Abstract
Four Ru(II) complexes were prepared bearing two new tetradentate ligands, cyTPA and 1-isocyTPQA, which feature a piperidine ring that provides a structurally rigid backbone and facilitates the installation of other donors as the fourth chelating arm, while avoiding the formation of stereoisomers. The photophysical properties and photochemistry of [Ru(cyTPA)(CH3CN)2]2+ (1), [Ru(1-isocyTPQA)(CH3CN)2]2+ (2), [Ru(cyTPA)(py)2]2+ (3), and [Ru(1-isocyTPQA)-(py)2]2+ (4) were compared. The quantum yield for the CH3CN/H2O ligand exchange of 2 was measured to be Φ400 = 0.033(3), 5-fold greater than that of 1, Φ400 = 0.0066(3). The quantum yields for the py/H2O ligand exchange of 3 and 4 were lower, 0.0012(1) and 0.0013(1), respectively. DFT and related calculations show the presence of a highly mixed 3MLCT/3ππ* excited state as the lowest triplet state in 2, whereas the lowest energy triplet states in 1, 3, and 4 were calculated to be 3LF in nature. The mixed 3MLCT/3ππ* excited state places significant spin density on the quinoline moiety of the 1-isocyTPQA ligand positioned trans to the photolabile CH3CN ligand in 2, suggesting the presence of a trans-type influence in the excited state that enhances ligand exchange. Ultrafast spectroscopy was used to probe the excited states of 1–4, which confirmed that the mixed 3MLCT/3ππ* excited state in 2 promotes ligand dissociation, representing a new manner to effect photoinduced ligand exchange. The findings from this work can be used to design improved complexes for applications that require efficient ligand dissociation, as well as for those that require minimal deactivation of the 3MLCT state through low-lying metal-centered states.
Graphical Abstract
INTRODUCTION
The excited states of ruthenium polypyridyl complexes have been used extensively in the areas of dye-sensitized solar cells, photocatalysis, synthetic chemistry, photochromic switching, photochemotherapy, and as biological sensors, among others.1–32 The utility of these complexes for these applications relies on their relatively strong absorption and emission intensity in the visible region, long-lived triplet metal-to-ligand charge transfer (3MLCT) excited state lifetimes, and high stability under various experimental conditions.1–33 In contrast, the efficient photoinduced ligand dissociation for the release of drugs or biological probes with spatiotemporal control necessitates the population of the dissociative metal-centered, ligand field states (3LF), known to lead to nonradiative deactivation of the emissive 3MLCT state.14,34–41 Therefore, understanding the interplay between the 3MLCT and 3LF states is important to improve the function of Ru(II) complexes, both when the long-lived 3MLCT state is desired, as well as for cases where increased 3LF population is required.14,42 Therefore, the improvement of agents for this wide range of applications requires understanding of the molecular and electronic factors that result in 3MLCT deactivation and ligand photodissociation through population of the 3LF state(s).
The excited state ligand exchange photochemistry of Ru(II) complexes has long been believed to arise from 3LF states with electron configurations that result in electron density in molecular orbitals of Ru–L(σ*) character.14 In complexes with low-lying 3MLCT and 3LF states, such as in ruthenium polypyridyl compounds, it is generally accepted that those with lower energy 3LF states should exhibit greater ligand photo-dissociation quantum yields.14,27,30,39,42–44 This trend was shown by Ford and co-workers on the series [Ru(NH3)5(py-X)]2+ (py-X = substituted pyridine) and trans-[Ru(NH3)4(py)-(L)]n+ (py = pyridine; L = pyrazine, pyrazinium, 4-acetylpyridine), which resulted in quantum yields of ligand substitution that spanned over 3 orders of magnitude.45 The incorporation of electron donating substituents on pyridine led to mainly 3LF character in the lowest triplet excited states and efficient photosubstitution, whereas electron withdrawing substituents resulted in mostly 3MLCT character and decreased photosubstitution efficiency.34,45,46 In addition, it has been shown that in complexes where the 3MLCT state remains the lowest energy triplet state, reducing the 3MLCT–3LF energy gap by either raising the 3MLCT state or lowering the 3LF state, can also lead to increased population of the dissociative 3LF states.39,47–50 On the basis of this understanding of photoinduced ligand dissociation in Ru(II) polypyridyl complexes, it follows that the photochemical ligand exchange should be more efficient in complexes where the lowest energy excited state is metal-centered, 3LF, and not 3MLCT. The latter condition should hold provided that the energy of the 3LF states are not so low that intersystem crossing back to the ground state becomes too rapid and competes with ligand dissociation in accordance with the energy gap law.44,50
The majority of studies concerning the photochemical ligand exchange of polypyridyl Ru(II) complexes have focused on complexes containing planar bi- or tridentate ligands, such as the prototypical 2,2′-bipyridine or 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine, respectively, and their derivatives.27,41,48,51–55 Recently, the photochemistry of Ru(II) complexes bearing tetradentate ligands based on tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine (TPA) was examined. In both [Ru(TPA)(CH3CN)2]2+ and [Ru(TPA)-(py)2]2+, the monodentate ligand cis to the basic amine nitrogen of the TPA ligand was shown to undergo preferential ligand photodissociation, with quantum yields (Φ) in H2O of 0.012(1) with λirr = 350 nm and 0.0097(8) with λirr = 400 nm, respectively.56,57 The photochemistry of a related nitrile complex containing the tetradentate ligand tris(2-quinolinylmethyl)amine (TQA), [Ru(TQA)(CH3CN)2]2+, resulted in Φ400 = 0.027(1) in H2O, ~2-fold greater than that of [Ru(TPA)(CH3CN)2]2+. Like [Ru(TPA)(CH3CN)2]2+ and [Ru(TPA)(py)2]2+, irradiation of [Ru(TQA)(CH3CN)2]2+ only results in ligand exchange of the CH3CN positioned cis to the basic amine nitrogen of the TQA ligand.58 Calculations provided an explanation for the increase and selectivity of ligand exchange, showing the presence of favorable orbital overlap in the excited state between the coplanar quinoline arms of the TQA ligand and the photolabile CH3CN ligand that is not present in the TPA complex.59
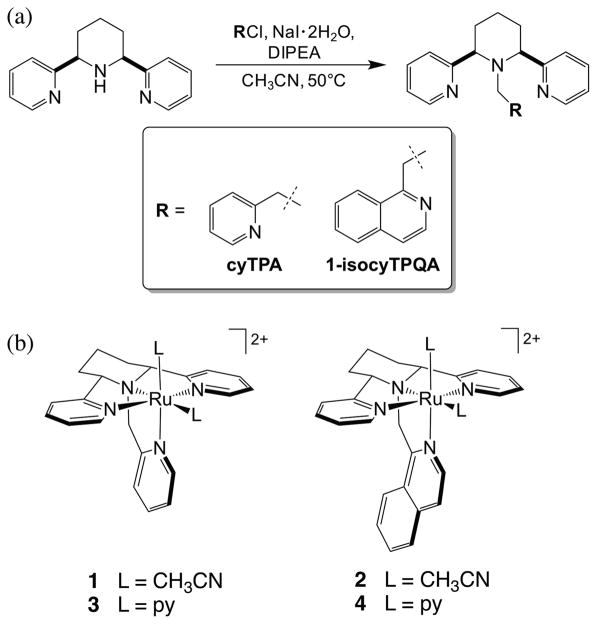
In the present work, four new Ru(II) complexes were prepared bearing two new tetradentate ligands related to TPA, cyTPA (2,2′-((2R,6S)-1-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)piperidine-2,6-diyl)dipyridine) and 1-isocyTPQA (1-(((2R,6S)-2,6-di-(pyridin-2-yl)piperidin-1-yl)methyl)isoquinoline), depicted in Figure 1. These ligands feature a piperidine ring, which locks the adjacent pyridine arms into the trans position to form a planar tridentate moiety within the tetradentate ligand. This structurally rigid backbone facilitates the installation of other donors as the fourth chelating arm, while avoiding the formation of stereoisomers. The photophysical properties and photochemistry of [Ru(cyTPA)(CH3CN)2]2+ (1) and [Ru(1-isocyTPQA)(CH3CN)2]2+ (2) were compared, as well as to those of the corresponding pyridine complexes, [Ru(cyTPA)-(py)2]2+ (3) and [Ru(1-isocyTPQA)(py)2]2+ (4). Photo-induced ligand exchange was found to be significantly more efficient for 2, a property that was investigated using ultrafast transient absorption spectroscopy and computational studies. The findings provide a new mechanism that leads to ligand dissociation that does not involve a low-lying 3LF state and can now be exploited in the design of new complexes for efficient photoinduced drug delivery with low energy excitation. These results also provide insight into an additional mode of deactivation of Ru(II) complexes important for solar energy conversion applications and the use of these systems as emissive probes, all of which require long-lived 3MLCT excited states and minimum deactivation through nonradiative channels.
Figure 1.
(a) Synthetic route of the ligands cyTPA and 1-isocyTPQA and (b) molecular structures of complexes 1–4.
EXPERIMENTAL SECTION
Materials
All materials for synthesis were used as received without further purification and the solvents were of reagent grade quality. Dry methanol, absolute ethanol, dry acetonitrile, acetone, ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, hexane, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), diethyl ether and pyridine were purchased from Fisher Scientific. Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, 2-picolyl chloride hydrochloride, N,N-diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA), and tetrakis(dimethyl sulfoxide)-dichlororuthenium(II) (cis-[Ru(DMSO)4Cl2]) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Ammonium hexafluorophosphate was obtained from AK Scientific, and NaI·2H2O was purchased from ACROS Organics. The precursors (2R,6S)-2,6-di(pyridin-2-yl)piperidine60 and 1-(chloromethyl)isoquinoline61 were synthesized according to literature procedures. All reactions were performed under ambient atmosphere unless otherwise noted. Anaerobic reactions were performed by purging the reaction solutions with Ar or N2. For transient absorption experiments acetone was dried using anhydrous MgSO4, and acetonitrile was distilled over CaH2.
cyTPA (2,2′-((2R,6S)-1-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)piperidine-2,6-diyl)-dipyridine)
To a solution of (2R,6S)-2,6-di(pyridin-2-yl)piperidine (36 mg, 0.15 mmol) in 11 mL of dry CH3CN, 2-picolyl chloride hydrochloride (25 mg, 0.15 mmol) was added. To this, DIPEA (52 μL, 0.30 mmol) and NaI·2H2O (28 mg, 0.15 mmol) were added and the reaction mixture was heated at 50 °C for 16 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue was extracted with dichloromethane and an aqueous solution of saturated NaHCO3. The organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude product, which was purified by chromatography on silica using ethyl acetate as the eluent to give cyTPA as a yellow solid (26 mg, 52%): 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.46 (d, 2H, J = 4.8 Hz), 8.18 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz), 7.57 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.50 (t, 2H, J = 7.6 Hz), 7.31 (t, 1H, J = 7.6 Hz), 7.04–7.00 (m, 3H), 6.84 (t, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz), 3.86 (d, 2H, J = 9.6 Hz), 3.63 (s, 2H), 1.90–1.81 (m, 4H), 1.64–1.58 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3) δ 163.7, 159.4, 148.8, 148.1, 136.2, 135.1, 123.8, 123.0, 122.0, 120.8, 70.2, 59.6, 34.8, 24.3; ESMS calculated for ([M + H]+) C21H23N4: 331.1878, found ([M + H]+): 331.1919.
