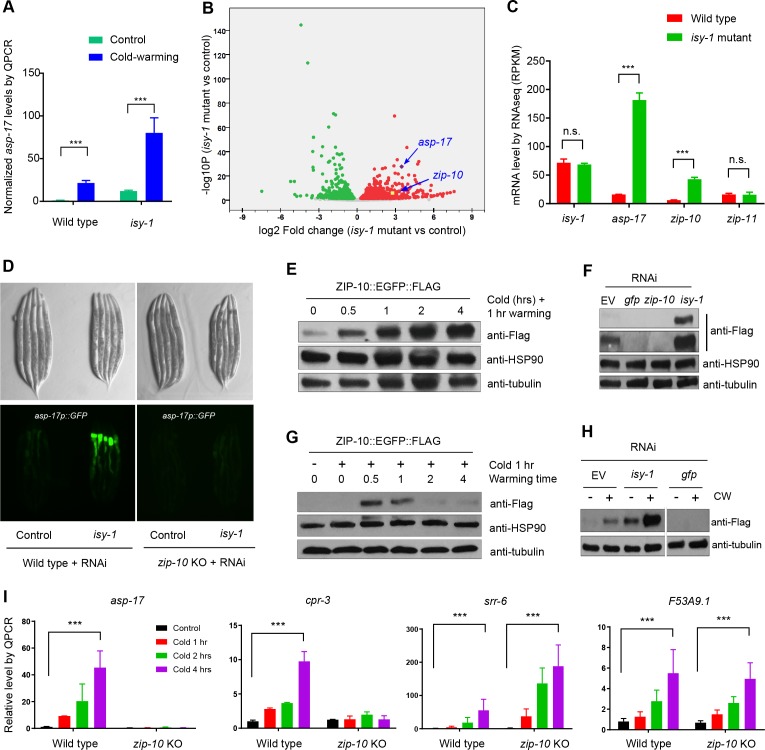
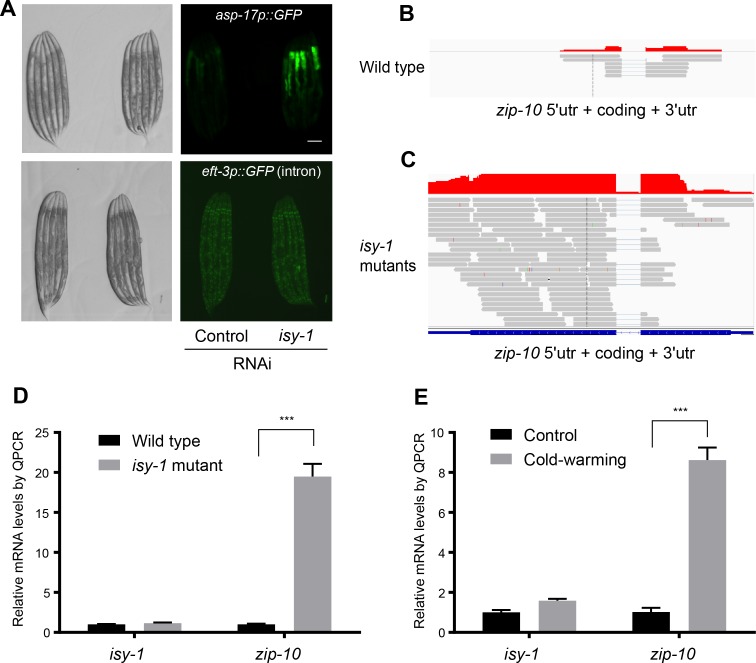
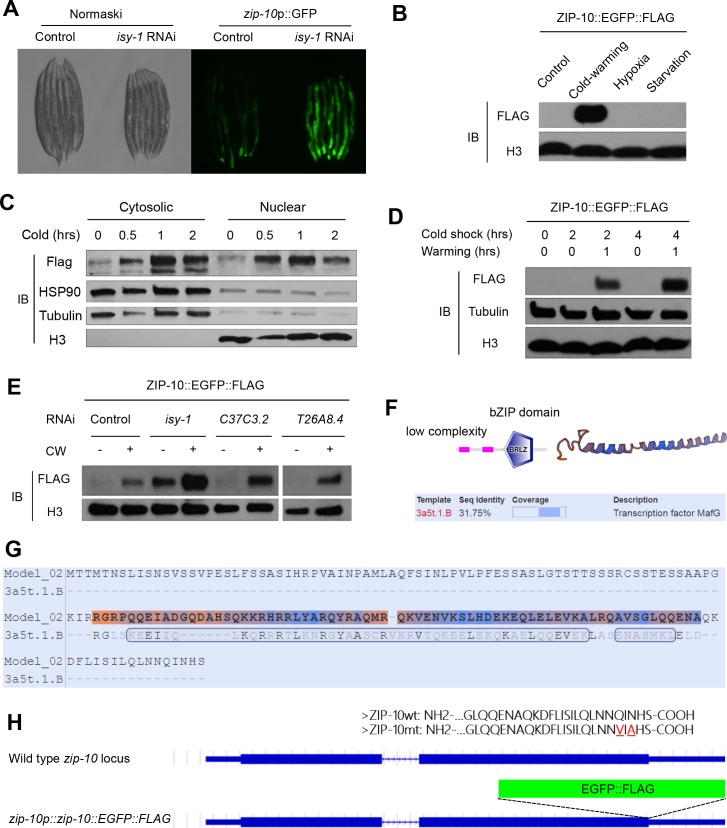
Figure 3. ZIP-10 acts downstream of ISY-1 and mediates transcriptional response to CW.
(A) QPCR measurements of asp-17 levels induced by CW in wild type and isy-1(dma50) mutants. (B) Volcano plot of RNA-seq showing differentially regulated genes (up-regulated genes in red; down-regulated genes in green) in isy-1 mutants compared with wild type. (C) RNA-seq measurements of expression levels for indicated genes in wild type and isy-1(dma50) mutants. (D) Nomarski and fluorescence images showing asp-17p::GFP induction by isy-1 RNAi was blocked in zip-10 mutants. (E) Western blots of the integrated zip-10p::zip-10::EGFP::FLAG strain showing time-dependent protein induction by CW. (F) Western blots of the integrated zip-10p::zip-10::EGFP::FLAG strain showing its up-regulation by isy-1 RNAi and down-regulation by GFP or zip-10 RNAi. Both short- and long-exposure blots are shown. (G) Western blots of the integrated zip-10p::zip-10::EGFP::FLAG strain showing its up-regulation strictly required warming after cold shock. (H) Western blots of the integrated zip-10p::zip-10::EGFP::FLAG strain showing its up-regulation by CW was further enhanced by isy-1 RNAi. (I) QPCR measurements of gene expression levels showing ZIP-10 dependent up-regulation of asp-17 and cpr-3 but not srr-6 or F53B9.1 after cold for indicated durations and 1 hr warming. n ≥ 20 total animals for each group with N ≥ 3 independent biological replicates; *** indicates p<0.001. Scale bar: 20 µm.