Significance
This study identifies and outlines a nontranscriptional branch of the canonical GA signaling pathway that redirects protein traffic from the vacuolar degradation route to the plasma membrane. As a result, the amount of receptors and transporters, such as PIN transporters for the plant hormone auxin, is functionally regulated at the cell surface. The identified branching occurs at the level of DELLA proteins that, besides transcriptional regulation, also target the microtubule (MT) network and protein trafficking. In this work, we provide multiple lines of evidence that DELLA proteins act via their interacting partners Prefoldins and that a downstream MT/CLASP1 module regulates the activity of the retromer complex that directs protein trafficking at the intersection of the vacuolar and recycling pathways.
Keywords: gibberellin, DELLA, polar auxin transport, microtubules, vesicle trafficking
Abstract
The plant hormone gibberellic acid (GA) is a crucial regulator of growth and development. The main paradigm of GA signaling puts forward transcriptional regulation via the degradation of DELLA transcriptional repressors. GA has also been shown to regulate tropic responses by modulation of the plasma membrane incidence of PIN auxin transporters by an unclear mechanism. Here we uncovered the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which GA redirects protein trafficking and thus regulates cell surface functionality. Photoconvertible reporters revealed that GA balances the protein traffic between the vacuole degradation route and recycling back to the cell surface. Low GA levels promote vacuolar delivery and degradation of multiple cargos, including PIN proteins, whereas high GA levels promote their recycling to the plasma membrane. This GA effect requires components of the retromer complex, such as Sorting Nexin 1 (SNX1) and its interacting, microtubule (MT)-associated protein, the Cytoplasmic Linker-Associated Protein (CLASP1). Accordingly, GA regulates the subcellular distribution of SNX1 and CLASP1, and the intact MT cytoskeleton is essential for the GA effect on trafficking. This GA cellular action occurs through DELLA proteins that regulate the MT and retromer presumably via their interaction partners Prefoldins (PFDs). Our study identified a branching of the GA signaling pathway at the level of DELLA proteins, which, in parallel to regulating transcription, also target by a nontranscriptional mechanism the retromer complex acting at the intersection of the degradation and recycling trafficking routes. By this mechanism, GA can redirect receptors and transporters to the cell surface, thus coregulating multiple processes, including PIN-dependent auxin fluxes during tropic responses.
Because plants have a sessile lifestyle, they constantly need to adapt to a changing environment. Through hormonal signaling, environmental cues can be integrated and developmental programs are modified accordingly. Increasing evidence supports the idea that the signaling crosstalk between different hormonal pathways, rather than specific activity of a single hormone, determines the final signaling outcome (1, 2).
Auxin and gibberellic acid (GA) are prominent growth regulators, and their signaling pathways positively interact in the regulation of cell expansion and tissue differentiation (3). In roots, auxin promotes GA responses via the degradation of major components of the GA pathway, namely, DELLA transcriptional repressors (4), and via transcriptional activation of GA biosynthesis (5). On the other hand, DELLAs have been proposed to negatively regulate polar auxin transport (PAT) by a multistep inhibition of the transcription of PIN auxin transporters (6). Moreover, during gravitropic responses, GA regulates the transcription of the indole-3-acetic acid 19/MASSAGU2 repressor of auxin signaling (7).
Notably, the developmental output of the auxin pathway can also be modulated by the GA effect on the abundance of PIN transporters (8, 9) that are important for the formation and maintenance of the developmentally crucial local auxin gradients and maxima (10, 11). Generally, GA-deficient conditions lead to increased vacuolar trafficking and reduced incidence of PINs at the plasma membrane (PM) (8, 9). Conversely, high GA levels inhibit PIN vacuolar delivery and promote PIN incidence at the PM (9). The precise mechanism of PIN trafficking to the vacuole and its regulation is unclear, but it depends on sorting nexin (SNX1) components associated with the retromer complex (12). A direct association between SNX1 and CLASP1 (one of MT-associated proteins) suggests that cortical MT-decorating CLASP1 increases the residency time of SNX-positive vesicles close to the PM to promote recycling of cargos back to the PM (13). PIN trafficking regulation by GA appears to be developmentally relevant, e.g., during root gravitropic bending, which is regulated by GA signaling and during which asymmetric GA distribution has been detected (9).
Here we show that GA regulates the cell surface incidence of proteins by specifically targeting the SNX1-mediated switch between vacuolar trafficking and recycling to the PM. This reveals a cellular mechanism, by which GA controls auxin transport-mediated development and other cell surface-based regulations.
Results and Discussion
GA Modulates the Balance Between Vacuolar Trafficking and Exocytosis.
To dissect the cellular GA-targeted processes that regulate PIN levels at the PM, we used the photoconvertible pPIN2::PIN2-Dendra line. The irreversible conversion of the Dendra fluorochrome from green to red allowed us to follow the subcellular fate of the already present PIN2 in GA-deficient and GA-treated conditions. Conceptually, GA can enhance PIN levels at the PM by (i) inhibiting PIN endocytosis, (ii) promoting its exocytosis, or (iii) inhibiting PIN vacuolar delivery and degradation.
