Abstract
The E3 ubiquitin ligase adaptor speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP) is frequently dysregulated in prostate adenocarcinoma (PC), via either somatic mutations or mRNA downregulation, suggesting an important tumor suppressor function. To examine its physiologic role in the prostate epithelium in vivo, we generated mice with prostate-specific biallelic ablation of Spop. These mice exhibited increased prostate mass, prostate epithelial cell proliferation, and expression of c-MYC protein compared to littermate controls, and eventually developed prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN). We found that SPOPWT can physically interact with c-MYC protein and, upon exogenous expression in vitro, can promote c-MYC ubiquitination and degradation. This effect was attenuated in PC cells by introducing PC-associated SPOP mutants or upon knockdown of SPOP via short-hairpin-RNA, suggesting that SPOP inactivation directly increases c-MYC protein levels. Gene set enrichment analysis revealed enrichment of Myc-induced genes in transcriptomic signatures associated with SPOPMT. Likewise, we observed strong inverse correlation between c-MYC activity and SPOP mRNA levels in two independent PC patient cohorts. The core SPOPMT;MYCHigh transcriptomic response, defined by the overlap between the SPOPMT and c-MYC transcriptomic programs, was also associated with inferior clinical outcome in human PCs. Finally, the organoid-forming capacity of Spop-null murine prostate cells was more sensitive to c-MYC inhibition than that of Spop-WT cells, suggesting that c-MYC upregulation functionally contributes to the proliferative phenotype of Spop knock-out prostates. Taken together, our data highlight SPOP as an important regulator of luminal epithelial cell proliferation and c-MYC expression in prostate physiology, identify c-MYC as a novel bona fide SPOP substrate, and help explain the frequent inactivation of SPOP in human PC. We propose SPOPMT–induced stabilization of c-MYC protein as a novel mechanism that can increase total c-MYC levels in PC cells, in addition to amplification of c-MYC locus.
Keywords: SPOP, Cullin-3, c-Myc turnover, knockout mouse, CRPC, tumor suppressor
INTRODUCTION
Whole exome sequencing studies have identified the Cullin-3-based ubiquitin (Ub) ligase adaptor SPOP as one of the genes that is most frequently affected by non-synonymous somatic point mutations in primary prostate adenocarcinoma (PC or PRAD) 1–4. Mutation of conserved residues in the SPOP substrate-binding pocket altering its substrate specificity 5–7 is an early event in prostate carcinogenesis 2, 8, suggesting that they are an important oncogenic driver.
The list of known SPOP substrates has rapidly expanded and currently includes the death domain-associated protein Daxx 9, the phosphatase Puc 7, the transcriptional regulators Ci/Gli 7, 10, MacroH2A 7, and DDIT3/CHOP 11, the desumoylase SENP712, CDC2013, DEK 14 and ERG 15, 16, the androgen receptor (AR) 6, 17 and its coactivators Steroid Receptor Coactivator (SRC)-3 5, 14, 18 and TRIM24 14, 19. Previously, we demonstrated that PC-associated SPOP mutants are unable to interact with AR or SRC-3 5, 6, leading to stabilization of AR and SRC-3 and an increase in AR-axis transcriptional output, thus providing a possible mechanism to explain their role in PC pathophysiology. Indeed, the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) analysis of 333 primary prostate carcinomas has confirmed that SPOPMT tumors have the highest levels of AR-induced transcripts 4.
However, the physiological role of endogenous SPOPWT in the prostate epithelium remains to be fully elucidated. Towards this goal, we utilized two Spop (also known as Pcif1) KO mouse models; one whole-body hemizygous and one conditional prostate-specific biallelic ablation model. Ablation of one or two Spop alleles resulted in increased prostate mass, cell proliferation, and higher expression of AR and c-MYC proteins in the mouse prostate luminal epithelial cells, compared to respective controls. Ablation of both Spop alleles in the prostate resulted in hyperplasia, dysplasia, and nuclear atypia in the luminal epithelium which, by 38 weeks of age, developed into prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN). Our studies further revealed c-MYC as a novel bona fide SPOP substrate. SPOPWT promotes c-MYC ubiquitination and degradation and this capacity is attenuated in the PC-associated SPOP mutants. Bioinformatics analysis of transcriptomic signatures associated with SPOPMT – derived from human PC specimens (TCGA-PRAD)4 and from in vitro expression of SPOPMT in PC cells6– revealed enrichment for cMyc-induced genes. Additionally, the core geneset, defined by the overlap between the SPOPMT and c-Myc transcriptomic program, was prognostic of inferior clinical outcome when applied to a human PC dataset. Taken together, our data highlight SPOP as an important regulator of luminal cell proliferation and c-Myc expression in the normal prostate epithelium and help explain why SPOP is frequently inactivated in human PC.
RESULTS
Prostate-specific biallelic ablation of Spop increases prostate mass and luminal epithelial cell proliferation
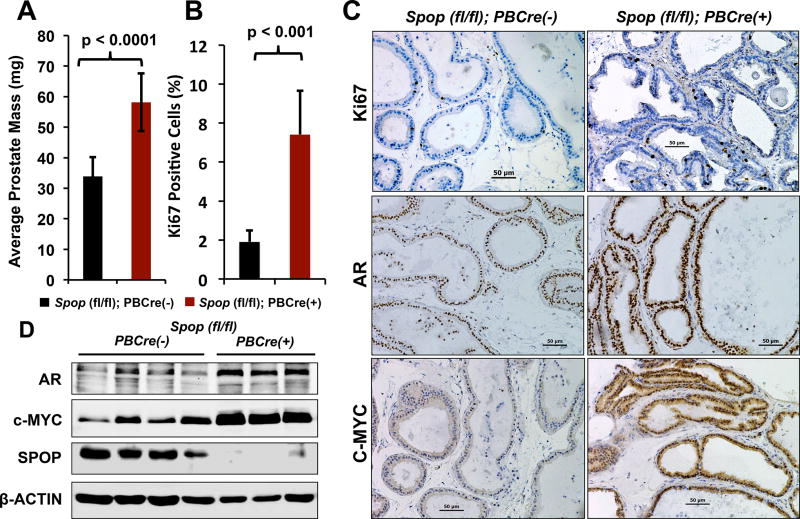
Surveys of numerous clinical PC datasets unequivocally demonstrate that Spop mRNA levels are frequently decreased in primary and hormone-naïve metastatic PC compared to normal prostate tissue (2, 20 and Supp. Fig. 1). This observation led us to examine the exact function of SPOPWT in normal prostate physiology. As homozygous Spop deletion results in neonatal lethality (between E18.5 and P1) 21, we generated a prostate specific biallelic knockout mouse model (Suppl. Fig. 2). Targeted biallelic ablation of Spop in the prostates of Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) mice resulted in significantly increased prostate mass compared to Spopfl/fl;PBCre(-) littermates (p-value<0.0001, Fig. 1A) and increased proliferation in the prostate luminal epithelium (as determined by immunohistochemistry for Ki67, p-value<0.001, Fig. 1B-C and Suppl. Fig. 3), while it had no effect on the overall mass of the mice (Suppl. Fig. 3). This finding led us to examine the expression of two key regulators of prostate cell proliferation, AR and c-MYC 22,23, 24, and we found that the Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) prostates exhibited significantly increased expression of AR and c-MYC as determined by immunohistochemistry (Fig. 1C and Suppl. Fig. 4A-B) and immunoblot (Fig. 1D and, for quantification by densitometry, Suppl. Fig. 4C-D) compared to Spopfl/fl;PBCre(-) controls.
Figure 1. Prostate-specific biallelic ablation of Spop leads to significantly increased prostate mass, enhanced cell proliferation, and elevated expression of AR and c-MYC proteins.
A. Prostate mass of 8-week Spopfl/fl;PBCre(-) (n=13) and Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) (n=10) mice. B. Presence of Ki67(+) cells in the ventral prostates of 8-week old Spopfl/fl;PBCre(-) (n=7) and Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) (n=8) mice. C. Immunohistochemical analysis of AR and c-MYC expression in the ventral prostates of 8-week old Spopfl/fl;PBCre(-) (n=7) and Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) (n=8) mice. Note: higher magnifications are shown in Suppl. Fig. 4. D. Total tissue lysates were prepared from prostates of 8-week Spopfl/fl;PBCre(-) (n=4) and Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) (n=3) and analyzed by immunoblot for SPOP, AR, c-MYC and β-ACTIN.
