Abstract
Background
Brucea javanica oil emulsion (BJOE) is traditional Chinese medicine with implicated anti-tumor activity, which has been used for treating lung cancer in China. The aim of this investigation was to evaluate the effects and safety of intrapleural injection of BJOE in treating malignant pleural effusion (MPE).
Methods
The randomised controlled trials (RCTs) on the effects and safety of BJOE in treating MPE were searched from electronic medical database including MEDLINE, SCI, EMBASE, Cochrance Library and CNKI. A total of 14 RCTs with 1085 patients were involved in this meta-analysis.
Results
The overall response rate (ORR) of traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE was higher than that of traditional chemotherapy drugs alone (p = 0.001; odds ratio = 1.39). Meanwhile, the combination of BJOE and traditional chemotherapy drugs improved the quality of life (QOL) of patients with MPE (p < 0.001; odds ratio = 1.56) compared with traditional chemotherapy drugs alone. Moreover, the participation of BJOE reduced the myelotoxicity and digestive reactions caused by traditional chemotherapy drugs (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
The efficacy and safety of traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE was superior to traditional chemotherapy drugs alone via intrapleural injection in controlling MPE, which suggested that BJOE can be used to treat MPE.
Keywords: Brucea javanica oil emulsion, BJOE, Malignant pleural effusion, MPE, Meta-analysis, Efficacy, Safety
Background
Malignant pleural effusion (MPE) is a common complication of many malignancies, which denotes an advanced malignant disease process. Most of the MPE are metastatic involvement of the pleura from primary malignancy at lung, breast, and other body sites apart from lymphomas [1]. Clinical practice has found that most lung cancer patients will always be associated with MPE, and lead to lower QOL, and ultimately reduce the life expectancy. Therefore, the treatment of MPE caused more attention of doctors [2]. The present treatments of MPE include the drainage of pleural effusion, intrapleural chemotherapy and systemic chemotherapy. Unfortunately, not all patients with MPE can benefit from quasi chemotherapy and treatment [3]. During the last decade there has been significant progress in unravelling the pathophysiology of MPE, as well as its diagnostics, imaging, and management [4]. Despite its frequent occurrence, current knowledge of MPE remains limited and controversy surrounds almost every aspect in its diagnosis and management [5]. At present, some new drugs studied in China have a certain effect on MPE. These drugs seem to exhibit antitumor activity and low toxicity, they have been used to control MPE [2, 3, 6].
Traditional Chinese Medicines (TCMs) have become increasingly popular in the treatment of cancer in China. Brucea javanica oil emulsion (BJOE) is one of TCMs products, which takes Brucea Jen petroleum ether extracts as raw material and purified soybean lecithin as emulsifier [7]. BJOE (also named yadanzi oil in China) is an extract of the ripe fruit of the simaroubaceae plant Brucea javanica (L.) Merr., which was first recorded in the Supplement to Compendium of Materia Medica. Brucea javanica oil (BJO) contains oleic acid, linoleic acid, stearic acid, palmitic acid, arachidonic acid, and other unsaturated fatty acids [8], which mainly produced in the People’s Republic of China’s coastal tropical and subtropical regions such as Hainan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Yunnan, and other places [9]. The fruit of Brucea javanica has been used for the treatment of various types of cancer in China for centuries. Dozens of single compounds have been isolated and identified from B. javanica, which have demonstrated relatively high activities and broad antitumor spectrums in vitro [10]. Previous investigations indicates that BJOE can enhance the chemotherapeutic effect on non-mall cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, improve the QOL and reduce adverse effects of platinum-contained chemotherapeutics and thus it is worth referring in clinic [11]. In addition, BJOE combined with chemotherapy could be considered as a safe and effective regimen in treating patients with advanced gastric cancer according to previous study [12].
So far, many investigations have specially disclosed the clinical effectiveness and safety of traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE versus traditional chemotherapy drugs alone in controlling MPE via intrapleural injection. Whether or not BJOE has the potential therapeutic and/or adjuvant therapeutic application in the treatment of human MPE is conflicting. Thus, we performed a systematic literature review to assess the clinical benefit and safety of BJOE combined therapy in controlling MPE.
Methods
Identification of literature
We searched and identified relevant RCTs from the databases of MEDLINE/PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrance Library, Web of Science, and CNKI database (from January 2000 to April 2017). The key words applied in the search were as followed: “malignant pleural effusion”, “MPE”, “Brucea javanica oil emulsion”, “BJOE injection”, “BJOEI,” “BJOE,” “Yadanzi”, and “chemotherapy”, “Brucea javanica oil emulsion injection,” “Yadanzi injection,” and “Ya-dan-zi injection.” In addition, if we find that the references of the included studies are closely related to BJOE, we should further search and identify them. The retrieved studies were regarded as potential source and reviewed manually. Moreover, although the published year of these literatures were unlimited, only English and Chinese literatures were involved in this study.
Data variables of studies
The general data that we selected are as follows: (1) the publication date of each randomized controlled trial; (2) the number of patients included in each study and grouping; (3) the clinical and pathologic features of patients included each study, (4) the patterns of treatment intervention for treating MPE; (5) trials design and implementation. The data on outcomes in present meta-analysis included clinical efficacy, QOL, and adverse effects (AEs) according to World Health Organization (WHO) criteria and Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST). The tumor response included complete response (CR), partial response (PR), stable disease (SD), and progressive disease (PD). The overall response rate (ORR) was defined as CR + PR/overall cases and disease control rate (DCR) was calculated as CR + PR+ SD /overall cases. Toxicity was graded from 0 to IV in severity on the basis of the WHO Recommendations. This meta-analysis only investigated the incidence of Grade II or above.
Inclusion criteria of the study
Inclusion criteria: (1) study design was confined to RCTs on comparing traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE with chemotherapy drugs alone for treating the MPE; (2) study subjects with MPE must be diagnosed pathologically and (or) cytologically; (3) drugs must be administered by intraluminal injection; (4) outcome measures determined by WHO criteria or RECIST, improvement of QOL evaluated by Karnofsky score (KPS), and AEs assessed by WHO Recommendations for Grading of Acute and Subacute Toxicity must be showed and (6) the sample size of the study must be more than or equal to 60.
Exclusion criteria of the study
The following criteria were used for the literature exclusion: (1) animal experiments, review, and other irrelevant studies; (2) patient also received other medications; (3) non-RCTs studies; (4) no detailed data about ORR, DCR, evaluation of QOL, and AEs or no indicators for them; (5) investigations were supported by drug producers; (6) lack of comparable control group and (7) single-arm study.
Supervision of the implementation process
The test design must meet the following rules: (1) RCTs of traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE versus traditional chemotherapy drugs alone via intrapleural injection for controlling MPE; (2) the dosage of BJOE was determined by the suggestions of producers; (3) dosing interval: once a week; (3) number of times of administration: more than or equal to 2 times; and (3) observations on efficacy and safety: ORR, DCR, QOL, and AEs.