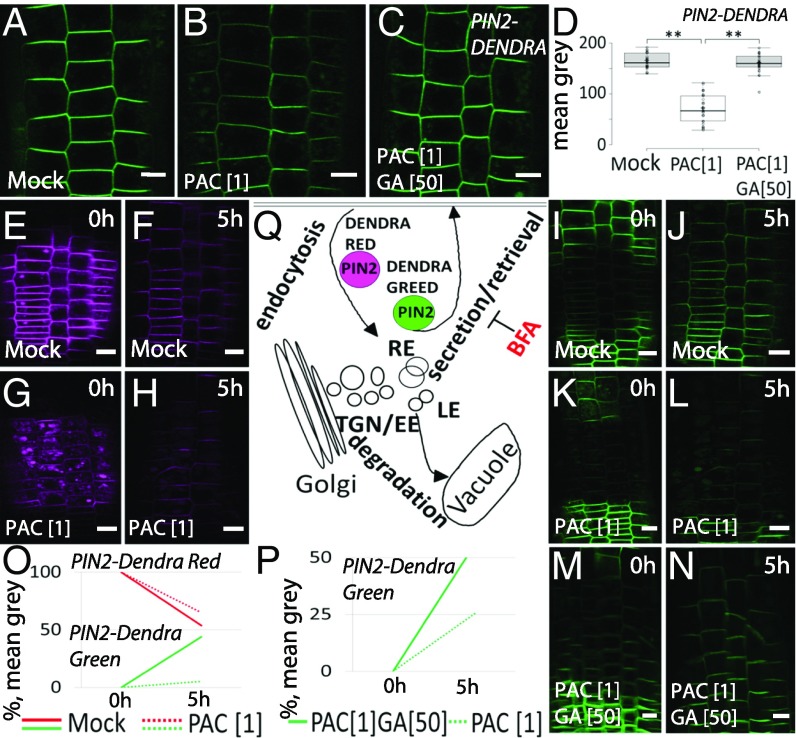
In the nonphotoconverted situation, a GA synthesis inhibitor, paclobutrazol (PAC) (14), strongly decreased the total PIN2-Dendra signal, whereas GA treatment rapidly reverted this effect (Fig. 1 A–D). Therefore, PIN2-Dendra reacted identically to PAC and GA treatments as PIN2-GFP, the regulation of which by GA has been verified both by microscopy (Fig. S1 A–D) and Western blot analysis (Fig. S1 E–H). However, when PIN2-Dendra was photoconverted into its red form and its depletion from the PM was followed, the decrease in the red signal over time was not affected by PAC pretreatment (Fig. 1 E–H and O), suggesting that PIN2 internalization from the PM is not affected by GA availability and, thus, that the observed PIN2 depletion from the PM in GA-deficient conditions (8) is not due to enhanced PIN2 endocytosis. To assess the alternative scenario of GA promoting exocytosis, we photoconverted PIN2-Dendra and monitored the green signal recovery at the PM, which reflects the delivery of de novo synthesized PIN2-Dendra proteins (Fig. 1Q). Notably, in GA optimal conditions, the green signal intensity increased up to 40% within 5 h (Fig. 1 I, J, and O). On the contrary, in PAC-treated roots, the recovery was severely inhibited, reaching only ∼5% (Fig. 1 K, L, and O). GA treatment was sufficient to revert the PAC effect and to recover the green PIN2-Dendra at the PM (Fig. 1 M, N, and P). Treatment with Brefeldin A (BFA), an established inhibitor for PIN delivery to the PM (15, 16), had no obvious effect on PAC- and GA-modulated PIN2 recovery at the PM (Fig. S2 A–D and G). This illustrates a BFA-insensitive delivery of newly synthesized PIN2 to the apical membranes of root epidermis cells, consistent with previous studies (17, 18).
Fig. 1.
GA effects on PIN2 vacuolar trafficking and exocytosis. (A–C) Decrease of total PIN2-Dendra signal at PM in seedlings pretreated with 1 µM paclobutrazol (PAC) for 1 d (B) that was rescued by 50 µM GA treatment for 4 h (C) compared with nontreated seedlings (A). (D) PIN2-Dendra signal quantification. A rectangular region of interest (ROI) at the PM was used for PM signal intensity quantification, and the PM signal was measured in 16 epidermal cells, including trichoblasts and atrichoblasts in eight individual roots. (E–H) Photoconversion of PIN2-Dendra into its red form induced by illuminating the region of interest and the depletion of the red signal over time followed in nontreated seedlings (E and F) versus seedlings pretreated with 1 µM PAC (G and H). Note the increased PIN2-Dendra vacuolar delivery in PAC-treated samples (G). (I–N) Green signal recovery at the PM after photoconversion reflects the delivery of de novo synthesized protein in nontreated seedlings (I and J), pretreated with 1 µM PAC (K and L), and treated with 50 µM GA for 5 h after 1 µM PAC pretreatment (M and N). Note the faster accumulation of de novo PIN2 at the PM in seedlings untreated versus PAC treatment (I and J) and treated with GA (M and N). (O and P) Decrease in PIN2-Dendra red signal and increase in the green signal 5 h after photoconversion, reflecting the rate of endocytosis and exocytosis, respectively. The percentage of the increase in the green signal intensity was measured after 5 h, revealing the exocytosis rate in untreated epidermal cells versus 1 µM PAC treated (O) and roots pretreated with 1 µM PAC and followed by 50 µM GA treatment (P). Note the increase in the exocytosis rate of PIN2 in roots upon GA application. (Q) Schematic representation of PIN2-Dendra red internalization reflects the rate of endocytosis and delivery of a newly synthesized green PIN2-Dendra to the PM linked to the exocytosis rate. (Scale bar: 10 µm.)
Next, we confirmed the PIN2-Dendra observations by the fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) and live imaging of PIN2-mCherry. The PIN2-mCherry fluorescence was almost completely bleached in the whole cellular region, so that the signal recovery indicated predominantly the delivery of de novo synthesized PIN2. As shown for PIN2-Dendra, PAC treatment decreased the PM PIN2-mCherry recovery with a concomitantly increased vacuolar delivery (Fig. S2 E, F, and H–K).
In summary, the photoconversion and FRAP experiments revealed that GA-deficient conditions have little effect on PIN2 endocytosis but lead to a strong inhibition of PIN2 delivery to the PM and trafficking redirection to the vacuole. GA treatment is sufficient to completely revert this effect by inhibiting vacuolar targeting and recovering PIN2 at the PM. This suggests that GA signaling targets processes balancing PIN2 vacuolar trafficking and its recycling back to the PM.
Nontranscriptional GA Mechanism Regulates Trafficking of Multiple Cargoes.
We performed several experiments to confirm that GA increases PIN2 delivery to the PM but not through the regulation of PIN2 transcription or protein synthesis (Fig. S3). Quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) showed that PIN2 transcription was not influenced by PAC or GA treatments (Fig. S3 A and B). Moreover, real-time recording of PIN2 promoter activity (in pPIN2::NLS-GFP roots) showed no differences between mock, PAC, and PAC+GA treatments (Fig. S3 C–E). PIN2 promoter activity-independent action of GA was confirmed by the observation that PIN2 and PIN1 distributions in estradiol-inducible and 35S-driven lines were regulated by GA in a similar way as protein fusions under their native promoters (Fig. S3 H–K). Furthermore, PIN2-GFP levels were monitored microscopically following GA and PAC cotreatments with cycloheximide (CHX), an inhibitor of protein synthesis. Whereas CHX significantly decreased the level of PIN2 at the PM, PAC treatment led to an additional drop in PIN2 abundance, which was reversed by GA even in the presence of CHX (Fig. S3 G and F). These observations confirm that not only GA regulates PIN abundance independently of transcription but also that the GA effect itself utilizes a nontranscriptional mechanism.
