Abstract
Circadian clocks generate daily rhythms in gene expression, cellular functions, physiological processes and behavior. The core clock mechanism consists of transcriptional-translational negative feedback loops that turn over with an endogenous circa 24 h period. Classical genetic experiments in the fly Drosophila melanogaster played an essential role in identification of clock genes that turned out to be largely conserved between flies and mammals. Like in mammals, circadian clocks in flies generate transcriptional rhythms in a variety of metabolic pathways related to feeding and detoxification. Given that rhythms pervade metabolism and the loss of metabolic homeostasis is involved in aging and disease, there is increasing interest in understanding how the clocks and the rhythms they control change during aging. The importance of circadian clocks for healthy aging is supported by studies reporting that genetic or environmental clock disruptions are associated with reduced healthspan and lifespan. For example, arrhythmia caused by mutations in core clock genes lead to symptoms of accelerated aging in both flies and mammals, including neurodegenerative phenotypes. Despite the wealth of descriptive data, the mechanisms by which functional clocks confer healthspan and lifespan benefits are poorly understood. Studies in Drosophila discussed here are beginning to unravel causative relationships between the circadian system and aging. In particular, recent data suggest that clocks may be involved in inducing rhythmic expression of specific genes late in life in response to age-related increase in oxidative stress. This review will summarize insights into links between circadian system and aging in Drosophila, which were obtained using powerful genetics tools available for this model organism and taking advantage of the short adult lifespan in flies that is measured in days rather than years.
Keywords: longevity, metabolic rhythms, circadian clocks
Graphical abstract
1. Clock mechanism and the organization of the circadian systems in Drosophila
Circadian clocks are cell-autonomous molecular feedback loops that impose daily rhythms on gene transcription, protein activity, metabolic functions, physiological processes and behavior. Their functions have been mostly studied in young organisms, but there is increasing interest in the analysis of clock mechanism across lifespan [1]. Early experiments determined that daily behavioral rhythms are not simply a response to day/night cycles but can persist in constant darkness with a “circa” 24 hour period, suggesting their endogenous nature [2]. The genetic basis of circadian rhythms was convincingly demonstrated in Drosophila melanogaster by the discovery of the gene named period (per) [3]. A null allele of this “clock” gene resulted in loss of rhythmic behaviors, while missense alleles resulted in flies with short (~19h) or long (~29h) free-running periods of two behavioral rhythms [3]. Subsequent studies in Drosophila resulted in the cloning of the per gene and the discovery of several other conserved core clock genes that form transcriptional-translational negative feedback loops that turn over every ~24hr [4]. Molecular principles of clock organization are well conserved between flies and mammals including humans [5] and, remarkably, the three scientists instrumental in deciphering fly clock mechanism (Drs. Jeff Hall, Michael Rosbash, and Michael Young) were awarded the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. This award consolidates the value of Drosophila as an excellent model in biomedical studies.
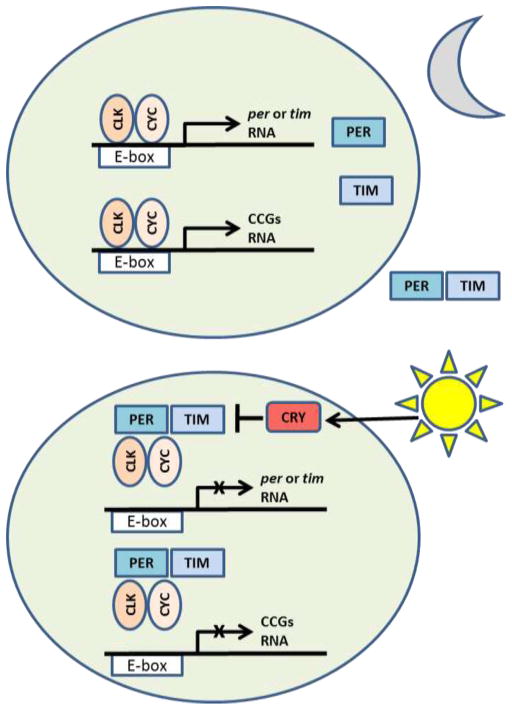
The simplified version of the core feedback loop in Drosophila is shown in Fig. 1. Two transcription factors encoded by the genes Clock (Clk) and cycle (cyc) act as the positive limb of the clock whereby CLK-CYC form heterodimers and bind to the E-box sequences in the promoters of period (per) and timeless (tim) genes, stimulating their transcription in the early night. PER and TIM proteins act as a negative limb of the clock when they accumulate in the cell nuclei late at night and repress CLK-CYC activity. This results in the suppression of per and tim transcription until the repressive PER and TIM are degraded and the positive clock limb can restart [4]. Clock oscillations are additionally enhanced via posttranslational modifications of clock proteins, especially via sequential phosphorylation [4]. While clock oscillations persist in experimental conditions of constant darkness (DD), they are normally entrained to daily light/dark (LD) cycles in flies via light-sensitive CRY protein encoded by the cryptochrome (cry) gene. Upon activation by light, CRY binds to TIM leading to its degradation. Because TIM stabilizes PER, the latter is also degraded within few hours of lights-on. However, TIM (and PER) are also degraded in DD by a different mechanism [6]. While most core clock genes are highly conserved between Drosophila and mammals [5], flies have a single copy of each clock gene, whereas mammals often have two or more paralogs that are partially redundant, so that multiple genes have to be knocked down to make an animal arrhythmic [7].
Fig. 1.
Schematic depiction of the negative feedback loop that forms the core mechanism of the Drosophila clock. At night (upper panel) the CLK/CYC heterodimers bind to E-box sequences in per and tim promoters and activate transcription of these genes. Resulting PER and TIM proteins form heterodimers, enter the nucleus and bind to CLK/CYC repressing further transcription of per and tim. Morning light activates CRY protein (lower panel) which binds to TIM causing its degradation. PER, which is stabilized by TIM, also degrades ending repressive phase of the clock and allowing positive arm of the clock to restart. Note that degradation of TIM and PER proteasome is also accomplished in constant darkness. Many clock-controlled genes (CCGs) also contain E-box in their promoters and their transcription is directly stimulated by CLK/CYC. Some of these CCGs encode transcription factors, which indirecly generate rhythmic transcription of additional CCGs. Figure based on reference [1].