Assessment for quality of RCTs
The criteria of assessment that provided by Cochrane Handbook was employed to evaluate the quality of included investigations. It contained the following Items: (1) sequence generation; (2) how to carry out blinding; (3) how to carry out allocation concealment; (4) how to perform outcome data selective; (5) a description of intention to treat and (6) other sources. According to the above criterion, the quality of trials was defined into three levels: low risk of bias, unclear risk of bias, and high risk of bias [7].
Statistical methods and analysis
All of the data was calculated by 14.0 (Stata Corporation, TX, USA) software package and Review Manager 5.3 software. The odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) was applied to analyze the dichotomous data [6]. By calculating the Z-value of the chi-square test, the statistical p-value < 0.05 was considered to be significantly different. The fixed effect model and the random effect model are commonly used statistical models for meta-analysis. According to the presence or absence of heterogeneity, both were selected to measure the safety and efficacy of BJOE pleural perfusion in the treatment of MPE. The χ2 statistic and the I2 statistic tests were used to assess statistical heterogeneity among included studies [3]. A more common way to indicate the degree of heterogeneity is the statistical test, which is often described as the Cochran chi-square test. A p value is often cited as an indicator of the degree of variability in the study. If the P value is less than 0.05, no statistical difference is considered, suggesting that the heterogeneity is small. The I2 value describes the percentage of variability in point estimates that is due to heterogeneity rather than sampling error, may be readily calculated from most published meta-analyses, and a closed form uncertainty interval is available. If the I2 value is less than 50%, the heterogeneity of the study is considered acceptable. If no heterogeneity existed, the method of fixed effects model was adopted, or using the random effects model. To assess the impact of a single study on overall statistical performance, we removed each study from the estimated library one by one, to analyze the impact of each study on overall effectiveness [2]. Further, we employed Begg’s funnel plot and Egger’s test to test the publication bias [7]. The SPSS (version 19.0, Chicago, USA) software was employed to finish the statistics of varying variables. The statistical p-value < 0.05 was considered to be significantly different.
Results
Literature retrieval process
Originally, we conducted the systematic research from online database, and 96 potentially relevant references were yielded. Of them, 25 studies were discarded because the design and implementation of these studies are not eligible for our research analysis. After further screening and eligibility assessment, 29 trials were excluded because some of them were not RCTs and others did not belong to first-hand research data such as summary of meetings, medical reviews and newsletters. Remaining 42 studies seemed to meet the inclusion criterion, but 28 studies were deleted because of the following reasons: repeated data reporting, animal studies, statistical irregularities and too little sample size. Finally, 14 trials were selected as appropriate for inclusion in this meta-analysis. The flow chart showing the selection process was presented in Fig. 1A.
Fig. 1.
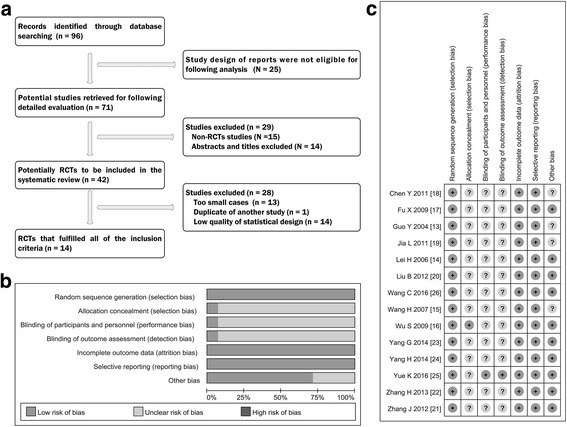
Selection and assessment of literature. a Studies were retrieved from the electronic bibliographic databases such as PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science and CNKI database. b and c According to the criteria made by the Cochrane Handbook (Version 5.0.1), no heterogeneity existed in eligible RCTs; Overall, these studies had moderate to higher quality
General characteristics of included studies
The 14 selected trials [13–26] were all RCTs and conducted in China. The qualified 14 studies included a total of 1085 patients, the total number of samples included in the study was from 60 [13, 26] to 123 [16] patients. The volume of pleural effusion of all patients in the amount were all more than 1000 mL and patients’ age varied from 25 [17] to 86 [22] years. From these studies, lung cancer and breast cancer were the most common cause of MPE. A detailed database for meta-analysis on general characteristics was listed in Table 1.
Table 1.
Data analysis of included studies
| Study | N | Male | Female | Age (average) |
Histology of Lung cancer | Volume of MPE(N) |
Quality of Life |
End point | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPE | LAC | LSCC | SCLC | Others | ||||||||
| Guo Y 2004 [13] | 60 | 40 | 20 | 59.5 | 60 | – | – | – | – | > 1000 ml | KPS | RR, DCR, AEs |
| Lei H 2006 [14] | 61 | – | – | 58–79 | 61 | 31 | 9 | – | > 1000 ml | KPS | RR, DCR, SI, AEs | |
| Wang H 2007 [15] | 70 | 45 | 25 | 26–81 | 70 | 42 | 7 | 13 | 8 | Large(46) Moderate(24) |
KPS | RR, DCR, SI, AEs |
| Wu S 2009 [16] | 123 | 86 | 37 | 39–75 | 123 | – | – | – | – | > 1000 ml | KPS | RR, DCR, AEs |
| Fu X 2009 [17] | 120 | 82 | 38 | 25–78 | 120 | – | – | – | – | Large(88) Moderate(32) |
KPS | RR, DCR, AEs |
| Chen Y 2011 [18] | 61 | 27 | 34 | 43–75 | 61 | – | – | – | – | > 1000 ml | KPS | RR, DCR, AEs |
| Jia L 2011 [19] | 70 | 38 | 32 | 39–85 | 70 | – | – | – | – | > 1000 ml | KPS | RR, DCR, SI, AEs |
| Liu B 2012 [20] | 64 | 31 | 33 | 36–77 | 64 | 46 | 13 | 5 | 0 | Large(36) Moderate(28) |
KPS | RR, DCR, SI, AEs |
| Zhang J 2012 [21] | 64 | 45 | 19 | 28–81 | 64 | 20 | 29 | 12 | 3 | > 1000 ml | KPS | RR, DCR, SI, AEs |
| Zhang H 2013 [22] | 64 | 52 | 12 | 33–86 | 64 | 39 | 11 | 14 | 0 | > 1000 ml | KPS | RR, DCR, SI, AEs |
| Yang G 2014 [23] | 94 | – | – | – | 94 | – | – | – | – | > 1000 ml | KPS | RR, DCR, SI, AEs |
| Yang H 2014 [24] | 64 | 42 | 22 | 38–72 | 64 | 19 | 24 | 13 | 8 | > 1000 ml | KPS | RR, DCR, SI, AEs |
| Yue K 2016 [25] | 111 | 57 | 53 | – | 110 | – | 70 | 19 | 21 | > 1000 ml | KPS | RR, DCR, SI, AEs |
| Wang C 2016 [26] | 60 | 34 | 26 | 40–74 | 60 | 11 | 17 | – | 32 | > 1000 ml | KPS | RR, DCR, SI, AEs |
N number of patients, MPE malignant pleural effusion, LAC lung adenocarcinoma, LSCC lung squamous cell carcinoma, SCLC small cell lung cancer, KPS karnofsky physical status score, RR response rate, DCR disease control rate, SI symptom improvement, AEs adverse effects
Quality of study design
We found that the number of males (569) was more than the females (546) in the BJOE combined group and control group, respectively. The design of 12 studies were that BJOE combined with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone through thoracic perfusion for treating MPE [13–18, 20, 22–26], one study was BJOE combined with bleomycin versus bleomycin alone [21], another was BJOE combined with oxaliplatin versus oxaliplatin alone [19]. The dosages of BJOE via thoracic perfusion and follow-up times for efficacy evaluation had a good consistency, which was shown in Table 2. All studies had a certain tumor diagnosis by pathology or pleural effusion cytology diagnosis, and KPS score of each patient greater than 50 points. Generally, the dosage of BJOE was administered at the range of 40-100 mg per one time and frequency of administration was two times at least, which were given by thoracic perfusion after drainage of pleural effusions. There was no significant difference between the two groups in the general data (p > 0.05), indicating that they had good comparability.