To test the specificity of these GA effects on PIN proteins, we examined vacuolar targeting of different cargo proteins in GA-deficient conditions. The vacuolar degradation increased not only for PIN2 but also for several other PM proteins, such as Boron transporter 1 (BOR1), Brassinosteroid insensitive 1 (BRI1), P-glycoprotein 19 (PGP19), and PM intrinsic protein 1;4 (PIP1;4) (Fig. S4 A–I). These findings are not consistent with previous observations that GA did not visibly affect PM stability of AUX1, PGP19, and PIP2 (9). This discrepancy might be explained by a different evaluation method: GA effect on the PM proteins abundance (9) versus the dark-visualized protein vacuolar delivery, which seems to be more sensitive (12). Using the dark conditions or concanamycin A treatment, we detected a pronounced PIN2 vacuolar degradation following PAC treatment, which was reversed by GA (Fig. S4 J–O). Similar differences in vacuolar accumulation of cargo proteins like BOR1 or PGP19 were observed despite the absence of obvious differences in abundance at the PM (Fig. S4 A, B, F, and G). qRT-PCR for these proteins in identical conditions showed no significant difference in mRNA levels following PAC or GA treatment, with the exception of PIP1;4 (Fig. S5).
These results imply a nontranscriptional mechanism of GA regulation of the balance between vacuolar trafficking and recycling back to the PM of multiple PM cargoes.
Gibberellin Targets the Retromer Complex for Trafficking Modulation.
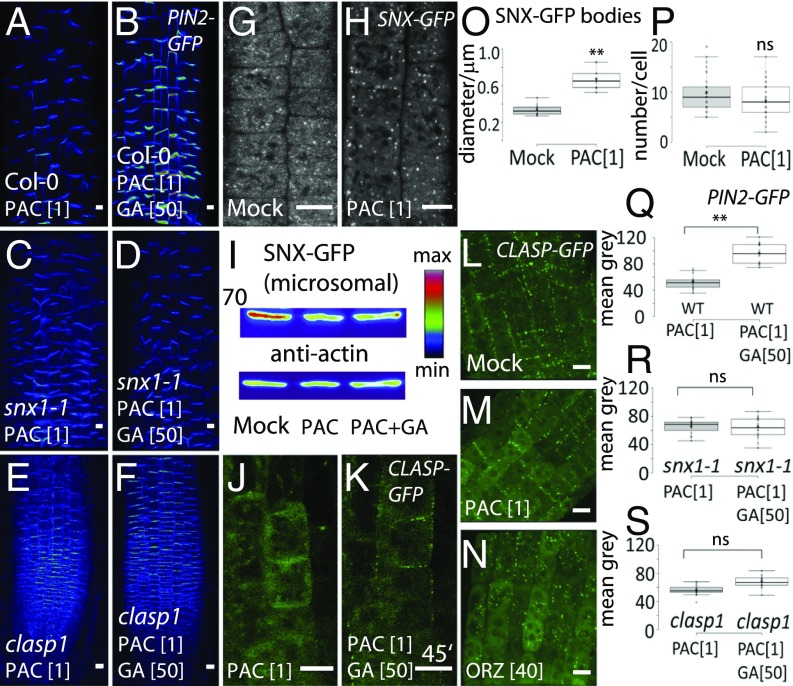
The evolutionarily conserved retromer complex that functions at the interface of exocytosis/recycling and vacuolar trafficking mediates the recovery of proteins from the vacuolar degradation pathway back to the recycling pathway (19). As shown previously (20, 21), SNX1 and other components of the retromer complex are involved in PIN protein sorting from the prevacuolar compartment to make them again available for recycling to the PM (12). To test whether SNX1-dependent protein retrieval is required for GA action on PIN2 trafficking, we analyzed the GA sensitivity of snx1 mutants. In PAC-pretreated snx1-1 seedling roots, GA application was largely ineffective to restore PIN2-GFP levels at the PM (Fig. 2 A–D, Q, and R). Moreover, snx1-1 seedlings were less sensitive to the application of PAC because we observed a less pronounced decrease of the total PM PIN2 in the snx1-1 mutant in comparison with the control (Fig. S6 A–D, G, and H). Similar observations were made in the protein affected trafficking 3 (pat3) mutant defective in the VACUOLAR PROTEIN SORTING35A (VPS35A), another subunit of the retromer complex (21). Also in pat3-3 roots, GA was unable to restore PIN2-GFP incidence at the PM (Fig. S7 A, B, and E), confirming the importance of the retromer function for GA effect on PIN trafficking. However, in mutants generally defective in vacuolar trafficking and function, such as pat4 (22), the sensitivity to GA was not affected (Fig. S7 C–E). This observation together with previously shown GA-insensitive PIN2 accumulation in Wortmannin bodies (9) indicates that the GA regulation of the PM protein accumulation is not due to decreased transit into prevacuolar compartments of PIN2 but is regulated more upstream and specifically requires the retromer complex components.
Fig. 2.
GA action on PIN2 requires SNX1 and its associated protein CLASP1. (A–F) PIN2-GFP (A and B), snx1-1×PIN2-GFP (C and D), and clasp1×PIN2-GFP (E and F) seedlings pretreated with 1 µM PAC and subsequently treated with 50 µM GA. Reduced sensitivity to GA was observed in snx1-1 (C and D) and clasp1 (E and F) mutant seedlings in comparison with wild type (A and B). (G and H) SNX1-GFP-labeled endomembranes in the root epidermis of untreated seedlings (G) and treated with 1 µM PAC (H). Note the abnormally enlarged SNX1-GFP–labeled bodies in the PAC-treated seedlings (H) in comparison with the punctate bodies in untreated seedlings (G). (I) Decrease in microsomal (membrane) SNX1 protein upon PAC treatment and increase upon GA in Arabidopsis root tips by Western blot analysis. (J and K) GFP-CLASP1 association with the cell edges at 0 min (J) and after 45 min (K) of GA application in epidermal cells. Note the gradual enrichment of the GFP-CLASP1 at the cell edges starting 45 min after GA application (K). (L–N) Cellular localization of GFP-CLASP1 in untreated seedlings (L), treated with 1 µM PAC (M) and treated with 40 µM oryzalin (N). Note that PAC-treated roots have less cell edge-localized GFP-CLASP1 but more GFP-CLASP1 accumulated in the cytoplasm (M) compared with mock (L), whereas oryzalin treatment entirely removed GFP-CLASP1 from the cell edges, and most of it localized in cytoplasm and vesicles (N). (O and P) Quantification of the size of SNX1-GFP–labeled bodies (O) and total amount of endosomes (P). (Q–S) Quantified relative increase of PIN2-GFP signals after GA treatment in the root epidermis of wild type (Q), snx1-1 (R), and clasp1 (S). Measurements were performed as described in Fig. 1. Color code was used for PIN2-GFP intensity visualization. (Scale bar: 10 μm.)
