysis | (43) | |
| 145 patients | |||||||
| SZ | 199 controls | 1 | rs180260 | P < 0.05 | Pearson’s chi-squared test | (44) | |
| 145 patients | |||||||
| MD | 776 controls | 32 | rs180260 | P = 0.028 (Male patients) | Pearson’s chi-squared test | (45) | |
| 592 patients | |||||||
| AD | 423 controls | 1 | rs180260 | P < 0.0001 | Pearson’s chi-squared test | (46) | |
| 296 patients | |||||||
| BPD | 405 controls | 92 | rs17777929 | P = 0.0317 | Association testing using FBAT | (38) | |
| 465 patients | |||||||
| BPD | 614 controls | 62 | rs534654 | P = 0.0097 | Pearson’s chi-squared test | (47) | |
| 518 patients | rs4340844 | P = 0.015 | |||||
| rs6850524 | P = 0.012 | ||||||
| BPD | 444 BPD families | 197 | rs6850524 | P = 0.032 | Pearson’s chi-squared test | (48) | |
| 130 unrelated BPD families | rs3805148 | P = 0.009 | |||||
| rs3736544 | P = 0.024 | ||||||
| rs12504300 | P = 0.009 | ||||||
| rs4864542 | P = 0.01 | ||||||
| rs12648271 | P = 0.037 | ||||||
| BPD | 440 controls | 209 | rs10462028 | P = 0.02 | Logistic regression analysis | (49) | |
| 199 patients | |||||||
| AD | 188 controls | 1 | rs1554483 | P = 0.009 | Pearson’s chi-squared test | (50) | |
| 130 patients | |||||||
| AD | 423 controls | 1 | rs4580704 | P < 0.0001 | Pearson’s chi-squared test | (51) | |
| 296 patients | |||||||
| CRY1 | MD | 654 BPD patients | 7 | rs10861688 | P = 0.0048* | Covariated linear regression | (52) |
| MD | 440 controls | 209 | rs2287161 | P = 0.007† | Logistic regression analysis | (49) | |
| 335 patients | |||||||
| MD | 485 controls | 3 | rs2287161 | P = 0.010 | Logistic regression analysis | (53) | |
| 105 patients | |||||||
| CRY2 | BPD | 477 controls | 268 | rs1554338 | P = 0.031 | Cochran-Armitage trend test | (34) |
| 523 patients | |||||||
| MD | 1011 controls | 4 | rs10838524 | P = 0.0017 | Logistic regression analysis | (54) | |
| 118 patients | rs10838327 | P = 0.00074 | |||||
| rs3824872 | P = 0.007 | ||||||
| DT | 3871 controls | 48 | rs10838524 | q = 0.04 | Linear and logistic regression analysis | (55) | |
| 136 patients | rs7121611 | q = 0.04 | |||||
| rs7945565 | q = 0.04 | ||||||
| rs1401419 | q = 0.04 | ||||||
| DT | 4154 controls | 48 | rs10838524 | q = 0.003 | Logistic regression analysis | (56) | |
| 166 patients | rs7121611 | q = 0.002 | |||||
| rs7945565 | q = 0.002 | ||||||
| rs1401419 | q = 0.002 | ||||||
| rs3824872 | q = 0.02 | ||||||
| MD | 4154 controls | 48 | rs7123390 | q = 0.05 | Logistic regression analysis | (56) | |
| 862 patients | rs2292910 | q = 0.05 | |||||
| rs7121611 | q = 0.02 | ||||||
| rs7945565 | q = 0.02 | ||||||
| rs1401419 | q = 0.03 | ||||||
| NR1D1 | BPD | 444 BPD families | 197 | rs2071427 | P = 0.0019 | Pearson’s chi-squared test | (48) |
| 130 control families | rs2269457 | P = 0.0292 | |||||
| rs2314339 | P = 0.0005 | ||||||
| PD | 1342 controls | 125 | rs3744805 | P = 0.00294 | Cochran-Armitage trend test | (40) | |
| 1394 patients | |||||||
| PER1 | PD | 1342 controls | 125 | rs2253820 | P = 0.00067* | Cochran-Armitage trend test | (40) |
| 1394 patients | |||||||
| PER2 | SAD | 173 controls | 13 | rs10870 | P = 0.03 | Logistic regression analysis | (35) |
| 177 patients | |||||||
| MD | 459 controls | 115 | rs2304672 | P = 0.0087 | Logistic regression analysis | (57) | |
| 926 patients | rs10462023 | P = 0.0033 | |||||
| rs6431590 | P = 0.036 | ||||||
| rs3739064 | P = 0.018 | ||||||
| SZ | 477 controls | 268 | rs2304672 | P = 0.048 | Cochran-Armitage trend test | (34) | |
| 527 patients | rs2304674 | P = 0.033 | |||||
| BPD | 180 controls | 44 | rs2859387 | P = 0.039 | Cochran-Armitage trend test | (33) | |
| 138 patients | |||||||
| PER3 | SZ | 180 controls | 44 | rs228729 | P = 0.028 | Cochran-Armitage trend test | (33) |
| 331 patients | |||||||
| SZ | 477 controls | 268 | rs10462021 | P = 0.036 | Cochran-Armitage trend test | (34) | |
| 527 patients | rs2640909 | P = 0.031 | |||||
| MD | 2915 controls | 529 | rs12137927 | P = 0.00054 | Logistic regression analysis | (58) | |
| 1296 patients | rs228644 | P = 0.00013 | |||||
| rs228682 | P = 0.00014 | ||||||
| MD | 776 controls | 32 | rs17031614 | P = 0.017 | Pearson’s chi-squared test | (45) | |
| 592 patients | rs228697 | P = 0.007 | |||||
| RORA | MD | 459 controls | 115 | rs2028122 | P = 0.044 | Logistic regression analysis | (57) |
| 926 patients | |||||||
| MD | 4811 participants | Whole genome | rs12912233 | P = 6.3 × 10−7 | Weighted z score-based fixed effects meta-analysis | (59) | |
| rs4775340 | P = 6.3 × 10−6 | ||||||
| rs8028646 | P = 7.2 × 10−6 | ||||||
| rs8023563 | P = 1.5 × 10−5 | ||||||
