Abstract
Entamoeba histolytica has been rarely reported as superadded infection over carcinomatous growth on rectal brushings. We present a case of 68-year-old male who presented with abdominal pain and bleeding per rectum who was found to have an ulceroproliferative growth on sigmoidoscopy. Rectal brushings revealed coexistence of E. histolytica with malignant cells of adenocarcinoma. No organism was detected on biopsy of the tumor, which also showed adenocarcinoma, because of possible surface colonization of the tumor by Entamoeba. This case highlights the role of rectal brushings in detecting superadded infection in a case where both brushings and biopsy were performed. It is always important to report infection superadded on malignancies for optimum management of the patients.
Keywords: Adenocarcinoma, brushings, Entamoeba, rectal, superadded
Introduction
Intestinal amoebiasis caused by Entamoeba histolytica occurs throughout the world and about 40 million develop colitis or extraintestinal abscesses out of which 40,000 die annually.[1] The maximum incidence of E. histolytica infection is seen in Central and South America, Africa, and the Indian subcontinent.[2]
Colonic amoebiasis is the most common presentation of intestinal amoebiasis while extraintestinal amoebiasis most commonly presents as amoebic liver abscess.[3] Microscopic examination is a cost-effective and confirmatory diagnostic modality in endemic areas.[4,5]
There are several case reports describing the cytology of E. histolytica in hepatic abscesses. However, coexistence of this organism, with rectal carcinoma, and detected on rectal brushings, has been rarely reported. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case report describing cytology of E. histolytica present concomitantly with a rectal malignancy.
Case Report
A 68-year-old man presented with complaints of pain abdomen for 15 days and recurrent episodes of hematochezia for 5 days. A nondiabetic with no other significant medical history, he underwent sigmoidoscopy with rectal brushings and biopsy which were sent for cytological and histopathological evaluation, respectively. Stool examination was not performed. Sigmoidoscopy revealed a broad based, lobulated proliferative growth measuring 5 cm × 4.1 cm in size, in the rectosigmoid region, located at 14 cm from anal verge and was partially obliterating the rectosigmoid lumen [Figure 1].
Figure 1.
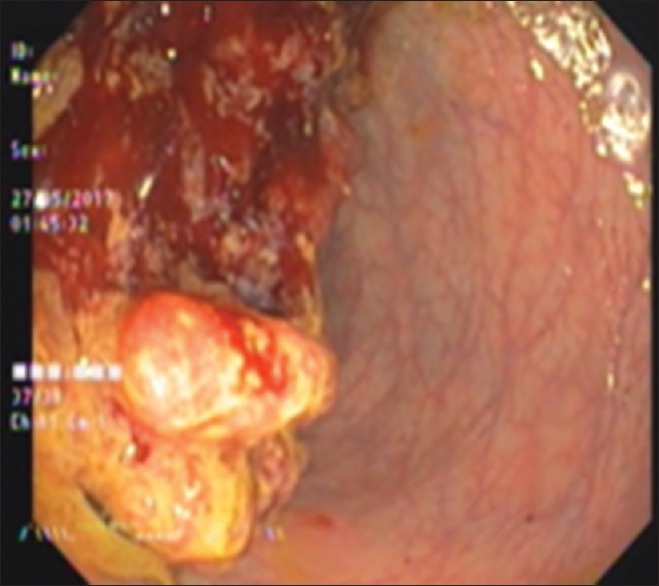
Sigmoidoscopy showing lobulated proliferative growth occluding recto sigmoid lumen
Cytological examination of the rectal brushings showed few cohesive clusters, some with attempted gland formation, composed of cells exhibiting moderate nuclear pleomorphism, nucleomegaly, irregular nuclear contours, clumped chromatin, and scanty cytoplasm [Figure 2]. Also seen were numerous cysts of E. histolytica surrounded by a halo along with trophozoites containing granular cytoplasm and exhibiting hemophagocytosis [Figure 3]. periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) and phosphotungstic acid hematoxylin (PTAH) stains were also done to highlight the trophozoites [Figure 4]. Thus, cytological diagnosis of E. histolytica infection with adenocarcinoma rectum was made.