1-IsocyTPQA (1-(((2R,6S)-2,6-di(pyridin-2-yl)piperidin-1-yl)-methyl)isoquinoline)
To a solution of (2R,6S)-2,6-di(pyridin-2-yl)piperidine (20 mg, 0.084 mmol) in 6.0 mL of dry CH3CN, 1-(chloromethyl)isoquinoline (15 mg, 0.084 mmol) was added. To this, DIPEA (29 μL, 0.17 mmol) and NaI·2H2O (16 mg, 0.084 mmol) were added and the reaction mixture was heated at 50 °C for 16 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue was extracted with dichloromethane and an aqueous solution of saturated NaHCO3. The organic layer was dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude product, which was purified by chromatography on silica using methanol/ethyl acetate (1:9, v/v) as the eluent to give 1-isocyTPQA as an orange solid (15 mg, 47%): 1H NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD) δ 8.19–8.15 (m, 3H), 7.92 (d, 1H, J = 8.5 Hz), 7.67 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.62 (d, 3H, J = 7.5 Hz), 7.52–7.46 (m, 3H), 7.39 (s, 1H), 7.02–6.99 (m, 2H), 4.09 (s, 2H), 4.03 (dd, 2H, J = 10 Hz), 1.95–1.83 (m, 4H), 1.73–1.70 (m, 2H); 13C NMR (500 MHz, CD3OD) δ 163.0, 157.9, 147.6, 139.4, 136.7, 135.9, 130.2, 126.9, 126.8, 126.6, 125.4, 123.3, 122.1, 120.3, 70.1, 54.5, 34.6, 23.7; ESMS calculated for C25H25N4 ([M + H]+): 381.2079, found ([M + H]+): 381.1794.
[Ru(cyTPA)(CH3CN)2](PF6)2 (1)
To a solution of cyTPA (13 mg, 0.040 mmol) in 4.0 mL of dry MeOH under inert atmosphere in a pressure flask, cis-[Ru(DMSO)4Cl2] (19 mg, 0.040 mmol) was added. The solution was then purged with Ar for 10 min at room temperature, and the reaction mixture was allowed to reflux for 5 h under inert atmosphere, during which time the color of the reaction mixture darkened slightly. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and concentrated under reduced pressure. To the flask, a mixture of CH3CN:H2O (1:1 v/v, 4.0 mL) was added, and the reaction mixture was refluxed for another 16 h under inert atmosphere. The reaction mixture was again cooled to room temperature. Ice cold water (15 mL) and NH4PF6 (15 mg) were then added, resulting in the formation of a yellow precipitate which was filtered, washed with ice cold water (200 mL) and dried under reduced pressure to give 1 as a yellow solid (26 mg, 82%): 1H NMR (400 MHz, (CD3)2CO) δ 9.25 (d, 1H, J = 4.4 Hz), 8.90 (d, 2H, J = 4.4 Hz), 7.95 (t, 2H, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.64 (t, 1H, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.49 (d, 2H, J = 7.6 Hz), 7.40 (t, 2H, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.33 (t, 1H, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.12 (d, 1H, J = 7.6 Hz), 5.53 (t, 2H, J = 7.2 Hz), 4.65 (s, 2H), 2.93 (s, 3H), 2.57 (s, 3H), 2.68–2.42 (m, 6H); IR (KBr) νmax (cm−1) 3247, 3116, 2943, 2874, 2360, 2342, 2271, 1701, 1608, 1570, 1486, 1443, 1426, 1365, 1317, 1287, 1250, 1211, 1160, 1114, 1084, 1053, 1036, 991, 932, 838, 764, 751, 740, 715, 668; UV–vis (DMSO) λmax = 390 nm (ε = 9200 M−1 cm−1); ESMS calculated for C25H28F6N6PRu ([M – PF6−]+): 659.1068, found ([M – PF6−]+): 659.0580; Anal. Calcd for C26.3H32F12N6P2O0.6Ru (1·0.3Et2O· 0.3H2O): C, 37.91; H, 3.87; N, 10.07, found: C, 37.91; H, 3.74; N, 10.21.
[Ru(1-isocyTPQA)(CH3CN)2](PF6)2 (2)
To a solution of 1-isocyTPQA (15 mg, 0.040 mmol) in 4.6 mL of dry MeOH under inert atmosphere in a pressure flask, cis-[Ru(DMSO)4Cl2] (19 mg, 0.040 mmol) was added. The solution was then purged with Ar for 10 min at room temperature, and the reaction mixture was allowed to reflux for 5 h under inert atmosphere, during which time the color of the reaction mixture changed from pale yellow to dark red. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and concentrated under reduced pressure. To the flask, a mixture of CH3CN:H2O (1:1 v/v, 4.6 mL) was added, and the reaction mixture was refluxed for another 16 h under inert atmosphere. The reaction mixture was again cooled to room temperature. Ice cold water (15 mL) and NH4PF6 (15 mg) were then added, resulting in the formation of a yellow precipitate which was filtered, washed with ice cold water (200 mL) and dried under reduced pressure to give 2 as a yellow solid (16 mg, 47%): 1H NMR (400 MHz, (CD3)2CO) δ 9.12 (d, 1H, J = 6.4 Hz), 8.97 (d, 2H, J = 5.2 Hz), 8.03 (d, 1H, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.94–7.86 (m, 3H), 7.81 (d, 1H, J = 6.4 Hz), 7.74 (t, 1H, J = 7.6 Hz), 7.60 (t, 1H, J = 7.6 Hz), 7.50 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.36 (t, 2H, J = 6.8 Hz), 5.63 (d, 2H, J = 10 Hz), 5.24 (d, 2H, J = 6.4 Hz), 2.98 (s, 3H), 2.60 (s, 3H), 2.56–2.53 (m, 4H), 2.50–2.44 (m, 2H); IR (KBr) νmax (cm−1) 3422, 2950, 2876, 2276, 1701, 1606, 1563, 1508, 1467, 1421, 1405, 1362, 1319, 1251, 1221, 1160, 1117, 1083, 1050, 992, 966, 840, 768, 758, 740; UV–vis (DMSO) λmax = 390 nm (ε = 11 900 M−1 cm−1); ESMS calculated for C29H30F6N6PRu ([M – PF6−]+): 709.1225, found ([M – PF6−]+): 709.1170; Anal. Calcd for C30.5H33F12N6O0.5P2Ru (2·0.5(CH3)2CO): C, 41.50; H, 3.77; N, 9.52, found: C, 41.17; H, 3.78; N, 9.73.
[Ru(cyTPA)(py)2](PF6)2 (3)
To a solution of cyTPA (20 mg, 0.061 mmol) in 6.0 mL of dry MeOH under inert atmosphere in a pressure flask, cis-[Ru(DMSO)4Cl2] (29 mg, 0.061 mmol) was added. The solution was then purged with Ar for 10 min at room temperature, and the reaction mixture was allowed to reflux for 5 h under inert atmosphere, during which time the color of the reaction mixture darkened slightly. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and concentrated under reduced pressure. To the flask, a mixture of pyridine:H2O (1:1 v/v, 6.0 mL) was added, and the reaction mixture was refluxed for another 16 h under inert atmosphere. The reaction mixture was then cooled to room temperature. Ice cold water (15 mL) and NH4PF6 (15 mg) were added to the reaction mixture, resulting in the formation of an orange precipitate which was filtered, washed with ice cold water (200 mL) and dried under reduced pressure to give 3 as an orange solid (45 mg, 84%): 1H NMR (400 MHz, (CD3)2CO) δ 8.98 (d, 2H, J = 4.8 Hz), 8.85 (d, 2H, J = 5.2 Hz), 8.76 (d, 1H, J = 5.6 Hz), 8.33 (d, 2H, J = 6.0 Hz), 8.14 (t, 1H, J = 7.6 Hz), 8.00 (t, 2H, J = 7.6 Hz), 7.95 (t, 1H, J = 7.6 Hz), 7.70 (t, 2H, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.62 (t, 1H, J = 7.6 Hz), 7.57 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.48 (t, 2H, J = 6.4 Hz), 7.39 (t, 2H, J = 7.2 Hz), 7.26–7.22 (m, 2H), 5.17 (dd, 2H, J = 11.2 Hz), 4.71 (s, 2H), 2.61–2.41 (m, 6H); IR (KBr) νmax (cm−1) 3441, 2963, 2350, 1777, 1708, 1605, 1485, 1466, 1445, 1321, 1297, 1217, 1162, 1117, 1066, 993, 838, 770, 759, 711, 701; UV–vis (DMSO) λmax = 360 nm (ε = 12 800 M−1 cm−1), 410 nm (ε = 9140 M−1 cm−1); ESMS calculated for C31H32F6N6PRu ([M – PF6−]+): 735.1382, found ([M – PF6−]+): 735.1263; Anal. Calcd for C31H32F12N6P2Ru: C, 42.33; H, 3.67; N, 9.55, found: C, 42.25; H, 3.71; N, 9.48.
