The 2.2 Å resolution crystal structure of the homologous recombination protein RecR from P. aeruginosa PAO1 is reported. The crystal structure shows that dimeric P. aeruginosa RecR forms a ring-like tetramer architecture via crystal symmetry.
Keywords: crystal structure, homologous recombination, RecR, DNA repair, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
DNA damage is usually lethal to all organisms. Homologous recombination plays an important role in the DNA damage-repair process in prokaryotic organisms. Two pathways are responsible for homologous recombination in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: the RecBCD pathway and the RecFOR pathway. RecR is an important regulator in the RecFOR homologous recombination pathway in P. aeruginosa. It forms complexes with RecF and RecO that can facilitate the loading of RecA onto ssDNA in the RecFOR pathway. Here, the crystal structure of RecR from P. aeruginosa PAO1 (PaRecR) is reported. PaRecR crystallizes in space group P6122, with two monomers per asymmetric unit. Analytical ultracentrifugation data show that PaRecR forms a stable dimer, but can exist as a tetramer in solution. The crystal structure shows that dimeric PaRecR forms a ring-like tetramer architecture via crystal symmetry. The presence of a ligand in the Walker B motif of one RecR subunit suggests a putative nucleotide-binding site.
1. Introduction
Maintaining genomic integrity and stability is crucial for all organisms. Damage to DNA is unavoidable following exposure to ultraviolet radiation, ionizing radiation and chemical mutagens (Inoue et al., 2008 ▸; Lindahl, 1993 ▸). Cells have therefore evolved several different mechanisms to maintain the structural and informational fidelity of their DNA, including homologous recombination, nonhomologous end joining, base-excision repair, nucleotide-excision repair, mismatch repair and reversion repair (West, 2003 ▸; Burma et al., 2006 ▸; Shuman & Glickman, 2007 ▸). In all cells, homologous recombination plays a key role in the generation of genetic diversity, the maintenance of genomic integrity and the proper segregation of chromosomes (Cox et al., 2000 ▸; Spies & Kowalczykowski, 2005 ▸). In wild-type Escherichia coli, two distinct recombination pathways are responsible for the repair of DNA damage by recombination: the RecBCD pathway and the RecFOR (or RecF) pathway (Kowalczykowski et al., 1994 ▸; Tseng et al., 1994 ▸; Kowalczykowski, 2000 ▸). These pathways are conserved in the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. The recF gene in P. aeruginosa PAO1 has been shown to be downregulated following treatment with the antibiotic ciprofloxacin as part of the SOS response system (Cirz et al., 2006 ▸).
In prokaryotic cells, RecA is important for strand exchange during homologous recombination, stabilizing stalled replication forks. The RecBCD and RecF pathways both load RecA onto single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) to allow homologous strand invasion, but differ in the type of damaged DNA that they can repair (Bork et al., 2001 ▸; Cox, 2007 ▸; Lenhart et al., 2014 ▸). RecBCD is a multifunctional enzyme complex with highly processive helicase activity, ATP-dependent exonuclease activity and RecA-loading activity (Singleton et al., 2004 ▸; Dillingham & Kowalczykowski, 2008 ▸). The RecBCD pathway is responsible for the repair initiated at double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) breaks. During the repair process, RecBCD generates a 3′ ssDNA extension after encountering a Chi site and facilitates the loading of RecA onto ssDNA produced by its helicase/nuclease activity (Spies & Kowalczykowski, 2006 ▸; Spies et al., 2007 ▸; Dillingham & Kowalczykowski, 2008 ▸).
Compared with the RecBCD pathway, the RecF pathway is mainly responsible for single-stranded DNA damage, and requires several proteins (RecA, RecF, RecO, RecR, RecJ and RecQ) to process the DNA into a presynaptic intermediate. The DNA is unwound by the RecQ helicase and the 5′ end is digested by RecJ, leaving the 30-tailed ssDNA coated with single-stranded DNA-binding proteins (SSBs). RecR and RecO form a complex that directs the specific loading of the RecA protein onto ssDNA; RecF can accelerate this process and ATP is needed at the same time (Umezu & Kolodner, 1994 ▸; Ryzhikov et al., 2011 ▸; Morimatsu et al., 2012 ▸).