Table 2.
Assessment method of administration of included studies
| Study | Trial group (N) |
Control group (N) |
Interventions (Groups) | Treatment cycle | Termination of treatment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brucea javanica oil emulsion (BJOE) combined with chemotherapeutic agents | Chemotherapeutic agents alone | |||||
| Guo Y 2004 [13] | 30 | 30 | Cisplatin 150 mg, 1/week BJOE 50 mL, 1/week |
Cisplatin 150 mg, 1/W | 1 week | > 2 weeks, or pleural effusion disappeared |
| Lei H 2006 [14] | 31 | 30 | Cisplatin 40-60 mg, 1/week BJOE 40-60 mL, 1/week |
Cisplatin 40-60 mg, 1/W | 1 week | > 1 weeks, or pleural effusion disappeared |
| Wang H 2007 [15] | 35 | 35 | Cisplatin 20-30 mg/m2, 1/week BJOE 80-100 mL, 1/week |
Cisplatin 20-30 mg/m2, 1/5-7D | 1/5-7D | > 2 weeks, or pleural effusion disappeared |
| Wu S 2009 [16] | 68 | 55 | Cisplatin 60 mg, 1/week BJOE 50 mL, 1/week |
Cisplatin 60 mg, 1/W | 1 week | > 4 weeks, or pleural effusion disappeared |
| Fu X 2009 [17] | 60 | 60 | Cisplatin 40/m2, 1/week BJOE 100 mL, 1/week |
Cisplatin 40/m2, 1/W | 1 week | > 4 weeks, or pleural effusion disappeared |
| Chen Y 2011 [18] | 31 | 30 | Cisplatin 60 mg, 1/week BJOE 60 mL, 1/week |
Cisplatin 60 mg, 1/W | 1 week | > 4 weeks, or pleural effusion disappeared |
| Jia L 2011 [19] | 35 | 35 | Oxaliplatin 100/m2, 1/week BJOE 60 mL, 1/week |
Oxaliplatin 100/m2, 1/W | 1 week | > 4 weeks, or pleural effusion disappeared |
| Liu B 2012 [20] | 32 | 32 | Cisplatin 40/m2, 1/week BJOE 100 mL, 1/week |
Cisplatin 40/m2, 1/W | 1 week | > 4 weeks, or pleural effusion disappeared |
| Zhang J 2012 [21] | 28 | 36 | Bleomycin 45-60 mg, 1/week BJOE 80-100 mL, 1/week |
Bleomycin 45-60 mg, 1/W | 1 week | > 2 weeks, or pleural effusion disappeared |
| Zhang H 2013 [22] | 34 | 30 | Cisplatin 40-60 mg, 1/week BJOE 40-50 mL, 1/week |
Cisplatin 40-60 mg, 1/W | 1 week | > 2 weeks, or pleural effusion disappeared |
| Yang G 2014 [23] | 48 | 46 | Cisplatin 40 mg/m2, 1/week BJOE 80 mL, 1/week |
Cisplatin 40 mg/m2, 1/W | 1 week | > 3 weeks, or pleural effusion disappeared |
| Yang H 2014 [24] | 32 | 32 | Cisplatin 40 mg/m2, 1/week BJOE 50 mL/m2, 1/week |
Cisplatin 40 mg/m2, 1/W | 1 week | > 4 weeks, or pleural effusion disappeared |
| Yue K 2016 [25] | 60 | 50 | Cisplatin 40 mg/m2, 1/week BJOE 80-100 mL, 1/week |
Cisplatin 80 mg/m2, 1/W | 1 week | > 2 weeks, or pleural effusion disappeared |
| Wang C 2016 [26] | 45 | 45 | Cisplatin 40 mg/m2, 1/week BJOE 60 mL, 1/week |
Cisplatin 40 mg/m2, 1/7d | 7D/cycle,2 cycles | > 2 cycles, or pleural effusion disappeared |
BJOE Brucea javanica oil emulsion, N numbers of patients, D day, W week
The assessment of heterogeneity
Two investigators of us independently reviewed and assessed the quality of each study according to the criteria shaped by the Cochrane Handbook, which was specialized in evaluating the systematic reviews of Interventions (Version 5.0.1) [3]. As shown in Table 3, we found that 8 of the 14 studies (57.1%) showed the low risk of bias [17, 20–26] and that the remaining 6 investigations [13–16, 18, 19] displayed the unclear risk of bias (42.9%) (Table 3, Fig. 1B, C). We conducted a heterogeneity analysis of included studies. The results showed that chi-squared was 1.61 (Degrees of freedom = 13; p = 1.000) and that the value of I-squared (variation in OR attributable to heterogeneity) showed as 0.0%. These results indicated that these included RCTs had very good homogeneity. Combining the clinical information of these studies, we believe that these studies have very good comparability. Based on no heterogeneity, we completed the subsequent statistical analysis using the fixed effects model.
Table 3.