Prostate-specific biallelic ablation of Spop leads to the development of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia
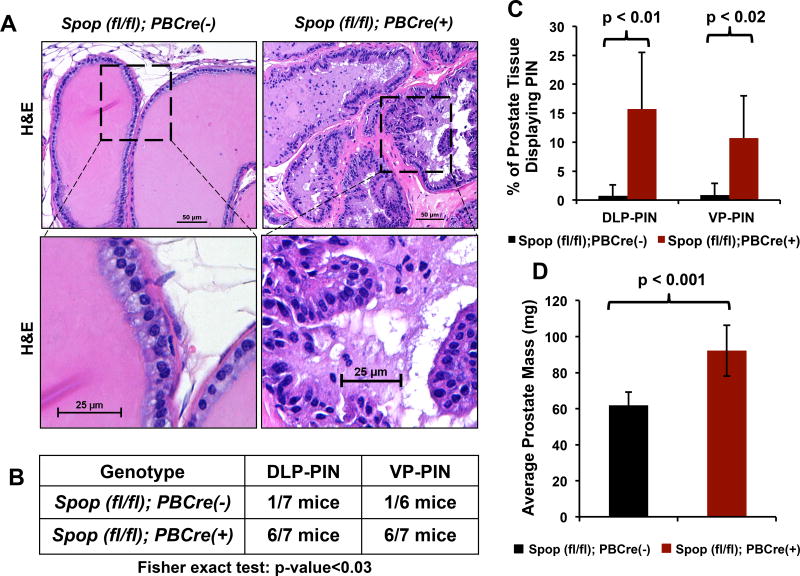
Having established a critical role for Spop as a regulator of prostate epithelial cell proliferation and expression of AR and c-MYC protein levels in 8-week old mice, we next examined prostates from 38-week old Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) and Spopfl/fl;PBCre(-) mice to determine the effects of prolonged absence of Spop on the mouse prostate. We found that biallelic ablation of Spop resulted in increased cellularity, hyperplasia, nuclear atypia, and dysplasia in the luminal epithelium developing into prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) in the dorsolateral prostate (DLP) and ventral prostate (VP) (Fig. 2A-C). These cells stained positive for the luminal marker cytokeratin-8 (Suppl. Fig. 5A-B). Similar to the observations in the 8-week old mice, 38-week old Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) mice continued to have significantly increased prostate mass compared to their Spopfl/fl;PBCre(-) littermates (p-value<0.001, Fig. 2D), despite no difference in overall body mass (Suppl. Fig. 3B).
Figure 2. Prostate-specific biallelic ablation of Spop leads to prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia by week-38.
A. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of VP sections from 38-week old Spopfl/fl;PBCre(-) and Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) mice (representative photographs at low and high power magnification). Prostates with biallelic ablation of Spop exhibit epithelial hyperplasia, dysplasia, nuclear atypia and morphologic features consistent with the development of PIN. B. Quantification of prostates with PIN lesions in DLP and VP from 38-week old Spopfl/fl;PBCre(-) and Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) mice. PIN lesions were found in 6/7 Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) mice. The 7th Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) prostate was also abnormal (hyperplastic/dysplastic), but did not reach the level of PIN. C. Percentage of tissue affected by PIN in the dorsolateral prostate (DLP) and ventral prostate (VP) from 38-week old Spopfl/fl;PBCre(-) and Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) mice. D. Prostate mass of 38-week old Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) mice is increased compared to that of 38-week old Spopfl/fl;PBCre(-) mice.
Loss of one Spop allele increases AR and c-MYC expression and epithelial cell proliferation in Spop−/+ mouse prostates
Having demonstrated in our prostate-specific conditional knockout model that biallelic ablation of Spop increases prostate mass, luminal epithelial cell proliferation and c-MYC protein levels, we next examined the effects of loss of a single Spop allele. For that purpose, we used our whole body Spop hemizygous (Spoptm1a(KOMP)Wtsi or, for simplicity, Spop−/+) mice. Similar to our Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+), we found that disruption of one Spop allele also resulted in increased mouse prostate mass (p<0.05, Suppl. Fig. 6A) at 8-week of age compared to wildtype mice, without any significant difference in overall body mass (Suppl. Fig. 6B). Immunohistochemical analysis demonstrated that Ki67 expression was also higher (p-value<0.02, Suppl. Fig. 6C) in the prostate luminal epithelium of Spop heterozygotes compared to wildtype mice. In agreement with our prior results6 and current finding in prostate-specific biallelic knockout model, we observed an increase in both AR and c-MYC expression in Spop heterozygote prostates compared to wildtype littermates (Suppl. Fig. 7).
Biallelic loss of Spop results in an increase in TUNEL-positive cells in mouse prostate tissue and decrease in organoid size
Stemming from our hypothesis that SPOP plays a critical role in the prostate epithelium, we next examined whether SPOP can regulate cell death. Indeed, we found an increase in the presence of TUNEL-positive cells in both prostate tissue and organoids generated from 8-week old Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) mice (Suppl. Fig. 8 and 9). We found that organoids from 8-week old Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) mice were significantly smaller than those from control littermates (Suppl. Fig. 9).
In order to further understand the fate of the Spop knockout cells, we used the Cre-recombinase enzyme to track the fate of SPOP KO cells. Immunohistochemical staining revealed that prostate epithelium of 8-week mice had high expression of Cre-recombinase protein (in the ventral and dorsolateral prostate), while Cre-negative littermate controls had no staining, as expected (Suppl. Fig. 10). Interestingly, the population of Cre-positive cell decreased in the prostate of older Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) mice while it remained high in 12-month old SpopWT;PBCre(+) mice, suggesting that the reduction in population of Cre-positive cell in the knockout mice was not due to an age-related decrease in testosterone and/or activity of probasin promoter (Suppl. Fig. 10).
c-Myc induced genes are enriched in the SPOPMT transcriptional output
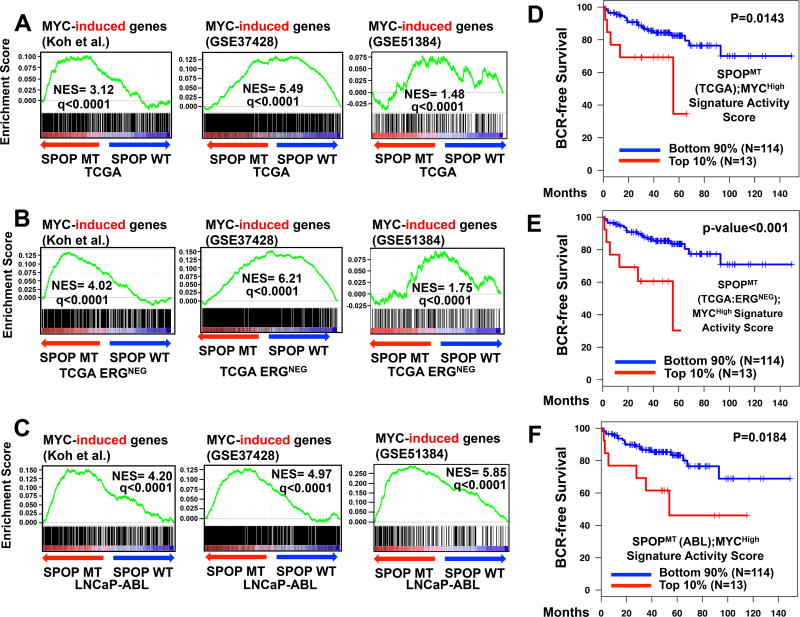
The increased expression of c-MYC in prostate of Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) suggests a possible regulation of c-MYC by SPOP. Hence, we examined the contribution of c-MYC to the cellular response triggered by SPOP. First, we derived gene signatures of high versus low c-MYC states (MYCHigh/MYCLow) using three published datasets: a) knockdown of c-Myc via siRNA in LNCaP cells25, b) c-Myc overexpression in LNCaP cells (GSE51384 and 26), and 3) c-Myc overexpression in epithelial cells isolated from the mouse ventral prostate (GSE37428 and 27). We next derived two gene signatures of SPOPMT versus SPOPWT by considering either all primary patient specimens in the TCGA-PRAD cohort4 or by focusing only on the ERG-fusion negative patient specimens (because SPOP mutations are restricted to ERG-fusion negative PCs). Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) analysis revealed significant enrichment of MYC-induced genes in both SPOPMT(TCGA) and SPOPMT(TCGA-ERGNEG) (Fig. 3A-B). We also compared the MYCHigh signature against a transcriptomic signature induced by SPOPMT in LNCaP-Abl PC cells in vitro (further denoted SPOPMT(Abl)), that we have previously reported6 and observed strong enrichment score (Fig. 3C).
Figure 3. Mutant SPOP and MYC share a common transcriptional program that is associated with inferior clinical outcomes in PC patients.
