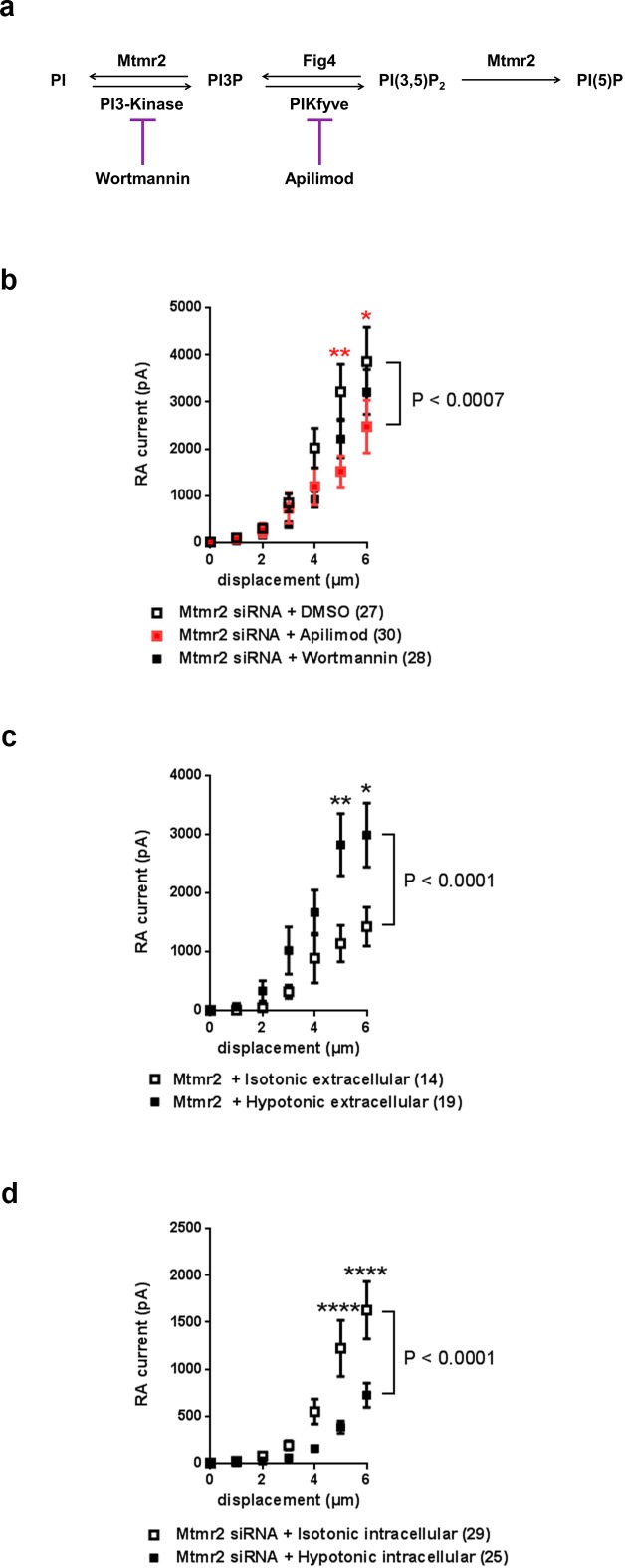
Figure 4. Mtmr2 modulates Piezo2-mediated RA-MA currents mainly via PI(3,5)P2.