Design quality of included trials
| Study | Region | Sequence generation | Allocation concealment | Blind | Outcome data | Selective outcome reporting | Other sources of bias | ITT | Risk of bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guo Y 2004 [13] | Single center | Random number table (SPSS) | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Unclear | Yes | Unclear risk of bias |
| Lei H 2006 [14] | Single center | Random number table (SPSS) | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Unclear | Yes | Unclear risk of bias |
| Wang H 2007 [15] | Single center | Random number table (SPSS) | Clear | Unclear | Yes | No | Unclear | Yes | Unclear risk of bias |
| Wu S 2009 [16] | Single center | Random number table (SPSS) | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Unclear | Yes | Unclear risk of bias |
| Fu X 2009 [17] | Single center | Random number table (SPSS) | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Clear | Yes | Low risk of bias |
| Chen Y 2011 [18] | Single center | Random number table (SPSS) | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Unclear | Yes | Unclear risk of bias |
| Jia L 2011 [19] | Single center | Random number table (SPSS) | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Unclear | Yes | Unclear risk of bias |
| Liu B 2012 [20] | Single center | Random number table (SPSS) | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Clear | Yes | Low risk of bias |
| Zhang J 2012 [21] | Single center | Random number table (SPSS) | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Clear | Yes | Low risk of bias |
| Zhang H 2013 [22] | Single center | Random number table (SPSS) | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Clear | Yes | Low risk of bias |
| Yang G 2014 [23] | Multiple center | Random number table (SPSS) | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Clear | Yes | Low risk of bias |
| Yang H 2014 [24] | Single center | Random number table (SPSS) | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Clear | Yes | Low risk of bias |
| Yue K 2016 [25] | Single center | Random number table (SPSS) | Unclear | Clear | Yes | No | Clear | Yes | Low risk of bias |
| Wang C 2016 [26] | Single center | Random number table (SAS) | Unclear | Unclear | Yes | No | Clear | Yes | Low risk of bias |
SAS SAS software, SPSS SPSS software, ITT intention-to-treat
Comparison of ORR and DCR between traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE versus traditional chemotherapy drugs alone via intrapleural injection for controlling MPE
As shown in Table 4, all of fourteen RCTs [13–26] in this meta-analysis showed the data on comparison of ORR between traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE versus traditional chemotherapy drugs alone via intrapleural injection for controlling MPE. Via the fixed effects model analysis, we found that odds ratio was 1.39 (95% CI 1.15 to 1.67; Z value = 3.46, p = 0.001), which suggested that the ORR of traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE was remarkably higher than that of traditional chemotherapy drugs alone (Fig. 2A). In addition, fourteen studies [13–26] showed the data about DCR and displayed that the BJOE combination arms and chemotherapeutic agents single group had the same DCR rate (odds ratio = 1.04, 95% CI 0.888 to 1.23; test for overall effect: Z = 0.44, p = 0.663).
Table 4.
Efficacy of BJOE injection in treating malignant pleural effusion
| Study | Study design (N) | Pleural perfusion (N) | Efficacy of therapy | Improvement of SI (N,%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 1 | Group 2 | ||||||||||||
| Group 1 | Group 2 | CR | PR | SD | PD | CR | PR | SD | PD | Group 1 | Group 2 | ||||
| Guo Y 2004 [13] | 30 | 30 | BJOE + P | P | 11 | 15 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 11 | 14 | 0 | – | – | |
| Lei H 2006 [14] | 31 | 30 | BJOE + P | P | 11 | 14 | 6 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 0 | 24(77.4) | 12(40) | |
| Wang H 2007 [15] | 35 | 35 | BJOE + P | P | 13 | 16 | 6 | 0 | 7 | 13 | 15 | 0 | 32(91.4) | 20(57.1) | |
| Wu S 2009 [16] | 68 | 55 | BJOE + P | P | 39 | 20 | 9 | 0 | 16 | 28 | 11 | 0 | – | – | |
| Fu X 2009 [17] | 60 | 60 | BJOE + P | P | 22 | 28 | 8 | 2 | 14 | 21 | 18 | 7 | 44(73.3) | 33(55) | |
| Chen Y 2011 [18] | 31 | 30 | BJOE + P | P | 12 | 13 | 6 | 0 | 8 | 9 | 13 | 0 | – | – | |
| Jia L 2011 [19] | 35 | 35 | BJOE+ L-OHP | L-OHP | 10 | 18 | 7 | 0 | 8 | 15 | 12 | 0 | – | – | |
| Liu B 2012 [20] | 32 | 32 | BJOE + P | P | 18 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 13 | 4 | 9 | 6 | 28(75) | 24(50) | |
| Zhang J 2012 [21] | 28 | 36 | BJOE + BLM | BLM | 10 | 16 | 2 | 0 | 9 | 17 | 10 | 0 | 25(89.3) | 21(58.3) | |
| Zhang H 2013 [22] | 34 | 30 | BJOE + P | P | 19 | 10 | 5 | 0 | 11 | 6 | 13 | 0 | – | – | |
| Yang G 2014 [23] | 48 | 46 | BJOE + P | P | 14 | 26 | 8 | 0 | 4 | 22 | 16 | 4 | 42(87.5) | 24(52.17) | |
| Yang H 2014 [24] | 32 | 32 | BJOE + P | P | 18 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 13 | 4 | 9 | 6 | – | – | |
| Yue K 2016 [25] | 60 | 50 | BJOE + P | P | 23 | 27 | 10 | 0 | 13 | 14 | 23 | 0 | 43(71.7) | 18(36) | |
| Wang C 2016 [26] | 30 | 30 | BJOE + P | P | 10 | 14 | 5 | 1 | 8 | 11 | 7 | 4 | 24(80) | 16(53.3) | |
N cases; Group 1 BJOE combined with chemotherapeutic agents; Group 2 Chemotherapeutic agents alone, BJOE Brucea javanica oil emulsion; P cisplatin, L-OHP Oxaliplatin, BLM bleomycin, CR complete response, PR partial response, SD stable disease, PD progressive disease
Fig. 2.
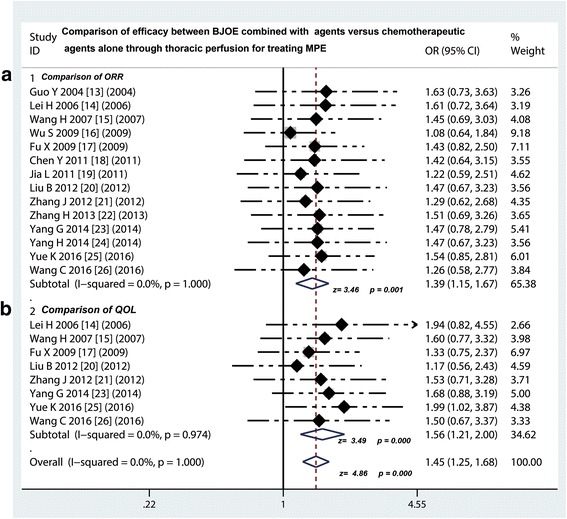
Efficacy comparison of BJOE combined with another agent versus another agent alone by thoracic perfusion for controlling MPE. a Thoracic perfusion of BJOE combined with other agents had a higher ORR compared with other agents alone; b Thoracic perfusion of BJOE combined with other agents improved the QOL of patients with MPE compared with other agents alone. BJOE, brucea javanica oil emulsion; ORR, overall response rate; MPE, malignant pleural effusion; OR, odds ratio; QOL, quality of life
Comparison of QOL between traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE versus traditional chemotherapy drugs alone via intrapleural injection for controlling MPE
As shown in Table 4, a total of 8 trials [14, 15, 17, 20, 21, 23, 25, 26] provided the data on comparing the QOL between the BJOE plus traditional chemotherapy drugs versus traditional chemotherapy drugs alone via intrapleural injection for controlling MPE. The QOL improvement was evaluated by the KPS score of patient. After treatment, the KPS score increased by ≥10 points was defined as improvement of QOL. We found that the improvement rate of BJOE combined perfusion group (262/324, 80.86%) was significantly higher than that of chemotherapy group alone (168/319, 52.66%). The results of meta-analysis showed that the odds ratio ranged from 1.17 to 1.99 and the pooled odds ratio in this analysis displayed a value of 1.56 (95% CI 1.21 to 2.00; Z = 3.49, p < 0.001), which suggested that BJOE combined with chemotherapeutic agents significantly improved the QOL of patients with MPE, as compared with single chemotherapeutic agents (Fig. 2B).
