Abstract
Cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP are ubiquitous second messengers that regulate the activity of effector proteins in all forms of life. The main effector proteins, the 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and the 3′,5′-cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-dependent protein kinase (PKG), are preferentially activated by cAMP and cGMP, respectively. However, the molecular basis of this cyclic nucleotide selectivity is still not fully understood. Analysis of isolated cyclic nucleotide-binding (CNB) domains of PKA regulatory subunit type Iα (RIα) reveals that the C-terminal CNB-B has a higher cAMP affinity and selectivity than the N-terminal CNB-A. Here, we show that introducing cGMP-specific residues using site-directed mutagenesis reduces the selectivity of CNB-B, while the combination of two mutations (G316R/A336T) results in a cGMP-selective binding domain. Furthermore, introducing the corresponding mutations (T192R/A212T) into the PKA RIα CNB-A turns this domain into a highly cGMP-selective domain, underlining the importance of these contacts for achieving cGMP specificity. Binding data with the generic purine nucleotide 3′,5′-cyclic inosine monophosphate (cIMP) reveal that introduced arginine residues interact with the position 6 oxygen of the nucleobase. Co-crystal structures of an isolated CNB-B G316R/A336T double mutant with either cAMP or cGMP reveal that the introduced threonine and arginine residues maintain their conserved contacts as seen in PKG I CNB-B. These results improve our understanding of cyclic nucleotide binding and the molecular basis of cyclic nucleotide specificity.
Introduction
After the discovery of 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) by Sutherland [1], cyclic nucleotides have been described as ubiquitous second messengers in all forms of life [2]. In the cell, cAMP and 3′,5′-cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) are generated by cyclases, while phosphodiesterases (PDEs) catalyze their degradation. The coupling of cyclic nucleotide synthesis and degradation to the extracellular first messenger signals provides the basis of cyclic nucleotide signaling.
Both cAMP and cGMP allosterically regulate the activity of eukaryotic effector proteins like PDEs, the exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (Epac), cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channels, hyperpolarization-activated and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels, and as main effectors, the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and the cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) [3–8]. Besides the ubiquitous second messengers cAMP and cGMP, in the last decade, so-called non-canonical cyclic nucleotides like 3′,5′-cyclic inosine monophosphate (cIMP) have been described to regulate cyclic nucleotide effectors under certain physiological conditions [9,10]. These effector proteins share conserved cyclic nucleotide-binding (CNB) domains [11,12]. The structure of a CNB domain was first described for the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein and consists of an eight-stranded β-barrel which is flanked by a variable number of helices at either terminus [13]. The most conserved structural motif within the CNB domain is the phosphate-binding cassette (PBC), which consists of a short helix and a loop and is located between β-sheets 6 and 7. Residues of the PBC interact mainly with the sugar–phosphate moiety of the cyclic nucleotide.
Despite the structural similarities of CNB domains, cyclic nucleotide effector proteins have been shown to preferentially bind either cAMP or cGMP that only differ in their purine nucleobase [14,15]. While adenine has an amino group in position 6 of the purine ring, guanine has a carbonyl group in the corresponding position and an amino group in position 2. Previous studies suggested that an alanine/threonine amino acid difference within the PBC is a determinant for cGMP specificity [15–19]. However, introduction or exchange to alanine was not sufficient to reverse the selectivity of PKA or PKG, suggesting that cyclic nucleotide specificity cannot be mediated by this single amino acid difference alone [18,19]. Thus, additional contacts within the CNB domain must contribute to specificity either by increasing the affinity for one cyclic nucleotide or by reducing the affinity of the other cyclic nucleotide [19]. Indeed, our recent studies showed that a non-PBC residue, R297 at β5 (base-binding region, BBR), interacts specifically with the guanine moiety providing over 200-fold selectivity for cGMP [20,21]. PKA regulatory subunit type Iα (RIα) does not have this arginine (R297) but a glycine (G316) instead, not allowing for direct interaction. Mutating this residue to alanine significantly increased the cGMP activation constant of PKG I, demonstrating its critical role in cGMP-dependent activation.
In the present study, we investigated the molecular basis of cyclic nucleotide specificity of the two CNB domains in PKA and PKG by grafting key cGMP contact residues of the CNB domain C-terminal of PKG I (in the following, the term ‘CNB-A’ will be used to describe the N-terminal CNB domain, whereas ‘CNB-B’ will be used to describe the C-terminal CNB domain) into the corresponding positions in PKA RIα CNB domains (Figure 1). Our data show for the first time that the mutations in PKA RIα CNB-A dramatically reverse its cyclic nucleotide selectivity, turning a highly cAMP-selective domain into a highly cGMP-selective domain with an over 200-fold preference. Unlike CNB-A, similar mutations in CNB-B significantly increase its affinity for cGMP, but without reducing its affinity for cAMP, suggesting that additional structural or dynamic features are necessary for filtering out cAMP. Co-crystal structures of the CNB-B mutant with cGMP or cAMP confirm that the introduced residues maintain their cGMP-specific contacts.
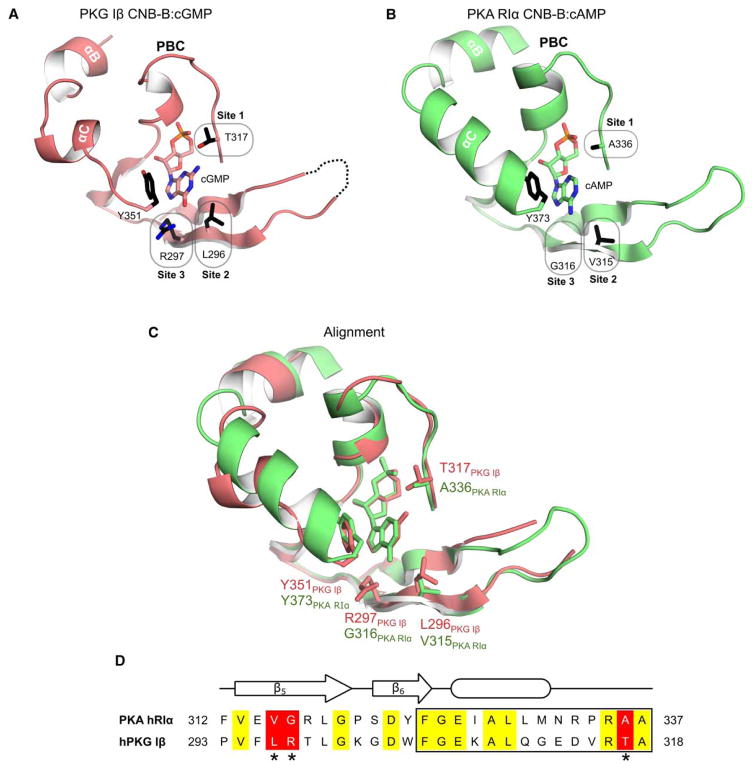
Figure 1. Structural alignment of CNB domains from PKG and PKA.