[Ru(1-isocyTPQA)(py)2](PF6)2 (4)
To a solution of 1-isocyTPQA (15 mg, 0.039 mmol) in 4.5 mL of dry MeOH under inert atmosphere in a pressure flask, cis-[Ru(DMSO)4Cl2] (19 mg, 0.039 mmol) was added. The solution was then purged with Ar for 10 min at room temperature, and the reaction mixture was allowed to reflux for 5 h under inert atmosphere, during which time the color of the reaction mixture changed from pale yellow to dark red. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and NH4PF6 (15 mg) was then added, resulting in the formation of a yellow precipitate which was filtered and washed with ice cold water (200 mL). The solid was collected, distilled water (6.0 mL) and 3 to 4 drops of trifluoromethanesulfonic acid were added, and the reaction mixture was refluxed for another 4 h under inert atmosphere. During this time, the color of the reaction mixture changed from dark red to green. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, and ice cold water (15 mL) and NH4PF6 (15 mg) were then added, resulting in the precipitation of green [Ru(1-isocyTPQA)(H2O)2](PF6)2. The green solid was filtered, washed with ice cold water (200 mL) and dried under reduced pressure. It was then treated with pyridine (31 mg, 0.39 mmol) in 6.0 mL of absolute EtOH under inert atmosphere in a pressure flask. The solution was purged with argon for 10 min at room temperature. The mixture was then allowed to reflux for another 16 h under inert atmosphere, and the color of the reaction mixture was observed to change from green to dark red. The reaction mixture was again cooled to room temperature and concentrated under reduced pressure, washed with toluene (20 mL), and extracted with dichloromethane and water. The organic layer was collected, dried over Na2SO4, and concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude product. The crude product was purified by chromatography on alumina using acetone/hexane (8:2, v/v) as the eluent to give 4 as a red solid (14 mg, 38%): 1H NMR (400 MHz, (CD3)2CO) δ 9.06 (d, 2H, J = 5.2 Hz), 8.93 (d, 2H, J = 5.6 Hz), 8.60 (d, 1H, J = 6.8 Hz), 8.38 (d, 2H, J = 5.2 Hz), 8.18–8.14 (m, 2H), 7.98–7.90 (m, 4H), 7.77–7.71 (m, 4H), 7.63 (t, 1H, J = 7.6 Hz), 7.57 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz), 7.46–7.39 (m, 4H), 5.31–5.25 (m, 4H); IR (KBr) νmax (cm−1) 3437, 2959, 1607, 1566, 1508, 1487, 1465, 1445, 1404, 1276, 1161, 1085, 839, 759, 740, 704; UV–vis (DMSO) λmax = 360 nm (ε = 10 600 M−1 cm−1), 415 nm (8020 M−1 cm−1); ESMS calculated for C35H34F6N6PRu ([M – PF6−]+): 785.1540, found ([M – PF6−]+): 785.1445; Anal. Calcd for C39H44F12N6OP2Ru (4·Et2O): C, 46.66; H, 4.42; N, 8.37, found: C, 46.37; H, 4.27; N, 8.25.
Methods and Instrumentation
1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on either a Varian FT-NMR Agilent 400 MHz, Oxford 500 MHz, or Agilent DD2 600 MHz spectrometer in CDCl3, CD3OD or (CD3)2CO, and the spectra were referenced to the residual protonated solvent peaks. Mass spectra were recorded on a time-of-flight Micromass LCT Premier XE Spectrometer, IR spectroscopy was conducted on a Nicolet FT-IR spectrophotometer (KBr pellet), and electronic absorption spectra were recorded on a Varian Cary 50 or an Agilent 8454 spectrophotometer.
Single crystal X-ray diffraction data were collected at 100 K with Mo Kα radiation using a Bruker X8 diffractometer equipped with a kappa geometry goniometer, graphite monochromator, and an APEX-II CCD. The frames were integrated with the Bruker SAINT software package62 using a narrow-frame algorithm, and the data were corrected for absorption effects using the multiscan method (SADABS).63 Using Olex2,64 structures of 1 and 2 were solved with the SHELXS-1997 structure solution program65 using direct methods and refined with the SHELXL refinement package66 using least-squares minimization. The structure of 3 was solved with the SHELXT structure solution program67 using direct methods and refined as with 1 and 2. During the refinement of structure 1, a disordered PF6− counterion was removed and modeled using a solvent mask. All non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically, and hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions. Crystals of 1 were yellow. 200 837 reflections were collected and merged into 12 344 independent reflections with Rint = 0.0334. The asymmetric unit contains one Ru complex and 1.5 PF6− counterions. The phosphorus atom of one of the PF6− ions sits on a special position and is 1/2 occupied, which may be due to an invisible counterion (like H+) in the electron density map. Crystals of 2 were also yellow. 23 2068 reflections were collected and merged into 21 952 independent reflections with Rint = 0.0273. The asymmetric unit contains one Ru complex, two PF6− counterions and one CH3CN in the solvent area. Crystals of 3 were again yellow, and 91 822 reflections were collected and merged into 6547 independent reflections with Rint = 0.0837. The asymmetric unit contains one Ru complex and two PF6− counterions. Any counterions or solvent molecules present were not shown in the ORTEP diagrams for clarity.
The irradiation source for photolysis and ligand exchange quantum yield experiments was a 150 W Xe arc lamp (USHIO) in a MilliArc lamp housing unit powered by a LPS-220 power supply equipped with a LPS-221 igniter (PTI). A 395 nm long-pass filter (CVI Melles Griot) was used for the photolysis experiments, while a 400 nm bandpass filter (Thorlabs) with a 335 nm long-pass filter (CVI Melles Griot) was used to measure quantum yields of ligand exchange. For both the photolysis and ligand exchange quantum yield experiments, the samples were dissolved in H2O with <5% acetone added for solubility. Potassium tris(ferrioxalate) was used as a chemical actinometer to determine the photon flux of the lamp at 400 nm as previously described (1.6 × 10−7 mol photons/min).68 For NMR studies, solutions of 1 and 2 in CD3CN (~2 mM) were prepared and stored for 1 h in the dark, and then were irradiated in an NMR tube using the 150 W Xe arc lamp and a 395 nm long-pass filter. 1H NMR spectra were collected using a Bruker DPX 400 MHz spectrometer at the indicated time intervals, and all chemicals shifts were referenced to the residual protonated solvent peak (δ = 1.94 ppm).
Spin restricted and unrestricted density functional theory (DFT) calculations were performed with the Gaussian 09 package.69 All geometry optimization and vibrational frequency calculations were performed with the SDD70 basis set on Ru and the TZVP71 basis set on all other atoms with the PBE72,73 exchange-correlation functional. The geometries of all complexes were fully optimized starting from X-ray crystal structures, when available. All optimized geometries have positive harmonic frequencies, confirming the calculated structures as electronic energy minima. Further calculations of molecular orbitals and time-dependent DFT (TD-DFT) utilized the B3LYP74–76 hybrid functional, again with the SDD basis set on Ru and with the TZVP basis set on all other atoms with the inclusion of solvation effects using the polarized continuum model (PCM) with acetonitrile as the solvent in the TD calculations.77 TD-DFT was used to calculate the electronic transition state energies and intensities of the 75 lowest-energy states. Spin densities were calculated using Mulliken population analysis methods (MPA). Orbitals from the Gaussian calculations were plotted using the Chemcraft program. The analysis of the MO compositions in terms of fragment orbitals, Mayer bond orders, and charge decomposition analyses78,79 (CDA) were performed using AOMix-FO80 within the AOMix program.80,81 CDA and its applications have been previously described in detail by Gorelsky and co-workers.82,83
Ultrafast transient absorption data were collected on a broadband UV–vis system (Figure S23, Supporting Information) consisting of a Ti:sapphire oscillator (Vitara-S, Coherent), which generated 20 fs pulses at 80 MHz to seed a high-energy Ti:sapphire regenerative amplifier (Astrella 1K-USP, Coherent) to produce 7 mJ, 35 fs pulses at 1 kHz. The output from the regenerative amplifier was then split, where 1 mJ was used to generate a white light continuum as previously described,84 and the remaining 6 mJ was split again using a 50:50 beamsplitter. From the latter, 3 mJ was used to pump an OPA (OPerA Solo, Coherent/Positive Light) to generate a pump pulse tunable from 300–2500 nm. A thermoelectrically cooled CCD camera (Princeton Instruments, 1340 × 100 pixels) and home-developed software, written in LabVIEW 2015, were used to collect the spectral data. An instrument response full width at half-maximum (fwhm) of ~85 fs was measured using the optical Kerr effect in cyclohexane. Typically, a total sample volume of ~10–20 mL was circulated through a Harrick Scientific flow cell (1 mm thick CaF2 windows, 1 mm optical path length). The sample solutions were prepared with an absorbance at the excitation wavelength of ~0.5–0.6, and the pump pulse energy was set to ~2 μJ at the sample. All other aspects of the optical setup and data collection are as previously described.84 The samples were excited with 350 nm, and the polarization angle between the pump and probe beams was set to the magic angle of 54.7° to avoid effects caused by rotational diffusion. Measurements were repeated three times at each time delay by collecting three retroreflector cycles and the spectra were corrected for the chirp in the white light continuum.85 The kinetic traces were fit to mono- or biexponential decays as needed.86
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Synthesis and X-ray Crystallography
The precursor (2R,6S)-2,6-di(pyridin-2-yl)piperidine (structure shown in Figure 1) was synthesized according to a known literature procedure60 in which the commercially available starting material 2-pyridinecarboxaldehyde was treated with 1,3-acetonedicarboxylic acid in the presence of ammonium acetate, followed by a Wolff–Kishner reaction. The ligand cyTPA was prepared by treating (2R,6S)-2,6-di(pyridin-2-yl)piperidine with 2-picolyl chloride hydrochloride, NaI·2H2O and DIPEA in CH3CN at 50 °C through alkylation. The ligand 1-isocyTPQA was synthesized following a similar procedure using 1-(chloromethyl)isoquinoline (Figure 1).
Treating each ligand with 1 equiv of cis-[Ru(DMSO)4Cl2] in MeOH at 70 °C provided a 2:1 mixture of [Ru(L)(DMSO)-Cl]Cl stereoisomers (L = cyTPA, 1-isocyTPQA) as previously described in the literature.87 Heating [Ru(L)(DMSO)Cl]Cl in a CH3CN:H2O mixture (1:1, v/v) resulted in the formation of the corresponding [Ru(cyTPA)(CH3CN)2]2+ (1) and [Ru(1-isocyTPQA)(CH3CN)2]2+ (2) complexes in good yield. Heating [Ru(cyTPA)(DMSO)Cl]Cl at 80 °C under similar conditions in the presence of 10 equiv of pyridine, followed by precipitation with NH4PF6 resulted in [Ru(cyTPA)(py)2]-(PF6)2 (3) in 84% yield. The precipitation of [Ru(1-isocyTPQA)(DMSO)Cl]Cl with NH4PF6, followed by heating in distilled H2O with trifluoromethanesulfonic acid at 100 °C afforded the intermediate complex [Ru(1-isocyTPQA)-(H2O)2](PF6)2 as a green solid. Treating [Ru(1-isocyTPQA)-(H2O)2](PF6)2 with 10 equiv of pyridine in absolute EtOH at 80°C resulted in [Ru(1-isocyTPQA)(py)2](PF6)2 (4) in moderate yield.