(a) Scheme illustrating the major steps of PI(3,5)P2 synthesis and turnover including commonly used inhibitors and their targets. Wortmannin is an inhibitor of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-Kinase) while Apilimod inhibits phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate 5-kinase (PIKfyve). The Fig4 gene encodes a polyphosphoinositide phosphatase. (b) Stimulus-current curves after addition of Wortmannin, Apilimod or vehicle (DMSO) to Mtmr2 siRNA-treated neurons (Mtmr2 siRNA + DMSO: n = 27 neurons; Mtmr2 siRNA + Wortmannin: n = 28 neurons; Mtmr2 siRNA + Apilimod: n = 30 neurons). 2-way ANOVA suggested a significant (P<0.0007) overall effect on RA-MA currents. Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test was performed to compare both conditions to DMSO at individual stimulus magnitudes. While no significant difference between Wortmannin and DMSO at individual stimulus magnitudes was observed, Apilimod application showed a significant reduction of currents compared to DMSO, p-values are indicated by * in the graph. Similarly, only Apilimod treatment increased the displacement threshold (p=0.0055 compared to DMSO-treated neurons, Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn´s multiple comparisons test; Supplementary file 1). The inactivation time constants were unaltered by either treatment (Supplementary file 1). (c) Hypotonic extracellular solution counteracted the inhibition of Piezo2 RA-MA currents caused by Mtmr2 overexpression. Stimulus-current curves for Piezo2 RA-MA currents upon extracellular hypotonic stress application to DRG neurons overexpressing Mtmr2 (Mtmr2 + Isotonic extracellular solution: n = 14 neurons; Mtmr2 + Hypotonic extracellular solution: n = 19 neurons; 2-way ANOVA suggested that extracellular hypotonic stress had a significant (P<0.0001) effect on RA-MA currents. Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test was performed to compare both conditions at individual stimulus magnitudes, p-values are indicated by * in the graph. The displacement threshold of RA-MA currents and inactivation time constant of RA-MA currents were unchanged (Supplementary file 1). (d) Hypotonic intracellular solution counteracted the potentiation of Piezo2 RA-MA currents caused by Mtmr2 knockdown. Stimulus-current curves for Piezo2 RA-MA currents upon intracellular hypotonic stress application to DRG neurons treated with Mtmr2 siRNA (Mtmr2 siRNA + Isotonic intracellular solution: n = 29 neurons; Mtmr2 siRNA + Hypotonic intracellular solution: n = 25 neurons; 2-way ANOVA suggested that intracellular hypotonic stress had a significant (P<0.0001) effect on RA-MA currents. Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons test was performed to compare both conditions at individual stimulus magnitudes, p-values are indicated by * in the graph. The displacement threshold of RA-MA currents was increased upon intracellular hypotonic stress (p=0.0131; Mann-Whitney test; Supplementary file 1). The inactivation time constant of RA-MA currents was unchanged (Supplementary file 1).
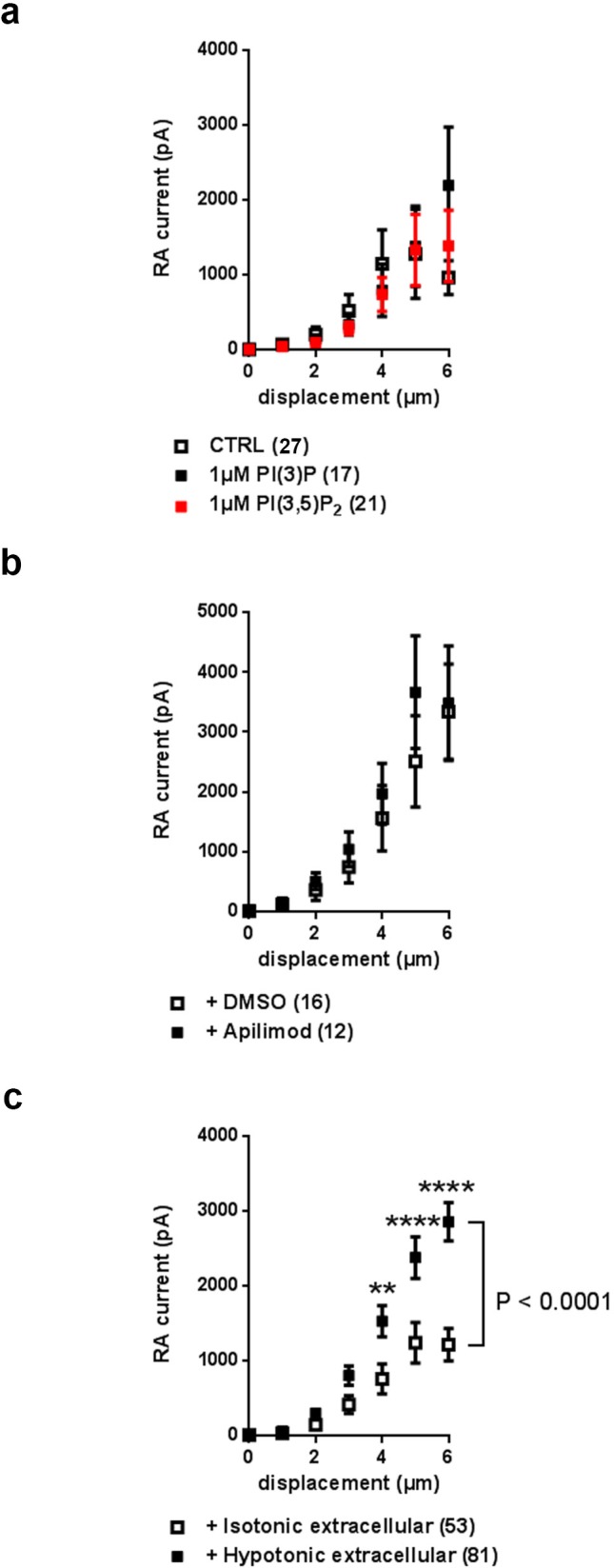
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Effect on Piezo2 RA-MA currents upon application of PIPs or Apilimod in cultured DRG.