(A) Co-crystal structure of the C-terminal CNB domain (CNB-B) of PKG Iβ with cGMP (PDB code 4KU7) [20]. Key cGMP contact residues are highlighted (sites 1–3). Y351 at the C-terminal loop provides a capping interaction for cGMP. (B) Crystal structure of human PKA RIα CNB-B. Corresponding residues of sites 1–3 differ from PKG Iβ. Tyrosine 373 (Y373) is homologous to Y351 of PKG Iβ and caps the bound cAMP. (C) Structural alignment of the CNB-Bs of PKG Iβ and PKA RIα. (D) Sequence alignment from the β5 strands to the end of the PBC (box). Sequences were aligned using Clustal Omega [46,47]. Identical residues are shown in yellow. The three differing sites are shaded in red and marked with asterisks. All structure figures were generated using PyMOL (DeLano Scientific, Palo Alto, CA, U.S.A.).
Materials and methods
Materials
The cyclic nucleotides, cAMP and cGMP, and the analogs 2-(6-aminohexylamino)adenosine- 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (2-AHA-cAMP), N6-(6-aminohexyl)adenosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (6-AH-cAMP), 8-(6-aminohexylamino)adenosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (8-AHA-cAMP), N2-(6-aminohexyl) guanosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (2-AH-cGMP), 8-(2-aminoethylthio)guanosine-3′,5′-monophosphate (8-AET-cGMP), 8-(6-aminohexylthio)guanosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (8-AHT-cGMP), 8-(2-[fluoresceinyl]aminoethylthio)adenosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (8-Fluo-cAMP), and 8-(2-[fluoresceinyl]aminoethylthio)guanosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (8-Fluo-cGMP; Biolog Life Science Institute, Bremen, Germany) were dissolved in 20 mM 3-morpholinopropane-1-sulfonic acid (MOPS; pH 7.0) and 150 mM NaCl, and concentrations were determined from UV spectra using a spectrophotometer (SPECORD 205; Analytik Jena, Jena, Germany).
The plasmid pRSETB-hRIα harboring the cDNA of the human PKA RIα was a kind gift of Susan S. Taylor (University of California San Diego, La Jolla, CA, U.S.A.).
Construct design and mutagenesis
Plasmids to express His-tagged constructs of the isolated CNB-A (amino acids 115–274) and CNB-B (amino acids 234–381) of PKA hRIα were subcloned into the vector pQTEV [22] using BamHI and HindIII restriction sites.
Mutants were generated by site-directed mutagenesis using the KAPA HiFi Kit (Kapa Biosystems, Wilmington, MA, U.S.A.). The following forward primers and their respective reverse complementary primers were used to mutate the PKA hRIα CNB-B: V315L: 5′-GTTTGTTGAACTGGGAAGATTGGGG-3′, G316R: 5′-GTTGAAGTGCGCAGATTGGGGCC-3′, A336T: 5′-CGTCCTCGTACTGCCACAGTTG-3′, V315L/G316R: 5′-GTCAGAAAATGAAGAGTTTGTTGAATTGCGCAGATTGGG-3′. The following primers were used to mutate the CNB-A of PKA hRIα: T192R: 5′-GAATGGGCAAGGAGTGTTGGG-3′; A212T: 5′-GAACACCGAGAACAGCCACTGTC-3′.
The sequences of the coding regions were verified by Sanger sequencing at GATC Biotech, Konstanz, Germany.
Protein expression and purification
Expression plasmids were transformed into E. coli TP2000 Δcya using electroporation [23]. Seed cultures were grown overnight at 37°C and 180 rpm. Main cultures were inoculated 1: 10 with seed culture and incubated at 37°C and 180 rpm until an OD600 of 0.6–0.8 was reached. Expression was induced by adding 400 μM isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside and proteins were expressed overnight at room temperature.
Cells were harvested at 7000×g for 30 min and cell pellets were stored at −20°C until further processed. Cells were homogenized in lysis buffer containing 50 mM potassium phosphate (pH 8.0), 500 mM NaCl, 20 mM imidazole, either 5 mM 2-mercaptoethanol or 1 mM tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) plus 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride and EDTA-free protease inhibitor (cOmplete™, Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Cell lysis was performed by pressing the homogenate three times at 16 000 psi using a French press (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, U.S.A.). Insoluble fractions were spun down at 45 000×g for 45 min. The supernatant was incubated with Protino Ni-NTA agarose (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany) rotating at 4°C for at least 1 h. The resin was washed twice with lysis buffer containing 60 mM imidazole and once with lysis buffer containing 100 mM imidazole. Finally, the His-tagged proteins were eluted with 250 mM imidazole and elution fractions were passed through a PD-10 desalting column (GE Healthcare, Chalfont St Giles, U.K.) to exchange the buffer to 20 mM MOPS (pH 7.0), 150 mM NaCl, 2 mM EDTA, 2 mM EGTA, and either 5 mM 2-mercaptoethanol or 1 mM TCEP. Protein aliquots were stored either at 4°C on ice or at −20°C. Sample purity was checked on SDS–PAGE [24]. Protein concentrations were determined using a Bradford assay (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, U.S. A.) [25]. Purified protein samples were soluble and stable. However, CNB-B partially precipitated after freezing and thawing, and long-term storage led to oxidation-dependent dimer formation as previously shown [26].
Fluorescence polarization
Fluorescence polarization (FP) assays were performed following the protocol of Moll et al. [27]. For direct binding assays, a dilution series of the protein was mixed with a final concentration of 0.5 nM 8-Fluo-cAMP or 8-Fluo-cGMP in a black OptiPlate-384 F (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, U.S.A.).
For FP competition assays, cAMP or cGMP dilutions were mixed with 8-Fluo-cAMP or 8-Fluo-cGMP, respectively, at a final concentration of 0.5 nM and a fixed protein concentration, resulting in a half-maximal FP signal of the respective direct binding assay.
All samples were diluted in 20 mM MOPS (pH 7.0), 150 mM NaCl plus 0.005% (w/v) 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate; CHAPS). Data were obtained from either a Fusion α-FP (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, U.S.A.) or a Clariostar (BMG Labtech, Ortenberg, Germany) micro-plate reader.
The FP signal was plotted against the half logarithmic concentration of the cyclic nucleotide competitor. EC50 (half-maximal effective concentration) values were calculated from sigmoidal dose–response curves using Prism 6.01 (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA, U.S.A.).
Surface plasmon resonance
All surface plasmon resonance (SPR) measurements were performed at 25°C with 20 mM MOPS (pH 7.0), 150 mM NaCl, and 0.05% (v/v) P20 as running buffer. SPR measurements with wild-type CNB-B were performed with running buffer plus 1 mM TCEP. The interaction analyses were monitored on a Biacore T100/T200 system (GE Healthcare, Chalfont St Giles, U.K.) and an SPR-2/4 sensor (Sierra Sensors, Hamburg, Germany).
Cyclic nucleotide analogs were coupled to sensor chip surfaces of either an S-series CM5 chip (GE Healthcare) or a high-capacity amine chip (Sierra Sensors, Hamburg, Germany) as previously described [28]. All coupling steps were performed at a flow rate of 10 μl/min. Sensor chip surfaces were activated with N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS)/N-ethyl-N′-(dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (EDC) for 10 min. The respective analog (3 mM) in 100 mM borate (pH 8.5) was coupled for 15 min. Subsequently, the surface was deactivated by injecting 1 mM ethanolamine–HCl (pH 8.5) for 10 min. As a reference, the first flow cell of each chip was only activated and deactivated without any cyclic nucleotide coupled. Chips with cAMP analogs were generated by coupling 8-AHA-cAMP, 6-AH-AMP, and 2-AHA-cAMP to flow cells 2–4, while cGMP-analog chips were produced by coupling 2-AH-cGMP, 8-AET-cGMP, and 8-AHT-cGMP to the respective flow cells.