A-C. We compared the transcriptomic footprint of SPOPMT derived from the TCGA-PRAD PC patient cohort (via comparison of the gene expression profiles of SPOPMT versus SPOPWT in all primary patients (SPOPMT(TCGA)), in ERG-fusion negative cohort (SPOPMT(TCGA-ERGNEG)), and the transcriptomic footprint derived from an in-vitro LNCaP-Abl PC cell model (SPOPMT(Abl))) with three publicly available gene signatures of prostate high MYC versus low MYC states (Koh et al.25, GSE5138426 and GSE3742827) using GSEA. We observed significant positive enrichment of MYC-induced genes (q<0.001, normalized enrichment score or NES greater than zero) for all nine comparisons.
D-F. Core (overlapping) genes regulated by both MYC and SPOPMT in TCGA-PRAD ((D)SPOPMT(TCGA); MYCHigh and (E) SPOPMT(TCGA-ERGNEG); MYCHigh) or in PC cell-line SPOPMT(LNCaP-Abl);MYCHigh) were inferred by selecting genes that are significantly and concordantly regulated in the respective SPOPMT and in the Koh et al.25 MYCHigh/MYCLow gene signatures. We then applied both SPOPMT(TCGA);MYCHigh and SPOPMT(Abl);MYCHigh signatures to a PC dataset for which clinical outcomes (biochemical recurrence, BCR) have been reported28; for each PC specimen we calculated the signature activity score, as described in Methods. All three SPOPMT;MYCHigh core geneset have significantly shorter BCR-free survival in the upper 10% compared to the bottom 90% (log-rank test, p<0.02).
Myc and mutant SPOP share a common core transcriptional program that is is associated with inferior clinical outcomes in PC patients
We next intersected the c-MYCHigh transcriptomic program (from 25) separately with the SPOPMT(TCGA), SPOPMT(TCGA-ERGNEG), or SPOPMT(Abl) signatures and applied these three core signatures to a large PC patient dataset28. In all three analyses, we found that the core MYCHigh;SPOPMT; transcriptional program was strongly associated with inferior clinical outcomes (decreased BCR-free survival, p-value<0.02 by log-rank test, Fig. 3D-F)) in human PCs, while the individual SPOPMT and MYCHigh transcriptional programs did not reach statistical significance (Suppl. Fig. 11, an observation that is in agreement with the fact that SPOPMT status, as a single biomarker, is not associated with poor clinical outcomes in PC27). Thus, we now propose that the shared core SPOPMT;MycHigh transcriptional program is reflective of a critical cooperation between SPOP and c-Myc that is used to drive clinically aggressive PC. Over-representation analysis (ORA) of pathways and processes highlighted that the combined signature SPOPMT(TCGA);MycHigh enriched for key cell cycle-related cellular pathways (Suppl. Fig. 12).
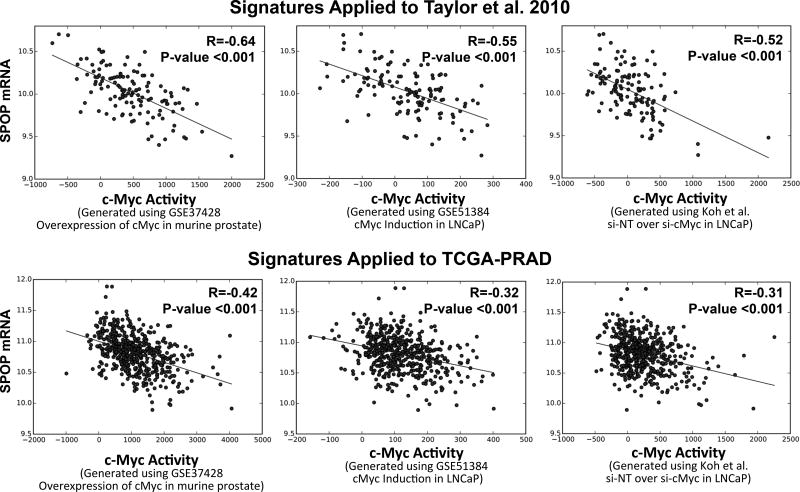
Lastly, we computed MYC activity scores by applying the above mentioned gene signatures to the Taylor et al. and TCGA-PRAD patient datasets. We found significant inverse correlation between SPOP mRNA level and MYC activity, suggesting that SPOP suppresses MYC activity in human PC (Fig. 4).
Figure 4. Myc activity scores derived using three independent gene signatures applied to two separate human PC patients cohorts show significant correlation with mRNA levels of SPOP.
To obtain cMyc activity score, we computed a sum of z-score for all the genes in the various Myc signatures (cMyc overexpression in murine (GSE37428), cMyc overexpression in LNCaP (51384), and cMyc inhibition (Koh et al.) and applied them to the Taylor et al. (2010) or the TCGA-PRAD (2015) patient dataset. Scatterplots of Myc activity score versus SPOP mRNA level in Taylor et al. 2010 specimen and in TCGA-PRAD 2015 are shown in A and B (respectively). Corresponding correlation (R values) by Pearson’s are included.
SPOP directly binds the c-Myc protein, resulting in ubiquitination and degradation of c-Myc
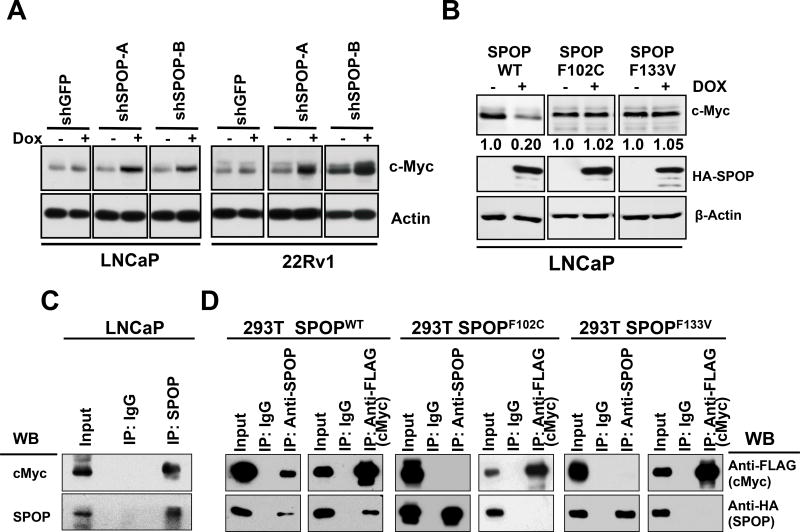
Our finding of increased AR protein levels in mouse prostates with Spop ablation is in agreement with our prior finding that AR is a bona fide SPOP substrate 6. However, the impact of SPOP on c-MYC turnover has not been previously reported. Our in vivo observation of increased c-Myc protein levels in Spop-ablated mouse prostates, along with identification of a critical, shared core transcriptional program between these two important PC drivers, led us to hypothesize that c-MYC is also a SPOP substrate. Thus, we next examined the expression of c-MYC upon knockdown of SPOP via short-hairpin RNA using a doxycycline inducible system. We found that inhibition of SPOP in PC cell lines resulted in an increase in c-MYC protein in PC cell lines (Fig. 5A and Suppl. Fig. 13). We next utilized previously generated LNCaP cells expressing SPOPWT or PC-associated substrate binding pocket mutants (SPOP-F102C and SPOP-F133V) under the control of a tetracycline-inducible promoter and found that SPOPWT, but not its PC-associated mutants, caused significant depletion of c-MYC protein (Fig. 5B).
Figure 5. SPOP directly binds the c-Myc protein, resulting in ubiquitination and degradation of c-Myc.
(a) LNCaP and 22Rv1 cells with Tet-inducible expression of two different shSPOP constructs were treated with 500 ng/mL of doxycycline. Supplementary Figure 13 shows the corresponding RTqPCR data for Spop mRNA knockdown. Inhibition of Spop via shRNA results in up-regulation of c-MYC protein. (b) LNCaP cells with Tet-inducible expression of SPOPWT or PC-associated mutant SPOPF102C or SPOPF133V were induced with 500 ng/mL of doxycycline (Dox) for 48 h. Immunoblot analyses were conducted for HA-tagged SPOP, c-Myc and β actin. The numbers beneath the bands represent densitometry analysis and are normalized to β-actin expression. (c) LNCaP cells were treated with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (250 nM for 6 h) and total cell lysates were prepared. Immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-SPOP antibody. Immunoblot analyses (WB) were conducted for expression of c-Myc and SPOP in the immunoprecipitates. (d) SPOPWT binds c-Myc protein and this capacity is attenuated by the PC-associated mutations, SPOPF102C and SPOPF133V. 293T cells were co transfected with HA-tagged SPOPWT (or SPOPF102C or SPOPF133V) and FLAG-tagged c-Myc expression vectors for 24 h and treated with 250 nM of bortezomib for 6 h. At the end of treatment, total cell lysates were prepared and FLAG-Myc or HA-SPOP were immunoprecipitated from the lysates. Immunoblot analyses were conducted for FLAG-Myc and HA-SPOP in the immunoprecipitates.
