Abstract
Gliomas are primary malignancies of the brain. Tumors are staged based on malignancy, nuclear atypia, and infiltration of the surrounding brain parenchyma. Tumors are often diagnosed once patients become symptomatic, at which time the lesion is sizable. Glioblastoma (grade IV glioma) is highly aggressive and difficult to treat. Most tumors are diagnosed de novo. The gold standard of therapy, implemented over a decade ago, consists of fractionated radiotherapy and temozolomide, but unfortunately, chemotherapeutic resistance arises. Recurrence is common after initial therapy. The tumor microenvironment plays a large role in cancer progression and its manipulation can repress progression. The advent and implementation of immunotherapy, via manipulation and activation of cytotoxic T cells, have had an outstanding impact on reducing morbidity and mortality associated with peripheral cancers under certain clinical circumstances. An arsenal of immunotherapeutics is currently under clinical investigation for safety and efficacy in the treatment of newly diagnosed and recurrent high grade gliomas. These immunotherapeutics encompass antibody-drug conjugates, autologous infusions of modified chimeric antigen receptor expressing T cells, peptide vaccines, autologous dendritic cell vaccines, immunostimulatory viruses, oncolytic viruses, checkpoint blockade inhibitors, and drugs which alter the behavior of innate immune cells. Effort is focusing on determining which patient populations will benefit the most from these treatments and why. Research addressing synergism between treatment options is gaining attention. While advances in the treatment of glioma stagnated in the past, we may see a considerable evolution in the management of the disease in the upcoming years.
Keywords: Glioma, immunotherapies, Clinical Trials
Glioma
Gliomas are primary malignancies of the central nervous system (CNS), accounting for 80% of all malignant CNS tumors that are diagnosed in the USA (1; 2). In 2017 the NCI estimated that CNS malignancies constitute 23,800 cases with 16,700 deaths attributable to these diseases per year. The incidence is relatively similar world-wide with a marginally higher rate of diagnosis in men (3). Reported risk factors for the development of glioma are pre-natal X-rays and prior radiotherapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia, but are both rare occurrences and have been contested (4; 5). Peak disease incidence increases with age, but pediatric forms are commonly diagnosed as well. However, the origin and presentation of pediatric gliomas differ from the adult ones, as pediatric tumors often originate in the brain stem, whereas adult gliomas generally develop in the frontal regions of the brain (1).
Gliomas derive from a cancerous glial cell of either ependymal cell (ependymoma), oligodendroglial (oligodendrogliomas), or astrocytic (astrocytomas) origin and sometimes present with gene signatures of multiple cell types (oligoastrocytomas/mixed gliomas). Astrocytomas are generally more commonly diagnosed, and different subtypes of glioma are more common in specific age groups (6). Following the older scheme of tumor classification, gliomas are graded on a scale of I–IV by the World Health Organization (WHO) depending on tissue histology and the tumor’s invasion into surrounding tissue. Aggressive forms of grade III and all grade IV gliomas are classified as high grade gliomas (HGG). Grade III tumors are referred to as ‘anaplastic’ while Grade IV gliomas are referred to as Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) (7). GBM is highly invasive, well vascularized, and almost always fatal.
More recently, gliomas have been classified differently based on TCGA criteria into proneural, neural, classical, and mesenchymal subtypes based on the mutations and molecular signatures the tumors carry. Classical gliomas often present with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, amplification of chromosome 7, and have genetic signatures most indicative of astrocytic origin. Proneural tumors commonly have isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) and platelet derived growth factor receptor A (PDGFRA) mutations and express genes indicative of oligodendroglial origin. Neural gliomas express genes primarily seen in neuronal cell types. Finally, mesenchymal tumors often present with neurofibromin 1 (NF1) mutations and are characterized by gene signatures of astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and neurons. (8). Gliomas are most often discovered when neuroimaging is performed on patients who present with new onset chronic headaches, new onset seizures, new neurological deficits, and signs of increased intracranial pressure. In this review, we summarize progress in glioma immunotherapy and provide a list of ongoing immunotherapy-based clinical trials.
Current Management of Glioma
The current standard therapy consists of resection, when possible, followed by concomitant radio- and chemotherapy with temozolomide (TMZ), but is far from optimal in combating disease progression. This therapy and dosing regimen were implemented in 2005 and have yet to be revised, despite advancements in cancer therapeutics (9). Average time of survival after GBM diagnosis and treatment with the gold standard therapy of temozolomide and fractionated radiation is dismal, ranging between 12 to 15 months (10).
Resection to gain a negative tumor margin is nearly impossible as the tumors are highly infiltrative and often invade vital brain regions. Patients incur frequent complications of both the disease and its treatment, including seizures, neurological symptoms, hydrocephalus, and the adverse effects of chemotherapy. Thus, there is substantial need to identify more effective and specific targets for treatment. Apart from cytotoxic and anti-angiogenic therapies, modulation of the immune system is a promising approach, as innate and adaptive immunity play crucial roles in cancer progression and patient survival (11).
The Blood Brain Barrier and Angiogenesis in Glioma
The blood brain barrier (BBB), which is composed of tight junctions made by endothelial cells, pericytes, and astrocytes, serves to keep the CNS as an immune-privileged environment, in that cells of the peripheral immune system are excluded from entry unless a perturbation to the BBB occurs. The breakdown of the BBB in glioma is a well-documented occurrence, however, due to high concentrations of soluble factors secreted from the tumors, such as VEGF and MMPs, which compromise endothelial tight junctions, degrade proteoglycans in the surrounding extracellular matrix, and allow for the infiltration of various immune cells and blood derived factors (12; 13). This leakiness may be exploited to deliver drugs to the tumor, which might not have otherwise crossed the BBB. There is heterogeneity, however, in BBB leakiness in glioma with some areas more susceptible to drug penetrance, whereas other portions remain rather impermeant.