| MD | 2915 controls | 529 | rs11632098 | P = 0.00056 | Logistic regression analysis | (58) | |
| 1296 patients | |||||||
| BPD | 1759 controls | 353 | rs782931 | P = 0.01* | Pearson’s chi-squared test | (60) | |
| 479 patients | |||||||
| BPD | 200 controls | 27 | rs4774388 | P = 0.024 | Additive, dominant and recessive genetic models with a maximum test for associations | (61) | |
| 280 patients | |||||||
| BPD | 1770 controls | 429 | 43 SNPs reached nominal significance | P = 0.002–0.044 | |||
| 448 patients | |||||||
| RORB | SZ | 477 controls | 268 | rs10491929 | P = 0.023 | Cochran-Armitage trend test | (34) |
| 527 patients | |||||||
| BPD | 477 controls | 268 | rs17691363 | P = 0.035 | Cochran-Armitage trend test | (34) | |
| 527 patients | rs10217594 | P = 0.026 | |||||
| rs10491929 | P = 0.023 | ||||||
| PD | 1342 controls | 125 | rs10491929 | P = 0.0264 | Cochran-Armitage trend test | (62) | |
| 1394 patients | rs10869412 | P = 0.0097 | |||||
| rs17611535 | P = 0.0037 | ||||||
| rs17612113 | P = 0.0163 | ||||||
| rs10521463 | P = 0.0068 | ||||||
| BPD | 200 controls | 27 | rs1327836 | P = 0.003 | Additive, dominant and recessive genetic models with a maximum test for associations | (61) | |
| 280 patients | rs17611535 | ||||||
| BPD | 1770 controls | 429 | rs1761135 | P = 0.027 | |||
| 448 patients | rs499922 | P = 0.042 |
denotes a Bonferroni corrected P value, † denotes a permutation corrected P value. All other P values are not adjusted for multiple comparisons. q denotes the false discovery rate q-values, used to correct for multiple comparisons. q < 0.05 was taken to be statistically significant.
Abbreviations: AD: Alzheimer’s disease; BPD: Bipolar disorder; DT: dysthymia; MD: major depression; PD: Parkinson’s disease; PS: psychosis; SAD: seasonal affective disorder; SZ: schizophrenia.
Currently the functional consequence of these SNPs and the strength of their association with disease remains unclear, however, recent work has provided insight into how mutations may impact clock function. Two rare missense mutations in the PERIOD3 gene (PER3-P415A/H417RI), found to be associated with seasonal depression, were demonstrated to generate a mutant PER3 protein unable to stabilise PER1/2 and induce their nuclear localisation, resulting in circadian rhythm disruption (63).
A similar relationship has been found in patients with neurodegenerative diseases. Many conditions are associated with the disruption of sleep, circadian outputs and the core molecular clock (64). Patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) exhibit neuronal loss in the SCN (65), and a recent study by Lim et al. found that the diurnal and seasonal transcriptional rhythmicity of core clock genes in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex is disrupted in AD patients (66). In addition, the expression of BMAL1/2 is dampened in peripheral blood leukocytes isolated from Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients (67,68).
As with neuropsychiatric illness, disruption of the core molecular clock is both a consequence of, and a contributor towards, neurodegenerative diseases. For example β-amyloid (Aβ), the neuronal aggregation of which is the hallmark of AD, causes BMAL1 degradation and therefore molecular clock disruption (69) (Fig. 1). In animal models it has been shown that sleep deprivation leads to increased Aβ plaque formation and that sleep is required for the clearance of Aβ (70). Additionally, the circadian clock regulates many molecular processes commonly involved in neurodegeneration, such as oxidative stress (71), metabolism (see next section), neuroinflammation (72,73) and protein dynamics (74). Evidence linking SNPs in core clock genes with neurodegenerative diseases is currently scarce, with only a limited number of studies demonstrating the association of SNPs in CLOCK, BMAL1 and/or PER1 with AD or PD. Collectively, there is currently compelling evidence that disruption of the molecular clock contributes to the progression of both neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric conditions.
Metabolic Disorders
The metabolic system is under strong circadian control, and these relationships are summarised in Figure 3. One of the first indications of the strong coupling between circadian clocks and metabolism was suggested by the observation that the majority of cycling transcripts in the liver are implicated in multiple metabolic pathways (19,75). Processes such as glucose, cholesterol and triglyceride metabolism are a few examples, whose rate-limiting steps were shown to be major sites of circadian regulation.
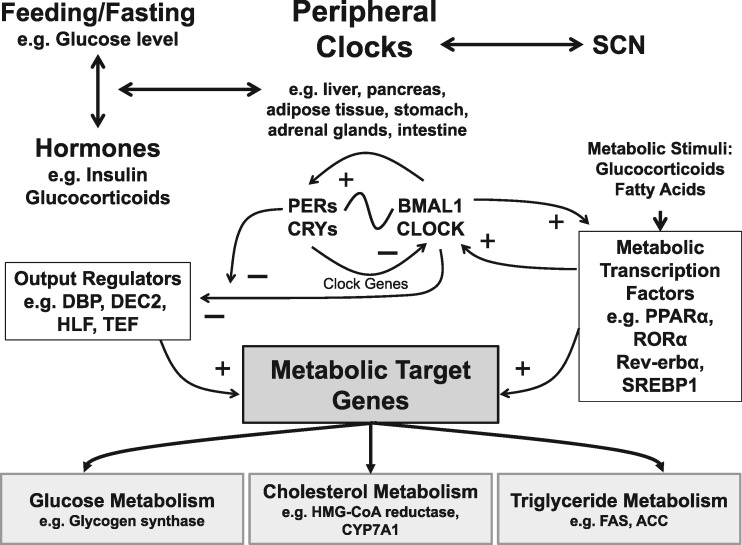
Figure 3.