Solution competition assays were performed at a flow rate of 30 μl/min as previously described [27]. Protein was preincubated with various concentrations of cAMP, cGMP, or cIMP before injection. Association and dissociation phases were monitored for at least 150 and 60 s, respectively. The surfaces were regenerated by two injections of 0.5% (w/v) SDS and a single injection of 1 M NaCl for 60 s each.
Protein purification for crystallization
His-tagged PKA hRIα CNB-B (234–381) wild type and G316R/A336T double mutant were expressed in E. coli BL21(DE3) as described above. Proteins were purified by Ni2+-immobilized metal affinity chromatography on a Profinia Fast Protein Liquid Chromatography (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, U.S.A.). The N-terminal 7× His-tag was removed by Tobacco Etch Virus protease treatment, and then the protein samples were applied onto an additional Ni2+ affinity column to isolate non-His-tagged proteins. Later, the proteins were further purified using a Superdex 75 16/60 size-exclusion column on an ÄKTA purifier (GE Healthcare, Chalfont St Giles, U.K.).
Protein crystallization and structure determination
The protein samples were preincubated with either 5 mM cGMP or cAMP and concentrated to 15–50 mg/ml using a 10 kDa cutoff Amicon Ultra (Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA, U.S.A.). Wild-type crystals of PKA RIα with cAMP were obtained at 4°C using the hanging-drop method in 20% (w/v) PEG 8000, 100 mM imidazole/hydrochloric acid (pH 6.5), and 3% (v/v) 2-methyl-2,4-pentanediol. Crystals of the G316R/A336T mutant with cAMP bound were obtained at 4°C in 2.5 M NaCl, 0.1 M NaOAc/acetic acid (pH 4.7), and 0.2 M Li2SO4. Crystals of the G316R/A336T mutant with cGMP bound were obtained at 4°C in 24% (w/v) PEG 1500 and 20% (v/v) glycerol. Diffraction experiments of the wild type in complex with cAMP, double mutant with cAMP, and double mutant with cGMP co-crystals were performed at the X-ray facility core in the Baylor College of Medicine (a Rigaku FR-E+ SuperBright microfocus rotating anode generator with VariMax HF optics), at LRL-CAT (31-ID-D) at the APS (Argonne, IL, U.S.A.), and at beamline 8.2.1 at the ALS (Berkeley, CA, U.S.A.), respectively. Diffraction data were processed using iMosflm [29] and HKL2000 [30]. The structures were determined by molecular replacement (MR) using the truncated PKA RIα CNB-B structure (residues 234–381; PDB code 1RGS) as an MR probe using Phaser-MR [31,32]. The models were manually built using Coot [33] and refined using Phenix.refine [34] with restrained-structure-refinement implementing TLS refinement [35]. The data collection and refinement statistics are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2.
X-ray data and refinement statistics
| PKA hRIα 234–381 | Wild type with cAMP | G316R/A336T with cAMP | G316R/A336T with cGMP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data collection | |||
| X-ray source | Rigaku FR-E+ | LRL-CAT at APS | BL 8.2.1 at ALS |
| Wavelength (Å) | 1.5418 | 0.97931 | 0.97931 |
| Space group | P212121 | P65 | P212121 |
| Cell dimensions | |||
| a, b, c (Å) | 37.90, 52.21, 74.82 | 98.70, 98.70, 36.17 | 29.46, 67.78, 77.96 |
| α, β, γ (°) | 90, 90, 90 | 90, 90, 120 | 90, 90, 90 |
| Resolution (Å) | 24.65–1.90 | 33.31–2.00 | 24.26–1.35 |
| Rmerge | 6.6 (20.8)1 | 12.0 (53.1) | 6.2 (23.8) |
| I/σ (I) | 50.71 (4.5) | 8.9 (3.1) | 22.01 (6.7) |
| Completeness (%) | 97.08 (74.40) | 99.6 (99.8) | 98.6 (83.6) |
| Redundancy | 9.3 (5.4) | 5.5 (5.0) | 9.1 (4.6) |
| Refinement | |||
| Resolution (Å) | 24.65–1.90 | 32.31–2.00 | 24.26–1.35 |
| No. of reflections | 11 873 | 13 491 | 34 711 |
| Rwork/Rfree2 | 0.178/0.226 | 0.175/0.221 | 0.181/0.198 |
| No. of atoms | |||
| Proteins | 1075 | 1114 | 1210 |
| Ligand/ion | 22 | 22 | 23 |
| Water | 115 | 84 | 262 |
| B-factors | |||
| Protein | 33.93 | 35.09 | 23.16 |
| Ligand/ion | 26.35 | 26.99 | 16.27 |
| Water | 36.66 | 40.62 | 41.76 |
| r.m.s. deviations | |||
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.007 |
| Bond angles (°) | 1.223 | 1.082 | 1.226 |
| PDB ID | 5KJX | 5KJY | 5KJZ |
Abbreviations: r.m.s., root mean square.
Highest resolution shell is shown in parenthesis.
5.0% of the observed intensities was excluded from refinement for cross-validation purposes.
In silico modeling experiments
All in silico experiments were performed with YASARA software v.17.1.28 (www.yasara.org) [36], and all figures were prepared with PyMOL (www.pymol.org; DeLano Scientific, Palo Alto, CA, U.S.A.). The structure of the bovine PKA RIα including the bound cAMP was obtained from the PDB (PDB code 1RGS) [32]. The cGMP molecule was constructed manually by atom exchange in the already bound cAMP, and subsequent updating of the bond order. The structure was gradually energy-minimized in vacuo with the force field YAMBER3 in a defined cell of 5 Å around all atoms. At first, all atoms of the protein were fixed and the cAMP or cGMP was energy-minimized to be properly oriented in the binding site. In a second step, the protein was allowed free and another round of energy minimization was performed, in order to optimize the interactions between the amino acids of the binding pocket and the cyclic nucleotide. For the mutant, a similar procedure was followed; starting from the structure 1RGS, using YASARA we mutated (‘swapped’) the residues in positions 192 and 212. The whole protein and the cyclic nucleotide (cAMP or cGMP) were fixed, and only the two residues were allowed free to be energy-minimized, to identify the proper orientation of their side chains in the binding pocket. Once this was performed, the whole structure was energy-minimized.