Aberrant neovascularization is a hallmark of GBM, another explanation why the BBB is so abnormal in the disease (14). Tissue edema and interstitial pressure increase as the tumors expand. Functional MRI revealed that blood flow rate is increased to the tumoral area relative to the surrounding healthy brain tissue in patients (15). Vessels present in glioma biopsies are often described as tortuous and differ from normal vasculature in their integrity and composition. In GBMs the vessels have significantly larger diameters than normal blood vessels in the brain and are suboptimal for the efficient flow and distribution of blood. Pericytes that surround endothelial cells are sparser along blood vessels, resulting in increased leakiness. Due to this uneven distribution of blood flow through tumors, certain regions are prone to outgrowing their blood supply leading to tissue necrosis and hypoxia. Tumor hypoxia, in turn, leads to glycolytic metabolic shifts in cancer cells and the attraction of various cell populations to infiltrate the tumor.
The tumor microenvironment
Tumors represent a complex ecosystem populated by tumor stem cells, stromal cells, blood vessels, infiltrating monocytic populations, and resident immune cells (See Figure 1). Microglia, the resident macrophages of the CNS, are responsible for combating infection and responding to injury. Microglia, unlike macrophages in the rest of the body, derive from a population of yolk-sac progenitors and migrate to the CNS early in development. After populating the CNS, the resident pool of microglia is replenished over time by a resident pool of stem cells, rather than via the bone marrow, as most other monocytic populations do (16).
Figure 1. Immunosuppression within the tumor microenvironment.
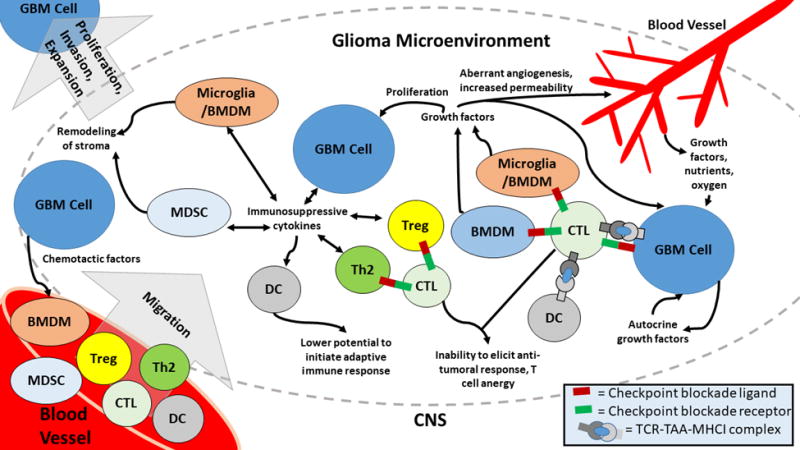
GBM cells express various autocrine growth factors which increase their own proliferation. Additionally, GBM cells produce immunosuppressive cytokines which polarize T cells, MDSCs, microglia, and DCs to more pro-tumorigenic phenotypes which also produce immunosuppressive cytokines. Cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) receive inhibitory signals via checkpoint blockade receptors expressed by other cells in the glioma microenvironment and become anergic. DCs have a poorer capacity to elicit an immune response due to their pro-tumorigenic polarization. Growth factors released by immune cells and GBM cells enhance neovascularization of the tumor and increase blood vessel permeability allowing for infiltration of the tumor by blood-derived monocytes which are attracted to the tumor by various chemotactic factors released by GBM cells. Proteases released by the various immune cells serve to remodel the stroma, leading to glioma’s invasion into the surrounding, healthy CNS.
In glioma, bone marrow derived monocytes (BMDMs) are mobilized and migrate into the tumor following the secretion of chemotactic factors such as colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF1) and CCL2 by tumor cells (17). Once recruited to the tumor interior, BMDMs develop immunosuppressive phenotypes and secrete growth factors and cytokines, which help to nurture the growth and spread of the tumor (18). Due to gene expression similarities between microglia and macrophages, it is often difficult to differentiate whether peripherally-derived BMDMs or microglia constitute the bulk of Glioma Associated Macrophages (GAMs). Additionally, there are frequently regional variations within tumors in the distribution of immune infiltrate, since the microenvironment encountered at a necrotic core of a tumor is different than its invasive edge in cellular, cytokine, or metabolic activity (18).
Classically, almost all chemotherapeutics were designed against and have targeted the rapid growth and division of cancer cells by hindering vital cellular processes. Aside from TMZ, the cytotoxic agents procarbazine, lomustine and vincristine have been used for the treatment of certain subtypes of low grade glioma (19; 20). Newer treatment modalities have targeted hyperactive receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and/or the neovascularization of tumors by inhibiting angiogenesis, but have often failed to show clinical efficacy over the current standards of care because tumor cells upregulate the activity of other complementary pathways. For example, VEGF-A overexpression is well documented in glioma and has received a great deal of attention as a therapeutic target in recent years. Phase III clinical trials were performed in 2014, evaluating concomitant Avastin (bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody) with TMZ and RT as first line defense for newly diagnosed glioma. While increasing PFS significantly, the trials failed to meet pre-defined criteria for success and failed to show any increase in overall survival time (OST) for patients (21). However, individual patients responded quite well, showing that some may serve to benefit from the adjuvant therapy. Anti-angiogenic therapy was recently shown to bolster the efficacy of certain immunotherapeutics, which has necessitated further exploration of the use of such drugs in combination with other treatment modalities in a case-specific manner for GBM. Indeed, concomitant treatment with bevacizumab is a component to many ongoing clinical trials (See Table 1).
Table 1. Active Immunotherapy Clinical Trials.