The circadian control of metabolic pathways. Metabolism is under strong circadian control. Peripheral clocks (e.g. liver, pancreas, adipose tissue, etc.) are regulated by the SCN and in turn feedback upon the SCN. Light regulates the phase of the molecular clockwork in the SCN, whilst hormonal signals (e.g. insulin and glucocorticoids) and feeding/fasting behaviours that change the levels of glucose alter the phase of peripheral clocks. The molecular clockwork of both peripheral and SCN cells then interacts with the metabolic control systems. The molecular clock comprises a Per/Cry and Clock/Bmal1 feedback loop (See Figure 1). These genes and their protein products also control the expression of downstream transcription factors which in turn regulate metabolic target genes. General regulators include DBP (D site of albumin promoter (albumin D-box) binding protein), which binds to an upstream promoter in the insulin gene; HLF (Hepatic leukaemia factor), which regulates aspects of liver function; and TEF (Thyrotroph embryonic factor), involved in thyroid-stimulating hormone release. The circadian coordination of metabolism also involves members of the rev-erb (REV-ERB) receptor family, retinoic acid orphan receptors (ROR), PPARs (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors) and other nuclear receptors (NR). Metabolic regulators, such as REV-ERBα and ROR, also participate directly in the clock mechanism by regulating Bmal1 transcription (See Figure 1). In addition, hepatic PPARα, which is activated by fatty acids, is regulated rhythmically by CLOCK and BMAL1 and is also regulated by glucocorticoids. These transcriptional regulators in-turn interact with genes associated with glycogen, fatty acid and triglyceride metabolism. Such target genes include: Glycogen synthase, involved in converting glucose to glycogen; HMG-CoA reductase which is the rate-controlling enzyme that produces cholesterol; CYP7A1 is a rate-limiting enzyme in bile acid synthesis; Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and Fatty acid synthase (FAS) are involved in catalysing the synthesis of fatty acids. This regulation can be immensely complex, with multiple interlocking feedback loops between the clock and metabolic genes/proteins. For example, transcriptional regulation of rhythmic CYP7A1, is driven by DBP, the clock protein DEC2, and by nuclear receptors including PPARα. PPARα also regulates Rev-erbα expression in both liver and adipose cells, whilst ROR and Rev-erbα regulate lipid metabolism as well as being involved in Clock and Bmal1 expression.
Clock genes are linked directly to metabolic syndrome (MetS), both in mutant mice and humans. For example, homozygous Clock mutant mice (ClockΔ19/Δ19), which show a loss of function of this core clock gene, are obese and hyperphagic and develop a myriad of metabolic symptoms including hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, hepatic steatosis and dyslipidemia (76), all of which are significant markers of MetS. In addition, impairing Clock function in mice suppresses gluconeogenesis and the complete knock out of Bmal1 gene abolishes it (77). It has also been shown that diabetes mellitus can be triggered by conditional ablation of the Clock gene in pancreatic β-cells. Clock disruption in pancreatic islets results in transcriptome-wide variations in the expression of genes involved in survival, growth and synaptic vesicle assembly within these cells. Furthermore, ClockΔ19/Δ19 mutant mice exhibit significant hypoinsulinemia and hyperglycemia as a result of abolishing their pancreatic clocks (4). In addition, Bmal1 levels have been shown to increase significantly during adipose differentiation in 3T3-L1 mouse embryonic cells and both knock-in and knock-down of Bmal1 support its critical involvement in adipose differentiation and lipogenesis (78). Cry1-/- and Cry2-/- mice show no difference in food consumption and body weight compared to wildtype animals, however, when restricted to a high-fat diet, ablation of Cry1 (yet interestingly not Cry2) prevented obesity in these mutant mice (79). Finally, pharmacological induction of RORa transcription factor function, an enhancer of Bmal1 expression (Fig. 1), has been shown to increase significantly the amplitude of clock rhythms and, remarkably, prevent weight gain in mice fed high-fat diets and attenuate symptoms of MetS (80).
In humans, like mice, polymorphisms of CLOCK and BMAL1 have been associated with metabolic disorders. For example, Clock gene polymorphisms have been linked to a higher susceptibility to obesity (81,82) and two haplotypes of BMAL1 have been associated with hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus, replicated both in humans and in rodent models (83). Similar studies have also linked polymorphisms in other core clock genes like PER2 and NPAS2 to fasting hyperglycemia and hypertension respectively (84). In a small population of lean and obese women, a correlation between obesity and core clock components has been reported. Remarkably, being obese alters expression of core clock genes in adipocytes throughout the day and induces notable upregulation of CRY2 and REV-ERBa, two important negative feedback components of circadian clocks (85) (Fig. 1). Furthermore, a rare SNP in visfatin (NAMPT/PBEF1), a gene known to be involved in the negative arm of the clock (86) (not shown in Figures), has been associated with protection from obesity in human populations (87).
It is now evident that circadian clocks do not only regulate metabolism, but metabolic pathways can in turn feedback upon the circadian clockwork (Fig. 3). Restricting feeding to daytime (sleep phase) in mice causes uncoupling of peripheral clocks within the liver, kidney, heart and pancreas from SCN rhythms (13,88). In addition, a high-caloric diet has been shown to disrupt behavioural and molecular circadian rhythms in mice (89). Furthermore, two important regulators of homeostasis and metabolism in Drosophila, FOXO and GSK3b/Shaggy, were shown to be necessary for robust circadian rhythms (90,91), which emphasises the connection between metabolism and circadian clocks across the animal kingdom.
Collectively, the results from humans and animal models highlight the considerable involvement of the circadian machinery in metabolic pathways. A two-way interplay between these two systems is clear and the mechanisms governing their intercommunication are slowly emerging (Fig. 3).