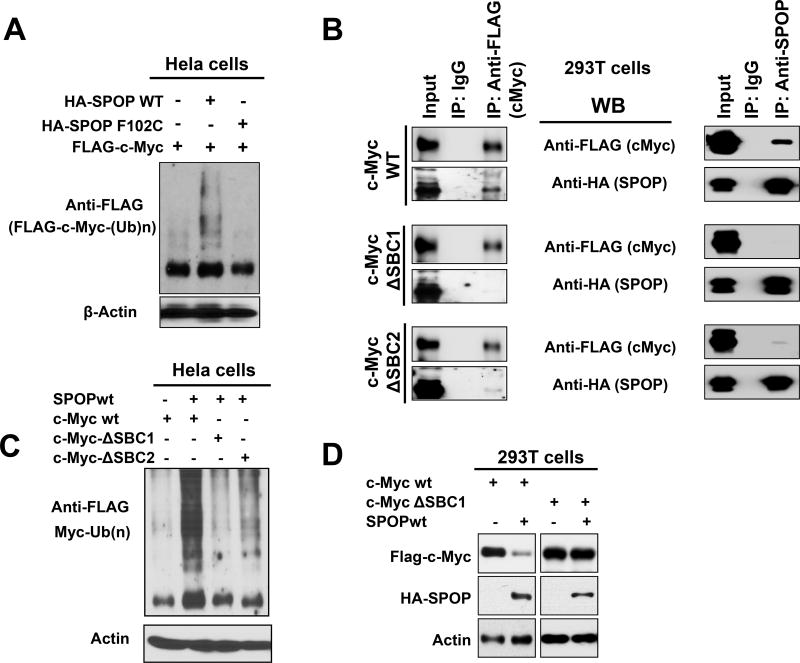
To examine whether SPOP physically associates with c-MYC in PC cells, we immunoprecipitated SPOP from the lysates of LNCaP PC cells. We found that endogenous SPOP (WT) can physically associate with c-Myc in human PC cells (Fig. 5C). We next co-expressed c-Myc and SPOPWT or the PC-associated substrate binding pocket mutant SPOPF102C and SPOPF133V in 293T cells and observed that SPOPWT could effectively co-immunoprecipitate with c-Myc. This capacity was attenuated by its PC-associated substrate binding pocket mutations (Fig. 5C). In agreement, in an ubiquitination assay, SPOPWT, but not the PC-associated mutant SPOPF102C, promoted ubiquitination of c-Myc (Fig. 6A).
Figure 6. SPOPWT, but not SPOPF102C, promotes ubiquitination of c-Myc.
A. Hela cells were transfected as indicated with pcDNA3.1-HA-SPOPWT or pcDNA3.1-HA-SPOP-F102C, along with pcDNA3.1-2xFlag-c-Myc, together with His-Ubiquitin, Cullin 3 and Rbx1 expression vectors for 24 hours and incubated with 250 nM bortezomib for an additional 6 hours. Ubiquitinated proteins in the cell lysates were purified using Ni-NTA beads. Ubiquitinated, Flag-tagged c-Myc was detected by immunoblotting using anti-Flag M2 antibody. Immunoblotting for actin was performed in the total cell lysates and served as input. SPOPWT, but not the PC-associated mutant SPOPF102C, promoted ubiquitination of c-Myc. B. Role of SBC1 and SBC2 in the direct interaction of SPOP with c-Myc. The c-Myc protein contains two putative SBC sequences: SBC1 (185 VCSTS 189) and SBC2 (261 PTTSS 265). 293T cells were transfected with expression vectors for SPOP-WT and FLAG-tagged wild-type c-Myc, or c-Myc mutated in SBC (ΔSBC) 1 or 2, for 24 hours. Then, bortezomib (250 nM) was added for 6 hours. Total cell lysates were prepared and immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-FLAG or anti-SPOP antibody. Immunoblot analyses (WB) were conducted with anti-FLAG (for Myc) and anti-HA-HRP (for HA-tagged SPOP) in the immunoprecipitates. While WT c-Myc can bind to the HA-tagged SPOPWT, mutation of SBC1 (ΔSBC1) abrogates the interaction of c-Myc with SPOP in vitro. Mutation at SBC2 (ΔSBC2) also impairs the SPOPWT-Myc interaction, but a faint residual binding persists. C. Ubiquitination of SBC-mutant c-Myc. Hela cells were transfected as indicated with pcDNA3.1-HA-SPOP along with pcDNA3.1-2xFlag-c-Myc or its SBC mutants, pcDNA3.1-2xFlag-c-Myc STS187/188/189AAA (ΔSBC1) and pcDNA3.1-2xFlag-c-Myc TSS263/264/265AAA (ΔSBC2), together with His-Ubiquitin, Cullin 3 and Rbx1 expression vectors for 24 hours. Then, the cells were incubated with 250 nM of bortezomib for an additional 6 hours. At the end of treatment, total cell lysates were prepared and total ubiquitinated proteins in the lysates were purified using Ni-NTA beads. The eluted proteins were loaded for immunoblot analyses for the detection of the ubiquitinated, Flag-tagged c-Myc using anti-Flag M2 antibody. Immunoblotting for actin was performed in the total cell lysates and served as input. SPOPWT-promoted ubiquitination of c-Myc was effectively suppressed by the mutation of SBC1 in c-Myc. Mutation at SBC2 also impaired the SPOPWT-promoted ubiquitination, but some residual ubiquitination persisted. D. 293T cells were transfected as indicated with pcDNA3.1-HA-SPOPWT along with pcDNA3.1-2xFlag-c-Myc or pcDNA3.1-2xFlag-c-Myc STS187/188/189AAA (ΔSBC1) for 24 hours. Immunoblot analyses (WB) were conducted for Myc, HA-tagged SPOP and actin. ΔSBC1 c-Myc was resistant to SPOP-promoted degradation.
We next examined whether the interaction between c-Myc and SPOPWT is due to SPOP directly binding to a specific sequence on c-Myc. A serine/threonine-rich SPOP Binding Consensus motif (SBC) has been previously defined7. Examination of the c-Myc protein sequence identified two such putative SBC sequences (SBC1: aa 185 VCSTS 189 and SBC2: aa 261 PTTSS 265). We generated expression vectors for c-Myc mutated at either of these putative SBCs and co-transfected them into 293T cells together with a SPOPWT vector. While WT c-Myc can bind to the HA-tagged SPOPWT, c-Myc mutated at SBC1 (ΔSBC1) is deficient in binding to SPOPWT (Fig. 6B). Mutation at SBC2 (ΔSBC2) also impaired the SPOPWT-Myc interaction, but a faint residual binding persisted.
In addition, ΔSBC1 c-Myc was largely insensitive to SPOP-promoted ubiquitination. ΔSBC2 c-Myc was also protected (albeit partially) from SPOP-promoted ubiquitination (Fig. 6C), in agreement with our finding of some weak persistent binding of SPOPWT to ΔSBC2 c-Myc. These data support the functional significance of the direct interaction between SPOP and c-Myc and identify the c-Myc SBC1 sequence as the dominant mediator of this binding (although a role for SBC2 is also likely, possibly in cooperation). In agreement, ΔSBC1 c-Myc was completely protected from SPOP-promoted degradation (Fig. 6D).
Post-translational regulation of c-Myc turnover by SPOPWT
Our finding that SPOPWT can directly bind the WT c-Myc protein and promote its ubiquitination, suggests that SPOPWT promotes post-translational degradation of c-Myc, similar to its effects on several other of its substrates 5, 6, 10, 14, 17. In support of a post-translational effect of SPOPWT on c-Myc turnover, we also found that upon co-transfection of SPOP and c-Myc expression vectors (i.e., conditions where SPOPWT suppresses c-Myc protein levels, Fig. 6D), we did not detect a decrease in mRNA levels of transfected c-Myc (Suppl. Fig. 14).