To date, crystal structures of RecR have been determined from Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis (also known as Caldanaerobacter subterraneus) and Deinococcus radiodurans, revealing that RecR forms a DNA clamp-like tetramer architecture that encircles dsDNA by forming a complex with RecO and RecF (Honda et al., 2008 ▸; Tang et al., 2012 ▸; Radzimanowski et al., 2013 ▸; Lee et al., 2004 ▸). In order to elucidate the structure of RecR from P. aeruginosa PAO1 (PaRecR), the recR (pa1534) gene was cloned for overexpression in E. coli, and PaRecR was purified and crystallized. Here, we report the crystal structure of PaRecR determined to 2.2 Å resolution.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Macromolecule production
The recR (pa1534) gene was amplified by polymerase chain reaction using the genome of P. aeruginosa PAO1 as a template, and the PCR product of full-length PA1534 (residues 1–197) was cloned into the pGEX-6p-1 vector (GE Healthcare, Beijing, People’s Republic of China). For expression of RecR, the recombinant plasmid for RecR was transformed into E. coli strain BL21(DE3) and the cells were grown in 1 l Luria–Bertani broth medium containing 100 µg ml−1 ampicillin at 310 K. When the OD600 reached 0.5, isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) was added to the growth medium to a final concentration of 0.5 mM to induce the expression of recombinant protein. The induced cultures were grown at 289 K for 18 h. The cells were harvested by centrifugation at 4000g for 15 min, resuspended in 25 ml lysis buffer (25 mM Tris, 50 mM NaCl pH 8.5) and then lysed using a high-pressure homogenizer (ATS Nano Technology, Suzhou, People’s Republic of China) at 277 K. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 40 000g for 40 min at 277 K. The supernatant was loaded onto a GST column (GE Healthcare) equilibrated with lysis buffer. The column was washed five times with 100 ml lysis buffer. Finally, 0.6 mg PreScission Protease (GE Healthcare) was added to the resin to remove the GST tag. The protein was eluted with 25 mM Tris, 20 mM NaCl pH 8.0 and then concentrated and purified using anion-exchange chromatography on a HiTrap Q column (GE Healthcare). The protein was further purified using a Superdex 200 Increase 10/300 GL column (GE Healthcare) equilibrated with 20 mM Tris, 100 mM NaCl pH 8.0. The purified protein was concentrated to 10 mg ml−1 using an Amicon Ultra centrifugal filter unit (Millipore; molecular-weight cutoff 30 kDa) and stored at 193 K. Macromolecule-production information is summarized in Table 1 ▸.
Table 1. Macromolecule production.
The BamHI site and the EcoRI site are underlined. The tag residues removed by PreScission protease are shown in italics.
| Source organism | P. aeruginosa PAO1 |
| DNA source | Genome |
| Forward primer | CGCGGATCCATGAGTTTCAGCCCGCTGATCC |
| Reverse primer | CCGGAATTCTCAGGAGATCGGCCGCCGTCCG |
| Cloning vector | pGEX-6P-1 |
| Expression vector | pGEX-6p-1 |
| Expression host | E. coli BL21(DE3) |
| Complete amino-acid sequence of the construct produced | GPLGSMSFSPLIRQLIESLRILPGVGQKSAQRMALMLLERDRSGGLKLAQALTAAMEGVGHCRQCRTLSEEELCPQCADPRRDDSLLCVVEGPLDVFAVEQTGYRGRYFVLKGHLSPLDGLGPEAIGIPELEARIRDGAFSEVILATNPTVEGEATAHYIAQLLAGRGLTLSRIAHGVPLGGELELVDGGTLAHALAGRRPIS |
2.2. Analytical ultracentrifugation
Analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC) was performed in sedimentation-velocity mode using a Beckman Coulter XL-I analytical ultracentrifuge (Beckman Instruments, Palo Alto, California, USA) with two-channel centrepieces and sapphire windows at 277 K and a rotor speed of 42 000 rev min−1 (142 000g) with interference detection. The purified protein was diluted to 1 mg ml−1 in 20 mM Tris, 100 mM NaCl pH 8.0 buffer. The protein partial specific volume and buffer density were estimated using SEDNTERP, and the sedimentation-equilibration data were analysed by the c(s) or ls-g*(s) method using the SEDFIT software (Dam & Schuck, 2004 ▸).
2.3. Crystallization
Crystallization screening for RecR was carried out using the sitting-drop vapour-diffusion method with the commercial kits Crystal Screen, Crystal Screen 2 and Index (Hampton Research, Aliso Viejo, California, USA) in 48-well sitting-drop plates. Snowflake-shaped crystals were observed after 3 d using Index condition No. 17 consisting of 1.26 M sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate, 0.14 M potassium phosphate dibasic. For crystal optimization, reservoir solutions were prepared by mixing 80 µl Index condition No. 17 and 20 µl of each of the solutions from the commercial Wizard 1 & 2 screening kits (Rigaku Reagents). This optimization strategy was based on the protocol described by Birtley & Curry (2005 ▸), whereby commercial screening solutions are employed as additives once initial crystallization conditions have been obtained. The optimized crystals were finally obtained with reservoir solution consisting of 80 µl 1.26 M sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate, 0.14 M potassium phosphate dibasic and 20 µl Wizard 1 condition No. 20 [10%(w/v) PEG 6000, 100 mM HEPES–NaOH pH 7.0]. Crystallization information is summarized in Table 2 ▸.
Table 2. Crystallization.
| Method | Sitting-drop vapour diffusion |
| Plate type | 48-well |
| Temperature (K) | 289 |
| Protein concentration (mg ml−1) | 5 |
| Buffer composition of protein solution | 25 mM Tris–HCl, 100 mM NaCl pH 8.5 |
| Composition of reservoir solution | 80 µl 1.26 M sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate, 0.14 M potassium phosphate dibasic and 20 µl 10%(w/v) PEG 6000, 100 mM HEPES–NaOH pH 7.0 |
| Volume and ratio of drop | 2 µl; 1:1 ratio of protein:reservoir |
| Volume of reservoir | 100 µl |
2.4. Data collection and processing
Prior to data collection, crystals were cryoprotected by adding 20%(v/v) glycerol to the crystallization buffer before flash-cooling them in liquid nitrogen. The PaRecR diffraction data set was collected on beamline BL19U1 of the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF) at 100 K. Data sets were integrated, scaled and merged using the HKL-2000 suite (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▸). Data-collection and processing statistics are summarized in Table 3 ▸.