Results and discussion
Generation of isolated CNB domain constructs based on structural comparison with PKG
The aim of this work is to decipher the molecular basis of cyclic nucleotide specificity of PKA and PKG. We recently demonstrated that R297 and T317 of PKG Iβ CNB-B provide cGMP-specific contacts that explain its selectivity for cGMP [20,21,37]. Although the overall fold of the CNB-Bs of PKA RIα and PKG Iβ is conserved, our structural alignment shows that cGMP-specific residues recently identified in PKG (L296, R297, and T317 in human PKG Iβ) are missing in PKA (corresponding residues in PKA hRIα are V315, G316, and A336, respectively; Figure 1; see Supplementary Figure S1 for complete alignment of PKA RIα and PKG I CNBs). To investigate cyclic nucleotide specificity in PKA RIα, we generated constructs of the isolated PKA RIα CNB-B (amino acids 234–381) and the CNB-A (amino acids 115–274). The CNB-A construct extended to the αA-helix of the CNB-B, which includes W260, which provides a capping interaction for cAMP [38,39]. All proteins were expressed using E. coli TP2000 Δcya, which lacks adenylate cyclase activity, and were purified under cyclic nucleotide-free conditions for affinity measurements using FP and SPR solution competition assays (Figure 2) [23]. The construct containing amino acids 234–381 (CNB-B) seemed to be less stable compared with CNB-A reflected in variations in the binding of cGMP. Only in the presence of 1 mM TCEP could reproducible data be obtained for cGMP binding.
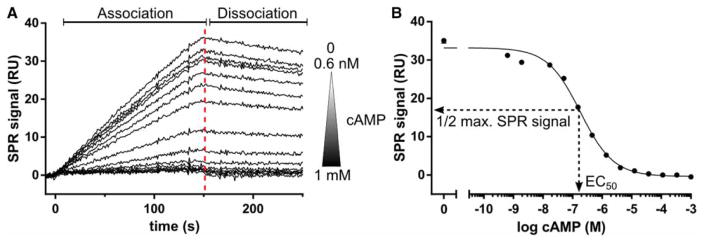
Figure 2. SPR solution competition experiments.
(A) SPR solution competition data of PKA hRIα CNB-A (115–274) with cAMP. hRIα CNB-A (2 nM) was preincubated with a cAMP concentration series ranging from 0.6 nM to 1 mM. Additionally, the protein sample was injected without cAMP. The samples were injected over a high-density 6-AH-cAMP surface for 150 s (association phase) before the dissociation was monitored for 100 s using a Biacore T100/T200 instrument (GE Healthcare, Chalfont St Giles, U.K.). A report point was set 3 s before the end of the association (red-dashed line) to monitor the SPR signal of each sample. RU: resonance unit. (B) The SPR signal was plotted against the logarithmic cAMP concentration and the data were fitted with a sigmoidal dose–response curve employing Prism 6.01 (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA, U.S.A.). The EC50 is the cAMP concentration which gives half-maximal competition of the SPR signal (1/2 max. SPR signal). The EC50 for this experiment was 184 nM.
Isolated CNB-A and -B of PKA RIα show different selectivity for cAMP
Competition SPR and FP measurements revealed that CNB-A binds cAMP with a 50-fold lower affinity compared with CNB-B (EC50 = 151 versus 3.6 nM). These results are consistent with previous studies where CNB-B was described as the high-affinity site for cAMP and CNB-A as the low-affinity site [40,41]. Furthermore, CNB-A binds cGMP with a lower affinity (EC50 = 4.6 versus 0.4 μM) than CNB-B (Figure 3 and Table 1). However, comparing the relative affinities, we demonstrate for the first time that CNB-B has a higher selectivity for cAMP compared with CNB-A (Figure 3 and Table 1). In contrast, previous studies using full-length PKA RIα revealed that CNB-A is more selective for cAMP than CNB-B [14,18,42]. However, as cAMP binding to PKA RIα is highly cooperative, cyclic nucleotide binding to the full-length protein and the isolated CNB domains cannot be directly compared [43]. Previous studies on isolated CNB domains of PKA RIα showed that CNB-B is more selective for cAMP compared with CNB-A [41,44]. In agreement with former studies, the selectivity of the isolated CNB-B remains the same as for CNB-B in the full-length PKA RIα [42]. In contrast, the isolated CNB-A shows a reduced selectivity compared with CNB-A in the full-length protein. This suggests that the selectivity of CNB-A may additionally depend on interactions with other domains in the intact protein. Indeed, CNB-A is known to interact with CNB-B, where CNB-B acts as a ‘gatekeeper’ that enables the binding of cyclic nucleotides to CNB-A by recruiting W260 as the capping residue for CNB-A [32,45]. Although this capping residue is included in our CNB-A construct, the capping might not be complete as in the full-length protein and this partial or lack of the capping interaction may explain the reduced selectivity of CNB-A.
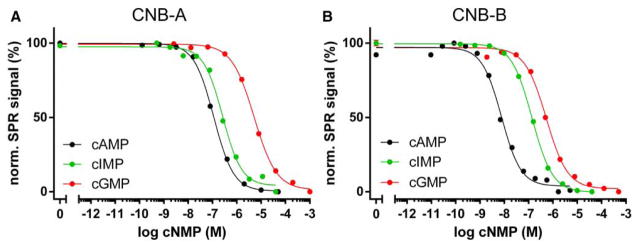
Figure 3. Cyclic nucleotide binding of individual CNB domains.
Competition curves were derived from SPR experiments as exemplified in Figure 2 (normalized data). (A) Binding competition of PKA hRIα CNB-A (residues 115–274). Cyclic AMP and cyclic IMP bind to CNB-A with high nanomolar affinities, while cGMP binds with a micromolar affinity. CNB-A shows a more than 30-fold preference for cAMP. (B) CNB-B (residues 234–381) has a significantly higher affinity for cAMP compared with CNB-A, but still binds cGMP with micromolar affinity, resulting in an 110-fold selectivity. Cyclic IMP is bound with an intermediate affinity between cAMP and cGMP.
Table 1.
EC50 values of PKA hRIα CNB domain constructs
| His-PKA hRIα | EC50 ± SD1 (nM) | Ratio EC50 (cAMP)/EC50 (cGMP) | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
| cAMP | cGMP | ||
| CNB-A (115–274) | |||
| Wild type | 151 ± 39 | 4554 ± 657 | 0.03 |
| T192R | 859 ± 197 | 1529 ± 53 | 0.56 |
| A212T | 420 ± 11 | 83 ± 33 | 5.06 |
| T192R/A212T | 5410 ± 1290 | 24 ± 5 | 225 |
| CNB-B (234–381) | |||
| Wild type | 3.6 ± 1.4 | 396 ± 25 | 0.009 |
| V315L | 7.5 ± 1.8 | 678 ± 100 | 0.011 |
| G316R | 15.3 ± 4.9 | 98 ± 41 | 0.156 |
| A336T | 4.9 ± 1.9 | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 2.45 |
| V315L/G316R | 11.5 ± 7.6 | 66 ± 2 | 0.174 |
| G316R/A336T | 15.8 ± 1.3 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 39.5 |
| V315L/G316R/A336T | 10 ± 1 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 16.7 |
Mean values with standard deviation (SD) of at least four replicates from N ≥ 2 independent protein preparations.