Composition ratio of AEs on traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE versus traditional chemotherapy drugs alone via intrapleural injection for controlling MPE
Nine [14, 15, 17, 18, 20, 23–25] of 14 studies compared the AEs on traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE versus traditional chemotherapy drugs alone via intrapleural injection for controlling MPE. As shown in Table 5, the most common AEs in combined group and single group were myelotoxicity (71/363, 19.5% versus 141/350, 40.3%), nausea/vomiting (55/392, 14.03% versus 104/386, 28.4%), liver and renal injury (7/124, 5.6% versus 10/124, 8.1%), chest pain (39/299, 13.04% versus 52/299, 17.39%) and fever (30/309, 9.7% versus 45/305, 14.75%).
Table 5.
Comparison of adverse events between BJOE combined with chemotherapeutic agents versus chemotherapeutic agents alone
| Study | Myelotoxicity (%) | Nausea/vomiting (%) | Liver and renal injury (%) | Chest pain (%) | Fever (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 1 | Group 2 | |
| Lei H 2006 [14] | 9(29) | 22(73.3) | 5(16.1) | 12(40) | 3(9.7) | 5(16.7) | 3(9.7) | 4(13.3) | ||
| Wang H 2007 [15] | 9(25.7) | 21(60) | 2(5.7) | 5(14.3) | – | – | 1(2.9) | 1(2.9) | – | – |
| Fu X 2009 [17] | 15(25) | 36(60) | 4(6.67) | 12(20) | 1(1.7) | 2(3.3) | 3(5) | 8(13.3) | 3(5) | 11(18.33) |
| Chen Y 2011 [18] | 9(29.03) | 22(73.33) | 5(16.13) | 12(40) | – | – | 3(9.68) | 5(16.67) | 3(9.68) | 4(13.33) |
| Jia L 2011 [19] | 8(22.86) | 9(25.7) | 15(42.86) | 14(40) | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Liu B 2012 [20] | 5(15.6) | 6(18.8) | 5(15.6) | 7(21.9) | 3(9.4) | 4(12.5) | 3(9.4) | 4(12.5) | 5(15.6) | 4(12.5) |
| Zhang J 2012 [21] | – | – | 2(7.14) | 6(16.6) | – | – | 0(0) | 3(8.3) | 3(10.7) | 11(30.6) |
| Zhang H 2013 [22] | – | – | – | – | – | – | 12(35.3) | 10(33.3) | – | – |
| Yang G 2014 [23] | 8(16.7) | 10(26.7) | 2(4.17) | 6(13.04) | – | – | 14(29.17) | 16(34.8) | – | – |
| Yang H 2014 [24] | 5(15.6) | 6(18.8) | 5(15.6) | 7(21.9) | 3(9.4) | 4(12.5) | – | – | 5(15.6) | 4(12.5) |
| Yue K 2016 [25] | 3 (5.0) | 9 (18) | 10(16.7) | 23 (46) | – | – | – | – | 8 (13.3) | 7(14) |
| P < 0.05 | P < 0.05 | P > 0.05 | P > 0.05 | P > 0.05 | ||||||
Values are given as number of patients (%).Group 1 Brucea javanica oil emulsion (BJOE) combined with chemotherapeutic agents; Group 2 Chemotherapeutic agents alone
Comparison of AEs between traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE versus traditional chemotherapy drugs alone via intrapleural injection for controlling MPE
Nine [14, 15, 17, 18, 20, 23–25] of 14 studie compared the myelotoxicity on traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE versus traditional chemotherapy drugs alone via intrapleural injection for controlling MPE, we found that the incidence rate of myelotoxicity in BJOE combined perfusion group was lower than that of traditional chemotherapy drugs alone group (odds ratio = 0.5, 95% CI 0. 36 to 0.70, p < 0.001) (Fig. 3A). Ten [14, 15, 17, 18, 20, 21, 23–25] of 14 studie compared the gastrointestinal reactions, the incidence rate of nausea/vomiting in BJOE combined group also showed a significant decrease compared with traditional chemotherapy drugs alone group (odds ratio = 0.50, 95% CI 0. 35 to 0.72, p < 0.001) (Fig. 3B). In addition, three studies compared liver and renal injury (odds ratio = 0.70, 95% CI 0. 25 to 1.91, p = 0.483), eight studies compared the incidence of chest pain (odds ratio = 0.70, 95% CI 0. 44 to 1.11, p = 0.130), and seven studies compared the incidence of fever (odds ratio = 0.67, 95% CI 0. 41 to 1.10, p = 0.111). However, these results suggested that the incidence rate of these AEs did not have differences between both of two projects (p > 0.05) (Fig. 4A-C).
Fig. 3.
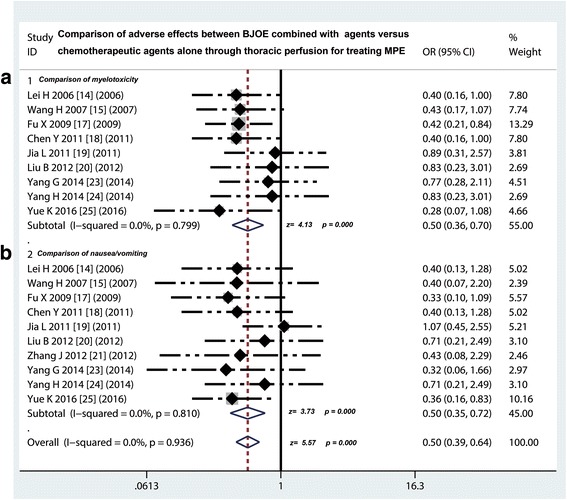
Safety evaluation of BJOE combined with another agent versus another agent alone by thoracic perfusion for controlling MPE. a The BJOE combination therapy displayed a lower incidence rate of myelotoxicity than the project of other agents alone; b The BJOE combined with other agents had a lower incidence of digestive reactions than and other agents alone. BJOE, brucea javanica oil emulsion; MPE, malignant pleural effusion; OR, odds ratio
Fig. 4.