A list of all the phase I–IV clinical trials currently being conducted in the United States as listed by the National Cancer Institute and organized by type of immunotherapy.
| Name | Identifying Number | Class | Phase | Indication | Lead Organization and Collaborators | Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rovalpituzumab Tesirine | NCT02709889 | Antibody Drug Conjugate | I/II | DLL-3 expressing advanced solid tumors | Stemcentrx | This anti-Delta like ligand 3 Ab conjugated to pyrrolobenzodiazepine (DNA crosslinking agent) is administered IV every 6 weeks |
| Iodine I 131 Monoclonal Antibody 3F8 | NCT00445965 | Antibody Drug Conjugate | II | GD2 expressing CNS and leptomeningeal tumors | Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center | Radioactive anti-Ganglioside G2 antibody administered IT |
| ABT-414 | NCT02573324 | Antibody Drug Conjugate | II | Newly Diagnosed GBM with EGFR Amplification | Abbvie | Anti-EGFR Ab conjugated to monomethyl auristatin F (Cytotoxic) given with standard TMZ and RT |
| Iodine I 131 Monoclonal Antibody 8H9 | NCT00089245 | Antibody Drug Conjugate | I | 8H9 Reactive CNS or Leptomeningeal tumor unresponsive to conventional therapy | Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center | Radioactive Ab targeting B7-H3 administered IT |
| D2C7-IT (anti-EGFRwt, EGFRvIII recombinant immunotoxin) | NCT02303678 | Antibody Drug Conjugate | I | Recurrent GBM | Duke University Medical Center | anti-EGFRwt, EGFRvIII Ab fragment conjugated to genetically engineered Pseudomonas Exotoxin delivered intratumorally |
| CC-122 | NCT01421524 | IFN immunomodulatory | I | Advanced Solid Tumors | Celgene Corporation | Dose escalation study of CC-122 (a pleiotropic pathway modifier) which enhances IFN production and is considered immunostimulatory |
| ICT-107 | NCT02546102 | Dendritic Cell Vaccine | III | Newly diagnosed GBM | ImmunoCellular Therapeutics, Ltd., Novella Clinical | TMZ and placebo vs TMZ and ICT-107, ICT-107 is a DC vaccine derived from autologous mononuclear DCs pulsed with six TAAs |
| CMV pp65 DC +/− Td vaccination +/− Basiliximab | NCT02366728 | Dendritic Cell Vaccine | II | Newly Diagnosed GBM with requirement for resection | Duke University Medical Center | Standard TMZ and RT followed by Tetanus toxoid (TD) preconditioning +/− Basiliximab (anti-CD25) + CMV pp65-LAMP mRNA-pulsed autologous DCs labeled with 111In injected ID |
| Bevacizumab, Minocycline Hydrochloride, + RT | NCT01580969 | Anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic | I/II | Recurrent GBM | Huntsman Cancer Institute/University of Utah | Dose escalation study of oral minocycline hydrochloride, an antiinflammatory antibiotic, given in addiation to treatment with the anti-VEGF Ab, bevacizumab, and fractionated RT |
| Pembroluzimab | NCT02337686 | Checkpoint blockade inhibitor | II | Recurrent GBM with requirement for resection | MD Anderson Cancer Center | Anti-PD1 Ab given IV 6 and 3 weeks prior to surgery and dosed every 3 weeks afterwards. |
| Pembrolizumab | NCT02852655 | Checkpoint Blockade Inhibitor | I | refractory GBM with prior RT | Dana-Farber Harvard Cancer Center | Anti-PD1 Ab monotherapy given IV 14 days prior to surgery and then dosed every 3 weeks afterwards |
| Pembrolizumab | NCT02658279 | Checkpoint Blockade Inhibitor | I | Recurrent HGG with prior RT and cytotoxic therapy, tumor has >30 mutations | Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center | IV administration of anti-PD1 Ab given every 3 weeks until disease progression |
| Pembroluzimab + RT + bevacizumab | NCT02313272 | Checkpoint Blockade Inhibitor | I | Recurrent HGG | Moffitt Cancer Center | Standard RT with IV anti-PD1 Ab administration every 3 weeks and bevacizumab IV every 2 weeks |
| MRI guided laser surgery + pembroluzimab | NCT02311582 | Checkpoint blockade inhibitor | I/II | Recurrent GBM | Siteman Cancer Center at Washington University | After MRI guided laser surgery, patients receive IV anti-PD1 Ab 1 week later followed by every 3 weeks for 24 months. |
| Tremelimumab and Durvalumab | NCT02794883 | Checkpoint blockade Inhibitor | II | Recurrent GBM | Northwestern University | Anti-CTLA4 (tremelimumab) and anti-PDL1 (durvalumab) antibodies given IV in combination or separately over multiple weeks |
| Urelumab (Anti-CD137 Antibody) or Anti-LAG3 Antibody +/− Nivolumab | NCT02658981 | Checkpoint Blockade Inhibitor | I | Progressive or Recurrent GBM | Adult Brain Tumor Consortium | Phase I study assessing combination of checkpoint blockade inhibitors targeting CD137, LAG3, and PD1 when administered IV. |
| Nivolumab + RT | NCT02617589 | Checkpoint blockade inhibitor | III | Newly diagnosed GBM, methylated and unmethylated | Bristol-Myers Squibb, Ono Pharmaceutical Company Limited | TMZ and fractionated RT vs anti-PD1 Ab given with fractionated RT every 2 weeks followed by Anti-PD1 Ab alone every 4 weeks |
| Nivolumab + RT | NCT02829931 | Checkpoint Blockade Inhibitor | I | Recurrent HGG | Moffitt Cancer Center | Fractonated RT given with anti-PD1 Ab administered IV every 2 weeks for 4 months then every 4 weeks |
| Nivolumab +/− pp65 RNA pulsed DC Vaccination | NCT02529072 | Checkpoint Blockade Inhibitor +/− DC vaccine | I | Progressive HGG | Duke University Medical Center | Pre-operative anti-PD1 Ab given every 2 weeks for 8 weeks followed by tumoral resection then multiple CMV pp65-LAMP mRNA-pulsed autologous DC vaccinations given with continued anti-PD1 Ab therapy |
| AGEN-1884 (Anti-CTLA4) | NCT02694822 | Checkpoint Blockade Inhibitor | I | Advanced Solid Tumors | Agenus Inc. | Phase I study of anti-CTLA4 Ab monotherapy |
| Ipilumamab and Imatinib mesylate | NCT01738139 | Checkpoint Blockade Inhibitor + RTK inhibitor | I | Unresectable, Kit+ Solid Tumors | MD Anderson Cancer Center | Dose escalation study of Anti-CTLA4 Ab administered IV and Kit inhibitor administered orally |