In addition, we observed a pronounced GA effect on SNX1-positive endosomal compartments. PAC treatments resulted in the appearance of abnormally enlarged SNX1-GFP bodies, distinct from the punctuated SNX1-GFP–labeled endosomes (Fig. 2 G–O); however, the total number of SNX1-GFP endosomes was not significantly changed (Fig. 2P). Prolonged PAC treatments led to an increased cytosolic SNX1-GFP signal (Fig. S7 F and G). GA application resulted in reduced numbers of these abnormal endosomes (Fig. S7 H and I). Overall, it has been common to observe in one root treated with PAC both patterns—cells with enlarged SNX1-GFP endosomes and the cells with SNX1-GFP in the cytosol. Western blots of root samples confirmed a decrease of SNX1-GFP protein in the membrane (microsomal) fraction following PAC treatment (Fig. 2I). When other markers for the endosomal compartments, such as VHA-GFP or FYVE-GFP, were studied, no such effects occurred (Fig. S7 J–M), which hinted at a more specific GA effect on the retromer-related compartments.
The observations that mutants defective specifically in retromer components are insensitive to GA in terms of regulation of trafficking together with GA effects on the SNX1-labeled endomembranes suggest that GA targets the retromer or related components to balance vacuolar trafficking and PM delivery.
Gibberellin Effect on Trafficking Requires CLASP1 Activity.
The MT-associated protein CLASP1 has been shown to interact directly with SNX1 and this interaction is important for retromer-mediated trafficking regulation (13). Therefore, we assessed the potential contribution of CLASP1 in GA-mediated regulation of PIN2 trafficking. The clasp1 mutant was less sensitive to PAC treatment in terms of PIN2 depletion from the PM (Fig. S6 E, F, and I), and more importantly, GA treatment was ineffective to recover PIN2 at the PM (Fig. 2 E, F, and S), suggesting that both retromer complex and CLASP1 activity are necessary for the GA effect on trafficking.
Next, we used GFP-CLASP1 fusion protein driven by its endogenous promoter to visualize the subcellular CLASP1 distribution. PAC-treated roots showed slightly but significantly fewer cells with cell edge-localized GFP-CLASP1 compared with mock (Fig. 2 L and M). PAC treatment also led to an increase of the GFP-CLASP1 cytosolic signal, similarly to our observations when MTs were depolymerized by oryzalin. The complete MT depolymerization with oryzalin removed GFP-CLASP1 from cell edges entirely (Fig. 2N). By using time lapse imaging following GA treatment, we perceived a gradual enrichment of GFP-CLASP1 association with the cell edges, starting as early as 45 min after GA application (Fig. 2 J and K). These observations suggest that GA targets both the retromer complex and its associated protein CLASP1, further strengthening the notion that these regulators are part of the mechanism by which GA regulates PIN2 trafficking.
The Gibberellin Effect on Trafficking Needs Intact and Dynamic Microtubules.
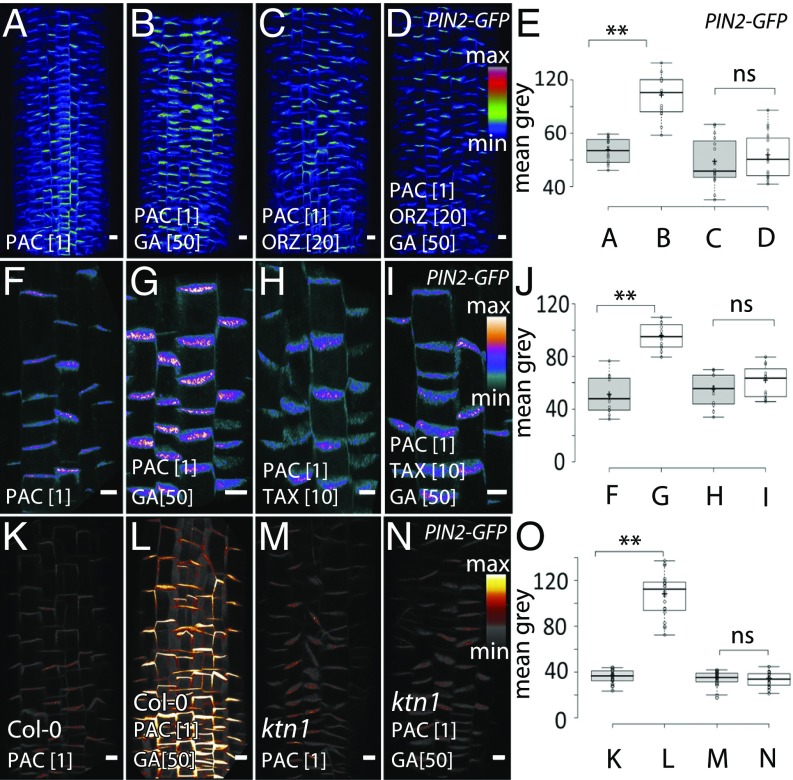
Because CLASP1 is known to be associated with MTs in different eukaryotes (23–25), we tested the role of MTs in the GA effect on PIN2 trafficking. The effect of GA on MT orientation is well described, and in the majority of the studies, GA promotes the transversal orientation of MTs (26, 27). Taking into account that SNX1 and CLASP1 might be involved in the GA effect on trafficking, we studied MT behavior after PAC treatment. We used live imaging of different MT reporter lines (such as MAP4-GFP, VENUS-TUA6, and EB1b-GFP) and found that PAC treatment resulted in the transition of the MT array from a more organized pattern with a distinctive bundled network to a more randomized pattern with fewer MTs per area unit (Fig. S8 A and B). Using an Eb1b-GFP marker line, we recorded the enrichment in longitudinally or obliquely oriented MTs in the roots treated with PAC (Fig. S8 E–H). Similarly, as observed for SNX1-GFP and GFP-CLASP1, we found that prolonged PAC treatment led to an overall decrease in the MT network labeled with VENUS-TUA6 and an increase in fluorescent signal in the cytoplasm (Fig. S8 C and D). Overall, we observed that at the early stages of GA deficiency, MT network stayed intact although it reoriented randomly or longitudinally coinciding with mostly cell-edge localized CLASP1, and SNX1 present in enlarged endosomes. At later stages, polymerization of MTs was visibly affected correlating with an increase in the cytosolic CLASP1 and SNX1.