Based on early observations of behavioral rhythms in sleep/activity, feeding and cognitive functions, it was assumed that the clock would reside in specialized neurons. Indeed, the circadian clocks with anatomical and functional similarities have been identified in the brains of mammals and insects using perturbation of locomotor activity rhythms as a readout of clock function [5]. These master clocks are composed of multiple neurons, which are organized in populations with different morphology sub-serving different functions [8]. The mammalian central clock consist of thousands of neurons located in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) while the fly central clock consists of the network of less than 200 pacemaker neurons controlling different aspects of sleep-activity rhythms [9]. It is now well established that animals possess multi-oscillatory circadian systems with master clocks residing in the central nervous system and peripheral clocks in cells forming most other tissues. The existence of peripheral clocks was first demonstrated in insects [10, 11] and later in mammals [12]. In flies, bona fide clock mechanisms reside in a multitude of peripheral cells such as retinal photoreceptors, olfactory and gustatory neurons, glial cells, fat bodies, as well as gut and excretory epithelia [13–19]. These clocks are called peripheral because they do not contribute directly to the behavioral sleep/activity rhythms, which persist in flies displaying clock function exclusively in central pacemaker neurons [20, 21].
In contrast to mammals [22], peripheral clocks in flies are directly entrained by LD cycles whereby the light-activated CRY protein interacts with TIM protein leading to its degradation [23]. There is ample evidence that peripheral clocks can function independently of the central clock in flies [24, 25]; however, emerging data (discussed below) suggest that, similar to mammals, the outputs of the fly central clock can regulate rhythmic transcription of specific genes in peripheral tissues.
2. Metabolic rhythms related to feeding
One of the major functions of mammalian circadian systems is to coordinate periods of food intake with digestion and nutrient processing to maintain metabolic homeostasis [26]. Clock-dependent feeding rhythms have been also reported in Drosophila [16, 27]. It was then established that clocks in the fly fat body cells (which serve as both fat tissue and liver in insects) drive rhythmic expression of many genes involved in metabolism; however, some of these genes remain rhythmic when the fat body clock is genetically disrupted [28]. More recent experiments revealed that the rhythmic transcription of those genes depends upon clocks in neurons expressing neuropeptide F (NPF) [29]. Interestingly, the mammalian ortholog of NPF called neuropeptide Y (NPY), functions similarly to regulate cycling of specific metabolic genes in the mouse liver [29]. Another study demonstrated rhythmic control of metabolism via insulin-producing cells in the fly brain that are functionally connected to the central clock neurons; this endocrine axis appears necessary for rhythmic expression of a lipase transcript in the fat body [30]. Taken together, these studies uncover circuit level coordination and systemic signaling between central and peripheral clocks that may synchronize food intake and nutrient utilization. In fact, the coordination between functional circadian clocks in the brain and peripheral tissues was shown to optimize metabolic homeostasis as measured by reproductive fitness [28]. Moreover, the metabolic state of the fly can influence the central clock to affect locomotor and foraging rhythms [31]. In summary, these studies show that systemic signals from the brain are required for transcriptional rhythms not only in the mammalian liver but also in the Drosophila fat body. Thus, another facet of circadian regulation is evolutionary conserved and genetic manipulations in flies may help to understand reciprocal relationships between the circadian and metabolic system.
3. Metabolic rhythms related to redox maintenance and detoxification
Several lines of evidence suggest that circadian clocks regulate processes that protect organisms from oxidative stress. First, genome-wide analyses of the circadian transcriptome in fly heads by microarray [32–35] or RNA-seq [36, 37] uncovered that the expression of many genes involved in defense from reactive oxygen species (ROS) occur in a circadian manner. Remarkably, genes belonging to the GO term “Glutathione metabolism” were significantly enriched among rhythmic transcripts identified by RNA-seq in fly heads [37]. These transcriptional oscillations are consistent with previous functional studies showing that the levels of ROS and oxidatively damaged (carbonylated) proteins fluctuate in a daily rhythm in heads of wild type flies, whereas these parameters are non-rhythmic and significantly higher in flies with a null mutation in the per clock gene [38]. Accordingly, mortality after a constant dose of hydrogen peroxide varied with time of its application in wild type flies but was constitutively higher in flies with disrupted clock [38]. Apparently, the circadian system affects redox pathways and regulate fly survival in concert with the presence or absence of detoxifying enzymes.
Consistent with the fluctuations in oxidative stress response, the circadian clock was shown to modulate pathways involved in the synthesis of glutathione (GSH), which plays a central role in antioxidant defenses that minimize the accumulation of oxidative damage [39, 40]. We demonstrated that circadian clocks in the fly heads regulate concentrations of GSH as well as the level of its precursor, gamma-glutamylcysteine [41]. In addition, significant rhythms were observed in mRNA levels of genes encoding the glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL) holoenzyme. This is a rate limiting enzyme in GSH synthesis comprising the catalytic (Gclc) and modulatory (Gclm) subunits, both showing rhythmic transcription. These rhythms were abolished in flies with mutations in core clock genes, thus linking glutathione production and utilization to the circadian system [41]. Subsequent studies showed that rhythmic expression of Gclc mRNA occurs independently of the central pacemaker neurons, because it persisted in heads of behaviorally arrhythmic flies with a disabled central clock but intact peripheral clocks [21]. Among cells harboring peripheral clocks, the glial cells appear to generate rhythms in Gclc mRNA levels as genetic disruption of clocks only in glia abolished Gclc mRNA oscillations [21]. Taken together, these studies suggest the involvement of circadian clocks in redox regulation in flies, adding to the ample evidence from mammalian studies that these systems are tightly interlinked [42]. Additional support for clock-redox links can be gleaned from a study that reported rhythmic peroxiredoxin oxidation patterns in heads of wild-type flies, which persisted in clock mutants albeit with altered circadian phase relative to wild type flies [43]. Whether these rhythms are involved in regulating cellular ROS has not been determined in flies.