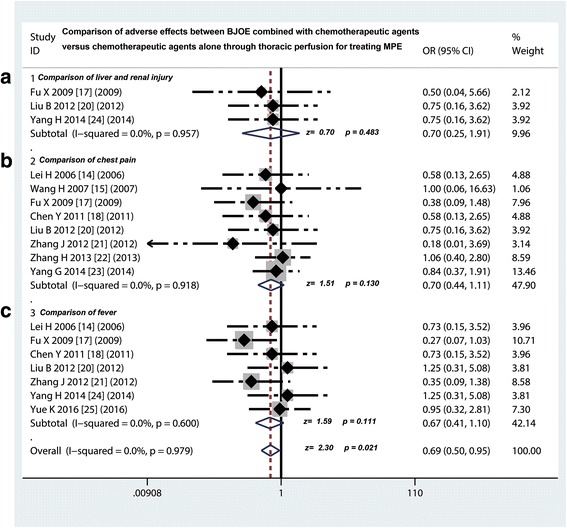
Safety evaluation of BJOE combined with another agent versus another agent alone by thoracic perfusion for treating MPE.a No difference in incidence rate of liver and renal injury was testified between BJOE combined with other agents and other agents alone; b The incidence of chest pain caused by BJOE combination therapy had the same occurrence probability compared with the other agents alone; c The BJOE combined with other agents had the same incidence of fever with other agents alone. BJOE, brucea javanica oil emulsion; MPE, malignant pleural effusion; OR, odds ratio
Assessment of publication bias and sensitivity analysis
Through removing each study, a further meta-analysis was performed to compare with previous results of meta-analysis to explore whether the deleted study have an certain impact on the overall statistical effect [27]. Sensitivity analysis shows that excluding of any study could not change the overall statistical effect, nor could it affect the final statistical conclusion, with an OR pool oscillating between 1.08 and 1.63 (Fig. 5A). We also drew a funnel plot of included studies and noticed that the included studies are symmetrically distributed on both sides of the funnel (Fig. 5B). In addition, for comparing traditional chemotherapy drugs with chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE for controlling MPE, we performed the Egger’s test and the results were as the following: t = 1.75 with 13 d.f, p = 0.105 (Fig. 5C). We also performed a Begg’s test and the test results showed that Std. Dev. of Score was 18.27, p value was 0.112 (Fig. 5D). Come together, the funnel plot, Egger’s tests and the Begg’s test all suggested that publication biases did not have a significant influence on the results.
Fig. 5.
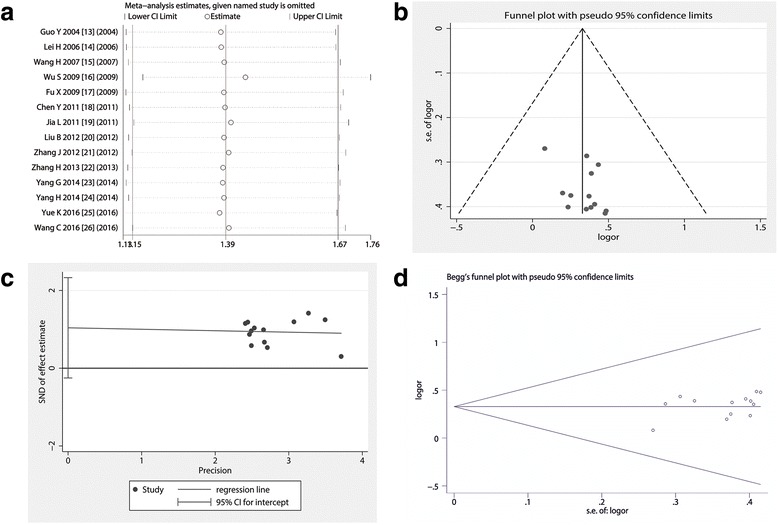
Sensitivity and publication bias analysis.a Omitting any trial did not shake the pooled effect of meta-analysis; b The shape of the funnel plot appeared to be approximately symmetrical; c Egger’s test showed that p was 0.105, suggesting included trials did not have a potential impact on the pooled effect of present meta-analysis; d Begg’s test showed that p value was 0.112, and the funnel plot seems to be nearly symmetrical
Discussion
BJOE is composed of the active ingredients extracted from the ripe fruit of Sophora flavescens. The main components are oleic acid and linoleic acid. BJOE is a traditional Chinese medicine. It has been shown that BJOE could directly kill the cancer cells by up-regulating the tumor suppress or genes [7]. Moreover, BJOE has also been found to reverse the tumor cell resistance to chemotherapy and improve the body immunity, without significant AEs [28]. Some experiments show that BJOE is cell cycle non-specific anti-cancer drug, which has an efficacy of killing and inhibition in the G0, G1, S, G2, M phases of tumor cells, and can significantly inhibits DNA synthesis of tumor cells [15, 26, 29]. In addition, previous studies also suggest that the anti-tumor activity of BJOE might be correlated to the mechanism of tumor cell apoptosis, which affects the process of cell cycle, disrupts the cellular energy metabolism, and depresses the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor [7]. So far, a great number of published studies have reported that BJOE can perform a synergetic effect for controlling MPE by improving tumor response and QOL and reducing the incidence of AEs [12–16, 19, 20, 26, 28–30].
We conducted a comprehensive literature search and screening, and finally 14 trials were selected as appropriate for this meta-analysis. By statistical verification and combining the clinical information of these studies, we found that these included RCTs had very good homogeneity and comparability, and further performed a meta-analysis. Our analysis showed that traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE via intrapleural injection had a better ORR benefit compared with traditional chemotherapy drugs alone (odds ratio = 1.39) for controlling MPE, translating into a 22.95% absolute improvement. The results suggested that participation of BJOE exerted an important effect in treating MPE, indicating that BJOE can be used as an alternative drug for controlling the MPE in clinical practice. Previous studies show that the BJOE combination therapy could promote liver cancer cell apoptosis by regulating the expression of soluble Fas/soluble Fas ligand [28] and BJOE also induces apoptosis in the colon cancer cells [28]. Another study finds that BJO-loaded liposomes inhibits the proliferation of hepatocellular cancer HepG2 cells, which appears be dose-dependent, possibly by inducing apoptosis of cancer cells [31]. However, in our study, the BJOE combination seemed to have the same DCR rate (odds ratio = 1.04, p = 0.663) compared with chemotherapeutic agents alone. High ORR indicates that the drug can control the disease progress of patients with MPE, meaning that the disease condition of patients was significantly alleviated. At this point, its significance is greater than the control rate because reversing the patient’s disease condition is critical aim of treating malignant tumors [32]. Since the DCR of BJOE combination is comparable to the existing traditional chemotherapy drugs, and it has a high ORR, then the drug should have a certain application value.
Although the control of primary disease is very important, the improvement of QOL in patients is also very critical. Overall survival (OS) has always been considered the “gold standard” for tumor therapy in the study of the therapeutic effects of cancer patients. In today’s clinical trials, the improvement in QOL in patients is increasingly being used to examine efficacy of therapy [32]. Our study showed that presence of BJOE remarkably elevated the QOL of patients with MPE (OR = 1.56, 95% CI 1.21 to 2.0), which responding an absolute 28.2% increase of the QOL, as compared with chemotherapeutic agents alone. That is to say that BJOE-containing therapy improves the ability of QOL of patients with MPE to be about 1.56 times compared with therapy of chemotherapy alone. Previous study points out that BJOE inhibits the proliferation of C6 glioma cells by suppressing the phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K), protein Kinase B (AKT), and nuclear transcription factor-κB (NF-κB) protein expression, which also leads to inhibition of invasiveness of glioma cells, suggesting that the anti-tumor effect of BJOE relates to the inhibition of PI3K/AKT signal pathway [30]. The molecular mechanism that BJOE induces apoptosis of T24 bladder cancer cells may be the activation of caspase apoptotic pathway by upregulation of the expression of caspase-3 and caspase-9 proteins and inhibition of the expression of NF-κB and cyclo-oxyge-nase-2 (COX-2) proteins [29]. A meta-analysis has showed that intravenous therapy of BJOE plus chemoradiotherapy may have positive effects on lung cancer patients in response rate, improvement of QOL, and reducing incidences of some AEs compared with chemoradiotherapy alone. However, the results need to be viewed with caution because of low quality of the included studies [33].