Disorders of Sleep Timing
The human population displays a wide spread of circadian phenotypes or chronotypes, with early types (larks) at one end of the spectrum and late types (owls) at the other. Chronotype is influenced by an individual’s genetics, development and exposure to light and dawn and dusk. In terms of the genetics, clock gene mutations can explain some of the differences in chronotype. Two recent large scale genomic studies identified variants in several clock-related loci (92,93), particularly PER2/3, underlying morningness in the general population. Different chronotypes can usually alter sleep patterns to accommodate both their social demands and circadian clock; Winston Churchill believed in the importance of good sleep, but was a very late chronotype and compensated with long afternoon naps (94). However, extreme misalignment with the external light-dark cycle leads to severely disrupted sleep-wake cycles, chronic fatigue and exhaustion. The underlying cause could be either deficits in core clock machinery leading to non-24h rhythms or deficits in the input pathways and entrainment systems that result in a misaligned rhythm. Examples of the first include delayed or advanced sleep phase disorders; Familial Advanced Sleep Phase syndrome is linked to mutations in Per2 (95) and Familial Delayed Sleep Phase Syndrome to mutations in Casein Kinase 1 Delta (96) (Fig. 1). Recently, mutations in Cry1 have been linked to Familial Delayed Sleep Phase syndrome, with a remarkably high frequency of 0.6% in the population, thereby affecting sleep in large numbers of individuals (97). In these conditions, due to a faster or slower molecular clock, the time window defined by the clock as optimal to sleep is shifted with respect to the external light-dark cycle, resulting in severe misalignment. In addition, situations where input pathways are deficient are also relatively common. Low levels of light within the nursing home environment result in circadian rhythm disruption (98) and patients with severe eye damage due to either genetic causes or trauma lose light input to the circadian clock resulting in severe misalignment (99). In these situations, behavioural rhythms imposed by care or feeding may help mask this disruption, but desynchronised and drifting peripheral clocks demonstrate the lack of entrainment which is manifest as poor and disrupted sleep.
Treatment of Sleep and Circadian Rhythm Disruption (SCRD)
Despite our growing knowledge of the molecular mechanisms underlying the 24h circadian clock and its role in the development of chronic and debilitating diseases, there are limited therapeutic options available for the treatment of SCRD. As light is the primary zeitgeber for the SCN clock, bright light therapies and cognitive behavioural therapies that strengthen natural zeitgebers such as scheduled outdoor exercise (100,101) have been shown to have some success. However, potent pharmacological interventions are still lacking. Melatonin has long been characterised as an output of the circadian clock and can be used to modify the phase of the clock, presumably acting via the melatonin receptors that are expressed in the neurones of the SCN and multiple other cell populations across the body. Melatonin has therefore been studied as a possible chronotherapeutic drug and shows promise in certain circadian-related conditions (102,103). Prolonged release melatonin (tradename Circadin) is used to treat primary insomnia (104) in the aged and the agonist Agomelatine in the treatment of major depressive disorder (105). Most recently, Tasimelteon was approved in the United States in an orphan circadian disorder, non-24h sleep-sake disorder in the totally blind (106). Targeting the melatonin system, however, has limited efficacy; for example, Tasimelteon showed a beneficial effect on stabilising sleep-wake in 20% of the patient population after one month of treatment (106). As a consequence, recent efforts have focussed on developing alternatives, mainly targeting the core clock. Solt et al. reported a novel REV-ERBa receptor agonist was effective at regulating both sleep as well as metabolism in mice (6,107) and Hirota et al. have developed a small molecule Cryptochrome activator (108). An alternative strategy that has yet to be employed is the development of molecules that act on the light input pathway to the clock, providing a pharmacological replacement for light for the treatment of SCRD.
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful for valuable input and critical comments from Prof. Andrea Nemeth and Dr. Jing Yu.
Conflict of Interest statement. None declared.
Funding
We would like to acknowledge the following sources of funding: BBSRC ref. BB/N01992X/1 to AJ, Wellcome Trust ref. 106174/Z/14/Z to RGF, BBSRC ref. BB/N001664/1 to SV, and a Said Foundation scholarship to ZW. AJ, SRV and RGF are in receipt of funding from Circadian Therapeutics.
References
- 1. Arendt J. (2010) Shift work: coping with the biological clock. Occup. Med. (Lond), 60, 10–20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Wulff K., Gatti S., Wettstein J.G., Foster R.G. (2010) Sleep and circadian rhythm disruption in psychiatric and neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 11, 589–599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Laposky A., Easton A., Dugovic C., Walisser J., Bradfield C., Turek F. (2005) Deletion of the mammalian circadian clock gene BMAL1/Mop3 alters baseline sleep architecture and the response to sleep deprivation. Sleep, 28, 395–409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Marcheva B., Ramsey K.M., Buhr E.D., Kobayashi Y., Su H., Ko C.H., Ivanova G., Omura C., Mo S., Vitaterna M.H.. et al. (2010) Disruption of the clock components CLOCK and BMAL1 leads to hypoinsulinaemia and diabetes. Nature, 466, 627–631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Jagannath A., Peirson S.N., Foster R.G. (2013) Sleep and circadian rhythm disruption in neuropsychiatric illness. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 23, 888–894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Solt L.A., Wang Y., Banerjee S., Hughes T., Kojetin D.J., Lundasen T., Shin Y., Liu J., Cameron M.D., Noel R.. et al. (2012) Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by synthetic REV-ERB agonists. Nature, 485, 62–68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Hatori M., Vollmers C., Zarrinpar A., DiTacchio L., Bushong E.A., Gill S., Leblanc M., Chaix A., Joens M., Fitzpatrick J.A.. et al. (2012) Time-restricted feeding without reducing caloric intake prevents metabolic diseases in mice fed a high-fat diet. Cell Metab., 15, 848–860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Reppert S.M., Weaver D.R. (2002) Coordination of circadian timing in mammals. Nature, 418, 935–941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Klein D.C., Moore R.Y., Reppert S.M. (1991) Suprachiasmatic nucleus: the mind's clock. Oxford University Press, New York. [Google Scholar]