| MEDI4736 + bevacizumab | NCT02336165 | Checkpoint blockade inhibitor | II | Newly Diagnosed GBM | Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research | Anti-PDL1 Ab administered IV +/− bevacizumab IV +/− standard RT to assess clinical efficacy of PDL1 blockade in different combination therapies |
| Nivolumab + TMZ +RT | NCT02667587 | Checkpoint blockade Inhibitor | II | Newly Diagnosed GBM | Bristol-Myers Squibb, Ono Pharmaceutical Company Limited | Anti-PD1 Ab given in combination to standard RT and TMZ |
| Pembroluzimab +/− bevacizumab | NCT02337491 | Checkpoint blockade inhibitor + anti-angiogenic | II | Recurrent GBM, no prior treatment with bevacizumab | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute | Trial assessing anti-PD1 Ab combined with anti-VEG Ab, both administered IV |
| Epacadostat + Nivolumab | NCT02327078 | IDO1 Inhibitor + Checkpoint blockade inhibitor | II | Select Advanced Cancers | Incyte Corporation | Anti-PD1 Ab given every 2 weeks with dose escalation of epadostat, an IDO1 inhibitor |
| BLZ945 + PDR001 | NCT02829723 | Checkpoint blockade inhibitor + Csf1 R inhibitor | I/II | Advanced solid tumors | Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation | Oral CSF1R inhibitor combined with IV anti-PD1 Ab administration |
| Pembrozluzimab + TMZ + RT +/− Vitespen (heat shock protein-peptide complex [HSPPC]-96 vaccine) | NCT03018288 | Checkpoint blockade Inhibitor + Vaccine | II | Newly Diagnosed GBM | NCI - Center for Cancer Research | Standard of care RT and TMZ with anti-PD1 Ab therapy +/− 4 weekly doses of vitespen (vaccine developed from heat shock protein (gp96)-peptide complex purified patient’s own tumoral tissue) |
| USL311 +/− Lomustine | NCT02765165 | CXCR4 inhibitor + cytotoxic agent | I/II | Recurrent GBM, Advanced solid tumors | MD Anderson Cancer Center | CXCR4 inhibitor administered +/− lomustine (alkylating agent) |
| PLX3397 | NCT02390752 | CSF1R, cKit inhibitor | I/II | Brain tumors in patients age 3–30 | NCI - Center for Cancer Research | Safety and tolerability study for PLX3397 (CSF1R and Kit inhibitor) dosing in adolescents with refractory solid tumors. |
| Low-Dose Capecitabine and Bevacizumab | NCT02669173 | Anti-MDSC, antiangiogenic | I | GBM with planned resection | Case Comprehensive Cancer Center | Capecitabine (thymidylate synthase inhibitor) dosed orally with bevacizumab IV given on days 1, 15, and every 28 days after |
| IL13R alpha 2-specific, CD19 CAR T cells | NCT02208362 | CAR-T Therapy | I | IL13R alpha 2+ Recurrent and refractory GBM | City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center | Intratumoral infusion of IL13R alpha 2-specific, CD19 CAR T cells with potential for additional intraventricular infusions |
| EGFRvIII CAR T cell therapy | NCT02209376 | CAR-T Therapy | I | EGFRvIII + Relapsed and Recurrent GBM | University of Pennsylvania/Abramson Cancer Center | Open label, phase I pilot study of EGFRvIII CAR T cell monotherapy |
| HER2-CD28-CMV CAR T Cell Therapy | NCT01109095 | CAR-T Therapy | I | HER2+ Recurrent or Progressive GBM | Baylor College of Medicine/Dan L Duncan Comprehensive Cancer Center | IV infusion of HER2-CAR CMV-T cells with potential for 6 additional doses if radiographic response recognized |
| EGFRvIII CAR T cell therapy | NCT02664363 | CAR-T Therapy | I | EGFRvIII + Newly Diagnosed GBM | Duke University Medical Center | IV administration of EGFRvIII CAR T cells |
| Autologous CMV-reactive CTLs + TMZ | NCT02661282 | T cell therapy | I/II | Newly diagnosed and recurrent GBM | MD Anderson Cancer Center | Patients undergo leukapheresis and their CTLs are lentivirally infected and reintroduced to patient IV after TMZ therapy. |
| HSPPC96 vaccine +/− bevacizumab | NCT01814813 | Vaccine +/− antiangiogenic | II | Recurrent, resectable GBM | Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology | Heat shock protein-peptide complexes made from a patient’s own tumor tissue given ID with anti-VEGF Ab given IV |
| Gliovac + GM-CSF + Cyclophosphamide +/− bevacizumab | NCT01903330 | Vaccine + Immunomodulatory agent + Cytotoxic agent | II | First or secondly relapsing GBM | UC Irvine Health/Chao Family Comprehensive Cancer Center | Vaccine derived from tumor lysates and GM-CSF given ID with oral administration of Cyclophosphamide. Anti-VEGF Ab given IV. |
| SurVaxM peptide vaccine + TMZ | NCT02455557 | Peptide Vaccine | II | Survivin +, Newly Diagnosed GBM | Roswell Park Cancer Institute | SurVaxM peptide vaccine targeting survivin given ID 4 times over 8 weeks with standard TMZ dosing PO or IV |
| Personalized neoantigen peptide vaccine + poly-ICLC | NCT02510950 | Peptide Vaccine | No Phase | Newly diagnosed GBM with consent for genome sequencing | Siteman Cancer Center at Washington University | After maintenance TMZ therapy and preparation of personalized neo-antigen vaccine, personalized neo-angtien vaccine + poly-ICLC vaccine given in multiple dosing cycles |
| NeoVax (neoantigen-based melanoma-poly-ICLC vaccine) +RT | NCT02287428 | Peptide Vaccine | I | Newly Diagnosed or Recurrent GBM | Dana-Farber Harvard Cancer Center | Six weeks of standard RT followed by a series of personalized tumor vaccinations |
| DSP-7888 | NCT02498665 | Peptide Vaccine | I | Advanced Solid Tumors | Boston Biomedical, Inc | Peptide vaccine derived from the gene products of the Wilms Tumor 1 gene which is expressed by subsets of tumor cells |
| insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGF-1 R)/antisense oligodeoxynucleotide (AS ODN)-treated tumor cells | NCT02507583 | Tumor Cell Vaccine | I | IGF-1R+ GBM | Thomas Jefferson University Hospital | Tumor cells from patient are purified and treated with insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGF-1 R)/antisense oligodeoxynucleotide, and reinjected into patient to induce immune response |