GSH is an integral part of organismal detoxification system, which is controlled by circadian clock at many levels. In phase I of detoxification pathway, enzymes such as cytochrome P450 oxidases introduce reactive or polar groups into xenobiotics. These modified compounds are then conjugated to polar compounds in phase II reactions performed by enzymes such as glutathione S-transferases that catalyze the conjugation of the reduced GSH to xenobiotic substrates. Genome-wide circadian transcription studies determined that many genes encoding xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes are rhythmically expressed in Drosophila [44]. Similarly in mammals, both basal and inducible xenobiotic detoxification in the liver is regulated in a circadian fashion via set of clock-controlled transcription factors [45]. Insects including Drosophila encounter a variety of xenobiotics such as potentially toxic food components produced by plants or introduced by humans as pesticides. Since feeding in flies is rhythmic (see previous section) it may be expected that susceptibility to toxins is clock-controlled. Indeed, flies display daily variation in mortality after exposure to the same dose of specific toxic compound at different time of day [46]. Daily rhythms in xenobiotic response were associated with diurnal fluctuations in the activity of several phase-I xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes [46]. Further genetic experiments established that the positive clock transcription factors CLK and CYC are necessary for rhythmic expression of several Cytochrome P450 enzymes, and that survival of flies with a null mutation in the cyc gene is decreased after toxin exposure compared to wild-type flies [47]. Thus, the functional circadian clock contributes to survival of flies challenged with chemical compounds by helping the organism to be most resistant at the time that toxins are most likely to be encountered as a consequence of the feeding rhythm [28]. Due to conservation of the clock mechanism and detoxification system, flies could serve as an effective model for chronotoxicological and chronopharmacological studies, a very active field due to well-known circadian responses to many therapeutic compounds including anti-cancer drugs [48–50].
4. Links between circadian rhythms and aging
4.1 Functional clocks support healthy aging in flies
As discussed above, many metabolic pathways are controlled by circadian clocks; therefore young flies with disrupted clock mechanisms show higher susceptibility to oxidative stress and toxic compounds [38, 46]. These results suggest that the disruption of the clock function may affect aging organisms even more adversely. Indeed, several studies demonstrated that longevity is compromised in flies with loss of functions mutations in core clock genes (for review see [51]). Disruption of circadian clock also affect healthspan, which can be defined broadly as the time of robust organismal function before the onset of age-associated decline. For assessment of healthspan in clock-deficient flies, middle-aged per-null (per01) mutants or control flies were exposed to 24-h of mild oxidative stress (100% oxygen) and their survival was monitored. While none of the flies died during the 24-h of hyperoxia, subsequent mortality rates increased significantly in per01 mutants compared to age-matched wild-type flies exposed to this stress [52]. This suggests that flies with disrupted clocks have a reduced ability to survive homeostatic challenge during aging. Other experiments confirmed that per01 mutants are physiologically older when tested at the same chronological age as control flies with functional clocks. For example, the aging per01 mutants show significantly higher accumulation of oxidatively damaged proteins and lipids along with accelerated loss of vertical climbing ability [52]. Poor climbing ability in per01 flies was associated with increased neurodegeneration [52], suggesting that clocks may have neuroprotective functions during aging.
Neuroprotective roles of clocks were further supported by testing effects of disrupted clocks on two neurodegeneration-prone mutants. One of the genes, sniffer (sni) encodes carbonyl reductase involved in protection against oxidative stress-induced neurodegeneration and apoptosis [53] The other gene, swiss cheese (sws) encodes a transmembrane protein that hydrolyzes phosphatidylcholine and supports health of neurons and glia [54, 55]. Aging parameters were tested in flies carrying either sni or sws mutation in per-positive and per01 backgrounds. Importantly, double mutants combining both sni and sws mutation with per01 exhibited shortened lifespan and more severe neurodegeneration at a younger age compared to either sni or sws single mutants with normal clock function [56]. Together, these results provide substantial evidence for detrimental pro-aging effects of circadian disruption and suggest that a functional circadian system plays neuroprotective roles during aging, presumably by coordinating temporal homeostasis in the aging brain. Similarly to flies, accumulating evidence in mammals suggests that circadian disruption contributes to accelerated aging [57, 58] and neurodegenerative pathologies [59–61], but understanding of the mechanisms involved will require further studies to identify critical clock-controlled genes involved in maintaining neuronal homeostasis.
4. 2. The circadian system is involved in anti-aging interventions
As discussed above, disruptions of the circadian system is associated with accelerated aging; however, molecular bases of these links are poorly understood. Emerging evidence suggest that functional clocks may be involved in known life-extending pathways, such as dietary restriction (DR). A recent study addressing this question showed that functional clocks are necessary for the lifespan responses to low protein DR in Drosophila since knockout of the core clock genes tim or per abolished lifespan extension by DR [62]. The lifespan extension in flies appears to be mediated through enhanced fat turnover, whereby the clock gene tim is necessary for cycling of medium chain triglycerides under DR [62]. Importantly, DR increased the amplitude of cycling in most circadian clock genes in heads and bodies of wild type flies [62]. Similar results were obtained in mice where the amplitudes of expression of several clock genes were significantly induced by calorie restriction in the liver [63] and also in the SCN [64]. Taken together, these studies indicate that the clock mechanism becomes more robust under low nutrients, and DR regulates the expression of core clock gene in different organisms and in different tissues. This opens an important question whether peripheral clocks are affected by the metabolic changes associated with low nutrients directly or via strengthening of central clock. Secondly, identification of putative metabolites that are targeted by enhanced circadian system could be of high clinical importance.