Interestingly, both isolated CNB domains of PKA hRIα bound the generic purine nucleotide cIMP with EC50 values between the respective EC50 values for cAMP and cGMP (Figure 3). However, CNB-A bound cIMP with slightly weaker affinity than cAMP (EC50 = 273 ± 16 nM; Figure 3A), whereas CNB-B had a markedly reduced affinity (30-fold) for cIMP in comparison with cAMP (EC50 = 114 ± 51 nM; Figure 3B). Cyclic IMP is a purine nucleotide like cAMP and cGMP. The structural formula of cIMP can be classified between the structural formulas of cAMP and cGMP because hypoxanthine, the nucleobase of cIMP, lacks an amino group in position 2, but carries a carbonyl oxygen in position 6 as is found in guanosine (Supplementary Figure S2).
Mutants of CNB-B switch cyclic nucleotide selectivity
In the 1980s and the 1990s, Shabb, Corbin and co-workers showed that a key alanine/threonine difference between PKA and PKG is a strong determinant for cGMP specificity [15,17–19]. Based on our recent crystal structures [20], we hypothesized additional determinants for cGMP selectivity. We attempted to turn the cAMP-selective CNB-B of PKA RIα into a cGMP-selective domain by grafting key cGMP contact residues as seen in the recent crystal structure of PKG Iβ CNB-B bound with cGMP [20].
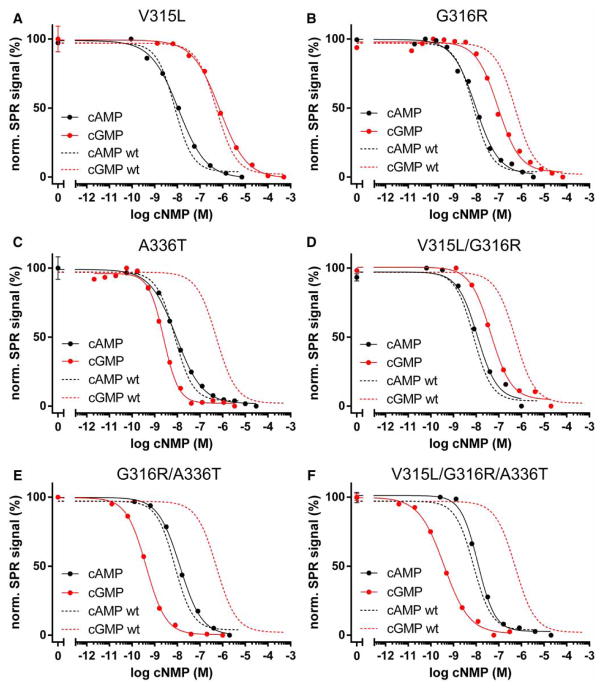
All mutant constructs showed a reduced cAMP selectivity in comparison with the wild type (Figure 4 and Table 1). Replacing valine at position 315 with a leucine (V315L) did not change the affinity for cAMP and showed a modest increase in cGMP affinity (Figure 4A). Mutating glycine at position 316 to an arginine (G316R) slightly reduced cAMP affinity, while its cGMP affinity was increased 4-fold (Figure 4B). As shown before, introducing a threonine residue at the corresponding position (A336T) had dramatic effects on cyclic nucleotide selectivity (Figure 4C) [17,18]. Our data demonstrate that grafting key cGMP contact residues into the PKA RIα CNB-B changes its cyclic nucleotide selectivity by increasing cGMP affinity, rather than reducing the affinity for cAMP.
Figure 4. Cyclic nucleotide binding of PKA RIα CNB-B mutants.
Binding competition experiments were performed as described in Figure 2. The following mutants were characterized: (A) V315L, (B) G316R, (C) A336T, (D) V315L/G316R, (E) G316R/A336T, and (F) V315L/G316R/A336T. Dashed lines show binding competition curves of wild-type CNB-B for cAMP (black) and cGMP (red).
We then tested if combinations of these mutations have additive effects on cyclic nucleotide selectivity. Combining V315L with G316R (V315L/G316R) yielded a construct with similar affinities for cAMP and cGMP like the G316R mutant (Figure 4D). In contrast, combining G316R with A336T (G316R/A336T) further increased the affinity for cGMP (from 84 to 0.4 nM), without changing cAMP affinity. This construct displayed the highest selectivity for cGMP (~40-fold) among the CNB-B mutants (Figure 4E). This effect could not be achieved by the single alanine-to-threonine mutation described before by Corbin and co-workers [17,18]. Combining all three mutations (V315L/G316R/A336T) did not significantly change the cyclic nucleotide affinities, suggesting that the V315L mutation contributes little to cGMP binding (Figure 4F), which is in agreement with what was previously described for the corresponding residue (L296) in PKG Iβ CNB-B [20].
Overall structures of PKA hRIα CNB-B G316R/A336T in the presence of either cAMP or cGMP
Since the G316R/A336T mutation did not affect the cAMP affinity of the CNB-B, we reasoned that either additional contacts or structural features within CNB-B may stabilize cAMP binding. To test this hypothesis, we solved three co-crystal structures of PKA hRIα CNB-B: wild type bound with cAMP and G316R/A336T bound with cAMP or cGMP (Figures 5A and 6A and Table 2). The wild-type CNB-B bound with cAMP was crystallized in the P212121 space group with one molecule per asymmetric unit. The final model showed clear density for the residues 241–381. The double mutant bound to cAMP was crystallized in the P65 space group and the final model showed clear density for the residues 238–379 excluding the β4–β5 loop. The double mutant bound to cGMP was crystallized in the P212121 space group with the final model including the entire CNB-B (234–381) used for crystallization.
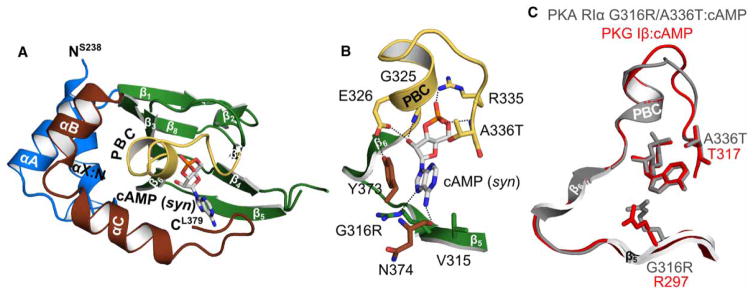
Figure 5. Crystal structure of PKA hRIα CNB-B (234–381) G316R/A336T bound with cAMP.
(A) Overall structure of the PKA RIα CNB-B G316R/A336T double mutant bound with cAMP. The protein is shown in cartoon representation with the secondary structure elements labeled, while cAMP is shown as sticks. (B) Detailed view of the CNB pocket with the bound cAMP. The introduced A336T does not interact with cAMP. The side chain of G316R moves away from the cAMP, indicating a steric clash between the position 6 amino group and the arginine side chain. Therefore, R316 is a negative determinant for binding of cAMP as recently described for PKG Iβ [21]. However, a hydrogen bond with the N7 of the purine ring can still be formed. Residues are labeled and hydrogen bond interactions are shown as dashed lines. (C) Structural alignment of the PKA RIα CNB-B G316R/A336T: cAMP complex (gray) with the PKG Iβ CNB-B: cAMP complex structure (red; PDB code 4QX5) [21].