Figure 2.
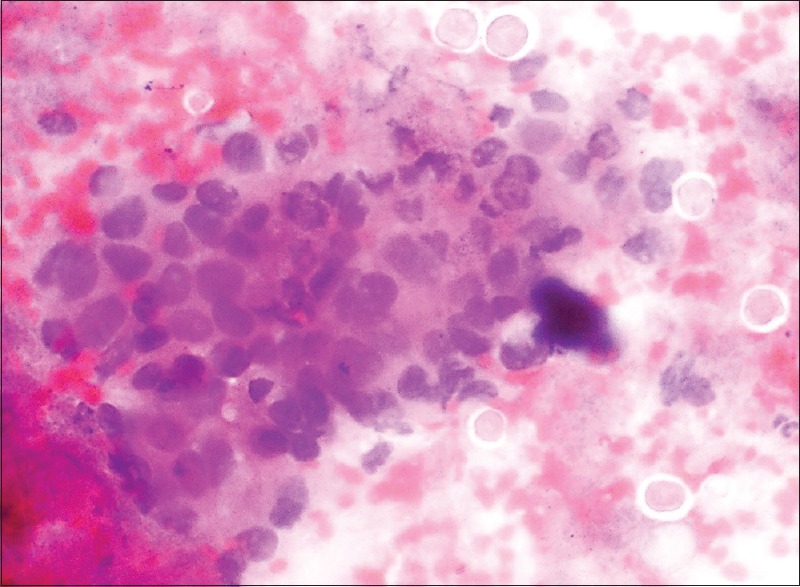
Rectal brushings showing Entamoeba cysts and clusters of malignant cells on (H and E, ×400) smear
Figure 3.
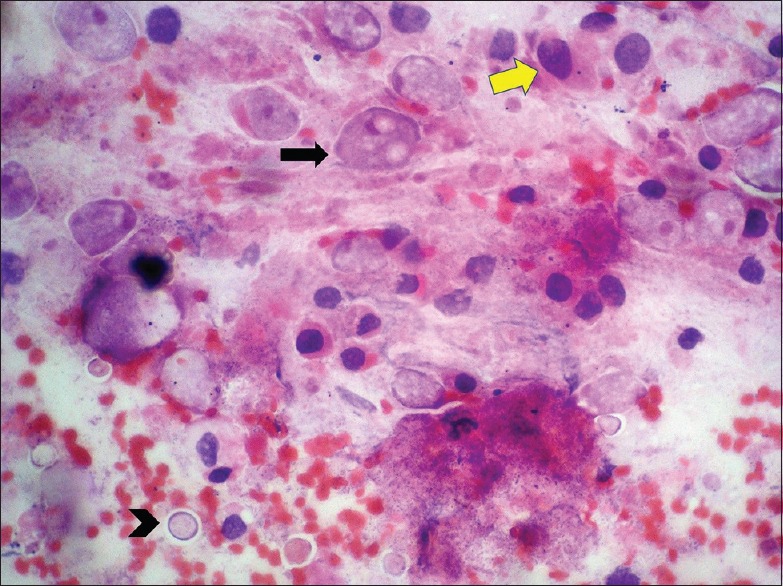
Rectal brushings showing trophozoites displaying erythrophagocytosis (arrow) and cysts (arrowhead) along with malignant cells (yellow arrow) on (H and E, ×400) smear
Figure 4.