Another approach to DR, namely time-restricted feeding (TRF) was also shown to improve the amplitude of oscillation of circadian clock components and clock controlled genes in mouse liver and to provide overall health benefits [65]. Remarkably, TRF also had anti-aging effects on neural, peripheral, and cardiovascular physiology in Drosophila. In this study, flies (which are diurnal) had access to food only during 12 h of light in the 12:12 LD cycle or had constant ad libitum (AL) access to food [66]. Improved sleep patterns, prevention of body weight gain, and deceleration of cardiac aging were observed under TRF relative to age-matched AL flies, despite that total caloric intake and activity levels were similar in both groups of flies. Importantly, these effects were dependent on a functional clock, as the imposition of TRF was insufficient for protecting against cardiac aging in flies with disrupted clock function [66]. Altogether, these studies suggest that a cross-talk between DR or TRF and functional circadian clocks may delay aging; however, understanding of the nature of reciprocal links between dietary interventions and clock mechanisms will require further studies.
Involvement of the clock in healthy aging in Drosophila is also supported by two studies showing that the overexpression of specific clock genes could slow down deterioration of rest/activity rhythms that occurs in old flies [67]. The first study focused on the pigment dispersing factor (PDF) peptide, which is necessary for maintaining robust central clock network [68]. It was shown that overexpression of PDF specifically in the PDF-positive neurons partially rescued behavioral rhythms in old flies and shortened their free-running periods, causing apparent rejuvenation of these rhythms [69]. The second study tested effects of the overexpression of the cry gene encoding a blue light sensitive protein CRY, which is also required in peripheral clocks for their free-running oscillations in constant darkness [70, 71]. Overexpression of CRY in all clock cells strengthened rest/activity rhythms in constant darkness late in life [72]. Importantly, flies with elevated CRY levels also showed better climbing ability and decreased oxidative damage pointing to their extended healthspan [72]. Interestingly, overexpression of cry in PDF-positive central clock neurons alone was not sufficient to restore rest/activity rhythms suggesting that peripheral clocks also play an active role in delaying behavioral and physiological aging [72]. Consistent with these findings, in the DR study discussed above, overexpression of tim in peripheral tissues, especially fat body extended lifespan under ad libitum feeding [62].
5. Changes in the expression of clock genes across lifespan
As mentioned above, significant weakening of sleep/activity rhythms was reported in aging Drosophila with more frequent and shorter sleep bouts and declining strength of overall rest/activity rhythms [67]. These observations opened the question of whether the dampening of rest/activity rhythms is caused by age-related changes in the expression of core clock genes or rhythm impairments downstream of the clock. To address this, two studies compared diurnal rhythms of clock gene expression in heads of young and old flies [73, 74]. Measuring mRNA levels by quantitative RT-PCR, it was determined that all clock genes retained rhythmic expression, albeit several showed reduced oscillatory amplitude in heads of old flies compared to young [73, 74]. Cell-type specific analysis of the PER protein revealed that PER maintained relatively strong rhythms in central pacemaker neurons of old flies [69, 73], while its levels were significantly reduced in retinal photoreceptor of the compound eyes in old flies compared to young [73, 74]. Photoreceptors form the bulk of clock cells in the head and significant age-dependent decreases in the levels of PER protein were also detected by Western blotting [73, 74].
Recent comparison of clock gene expression in heads of young and old flies around the clock by direct RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) technology rather than qPCR did not detect age-related reduction in the amplitude of most clock genes; in fact, the oscillations of per mRNA were enhanced with aging [75]. On the other hand, this study confirmed a significant decrease in the PER protein levels in whole heads of old flies [75]. Since PER repression of CLK-CYC activity reduces per transcription via negative feedback loop (Fig. 1), diminished repression due to PER deficiency could result in the age-related increase of per mRNA. In summary, the core circadian mechanism known in young flies is altered during aging mainly by weakening of the repressive arm of the clock feedback loop. Nevertheless, the clocks remain functional throughout fly lifespan and, interestingly, studies in mammals lead to similar conclusions, at least in the entrained conditions [76].
While patterns of clock gene expression do not change dramatically in flies entrained by LD cycles across lifespan, aging appears to weaken cross-talk between cellular oscillators in constant conditions. Significant dampening of clock gene oscillations was observed in constant darkness (DD) both in flies [73] and mice [76]. The latter study found that the amplitude of PER2::LUC rhythms in single cells differed only slightly between SCN explants from young and aged animals under LD conditions, while under DD conditions, the PER2::LUC rhythms of aged animals showed markedly lower amplitudes because the rhythms of individual cells became desynchronized very rapidly. Aging in flies is associated with reduced expression of the PDF peptide, which is necessary for maintaining robust central clock network [69]. As discussed above, overexpression of PDF specifically in the PDF-positive neurons improved behavioral rhythms in old flies [69]. Altogether, these data suggest that aging degrades circadian network properties resulting in decreased pacemaker robustness that could contribute to age-related sleep and circadian disturbances.
6. Age related changes in the expression of clock-controlled genes
An important mechanism for producing circadian output that is used by all known molecular clock circuits is to generate rhythms in the expression of clock-controlled genes (CCGs). Oscillating clock components impose rhythmic expression on a diverse set of target CCGs in young flies [36, 37, 77]. The CCGs encode transcription factors, metabolic enzymes, and regulators of neuronal processes and cellular redox [28, 44, 46]. How does aging affect expression of CCGs? To address this question for a single gene, we conducted a functional study of GSH biosynthesis in old flies, which revealed that aging is associated with abolished daily oscillations and increased constitutive expression of Gclc mRNA, leading to the significant increase in the catalytic activity of the GCL holoenzyme [78]. This may be due to the “overriding” of the clock by oxidative stress-induced pathways, which are known to stimulate Gclc transcription in a clock-independent fashion in mammals [79].