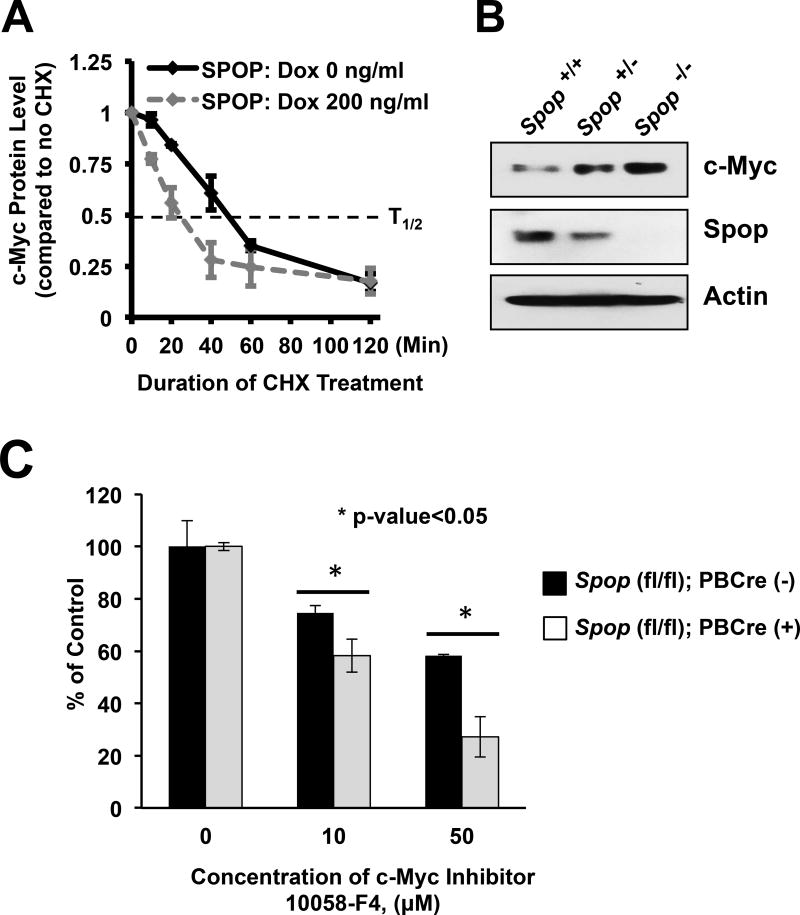
For further validation, we quantified the half-life of endogenous c-Myc in our PC LNCaP cells expressing SPOPWT upon induction with doxycycline. Using cycloheximide treatment to suppress new protein synthesis, we determined that induction of SPOPWT decreased the half-life of c-Myc in these cells from ~50 min to ~25 min (Fig. 7A and Suppl. Fig. 15). These data confirm that SPOPWT can post-translationally promote c-Myc protein turnover.
Figure 7. SPOP promotes degradation of c-Myc protein.
(a) Average protein levels of endogenous c-Myc in cycloheximide-treated LNCaP-HA-SPOPWT cells with or without Dox induction), plotted as the percentage of no cycloheximide treatment control (±S.E.) normalized to β-actin (data from at least three independent experiments). Induction of SPOPWT decreased the half-life of c-Myc protein in these cells from ~50 min to ~ 25 min, suggesting that SPOPWT can post translationally promote c-Myc protein turnover in PC cells. (b) Ablation of Spop in MEFs increases c-Myc protein levels in a dose-dependent manner. MEF cells were isolated from mice lacking both Spop alleles Spoptm1a(KOMP)Wtsi/tm1a(KOMP)Wtsi (for simplicity, Spop−/−), or one allele (Spop−/+), or none (Spop+/+) of the Spop alleles and subjected to immunoblot analysis for c-Myc protein and SPOP. (c) Increased expression of c-Myc protein is functionally important in Spop-null prostate cells. Organoids generated from whole prostates of 8-week-old Spop-null mice were more sensitive to a c-Myc inhibitor than those of control Spop-wildtype mice (* indicates p<0.05), suggesting that c-Myc protein upregulation contributes, at least partly, to the pathophysiology of Spop-null prostate luminal epithelial cells.
Ablation of Spop in MEFs increases c-Myc levels in a dose-dependent manner
We next examined whether SPOPWT can regulate c-Myc protein levels in non-prostate cells. Biallelic whole-body loss of Spop (Spop−/−) is incompatible with postnatal survival 21. However, we were able to generate mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) from mice lacking one (Spop−/+) or both (Spop−/−) Spop alleles and from wildtype littermates (Spop+/+). Using these MEFs, we found an inverse correlation between Spop and c-Myc protein levels (Fig. 7B), suggesting that the regulation of c-Myc protein levels by SPOPWT is not restricted to prostate cells.
MYC levels are tightly regulated by ubiquitin-proteasome system and multiple ubiquitin ligases have been identified to targets Myc as a substrate29–37. Based on this literature, we identified 16 regulators (E3 ligases and their adaptors, including SPOP itself), which have been proposed to regulate cMYC protein stability and thus, alter its function, and examined the mRNA expression levels of these regulators in PC patient dataset (Suppl. Fig. 16). We also examined whether the mRNA levels of these regulators showed any significant correlation with MYC activity in prostate. Like SPOP, we found that the mRNA levels of several other MYC regulators was lower in PC compared to normal tissue and generally showed an inverse correlation with MYC activity in patient datasets (Suppl. Table 1–6). Thus, we conclude that SPOP is one of several regulators that play critical role in tightly controlling MYC turnover rate in prostate tissue.
Loss of Spop increases sensitivity to Myc inhibition
Finally, we examined the functional significance of the regulation of c-MYC by SPOP in prostate cells. We examined c-MYC levels in our organoids generated from whole prostate of Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) mice and found that these cells retained their increased c-MYC protein level compared to organoids from Spopfl/fl;PBCre(-) littermates (Suppl. Fig. 17). Consequently, we found that the organoids generated from the Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) mice were more sensitive to MYC inhibition compared to those generated from control littermates (Fig. 7C), suggesting that the upregulation of MYC protein contributes, at least partly, to the pathophysiology of Spop-null prostate luminal epithelial cells.
DISCUSSION
The frequent presence of SPOP missense mutations and downregulation of its mRNA in PC suggests that SPOP plays an important tumor suppressor role in the normal prostate. We have previously reported that overexpression of SPOPWT decreases proliferation of PC cells in vitro 5. A similar tumor suppressor role has been proposed for SPOP in gastric cancer 38, colorectal cancer 39, 40, and in glioma 41. To date, SPOP deletion has never been observed in PC. We now examined the physiologic role of Spop in the mouse prostate utilizing whole-body heterozygous and prostate-specific biallelic ablation models. We should reiterate that these models were not intended to mimic human SPOPMT PC, where hotspot SPOP mutations always occur in heterozygote fashion (without LOH of the WT allele, thus suggesting that complete loss of SPOP expression and function never happens in human PC), but were rather designed to investigate the role of SPOP in the prostate epithelium. However, as SPOP mRNA levels in many human PCs are suppressed to, on average, half of normal prostate levels2, the hemizygous prostates may resemble the SPOP status of a subset of SPOPWT human PCs. For biallelic loss of Spop, a prostate-specific targeting approach was necessary (whole-body complete loss of Spop is incompatible with postnatal survival21). In both models, ablation of Spop resulted in increased prostate mass and luminal epithelial cell proliferation. In the homozygous prostate-specific knockout model, by week-38, the mice developed PIN lesions in the dorsolateral and ventral prostate.
Both models also showed increased expression of AR and c-MYC protein in the luminal cells. c-Myc is a proto-oncogene22 with an established role in PC23–25, 42–50, including the fact that the MYC locus on 8q24 is frequently amplified in human PC46, 51–54. As c-Myc previously had not received attention as a possible SPOP substrate, we examined further its relationship with SPOP. We found that SPOPWT, but not its PC-associated substrate binding pocket mutants, can promote ubiquitination and subsequent depletion of c-MYC protein. SPOPWT physically associates with c-MYC in PC cells, and this interaction is attenuated by the substrate binding pocket SPOP mutations found in PC, as well as by SBC mutation in c-Myc. Thus, we conclude that c-MYC is a newly identified bona fide SPOP substrate and propose Cul3/Rbx1 as a novel E3 ligase system for c-MYC, in addition to the already well-known FBXW732–34 and SKP2 35–37. We propose SPOPMT–induced stabilization of c-Myc protein as another mechanism that can raise c-MYC levels in PC cells, in addition to c-Myc locus amplification.