Table 3. Data collection and processing.
Values in parentheses are for the outer shell.
| Diffraction source | BL19U1, SSRF |
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.97776 |
| Temperature (K) | 100 |
| Detector | PILATUS3 6M |
| Crystal-to-detector distance (mm) | 400.00 |
| Rotation range per image (°) | 0.5 |
| Total rotation range (°) | 360 |
| Exposure time per image (s) | 0.5 |
| Space group | P6122 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 70.1, 70.1, 369.0 |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 90, 120 |
| Mosaicity (°) | 0.3 |
| Resolution range (Å) | 50.00–2.20 (2.24–2.20) |
| Total No. of reflections | 621073 |
| No. of unique reflections | 27394 (2318) |
| Completeness (%) | 99.7 (97.9) |
| Multiplicity | 21.4 (16.0) |
| 〈I/σ(I)〉 | 20.3 (3.3) |
| CC1/2 | 0.999 (0.949) |
| R r.i.m. | 0.034 (0.215) |
| Overall B factor from Wilson plot (Å2) | 35 |
2.5. Structure solution and refinement
The structure of PaRecR was determined by molecular replacement with Phaser (McCoy et al., 2007 ▸) in the PHENIX suite (Adams et al., 2010 ▸) using a monomer of T. tengcongensis RecR (PDB entry 3vdp; 48% sequence identity; Tang et al., 2012 ▸) as a search model. The molecular-replacement model was subjected to automatic building using AutoBuild in PHENIX, which built 386 residues in two chains. The structure of PaRecR was then refined with PHENIX (Adams et al., 2010 ▸) combined with cycles of manual building in Coot (Emsley et al., 2010 ▸). The final model was optimized using PDB_REDO (Joosten et al., 2014 ▸). The structure was validated with MolProbity (Chen et al., 2010 ▸). All structure figures were drawn with PyMOL (v.2.0; Schrödinger). Refinement statistics are summarized in Table 4 ▸.
Table 4. Structure solution and refinement.
Values in parentheses are for the outer shell.
| Resolution range (Å) | 36.72–2.19 (2.25–2.19) |
| Completeness (%) | 94.5 (80.9) |
| No. of reflections, working set | 27392 (2317) |
| No. of reflections, test set | 1895 (165) |
| Final R cryst † | 0.189 (0.245) |
| Final R free † | 0.221 (0.254) |
| No. of non-H atoms | |
| Protein | 2938 |
| Ions (Na+, Zn2+, PO4 3−) | 8 |
| Ligand | 25 |
| Water | 182 |
| Total | 3153 |
| R.m.s. deviations | |
| Bonds (Å) | 0.016 |
| Angles (°) | 1.8 |
| Average B factors (Å2) | |
| Protein | 30 |
| Ions (Na+, Zn2+, PO4 3−) | 36 |
| Ligand | 58 |
| Water | 35 |
| Ramachandran plot‡ | |
| Most favoured (%) | 97.9 |
| Allowed (%) | 2.1 |
R
cryst = 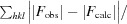
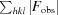 ; R
free is the R factor for a selected subset of the reflections that was not included in refinement calculations.
; R
free is the R factor for a selected subset of the reflections that was not included in refinement calculations.
Ramachandran plot calculated using MolProbity (Chen et al., 2010 ▸).
3. Results and discussion
3.1. The structure of P. aeruginosa RecR
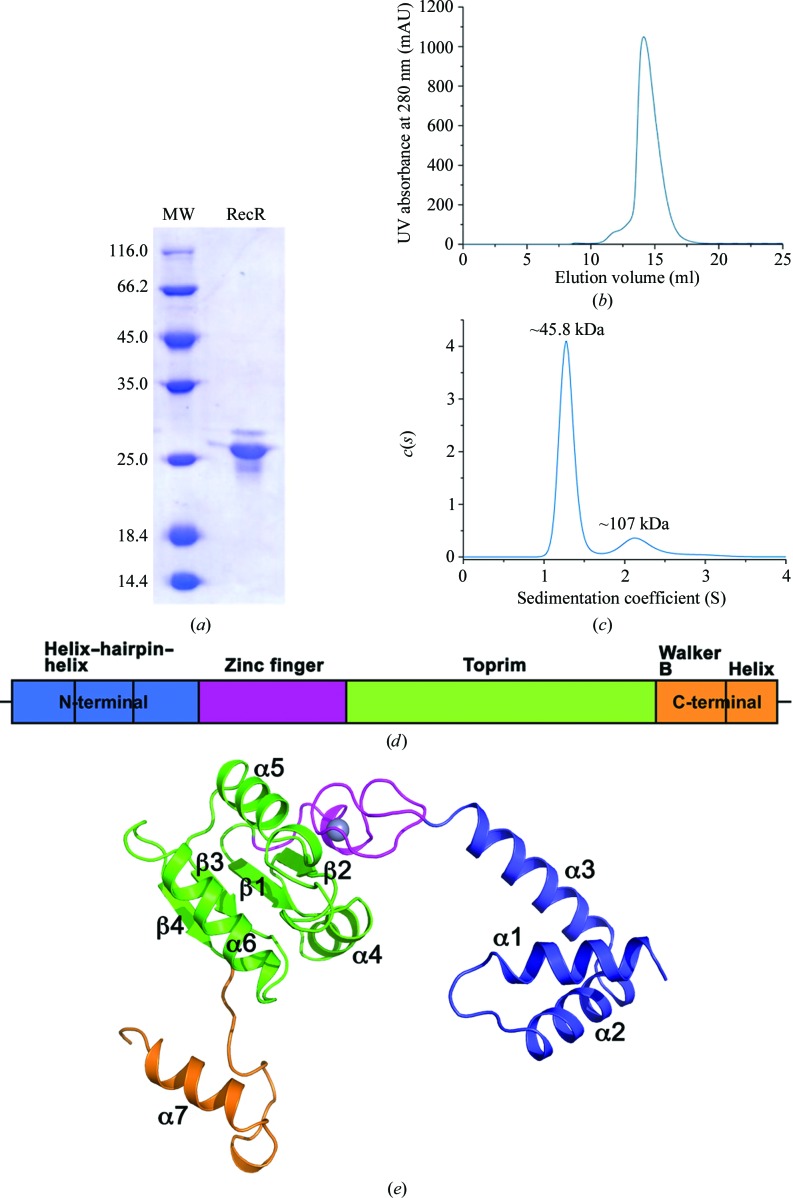
The full-length purified recombinant RecR protein (Figs. 1 ▸ a and 1 ▸ b) from P. aeruginosa PAO1 (PaRecR; residues 1–197) was crystallized with symmetry consistent with space group P6122 with two monomers in an asymmetric unit, corresponding to a Matthews coefficient of 2.94 Å3 Da−1 and an estimated solvent content of 58%. Analytical ultracentrifugation analysis confirms that PaRecR largely forms a homodimer in solution, as shown by a peak at ∼46 kDa corresponding to twice the theoretical monomer molecular mass of 21 