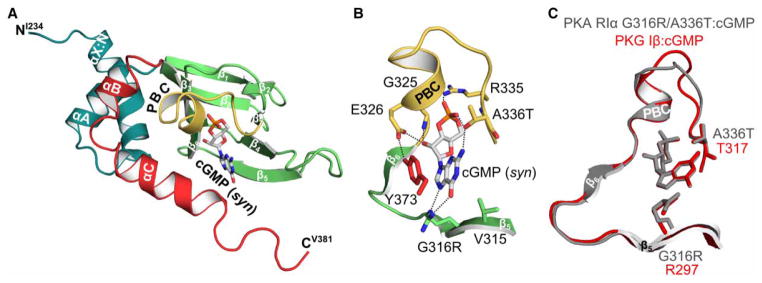
Figure 6. Crystal structure of PKA hRIα 234–381 G316R/A336T bound with cGMP.
(A) Overall structure of the PKA RIα CNB-B G316R/A336T mutant bound with cGMP. The same representations and labels are used as described in Figure 5. (B) Detailed view of the CNB pocket and the bound cGMP. The side chain of T336 forms a hydrogen bond with the 2 amino group of cGMP. Additionally, the hydroxyl group of the threonine residue hydrogen bonds the axial oxygen of the cyclic phosphate. The cGMP co-crystal structure reveals that both hydrogen bonds seen in the PKG I CNB-B: cGMP complex (PDB code 4KU7) can be formed with cGMP. The guanidinium side chain of G316R hydrogen bonds both the N7 and the 6 carbonyl of the guanine nucleobase. (C) Structural alignment of the binding pockets of the PKA RIα CNB-B G316R/A336T: cGMP structure (gray) with the PKG Iβ CNB-B: cGMP complex (red; PDB code 4KU7) [20].
Both mutant structures show little changes in their overall conformation compared with the wild type except at the C-terminal loop (Figures 5 and 6 and Supplementary Figure S3) [32]. The structure of the double mutant (G316R/A336T) bound to cAMP shows that its C-terminal loop curls back toward the PBC, shielding the base of the binding pocket, similarly seen in the wild-type CNB-B (Supplementary Figure S3A,B). In particular, the backbone carbonyl of N374 directly interacts with the 6 NH2 of cAMP via a hydrogen bond. Additionally, the C-terminal loop residues, S375 and F376, interact with Q304 and R306 at the β4–β5 loop through a hydrogen bond and hydrophobic interaction, respectively. These interactions stabilize the curled conformation, placing the C-terminal loop near the base of the binding pocket when cAMP is bound (Supplementary Figure S3A,B). This structural feature can explain the high affinity of CNB-B for cAMP even with key cGMP contacts grafted into its binding pocket.
In contrast, the structure of the cGMP-bound mutant shows that its C-terminal loop extends out toward the solvent without shielding the binding pocket (Supplementary Figure S3C). Unlike the cAMP-bound structure, the backbone carbonyl oxygen of N374 does not interact with cGMP, because a carbonyl replaces NH2 in cGMP at position 6 and causes charge repulsion. The structure shows that the side chain of N374 alternatively interacts with the side chain of R306 through a hydrogen bond. Structural alignment of the cAMP-bound mutant with the cGMP-bound mutant reveals that this change is due to a rotation of the amide bond between Y373 and N374, causing the C-terminal loop to move away from the binding pocket (Supplementary Figure S3).
In addition, the co-crystal structure with cGMP revealed that introducing arginine (G316R) and threonine residues (A336T) maintains the cGMP-specific binding mechanism as recently described for the cGMP-selective CNB-B of PKG Iβ [20]. G316R recognizes cGMP by forming guanine-specific hydrogen bonds as seen in the PKG Iβ CNB-B: cGMP complex (Figure 7; for further details see figure legend). Additionally, A336T forms a specific hydrogen bond with the position 2 amino group of the guanine nucleobase. This is consistent with work by Shabb et al. [17,18], demonstrating that the interaction between these conserved threonine residues (A212T in CNB-A and A336T in CNB-B) and the position 2 amine group of guanine is the strongest determinant for cGMP binding and specificity. Our crystal structures show that the introduced residues maintain their cGMP-specific interactions in the cAMP-binding pockets. Furthermore, the co-crystal structures of the most cGMP-selective CNB-B mutant reveal that G316R and A336T provide cGMP-specific interactions with different positions of the guanine moiety which explains the additive effect when these mutations are combined.
Figure 7. Cyclic nucleotide binding of PKA RIα CNB-A mutants.
Binding curves as derived from SPR solution competition experiments. (A) The PKA hRIα 115–274 double-mutant T192R/A212T has a switched selectivity compared with the wild-type CNB-A (black- and red-dashed lines for cAMP and cGMP, respectively). (B) The T192R mutant and (C) the A212T single mutants have a reduced affinity for cAMP and an increased affinity for cGMP compared with the wild-type CNB-A.
Grafting cGMP-specific contacts into CNB-A reverses its cyclic nucleotide selectivity
In the next step, we introduced the same mutations (G316R/A336T) into the isolated CNB-A (T192R/A212T) to challenge its cyclic nucleotide selectivity. Introducing cGMP-specific contacts into CNB-A completely reverses selectivity, turning a cAMP-specific domain (30-fold preference for cAMP over cGMP) into a cGMP-specific domain (225-fold preference for cGMP over cAMP; Figure 5A and Table 1). In line with this CNB-A T192R/A212T displayed a surprisingly high selectivity compared with the corresponding CNB-B double mutant. This is in part because the wild-type CNB-A binds cAMP with a significantly lower affinity compared with the wild-type CNB-B (Figure 3), and grafting key cGMP contacts into CNB-A (T192R/A212T) further reduces its affinity for cAMP (from 151 nM to 5.4 μM).
To evaluate how each of these residues contributes to the increased cGMP selectivity, we generated the respective single mutants and measured their affinity for cAMP and cGMP. Grafting an arginine residue at β5 (T192R) reduced the affinity for cAMP (from 151 to 859 nM), while the cGMP affinity was only slightly increased (EC50 = 1529 versus 4554 nM for the wild type; Figure 5B). In contrast with the corresponding mutant in CNB-B (A336T), CNB-A A212T displayed a reduced affinity for cAMP in comparison with the wild type (from 151 to 420 nM; Figure 5C). Additionally, this mutant bound cGMP with a significantly increased affinity (EC50 = 83 versus 4554 nM for the wild type). Our data reveal that the mutations reduce the affinity for cAMP, while the affinity for cGMP is increased, which results in a switch of selectivity.
To decipher the molecular basis for its high cGMP selectivity and due to the lack of a crystal structure, we generated structural models of both the wild-type and the T192R/A212T CNB-A (Supplementary Figure S4). While the model of the wild-type CNB-A with cGMP shows no interaction with the nucleotide (Supplementary Figure S4B), the model of the T192R/A212T double mutant displays key cGMP interactions with the position 2 amine group and the position 6 carbonyl oxygen (Supplementary Figure S4D). The model suggests that CNB-A T192R/A212T does not interact specifically with cAMP (Supplementary Figure S4C) and, moreover, T192R causes a steric hindrance that potentially contributes to the reduction in cAMP affinity.