The antineoplastic agent cisplatin is widely used for treating lung cancer as it is highly effective. Unfortunately, the AEs are frequently encountered in platinum-based chemotherapy. With rising cancer survival rates, a greater proportion of patients with cancer are living with the AEs of their chemotherapy treatments. Consequently, the QOL of cancer survivors has now become a major concern for clinicians [34]. In our study, whether BJOE plus traditional chemotherapy drugs or traditional chemotherapy drugs alone via thoracic perfusion, the most common AEs are hematopoietic dysfunction and gastrointestinal symptoms, but most of them are grade 1 and grade 2, and patients are better tolerated. However, we excitedly found that the incidence of myelotoxicity and digestive reactions in treatment of traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE was significantly lower than that in traditional chemotherapy drugs alone, indicating that the BJOE not only exert a impact for treating MPE but also decrease the incidence of myelotoxicity and digestive reactions. Unlike traditional antineoplastic agents, previous studies show that BJOE can not only directly kill cancer cells, but also has enhanced immune function and bone marrow hematopoietic function [7, 11]. Our further analysis found that the incidence rate of liver and renal injury, chest pain and fever of BJOE combination therapy had the same occurrence compared with chemotherapeutic agents alone (P > 0.05), suggesting that BJOE participation did not increase the incidence of these AEs. So far, more data have exhibited that the BJOE therapy could be well tolerated and had a better safety for clinical application.
For meta-analysis, heterogeneity testing is important because the heterogeneity of the study will affect the overall statistical effect. In order to insure the comparability, it is necessary to do method comparison and bias evaluation. In the funnel plot analysis of publication biases (the contrast of homozygous genotype plotted against the precision) [35], the shape of the funnel plot appeared to be approximately symmetrical, and the magnitude of the main ORs was in dispersion on the right side of 1. The Egger’s test is based on a linear regression of the standard normal deviate against its precision [35]. In our study, the Egger’s tests and the Begg’s test all suggested that publication biases may not have a significant influence on the results. Sensitivity analysis can estimate the impact of a single study on overall statistical performance. Our study suggested that the included studies had excellent homogeneity and were comparable.
However, we also found some of the defects that existed in the meta-analysis study. First, the vast majority of the samples included in the study were small, thus reducing the test efficiency. Second, included studies in this meta-analysis rarely describes whether implements the allocation hiding, inadequate implementation may exaggerate efficacy. Third, most of patients were from China (because BJOE was approved by the China State Food and Drug Administration), which may lead to geographical and ethnic differences. In spite of this, our results still propose a significant suggestion that the BJOE is effective and safe, and it is an alternative for controlling MPE.
Conclusion
Intrapleural injection of traditional chemotherapy drugs plus BJOE has a better benefit of ORR for treating MPE and improves the QOL of MPE patients, compared with traditional chemotherapy drugs alone. In addition, the participation of BJOE can reduce the toxicity caused by chemotherapy drugs. However, rigorously RCTs should be needed before it is recommended widely.
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the great help of Mr. Rong BX, and Miss Li M as interviewers.
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Provincial, China (No. 1606RJZA154). The funders of this project had no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis and in writing the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article.
Abbreviations
- AEs
Adverse effects
- AKT
Protein Kinase B
- BJO
Brucea javanica oil
- BJOE
Brucea javanica oil emulsion
- CI
Confidence intervals
- CNKI
China National Knowledge Infrastructure
- COX-2
Cyclooxygenase-2
- CR
Complete response
- DCR
Disease control rate
- EMBASE
Excerpt Medica Database
- HRQOL
Health-related quality of life
- KPS
Karnofsky score
- MPE
Malignant pleural effusion
- NF-Κb
Nuclear transcription factor-κB
- NSCLC
Non-mall cell lung cancer
- OR
Odds ratio
- ORR
Overall response rate
- OS
Overall survival
- PD
Progressive disease
- PI3K
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- PR
Partial response
- QOL
Quality of life
- RCTs
Randomised controlled trials
- RECIST
Response evaluation criteria in solid tumors
- SD
Stable disease
- sFas/sFasL
Soluble Fas/soluble Fas ligand
- SFDA
China State Food and Drug Administration
- TCMs
Traditional Chinese Medicines
- WHO
World Health Organization
- Yadanzi
The another name of BJOE in Chinese
Authors’ contributions
D FH and G X conception, design and selection of data, L HY, W JY, G XM and C WX data collation, statistical analysis and composition of manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical approval is not required for this review.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Dai Fuhong, Email: 573751620@qq.com.
Gao Xiang, Phone: (+86) 0931-8181512, Email: gaoxiangyffs68@aliyun.com.
Li Haiying, Email: lihy8111@126.com.
Wang Jiangye, Email: 369807908@qq.com.
Gao Xueming, Email: dwbgs1972@sina.com.
Chai Wenxiao, Email: haiwenxiao@126.com.
