Fig 4 is incorrect. Please see the corrected Fig 4 here.
Fig 4.
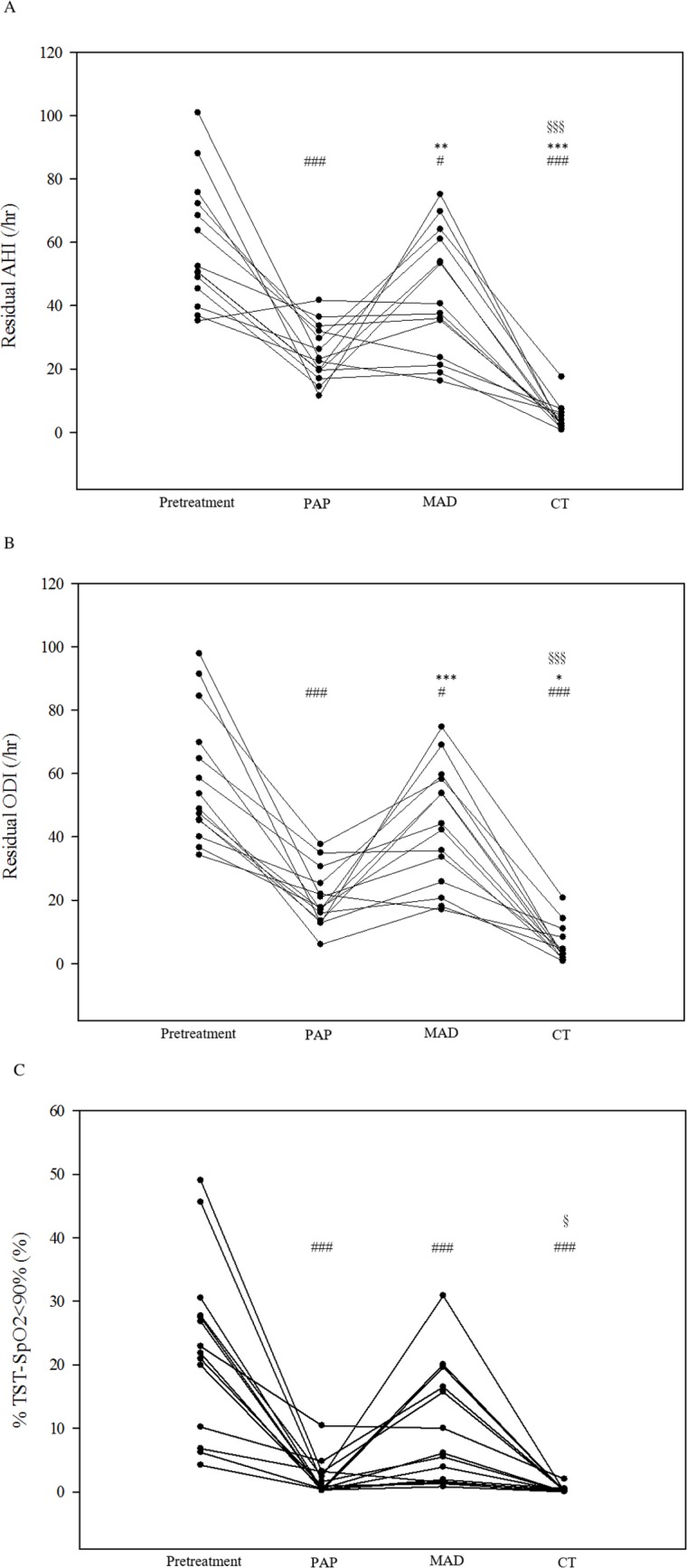
The (A) residual apnea-hypopnea index (AHI), (B) residual oxygen desaturation index (ODI), and (C) residual percentage of total sleep time with SpO2 <90% (%TST-SpO2 <90%) before and under treatments with PAP, MAD, and CT in 14 patients. PAP, continuous positive airway pressure; MAD, mandibular advancement device; CT, combination therapy. Each dot represents a measurement of an individual patient. The p values were analyzed by Tukey’s correction: # p < 0.05 and ### p < 0.005 compared with pretreatment values; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.005 compared with PAP therapy; § p < 0.05 and §§§ p < 0.005 compared with MAD therapy.
Reference
- 1.Liu H-W, Chen Y-J, Lai Y-C, Huang C-Y, Huang Y-L, Lin M-T, et al. (2017) Combining MAD and CPAP as an effective strategy for treating patients with severe sleep apnea intolerant to high-pressure PAP and unresponsive to MAD. PLoS ONE 12(10): e0187032 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