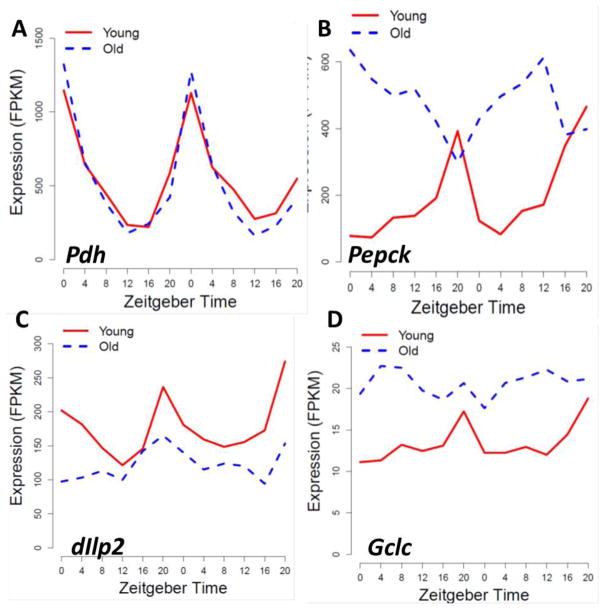
To elucidate changes in CCGs at the genome-wide level, we recently measured diurnal gene expression profiles in heads of young and old female flies by RNA-seq [75]. Data analysis revealed that several hundred CCGs maintained robust rhythmicity from young to old flies while other genes changed expression in a variety of ways (Fig 2). For example, a very strong rhythm in NAD-dependent oxidoreductase (photoreceptor dehydrogenase, Pdh) was detected in heads of young and old flies with the peak occurring at the same phase (Fig. 2A). In contrast, a group of few genes showed significant rhythm in young and old flies but with large shift in the expression phase; among them was Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (Pepck) (Fig. 2B), an enzyme essential for glucose and glycerol homeostasis [80]. However, many other CCGs showed dampened or abolished oscillations in old flies. Some genes become constitutively low, including those encoding important signaling molecules, for example Insulin-like peptide 2 (Ilp2, Fig. 2C). Other genes become constitutively high, for example Gclc (Fig 2D) in agreement with our published data [78].
Fig. 2.
Comparative analysis of diurnal transcriptome in heads of young and old flies revealed several age-dependent trends in gene expression. Several hundred genes that were rhythmic in young flies remained rhythmic in old, such as gene encoding photoreceptor dehydrogenase, Pdh (A). A few genes remain rhythmic in heads of old flies but adopt a new phase, with a prominent example of Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, Pepck (B). Many genes showed significantly reduced oscillatory amplitude or loss of rhythmicity with age, for example, Insulin-like peptide2, Ilp2 (C) or glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit, Gclc (D). Gene expression profiles shown are based on data obtained by RNA-seq and published recently [75].
The most surprising outcome of the genome wide comparative analysis of CCGs was the identification of the gene subset that showed significantly larger expression amplitudes or even de novo rhythmicity in old flies [75]. Stress-response genes were enriched among transcripts with age-induced rhythmicity, and subsequent experiments demonstrated that exogenous oxidative stress can induce rhythmic expression of these genes in young flies [75]. These data suggest that late life activation of stress responsive genes may be an organismal response to endogenous oxidative stress that tends to accumulate during aging [52]. In summary, this study revealed dynamic reprogramming of the subset of circadian transcriptome including unexpected outcomes, such as age-related gain of rhythmicity in the expression of several genes. Remarkably, recent comparison of young and old mice revealed extensive reprogramming of the circadian transcriptome in a tissue-specific manner with genes gaining or losing rhythmicity in age-related fashion [81, 82]. Together, these new findings demonstrate that the degradation of the physiological and behavioral rhythms in aging flies and mammals is not caused by the general dampening of the clock controlled genes or global arrhythmia. While some genes become less rhythmic, physiological aging is also associated with de novo or increased rhythmicity in other genes. Further studies are needed to determine whether late life transcriptional rhythmicity of these genes is regulated by the circadian clock and what is the functional significance of these oscillations. The fact that circadian genomic signatures of aging in the liver are reverted by caloric restriction [81] suggests caution in interpreting age-related transcriptional changes as generally beneficial.
7. Conclusions and future directions
Studies on the reciprocal links between circadian clocks and aging are in an exciting exploratory phase with many questions awaiting further research. It is becoming clear that the central clock mechanism is functional during aging, yet the rest/activity rhythms become impaired by normal or pathological aging despite strong oscillations of clock genes in the master clock neurons [73, 83, 84]. It is possible that peripheral clocks in the fly head, while dispensable for strong rest/activity rhythms in young flies may be important in old flies via their role in maintaining temporal homeostasis in the nervous system and metabolic functions. To address these questions, future research needs to focus on age-related changes in clock-controlled genes and processes in specific tissues, as well as their functional significance in the regulation of healthy aging.
This review highlights Drosophila as a model for studying metabolic rhythms and age-associated changes in the clock mechanism and clock-controlled processes. Features that make flies a great model for such studies include their short lifespan (in the range of 50–80 days), the vast array of genetic tools, and evolutionary conservation of molecular pathways involved in both the circadian system and aging processes between flies and mammals. It is our hope that studies on flies can provide a better understanding of the important outstanding issues in the field, for example: What are the consequences of age-related reprogramming of the circadian transcriptome for heathy aging? How this reprogramming is regulated? Non-clock transcription factors are likely to be involved and it would be important to identify them. Recent studies suggest that circadian clocks are “called upon” to mediate various anti-aging interventions, such as DR. Furter studies in flies should help to define circadian conditions and interventions that would be applicable to promoting healthy aging in humans.
Highlights.
Circadian systems are evolutionary conserved between Drosophila and mammals.
Circadian clocks regulate feeding, metabolic processes and detoxification.
Age-related increase in oxidative stress induce rhythmic expression of stress response genes.
