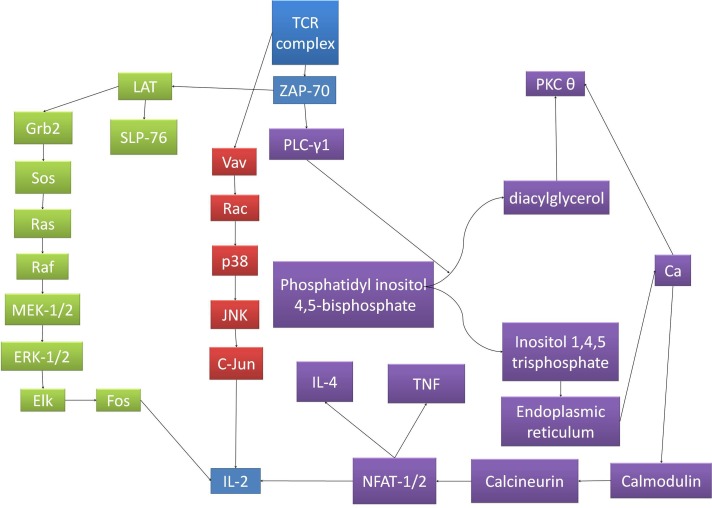
Figure 3. The signaling pathways for TCR complex activation.
The pathways converge to IL-2 transcription, which determines T cell clonal expansion and subsequent immune response. TCRs functions together with other structures, with which forms the T-cell receptor complex. After the TCR binds the peptide-MHC complex, the TCR undergoes conformational changes that determine the phosphorylation of the ITAMs (immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs) located on CD247 and the CD3 polypeptides. ITAM phosphorylation creates binding sites for proteins presenting Src homology 2 (SH2) domains, one of the more important ones being the zeta associated protein of 70 kDa (ZAP-70). After binding and activation, ZAP-70 recruits linker of activation of T cells (LAT). After the binding and activation of LAT, other signaling molecules are recruited. Such is the case of SH2-binding leukocyte phosphoprotein of 76-kDa (SLP-76) and Grb2. Grb2 activates SOS, which catalyzes the exchange of GDP to GTP linked to Ras, activating the MAPK pathway, phosphorylating the extracellular receptor-activated kinase 1 and 2 (ERK1/2), which in turn, phosphorylates Elk. Thus determines the transcription of Fos, important for the transcription of interleukin-2 (IL-2). Other pathway that branches off the TCR and phosphorylated proteins complex determine the activation of Vav, which determines the GDP/GTP exchange on Rac, which in turn activates p38. This action determines, in the end, the activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), which phosphorylates c-Jun, representing the second molecule implicated in the transcription of IL-2.