Diffusion of diethyl ether into solutions of 1–3 in acetone provided single crystals suitable for X-ray crystallographic analysis (Figure 2). Additional crystallographic data for 1–3, including data collection parameters, are detailed in Tables S1–S3 (Supporting Information), with selected bond lengths and bond angles listed in Tables S2 and S3. For all three structures, the N6 donor is defined as that which is positioned cis to the basic nitrogen N3, while the N1 atom is positioned trans to N3 (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
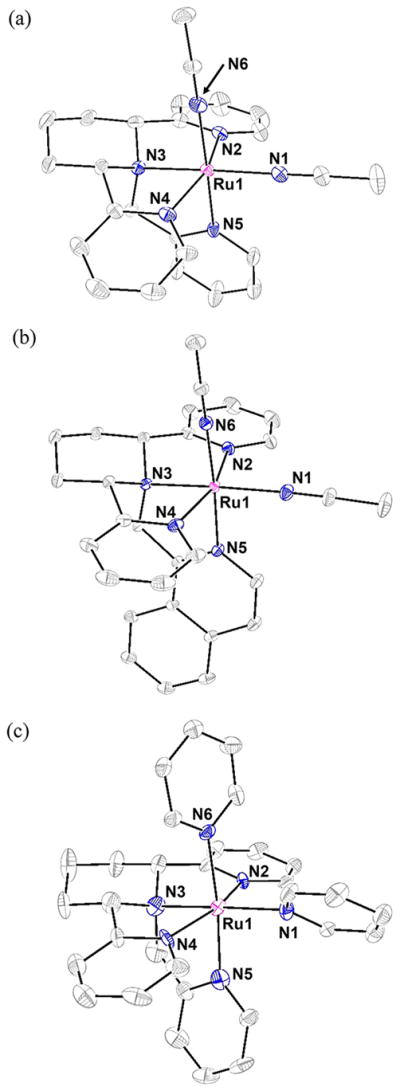
ORTEP diagrams of the dications (a) 1 [Ru(cyTPA)-(CH3CN)2]2+, (b) 2 [Ru(1-isocyTPQA)(CH3CN)2]2+ and (c) 3 [Ru(cyTPA)(py)2]2+ (thermal ellipsoids shown at 50% probability, hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity). Selected bond distances (Å) for 1: Ru1–N1, 2.047(2); Ru1–N6, 2.047(2). Selected bond distances (Å) for 2: Ru1–N1, 2.0312(8); Ru1–N6, 2.0331(8). Selected bond distances (Å) for 3: Ru1–N1, 2.13(1); Ru1–N6, 2.12(1).
Complex 1 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group C2/c with Z = 4. The coordination environment around the Ru(II) metal center exhibits a slightly distorted octahedral geometry, with bond angles ranging from 79.36(7)° to 101.15(7)°. In 1, the fourth arm of the tetradentate cyTPA ligand (the N5 arm) is slightly tilted toward the N2 arm, causing the N5–Ru1–N2 angle to be 84.95(7)°, a value smaller than the analogous angle in [Ru(TPA)(CH3CN)2]2+, 90.4(2)°.56 Furthermore, the rigidity afforded by the piperidine ring in 1 appears to cause a small amount of additional steric strain in the cyTPA ligand as evidenced by the slightly smaller N2–Ru1–N4 angle of 159.15(7)° as compared to 164.1(2)° in [Ru(TPA)-(CH3CN)2]2+.56 These small distortions do not cause a significant lengthening of any of the Ru–N bonds in 1, since the bond distances are all within a few hundredths of an Ångstrom to those reported for [Ru(TPA)(CH3CN)2]2+,56 and the Ru–N(CH3CN) bond lengths in 1 are comparable to those reported for cis-[Ru(bpy)2(CH3CN)2]2+.88
Complex 2 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/n with Z = 4. The coordination environment around the metal center also exhibits a slightly distorted octahedral geometry, with bond angles ranging from 80.98(3)° to 99.80(4)°. As expected, the substitution of a pyridine for an isoquinoline moiety in the N5 arm of the tetradentate ligand does not produce steric strain around the metal center. A comparison between the bond angles of 1 and 2 reveals that the only difference is that in 2 the N6 CH3CN cis to the basic amine nitrogen is tilted slightly toward the N2 arm, as evidenced by the slightly smaller N6–Ru1–N2 angle of 86.99(3)° in 2 as compared to 93.00(7)° in 1. Again, the Ru–N bond lengths in 2 are comparable to 1, as well as to those of the previously reported [Ru(TQA)(CH3CN)2]2+.58 In addition, the Ru–N(CH3CN) bond lengths in 2 also compare well with those reported for cis-[Ru(bpy)2(CH3CN)2]2+.88
Complex 3 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group P21/c with Z = 4. The coordination environment around the Ru(II) metal center again exhibits a slightly distorted octahedral geometry with bond angles ranging from 76.8(4)° to 101.9(4)°. In 3, the N5 arm of the cyTPA ligand is bent toward the N4 arm to a larger degree than that in 1 or 2, as evidenced by the smaller N5–Ru1–N4 angle of 80.7(5)° in 3. This difference is attributed to the steric bulk afforded by a py ligand as compared to an CH3CN in 1 and 2. The N2 and N4 arms of the cyTPA ligand cause the N1 py ligand to be canted rather than coplanar, as is the case in 1 and 2 with CH3CN ligands, which pushes the N5 arm of cyTPA closer to the N4 arm, as well as the N2 arm closer to the central piperidine ring. This steric clashing between the N1 py and the tetradentate ligand is also observed in [Ru(TPA)(py)2]2+.57 The Ru–N bond lengths of the tetradentate ligand in 3 are similar to the corresponding bond lengths in 1 and 2, and the Ru–N(py) bond lengths of 3 are similar to those measured in [Ru(TPA)(py)2]2+,57 as well as in cis-[Ru(bpy)2(py)2]2+.89
Electronic Absorption Spectroscopy and Photochemistry
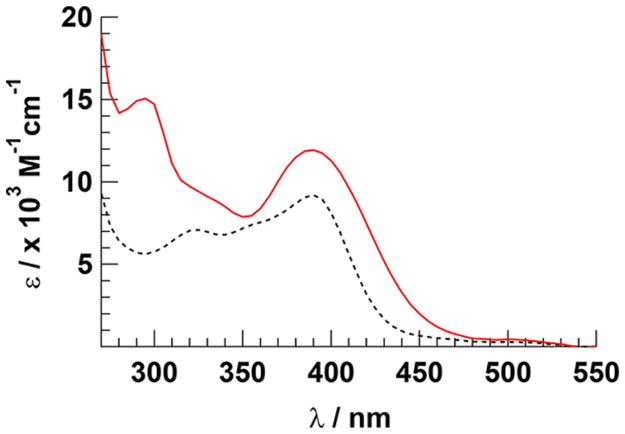
The electronic absorption spectra of the CH3CN complexes 1 and 2 are displayed in Figure 3 and exhibit 1MLCT-based absorption features with maxima at 390 nm (ε = 9200 M−1 cm−1 and 11 900 M−1 cm−1, respectively). Ligand-centered 3ππ* transitions of the ligands in 1 and 2 result in strong absorption in the ultraviolet range. The intensities of these transitions correlate well with those of [Ru(TPA)-(CH3CN)2]2+; however, the 1MLCT absorption of 2 is red-shifted as compared to those of 1 and [Ru(TPA)-(CH3CN)2]2+,56 attributed to the presence of the quinoline moiety in the tetradentate ligand (Figure 3). The pyridine complexes 3 and 4 exhibit 1MLCT transitions at 360 nm (ε = 12 800 M−1 cm−1 and 10 600 M−1 cm−1, respectively). Shoulders of this peak in 3 and 4 are observed at ~410 nm (ε ~ 9140 M−1 cm−1) and ~415 nm (ε ~ 8020 M−1 cm−1), respectively, that tail to ~500 nm (Figure S24, Supporting Information). The 1MLCT absorption maxima of 3 and 4 are red-shifted compared to the analogous CH3CN complexes, as is well-known for other cis-Ru(II) complexes coordinated by two CH3CN and py ligands.37,90 The quinoline moiety in 4 leads to a further red shift as compared to 3. Again, the intensities of these transitions are in good agreement with those of [Ru(TPA)(py)2]2+.57
Figure 3.
Electronic absorption spectra of 1 (black, dashed) and 2 (red, solid) in DMSO.
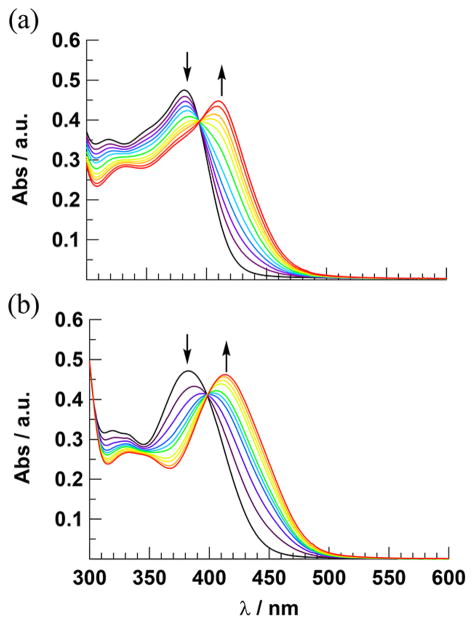
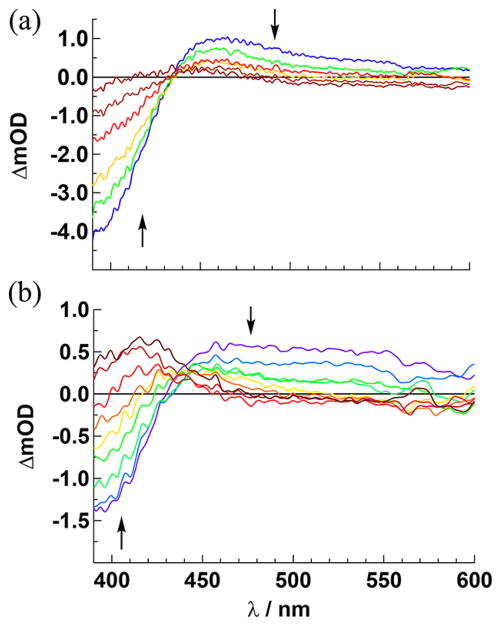
The irradiation of 1–4 in H2O (<5% acetone) results in changes to the absorption spectra of each complex (λirr ≥ 395 nm), whereas no changes are observed under similar conditions when the solutions of each complex are kept in the dark for at least 6 h (Figure S25, Supporting Information). The spectral changes observed for 1 and 2 are shown in Figure 4, and those for 3 and 4 appear in Figure S26 (Supporting Information). The photolysis of 1 is complete within 27 min, as no additional spectral changes are observed after this time. In contrast, the conversion of 2 to product is complete within only 9 min under similar experimental conditions. This difference in photo-chemical activity is reflected in the difference in the measured quantum yields, Φ400, for the two complexes (λirr = 400 nm, Table 1), where 2 is 5-fold more photoactive than 1. In contrast to the CH3CN complexes 1 and 2, those containing py at the N1 and N6 positions, 3 and 4, require at least 2 h of irradiation to reach completion under similar experimental conditions. The values of Φ400 for 3 and 4 are comparable, but both are ~30-fold lower than that measured for 2 (Table 1). The less efficient photochemistry of py Ru(II) complexes as compared to analogous CH3CN compounds is well documented in the literature.14,27,48,51
Figure 4.
Changes to the electronic absorption spectra upon irradiation (λirr ≥ 395 nm) of (a) 1 (tirr = 0–27 min) and (b) 2 (tirr = 0–9 min) in H2O (<5% acetone).