kDa (Fig. 1 ▸ c). A secondary peak at ∼107 kDa also indicates the presence of homotetramers in solution. The resulting structure was refined to 2.2 Å resolution and includes two PaRecR monomers in an asymmetric unit, forming a stable dimer involving exchange of the N-terminal domains. The quality of the experimental electron-density maps was good (Supplementary Fig. S1), such that subunit A could be traced in continuous electron density from residues 3 to 197 and subunit B from residues 1 to 197. The two RecR monomers in an asymmetric unit adopt a similar conformation, with an r.m.s.d. of 1.1 Å for 195 Cα atoms.
Figure 1.
The PaRecR structure. (a) A representative SDS–PAGE gel (stained with Coomassie Blue) of the main peak eluted from the size-exclusion chromatography column, with molecular-weight markers shown (lane MW; labelled in kDa). (b) Elution profile of full-length PaRecR (residues 1–197) from a Superdex 200 10/300 GL size-exclusion chromatography column with absorbance measured at 280 nm. (c) Analytical ultracentrifugation profile of PaRecR. (d) The PaRecR monomer structure coloured according to the domain orientation shown above: blue, N-terminal helix–hairpin–helix motif; magenta, Cys4 zinc-finger motif; green, Toprim domain; orange, C-terminal Walker B motif.
The structure of the PaRecR monomer, which has approximate dimensions of 70 × 50 × 40 Å, is divided into three regions (Fig. 1 ▸ d). The N-terminal region is composed of a helix–hairpin–helix (HhH) motif (residues 1–54). The HhH motif is formed by helices α1 and α2, with an additional helix α3 linking the HhH motif to the Cys4 zinc-finger motif. The HhH motif is associated with DNA binding, and in the context of RecR has been shown to be essential for DNA binding and association with RecO (Lee et al., 2004 ▸).
The middle region consists of a zinc-finger motif (residues 55–78) and a Toprim domain (residues 79–167). The Cys4 zinc-finger motif consists of four strictly conserved cysteine residues (Cys69, Cys72, Cys57 and Cys60) which coordinate a zinc ion. The Cys4 zinc finger lies on the outside of the RecR monomer. An E. coli strain carrying RecR with a mutated zinc finger showed reduced survival (Clark, 1991 ▸), suggesting its importance for the function of RecR, most likely in DNA binding. The Toprim domain resembles a Rossmann-like nucleotide-binding fold with a parallel four-stranded β-sheet flanked on one side by one α-helix (α4) and on the other by two α-helices (α5 and α6). The Toprim domain in RecR lacks the fingerprint acidic DxD sequence found in the Toprim domains of topoisomerases, but is rich in conserved acidic residues.
The C-terminal region (residues 168–197) includes a Walker B motif and a C-terminal helix. The Walker B motif in RecR has a sequence motif that diverges from the signature motif (R/K)xxxGxxx(L/V)hhhhDE, where x is any residue and h is a hydrophobic residue (Hanson & Whiteheart, 2005 ▸). The aspartate in the consensus Walker B motif coordinates the magnesium required for ATP hydrolysis, and the glutamate is thought to prime a water molecule for nucleophilic attack (Hanson & Whiteheart, 2005 ▸). In PaRecR, the Walker B motif, with sequence 168RIAHGVPLGGELELVDG184, forms a long loop with a 310-helix at its C-terminus and is followed by the C-terminal helix α7. PaRecR lacks the catalytic glutamate of the consensus Walker B motif; mutation at this position has been linked to impaired ATP hydrolysis but not ATP binding (Hanson & Whiteheart, 2005 ▸).