- 10. Schwartz W.J., Tavakoli-Nezhad M., Lambert C.M., Weaver D.R., de la Iglesia H.O. (2011) Distinct patterns of period gene expression in the suprachiasmatic nucleus underlie circadian clock photoentrainment by advances or delays. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U S A, 108, 17219–17224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Hughes S., Jagannath A., Hankins M.W., Foster R.G., Peirson S.N. (2015) Photic regulation of clock systems. Methods Enzymol., 552, 125–143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Jagannath A., Butler R., Godinho S.I., Couch Y., Brown L.A., Vasudevan S.R., Flanagan K.C., Anthony D., Churchill G.C., Wood M.J.. et al. (2013) The CRTC1-SIK1 pathway regulates entrainment of the circadian clock. Cell, 154, 1100–1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Stokkan K.A., Yamazaki S., Tei H., Sakaki Y., Menaker M. (2001) Entrainment of the circadian clock in the liver by feeding. Science, 291, 490–493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Balsalobre A., Brown S.A., Marcacci L., Tronche F., Kellendonk C., Reichardt H.M., Schutz G., Schibler U. (2000) Resetting of circadian time in peripheral tissues by glucocorticoid signaling. Science, 289, 2344–2347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Morf J., Rey G., Schneider K., Stratmann M., Fujita J., Naef F., Schibler U. (2012) Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein modulates circadian gene expression posttranscriptionally. Science, 338, 379–383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Ramsey K.M., Yoshino J., Brace C.S., Abrassart D., Kobayashi Y., Marcheva B., Hong H.K., Chong J.L., Buhr E.D., Lee C.. et al. (2009) Circadian clock feedback cycle through NAMPT-mediated NAD+ biosynthesis. Science, 324, 651–654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Yamakawa G.R., Basu P., Cortese F., MacDonnell J., Whalley D., Smith V.M., Antle M.C. (2016) The cholinergic forebrain arousal system acts directly on the circadian pacemaker. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U S A, 113, 13498–13503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Davies S.K., Ang J.E., Revell V.L., Holmes B., Mann A., Robertson F.P., Cui N., Middleton B., Ackermann K., Kayser M.. et al. (2014) Effect of sleep deprivation on the human metabolome. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U S A, 111, 10761–10766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Panda S., Antoch M.P., Miller B.H., Su A.I., Schook A.B., Straume M., Schultz P.G., Kay S.A., Takahashi J.S., Hogenesch J.B. (2002) Coordinated transcription of key pathways in the mouse by the circadian clock. Cell, 109, 307–320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Duffield G.E., Best J.D., Meurers B.H., Bittner A., Loros J.J., Dunlap J.C. (2002) Circadian programs of transcriptional activation, signaling, and protein turnover revealed by microarray analysis of mammalian cells. Curr. Biol., 12, 551–557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Kornmann B., Schaad O., Bujard H., Takahashi J.S., Schibler U. (2007) System-driven and oscillator-dependent circadian transcription in mice with a conditionally active liver clock. PLoS Biol., 5, e34.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Perelis M., Marcheva B., Ramsey K.M., Schipma M.J., Hutchison A.L., Taguchi A., Peek C.B., Hong H., Huang W., Omura C.. et al. (2015) Pancreatic beta cell enhancers regulate rhythmic transcription of genes controlling insulin secretion. Science, 350, aac4250.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Kiessling S., Beaulieu-Laroche L., Blum I.D., Landgraf D., Welsh D.K., Storch K.F., Labrecque N., Cermakian N. (2017) Enhancing circadian clock function in cancer cells inhibits tumor growth. BMC Biol., 15, 13.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Scheiermann C., Kunisaki Y., Frenette P.S. (2013) Circadian control of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 13, 190–198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Jagannath A., Peirson S.N., Foster R.G.. Sleep and circadian rhythm disruption in neuropsychiatric illness. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 23, 888–894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Krystal A.D. (2012) Psychiatric disorders and sleep. Neurol. Clin., 30, 1389–1413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Johansson A.S., Owe-Larsson B., Hetta J., Lundkvist G.B. (2016) Altered circadian clock gene expression in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res., 174, 17–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Yin L., Wang J., Klein P.S., Lazar M.A. (2006) Nuclear receptor Rev-erbalpha is a critical lithium-sensitive component of the circadian clock. Science, 311, 1002–1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Li J.Z., Bunney B.G., Meng F., Hagenauer M.H., Walsh D.M., Vawter M.P., Evans S.J., Choudary P.V., Cartagena P., Barchas J.D.. et al. (2013) Circadian patterns of gene expression in the human brain and disruption in major depressive disorder. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U S A, 110, 9950–9955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Hampp G., Albrecht U. (2008) The circadian clock and mood-related behavior. Commun. Integr. Biol., 1, 1–3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Chung S., Lee E.J., Yun S., Choe H.K., Park S.B., Son H.J., Kim K.S., Dluzen D.E., Lee I., Hwang O.. et al. (2014) Impact of circadian nuclear receptor REV-ERBalpha on midbrain dopamine production and mood regulation. Cell, 157, 858–868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Ikeda Y., Kumagai H., Skach A., Sato M., Yanagisawa M. (2013) Modulation of circadian glucocorticoid oscillation via adrenal opioid-CXCR7 signaling alters emotional behavior. Cell, 155, 1323–1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Mansour H.A., Wood J., Logue T., Chowdari K.V., Dayal M., Kupfer D.J., Monk T.H., Devlin B., Nimgaonkar V.L. (2006) Association study of eight circadian genes with bipolar I disorder, schizoaffective disorder and schizophrenia. Genes Brain Behav., 5, 150–157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Mansour H.A., Talkowski M.E., Wood J., Chowdari K.V., McClain L., Prasad K., Montrose D., Fagiolini A., Friedman E.S., Allen M.H.. et al. (2009) Association study of 21 circadian genes with bipolar I disorder, schizoaffective disorder, and schizophrenia. Bipolar Disorders, 11, 701–710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Partonen T., Treutlein J., Alpman A., Frank J., Johansson C., Depner M., Aron L., Rietschel M., Wellek S., Soronen P.. et al. (2007) Three circadian clock genes Per2, Arntl, and Npas2 contribute to winter depression. Ann. Med., 39, 229–238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Lavebratt C., Sjoholm L.K., Partonen T., Schalling M., Forsell Y. (2010) PER2 variantion is associated with depression vulnerability. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet., 153B, 570–581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Liu J.J., Hukic D.S., Forsell Y., Schalling M., Sby U., Lavebratt C. (2015) Depression-associated ARNTL and PER2 genetic variants in psychotic disorders. Chronobiol. Int., 32, 579–584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Gonzalez R., Gonzalez S., Villa E., Ramirez M., Zavala J., Armas R., Contreras J., Dassori A., Leach R.J., Flores D.. et al. (2015) Identification of circadian gene variants in bipolar disorder in Latino populations. J. Affect. Disord., 186, 367–375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Chen Q., Peng X.D., Huang C.Q., Hu X.Y., Zhang X.M. (2015) Association between ARNTL (BMAL1) rs2278749 polymorphism T >C and susceptibility to Alzheimer disease in a Chinese population. Genet. Mol. Res., 14, 18515–18522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Gu Z., Wang B., Zhang Y.-B., Ding H., Zhang Y., Yu J., Gu M., Chan P., Cai Y. (2015) Association of ARNTL and PER1 genes with Parkinson's disease: a case-control study of Han Chinese. Sci. Rep., 5, 15891.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Benedetti F., Serretti A., Colombo C., Barbini B., Lorenzi C., Campori E., Smeraldi E. (2003) Influence of CLOCK gene polymorphism on circadian mood fluctuation and illness recurrence in bipolar depression. Am. J. Med. Genet., 123B, 23–26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Dmitrzak-Weglarz M.P., Pawlak J.M., Maciukiewicz M., Moczko J., Wilkosc M., Leszczynska-Rodziewicz A., Zaremba D., Hauser J. (2015) Clock gene variants differentiate mood disorders. Mol. Biol. Rep., 42, 277–288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Takao T., Tachikawa H., Kawanishi Y., Mizukami K., Asada T. (2007) CLOCK gene T3111C polymorphism is associated with Japanese schizophrenics: A preliminary study. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol., 17, 273–276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Zhang J., Liao G., Liu C., Sun L., Liu Y., Wang Y., Jiang Z., Wang Z. (2011) The association of CLOCK gene T3111C polymorphism and hPER3 gene 54-nucleotide repeat polymorphism with Chinese Han people schizophrenics. Mol. Biol. Rep., 38, 349–354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Shi S-q., White M.J., Borsetti H.M., Pendergast J.S., Hida A., Ciarleglio C.M., de Verteuil P.A., Cadar A.G., Cala C., McMahon D.G.. et al. (2016) Molecular analyses of circadian gene variants reveal sex-dependent links between depression and clocks. Transl. Psychiatry, 6, e748.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Yang Y.-K., Peng X.-D., Li Y.-H., Wang Z.-R., Chang-quan H., Hui W., Liu Q.-X. (2013) The Polymorphism of CLOCK gene 3111T/C C>T is associated with susceptibility of Alzheimer disease in Chinese population. J. Investig. Med., 61, 1084–1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Shi J., Wittke-Thompson J.K., Badner J.A., Hattori E., Potash J.B., Willour V.L., McMahon F.J., Gershon E.S., Liu C. (2008) Clock genes may influence bipolar disorder susceptibility and dysfunctional circadian rhythm. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B: Neuropsychiatr. Genet., 147B, 1047–1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Kripke D.F., Nievergelt C.M., Joo E., Shekhtman T., Kelsoe J.R. (2009) Circadian polymorphisms associated with affective disorders. J. Circadian Rhythms, 7, 2.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Soria V., Martínez-Amorós È., Escaramís G., Valero J., Pérez-Egea R., García C., Gutiérrez-Zotes A., Puigdemont D., Bayés M., Crespo J.M.. et al. (2010) Differential Association of Circadian Genes with Mood Disorders: CRY1 and NPAS2 are associated with unipolar major depression and CLOCK and VIP with bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology, 35, 1279–1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Chen Q., Huang C.-Q., Hu X.-Y., Li S.-B., Zhang X.-M. (2013) Functional CLOCK gene rs1554483 G/C polymorphism is associated with susceptibility to Alzheimer's disease in the Chinese population. J. Int. Med. Res., 41, 340–346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Chen H-f., Huang C-q., You C., Wang Z.-R., Si-qing H. (2013) Polymorphism of CLOCK gene rs 4580704 C>G is associated with susceptibility of Alzheimer’s disease in a Chinese population. Arch. Med. Res., 44, 203–207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Drago A., Monti B., De Ronchi D., Serretti A. (2015) CRY1 variations impacts on the depressive relapse rate in a sample of bipolar patients. Psychiatry Investig., 12, 118.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Hua P., Liu W., Chen D., Zhao Y., Chen L., Zhang N., Wang C., Guo S., Wang L., Xiao H.. et al. (2014) Cry1 and Tef gene polymorphisms are associated with major depressive disorder in the Chinese population. J. Affect. Disord., 157, 100–103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Lavebratt C., Sjöholm L.K., Soronen P., Paunio T., Vawter M.P., Bunney W.E., Adolfsson R., Forsell Y., Wu J.C., Kelsoe J.R.. et al. (2010) CRY2 is associated with depression. PLoS One, 5, e9407.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Kovanen L., Kaunisto M., Donner K., Saarikoski S.T., Partonen T. (2013) CRY2 genetic variants associate with dysthymia. PLoS One, 8, e71450.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Kovanen L., Donner K., Kaunisto M., Partonen T. (2017) PRKCDBP (CAVIN3) and CRY2 associate with major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord., 207, 136–140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Lavebratt C., Sjöholm L.K., Partonen T., Schalling M., Forsell Y. (2009) PER2 variantion is associated with depression vulnerability. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B: Neuropsychiatr. Genet., 9999B, n/a-n/a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Maglione J.E., Nievergelt C.M., Parimi N., Evans D.S., Ancoli-Israel S., Stone K.L., Yaffe K., Redline S., Tranah G.J. and Groups, S.o.O.F.i.W.S.a.O.F.i.M.S.M.R. (2015) Associations of PER3 and RORA circadian gene polymorphisms and depressive symptoms in older adults. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry, 23, 1075–1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Terracciano A., Tanaka T., Sutin A.R., Sanna S., Deiana B., Lai S., Uda M., Schlessinger D., Abecasis G.R., Ferrucci L.. et al. (2010) Genome-wide association scan of trait depression. Biol. Psychiatry, 68, 811–817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Etain B., Jamain S., Milhiet V., Lajnef M., Boudebesse C., Dumaine A., Mathieu F., Gombert A., Ledudal K., Gard S.. et al. (2014) Association between circadian genes, bipolar disorders and chronotypes. Chronobiol. Int., 31, 807–814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Lai Y.-C., Kao C.-F., Lu M.-L., Chen H.-C., Chen P.-Y., Chen C.-H., Shen W.W., Wu J.-Y., Lu R.-B., Kuo P.-H. (2015) Investigation of associations between NR1D1, RORA and RORB genes and bipolar disorder. plos One, 10, e0121245.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Bedrosian T.A., Fonken L.K., Nelson R.J. (2016) Endocrine effects of circadian disruption. Annu. Rev. Physiol., 78, 109–131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Zhang L., Hirano A., Hsu P.K., Jones C.R., Sakai N., Okuro M., McMahon T., Yamazaki M., Xu Y., Saigoh N.. et al. (2016) A PERIOD3 variant causes a circadian phenotype and is associated with a seasonal mood trait. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U S A, 113, E1536–E1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Musiek E.S. (2015) Circadian clock disruption in neurodegenerative diseases: cause and effect?. Front. Pharmacol., 6, 29.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Wang J.L., Lim A.S., Chiang W.Y., Hsieh W.H., Lo M.T., Schneider J.A., Buchman A.S., Bennett D.A., Hu K., Saper C.B. (2015) Suprachiasmatic neuron numbers and rest-activity circadian rhythms in older humans. Ann. Neurol., 78, 317–322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Lim A.S., Klein H.U., Yu L., Chibnik L.B., Ali S., Xu J., Bennett D.A., De Jager P.L. (2017) Diurnal and seasonal molecular rhythms in human neocortex and their relation to Alzheimer's disease. Nat. Commun., 8, 14931.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Cai Y., Liu S., Sothern R.B., Xu S., Chan P. (2010) Expression of clock genes Per1 and Bmal1 in total leukocytes in health and Parkinson's disease. Eur. J. Neurol., 17, 550–554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Ding H., Liu S., Yuan Y., Lin Q., Chan P., Cai Y. (2011) Decreased expression of Bmal2 in patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurosci. Lett., 499, 186–188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Song H., Moon M., Choe H.K., Han D.H., Jang C., Kim A., Cho S., Kim K., Mook-Jung I. (2015) Abeta-induced degradation of BMAL1 and CBP leads to circadian rhythm disruption in Alzheimer's disease. Mol. Neurodegener., 10, 13.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Kang J.E., Lim M.M., Bateman R.J., Lee J.J., Smyth L.P., Cirrito J.R., Fujiki N., Nishino S., Holtzman D.M. (2009) Amyloid-beta dynamics are regulated by orexin and the sleep-wake cycle. Science, 326, 1005–1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Musiek E.S., Lim M.M., Yang G., Bauer A.Q., Qi L., Lee Y., Roh J.H., Ortiz-Gonzalez X., Dearborn J.T., Culver J.P.. et al. (2013) Circadian clock proteins regulate neuronal redox homeostasis and neurodegeneration. J. Clin. Invest., 123, 5389–5400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Hayashi Y., Koyanagi S., Kusunose N., Okada R., Wu Z., Tozaki-Saitoh H., Ukai K., Kohsaka S., Inoue K., Ohdo S.. et al. (2013) The intrinsic microglial molecular clock controls synaptic strength via the circadian expression of cathepsin S. Sci. Rep., 3, 2744.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Fonken L.K., Frank M.G., Kitt M.M., Barrientos R.M., Watkins L.R., Maier S.F. (2015) Microglia inflammatory responses are controlled by an intrinsic circadian clock. Brain Behav. Immun., 45, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Musiek E.S., Holtzman D.M. (2016) Mechanisms linking circadian clocks, sleep, and neurodegeneration. Science, 354, 1004–1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Kornmann B., Schaad O., Reinke H., Saini C., Schibler U. (2007) Regulation of circadian gene expression in liver by systemic signals and hepatocyte oscillators. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol., 72, 319–330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Turek F.W., Joshu C., Kohsaka A., Lin E., Ivanova G., McDearmon E., Laposky A., Losee-Olson S., Easton A., Jensen D.R.. et al. (2005) Obesity and metabolic syndrome in circadian Clock mutant mice. Science, 308, 1043–1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Rudic R.D., McNamara P., Curtis A.M., Boston R.C., Panda S., Hogenesch J.B., Fitzgerald G.A. (2004) BMAL1 and CLOCK, two essential components of the circadian clock, are involved in glucose homeostasis. PLoS Biol., 2, e377.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Shimba S., Ishii N., Ohta Y., Ohno T., Watabe Y., Hayashi M., Wada T., Aoyagi T., Tezuka M. (2005) Brain and muscle Arnt-like protein-1 (BMAL1), a component of the molecular clock, regulates adipogenesis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U S A, 102, 12071–12076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Griebel G., Ravinet-Trillou C., Beeske S., Avenet P., Pichat P. (2014) Mice deficient in cryptochrome 1 (cry1 (-/-)) exhibit resistance to obesity induced by a high-fat diet. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne), 5, 49.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. He B., Nohara K., Park N., Park Y.S., Guillory B., Zhao Z., Garcia J.M., Koike N., Lee C.C., Takahashi J.S.. et al. (2016) The small molecule nobiletin targets the molecular oscillator to enhance circadian rhythms and protect against metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab., 23, 610–621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Scott E.M., Carter A.M., Grant P.J. (2008) Association between polymorphisms in the Clock gene, obesity and the metabolic syndrome in man. Int. J. Obes. (Lond), 32, 658–662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Sookoian S., Gemma C., Gianotti T.F., Burgueno A., Castano G., Pirola C.J. (2008) Genetic variants of Clock transcription factor are associated with individual susceptibility to obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 87, 1606–1615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Woon P.Y., Kaisaki P.J., Braganca J., Bihoreau M.T., Levy J.C., Farrall M., Gauguier D. (2007) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like (BMAL1) is associated with susceptibility to hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U S A, 104, 14412–14417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Englund A., Kovanen L., Saarikoski S.T., Haukka J., Reunanen A., Aromaa A., Lonnqvist J., Partonen T. (2009) NPAS2 and PER2 are linked to risk factors of the metabolic syndrome. J. Circadian Rhythms., 7, 5.