Circadian transcriptome changes in variety of ways during aging.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Eileen Chow for reading of the manuscript and David A. Hendrix for helpful discussions. Author’s research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health under award number R01 AG045830 and R21AG052950 to JMG.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Giebultowicz JM. The circadian system and aging of Drosophila. In: Jazwinski S, Belancio V, Hill S, editors. Circadian Rhythms and Their Impact on Aging. Springer International Publishing AG; Cham, Switzerland: 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pittendrigh CS. Circadian rhythms and circadian organization of the living systems. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol. 1960;25:159–182. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1960.025.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Konopka RJ, Benzer S. Clock mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1971;68:2112–2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hardin PE. Molecular genetic analysis of circadian timekeeping in Drosophila. Adv Genet. 2011;74:141–73. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387690-4.00005-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hardin PE, Panda S. Circadian timekeeping and output mechanisms in animals. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013;23(5):724–31. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2013.02.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Grima B, Lamouroux A, Chelot E, Papin C, Limbourg-Bouchon B, Rouyer F. The F-box protein slimb controls the levels of clock proteins period and timeless. Nature. 2002;420(6912):178–82. doi: 10.1038/nature01122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lowrey PL, Takahashi JS. Genetics of circadian rhythms in Mammalian model organisms. Adv Genet. 2011;74:175–230. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-387690-4.00006-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Helfrich-Forster C. The circadian clock in the brain: a structural and functional comparison between mammals and insects. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2004;190(8):601–13. doi: 10.1007/s00359-004-0527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nitabach MN, Taghert PH. Organization of the Drosophila circadian control circuit. Curr Biol. 2008;18(2):R84–93. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.11.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Giebultowicz JM, Riemann JG, Raina AK, Ridgway RL. Circadian system controlling release of sperm in the insect testes. Science. 1989;245:1098–1100. doi: 10.1126/science.245.4922.1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Giebultowicz JM, Hege D. Circadian clock in Malpighian tubules. Nature. 1997;386:664. doi: 10.1038/386664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Balsalobre A, Damiola F, Schibler U. A serum shock induces circadian gene expression in mammalian tissue culture cells. Cell. 1998;93:929–937. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hege DM, Stanewsky R, Hall JC, Giebultowicz JM. Rhythmic expression of a PER-reporter in the Malpighian tubules of decapitated Drosophila: evidence for a brain-independent circadian clock. J Biol Rhythms. 1997;12:300–308. doi: 10.1177/074873049701200402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cheng Y, Hardin PE. Drosophila photoreceptors contain an autonomous circadian oscillator that can function without period mRNA cycling. J Neurosci. 1998;18(2):741–50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-02-00741.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tanoue S, Krishnan P, Krishnan B, Dryer SE, Hardin PE. Circadian clocks in antennal neurons are necessary and sufficient for olfaction rhythms in Drosophila. Curr Biol. 2004;14(8):638–49. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Xu K, Zheng X, Sehgal A. Regulation of feeding and metabolism by neuronal and peripheral clocks in Drosophila. Cell Metab. 2008;8(4):289–300. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chatterjee A, Hardin PE. Time to taste: circadian clock function in the Drosophila gustatory system. Fly (Austin) 2010;4(4):283–7. doi: 10.4161/fly.4.4.13010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ng FS, Tangredi MM, Jackson FR. Glial cells physiologically modulate clock neurons and circadian behavior in a calcium-dependent manner. Curr Biol. 2011;21(8):625–34. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.03.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Karpowicz P, Zhang Y, Hogenesch JB, Emery P, Perrimon N. The circadian clock gates the intestinal stem cell regenerative state. Cell reports. 2013;3(4):996–1004. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.03.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Frisch B, Hardin PE, Hamblen-Coyle MJ, Rosbash M, Hall JC. A promoterless period gene mediates behavioral rhythmicity and cyclical per expression in a restricted subset of the Drosophila nervous system. Neuron. 1994;12:555–570. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90212-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chow ES, Long DM, Giebultowicz JM. Circadian rhythm in mRNA expression of the glutathione synthesis gene Gclc is controlled by peripheral glial clocks in Drosophila melanogaster. Physiol Entomol. 2016;41:369–377. doi: 10.1111/phen.12164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mohawk JA, Green CB, Takahashi JS. Central and peripheral circadian clocks in mammals. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2012;35:445–62. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-060909-153128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Busza A, Emery-Le M, Rosbash M, Emery P. Roles of the two Drosophila CRYPTOCHROME structural domains in circadian photoreception. Science. 2004;304(5676):1503–6. doi: 10.1126/science.1096973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Giebultowicz JM. Peripheral clocks and their role in circadian timing: insights from insects. Phil Trans R Soc B. 2001;356:1791–1799. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2001.0960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Giebultowicz JM. Multiple oscillators. In: Sehgal A, editor. Molecular Biology of Circadian Rhythms. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken: 2004. pp. 213–230. [Google Scholar]