To identify a possible requirement for MT cytoskeleton in GA-modulated PIN2 stability at the PM, we used oryzalin to disrupt the MTs (28, 29) and tested whether GA was still able to restore PIN2 abundance in PAC-grown roots. Whereas GA readily restored PIN2 at the PM in the mock control (Fig. 3 A and B), this effect was abolished when MTs were depolymerized by oryzalin (Fig. 3 C–E). Also, when MTs were stabilized by taxol (30), the GA effect on the PM restoration of PIN2 was abolished (Fig. 3 F–J). Oryzalin and taxol treatments themselves resulted in a decrease of PIN2 at the PM compared with control plants (Fig. S8 I–N). To test if genetic interference with MTs also changes PIN2 responses to GA, we used the katanin 1 (ktn1) mutant known to be compromised in severing MTs and proper formation of cortical MT arrays (31, 32). Notably, in ktn1 roots pretreated with PAC, GA application was not able to restore PIN2 at PM (Fig. 3 K–O) or to decrease vacuolar PIN2 degradation (Fig. S9 A–E). In general, ktn1 mutants contained less abundant PIN2 at PM, which was not further affected by PAC application (Fig. S8 O–Q). Furthermore, tortifolia 1 (tor1), another mutant defective in MTs (33), showed an unusual response to PAC, which rather increased instead of decreasing PIN2 incidence at the PM (Fig. S9 F–M).
Fig. 3.
Regulation of GA-dependent PIN2 trafficking by MTs. (A–E) Depolymerization of MTs with 20 µM oryzalin prevented GA (50 µM) effect on PIN2 restoration at the PM in PAC-treated seedlings (C and D) compared with the oryzalin-free mock (A and B). Quantifications (E). (F–J) Ability of GA to increase PIN2 at the PM of PAC-treated seedlings was abolished by 10 µM of MT-stabilizing agent taxol (H and I) compared with the taxol-free mock (F and G). Quantifications (J). (K–O) Efficiency of GA to increase PAC-compromised PIN2 amount (K and L) reduced in the ktn1 mutant (M and N). Quantifications (O). Color code was used for PIN2-GFP intensity visualization. (Scale bar: 10 µm.)
The pharmacological and genetic interferences with MTs revealed that an intact, dynamic MT cytoskeleton is essential for GA effect on PIN2 trafficking. Thus, GA regulation of trafficking requires retromer activity, MT cytoskeleton, and CLASP1 protein, which directly links these cellular structures.
The DELLA Components of GA Signaling Mediate GA Effect on Trafficking.
Next, we assessed which GA signaling mechanism acts upstream of MTs and retromer to regulate PIN trafficking. DELLA proteins are key components of GA signaling, and they are typically viewed as nucleus-based transcriptional modulators of downstream genes (34–36). Additionally, a supplementary mode of DELLA action has recently been proposed based on the DELLA interaction with Prefoldins (37), which are important factors of tubulin folding in the cytoplasm (38).
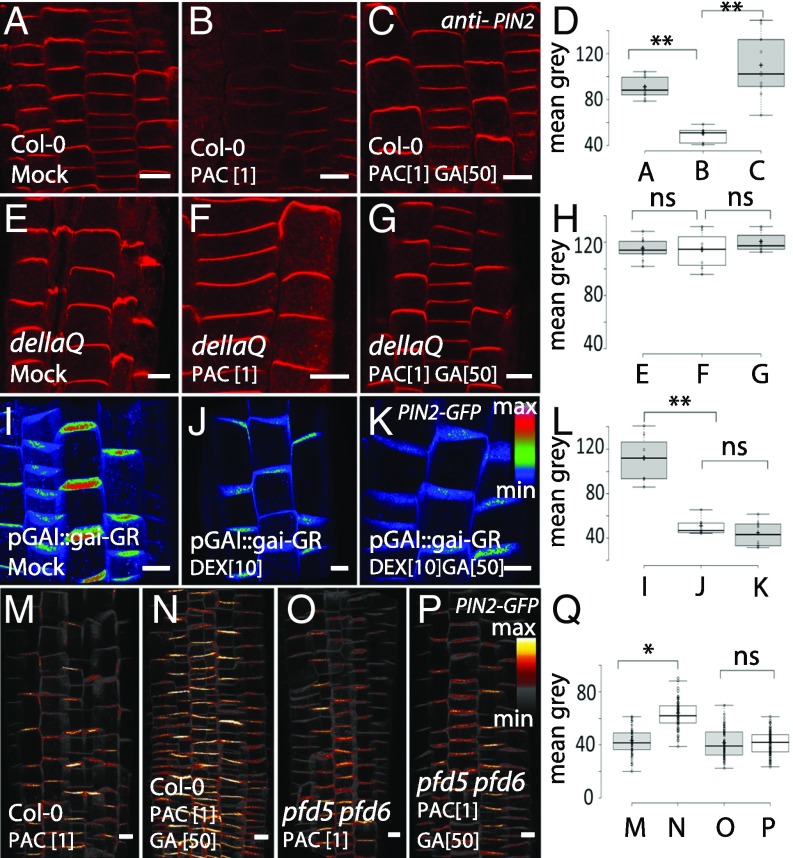
To test the involvement of DELLA proteins in trafficking regulation by GA, we used lines with deficient or modified DELLA activity. First, we studied the GA sensitivity of PIN2 trafficking in the quintuple della knockout mutant. Notably, in the quintuple della roots, PAC-based interference with GA biosynthesis did not result in a substantial decrease in PIN2 at the PM, and more importantly, GA treatment was ineffective in up-regulating PIN2 levels at the PM (Fig. 4 A–H). Furthermore, the dominant-negative DELLA mutant gaiΔ17 roots showed less PIN2 abundance in comparison with wild type or della knockout mutant (Fig. S10 A–C and E), similarly to the previous observations for PIN1 (9). Also, the gaiΔ17 mutant roots were insensitive to GA treatment such that it failed to restore the PIN2 levels (Fig. S10 D and E). Finally, we introduced PIN2-GFP into the GAI:gai-1-GR line, which after induction by the synthetic glucocorticoid dexamethasone (DEX) targets a dominant DELLA mutant protein from the cytosol to the nucleus (37). In this line, the DEX treatment resulted in a significant down-regulation of PIN2 levels at the PM (Fig. 4 I–L). Concurrent GA application and DEX induction did not recover PIN2 levels at the PM (Fig. 4K). Collectively, these experiments demonstrated that GA effect on PIN2 trafficking strictly requires the DELLA function.