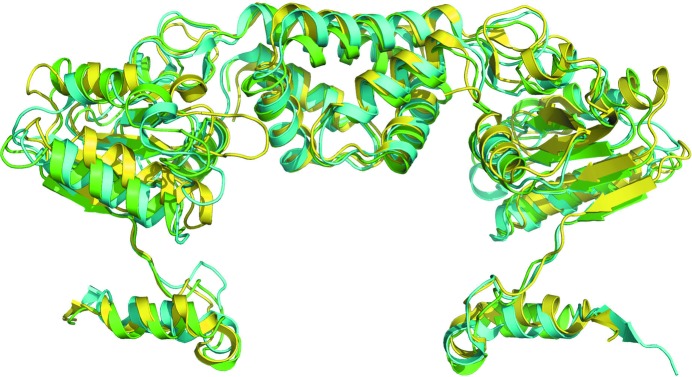
A DALI search for structural homology reveals closest similarity to the published monomeric structures of the RecR proteins from T. tengcongensis (PDB entry 3vdp; Z-score 22, r.m.s.d. of 1.7 Å for 195 aligned residues; 48% sequence identity; Tang et al., 2012 ▸) and D. radiodurans (PDB entry 2v1c; Z-score 20.4; r.m.s.d. of 1.9 Å for 193 aligned residues; 48% sequence identity; Timmins et al., 2007 ▸). The P. aeruginosa, T. tengcongensis and D. radiodurans RecR structures all share a similar fold but exhibit slightly different domain orientations (Fig. 2 ▸).
Figure 2.
Superposition of PaRecR (green), D. radiodurans RecR (cyan; PDB entry 1vdd; Lee et al., 2004 ▸) and T. tengcongensis RecR (yellow; PDB entry 3vdp; Tang et al., 2012 ▸) homodimer structures. All structures are shown in cartoon representation.
3.2. The P. aeruginosa RecR dimer and tetramer structures
RecR proteins are reported to have different oligomeric states in solution. D. radiodurans and Helicobacter pylori RecR have been shown to be tetrameric in solution at a concentration of 1 mg ml−1 by analytical ultracentrifugation (Lee et al., 2004 ▸), but more recently D. radiodurans RecR was shown to be dimeric in solution by SAXS analysis (Radzimanowski et al., 2013 ▸). Analytical ultracentrifugation confirms that P. aeruginosa RecR is predominantly dimeric at a concentration of 1 mg ml−1, but also exists as a tetramer at the same concentration. This ability to transition between dimers and tetramers has been ascribed to the ability of RecR tetramers to open and close at intracellular concentrations (Lee et al., 2004 ▸), thus enabling it to act as a clamp protein to encircle DNA.
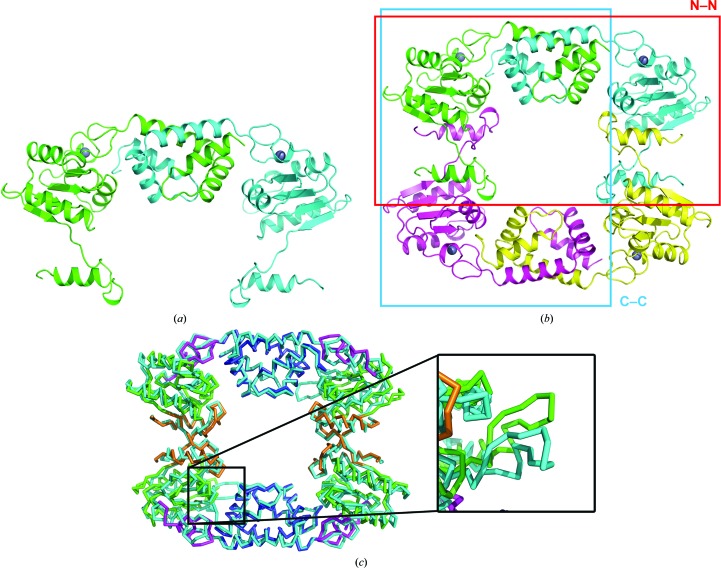
Two RecR monomers in the asymmetric unit form a dimer (termed the N–N dimer) with domain-swapped N-terminal helix–hairpin–helix (HhH) motifs (Fig. 3 ▸ a). This dimer has a buried interface area of ∼2400 Å2 and a solvation free-energy gain ΔG of −48.4 kcal mol−1 as calculated using PISA (Krissinel & Henrick, 2007 ▸). This region has been shown to be essential for the interaction with RecO in T. tengcongensis (Tang et al., 2012 ▸). Deletion of the N-terminal 15 amino acids from T. tengcongensis RecR also results in the formation of a dimer, but one which is unable to form a complex with RecO in solution (Tang et al., 2012 ▸).
Figure 3.