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Vieira E., Ruano E., Figueroa A.L., Aranda G., Momblan D., Carmona F., Gomis R., Vidal J., Hanzu F.A. (2014) Altered clock gene expression in obese visceral adipose tissue is associated with metabolic syndrome. PLoS One, 9, e111678.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Nakahata Y., Sahar S., Astarita G., Kaluzova M., Sassone-Corsi P. (2009) Circadian control of the NAD+ salvage pathway by CLOCK-SIRT1. Science, 324, 654–657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Blakemore A.I., Meyre D., Delplanque J., Vatin V., Lecoeur C., Marre M., Tichet J., Balkau B., Froguel P., Walley A.J. (2009) A rare variant in the visfatin gene (NAMPT/PBEF1) is associated with protection from obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring), 17, 1549–1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Damiola F., Le Minh N., Preitner N., Kornmann B., Fleury-Olela F., Schibler U. (2000) Restricted feeding uncouples circadian oscillators in peripheral tissues from the central pacemaker in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Genes Dev., 14, 2950–2961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Kohsaka A., Laposky A.D., Ramsey K.M., Estrada C., Joshu C., Kobayashi Y., Turek F.W., Bass J. (2007) High-fat diet disrupts behavioral and molecular circadian rhythms in mice. Cell Metab., 6, 414–421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Martinek S., Inonog S., Manoukian A.S., Young M.W. (2001) A role for the segment polarity gene shaggy/GSK-3 in the Drosophila circadian clock. Cell, 105, 769–779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Zheng X., Yang Z., Yue Z., Alvarez J.D., Sehgal A. (2007) FOXO and insulin signaling regulate sensitivity of the circadian clock to oxidative stress. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. U S A, 104, 15899–15904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Hu Y., Shmygelska A., Tran D., Eriksson N., Tung J.Y., Hinds D.A. (2016) GWAS of 89,283 individuals identifies genetic variants associated with self-reporting of being a morning person. Nat. Commun., 7, 10448.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Jones S.E., Tyrrell J., Wood A.R., Beaumont R.N., Ruth K.S., Tuke M.A., Yaghootkar H., Hu Y., Teder-Laving M., Hayward C.. et al. (2016) Genome-Wide Association Analyses in 128,266 Individuals Identifies New Morningness and Sleep Duration Loci. PLoS Genet., 12, e1006125.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Jenkins R. (2001) Churchill: A Biography. Farrar, Straus and Giroux, New York. [Google Scholar]
- 95. Toh K.L., Jones C.R., He Y., Eide E.J., Hinz W.A., Virshup D.M., Ptacek L.J., Fu Y.H. (2001) An hPer2 phosphorylation site mutation in familial advanced sleep phase syndrome. Science, 291, 1040–1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Xu Y., Padiath Q.S., Shapiro R.E., Jones C.R., Wu S.C., Saigoh N., Saigoh K., Ptacek L.J., Fu Y.H. (2005) Functional consequences of a CKIdelta mutation causing familial advanced sleep phase syndrome. Nature, 434, 640–644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Patke A., Murphy P.J., Onat O.E., Krieger A.C., Ozcelik T., Campbell S.S., Young M.W. (2017) Mutation of the human circadian clock gene CRY1 in familial delayed sleep phase disorder. Cell, 169, 203–215. e213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Most E.I., Scheltens P., Van Someren E.J. (2010) Prevention of depression and sleep disturbances in elderly with memory-problems by activation of the biological clock with light–a randomized clinical trial. Trials, 11, 19.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Sack R.L., Lewy A.J., Blood M.L., Keith L.D., Nakagawa H. (1992) Circadian rhythm abnormalities in totally blind people: incidence and clinical significance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 75, 127–134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Atkinson G., Edwards B., Reilly T., Waterhouse J. (2007) Exercise as a synchroniser of human circadian rhythms: an update and discussion of the methodological problems. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol., 99, 331–341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Zee P.C., Attarian H., Videnovic A. (2013) Circadian rhythm abnormalities. Continuum (Minneap Minn), 19, 132–147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Dahlitz M., Alvarez B., Vignau J., English J., Arendt J., Parkes J.D. (1991) Delayed sleep phase syndrome response to melatonin. Lancet, 337, 1121–1124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Mundey K., Benloucif S., Harsanyi K., Dubocovich M.L., Zee P.C. (2005) Phase-dependent treatment of delayed sleep phase syndrome with melatonin. Sleep, 28, 1271–1278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Lemoine P., Wade A.G., Katz A., Nir T., Zisapel N. (2012) Efficacy and safety of prolonged-release melatonin for insomnia in middle-aged and elderly patients with hypertension: a combined analysis of controlled clinical trials. Integr. Blood Press Control, 5, 9–17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Kennedy S.H., Emsley R. (2006) Placebo-controlled trial of agomelatine in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol., 16, 93–100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106. Lockley S.W., Dressman M.A., Licamele L., Xiao C., Fisher D.M., Flynn-Evans E.E., Hull J.T., Torres R., Lavedan C., Polymeropoulos M.H. (2015) Tasimelteon for non-24-hour sleep-wake disorder in totally blind people (SET and RESET): two multicentre, randomised, double-masked, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet, 386, 1754–1764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Banerjee S., Wang Y., Solt L.A., Griffett K., Kazantzis M., Amador A., El-Gendy B.M., Huitron-Resendiz S., Roberts A.J., Shin Y.. et al. (2014) Pharmacological targeting of the mammalian clock regulates sleep architecture and emotional behaviour. Nat. Commun., 5, 5759.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Hirota T., Lee J.W., St John P.C., Sawa M., Iwaisako K., Noguchi T., Pongsawakul P.Y., Sonntag T., Welsh D.K., Brenner D.A.. et al. (2012) Identification of small molecule activators of cryptochrome. Science, 337, 1094–1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]