Fig. 4.
DELLA proteins and their PFD interactors mediating GA effects on PIN2. (A–H) Immunolocalization of PIN2 at the PM in nontreated wild-type (A–C) and della knockout mutant (E–G) seedlings. Note reduced sensitivity of della knockout seedlings to 1 µM PAC and 50 µM GA (F and G) in comparison with wild type (B and C). Quantifications (D and H). (I–L) GAI::gai-1-GR induced in seedlings by treatment with 10 µM DEX. After induction of dominant-negative DELLA, PIN2 amount at the PM was significantly reduced (J), and GA treatment did not restore PIN2 levels at the PM (K). Quantifications (L). (M–Q) Reduced efficiency of 50 µM GA to increase PIN2 level at the PM in 1 µM PAC- treated seedlings of pfd5 pfd6 (O and P) mutant seedlings in comparison with wild type (M and N). Color code was used for PIN2-GFP intensity visualization. The 3D Z stacks are presented. Quantifications (Q). (Scale bar: 10 μm.)
A possible mechanism for DELLA proteins to regulate MTs and trafficking is through the tubulin-folding factors Prefoldins (PFDs) that are known to control MT folding and dynamics in nonplant organisms (39, 40) and have been shown to interact with DELLAs in plants (37). Indeed, the pfd6 mutant had clearly reduced levels of PIN2 at the PM (Fig. S10 F–H). To further confirm the role of PFDs in GA action on PIN2 trafficking, we analyzed GA sensitivity of the pfd5 pfd6 double mutant. In PAC-pretreated pfd5 pfd6 seedling roots, GA application was ineffective in restoring PIN2-GFP levels at the PM (Fig. 4 M–Q). Moreover, pfd5 pfd6 double mutants were less sensitive to PAC treatment in terms of PIN2 decrease in the PM (Fig. S10 I–L). This observation supports the hypothesis that the DELLA interacting partner PFD mediates GA-dependent regulation of PIN2 trafficking.
Conclusion
Gibberellin is a classical plant hormone that plays a crucial role in plant development and in response to environmental stimuli. Besides its traditionally studied roles in processes, such as germination, elongation growth, and flowering time (41), GA also modulates processes typically regulated by the plant hormone auxin, such as organ formation and gravitropism, by modulating trafficking and cell surface incidence of PIN auxin transporters (8, 9). Here we established the cellular mechanism and key molecular components of the GA-dependent trafficking of PIN auxin transporters and other proteins.
Live imaging and the use of photoconvertible cargos revealed that GA promotes the exocytic delivery of both newly synthesized and recycled cargos and, concomitantly, diminishes vacuolar trafficking and subsequent degradation. In contrast, GA deficiency had an opposite effect by promoting vacuolar degradation and diminishing cell surface cargo delivery, suggesting that GA targets processes at the intersection of exocytosis and vacuolar trafficking.
The retromer complex acts on retrieval of cargos, including PIN proteins from the degradation route back to the exocytic track (12, 20). This crucial switch between trafficking routes seems to be a specific target of GA signaling because mutants in different subunits of the retromer complex are insensitive to GA in terms of trafficking regulation, and GA deficiency modifies the intracellular distribution of the SNX1 retromer component. To further strengthen the link to the retromer, GA action on trafficking depends on the dynamic MTs, in line with previous observations that MT depolymerization affects both SNX1 distribution and PIN trafficking (13). This mechanism would be similar to that in animals, in which MTs and their associated motor proteins govern the endosomal trafficking and balance between recycling and degradation of PM receptors (42).
In plants, the connection between the endomembrane trafficking and MTs is mediated by the MT-associated protein CLASP1, which has been proposed to control tethering of endosomal vesicles to MTs via direct interaction with SNX1 (13). Again, CLASP1 activity is required for the GA effect on trafficking. Moreover, CLASP1 localization at sharp edges of the cells depends on GA availability. Therefore, our analysis suggests that retromer, MTs, and CLASP1 protein are linked as main targets of GA regulation of trafficking.
How can these evolutionarily conserved cell structures and functions be regulated by plant-specific signals, such as GA? The upstream processes involve the established components of GA signaling—the nuclear DELLA proteins, because manipulations with DELLA activity have an immediate effect on GA-mediated trafficking regulation. DELLAs can execute their effect on MTs and the retromer via their interactors, the PFDs (37), because in the double pfd mutants, PIN2 cell surface abundance is diminished, and this mutant is largely insensitive to GA. The exact role of PFDs in endomembrane trafficking has not been established yet, but they have been identified in a screen for exocytosis regulators in yeast (43). Given the tight association between MT and actin cytoskeletons (44) as well as the proposed role of PFD in both MT and actin polymerization (45) it is likely that GA as well influences actin-related processes. Whether it is in any way related to the reported auxin effect on actin-mediated vacuolar morphology and function (46) remains to be seen.