Our in vivo findings of c-MYC regulation by SPOP led us to further examine the relationship between c-MYC and SPOP signaling. We found that the transcriptomic footprints associated with SPOPMT in human PC specimens (TCGA cohort4) and in PC cells cultured in vitro6 both enriched for Myc-induced genes. Moreover, an overlapping, core transcriptomic program between the SPOPMT and MYCHigh gene signatures was predictive of inferior clinical outcomes in human PCs, regulating key cellular pathways (primarily cell cycle). Thus, while the SPOPMT status (as a single biomarker) does not appear so far to be associated with clinical outcomes in PC55, we now propose that the combined (dys)regulation of the SPOP and Myc pathways can cooperatively drive a clinically aggressive PC program. In agreement, we found that the organoid-forming capacity of Spop-null prostate cells is significantly more sensitive to MYC inhibition compared to that of SPOPWT cells, suggesting that MYC upregulation functionally contributes to the proliferative phenotype of Spop knockout prostates.
Another interesting observation of our study was the increased presence of TUNEL-positive nuclei in both prostate tissue and in organoids from 8-week old mice with biallelic loss of Spop. This, along with our observation that the population of Cre-positive cells decreased in Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+), prostates with time, while remaining high in aging SpopWT;PBCre(+) counterparts, likely suggest that the complete loss of SPOP may ultimately exert a negative selection pressure on the prostate cell. This dual role of SPOP is consistent with the clinical observation that although SPOP is frequently mutated and its mRNA expression downregulated in prostate cancer, the mutations are always heterozygous and there is always some residual SPOPWT mRNA expression. In other words, while the baseline levels of SPOP in the normal prostate likely exert a tumor suppressor role, and hence, it is favorable for the prostate cancer cell to partially suppress SPOP activity, however, some residual SPOP function remains critical for the survival of the prostate cancer cell.
In conclusion, our study highlights SPOP as an important regulator of cell proliferation and c-Myc expression in the prostate luminal epithelium and contribute to our understanding of its role in prostate physiology. We have identified c-MYC as a novel bona fide SPOP substrate and highlight a critical contribution of SPOPMT as a key partner of c-MYC in transcriptional regulation and clinical outcomes in PC. Collectively, these data help explain why SPOP is so frequently inactivated in human PC (by decreased expression and somatic point mutations).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell Culture
Human cells lines were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA), authenticated by STR profiling and subjected to mycoplasma testing, and passaged for fewer than 6 months. LNCaP cells harboring WT or mutant (F102C or F133V) SPOP under doxycycline-inducible promoter were described previously 5, 6 and were maintained in RPMI1640 medium with 10% tetracycline-free FBS (Atlanta Biotech. Inc., Atlanta, GA) and 300 µg/ml G-418 (Invitrogen). LNCaP and 22Rv1 harboring doxycycline-inducible shSPOP expression constructs, LNCaP-shSPOP-A, LNCaP-shSPOP-B, LNCaP-shGFP, 22Rv1-shSPOP-A, 22Rv1-shSPOP-B or 22Rv1-shGFP cell lines were maintained in RPMI1640 plus 10% Tet-tested FBS (Atlanta biotech.) and 0.5 µg/ml puromycin (Invitrogen).
Reagents and Antibodies
The antibodies used in this study were mouse-monoclonal anti-FLAG-M2 (#F1804), mouse anti-β-Actin (#A2228), mouse anti-FLAG-HRP (#A8592), anti-rat IgG-HRP (#A9037 Sigma), (from Sigma, St Louis, MO); rabbit-polyclonal anti-AR(N-20) (#SC-816), mouse-monoclonal anti-SPOP(B-8) (#SC-377206), and goat-polyclonal anti-SPOP(C-14) (#SC-66649), goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP (#SC-2004), and goat anti-mouse IgG-HRP (#SC-2005) (Santa Cruz Biotechnologies, Santa Cruz, CA); rat anti-HA-HRP (Roche); mouse anti-c-Myc-HRP (#MA1-81357, Thermo Scientific); rabbit monoclonal anti-c-Myc (#5605), mouse monoclonal anti-Cre Recombinase (#15036) (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA); mouse-monoclonal anti-K8 (#MMS-162P), rabbit polyclonal anti-K5 (#PRB-160P) (Covance, Berkeley, CA).
All animal experiments were performed under a protocol approved by the BCM IACUC.
Spop whole-body hemizygous mouse model
Spop Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion mice (Spoptm1a(KOMP)Wtsi), where a cassette containing β-galactosidase (LacZ) and neomycin-resistance genes was engineered into the Spop locus (after exon 3), interrupting the expression of the full-length Spop and resulting in a non-expressive allele (Suppl. Fig. 2), were obtained from the International Knockout Mouse Phenotyping Consortium (KOMP 56). We have documented that these heterozygote (Spop+/−) prostates express approximately half the amount of Spop mRNA compared to WT mice 6, which recapitulates its suppressed expression levels in SPOPWT hormone-naïve metastatic PCs 2.
Generation of Spopfl/fl;PBCre mice
Whole-body loss of both Spop alleles is incompatible with postnatal survival 21. Thus, biallelic ablation of Spop requires the development of a prostate-specific KO. For that purpose, we crossed our Spoptm1a(KOMP)Wtsi mice with ROSA-Flp mice (with the Flippase gene knocked into the ROSA26 locus), in order to remove the LacZ and neomycin-resistance cassettes (Suppl. Fig. 2). In doing so, we generated Spop floxed alleles (Spopfl), where Spop exons 4 and 5 (encoding the core of the MATH domain) are flanked by loxP sites. We then crossed our Spopfl/fl mice with a probasin (PB)-Cre transgenic mouse line 57 and, through multiple generations of matings, we obtained Spopfl/fl;PBCre(+) mice, where both Spop alleles are selectively ablated in the prostate luminal epithelium, and Spopfl/fl;PBCre(-) controls. Prostates from mice aged 8-week and 38-week were harvested for histology and immunoblot analysis.
Transient Transfection of Expression Vectors into Mammalian Cells
293T cells were transfected with expression vectors using Superfect transfection reagent (Qiagen) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Typically, for a 6-well plate, 3 μg of DNA/well was transfected; and for a 10-cm plate, 20 μg of DNA were utilized. Forty-eight hours post-transfection, the cells were harvested and washed with PBS. Total RNA or total cell lysates were prepared and used for RT-qPCR or immunoblot analyses as indicated.
Protein Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) Analysis
For determination of protein-protein interactions, 293T cells were co-transfected with FLAG-tagged c-Myc WT (or FLAG-tagged c-Myc ΔSBC1 or FLAG-tagged c-Myc ΔSBC2) and pcDNA3.1-HA-SPOPWT (or pcDNA3.1-HA-SPOPF102C or pcDNA3.1-HA-SPOPF133V) for 24hrs. Subsequently, the cells were treated with bortezomib for 16hrs, harvested and lysed in NP-40 lysis buffer containing protease inhibitor cocktail (F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd). Anti-FLAG and anti-SPOP antibodies were utilized for the immunoprecipitation reactions. The immuno-complexes were isolated by magnetic protein G-Dynabeads (Life Technologies), washed 4x with lysis buffer and eluted from the magnetic beads utilizing 1X SDS loading buffer and boiling the tubes at 100°C for 5 minutes. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose membranes, and detected by immunoblotting for FLAG-c-Myc (mouse anti-FLAG-HRP), HA-tagged SPOP (rat anti-HA-HRP), and SPOP.
LNCaP cells were collected and lysed in NP-40 lysis buffer with protease inhibitor cocktails. Anti-SPOP antibody was used in Co-IP analysis to precipitate SPOP-interacting protein complexes. The immuno-complexes were precipitated by protein G Dynabeads, washed, eluted, and separated by SDS-PAGE. SPOP and c-Myc protein were detected by immuno-blotting as described below.
Immunoblot analyses
After SDS-PAGE, the proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose or low-fluorescent PVDF membrane and detected by immunoblotting using monoclonal antibodies or specific anti-sera, as indicated. Blots were washed with 1X PBST and incubated with anti-mouse or anti-rabbit HRP-conjugated or IR-680 and IR-800 dye-conjugated secondary antibodies (LI-COR Biotechnology, Lincoln, NE) for 1hr. Protein signals were detected with SuperSignal Western chemiluminescent substrate (Thermo Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA) and developed with X-ray films according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Thermo Scientific, Inc) or via infrared detection of immunoblots using a LI-COR Odyssey 3000 infrared imager. Densitometric analysis was conducted using NIH ImageJ image analysis software 58 or QuantityOne Software (Bio-rad).