The PaRecR dimer and tetramer structures. (a) The PaRecR N–N dimer structure, shown in ribbon representation. Subunit A is coloured green and subunit B is coloured cyan. (b) The PaRecR tetramer structure shown in ribbon representation. Subunit A is coloured green, subunit B is coloured cyan, subunit A′ is coloured magenta and subunit B′ is coloured yellow. The N–N and C–C dimers are shown by red and blue boxes, respectively. (c) Superposition of PaRecR and T. tengcongensis RecR tetramers. Both tetramers are shown in PyMOL ribbon representation; PaRecR is coloured according to structural domain (blue, HhH motif; magenta, zinc-finger motif; green, Toprim domain; orange, Walker B motif) and T. tengcongensis RecR is coloured cyan. Inset: comparison of loop 106–121 of the two structures.
A ring-like tetramer is generated from the N–N dimer via a twofold-symmetry transformation (Fig. 3 ▸ b) and is consistent with the ring-like structures observed for the T. tengcongensis and D. radiodurans RecR structures (Lee et al., 2004 ▸; Tang et al., 2012 ▸). The PaRecR tetramer can be superimposed onto the T. tengcongensis RecR tetramer with an r.m.s.d. of 2.7 Å for 701 aligned residues, showing good overall agreement between the two tetramers. The N-terminal HhH and C-terminal Walker B motifs involved in dimerization align closely, but the Toprim domains of the two structures align less closely. In particular, a large deviation of as much as 12 Å is observed between loop 106–121 of the PaRecR (chain B) and T. tengcongensis RecR (chains B and D) structures. This loop has been reported to bind tightly into a hydrophobic pocket in RecO and is crucial for the interaction of RecR with RecO (Tang et al., 2012 ▸).
The dimensions of the tetramer are roughly 90 × 70 × 30 Å, with a central hole of approximately 35 × 30 Å. The tetramer is formed by interactions between subunits A–A′ and subunits B–B′, with a buried interface area of ∼2000 Å2 and a solvation free-energy gain ΔG of −32.1 kcal mol−1 for each pair of subunits. This generates another dimer interface (termed the C–C dimer) in which the C-terminal Walker B motifs are domain-swapped (Fig. 3 ▸ b). PaRecR lacks the C-terminal β-strand β7 observed in the D. radiodurans RecR structure, which lies antiparallel to the central β-sheet of the Toprim domain from a neighbouring monomer (Lee et al., 2004 ▸), but the mode of C–C dimerization is otherwise identical.
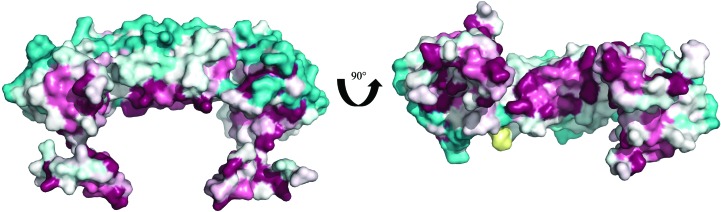
A ConSurf analysis (Ashkenazy et al., 2016 ▸) of the PaRecR structure with 150 unique homologous sequences revealed that the most conserved regions are on the inner surface of the protein lining the central hole, including the N-terminal HhH motif and the C-terminal Walker B motif (Fig. 4 ▸). This suggests a high conservation of function, as both the HhH motif and the Walker B motif are implicated in binding to DNA and to RecO.
Figure 4.
ConSurf analysis of the PaRecR dimer. The PaRecR dimer is shown in surface representation and coloured according to conservation calculated from 150 homologous sequences, from turquoise (low conservation) through white (average conservation) to maroon (high conservation).
3.3. A ligand-binding site in the RecR Walker B motif
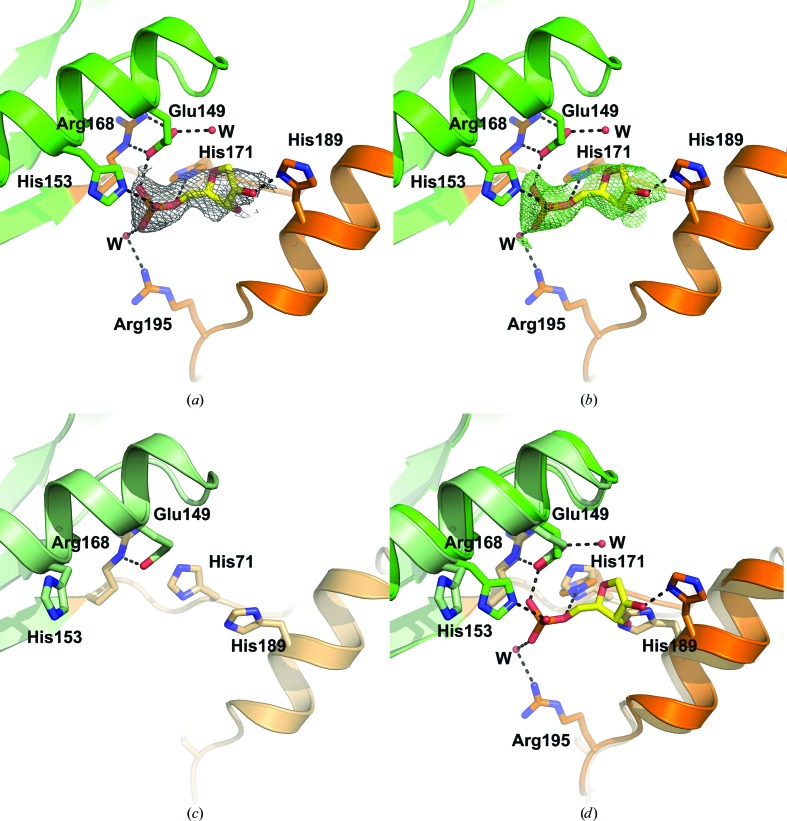
Careful examination of the electron-density maps identified a region of electron density in chain A corresponding to an unidentified ligand sandwiched between helix α6 in the Toprim domain and helix α7 in the Walker B motif (Fig. 5 ▸ a). The Walker B motif is associated with ATP binding and ATP hydrolysis. In the context of RecR, an increase in α-helical content in D. radiodurans and H. pylori RecR was observed by circular-dichroism spectroscopy in the presence of ATP, suggesting that the Walker B motif undergoes a conformational change upon ATP binding (Lee et al., 2004 ▸). No ATPase activity was detected for D. radiodurans, H. pylori or Streptomyces coelicolor RecR (Lee et al., 2004 ▸; Peláez et al., 2001 ▸), although the DNA-binding activity of Bacillus subtilis RecR was observed to be increased by ATP (Alonso et al., 1993 ▸). The size and shape of the electron density for the unidentified ligand is consistent with the ribose and phosphate moieties of a nucleotide, as shown by a 2mF o − DF c OMIT map (Fig. 5 ▸ a) and a polder OMIT map (Fig. 5 ▸ b; Liebschner et al., 2017 ▸). The phosphate group is coordinated by Glu149, which forms a salt bridge to Arg168, His153 in the Toprim domain, and His171 and Arg195 (via a water molecule) in the Walker B motif. The ribose moiety is coordinated by His189 in the Walker B motif.