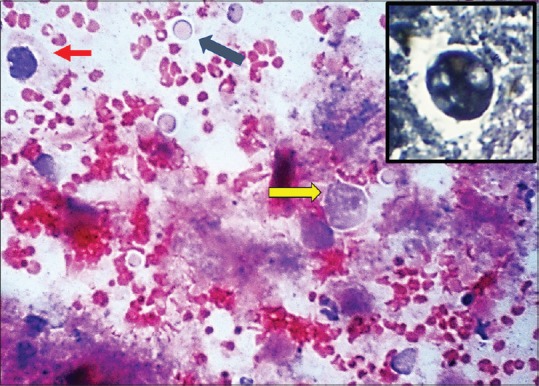
Periodic acid–Schiff stain highlighting trophozoites (yellow arrow), cysts (black arrow) and malignant cell (red arrow). Inset showing trophozoite on (PTAH, ×400)
Histopathological examination confirmed the diagnosis of adenocarcinoma seen as glands displaying crowding and back-to-back arrangement and nuclear stratification with villi formation. The individual cells displayed marked nuclear pleomorphism, hyperchromasia with many atypical mitotic figures [Figure 5]. Focus of invasion was noted in the underlying tissue which also showed dense inflammatory infiltrate composed of neutrophils, eosinophils, and lymphocytes. However, no cysts or trophozoites of E. histolytica were evident on biopsy sections.
Figure 5.
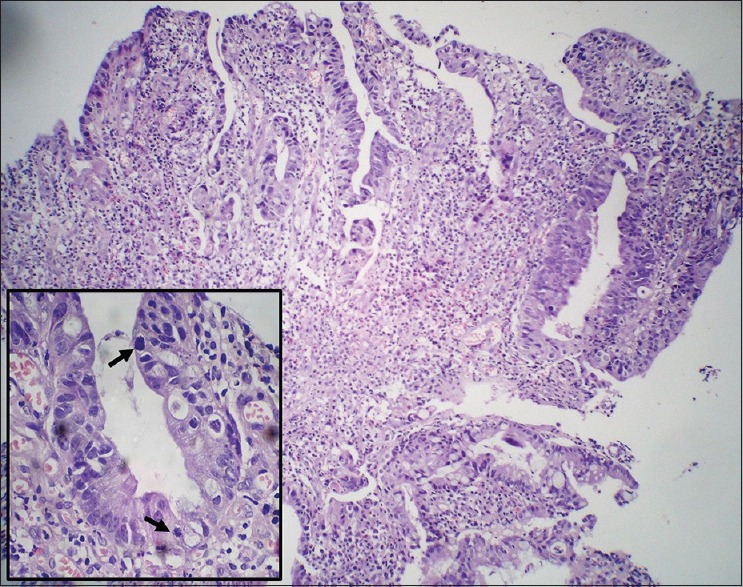
Rectal biopsy showing adenocarcinoma displaying nuclear stratification and crowding (H and E, ×40) with frequent atypical mitotic figures in inset (arrow) (×400)
Informed consent was obtained from the patient for utilizing his data for academic purpose. Thereafter, the patient refused further treatment and was lost to clinical follow-up.
Discussion
E. histolytica, an amoebic protozoan parasite, occurs in the cyst form and trophozoite form. The infection occurs through feco-oral route after consumption of water or food contaminated with cyst form.[2]
Amoebiasis is defined as infection with E. histolytica, regardless of symptomatology.[6] Although both genders and all ages are affected; males are more commonly affected than females.[4]
Patients may be asymptomatic or present with abdominal pain, copious diarrhea admixed with blood and mucus.[7,8] This patient only had abdominal pain. On sigmoidoscopy, flask shaped ulcers covered with slough are usually present.[8] However, in our case, a broad based, lobulated, soft-tissue density mass lesion was there in the rectosigmoid region measuring 5 cm × 4.1 cm which was partially obliterating the rectosigmoid lumen and through which scope was not negotiable. Microscopic examination is mandatory to determine nature of this growth and differentiate between amoeboma and carcinoma.[9] Since there was no history of diarrhea/clinical symptoms suggestive of amoebiasis in this case, detecting E. histolytica on rectal brushings was an unexpected finding which made this case unique.