| carcinoembryonic antigen-expressing measles virus | NCT00390299 | Oncolytic Viral Therapy | I | Recurrent GBM | Mayo Clinic | Oncolytic carcinoembryonic antigen-expressing measles virus injected intratumorally after resection |
| PVS-RIPO | NCT01491893 | Oncolytic Virus | I | Recurrent GBM | Duke University Medical Center | PVSRIPO (recombinant oncolytic poliovirus PVSRIPO) delivered intratumorally by convection-enhanced delivery |
| Veledimex + Ad-RTS-hIL-12 | NCT02026271 | Immunostimulatory Virus | I | Recurrent Grade III/IV glioma | Ziopharm Oncology Inc | Adenoviral vector causing overexpression of hIL-12 injected intratumorally with velemidex activator ligand taken orally to enhance the immunostimulatory effects of the virus |
| AdhCMV-Flt3L and Ad-hCMV-TK + TMZ + RT + Valacyclovir | NCT01811992 | Suicide Gene/Immuno-stimulatory Viral Therapy | I | Newly diagnosed Grade III/IV glioma | University of Michigan Comprehensive Cancer Center | Standard TMZ + RT therapy with adenoviral vectors injected intratumorally. One vector delivers a suicide gene to cancer cells; the other increases DC activation by delivering immunostimulatory gene, Flt3L |
| Combination Adenovirus + Pembrolizumab | NCT02798406 | Oncolytic Virus + Checkpoint blockade Inhibitor | II | Newly Diagnosed GBM and secondly recurrent GBM | DNAtrix, Inc., Merck and Company Inc | Oncolytic adenovirus, DNX-2401, administered intratumorally, followed by anti-PD1 Ab administered every 3 weeks |
The potential to harness the body’s own immune defenses against aberrant tumor growth has become a promising alternative to the exclusive use of cytotoxic chemotherapeutic treatment modalities. Ultimately the eradication of tumors is dependent on the activity of the adaptive immune system to recognize the irregularity of tumor neo-antigens, overcome the immunosuppressive nature of the tumor microenvironment, and mount an effective immune response against in the tumor. Many of these therapies have shown promise on their own but may be more efficacious in combination with other immunotherapies or classical chemotherapeutic regimens.
Antibody Drug Conjugates
Chemotherapeutics can be directly targeted to tumor associated antigens (TAAs) in the form of antibody drug conjugates (ADCs), which increases their specificity and decreases potential off-target effects. For example, ABT-414 is an anti-EGFR antibody conjugated to the cytotoxin, monomethyl auristatin F, and is currently in phase II evaluation for newly diagnosed GBM with EGFR amplification (NCT02573324) (22). Radioactive Iodine 131 is another cytotoxic agent being utilized in clinical trials evaluating its use when linked to anti-Ganglioside G2 and administered intracranially (NCT00445965) for GD2-overexpressing GBMs as well as when conjugated to anti-B7-H3 and administered intrathecally for B7-H3 expressing GBMs (NCT00089245). In the case of radioactive iodine 131, the damage delivered to tumors serves to potentiate immune responses in a similar fashion that targeted radiotherapy is believed to (23). ADCs offer more precision than older chemotherapeutics, but their specificity allows for the potential survival of cancer cells when expression of the targeted TAA is downregulated.
CAR T Cell Therapy
The power of harnessing cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) to kill tumors has been most successfully demonstrated in the treatment of leukemia, where T cells engineered to express high affinity chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) directly target cancer antigens, which are not expressed or expressed at very low levels by other cells of the body (24). A pilot study (NCT02209376) for CAR-T therapy was explored recently for GBM using T cells engineered to recognize EGFRvIII, a mutated fragment of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) which represents the most common mutation found in classical GBM (8; 25). All patients showed signs of CAR-T expansion 7–10 days after infusion, and five patients who had resection of their tumors for pathological evaluation had CAR-T cells present in the biopsies. In another report, a patient with recurrent GBM expressing high levels of IL-13Rα2 was administered CAR-T cells against this antigen, intraventricularly, and was reported to have sustained immune infiltrate in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and disease remission for 7.5 months (26). Although this was a single isolated case, a phase I clinical trial is currently being conducted to assess the efficacy of this therapy in a similar patient population (NCT02208362).
While there seems to be some applicability of CAR-T for therapy, most immunotherapeutic approaches, which have been explored more thoroughly for glioma treatment, exploit the body’s own immune system to educate and mobilize the patient’s own CTLs to target and eradicate the tumor. These early reports of the potential efficacy of CAR-T merit further exploration in patient populations with well-defined target cancer antigens.
Vaccine Development
Tumor vaccination relies upon the presence of highly immunogenic neo-antigens expressed by tumor-derived cells, and their capacity to elicit a long lasting anti-tumor, CTL-mediated response. Gliomas typically have a low mutational burden, relative to other cancers such as melanoma or non-squamous cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and thus the number of neo-antigens to vaccinate against are much lower (27). Moreover, gliomas typically vary widely in which mutations they carry, making genetic screening and personalized vaccination for each individual a necessity if therapy is to be efficacious. Rindopepimut, for example, was a vaccine developed against EGFRvIII, the same antigen used for the aforementioned CAR-T trial (28). While the vaccine was well tolerated and showed some efficacy in conjunction with TMZ treatment in early clinical trials, phase III trials were halted due to the unlikelihood that the vaccine would meet criteria for therapeutic efficacy (29).