Figure 5.
Ligand binding in the Walker B motif. (a) The ligand-binding site in subunit A of PaRecR. The ligand is shown in yellow stick representation and is covered by a 2mF o − DF c OMIT electron-density map shown as a grey mesh and contoured at 1.6 r.m.s.d. Residues coordinating the ligand are shown in stick representation and are coloured according to the scheme in Fig. 1 ▸(c) (blue, HhH motif; magenta, zinc-finger motif; green, Toprim domain; orange, Walker B motif). (b) The ligand in subunit A of PaRecR covered by a polder OMIT electron-density map shown as a green mesh and contoured at 3.0 r.m.s.d. (c) The equivalent ligand-free site in subunit B of PaRecR. Residues are shown in stick representation and are coloured pale green for the Toprim domain and pale orange for the Walker B motif. (d) Superposition of the ligand-binding sites in subunits A (Toprim domain in green, Walker B motif in orange) and B (Toprim domain in pale green, Walker B motif in pale orange).
The ligand binding is asymmetrical, as no corresponding electron density is observed in chain B (Fig. 5 ▸ c). The side chain of His171 in chain B instead interacts with the side chain of Glu141. The side chain of His189 in chain B rotates to occupy the position of the ribose moiety, and the side chains of His153 and Arg195 are directed out of the putative ligand-binding pocket. Superposition of chains A and B shows a movement of the Walker B motif by approximately 2 Å and of helix α7 by approximately 2.5 Å away from the Toprim domain in subunit A, indicating a minor conformational change to accommodate the ligand (Fig. 5 ▸ d).
The ligand-binding site in subunit A of PaRecR is distinct from the typical ATP-binding site observed in the Walker B motifs of proteins such as the AAA+ (ATPases associated with various cellular activities) family. The Walker B motif in AAA+ proteins forms contacts with the nucleotide: the aspartate residue in the hhhhDE sequence coordinates the magnesium required for ATP hydrolysis, and the glutamate activates water for the hydrolysis reaction (Hanson & Whiteheart, 2005 ▸). Asp183 in the hhhhDE sequence of PaRecR is situated approximately 10 Å from the ribose moiety of the ligand, while the glutamate in the hhhhDE sequence is substituted by Gly184. Mutation of the catalytic glutamate in the hhhhDE sequence is reported to abolish ATP hydrolysis but not ATP binding (Hanson & Whiteheart, 2005 ▸), suggesting that PaRecR might lack ATP-hydrolysis activity, consistent with other RecR proteins (Lee et al., 2004 ▸; Peláez et al., 2001 ▸). Further work is under way to investigate the relevance of this ligand-binding site as a putative ATP- or nucleotide-binding site, and to investigate the effects of ATP on the DNA-binding activity.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we have determined the 2.2 Å resolution structure of RecR, a member of the RecF homologous recombination pathway, from P. aeruginosa PAO1. PaRecR is predominantly a dimer in solution but can exist as a tetramer. The crystal structure confirms the existence of a PaRecR tetramer, consistent with other members of the RecR family. A ligand identified in the Walker B motif, which is associated with ATP binding and hydrolysis, suggests a putative nucleotide-binding site. Further work is under way to examine the function of RecR and to characterize its interaction with ssDNA or with its known binding partners, RecO or RecF.
Supplementary Material
PDB reference: RecR, 5z2v
Supplementary Figure S1.. DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X18003503/rf5004sup1.pdf
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff of the National Center for Protein Sciences Shanghai (NCPSS) beamline BL19U at Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility for assistance during data collection.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China grant 31570128. Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Commission grant 13JCYBJC20800.
References
- Adams, P. D. et al. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 213–221.