Arginine residues increase the affinity of PKA RIα CNB-A and -B for cIMP
Structures of the isolated CNB-B of PKG Iβ revealed that R297 specifically interacts with the position 6 carbonyl oxygen of the cGMP bound [20]. To test whether the grafted arginine residues T192R in CNB-A and G316R in CNB-B increased the affinity for cGMP via a similar mechanism, we analyzed the binding competition of cIMP. Grafting an arginine residue into the β5 strands of both CNB domains (T192R in CNB-A and G316R in CNB-B) increased the affinity for cIMP of CNB-A (EC50 = 156 ± 5 nM) slightly and of CNB-B (EC50 = 25 ± 9 nM) significantly (6-fold). This suggests that T192R and G316R form hydrogen bonds with the 6 carbonyl of hypoxanthine.
Conclusions
Cyclic nucleotide selectivity of PKA and PKG is a prerequisite for the fidelity of cAMP and cGMP signaling, which can lead to different or opposing physiological outcomes. Specificity of CNB domains has been solely attributed to a single alanine/threonine residue difference between the cAMP-specific PKA and Epac, and the cGMP-specific PKG and CNG channels. The present study demonstrates that an arginine residue in the BBR additionally contributes to cGMP specificity, and grafting these contacts into the cAMP-specific CNB domains of PKA switches selectivity. Introducing both threonine and arginine residues has an additional effect in both CNB domains, underlining the role of the newly described arginine residue in cGMP specificity. Mutating the corresponding two positions in the CNB-A causes a reversal of specificity.
Database depositions
Atomic coordinates and structure factors of the wild-type CNB-B structure with cAMP, double-mutant CNB-B with cAMP, and double-mutant CNB-B of human PKA RIα in complex with cGMP RIα have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank (www.pdb.org) under accession numbers 5KJX, 5KJY, and 5KJZ, respectively.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Funding
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft [He 1818/10] to F.W.H. C.K. was funded by the NIH [grant R01 GM090161]. I.V.P. was supported by the ‘Verband der chemischen Industrie’ [SK197/08] and the University of Kassel [HSP2020]. The Berkeley Center for Structural Biology is supported in part by the NIH, the National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. The Advanced Light Source is supported by the Director, Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, of the U.S. Department of Energy under contract no. DE-AC02-05CH11231.
We thank Daniela Bertinetti, Matthias J. Knape (both University of Kassel), and Giuseppe Melacini (McMaster University) for helpful discussions and critical reading of the manuscript. We also thank Michaela Hansch for expert technical assistance. R.L. was supported by the graduate program of the University of Kassel. This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under contract no. DE-AC02-06CH11357. Use of the Lilly Research Laboratories Collaborative Access Team (LRL-CAT) beamline at Sector 31 of the Advanced Photon Source was provided by Eli Lilly Company, which operates the facility. We thank Frank Schwede (BioLog Life Science Institute, Bremen, Germany) for supply of the designed cyclic nucleotide analogs.
Abbreviations
- 2-AHA-cAMP
2-(6-aminohexylamino)adenosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate
- 2-AH-cGMP
N2-(6-aminohexyl) guanosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate
- 6-AH-cAMP
N6-(6-aminohexyl)adenosine-3″,5″-cyclic monophosphate
- 8-AET-cGMP
8-(2-aminoethylthio)guanosine-3″,5″-monophosphate
- 8-AHA-cAMP
8-(6-aminohexylamino) adenosine-3″,5″-cyclic monophosphate
- 8-AHT-cGMP
8-(6-aminohexylthio)guanosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate
- 8-Fluo-cAMP
8-(2-[fluoresceinyl]aminoethylthio)adenosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate
- 8-Fluo-cGMP
8-(2-[fluoresceinyl]aminoethylthio)guanosine-3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate
- BBR
base-binding region
- Camp
3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate
- CGMP
3′,5′-cyclic guanosine monophosphate
- CIMP
3′,5′-cyclic inosine monophosphate
- CNB domain
cyclic nucleotide-binding domain
- CNB-A
N-terminal cyclic nucleotide-binding domain
- CNB-B
C-terminal cyclic nucleotide-binding domain
- CNG channel
cyclic nucleotide-gated channel
- EC50
half-maximal effective concentration
- Epac
exchange protein directly activated by camp
- FP
fluorescence polarization
- MOPS
3-morpholinopropane-1-sulfonic acid
- MR
molecular replacement
- PBC
phosphate-binding cassette
- PDEs
Phosphodiesterases
- PKA
cAMP-dependent protein kinase
- PKG
cGMP-dependent protein kinase
- RIα
regulatory subunit type Iα
- SPR
surface plasmon resonance
- TCEP
tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine
Footnotes
Author Contribution
R.L. designed all constructs and the purification protocols for cyclic nucleotide interaction analysis. R.L. and S. H.S. measured EC50 values for cyclic nucleotide binding. J.J.K., E.-W.M., and R.L. designed the purification protocols for crystallization. E.M., J.J.K., and C.K. identified and optimized crystallization conditions, solved the structures and refined the crystallographic models. E.M. and B.S. collected diffraction images. I.V.P. performed structural modeling of CNB-A mutant constructs. R.L., C.K., and F.W.H. wrote the bulk of the manuscript and created the figures. All authors commented on the manuscript.
