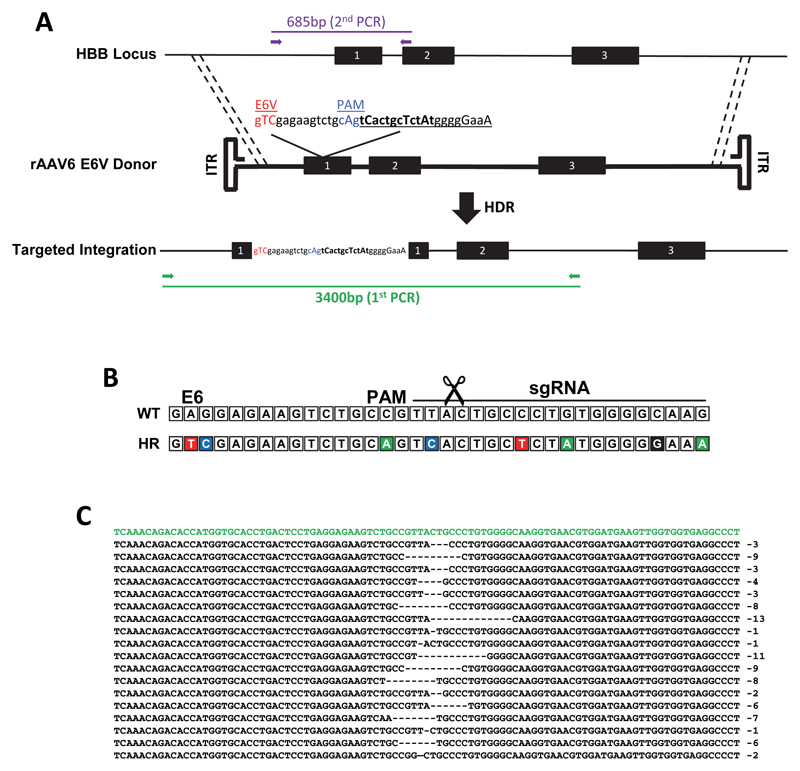
Extended Data Figure 2. Schematic of targeting rAAV6 E6V homologous donor to the HBB locus.
(A) The human HBB locus on chromosome 11 is depicted at the top of the schematic and consists of three exons (black boxes) and two introns. The rAAV6 E6V donor includes the glutamic acid (E) to valine (V) mutation at codon 6, which is the amino acid change causing sickle cell disease. Other SNPs (all SNPs are capitalized) were introduced to PAM site (blue) and sgRNA binding site (bold) to prevent recutting following HR in HSPCs. To analyze targeted integration frequencies in HSPCs, a 2-step PCR was performed. First, a 3400bp In-Out PCR (green) was performed followed by a nested 685bp PCR (purple) on a gel-purified fragment from the first PCR. This 2nd PCR fragment was cloned into TOPO vectors, which were sequenced to determine the allele genotype (WT, INDEL, or HR). (B) The sequence of a wild-type HBB allele aligned with the sequence of an allele that has undergone HR. (C) Representative INDELs from the data represented in Figure 1d. The HBB reference sequence is shown in green.