Table 1.
Photochemical and Photophysical Data for 1–4
| complex | Φ400a | lowest 3ESb | τTA/ps |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0066(3) | 3LF | 36c |
| 2 | 0.033(3) | 3MLCT/3ππ* | 42c |
| 3 | 0.0012(1) | 3LF | 160d |
| 4 | 0.0013(1) | 3LF | 120d |
H2O (<5% acetone) at 298 K.
From Mulliken Spin Density Calculations.
CH3CN.
Acetone.
During the photolysis of 1–4 in H2O, a decrease in the 1MLCT absorption band of each complex is observed with a concomitant increase in a peak at lower energies, as well as well-defined isosbestic points indicative of the formation of a single product from the reactant. For example, the irradiation of 2 in H2O results in a decrease of the 1MLCT absorption at 383 nm and a growth of a new absorption peak with maximum at 414 nm, resulting in an isosbestic point at 399 nm. On the basis of prior work on related complexes, it is expected that one of the CH3CN ligands in 1 and 2 and py in 3 and 4 exchanges with a solvent H2O molecule upon irradiation.
As discussed above, the ligand exchange quantum yield of 2 is 5-fold greater than that of 1, and it was shown in previous work that steric hindrance leads to enhanced ligand dissociation.91 The major structural difference between 1 and 2 is the substitution of the third pyridine in the cyTPA ligand in 1 for a quinoline moiety in the 1-isocyTPQA ligand in 2. However, the quinoline moiety in 2 is oriented away from the metal center, such that it is not expected to contribute to steric distortions around the metal or to weaken the Ru–N(CH3CN) bonds. In fact, the ground state bond lengths and angles observed in the X-ray crystal structures are similar between 1 and 2, inconsistent with a weaker Ru–N bond induced by steric clash. Therefore, it may be concluded that the increased quantum yield in 2 must be associated with differences in electronic structure afforded by the presence of the quinoline arm in 2 as compared to a pyridine arm in 1.
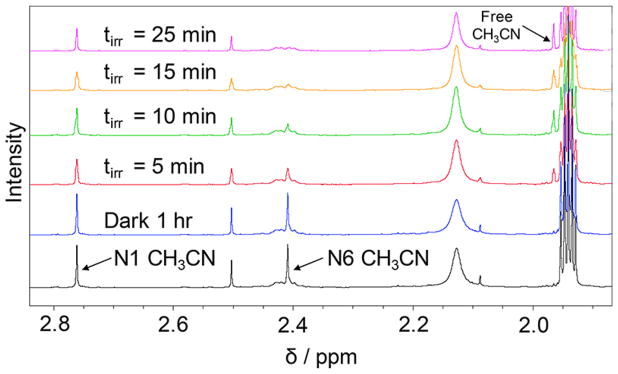
In order to gain additional structural information on the products formed upon irradiation, the photolyses of 1 and 2 were also followed using 1H NMR spectroscopy in CD3CN (Figure S27 and Figure 5, respectively). No spectral changes are observed for either complex in the dark in CD3CN (1 h). However, upon irradiation the resonance at 2.39 ppm in 1 (λirr ≥ 395 nm, 10 min) associated with the protons of the N6 CH3CN ligand cis to the basic nitrogen and trans to the pyridine arm of the cyTPA begins to decrease in intensity. A similar decrease is observed for the signal at 2.41 ppm upon irradiation of 2 (λirr ≥ 395 nm, 5 min), which corresponds to the bound N6 CH3CN ligand positioned cis to the basic nitrogen and trans to the quinoline arm of the 1-isocyTPQA ligand. This behavior is associated with the exchange of the bound CH3CN ligand for solvent CD3CN and continues until the process is complete. As expected, in both complexes there is an increase in intensity of the peak corresponding to free CH3CN, which appears at 1.96 ppm in CD3CN. Continued irradiation leads to the complete exchange of the N6 CH3CN ligand in 90 min for complex 1, a process that is complete in 25 min in 2. The aromatic regions of the NMR spectra of 1 and 2 remain unchanged throughout the photolysis experiments (Figures S28 and S29, respectively, Supporting Information), indicating that the only reaction is the exchange of CH3CN for CD3CN in the complex, thus retaining its electronic and structural characteristics.
Figure 5.
Comparison of the aliphatic region of the 1H NMR spectrum of 2 in CD3CN as initially prepared in the dark (black), after 1 h in the dark (blue), and at various irradiation times (λirr ≥ 395 nm).
CALCULATIONS
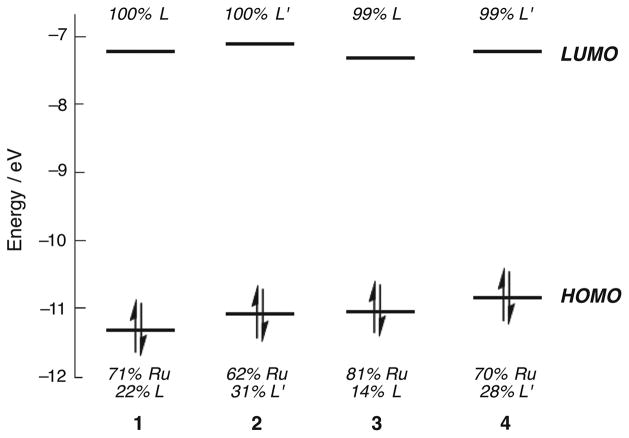
Density functional theory (DFT) calculations were utilized to gain a better understanding of the bonding and electronic structure of 1–4. Geometry optimizations for these complexes in the singlet ground state produced calculated structures in good agreement with crystallographic data (Tables S4–S7, Supporting Information), as well as ν(CN) of the CH3CN ligands of 1 and 2 that are in good agreement with experimental IR data. The electronic structures of these complexes in the ground state can be described by frontier molecular orbitals that are similar across the series. The HOMOs of 1–4 are mostly composed of Ru d-orbital character with some ligand mixing, featuring 70–81% metal localization in 1, 3, and 4 (Figure 6). Interestingly, the HOMO of 2 exhibits the lowest Ru d character, 62%, with the highest ligand mixing of the series. The LUMOs are exclusively either localized on the cyTPA ligand of 1 and 3 or 1-isocyTPQA of 2 and 4.
Figure 6.
Frontier molecular orbital diagram for complexes 1–4 in the ground state (L = cyTPA, L′ = 1-isocyTPQA).
Time-dependent DFT, TD-DFT, calculations for 1–4 show remarkable similarities for the four lowest energy transitions of the complexes, all of which involve the ruthenium metal center and the tetradentate ligand (Table S8, Supporting Information). The calculated lowest 1MLCT absorption bands of 1 and 3 exhibit Ru(dπ) → π*(cyTPA) character with energies of 26 500 cm−1 and 24 600 cm−1, respectively, which compare well with the corresponding experimental values of 25 800 cm−1 and 24 400 cm−1. Similarly, the lowest 1MLCT Ru(dπ) → π*(1-isocyTPQA) transitions are calculated for 2 at 25 600 cm−1 and 4 at 24 400 cm−1, in good agreement with the experimental maxima at 25 000 cm−1 and 24 200 cm−1, respectively. Notably, unlike 1, 3, and 4, one of the low-energy transitions calculated for 2 exhibits some mixing of ligand-centered 1-isocyTPQA 1ππ* character into the broad 1MLCT band and another is solely attributable to 1-isocyTPQA 1ππ* (Table S8). This finding is consistent with the larger amount of ligand mixing in the HOMO of 2, which is absent in 1, 3, and 4, as well as the participation of the ligand-centered HOMO–3 in the low energy transitions of 2.
Geometry optimizations and vibrational frequency calculations were also completed in the triplet states of 1–4. It should be noted that the optimized structures for 1, 3, and 4 yielded structures in which the Ru–N bonds of the tetradentate cyTPA and 1-isocyTPQA ligands were severely elongated in the triplet state, possibly suggesting facile dissociation of one of these arms in the excited state (Tables S4–S7). In contrast, these elongations were not observed in the optimized structure of the lowest triplet state of 2 (Table S5). These differences for 2 relative to the other complexes are of interest given its significantly more efficient ligand exchange upon irradiation.
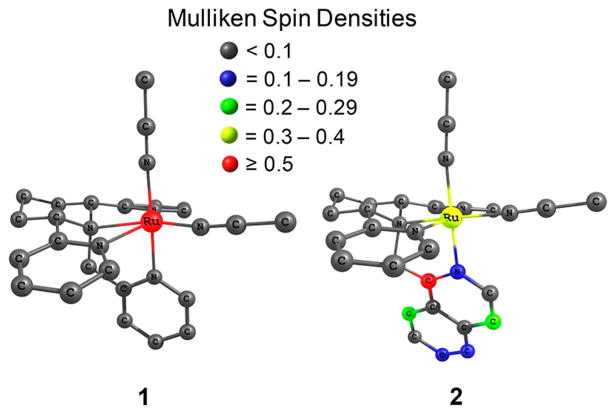
Mulliken spin density calculations were performed to determine the spin density on the Ru(II) center and to examine the nature of the triplet state. For complexes with a 3MLCT as the lowest energy triplet state, the Mulliken spin density on the ruthenium center should theoretically equal 1, indicative of one unpaired electron on the metal. Those complexes with a 3LF as the lowest energy triplet state should have a spin density of about 2 on the ruthenium center, indicating two unpaired electrons on the metal. Any complex with a spin density on the metal that is not close to values of 1 or 2 suggests some level of ligand mixing. For complexes 1, 3, and 4, the Mulliken spin densities on the Ru(II) center were calculated to be 1.63, 1.75, and 1.73, respectively. These spin densities are consistent with a 3LF state as the lowest energy triplet state with some spin localization on the ligands. Surprisingly, for complex 2, the Mulliken spin density on the metal was calculated to be 0.37, which is extremely low for a 3MLCT state and is more consistent with significant mixing from a ligand-centered state. Figure 7 shows a comparison of the Mulliken spin densities on the atoms of complexes 1 and 2. Notably, the majority of the spin density in 2 is localized on the quinoline arm of the 1-isocyTPQA ligand, with only minimal contributions from other atoms.
Figure 7.
Mulliken spin densities of the lowest energy triplet state calculated for 1 and 2.
Although 2 exhibits the most efficient photoinduced CH3CN ligand exchange with solvent, it is surprising that it is the only complex in the series that does not feature a 3LF state as the lowest energy triplet state. It should be noted, however, that the 3LF states of 1, 3, and 4 appear to be dissociative taking into account the elongated bonds of the tetradentate ligand. This result indicates that if the 3LF state is accessed in these complexes, then an arm of the tetradentate ligand may be dissociated upon irradiation, which would likely recoordinate without resulting in an overall chemical transformation. Therefore, irradiation of these complexes would not result in the exchange of CH3CN in 1 or py in 3 and 4.