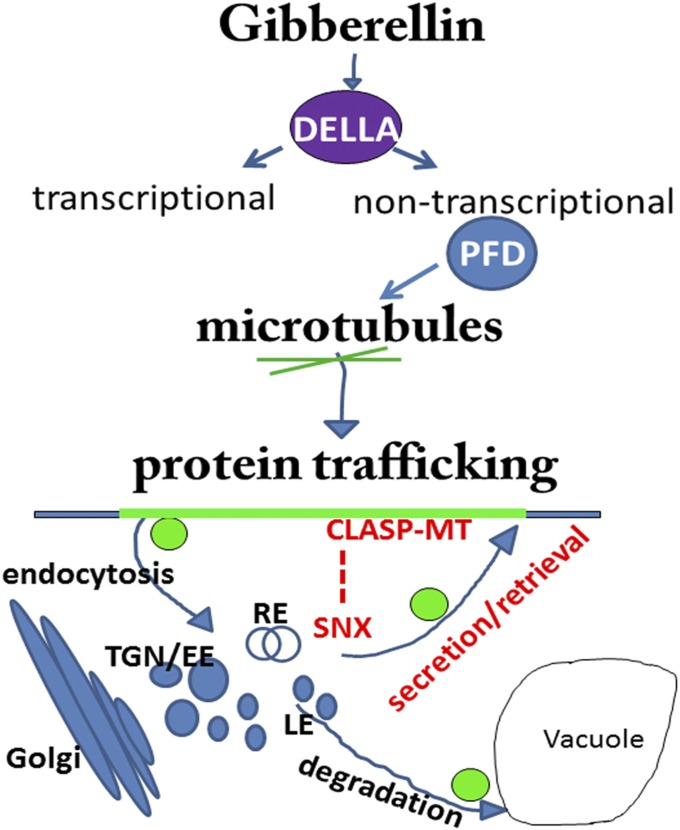
Based on these findings, we put forward a model (Fig. 5) in which the GA signaling pathway branches at the level of DELLA proteins that, besides their well-established role in transcriptional regulation, would, via their interacting partners, the PFDs, and the downstream MT/CLASP1 module, regulate the retromer activity and redirect protein trafficking from the vacuolar pathway to the PM. By this mechanism, GA can regulate, in addition to transcription, also the relocation of transporters and receptors to and from the cell surface, thus controlling a wide array of cell processes, including cell expansion for growth regulation.
Fig. 5.
Model summarizing the mechanism of GA action on PIN protein abundance. CLASP1, CLIP170-associated protein 1; LE, late endosomes; MT, microtubules; RE, recycling endosomes; SNX, sorting nexin; TGN/EE, trans-Golgi network/early endosomes.
Materials and Methods
Plant Material and Constructs.
The pfd5×PIN2-GFP, pfd6×PIN2-GFP, and pGAI::gai-1-GR×PIN2-GFP lines were obtained by manual hand-pollination of individual lines.
pPIN2::PIN2:DENDRA was generated by replacing the GFP fragment of the pPIN2::PIN2:GFP construct (47) with DENDRA. pPIN2::PIN2:mCherry was generated by replacing of the Venus tag with mCherry. To generate pPIN2::NLS-GFP and UBQ::VENUS:TUA6 the Gateway cloning system was used. For detailed information, see SI Materials and Methods.
Drug Application and Experimental Conditions.
Exogenous drugs were applied in solid agar-based or liquid Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium or by spraying 5-d-old seedlings. For treatments, 1 µM paclobutrazol and 50 µM GA3 were used. The confocal laser scanning microscopes (Zeiss CLSM 700 and 800) were used to image fluorescently labeled proteins in live or fixed plant cells. For detailed information, see SI Materials and Methods.
Protein Extraction, Western Blot Analysis, and Protein Immunolocalization.
For Western blotting, 15–20 mg of root material (4–5 d after germination) was homogenized and processed as described in ref. 48. Whole-mount immunolocalization in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heyhn. roots was performed as described in ref. 49.
qRT-PCR.
RNA was extracted with the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen) from excised root tips of 5-d-old seedlings. All PCRs were performed in technical triplicates. For detailed information, see SI Materials and Methods.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge M. Blázquez (Instituto de Biología Molecular y Celular de Plantas), M. Fendrych, C. Cuesta Moliner (Institute of Science and Technology Austria), M. Vanstraelen, M. Nowack (Center for Plant Systems Biology, Ghent), C. Luschnig (Universitat fur Bodenkultur Wien, Vienna), S. Simon (Central European Institute of Technology, Brno), C. Sommerville (Carnegie Institution for Science), and Y. Gu (Penn State University) for making available the materials used in this study; M. Muszkowski and M. Adamowski for help with data analysis; Arabidopsis Stock Centre for providing seed stocks; M. Fendrych for scientific discussions and technical help in confocal imaging; and M. De Cock for help in preparing the manuscript. The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013)/ERC Grant Agreement 282300.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
See Commentary on page 3521.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1721760115/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Bennett M, Bellini C, Van Der Straeten D. Integrative biology: Dissecting cross‐talk between plant signalling pathways. Physiol Plant. 2005;123:109. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Benková E, Hejátko J. Hormone interactions at the root apical meristem. Plant Mol Biol. 2009;69:383–396. doi: 10.1007/s11103-008-9393-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Weiss D, Ori N. Mechanisms of cross talk between gibberellin and other hormones. Plant Physiol. 2007;144:1240–1246. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.100370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fu X, Harberd NP. Auxin promotes Arabidopsis root growth by modulating gibberellin response. Nature. 2003;421:740–743. doi: 10.1038/nature01387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nemhauser JL, Hong F, Chory J. Different plant hormones regulate similar processes through largely nonoverlapping transcriptional responses. Cell. 2006;126:467–475. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.05.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Moubayidin L, et al. The rate of cell differentiation controls the Arabidopsis root meristem growth phase. Curr Biol. 2010;20:1138–1143. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.05.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gallego-Bartolomé J, Kami C, Fankhauser C, Alabadí D, Blázquez MA. A hormonal regulatory module that provides flexibility to tropic responses. Plant Physiol. 2011;156:1819–1825. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.173971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Willige BC, Isono E, Richter R, Zourelidou M, Schwechheimer C. Gibberellin regulates PIN-FORMED abundance and is required for auxin transport-dependent growth and development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell. 2011;23:2184–2195. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.086355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Löfke C, et al. Asymmetric gibberellin signaling regulates vacuolar trafficking of PIN auxin transporters during root gravitropism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:3627–3632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1300107110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Adamowski M, Friml J. PIN-dependent auxin transport: Action, regulation, and evolution. Plant Cell. 2015;27:20–32. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.134874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vanneste S, Friml J. Auxin: A trigger for change in plant development. Cell. 2009;136:1005–1016. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kleine-Vehn J, et al. Differential degradation of PIN2 auxin efflux carrier by retromer-dependent vacuolar targeting. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:17812–17817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808073105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ambrose C, et al. CLASP interacts with sorting nexin 1 to link microtubules and auxin transport via PIN2 recycling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Dev Cell. 2013;24:649–659. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rademacher W. Growth retardants: Effects on gibberellin biosynthesis and other metabolic pathways. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 2000;51:501–531. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.51.1.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Geldner N, Friml J, Stierhof Y-D, Jürgens G, Palme K. Auxin transport inhibitors block PIN1 cycling and vesicle trafficking. Nature. 2001;413:425–428. doi: 10.1038/35096571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dhonukshe P, et al. Clathrin-mediated constitutive endocytosis of PIN auxin efflux carriers in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol. 2007;17:520–527. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kleine-Vehn J, et al. ARF GEF-dependent transcytosis and polar delivery of PIN auxin carriers in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol. 2008;18:526–531. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.03.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kleine-Vehn J, et al. Cellular and molecular requirements for polar PIN targeting and transcytosis in plants. Mol Plant. 