- 26.McGinnis GR, Young ME. Circadian regulation of metabolic homeostasis: causes and consequences. Nat Sci Sleep. 2016;8:163–80. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S78946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Seay DJ, Thummel CS. The circadian clock, light, and cryptochrome regulate feeding and metabolism in Drosophila. J Biol Rhythms. 2011;26(6):497–506. doi: 10.1177/0748730411420080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Xu K, DiAngelo JR, Hughes ME, Hogenesch JB, Sehgal A. The circadian clock interacts with metabolic physiology to influence reproductive fitness. Cell Metab. 2011;13(6):639–54. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Erion R, King AN, Wu G, Hogenesch JB, Sehgal A. Neural clocks and Neuropeptide F/Y regulate circadian gene expression in a peripheral metabolic tissue. eLife. 2016;5 doi: 10.7554/eLife.13552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Barber AF, Erion R, Holmes TC, Sehgal A. Circadian and feeding cues integrate to drive rhythms of physiology in Drosophila insulin-producing cells. Genes Dev. 2016;30(23):2596–2606. doi: 10.1101/gad.288258.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Erion R, Sehgal A. Regulation of insect behavior via the insulin-signaling pathway. Frontiers in Physiology. 2013;4:353. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ceriani MF, Hogenesch JB, Yanovsky M, Panda S, Straume M, Kay SA. Genome-wide expression analysis in Drosophila reveals genes controlling circadian behavior. J Neurosci. 2002;22(21):9305–19. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-21-09305.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.McDonald MJ, Rosbash M. Microarray analysis and organization of circadian gene expression in Drosophila. Cell. 2001;107(5):567–78. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lin Y, Han M, Shimada B, Wang L, Gibler TM, Amarakone A, Awad TA, Stormo GD, Van Gelder RN, Taghert PH. Influence of the period-dependent circadian clock on diurnal, circadian, and aperiodic gene expression in Drosophilamelanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(14):9562–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.132269699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Claridge-Chang A, Wijnen H, Naef F, Boothroyd C, Rajewsky N, Young MW. Circadian regulation of gene expression systems in the Drosophila head. Neuron. 2001;32(4):657–71. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00515-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hughes ME, Grant GR, Paquin C, Qian J, Nitabach MN. Deep sequencing the circadian and diurnal transcriptome of Drosophila brain. Genome Res. 2012;22(7):1266–81. doi: 10.1101/gr.128876.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rodriguez J, Tang CH, Khodor YL, Vodala S, Menet JS, Rosbash M. Nascent-Seq analysis of Drosophila cycling gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(4):E275–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219969110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Krishnan N, Davis AJ, Giebultowicz JM. Circadian regulation of response to oxidative stress in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;374(2):299–303. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.07.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lu SC. Regulation of glutathione synthesis. Mol Aspects Med. 2009;30(1–2):42–59. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2008.05.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(1):44–84. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2006.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Beaver LM, Klichko VI, Chow ES, Kotwica-Rolinska J, Williamson M, Orr WC, Radyuk SN, Giebultowicz JM. Circadian regulation of glutathione levels and biosynthesis in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50454. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Milev NB, Reddy AB. Circadian redox oscillations and metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015;26(8):430–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2015.05.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Edgar RS, Green EW, Zhao Y, van Ooijen G, Olmedo M, Qin X, Xu Y, Pan M, Valekunja UK, Feeney KA, Maywood ES, Hastings MH, Baliga NS, Merrow M, Millar AJ, Johnson CH, Kyriacou CP, O’Neill JS, Reddy AB. Peroxiredoxins are conserved markers of circadian rhythms. Nature. 2012;485(7399):459–64. doi: 10.1038/nature11088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wijnen H, Young MW. Interplay of circadian clocks and metabolic rhythms. Annu Rev Genet. 2006;40:409–48. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.40.110405.090603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Gachon F, Olela FF, Schaad O, Descombes P, Schibler U. The circadian PAR-domain basic leucine zipper transcription factors DBP, TEF, and HLF modulate basal and inducible xenobiotic detoxification. Cell Metab. 2006;4(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hooven LA, Sherman KA, Butcher S, Giebultowicz JM. Does the clock make the poison? Circadian variation in response to pesticides. PLoS One. 2009;4(7):e6469. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Beaver LM, Hooven LA, Butcher SM, Krishnan N, Sherman KA, Chow ES, Giebultowicz JM. Circadian clock regulates response to pesticides in Drosophila via conserved Pdp1 pathway. Toxicol Sci. 2010;115(2):513–20. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Levi F, Schibler U. Circadian rhythms: mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;47:593–628. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.47.120505.105208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhang R, Lahens NF, Ballance HI, Hughes ME, Hogenesch JB. A circadian gene expression atlas in mammals: Implications for biology and medicine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(45):16219–24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1408886111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Dallmann R, Brown SA, Gachon F. Chronopharmacology: new insights and therapeutic implications. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014;54:339–61. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-011613-135923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Giebultowicz JM, Long DM. Ageing and Circadian rhythms. Current Opinion in Insect Science. 2015;7:82–86. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2015.03.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Krishnan N, Kretzschmar D, Rakshit K, Chow E, Giebultowicz J. The circadian clock gene period extends healthspan in aging Drosophila melanogaster. Aging. 2009;1(11):937–948. doi: 10.18632/aging.100103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Botella JA, Ulschmid JK, Gruenewald C, Moehle C, Kretzschmar D, Becker K, Schneuwly S. The Drosophila carbonyl reductase sniffer prevents oxidative stress-induced neurodegeneration. Curr Biol. 2004;14(9):782–6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.04.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kretzschmar D, Hasan G, Sharma S, Heisenberg M, Benzer S. The swiss cheese mutant causes glial hyperwrapping and brain degeneration in Drosophila. J Neurosci. 1997;17(19):7425–32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-19-07425.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Dutta S, Rieche F, Eckl N, Duch C, Kretzschmar D. Glial expression of Swiss cheese (SWS), the Drosophila orthologue of neuropathy target esterase (NTE), is required for neuronal ensheathment and function. Disease Models & Mechanisms. 2016;9(3):283–94. doi: 10.1242/dmm.022236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Krishnan N, Rakshit K, Chow ES, Wentzell JS, Kretzschmar D, Giebultowicz JM. Loss of circadian clock accelerates aging in neurodegeneration-prone mutants. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;45(3):1129–35. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Reddy AB, O’Neill JS. Healthy clocks, healthy body, healthy mind. Trends Cell Biol. 2010;20(1):36–44. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.10.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kondratova AA, Kondratov RV. The circadian clock and pathology of the ageing brain. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13(5):325–35. doi: 10.1038/nrn3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Musiek ES. Circadian clock disruption in neurodegenerative diseases: cause and effect? Frontiers in pharmacology. 2015;6:29. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Musiek ES, Holtzman DM. Mechanisms linking circadian clocks, sleep, and neurodegeneration. Science. 2016;354(6315):1004–1008. doi: 10.1126/science.aah4968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ali AA, Schwarz-Herzke B, Stahr A, Prozorovski T, Aktas O, von Gall C. Premature aging of the hippocampal neurogenic niche in adult Bmal1-deficient mice. Aging (Albany NY) 2015 doi: 10.18632/aging.100764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 62.Katewa SD, Akagi K, Bose N, Rakshit K, Camarella T, Zheng X, Hall D, Davis S, Nelson CS, Brem RB, Ramanathan A, Sehgal A, Giebultowicz JM, Kapahi P. Peripheral Circadian Clocks Mediate Dietary Restriction-Dependent Changes in Lifespan and Fat Metabolism in Drosophila. Cell Metab. 2016;23(1):143–54. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.10.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Patel SA, Chaudhari A, Gupta R, Velingkaar N, Kondratov RV. Circadian clocks govern calorie restriction-mediated life span extension through BMAL1- and IGF-1-dependent mechanisms. FASEB J. 2016;30(4):1634–42. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-282475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Mendoza J, Graff C, Dardente H, Pevet P, Challet E. Feeding cues alter clock gene oscillations and photic responses in the suprachiasmatic nuclei of mice exposed to a light/dark cycle. J Neurosci. 2005;25(6):1514–22. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4397-04.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Manoogian ENC, Panda S. Circadian rhythms, time-restricted feeding, and healthy aging. Ageing Res Rev. 2017;39:59–67. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2016.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Gill S, Le HD, Melkani GC, Panda S. Time-restricted feeding attenuates age-related cardiac decline in Drosophila. Science. 2015;347(6227):1265–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1256682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Koh K, Evans JM, Hendricks JC, Sehgal A. A Drosophila model for age-associated changes in sleep:wake cycles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(37):13843–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605903103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.He QK, Wu BB, Price JL, Zhao ZW. Circadian Rhythm Neuropeptides in Drosophila: Signals for Normal Circadian Function and Circadian Neurodegenerative Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017;18(4) doi: 10.3390/ijms18040886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Umezaki Y, Yoshii T, Kawaguchi T, Helfrich-Forster C, Tomioka K. Pigment-Dispersing Factor Is Involved in Age-Dependent Rhythm Changes in Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Rhythms. 2012;27(6):423–32. doi: 10.1177/0748730412462206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ivanchenko M, Stanewsky R, Giebultowicz JM. Circadian photoreception in Drosophila: functions of cryptochrome in peripheral and central clocks. J Biol Rhythms. 2001;16:205–215. doi: 10.1177/074873040101600303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Krishnan B, Levine JD, Lynch MK, Dowse HB, Funes P, Hall JC, Hardin PE, Dryer SE. A new role for cryptochrome in a Drosophila circadian oscillator. Nature. 2001;411(6835):313–7. doi: 10.1038/35077094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Rakshit K, Giebultowicz JM. Cryptochrome restores dampened circadian rhythms and promotes healthspan in aging Drosophila. Aging Cell. 2013;12:752–762. doi: 10.1111/acel.12100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Luo W, Chen WF, Yue Z, Chen D, Sowcik M, Sehgal A, Zheng X. Old flies have a robust central oscillator but weaker behavioral rhythms that can be improved by genetic and environmental manipulations. Aging Cell. 2012;11(3):428–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00800.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Rakshit K, Krishnan N, Guzik EM, Pyza E, Giebultowicz JM. Effects of aging on the molecular circadian oscillations in Drosophila. Chronobiol Int. 2012;29(1):1–10. doi: 10.3109/07420528.2011.635237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kuintzle RC, Chow ES, Westby TN, Gvakharia BO, Giebultowicz JM, Hendrix DA. Circadian deep sequencing reveals stress-response genes that adopt robust rhythmic expression during aging. Nature Communications. 2017;8 doi: 10.1038/ncomms14529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Nakamura TJ, Nakamura W, Tokuda IT, Ishikawa T, Kudo T, Colwell CS, Block GD. Age-Related Changes in the Circadian System Unmasked by Constant Conditions(1,2,3) eNeuro. 2015;2(4) doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0064-15.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Keegan KP, Pradhan S, Wang JP, Allada R. Meta-analysis of Drosophila circadian microarray studies identifies a novel set of rhythmically expressed genes. PLoS Comp Biol. 2007;3(11):e208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Klichko VI, Chow ES, Kotwica-Rolinska J, Orr WC, Giebultowicz JM, Radyuk SN. Aging alters circadian regulation of redox in Drosophila. Frontiers in genetics. 2015;6:83. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Forman HJ, Zhang H, Rinna A. Glutathione: overview of its protective roles, measurement, and biosynthesis. Mol Aspects Med. 2009;30(1–2):1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2008.08.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Bartok O, Teesalu M, Ashwall-Fluss R, Pandey V, Hanan M, Rovenko BM, Poukkula M, Havula E, Moussaieff A, Vodala S, Nahmias Y, Kadener S, Hietakangas V. The transcription factor Cabut coordinates energy metabolism and the circadian clock in response to sugar sensing. EMBO J. 2015;34(11):1538–53. doi: 10.15252/embj.201591385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Sato S, Solanas G, Peixoto FO, Bee L, Symeonidi A, Schmidt MS, Brenner C, Masri S, Benitah SA, Sassone-Corsi P. Circadian Reprogramming in the Liver Identifies Metabolic Pathways of Aging. Cell. 2017;170(4):664–677e11. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Solanas G, Peixoto FO, Perdiguero E, Jardi M, Ruiz-Bonilla V, Datta D, Symeonidi A, Castellanos A, Welz PS, Caballero JM, Sassone-Corsi P, Munoz-Canoves P, Benitah SA. Aged Stem Cells Reprogram Their Daily Rhythmic Functions to Adapt to Stress. Cell. 2017;170(4):678–692e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Chen KF, Possidente B, Lomas DA, Crowther DC. The central molecular clock is robust in the face of behavioural arrhythmia in a Drosophila model of Alzheimer’s disease. Disease models & mechanisms. 2014;7(4):445–58. doi: 10.1242/dmm.014134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Long DM, Blake MR, Dutta S, Holbrook SD, Kotwica-Rolinska J, Kretzschmar D, Giebultowicz JM. Relationships between the circadian system and Alzheimer’s disease-like symptoms in Drosophila. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e106068. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]