1H NMR spectroscopy shows that the CH3CN ligand that dissociates more readily in 2 is positioned trans to the quinoline moiety in the tetradentate ligand. In general, σ-donation from py- and quinoline-type ligands is stronger than that of nitrile-containing ligands. Instead, the CH3CN ligand relies heavily on π-back-donation for bonding to ruthenium. Charge decomposition analysis (CDA), a theoretical method used to quantify the total electron donation and back-donation between the metal and each ligand, was used to determine these quantities in 1 and 2. The back-donation from the Ru center to the photolabile N6 CH3CN ligand in 2 decreases by 23% in the triplet state as compared to the singlet ground state, as the ruthenium center is partially oxidized in the excited state (Table S17, Supporting Information). The corresponding cyTPA complex, 1, possesses a py moiety rather than quinoline in the tetradentate ligand, and shows a decrease in back-donation to the CH3CN ligand from the singlet state to the triplet state of less than 10%.
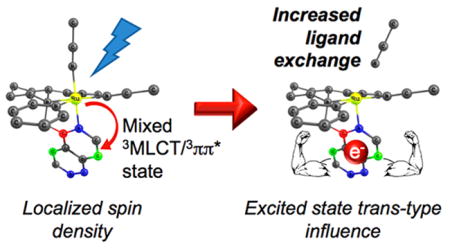
This trend was further examined by analyzing the Mayer bond orders (MBOs) of the Ru–N bonds. MBOs offer insight into the relative covalency vs ionicity of a bond and are an extension of Wiberg bond orders, a classical view of bonding, and can be related to the bond strength.92 Previous theoretical studies have shown that MBO analysis is a useful tool in describing bonding in transition metal systems.92–97 For 2, the MBO analysis shows a dramatic 57% increase in Ru–N(quinoline) bond strength and a 14% decrease in Ru–N(CH3CN) bond strength in the CH3CN ligand trans to the quinoline moiety (N6 CH3CN) in the triplet state. The quinoline moiety, therefore, exerts a trans-type influence on this CH3CN ligand, greatly weakening the Ru–N(CH3CN) bond, promoting dissociation in the triplet excited state. This weakening does not occur in the corresponding py complex, 4, due to the similar σ–bond strengths between quinoline and the leaving py ligand. In this complex, the MBO of the Ru–N(py) decreases only by ~2% in the triplet state, while the Ru–N(quinoline) MBO increases by 3%. A similar trend is observed for complexes 1 and 3 at the same positions, but with increased MBOs calculated from the ground state to the lowest triplet state for both Ru–N(CH3CN) and Ru–N(py) bonds, respectively (Table 2). The observation of trans influence and trans effect in ruthenium complexes has been reported previously, specifically with phosphine and py-type ligands in the ground state.98–101 To our knowledge, there are no reports of trans influence in the excited state that directly results in ligand dissociation. From the results of the Mulliken spin density calculations, in combination with the CDA and MBO analyses, it may be inferred that the high quantum yield of ligand dissociation observed for 2 is associated with the high spin density localized on the quinoline moiety in the mixed 3MLCT/3ππ* excited state. This 3MLCT/3ππ* state must induce a trans-type influence, allowing for efficient ligand dissociation of the N6 CH3CN ligand.
Table 2.
MBO Analysis for 1–4 in the Ground State Singlet and Lowest Energy Triplet State
| complex | Ru–N6a | Ru–N5b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||
| singlet | triplet | singlet | triplet | |
| 1 | 0.611 | 0.612 | 0.434 | 0.446 |
| 2 | 0.599 | 0.518 | 0.415 | 0.652 |
| 3 | 0.164 | 0.168 | 0.397 | 0.421 |
| 4 | 0.148 | 0.144 | 0.369 | 0.380 |
N atom of CH3CN in 1 and 2 and py in 3 and 4.
N atom of py arm of cyTPA in 1 and 3 and quinoline arm of 1-isocyTPQA in 2 and 4.
Time-Resolved Spectroscopy
Ultrafast transient absorption spectroscopy was used to compare the nature of the excited states of 1 and 2, since the latter undergoes ligand exchange with 5-fold greater efficiency than the former. In addition, the transient absorption spectra of 3 and 4 were also collected and are shown in the Supporting Information. It is well established that intersystem crossing (ISC) from the 1MLCT to the 3MLCT state occurs within 15–40 fs in [Ru(bpy)3]2+, as well as in other Ru(II) polypyridyl and related complexes.90,102,103 As such, the transient absorption signals observed for 1 and 2 after excitation of the 1MLCT state can be attributed to states in the triplet manifold due to the ~85 fs pulse employed in the present experiments.104
The transient absorption spectra of 2 collected in CH3CN following 350 nm excitation are shown in Figure 8a (fwhm = 85 fs), and consist of a ground state bleach from 390 to 438 nm, with positive absorption from 438 to 600 nm and an isosbestic point at 438 nm. Both the bleach at 400 nm and the positive signal with maximum at 465 nm decay monoexponentially with τ = 42 ps (Table 1). No spectral changes are observed from 200 fs to 1 ps (Figure S34a, Supporting Information). The intensity and position of the positive absorption is consistent with a 3MLCT state, similar to the spectral features of 3MLCT states 2+ of related Ru(II) complexes, including [Ru(bpy)2(CH3CN)2] in CH3CN.90 In addition, the simulated transient absorption spectrum of 2 shown in Figure S35b (Supporting Information), created from the subtraction of the calculated absorption spectrum of 3MLCT/3ππ* state and that of the ground state, agrees fairly well with experiment. The lifetime of 2 in CH3CN is similar to that reported for [Ru(bpy)2(CH3CN)2]2+ in the same solvent, 50 ps.90 In CH3CN, the photoinduced ligand exchange of 2 does not result in a product that is different than the starting material, such that any kinetics that may be associated with that process are not observed. These results are consistent with the formation of the 3MLCT/3ππ* state of 2 within the laser pulse, and that this state decays to regenerate the ground state with τ = 42 ps in CH3CN. The short lifetime of the 3MLCT/3ππ* state can be attributed to competing ligand dissociation.
Figure 8.
Transient absorption spectra of 2 in (a) CH3CN collected at 0.4, 8, 20, 51, 99, and 285 ps, and (b) acetone collected at 1, 3, 8, 17, 39 51, 192, 718, and 2681 ps following the laser pulse (λexc = 350 nm, fwhm = 85 fs, baseline collected at −20 ps).
When the transient absorption experiment is conducted in acetone under similar conditions (Figure 8b), the irreversible formation of the ligand exchange product, [Ru(1-isocyTPQA)-(CH3CN)(acetone)]2+, is observed at long delay times consistent with the spectral changes measured during steady-state photolysis. At earlier times, 1–17 ps, a broad positive signal is observed in the 450–600 nm range which can be fitted to a monoexponential decay with τ = 36 ps. Although the photoproduct absorbs in the 390–440 nm range, the kinetics of the bleach signal at 400 nm are also monoexponential with τ = 36 ps. It should be noted that there are no spectral changes from 100 fs to 1 ps (Figure S34b, Supporting Information). In addition, a power dependence of the product formed in the ultrafast experiment in acetone is consistent with a one-photon process (Figure S36).
Because of the overlap between the bleach signal and that of the product in Figure 8b, the kinetics of product formation could not be measured independently. There are two possibilities for the observation of the same monoexponential time constant for the bleach signal at 390 nm that overlaps with the product absorption and the positive 3MLCT signal at 500 nm, namely that the product is formed directly from the 3MLCT state or that it is generated within the laser pulse and its signal does not change throughout the experiment. In the latter scenario, the ligand exchange dynamics do not contribute to the transient absorption signal in the 1 ps –2.68 ns range, such that the signal of the last trace of Figure 8b collected at 2.68 ns would have been present at all time delays. In the case where the product is formed from the 3MLCT state, the signal in Figure 8b collected at early times would have little contribution from product, and the absorption of the latter would increase exponentially with the measured time constant of 36 ps. A series of additions of product signal collected at 2.68 ns in Figure 8b to the signal from the pure 3MLCT (Figure 8a) were undertaken as described in detail in the Supporting Information and shown in Figure S37. Two exemplary time points at early and late times in the decay, 8 ps (Figure S37c) and 51 ps (Figure S37d), respectively, are used to compare the simulated signals which are consistent with the formation of the photoproduct from the 3MLCT state and not within the laser pulse.
The transient absorption spectra collected for 1 in CH3CN are similar to those of 2 in the same solvent and are shown in Figure S38 (Supporting Information, λexc = 350 nm, fwhm = 85 fs). The dominant features are the ground state bleach at ~390 nm and a broad positive transient absorption signal in the 430–600 nm range with maximum at ~460 nm. Both features decay monoexponentially with τ = 36 ps to regenerate the ground state (Table 1). Similar absorption and bleach signals were observed for 1 in acetone with τ = 34 ps. The low quantum yield for ligand exchange in this complex precludes the observation of different kinetics in CH3CN and acetone in 1. Although the lowest energy triplet state of 1 was calculated to be 3LF in nature, from the intensity of the observed excited state absorption, together with spectral and kinetic similarities to 2 and other Ru(II) polypyridyl complexes, it may be concluded that the state observed with 34–36 ps lifetime is the 3MLCT, not the 3LF. In addition, it is evident that the calculated transient absorption spectrum of the 3LF state shown in Figure S39 (Supporting Information) features ~10-fold lower intensity of the positive signal as compared to that calculated for 2, inconsistent with the experimental data.
The transient absorption spectra of 3 and 4 are shown in Figure S40 (Supporting Information) and exhibit similar features that are red-shifted compared to those of 1 and 2, respectively. Complex 3 exhibits a ground state bleach at 420 nm and a weak positive transient absorption signal from 470 to 600 nm with τ = 160 ps (Table 1). The identical, monoexponential kinetics of the positive signal and the bleach measured for 3 are indicative of the population of a single state within the laser pulse that returns to the ground state. Similarly, the spectral features of 4 are red-shifted relative to those of the corresponding CH3CN complex, 2, and features a ground state bleach at 420 nm and a positive transient absorption signal at >480 nm (Figure S40). These signals decay monoexponentially with τ = 120 ps (Table 1). The 3LF state was calculated as the lowest energy triplet state in both 3 and 4, with simulated transient absorption spectra for these complexes shown in Figures S41 and S42, respectively (Supporting Information). As is the case with 1, the positive signal observed for 3 and 4 is significantly stronger than expected for a metal-centered state and can be assigned as 3MLCT states. The broad spectral profiles throughout the visible range are similar to those previously reported for the 3MLCT excited states of the related complexes [Ru(bpy)2(py)2]2+ and [Ru(bpy)2(NA)2]2+ (NA = nicotinamide), respectively.105–107
Excited State Populations and Ligand Exchange
Although the minimized 3LF state lies at a lower energy than the 3MLCT state in 1, the latter is observed in the time-resolved absorption spectrum. A possible explanation for this behavior is that ISC from the 1MLCT populates the 3MLCT state in <100 fs, as is typically observed in related Ru(II) polypyridyl complexes.102,103 Displacement of the 3LF potential energy surface along a given nuclear coordinate, such as elongation of one or more Ru–N bonds in the triplet state, would require that the system overcome an activation barrier to reach the 3LF state (Figure 9). Inspection of Tables S4–S7 reveal that indeed two of the Ru–N bonds to the tetradentate ligand, Ru–N3 and Ru–N4 in 1, and Ru–N2 and Ru–N4 in 3 and 4, are significantly elongated in the 3LF state as compared to the ground state. It is evident from Table S4 that the Ru–N3 and Ru–N4 bonds in 1 are elongated by 0.27 and 0.34 Å, respectively, whereas one of the Ru–N(CH3CN) bonds lengthens by 0.05 Å and the other contracts by 0.01 Å.