In Vivo (intracellular) Ubiquitination Assay
To examine intracellular ubiquitination of c-Myc that is specifically promoted by SPOP, Hela cells cultured in 10-cm plates were transiently co-transfected by 1.5 µg of plasmid pcDNA3.1-2xFLAG-cMyc, pcDNA3.1-2xFLAG-c-Myc STS187/188/189AAA (ΔSBC1) or pcDNA3.1-2xFLAG-c-Myc TSS263/264/265AAA (ΔSBC2), together with 1.5 µg each of protein expression vectors: pcDNA3.1-HA-SPOP (or pcDNA3.1-HA-SPOPF102C), pcDNA3-myc3-ROC1, pcDNA3-myc-CUL3, and pCI-His-hUbiquitin. 48 hours after the transfection, the cells were incubated with 250 nM of bortezomib for another 6 hours. The cells were collected and 1/10 of cells were lysed and sonicated in 1X RIPA buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 1% NP-40, 1% sodium deoxycholate, 2.5 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 1 mM β-glycerophosphate, 1 mM Na3VO4 and 1 μg/ml leupeptin). The RIPA lysates were measured for protein concentration, serving as total protein input control. The remaining cells were lysed in U-Lysis Buffer (6 M Guanidine-HCl, 0.1 M Sodium Phosphate, pH 8.0 and 10 mM imidazole) and sonicated. Supernatants were incubated with 100 μL of nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) agarose beads (Qiagen) at 4°C overnight. The Ni-NTA beads were washed with U-Lysis Buffer, Wash Buffer I (25 mM Tris-HCl, pH7.4, 150 mM NaCl and 15 mM imidazole), and Wash Buffer II (25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8 and 20 mM imidazole). Finally, the proteins bound to the Ni-NTA agarose beads were eluted by boiling in 1X SDS loading buffer containing 500 mM imidazole, resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to NC membrane and detected by immuno-blot analysis as described above.
Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence were performed as previously (17, 59, respectively). RT-qPCR and bioinformatics analysis were performed as previously 6, 60, 61. Additional details for Materials and Methods, including primer sequences and prostate organoid assay, are available in the Supplement. All reviews of all IHC slides were performed by a Board-certified pathologist and prostate cancer expert (M.I.). Due to the hypercellularity and larger size of the Spop KO prostates, it is practically impossible to truly blind these samples.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the joint participation by Adrienne Helis Malvin Medical Research Foundation through its direct engagement in the continuous active conduct of medical research in conjunction with Baylor College of Medicine.
Funding/Support: This work was also supported by the American Cancer Society RSG-14-218-01-TBG (to N.M.), the Prostate Cancer Foundation (to B.W.O. and N.M.); the Conquer Cancer Foundation of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Young Investigator and Career Development Awards (both to N.M.); the Pilot/Feasibility Program of the Diabetes & Endocrinology Research Center (P30-DK079638) at Baylor College of Medicine (N.M.), an Alkek Foundation for Molecular Discovery Pilot grant (C.C.), CPRIT awards RP170295 and RP170005 (CC); NIH R01CA190378 (L.X.); NIH 5T32CA174647-03 (S.K.); and NICHD 8818 and Department of Defense Breast Cancer Research Program Innovator Award (B.W.O.). N.M. is a Dan L. Duncan Scholar, a Caroline Wiess Law Scholar and member of the Center for Drug Discovery at Baylor College of Medicine. The authors also would like to acknowledge the assistance of the BCM Genetically Engineered Mouse and Human Tissue Acquisition and Pathology Core, Human Tissue Acquisition and Pathology Core, Integrated Microscopy Core funded via the NIH (DK56338, and CA125123), CPRIT (RP150578), and John S. Dunn Gulf Coast Consortium for Chemical Genomics and the Dan L. Duncan Cancer Center (supported by the NCI Cancer Center Support Grant P30CA125123).
Footnotes
Conflict of interest: All authors state that they have no relevant financial interests to disclose.
References
- 1.Berger MF, Lawrence MS, Demichelis F, Drier Y, Cibulskis K, Sivachenko AY, et al. The genomic complexity of primary human prostate cancer. Nature. 2011;470:214–220. doi: 10.1038/nature09744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Barbieri CE, Baca SC, Lawrence MS, Demichelis F, Blattner M, Theurillat JP, et al. Exome sequencing identifies recurrent SPOP, FOXA1 and MED12 mutations in prostate cancer. Nat Genet. 2012;44:685–689. doi: 10.1038/ng.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kan Z, Jaiswal BS, Stinson J, Janakiraman V, Bhatt D, Stern HM, et al. Diverse somatic mutation patterns and pathway alterations in human cancers. Nature. 2010;466:869–873. doi: 10.1038/nature09208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Electronic address scmo, Cancer Genome Atlas Research N. The Molecular Taxonomy of Primary Prostate Cancer. Cell. 2015;163:1011–1025. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Geng C, He B, Xu L, Barbieri CE, Eedunuri VK, Chew SA, et al. Prostate cancer-associated mutations in speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP) regulate steroid receptor coactivator 3 protein turnover. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:6997–7002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1304502110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Geng C, Rajapakshe K, Shah SS, Shou J, Eedunuri VK, Foley C, et al. Androgen Receptor Is the Key Transcriptional Mediator of the Tumor Suppressor SPOP in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2014;74:5631–5643. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhuang M, Calabrese MF, Liu J, Waddell MB, Nourse A, Hammel M, et al. Structures of SPOP-substrate complexes: insights into molecular architectures of BTB-Cul3 ubiquitin ligases. Mol Cell. 2009;36:39–50. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.09.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Haffner MC, Mosbruger T, Esopi DM, Fedor H, Heaphy CM, Walker DA, et al. Tracking the clonal origin of lethal prostate cancer. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:4918–4922. doi: 10.1172/JCI70354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kwon JE, La M, Oh KH, Oh YM, Kim GR, Seol JH, et al. BTB domain-containing speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP) serves as an adaptor of Daxx for ubiquitination by Cul3-based ubiquitin ligase. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:12664–12672. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600204200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhang Q, Shi Q, Chen Y, Yue T, Li S, Wang B, et al. Multiple Ser/Thr-rich degrons mediate the degradation of Ci/Gli by the Cul3-HIB/SPOP E3 ubiquitin ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:21191–21196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912008106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhang P, Gao K, Tang Y, Jin X, An J, Yu H, et al. Destruction of DDIT3/CHOP protein by wild-type SPOP but not prostate cancer-associated mutants. Hum Mutat. 2014;35:1142–1151. doi: 10.1002/humu.22614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhu H, Ren S, Bitler BG, Aird KM, Tu Z, Skordalakes E, et al. SPOP E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Adaptor Promotes Cellular Senescence by Degrading the SENP7 deSUMOylase. Cell Rep. 2015;13:1183–1193. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.09.083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wu F, Dai X, Gan W, Wan L, Li M, Mitsiades N, et al. Prostate cancer-associated mutation in SPOP impairs its ability to target Cdc20 for poly-ubiquitination and degradation. Cancer Lett. 2017;385:207–214. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.10.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Theurillat JP, Udeshi ND, Errington WJ, Svinkina T, Baca SC, Pop M, et al. Prostate cancer. Ubiquitylome analysis identifies dysregulation of effector substrates in SPOP-mutant prostate cancer. Science. 2014;346:85–89. doi: 10.1126/science.1250255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.An J, Ren S, Murphy SJ, Dalangood S, Chang C, Pang X, et al. Truncated ERG Oncoproteins from TMPRSS2-ERG Fusions Are Resistant to SPOP-Mediated Proteasome Degradation. Mol Cell. 2015;59:904–916. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.07.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gan W, Dai X, Lunardi A, Li Z, Inuzuka H, Liu P, et al. SPOP Promotes Ubiquitination and Degradation of the ERG Oncoprotein to Suppress Prostate Cancer Progression. Mol Cell. 2015;59:917–930. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.07.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.An J, Wang C, Deng Y, Yu L, Huang H. Destruction of full-length androgen receptor by wild-type SPOP, but not prostate-cancer-associated mutants. Cell Rep. 2014;6:657–669. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.01.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li C, Ao J, Fu J, Lee DF, Xu J, Lonard D, et al. Tumor-suppressor role for the SPOP ubiquitin ligase in signal-dependent proteolysis of the oncogenic co-activator SRC-3/AIB1. Oncogene. 2011;30:4350–4364. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Groner AC, Cato L, de Tribolet-Hardy J, Bernasocchi T, Janouskova H, Melchers D, et al. TRIM24 Is an Oncogenic Transcriptional Activator in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Cell. 2016 doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.04.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Garcia-Flores M, Casanova-Salas I, Rubio-Briones J, Calatrava A, Dominguez-Escrig J, Rubio L, et al. Clinico-pathological significance of the molecular alterations of the SPOP gene in prostate cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50:2994–3002. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2014.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Claiborn KC, Sachdeva MM, Cannon CE, Groff DN, Singer JD, Stoffers DA. Pcif1 modulates Pdx1 protein stability and pancreatic beta cell function and survival in mice. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:3713–3721. doi: 10.1172/JCI40440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kessler JD, Kahle KT, Sun T, Meerbrey KL, Schlabach MR, Schmitt EM, et al. A SUMOylation-dependent transcriptional subprogram is required for Myc-driven tumorigenesis. Science. 