More recently, the prospect of multi-target personalized cancer vaccination is being investigated for a broader range of patients and enhanced clinical efficacy. Two clinical trials are currently assessing the efficacy of vaccines derived from heat shock protein-peptide complexes purified from patients’ own tumor lysate (NCT01814813, NCT03018288). These peptide complexes have the capacity to elicit MHC I-dependent CTL responses against TAAs with few adverse or unintended events (30). Additionally, clinical trial NCT03018288 is including a cohort of patients treated with antibody-mediated PD1 blockade to discern any additive effect the two therapeutic strategies may have. Other clinical trials are assessing Gliovac, a personalized vaccine for first or secondarily relapsing GBM, developed from a patient’s own autologous TAAs and allogeneic TAAs from the GBMs of other patients. The vaccine was efficacious and well tolerated in phase I clinical trials, and is currently recruiting patients for a phase II trial (31). These vaccination methods have shown some promise in early clinical trials and will be exciting to follow up in the future.
Vaccination relies on the fact that dendritic cells (DCs) successfully present antigen and educate a patients’ T cells to attack the cells expressing this antigen. An additional approach is removing their DCs and exposing them to the antigen directly (DC vaccination). By pulsing patient DCs with tumor neo-antigens and a cocktail of inflammatory cytokines, the DC cells are educated to present tumor neo-antigens to T cells and induce an adaptive immune response against tumor cells that express them (32). The argument has been made that using antigens present in glioma-derived cells which are killed under cell stress conditions may be more efficacious over simply lysing tumor cells or using synthesized/recombinant antigens for the culture with DCs. Educating DCs with glioma cells undergoing immunogenic cell death via treatment with hypericin and photodynamic therapy (PDT) to induce toxic levels of intracellular reactive oxygen species in the tumor cells, has been shown to be associated with better DC maturation and education over simply exposing DCs to crude glioma cell debris. Mice receiving DC vaccinations from DCs exposed to immunogenically killed glioma cells have been shown to have significantly increased survival times (33). PDT has been investigated as an adjuvant therapy to radiation and chemotherapy, has been shown to be well tolerated, and is approved as an intraoperative treatment in Japan for malignant brain tumors (34).
The optimal route of DC administration for effective therapy is still under investigation, although intranodal injection has been shown to be superior in eliciting potent CTL responses in the treatment of other cancers (35). DCVax-L, developed by Northwest Biotherapeutics, showed safety and efficacy in Phase I and II trials, and is currently under examination in phase III clinical trials for the treatment of newly diagnosed GBM (36). Another DC vaccine, ICT-107, is currently under investigation in phase III trials as well. The vaccine contains autologous DCs pulsed with only a subset of commonly overexpressed TAAs: HER2, TRP-2, gp100, MAGE-1, IL13Rα2, and AIM-2 (37). DC vaccination has shown some promise in prolonging overall survival time (OST) and increasing progression free survival (PFS) times for patients (38). The phase III trials currently being performed should prove to be quite informative. DC vaccination could also synergize well with other immunotherapeutic treatment modalities.
Viral Therapy
Another immunotherapeutic approach, which has been explored and shown to have promising efficacy for patients is the use of modified oncolytic viruses. For example, exploiting the fact that glioma stem cells upregulate the poliovirus receptor, CD155, a genetically engineered poliovirus, PVSRIPO, was designed to efficiently and specifically target cancer cells, thus causing immunogenic cell death, leading to the release of tumor-derived debris and viral antigen, which, in turn, is taken up by DCs and presented to T cells to initiate an anti-tumoral immune response to both the viral and tumoral antigens. Clinical trials thus far have demonstrated safety and efficacy and are currently being evaluated further in recurrent GBM (39; 40).
Other groups have researched the potential for viral vectors to deliver suicide genes to glioma-derived cells. The basis of these suicide gene therapies is that they render the cells susceptible to a toxic metabolite that the cells produce when encountering a particular substrate. In the case of most genetic therapies, glioma-derived cells selectively receive a viral thymidine kinase (TK) gene and patients are administered either ganciclovir (GCV) or valacyclovir, irreparably damaging the DNA of the cells expressing the viral TK, leading to cell death, and hopefully eliciting a T-cell mediated immune response. For example, adenoviral vectors delivering Herpes Simplex Virus TK (HSVTK) with GCV administration have shown promise for patients in Phase II clinical trials for the treatment of recurrent GBM by significantly extending PFS and OS (41).
The potential for viruses to induce potent immunostimulatory effects has also been explored using modified adenovirus expressing IL12 with activator ligand veledimex to potentiate its effects (42). IL12 is believed to exert its effects by polarizing GAMs to more anti-tumorigenic phenotypes (43). A phase I trial is currently evaluating the safety and efficacy of this therapy for recurrent HGG (NCT02026271). Aside from these few examples, genetically modified HSV, reovirus, Newcastle disease virus, other adenoviral vectors, and measles are currently being evaluated in clinical trials for glioma therapy as well (40). The potential for this form of therapy to synergize with PD-1 blockade is currently under phase I investigation with the modified oncolytic adenovirus, DNX-2401 (NCT02798406). It would be interesting to see how additional therapies may synergize in the future.
Checkpoint Blockade Inhibitors
A key to the success of most immunotherapeutic treatment modalities is making sure that the therapeutics actually reach and are well sustained within the tumor microenvironment. The importance in converting the tumor microenvironment from an immunosuppressive, nutrient-depleted environment to one which can promote a robust anti-tumoral T cell response is becoming a critical point to address in the successful design and implementation of immunotherapeutics for patients. It has been observed that macrophage and tumor cell populations upregulate cell surface receptors, particularly PD-L1, which block checkpoint receptors on the surfaces of T cells. These checkpoint receptors, the most well defined being PD-1, CTLA-4, and LAG-3, are expressed by T cells to dampen potentially unwanted T cell receptor (TCR) activation by inappropriate antigen presentation e.g. a cell surface antigen expressed by a non-tumorigenic cell in one’s own body (44; 45). Cancer cells, as a natural defense mechanism, upregulate checkpoint blockade ligands to shutdown T cells which may have had the potential to elicit an attack on the cancer cells initiated by their recognition of neo-antigens which had been recognized as ‘foreign’. This observation is well documented, particularly in cancers, such as NSCLC and melanoma, where mutational burden is quite high (27). In addition to preventing the activation of checkpoint blockade to promote CTL functionality, depleting T regulatory cells (Tregs) to reduce immunosuppression from the tumor microenvironment is touted as another potential therapeutic angle. For example, anti-CTLA4 and OX-40 antibodies used in pre-clinical cancer models have been shown to lead to local depletion of Tregs from tumors, resulting in enhanced systemic anti-tumor immunity (46).