References
- 1.Dixit R, Agarwal KC, Gokhroo A, Patil CB, Meena M, Shah NS, et al. Diagnosis and management options in malignant pleural effusions. Lung India. 2017;34(2):160–166. doi: 10.4103/0970-2113.201305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Biaoxue R, Xiguang C, Hua L, Wenlong G, Shuanying Y. Thoracic perfusion of recombinant human endostatin (Endostar) combined with chemotherapeutic agents versus chemotherapeutic agents alone for treating malignant pleural effusions: a systematic evaluation and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2016;16(1):888. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2935-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Biaoxue R, Hui P, Wenlong G, Shuanying Y. Evaluation of efficacy and safety for recombinant human adenovirus-p53 in the control of the malignant pleural effusions via thoracic perfusion. Sci Rep. 2016;6:39355. doi: 10.1038/srep39355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Psallidas I, Kalomenidis I, Porcel JM, Robinson BW, Stathopoulos GT. Malignant pleural effusion: from bench to bedside. Eur Respir Rev. 2016;25(140):189–198. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0019-2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Azzopardi M, Porcel JM, Koegelenberg CF, Lee YC, Fysh ET. Current controversies in the management of malignant pleural effusions. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;35(6):723–731. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1395795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Biaoxue R, Shuxia M, Wenlong G, Shuanying Y. Thoracic perfusion of matrine as an adjuvant treatment improves the control of the malignant pleural effusions. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:329. doi: 10.1186/s12957-015-0729-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Xu W, Jiang X, Xu Z, Ye T, Shi Q. The efficacy of Brucea javanica oil emulsion injection as adjunctive therapy for advanced non-small-cell lung Cancer: a meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:5928562. doi: 10.1155/2016/5928562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ma S, Chen F, Ye X, Dong Y, Xue Y, Xu H, et al. Intravenous microemulsion of docetaxel containing an anti-tumor synergistic ingredient (Brucea javanica oil): formulation and pharmacokinetics. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:4045–4052. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S47956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Liu TT, Mu LQ, Dai W, Wang CB, Liu XY, Xiang DX. Preparation, characterization, and evaluation of antitumor effect of Brucea javanica oil cationic nanoemulsions. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:2515–2529. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S101918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yan Z, Zhang B, Huang Y, Qiu H, Chen P, Guo GF. Involvement of autophagy inhibition in Brucea javanica oil emulsion-induced colon cancer cell death. Oncol Lett. 2015;9(3):1425–1431. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.2875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang Q, Wang M, He X, Gao T, Cao H, Dou W, et al. Meta-analysis on treatment of non-small cell lung cancer with brucea javanica oil emulsion in combination with platinum-contained first-line chemotherapy. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012;37(13):2022–2029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Liu J, Huang XE, Tian GY, Cao J, Lu YY, Wu XY, et al. Phase II study on safety and efficacy of Yadanzi(R) (Javanica oil emulsion injection) combined with chemotherapy for patients with gastric cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(3):2009–2012. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.3.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Guo Y, Wu J, Yang H, Cao C. Treatment of malignant pleural effusion with Brucea javanica oil emulsion combined with cisplatin intravesical injection (in Chinese) J Oncol. 2004;10(2):129–130. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lei H, Zhao Y, Su L. Treatment of 111 cases of malignant pleural effusion by brucea javanica oil emulsion combined with chemotherapy (in Chinese) Ningxia Med J. 2006;28(5):372–373. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wang H, Liao G, Liu P, Qu Y, Xie G, Liu S. Brucea javanica oil emulsion combined with cisplatin treatment for 70 patients with malignant pleural effusion of lung cancer (in Chinese) Chinese cancer. 2007;16(12):1035–1036. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wu S, Rui L, Hong Y. Clinical observation on 68 cases of cancerous pleural effusion treated by brucea javanica oil emulsion combined with cisplatin (in Chinese) Hai Nan Med J. 2009;20(9):14–15. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fu X, Fu S, Yang G, Xue Y, Chen L, Yu S. Observation on the curative effect of continuous drainage combined with brucea javanica oil and cisplatin in the treatment of malignant pleural effusion (in Chinese) Clin J Med Offic. 2009;37(5):818–820. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chen Y. Therapeutic effect of brucea javanica oil emulsion combined with cisplatin in the treatment of malignant pleural effusion (in Chinese) Zhejiang J I T C W M. 2011;21(10):713–714. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jia L, Wang Y, Geng L. Treatment of 35 cases of malignant pleural effusion using brucea javanica oil emulsion combined with oxaliplatin (in Chinese) J Tradit Chin Med. 2011;52(22):1956–1957. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Liu B, Zhang L. Clinical observation of brucea javanica oil emulsion and cisplatinum on treating lung cancer malignant pleural effussion (in Chinese). China Modern Med. 2012;19(7):47–8
- 21.Zhang J, Liu X. The results of 28 patients with pleural effusion of lung cancer treated with brucea javanice oil emulsion combined with bleomycin hydrochloride for injection (in Chinese) Pract J Cancer. 2012;27(5):500–502. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhang H, Jing D, Zhao Y. Treatment of 34 cases of malignant pleural effusion with brucea javanica oil and cisplatin (in Chinese) Modern Distance Education of Chinese Med. 2013;11(5):41–42. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yang G, Song C. Clinical observation of Brucea javanica oil emulsion combined with cisplatin in the treatment of malignant pleural effusion (in Chinese) China Foreign Med Treatment. 2014;13:142–145. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yang H, Wu M. Clinical observation of cisplatin and interleukin-II combined with brucea javanica oil emulsion in the treatment of malignant pleural effusion caused by lung cancer (in Chinese) J Clin Pulmonary Med. 2014;19(10):1857–1862. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yue K. Efficacy of Brucea javanica oil emulsion combined with cisplatin in the treatment of pleural effusion of lung cancer (in Chinese) J Med Theor Prac. 2016;29(9):1164–1165. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wang C, Sun C. Thirty cases of lung cancer pleural effusion treated with brucea javanica oil emulsion in combination with cisplatin (in Chinese) Henan Traditional Chinese Med. 2016;36(4):665–666. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Biaoxue R, Hua L, Wenlong G, Shuanying Y. Increased serum amyloid a as potential diagnostic marker for lung cancer: a meta-analysis based on nine studies. BMC Cancer. 2016;16(1):836. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2882-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jin W, Han H, Zhou S, Wang Y, Dong T, Zhao C. Therapeutic efficacy of brucea javanica oil emulsion (BJOE) combined with transcatheter hepatic arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in patients with primary liver cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(10):18954–18962. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lou GG, Yao HP, Xie LP. Brucea javanica oil induces apoptosis in T24 bladder cancer cells via upregulation of caspase-3, caspase-9, and inhibition of NF-kappaB and COX-2 expressions. Am J Chin Med. 2010;38(3):613–624. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X10008093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Qin LJ, Jia YS, Zhao XQ, Zhang T, Zhang W, Sun N. Effect of Brucea Javanica oil emulsion on the invasiveness of glioma cells and its possible mechanism. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016;47(3):347–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yue Y, Yang Y, Shi L, Wang Z. Suppression of human hepatocellular cancer cell proliferation by Brucea javanica oil-loaded liposomes via induction of apoptosis. Arch Med Sci. 2015;11(4):856–862. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2015.53306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Anota A, Hamidou Z, Paget-Bailly S, Chibaudel B, Bascoul-Mollevi C, Auquier P, et al. Time to health-related quality of life score deterioration as a modality of longitudinal analysis for health-related quality of life studies in oncology: do we need RECIST for quality of life to achieve standardization? Qual Life Res. 2015;24(1):5–18. doi: 10.1007/s11136-013-0583-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Nie YL, Liu KX, Mao XY, Li YL, Li J, Zhang MM. Effect of injection of brucea javanica oil emulsion plus chemoradiotherapy for lung cancer: a review of clinical evidence. J Evid Based Med. 2012;5(4):216–225. doi: 10.1111/jebm.12001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Waissbluth S, Peleva E, Daniel SJ. Platinum-induced ototoxicity: a review of prevailing ototoxicity criteria. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017;274(3):1187–1196. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4117-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Biaoxue R, Shuanying Y, Xiguang C, Wei Z, Wei L. Differential diagnostic CYFRA 21-1 level for benign and malignant pleural effusions: a meta-analysis in the Chinese population. Arch Med Sci. 2012;8(5):756–766. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2012.30831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article.