2008;1:1056–1066. doi: 10.1093/mp/ssn062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Seaman MNJ. The retromer complex–Endosomal protein recycling and beyond. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:4693–4702. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jaillais Y, et al. The retromer protein VPS29 links cell polarity and organ initiation in plants. Cell. 2007;130:1057–1070. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nodzyński T, et al. Retromer subunits VPS35A and VPS29 mediate prevacuolar compartment (PVC) function in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant. 2013;6:1849–1862. doi: 10.1093/mp/sst044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zwiewka M, et al. The AP-3 adaptor complex is required for vacuolar function in Arabidopsis. Cell Res. 2011;21:1711–1722. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Carvalho P, Tirnauer JS, Pellman D. Surfing on microtubule ends. Trends Cell Biol. 2003;13:229–237. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(03)00074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Akhmanova A, Hoogenraad CC. Microtubule plus-end-tracking proteins: Mechanisms and functions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:47–54. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2004.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ambrose JC, Shoji T, Kotzer AM, Pighin JA, Wasteneys GO. The Arabidopsis CLASP gene encodes a microtubule-associated protein involved in cell expansion and division. Plant Cell. 2007;19:2763–2775. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.053777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shibaoka H. Regulation by gibberellins of the orientation of cortical microtubules in plant cells. Aust J Plant Physiol. 1993;20:461–470. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shibaoka H. Plant hormone-induced changes in the orientation of cortical microtubules: Alterations in the cross-linking between microtubules and the plasma membrane. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1994;45:527–544. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Morejohn LC. The molecular pharmacology of plant tubulin and microtubules. In: Lloyd CW, editor. The Cytoskeletal Basis of Plant Growth and Form. Academic; San Diego: 1991. pp. 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nakamura M, Naoi K, Shoji T, Hashimoto T. Low concentrations of propyzamide and oryzalin alter microtubule dynamics in Arabidopsis epidermal cells. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004;45:1330–1334. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pch300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Morejohn LC, Fosket DE. The biochemistry of compounds with anti-microtubule activity in plant cells. Pharmacol Ther. 1991;51:217–230. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90078-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lin D, et al. Rho GTPase signaling activates microtubule severing to promote microtubule ordering in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol. 2013;23:290–297. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nakamura M, Ehrhardt DW, Hashimoto T. Microtubule and katanin-dependent dynamics of microtubule nucleation complexes in the acentrosomal Arabidopsis cortical array. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:1064–1070. doi: 10.1038/ncb2110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Buschmann H, et al. Helical growth of the Arabidopsis mutant tortifolia1 reveals a plant-specific microtubule-associated protein. Curr Biol. 2004;14:1515–1521. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.08.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Peng J, et al. The Arabidopsis GAI gene defines a signaling pathway that negatively regulates gibberellin responses. Genes Dev. 1997;11:3194–3205. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.23.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Silverstone AL, et al. Repressing a repressor: Gibberellin-induced rapid reduction of the RGA protein in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2001;13:1555–1566. doi: 10.1105/TPC.010047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Harberd NP. Botany. Relieving DELLA restraint. Science. 2003;299:1853–1854. doi: 10.1126/science.1083217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Locascio A, Blázquez MA, Alabadí D. Dynamic regulation of cortical microtubule organization through prefoldin-DELLA interaction. Curr Biol. 2013;23:804–809. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.03.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hartl FU, Hayer-Hartl M. Molecular chaperones in the cytosol: From nascent chain to folded protein. Science. 2002;295:1852–1858. doi: 10.1126/science.1068408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Le Bot N, Tsai M-C, Andrews RK, Ahringer J. TAC-1, a regulator of microtubule length in the C. elegans embryo. Curr Biol. 2003;13:1499–1505. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00577-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lundin VF, Srayko M, Hyman AA, Leroux MR. Efficient chaperone-mediated tubulin biogenesis is essential for cell division and cell migration in C. elegans. Dev Biol. 2008;313:320–334. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Nakajima M, Motoyuki A, Matsuoka M. Gibberellin receptor and its role in gibberellin signaling in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2007;58:183–198. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.58.032806.103830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hoepfner S, et al. Modulation of receptor recycling and degradation by the endosomal kinesin KIF16B. Cell. 2005;121:437–450. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Proszynski TJ, et al. A genome-wide visual screen reveals a role for sphingolipids and ergosterol in cell surface delivery in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:17981–17986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509107102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sampathkumar A, et al. Live cell imaging reveals structural associations between the actin and microtubule cytoskeleton in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2011;23:2302–2313. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.087940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Simons CT, et al. Selective contribution of eukaryotic prefoldin subunits to actin and tubulin binding. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:4196–4203. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306053200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Scheuring D, et al. Actin-dependent vacuolar occupancy of the cell determines auxin-induced growth repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:452–457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1517445113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Leitner J, et al. Lysine63-linked ubiquitylation of PIN2 auxin carrier protein governs hormonally controlled adaptation of Arabidopsis root growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:8322–8327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1200824109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Abas L, Luschnig C. Maximum yields of microsomal-type membranes from small amounts of plant material without requiring ultracentrifugation. Anal Biochem. 2010;401:217–227. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2010.02.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Friml J, Benková E, Mayer U, Palme K, Muster G. Automated whole mount localisation techniques for plant seedlings. Plant J. 2003;34:115–124. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2003.01705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.