- Alonso, J. C., Stiege, A. C., Dobrinski, B. & Lurz, R. (1993). J. Biol. Chem. 268, 1424–1429. [PubMed]
- Ashkenazy, H., Abadi, S., Martz, E., Chay, O., Mayrose, I., Pupko, T. & Ben-Tal, N. (2016). Nucleic Acids Res. 44, W344–W350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Birtley, J. R. & Curry, S. (2005). Acta Cryst. D61, 646–650. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bork, J. M., Cox, M. M. & Inman, R. B. (2001). EMBO J. 20, 7313–7322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Burma, S., Chen, B. P. C. & Chen, D. J. (2006). DNA Repair, 5, 1042–1048. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chen, V. B., Arendall, W. B., Headd, J. J., Keedy, D. A., Immormino, R. M., Kapral, G. J., Murray, L. W., Richardson, J. S. & Richardson, D. C. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 12–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Cirz, R. T., O’Neill, B. M., Hammond, J. A., Head, S. R. & Romesberg, F. E. (2006). J. Bacteriol. 188, 7101–7110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Clark, A. J. (1991). Biochimie, 73, 523–532. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Cox, M. M. (2007). Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 42, 41–63. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Cox, M. M., Goodman, M. F., Kreuzer, K. N., Sherratt, D. J., Sandler, S. J. & Marians, K. J. (2000). Nature (London), 404, 37–41. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dam, J. & Schuck, P. (2004). Methods Enzymol. 384, 185–212. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dillingham, M. S. & Kowalczykowski, S. C. (2008). Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 72, 642–671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P., Lohkamp, B., Scott, W. G. & Cowtan, K. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 486–501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hanson, P. I. & Whiteheart, S. W. (2005). Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 519–529. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Honda, M., Fujisawa, T., Shibata, T. & Mikawa, T. (2008). Nucleic Acids Res. 36, 5013–5020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Inoue, J., Honda, M., Ikawa, S., Shibata, T. & Mikawa, T. (2008). Nucleic Acids Res. 36, 94–109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Joosten, R. P., Long, F., Murshudov, G. N. & Perrakis, A. (2014). IUCrJ, 1, 213–220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kowalczykowski, S. C. (2000). Trends Biochem. Sci. 25, 156–165. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kowalczykowski, S. C., Dixon, D. A., Eggleston, A. K., Lauder, S. D. & Rehrauer, W. M. (1994). Microbiol. Rev. 58, 401–465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Krissinel, E. & Henrick, K. (2007). J. Mol. Biol. 372, 774–797. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lee, B. I., Kim, K. H., Park, S. J., Eom, S. H., Song, H. K. & Suh, S. W. (2004). EMBO J. 23, 2029–2038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lenhart, J. S., Brandes, E. R., Schroeder, J. W., Sorenson, R. J., Showalter, H. D. & Simmons, L. A. (2014). J. Bacteriol. 196, 2851–2860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Liebschner, D., Afonine, P. V., Moriarty, N. W., Poon, B. K., Sobolev, O. V., Terwilliger, T. C. & Adams, P. D. (2017). Acta Cryst. D73, 148–157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, T. (1993). Nature (London), 362, 709–715. [DOI] [PubMed]
- McCoy, A. J., Grosse-Kunstleve, R. W., Adams, P. D., Winn, M. D., Storoni, L. C. & Read, R. J. (2007). J. Appl. Cryst. 40, 658–674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Morimatsu, K., Wu, Y. & Kowalczykowski, S. C. (2012). J. Biol. Chem. 287, 35621–35630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Peláez, A. I., Ribas-Aparicio, R. M., Gómez, A. & Rodicio, M. R. (2001). Mol. Genet. Genomics, 265, 663–672. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Radzimanowski, J., Dehez, F., Round, A., Bidon-Chanal, A., McSweeney, S. & Timmins, J. (2013). Nucleic Acids Res. 41, 7972–7986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ryzhikov, M., Koroleva, O., Postnov, D., Tran, A. & Korolev, S. (2011). Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 6305–6314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Shuman, S. & Glickman, M. S. (2007). Nature Rev. Microbiol. 5, 852–861. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Singleton, M. R., Dillingham, M. S., Gaudier, M., Kowalczykowski, S. C. & Wigley, D. B. (2004). Nature (London), 432, 187–193. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spies, M., Amitani, I., Baskin, R. J. & Kowalczykowski, S. C. (2007). Cell, 131, 694–705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Spies, M. & Kowalczykowski, S. C. (2005). The Bacterial Chromosome, edited by N. P. Higgins, pp. 389–403. Washington DC: ASM Press.
- Spies, M. & Kowalczykowski, S. C. (2006). Mol. Cell, 21, 573–580. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q., Gao, P., Liu, Y.-P., Gao, A., An, X.-M., Liu, S., Yan, X.-X. & Liang, D.-C. (2012). Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 11115–11125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Timmins, J., Leiros, I. & McSweeney, S. (2007). EMBO J. 26, 3260–3271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.-C., Hung, J.-L. & Wang, T.-C. V. (1994). Mutat. Res. 315, 1–9. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Umezu, K. & Kolodner, R. D. (1994). J. Biol. Chem. 269, 30005–30013. [PubMed]
- West, S. C. (2003). Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 435–445. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
PDB reference: RecR, 5z2v
Supplementary Figure S1.. DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X18003503/rf5004sup1.pdf