Figure 9.
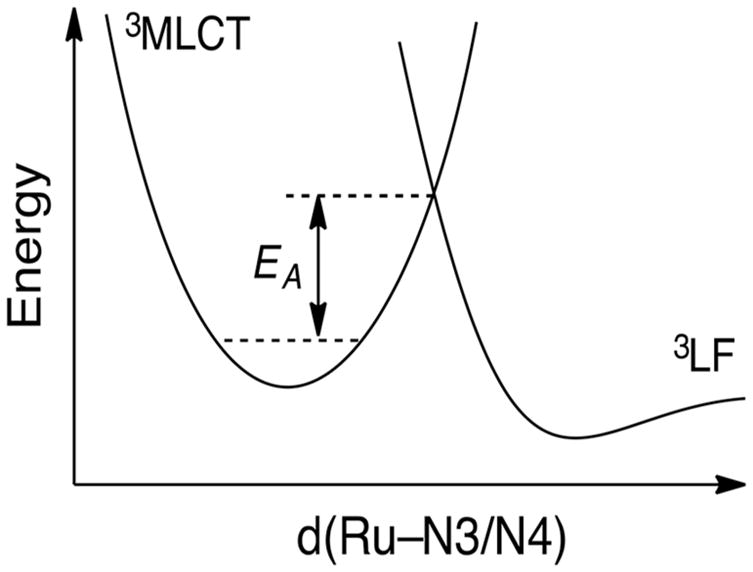
Schematic representation of the relative energies of the 3MLCT and 3LF potential energy surfaces in 1.
For comparison, the calculated bond changes in the 3MLCT/3ππ* state of 2 show a small contraction of three of the four Ru–N bonds to the 1-isocyTPQA ligand of <0.035 Å, while the Ru–N2 bond lengthens by only 0.015 Å. Therefore, significant structural changes are expected from the ground and 3MLCT states of 1 to the 3LF state, resulting in a high activation barrier to populate the 3LF state. The observation of the 3MLCT instead of the lowest energy 3LF states in the transient absorption of 1, explained by a high activation barrier to populate the 3LF state from the vibrationally cooled 3MLCT state, is consistent with the low quantum yield for ligand exchange in this complex and a lifetime that is similar to that of 2 and related complexes. Similar arguments can be made for complexes 3 and 4, which exhibit elongation of two of the RuN bonds to the tetradentate ligand of ≥0.3 Å.
CONCLUSIONS
A series of Ru(II) polypyridyl complexes containing two different tetradentate-based frameworks were synthesized and their effectiveness for use as photocages to deliver nitrile or pyridine ligands upon irradiation was explored. The quantum yield for the CH3CN/H2O ligand exchange of 2 was measured to be Φ400 = 0.033(3), 5-fold greater than that of 1, Φ400 = 0.0066(3), although this effect cannot be attributed to steric crowding in the former. DFT and related calculations show the presence of a highly mixed 3MLCT/3ππ* excited state as the lowest triplet state in 2, whereas the lowest energy triplet state in 1, 3, and 4 was calculated to be 3LF in nature. The mixed 3MLCT/3ππ* excited state places significant spin density on the quinoline moiety of the 1-isocyTPQA ligand that is trans to the photolabile N6 CH3CN ligand in 2. Additionally, MBO analysis reveals that in the triplet state of 2, the Ru–N(quinoline) bond strength increases while the Ru–N-(CH3CN) bond strength of the photolabile N6 CH3CN ligand decreases compared to the singlet ground state, suggesting the presence of a trans-type influence in the excited state that leads to the higher value of Φ400 measured in 2. The result that complexes with 3LF lowest energy excited states were less photolabile than that with 3MLCT/3ππ* lowest energy excited state is counter to the general understanding of Ru(II) photochemistry. Ultrafast spectroscopy was used to probe the excited states of 1–4, which reveal that the 3LF states are not populated in 1, 3, and 4, consistent with the low yields of ligand exchange product upon irradiation in these complexes. This unusual result is explained by the large elongation of two RuN bonds of the tetradentate ligands in these complexes, thus increasing the activation energy from the 3MLCT to the 3LF states in 1, 3, and 4.
Mixed 3MLCT/3ππ* excited states that promote ligand dissociation, such as that of 2, represent a new manner to effect photoinduced ligand exchange. In addition, 3MLCT deactivation through the lower-lying 3LF state was shown to be avoided through significant structural changes around the metal center in the latter. Both concepts can be used to design improved complexes for applications that require efficient ligand dissociation, such as drug delivery, as well as for those that require minimal deactivation of the 3MLCT state through low-lying metal-centered states. As such, these findings are expected to be useful to fields from photochemotherapy to solar energy conversion and sensing.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Institutes of Health (EB 016072) for their generous support, the Center for Chemical and Biophysical Dynamics (CCBD) at OSU, and the Ohio Supercomputer Center. C.T. acknowledges the partial support from the National Science Foundation (CHE-1465067).
Footnotes
ASSOCIATED CONTENT
The Supporting Information is available free of charge on the ACS Publications website at DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b09937.
Structural characterization data for ligands and complexes 1–4, X-ray crystallographic data for 1–3, electronic absorption data for 3–4, dark controls, 1H NMR photolysis of 1–2, experimental and calculated bond lengths and frequencies, TD-DFT energies and assignments, optimized ground and excited state atomic coordinates, charge decomposition analysis, calculated molecular orbital energy diagrams, experimental setup of transient absorption spectrometer, and additional experimental and simulated transient absorption data (PDF)
Notes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
References
- 1.Balzani V, Bergamini G, Ceroni P. Coord Chem Rev. 2008;252:2456. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Balzani V, Moggi L. Coord Chem Rev. 1990;97:313. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bonnet S, Collin JP. Chem Soc Rev. 2008;37:1207. doi: 10.1039/b713678c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bruijnincx PCA, Sadler PJ. Controlling Platinum, Ruthenium, and Osmium Reactivity for Anticancer Drug Design. In: van Eldik R, Hubbard CD, editors. Adv Inorg Chem. Vol. 61. Academic Press; Burlington, MA: 2009. pp. 1–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ceroni P, Credi A, Venturi M. Chem Soc Rev. 2014;43:4068. doi: 10.1039/c3cs60400d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Grätzel M. Inorg Chem. 2005;44:6841. doi: 10.1021/ic0508371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kalyanasundaram K, Graetzel M. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2010;21:298. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2010.03.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kalyanasundaram K. Coord Chem Rev. 1982;46:159. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Smith NA, Sadler PJ. Philos Trans R Soc, A. 2013;371:20120519. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2012.0519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Romanova J, Sadik Y, Ranga Prabhath MR, Carey JD, Jarowski PD. J Phys Chem C. 2017;121:2333. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.9b03019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pan J, Jiang L, Chan CF, Tsoi TH, Shiu KK, Kwong DWJ, Wong WT, Wong WK, Wong KL. J Lumin. 2017;184:89. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zigler DF, Morseth ZA, White TA, Canterbury TR, Sayre HJ, Rodríguez-Corrales JÁ, Brennaman MK, Brewer KJ, Papanikolas JM. Inorg Chim Acta. 2017;454:266. [Google Scholar]
- 13.O’Donnell RM, Sampaio RN, Li G, Johansson PG, Ward CL, Meyer GJ. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138:3891. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b00454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Knoll JD, Albani BA, Turro C. Acc Chem Res. 2015;48:2280. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ghosh R, Palit DK. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2014;16:219. doi: 10.1039/c3cp53886a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Horvath R, Lombard J, Leprêtre JC, Collomb MN, Deronzier A, Chauvin J, Gordon KC. Dalt Trans. 2013;42:16527. doi: 10.1039/c3dt52153b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Serpone N, Pelizzetti E, Gratzel M. Coord Chem Rev. 1985;64:225. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Thompson DW, Ito A, Meyer TJ. Pure Appl Chem. 2013;85:1257. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhang Y, Galoppini E, Johansson PG, Meyer GJ. Pure Appl Chem. 2011;83:861. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kärkäs MD, Johnston EV, Verho O, Åkermark B. Acc Chem Res. 2014;47:100. doi: 10.1021/ar400076j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hammarström L. Acc Chem Res. 2015;48:840. doi: 10.1021/ar500386x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hartings MR, Kurnikov IV, Dunn AR, Winkler JR, Gray HB, Ratner MA. Coord Chem Rev. 2010;254:248. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.08.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Anderson BL, Maher AG, Nava M, Lopez N, Cummins CC, Nocera DG. J Phys Chem B. 2015;119:7422. doi: 10.1021/jp5110505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lo KKW, Li SPY. RSC Adv. 2014;4:10560. [Google Scholar]
- 25.King AW, McClure BA, Jin Y, Rack JJ. J Phys Chem A. 2014;118:10425. doi: 10.1021/jp504078g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Weidmann AG, Komor AC, Barton JK. Comments Inorg Chem. 2014;34:114. doi: 10.1080/02603594.2014.890099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Knoll JD, Turro C. Coord Chem Rev. 2015;282–283:110. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.05.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Joshi T, Gasser G. Synlett. 2015;26:275. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Barragán F, López-Senín P, Salassa L, Betanzos-Lara S, Habtemariam A, Moreno V, Sadler PJ, Marchán V. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:14098. doi: 10.1021/ja205235m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Howerton BS, Heidary DK, Glazer EC. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:8324. doi: 10.1021/ja3009677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Shi G, Monro S, Hennigar R, Colpitts J, Fong J, Kasimova K, Yin H, DeCoste R, Spencer C, Chamberlain L, Mandel A, Lilge L, McFarland SA. Coord Chem Rev. 2015;282–283:127. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Loftus LM, White JK, Albani BA, Kohler L, Kodanko JJ, Thummel RP, Dunbar KR, Turro C. Chem - Eur J. 2016;22:3704. doi: 10.1002/chem.201504800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Campagna S, Puntoriero F, Nastasi F, Bergamini G, Balzani V. Photochemistry and Photophysics of Coordination Compounds: Ruthenium. In: Balzani V, Campagna S, editors. Photochemistry and Photophysics of Coordination Compounds I. Vol. 280. Springer-Verlag; Berlin: 2007. pp. 117–214. Topics in Current Chemistry. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Malouf G, Ford PC. J Am Chem Soc. 1974;96:601. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Caspar JV, Meyer TJ. Inorg Chem. 1983;22:2444. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Durham B, Caspar JV, Nagle JK, Meyer TJ. J Am Chem Soc. 1982;104:4803. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Durham B, Walsh JL, Carter CL, Meyer TJ. Inorg Chem. 1980;19:860. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Allen GH, White RP, Rillema DP, Meyer TJ. J Am Chem Soc. 1984;106:2613. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wacholtz WM, Auerbach RA, Schmehl RH, Ollino M, Cherry WR. Inorg Chem. 1985;24:1758. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sun Q, Mosquera-Vazquez S, Suffren Y, Hankache J, Amstutz N, Daku LML, Vauthey E, Hauser A. Coord Chem Rev. 2015;282–283:87. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Van Houten J, Watts RJ. J Am Chem Soc. 1976;98:4853. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wagenknecht PS, Ford PC. Coord Chem Rev. 2011;255:591. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Tfouni E. Coord Chem Rev. 2000;196:281. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sun Q, Mosquera-Vazquez S, Daku LML, Guénée L, Goodwin HA, Vauthey E, Hauser A. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:13660. doi: 10.1021/ja407225t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Malouf G, Ford PC. J Am Chem Soc. 1977;99:7213. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tfouni E, Ford PC. Inorg Chem. 1980;19:72. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Henderson LJ, Jr, Fronczek FR, Cherry WR. J Am Chem Soc. 1984;106:5876. [Google Scholar]