Identification of the parasite is possible because of characteristic morphology of trophozoites which exhibit erythrophagocytosis along with prominent karyosome. Foamy macrophages are a cause of confusion but they will not display hemophagocytosis.[8,10] PAS and PTAH stains highlight the trophozoites and distinguish them from foamy macrophages. The cyst forms are surrounded by refractile membrane with no chromatid body/glycogen mass seen.[8]
Other modalities for diagnosis of E. histolytica include examination of stools for trophozoites and cysts, serological tests, polymerase chain reaction, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay-based tests.[8,11] However, these were not performed in our case as there was no clinical suspicion of amoebiasis and the patient was lost to follow-up. E. histolytica was possibly present only as surface colonization of the carcinomatous growth, which explains the absence of E. histolytica in biopsy sections. Hence, rectal brushings proved to be instrumental in making the complete diagnosis of adenocarcinoma with superadded E. histolytica infection. Brush cytology has comparable diagnostic sensitivity for gastrointestinal lesions because brushings can cover larger mucosal surface and collect diagnostic material even from stenosed areas where sigmoidoscope may not be negotiable, like in this case.[12] Combining brush cytology with histopathology is a routine practice in our tertiary care institute to improve the diagnostic sensitivity.
Till date very few case reports have described coexistence of E. histolytica with malignancy, especially on cytology.[9] Other organism that has also been reported to be associated with gastrointestinal malignancies as superadded infection include Candida.[13]
Thus, the clinician as well as the pathologists needs to be vigilant about coexistence of malignancy with superadded infections like E. histolytica in patients belonging to endemic areas and presenting with abdominal complaints. This case highlights the role of cytology in diagnosing such superadded infections, which may be missed on biopsy alone. Hence, it is always pertinent to take brushings along with biopsy while investigating any colonic masses to obtain a comprehensive diagnosis.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the patient has given him consent for him images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patient understands that name and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Li E, Stanley SL., Jr Protozoa. Amebiasis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1996;25:471–92. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8553(05)70259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Singh U, Petri WA., Jr . Amoebas. In: Gillespie SH, Pearson RD, editors. Principles and Practice of Clinical Parasitology. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2001. pp. 197–218. [Google Scholar]
- 3.WHO/PAHO/UNESCO Report. A consultation with experts on amoebiasis. Mexico City, Mexico 28-29 January, 1997. Epidemiol Bull. 1997;18:13–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gupta KB, Manchanda M, Chaudhary U, Verma M. Superior vena cava syndrome caused by pulmonary amoebic abscess. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2006;48:275–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sultan A, Raza A, Khan HM, Khalid S, Akhtar A, Shameem M. Entamoeba histolytica pleuropulmonary infection case report. Int J Adv Case Rep. 2015;2:171–3. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ximénez C, Morán P, Rojas L, Valadez A, Gómez A. Reassessment of the epidemiology of amebiasis: State of the art. Infect Genet Evol. 2009;9:1023–32. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2009.06.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ng DC, Kwok SY, Cheng Y, Chung CC, Li MK. Colonic amoebic abscess mimicking carcinoma of the colon. Hong Kong Med J. 2006;12:71–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chatterjee KD, editor. Parasitology (Protozoology and Helminthology) in Relation to Clinical Medicine. 12th ed. Kolkata, India: Sree Saraswaty Press Ltd; 2001. Subphylum sarcomastigophora: Superclass sarcodina, class rhizopodea: Order amoebida; pp. 14–36. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Misra SP, Misra V, Dwivedi M. Ileocecal masses in patients with amebic liver abscess: Etiology and management. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:1933–6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i12.1933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhu H, Min X, Li S, Feng M, Zhang G, Yi X, et al. Amebic lung abscess with coexisting lung adenocarcinoma: A unusual case of amebiasis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:8251–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Skappak C, Akierman S, Belga S, Novak K, Chadee K, Urbanski SJ, et al. Invasive amoebiasis: A review of Entamoeba infections highlighted with case reports. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;28:355–9. doi: 10.1155/2014/745130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bardawil RG, D'Ambrosio FG, Hajdu SI. Colonic cytology. A retrospective study with histopathologic correlation. Acta Cytol. 1990;34:620–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Delsing CE, Bleeker-Rovers CP, van de Veerdonk FL, Tol J, van der Meer JW, Kullberg BJ, et al. Association of esophageal candidiasis and squamous cell carcinoma. Med Mycol Case Rep. 2012;1:5–8. doi: 10.1016/j.mmcr.2012.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