One criticism of the use of checkpoint blockade inhibitors and immunotherapy in glioma is that oftentimes the mutational burden and therefore the number of neo-antigens present to elicit an anti-tumorigenic immune response is limited. It is known, however, that GBM cells in subsets of patients often upregulate checkpoint blockade proteins, such as PD-L1, which serve to protect the cancer cells from any adaptive anti-tumorigenic response which could have been mounted.
Targeting PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 using neutralizing antibodies in addition to stereotactic RT +/− TMZ in pre-clinical mouse models has shown efficacy in greatly extending life expectancy of GL261-bearing mice where PD-L1 expression is high in the tumors (47). The reality for patients however is that gliomas generally present as ‘immune cold’ tumors in that there is generally very little T cell infiltration and few cells express PD-L1. However, PD-L1 expression has been reported in a subset of glioma biopsies, which has been correlated with more aggressive tumors and worse prognosis for these patients (48). Other groups have had similar findings that higher levels of PD-L1 expression are correlated with more aggressive tumors and poorer patient outcomes in GBM (48). Likewise, TAMs have also been seen to represent a large pool of PD-L1 expressing cells with the potential to anergize T cells, which enter the tumor microenvironment (48; 49). Stereotactic RT is well documented to enhance immune infiltration into the microenvironment of HGGs by inducing immunogenic cell death in the tumors, making the combined use of RT and checkpoint blockade inhibitors a promising therapeutic avenue. As a proof of principle, treatment with pembroluzimab, a PD-1 blocking antibody, was reported to cause massive lymphocytic infiltration of tumor tissue and radiographic tumor reduction in the case of a patient with a hyper-mutated GBM (50). A phase II clinical trial evaluating the efficacy of durvalumab which targets PD-L1 in recurrent GBM is ongoing and may benefit patients with a select immune signature in their tumors (NCT02336165). An important point to address for the future is how to profile which patients will benefit the most from this type of treatment as to not waste time or treat likely non-responders. Finding therapeutic synergism with checkpoint blockade inhibitors is of fundamental importance and is being explored in numerous clinical trials at the moment (See Table 1).
Targeting Innate Immune Cells in the tumor microenvironment
In addition to tumor cells upregulating cell surface ligands which directly render immune cells anergic, the tumor microenvironment contains high levels of inhibitory cytokines, such as IL-10 and Transforming growth factor β (TGFβ), which are secreted both by cancer cells and innate immune cells such as TAMs and myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), which constitute large cytokine reservoirs. These cytokines drive a senescent phenotype in T cells and polarize certain subsets to an immunosuppressive Treg phenotype. These TAMs are also responsible for the secretion of MMPs and other proteases which serve to remodel the stroma surrounding tumoral cells and allow for their spread and invasion. TAMs also serve to recruit endothelial cells to the microenvironment via the secretion of angiogenic factors, which cause blood vessel branching and tumor neovascularization [41].
In the context of glioma, it has been shown that glioma associated microglia and macrophages (GAMs) play vital roles in supporting tumor growth. GAMs are known to comprise up to 30% of the cellular bulk of gliomas upon biopsy (51). GAMs, similarly to TAMs in peripheral tumors, develop immunosuppressive phenotypes characterized by high expression of TGFβ, IL10, CXCL10, and CCR2. Patients whose tumors have high expression of these cytokines have been found to have poorer OS and PFS (52). Our group as well as others have shown that GAMs are vital to tumor support. Using HSV-TK expressing microglia and macrophages within gliomas and focally eradicating them with GCV infusion, our group showed that tumors developed poorly in mice that lacked these cell populations, and the animals had significantly extended survival times (53). Other groups have shown that pharmacological depletion of GAMs from tumors, in a similar fashion, helps to slow tumor progression. Du et al. demonstrated that hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF1α) is a critical transcription factor upregulated in gliomas, and results in attraction of BMDMs to tumors, while its inhibition abrogates BMDM accumulation, associated with less neovascularization and a less invasive phenotype of the tumors (54). PLX3397 is a CSF1R and c-Kit inhibitor, which selectively kills CSF1R-expressing macrophages and microglia (55). It was shown that mice given oral PLX3397 exhibited less GAM infiltrate in tumors and less invasive tumors, overall. The drug was shown to slow glioma recurrence after focal irradiation of the tumors in mouse xenograft models (56). The drug went to Phase II clinical trials for the treatment of recurrent GBM, was well tolerated orally, but failed to show any benefit for patients in terms of PFS at 6 months when dosed orally at 1000mg/day as a single agent (57). PLX3397 is currently being tested for use in adolescent GBM (NCT02390752) and drugs with similar mechanisms are currently under investigation for combination therapy with other treatment modalities (See Table 1).
A similar approach to the use of CSF1R inhibitors is the depletion and prevention of MDSCs from migrating to and accumulating in tumors. Capecitabine is a thymidylate synthase inhibitor which is theorized to preferentially target the replication of MDSCs (58). The drug is currently under evaluation in combination with bevacizumab for GBM (NCT02669173).
Some investigators have approached the therapeutic potential of manipulating GAMs towards acquiring an anti-tumorigenic phenotype and promoting an adaptive immune response. It was demonstrated that another CSF1R inhibitor, BLZ945, slowed GBM progression in a proneural inducible GBM mouse model and in a xenograft mouse model. Interestingly, this drug’s efficacy was attributed to causing an anti-tumorigenic shift in the GAMs populating tumors, primarily by selectively eliminating microglia while blocking pro-tumorigenic polarization of infiltrating macrophages. Gene signatures of macrophages in treated animals were found to parallel gene signatures from TCGA data from patients with pro-neural GBMs who had better survival outcomes. The authors concluded that the predominant phenotype of GAMs within tumors may be a better predictor of patient outcome rather than total GAM density (59). In a similar fashion, Kloepper et al. showed that the administration of a bispecific antibody against Ang-2 and VEGF was able to promote an anti-tumorigenic polarization of GAMs in both a syngeneic orthotopic and a xenograft murine glioma model (60). Another group showed that non-toxic doses of Amphotericin B had the potential to drive the anti-tumorigenic polarization of microglia and macrophages and that its administration to glioma-bearing mice greatly extended their survival (61). Another example, although hard to scale to human patients, was the use of a microRNA, miR-142-3p, in mice, which selectively caused the death of immunosuppressive, TGFβRI expressing GAMs while leaving other GAM populations untouched. These mice exhibited significant reductions in tumor burden (62).