- 48.White JK, Schmehl RH, Turro C. Inorg Chim Acta. 2017;454:7. doi: 10.1016/j.ica.2016.06.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wacholtz WF, Auerbach RA, Schmehl RH. Inorg Chem. 1986;25:227. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ross HB, Boldaji M, Rillema DP, Blanton CB, White RP. Inorg Chem. 1989;28:1013. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Pinnick DV, Durham B. Inorg Chem. 1984;23:1440. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Juris A, Balzani V, Barigelletti F, Campagna S, Belser P, von Zelewsky A. Coord Chem Rev. 1988;84:85. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Van Houten J, Watts RJ. Inorg Chem. 1978;17:3381. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Porter GB, Sparks RH. J Photochem. 1980;13:123. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Tachiyashiki S, Mizumachi K. Coord Chem Rev. 1994;132:113. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sharma R, Knoll JD, Martin PD, Podgorski I, Turro C, Kodanko JJ. Inorg Chem. 2014;53:3272. doi: 10.1021/ic500299s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Li A, White JK, Arora K, Herroon MK, Martin PD, Schlegel HB, Podgorski I, Turro C, Kodanko JJ. Inorg Chem. 2016;55:10. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5b02600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Sharma R, Knoll JD, Ancona N, Martin PD, Turro C, Kodanko JJ. Inorg Chem. 2015;54:1901. doi: 10.1021/ic502791y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Tu YJ, Mazumder S, Endicott JF, Turro C, Kodanko JJ, Schlegel HB. Inorg Chem. 2015;54:8003. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5b01202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Chen G, Crawford J, Skerlj R. Methods of Making 2,6-Diaryl Piperidine Derivatives. US 20050154201. US Patent Appl. 2005 Jun 14;
- 61.Mikata Y, Yamanaka A, Yamashita A, Yano S. Inorg Chem. 2008;47:7295. doi: 10.1021/ic8002614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc; Madison, WI: 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Sheldrick GM. SADABS. University of Göttingen; Göttingen, Germany: 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Dolomanov OV, Bourhis LJ, Gildea RJ, Howard JAK, Puschmann H. J Appl Crystallogr. 2009;42:339. doi: 10.1107/S0021889811041161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sheldrick GM. Acta Crystallogr, Sect A: Found Crystallogr. 2008;A64:112. doi: 10.1107/S0108767307043930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Sheldrick GM. Acta Crystallogr, Sect C: Struct Chem. 2015;C71:3. doi: 10.1107/S2053229614024218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Sheldrick GM. Acta Crystallogr, Sect A: Found Adv. 2015;A71:3. doi: 10.1107/S2053273314026370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Montalti M, Credi A, Prodi L, Gandolfi MT. Handbook of Photochemistry. 3. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL: 2006. Chemical Actinometry; pp. 601–616. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Caricato M, Li X, Hratchian HP, Izmaylov AF, Bloino J, Zheng G, Sonnenberg JL, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Vreven T, Montgomery JA, Jr, Peralta JE, Ogliaro F, Bearpark M, Heyd JJ, Brothers E, Kudin KN, Staroverov VN, Keith T, Kobayashi R, Normand J, Raghavachari K, Rendell A, Burant JC, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Cossi M, Rega N, Millam JM, Klene M, Knox JE, Cross JB, Bakken V, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R, Stratmann RE, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C, Ochterski JW, Martin RL, Morokuma K, Zakrzewski VG, Voth GA, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Dapprich S, Daniels AD, Farkas O, Foresman JB, Ortiz JV, Cioslowski J, Fox DJ. Gaussian 09, revision E01. Gaussian, Inc; Wallingford, CT: 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Andrae D, Häußermann U, Dolg M, Stoll H, Preuß H. Theor Chim Acta. 1990;77:123. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Schäfer A, Huber C, Ahlrichs R. J Chem Phys. 1994;100:5829. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M. Phys Rev Lett. 1996;77:3865. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M. Phys Rev Lett. 1997;78:1396. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Becke AD. J Chem Phys. 1993;98:1372. [Google Scholar]
- 75.Lee C, Yang W, Parr RG. Phys Rev B: Condens Matter Mater Phys. 1988;37:785. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.37.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Miehlich B, Savin A, Stoll H, Preuss H. Chem Phys Lett. 1989;157:200. [Google Scholar]
- 77.Tomasi J, Mennucci B, Cammi R. Chem Rev. 2005;105:2999. doi: 10.1021/cr9904009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Dapprich S, Frenking G. J Phys Chem. 1995;99:9352. [Google Scholar]
- 79.Gorelsky SI, Ghosh S, Solomon EI. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:278. doi: 10.1021/ja055856o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Gorelsky SI. AOMix: Program for Molecular Orbital Analysis, version 6.85. 2015 http://www.sg-chem.net/
- 81.Gorelsky SI, Lever ABP. J Organomet Chem. 2001;635:187. [Google Scholar]
- 82.Gorelsky SI, Basumallick L, Vura-Weis J, Sarangi R, Hodgson KO, Hedman B, Fujisawa K, Solomon EI. Inorg Chem. 2005;44:4947. doi: 10.1021/ic050371m. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Gorelsky SI, Solomon EI. Theor Chem Acc. 2008;119:57. [Google Scholar]
- 84.Burdzinski G, Hackett JC, Wang J, Gustafson TL, Hadad CM, Platz MS. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:13402. doi: 10.1021/ja061520i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Nakayama T, Amijima Y, Ibuki K, Hamanoue K. Rev Sci Instrum. 1997;68:4364. [Google Scholar]
- 86.Marcu L, French PMW, Elson DS, editors. Fluorescence Lifetime Spectroscopy and Imaging: Principles and Applications in Biomedical Diagnostics. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL: 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 87.Kojima T, Amano T, Ishii Y, Ohba M, Okaue Y, Matsuda Y. Inorg Chem. 1998;37:4076. doi: 10.1021/ic971049h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Heeg MJ, Kroener R, Deutsch E. Acta Crystallogr, Sect C: Cryst Struct Commun. 1985;C41:684. [Google Scholar]
- 89.Hitchcock PB, Seddon KR, Turp JE, Yousif YZ, Zora JA, Constable EC, Wernberg O. J Chem Soc, Dalton Trans. 1988:1837. [Google Scholar]
- 90.Liu Y, Turner DB, Singh TN, Angeles-Boza AM, Chouai A, Dunbar KR, Turro C. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:26. doi: 10.1021/ja806860w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Knoll JD, Albani BA, Durr CB, Turro C. J Phys Chem A. 2014;118:10603. doi: 10.1021/jp5057732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Bridgeman AJ, Cavigliasso G, Ireland LR, Rothery J. J Chem Soc Dalt Trans. 2001:2095. [Google Scholar]
- 93.Bridgeman AJ. J Chem Soc, Dalton Trans. 1996:2601. [Google Scholar]
- 94.Bridgeman AJ. J Chem Soc, Dalton Trans. 1997:4765. [Google Scholar]
- 95.Bridgeman AJ, Bridgeman CH. Chem Phys Lett. 1997;272:173. [Google Scholar]
- 96.Bridgeman AJ, Rothery J. J Chem Soc Dalt Trans. 2000:211. [Google Scholar]
- 97.Fillman KL, Przyojski JA, Al-Afyouni MH, Tonzetich ZJ, Neidig ML. Chem Sci. 2015;6:1178. doi: 10.1039/c4sc02791d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Harada T, Wada S, Yuge H, Miyamoto TK. Acta Crystallogr, Sect C: Cryst Struct Commun. 2003;C59:m37. doi: 10.1107/s0108270102022461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Galardon E, Le Maux P, Toupet L, Simonneaux G. Organometallics. 1998;17:565. [Google Scholar]
- 100.Johnson BA, Agarwala H, White TA, Mijangos E, Maji S, Ott S. Chem - Eur J. 2016;22:14870. doi: 10.1002/chem.201601612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Da Silva ACH, Da Silva JLF, Franco DW. Dalt Trans. 2016;45:4907. doi: 10.1039/c5dt03706a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.(a) Bhasikuttan AC, Suzuki M, Nakashima S, Okada T. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:8398. doi: 10.1021/ja026135h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Sun Y, Liu Y, Turro CJ. Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:5594. doi: 10.1021/ja101703w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Cannizzo A, Van Mourik F, Gawelda W, Zgrablic G, Bressler C, Chergui M. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2006;45:3174. doi: 10.1002/anie.200600125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Damrauer NH, Cerullo G, Yeh A, Boussie TR, Shank CV, McCusker JK. Science. 1997;275:54. doi: 10.1126/science.275.5296.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Borfecchia E, Garino C, Gianolio D, Salassa L, Gobetto R, Lamberti C. Catal Today. 2014;229:34. [Google Scholar]
- 106.Borfecchia E, Garino C, Salassa L, Ruiu T, Gianolio D, Zhang X, Attenkofer K, Chen LX, Gobetto R, Sadler PJ, Lamberti C. Dalt Trans. 2013;42:6564. doi: 10.1039/c3dt32865a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Greenough SE, Roberts GM, Smith NA, Horbury MD, McKinlay RG, Żurek JM, Paterson MJ, Sadler PJ, Stavros VG. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2014;16:19141. doi: 10.1039/c4cp02359e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.