2012;335:348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.1212728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gurel B, Iwata T, Koh CM, Jenkins RB, Lan F, Van Dang C, et al. Nuclear MYC protein overexpression is an early alteration in human prostate carcinogenesis. Mod Pathol. 2008;21:1156–1167. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2008.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Iwata T, Schultz D, Hicks J, Hubbard GK, Mutton LN, Lotan TL, et al. MYC overexpression induces prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and loss of Nkx3.1 in mouse luminal epithelial cells. PLoS One. 2010;5:e9427. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Koh CM, Gurel B, Sutcliffe S, Aryee MJ, Schultz D, Iwata T, et al. Alterations in nucleolar structure and gene expression programs in prostatic neoplasia are driven by the MYC oncogene. Am J Pathol. 2011;178:1824–1834. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.12.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Barfeld SJ, Fazli L, Persson M, Marjavaara L, Urbanucci A, Kaukoniemi KM, et al. Myc-dependent purine biosynthesis affects nucleolar stress and therapy response in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6:12587–12602. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ju X, Ertel A, Casimiro MC, Yu Z, Meng H, McCue PA, et al. Novel oncogene-induced metastatic prostate cancer cell lines define human prostate cancer progression signatures. Cancer Res. 2013;73:978–989. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Taylor BS, Schultz N, Hieronymus H, Gopalan A, Xiao Y, Carver BS, et al. Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell. 2010;18:11–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.05.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Amati B. Myc degradation: dancing with ubiquitin ligases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:8843–8844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0403046101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mei Z, Zhang D, Hu B, Wang J, Shen X, Xiao W. FBXO32 Targets c-Myc for Proteasomal Degradation and Inhibits c-Myc Activity. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:16202–16214. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.645978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Farrell AS, Sears RC. MYC degradation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2014;4 doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a014365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Akhoondi S, Sun D, von der Lehr N, Apostolidou S, Klotz K, Maljukova A, et al. FBXW7/hCDC4 is a general tumor suppressor in human cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:9006–9012. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kemp Z, Rowan A, Chambers W, Wortham N, Halford S, Sieber O, et al. CDC4 mutations occur in a subset of colorectal cancers but are not predicted to cause loss of function and are not associated with chromosomal instability. Cancer Res. 2005;65:11361–11366. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bredel M, Bredel C, Juric D, Harsh GR, Vogel H, Recht LD, et al. Functional network analysis reveals extended gliomagenesis pathway maps and three novel MYC-interacting genes in human gliomas. Cancer Res. 2005;65:8679–8689. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yada M, Hatakeyama S, Kamura T, Nishiyama M, Tsunematsu R, Imaki H, et al. Phosphorylation-dependent degradation of c-Myc is mediated by the F-box protein Fbw7. EMBO J. 2004;23:2116–2125. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.von der Lehr N, Johansson S, Wu S, Bahram F, Castell A, Cetinkaya C, et al. The F-box protein Skp2 participates in c-Myc proteosomal degradation and acts as a cofactor for c-Myc-regulated transcription. Mol Cell. 2003;11:1189–1200. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00193-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kim SY, Herbst A, Tworkowski KA, Salghetti SE, Tansey WP. Skp2 regulates Myc protein stability and activity. Mol Cell. 2003;11:1177–1188. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zeng C, Wang Y, Lu Q, Chen J, Zhang J, Liu T, et al. SPOP suppresses tumorigenesis by regulating hedgehog/Gli2 signaling pathway in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014;33:75. doi: 10.1186/s13046-014-0075-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Xu J, Wang F, Jiang H, Jiang Y, Chen J, Qin J. Properties and Clinical Relevance of Speckle-Type POZ Protein in Human Colorectal Cancer. J Gastrointest Surg. 2015;19:1484–1496. doi: 10.1007/s11605-015-2767-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhi X, Tao J, Zhang L, Tao R, Ma L, Qin J. Silencing speckle-type POZ protein by promoter hypermethylation decreases cell apoptosis through upregulating Hedgehog signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2569. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ding D, Song T, Jun W, Tan Z, Fang J. Decreased expression of the SPOP gene is associated with poor prognosis in glioma. Int J Oncol. 2015;46:333–341. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hubbard GK, Mutton LN, Khalili M, McMullin RP, Hicks JL, Bianchi-Frias D, et al. Combined MYC activation and Pten loss are sufficient to create genomic instability and lethal metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2015 doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Priolo C, Pyne S, Rose J, Regan ER, Zadra G, Photopoulos C, et al. AKT1 and MYC induce distinctive metabolic fingerprints in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2014;74:7198–7204. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pellakuru LG, Iwata T, Gurel B, Schultz D, Hicks J, Bethel C, et al. Global levels of H3K27me3 track with differentiation in vivo and are deregulated by MYC in prostate cancer. Am J Pathol. 2012;181:560–569. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.04.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nelson WG, De Marzo AM, Yegnasubramanian S. USP2a activation of MYC in prostate cancer. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:206–207. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Jenkins RB, Qian J, Lieber MM, Bostwick DG. Detection of c-myc oncogene amplification and chromosomal anomalies in metastatic prostatic carcinoma by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cancer Res. 1997;57:524–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fleming WH, Hamel A, MacDonald R, Ramsey E, Pettigrew NM, Johnston B, et al. Expression of the c-myc protooncogene in human prostatic carcinoma and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Cancer Res. 1986;46:1535–1538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Fan L, Peng G, Sahgal N, Fazli L, Gleave M, Zhang Y, et al. Regulation of c-Myc expression by the histone demethylase JMJD1A is essential for prostate cancer cell growth and survival. Oncogene. 2015 doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sun C, Dobi A, Mohamed A, Li H, Thangapazham RL, Furusato B, et al. TMPRSS2-ERG fusion, a common genomic alteration in prostate cancer activates C-MYC and abrogates prostate epithelial differentiation. Oncogene. 2008;27:5348–5353. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhang C, Zhang S, Zhang Z, He J, Xu Y, Liu S. ROCK has a crucial role in regulating prostate tumor growth through interaction with c-Myc. Oncogene. 2014;33:5582–5591. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Fromont G, Godet J, Peyret A, Irani J, Celhay O, Rozet F, et al. 8q24 amplification is associated with Myc expression and prostate cancer progression and is an independent predictor of recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Hum Pathol. 2013;44:1617–1623. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2013.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Koh CM, Bieberich CJ, Dang CV, Nelson WG, Yegnasubramanian S, De Marzo AM. MYC and Prostate Cancer. Genes Cancer. 2010;1:617–628. doi: 10.1177/1947601910379132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chen H, Liu W, Roberts W, Hooker S, Fedor H, DeMarzo A, et al. 8q24 allelic imbalance and MYC gene copy number in primary prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2010;13:238–243. doi: 10.1038/pcan.2010.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Pomerantz MM, Beckwith CA, Regan MM, Wyman SK, Petrovics G, Chen Y, et al. Evaluation of the 8q24 prostate cancer risk locus and MYC expression. Cancer Res. 2009;69:5568–5574. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Blattner M, Lee DJ, O'Reilly C, Park K, MacDonald TY, Khani F, et al. SPOP mutations in prostate cancer across demographically diverse patient cohorts. Neoplasia. 2014;16:14–20. doi: 10.1593/neo.131704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Brown SD, Moore MW. The International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium: past and future perspectives on mouse phenotyping. Mamm Genome. 2012;23:632–640. doi: 10.1007/s00335-012-9427-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Jin C, McKeehan K, Wang F. Transgenic mouse with high Cre recombinase activity in all prostate lobes, seminal vesicle, and ductus deferens. Prostate. 2003;57:160–164. doi: 10.1002/pros.10283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods. 2012;9:671–675. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Choi N, Zhang B, Zhang L, Ittmann M, Xin L. Adult murine prostate basal and luminal cells are self-sustained lineages that can both serve as targets for prostate cancer initiation. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:253–265. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.01.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.He B, Lanz RB, Fiskus W, Geng C, Yi P, Hartig SM, et al. GATA2 facilitates steroid receptor coactivator recruitment to the androgen receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:18261–18266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1421415111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Coarfa C, Fiskus W, Eedunuri VK, Rajapakshe K, Foley C, Chew SA, et al. Comprehensive proteomic profiling identifies the androgen receptor axis and other signaling pathways as targets of microRNAs suppressed in metastatic prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2016;35:2345–2356. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.