Competing Interests
The Authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
References
- 1.Sutherland EW, Rall TW. Fractionation and characterization of a cyclic adenine ribonucleotide formed by tissue particles. J Biol Chem. 1958;232:1077–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Beavo JA, Brunton LL. Cyclic nucleotide research — still expanding after half a century. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:710–718. doi: 10.1038/nrm911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Taylor SS, Buechler JA, Yonemoto W. cAMP-dependent protein kinase: framework for a diverse family of regulatory enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:971–1005. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hofmann F, Ammendola A, Schlossmann J. Rising behind NO: cGMP-dependent protein kinases. J Cell Sci. 2000;113(Pt 10):1671–1676. doi: 10.1242/jcs.113.10.1671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kaupp UB, Seifert R. Cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:769–824. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00008.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rehmann H, Prakash B, Wolf E, Rueppel A, de Rooij J, Bos JL, et al. Structure and regulation of the cAMP-binding domains of Epac2. Nat Struct Biol. 2003;10:26–32. doi: 10.1038/nsb878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wahl-Schott C, Biel M. HCN channels: structure, cellular regulation and physiological function. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66:470–494. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8525-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Francis SH, Busch JL, Corbin JD. cGMP-dependent protein kinases and cGMP phosphodiesterases in nitric oxide and cGMP action. Pharmacol Rev. 2010;62:525–563. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.002907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Seifert R, Schneider EH, Bähre H. From canonical to non-canonical cyclic nucleotides as second messengers: Pharmacological implications. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;148:154–184. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Seifert R. Recent progress in the field of cIMP research. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016;389:1045–1047. doi: 10.1007/s00210-016-1287-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Berman HM, Ten Eyck LF, Goodsell DS, Haste NM, Kornev A, Taylor SS. The cAMP binding domain: an ancient signaling module. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:45–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408579102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kannan N, Wu J, Anand GS, Yooseph S, Neuwald AF, Venter JC, et al. Evolution of allostery in the cyclic nucleotide binding module. Genome Biol. 2007;8:R264. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-12-r264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.McKay DB, Steitz TA. Structure of catabolite gene activator protein at 2.9 Å resolution suggests binding to left-handed B-DNA. Nature. 1981;290:744–749. doi: 10.1038/290744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Døskeland SO, Oegreid D, Ekanger R, Sturm PA, Miller JP, Suva RH. Mapping of the two intrachain cyclic nucleotide binding sites of adenosine cyclic 3′,5′-phosphate dependent protein kinase I. Biochemistry. 1983;22:1094–1101. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Corbin JD, Øgreid D, Miller JP, Suva RH, Jastorff B, Døskeland SO. Studies of cGMP analog specificity and function of the two intrasubunit binding sites of cGMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:1208–1214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Weber IT, Shabb JB, Corbin JD. Predicted structures of the cGMP binding domains of the cGMP-dependent protein kinase: a key alanine/threonine difference in evolutionary divergence of cAMP and cGMP binding sites. Biochemistry. 1989;28:6122–6127. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Shabb JB, Ng L, Corbin JD. One amino acid change produces a high affinity cGMP-binding site in cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:16031–16034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shabb JB, Buzzeo BD, Ng L, Corbin JD. Mutating protein kinase cAMP-binding sites into cGMP-binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:24320–24326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Reed RB, Sandberg M, Jahnsen T, Lohmann SM, Francis SH, Corbin JD. Fast and slow cyclic nucleotide-dissociation sites in cAMP-dependent protein kinase are transposed in type Iβ cGMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:17570–17575. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.29.17570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Huang GY, Kim JJ, Reger AS, Lorenz R, Moon EW, Zhao C, et al. Structural basis for cyclic-nucleotide selectivity and cGMP-selective activation of PKG I. Structure. 2014;22:116–124. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.09.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Huang GY, Gerlits OO, Blakeley MP, Sankaran B, Kovalevsky AY, Kim C. Neutron diffraction reveals hydrogen bonds critical for cGMP-selective activation: insights for cGMP-dependent protein kinase agonist design. Biochemistry. 2014;53:6725–6727. doi: 10.1021/bi501012v. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Büssow K, Scheich C, Sievert V, Harttig U, Schultz J, Simon B, et al. Structural genomics of human proteins – target selection and generation of a public catalogue of expression clones. Microb Cell Fact. 2005;4:21. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-4-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kim JJ, Huang GY, Rieger R, Koller A, Chow D-C, Kim C. A protocol for expression and purification of cyclic nucleotide–free protein in Escherichia coli. In: Cheng X, editor. Cyclic Nucleotide Signaling. CRC Press; 2015. pp. 191–202. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970;227:680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shabb JB, Kapphahn MA, Muhonen WM, Poteet CE, Baker NE, Corbin JD. Characterization of the isolated cAMP-binding B domain of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Protein Sci. 1995;4:2100–2106. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560041015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Moll D, Prinz A, Gesellchen F, Drewianka S, Zimmermann B, Herberg FW. Biomolecular interaction analysis in functional proteomics. J Neural Transm. 2006;113:1015–1032. doi: 10.1007/s00702-006-0515-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lorenz R, Hahnefeld C, Möller S, Bertinetti D, Herberg FW. Cyclic nucleotide analogues as chemical tools for interaction analysis. In: Cheng X, editor. Cyclic Nucleotide Signaling. CRC Press; 2015. pp. 203–224. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Leslie AGW, Powell HR. Processing diffraction data with MOSFLM. Evol Methods Macromol Crystallogr. 2007:41–51. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-6316-9_4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Minor W, Cymborowski M, Otwinowski Z, Chruszcz M. HKL-3000: the integration of data reduction and structure solution — from diffraction images to an initial model in minutes. Acta Crystallogr Sect D Biol Crystallogr. 2006;62:859–866. doi: 10.1107/S0907444906019949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.McCoy AJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Adams PD, Winn MD, Storoni LC, Read RJ. Phaser crystallographic software. J Appl Crystallogr. 2007;40:658–674. doi: 10.1107/S0021889807021206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Su Y, Dostmann W, Herberg F, Durick K, Xuong N, Ten Eyck L, et al. Regulatory subunit of protein kinase A: structure of deletion mutant with cAMP binding domains. Science. 1995;269:807–813. doi: 10.1126/science.7638597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Emsley P, Cowtan K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr Sect D Biol Crystallogr. 2004;60:2126–2132. doi: 10.1107/S0907444904019158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Afonine PV, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Moriarty NW, Mustyakimov M, et al. Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenixrefine. Acta Crystallogr Sect D Biol Crystallogr. 2012;68:352–367. doi: 10.1107/S0907444912001308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Painter J, Merritt EA. Optimal description of a protein structure in terms of multiple groups undergoing TLS motion. Acta Crystallogr Sect D Biol Crystallogr. 2006;62:439–450. doi: 10.1107/S0907444906005270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Krieger E, Vriend G. New ways to boost molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem. 2015;36:996–1007. doi: 10.1002/jcc.23899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kim JJ, Lorenz R, Arold ST, Reger AS, Sankaran B, Casteel DE, et al. Crystal structure of PKG I:cGMP complex reveals a cGMP-mediated dimeric interface that facilitates cGMP-induced activation. Structure. 2016;24:710–720. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2016.03.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Vigil D, Blumenthal DK, Taylor SS, Trewhella J. The conformationally dynamic C helix of the RIα subunit of protein kinase A mediates isoform-specific domain reorganization upon C subunit binding. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:35521–35527. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506769200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kim C, Cheng CY, Saldanha SA, Taylor SS. PKA-I holoenzyme structure reveals a mechanism for cAMP-dependent activation. Cell. 2007;130:1032–1043. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rannels SR, Corbin JD. Two different intrachain cAMP binding sites of cAMP-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1980;255:7085–7088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Schweinsberg S, Moll D, Burghardt NCG, Hahnefeld C, Schwede F, Zimmermann B, et al. Systematic interpretation of cyclic nucleotide binding studies using KinetXBase. Proteomics. 2008;8:1212–1220. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200700731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Muhonen WW, Shabb JB. Resonant mirror biosensor analysis of type Iα cAMP-dependent protein kinase B domain—cyclic nucleotide interactions. Protein Sci. 2000;9:2446–2456. doi: 10.1110/ps.9.12.2446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Herberg FW, Taylor SS, Dostmann WRG. Active site mutations define the pathway for the cooperative activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1996;35:2934–2942. doi: 10.1021/bi951647c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lorenz R, Bertinetti D, Herberg FW. cAMP-dependent protein kinase and cGMP-dependent protein kinase as cyclic nucleotide effectors. In: Seifert R, editor. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Springer International Publishing; 2017. pp. 105–122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Øgreid D, Døskeland SO. The kinetics of association of cyclic AMP to the two types of binding sites associated with protein kinase II from bovine myocardium. FEBS Lett. 1981;129:287–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80185-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Goujon M, McWilliam H, Li W, Valentin F, Squizzato S, Paern J, et al. A new bioinformatics analysis tools framework at EMBL-EBI. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38(Web Server Issue):W695–W699. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol. 2011;7:539. doi: 10.1038/msb.2011.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.