TGFβI and II overexpression, especially that of isoform II, has been correlated with poorer clinical outcomes in subsets of glioma (63; 64). Autocrine signaling within cancer cells serves to enhance epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and increases the invasive phenotype of tumor cells. TGFβ potentiates angiogenesis and is an immunosuppressive cytokine, which polarizes Tregs and attracts and polarizes immunosuppressive GAMs (65; 66). It can downregulate perforin, granzyme A/B, IFNγ, and FasL expression by CTLs, which are all mediators of CTL-mediated cytotoxicity (67). Downregulation of the expression of TGFβRII in human xenograft-derived gliomas has been shown to reduce their tumorigenicity (68). Inhibition of TGFβ-dependent pathways using TGFβRII inhibitors in GAMs has been shown to prevent their immunosuppressive polarization (69). Blocking TGFβ-mediated signaling using systemically administered neutralizing antibodies was efficacious in slowing glioma progression in immunocompetent mice, partially by preventing the immunosuppressive polarization of GAMs (70). For the treatment of glioma, clinical trials are ongoing, evaluating the TGFβRI small molecule inhibitor, LY2157299, for efficacy in combination with the standard of care. The drug is generally well tolerated and has shown efficacy in about 20% of patients (71).
In all these cases, efficacy was partially attributed to subversion of the communication between glioma cells and GAMs. While many of these approaches have shown some preclinical efficacy, most attention is given to T-cell targeted therapies. It may be reasonable to approach some of these GAM-targeting drugs as adjuvant therapies to synergize with the more popular immunotherapeutics.
Finally, pleitrophic pathway modifiers (PPMs) are another class of drugs, which serve to inhibit the function of immunosuppressive pathways in certain cells, thus shifting polarization of these cells to more anti-tumorigenic extremes. CC122, for example works by causing the degradation of Ikaros and Aiolos in cells leading to enhancement in the transcription of IFN response elements which all serve to boost anti-tumoral immunity (72). CC122 is currently being evaluated in the treatment for certain advanced solid cancers, including refractory GBM (NCT01421524). PPMs could synergize well with other immunotherapeutics such as checkpoint blockade inhibitors in future trials.
Conclusions
While therapeutic interventions for HGG have remained at an impasse for the past decade, the advent of immunotherapeutics holds great promise for the future. Judicious use of the appropriate therapies and combinatorial approaches to capitalize upon multiple, exploitable weaknesses in tumors will require significant amounts of clinical research going forward. The permutations of all the possible combinatorial treatments, and the identification of patient-specific neo-antigens make for a substantial level of research effort in such a short time frame. Tumor and immune-profiling of patients on an individual basis should be critical factors in devising the treatment plans these people are assigned to. Finally, cost, while not discussed here, would be an important consideration in streamlining these therapies for greater access to the people that need them most. Therapy may improve but at a steep price that far exceeds the research and development costs that went into the less personalized chemotherapeutics of the past.
Figure 2. Treatment Modalities for Immunotherapy.
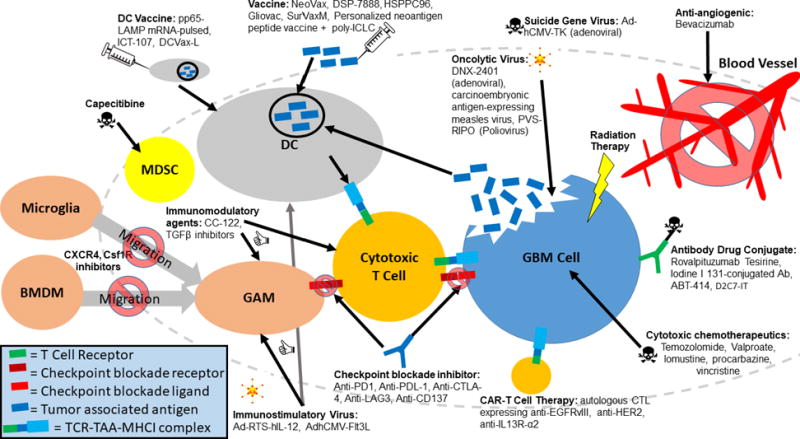
Immunotherapeutics are designed to exert their effects on various cell types within the glioma microenvironment. Anti-angiogenics block neovascularization of gliomas. Radiation and cytotoxic chemotherapeutics exert their effects on rapidly dividing glioblastoma (GBM) cells by causing irreparable DNA damage and/or inhibiting vital cellular processes. Antibody drug conjugates deliver cytotoxic chemotherapeutics to cells with higher specificity by targeting tumor associated antigens (TAAs). Oncolytic viruses and viruses carrying suicide genes are targeted to GBM cells overexpressing particular receptors and cause immunogenic cell death. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells are engineered to elicit efficient killing against cells expressing specific TAAs. Checkpoint blockade inhibitors prevent T cell anergy by blocking inhibitory interactions between T cells and target cells. CXCR4 and Csf1R inhibitors block bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs) and microglia from migrating to tumors. Capecitibine depletes immunosuppressive MDSCs (myeloid derived suppressor cells). Immunomodulatory agents and immunostimulatory viruses enhance anti-tumorigenic polarization of various immune cells within the glioma microenvironment. Vaccines and dendritic cell (DC) vaccines serve to elicit potent anti-tumor effects by education and stimulation of anti-TAA cytotoxic T cells. GAM = glioma associated microglia/macrophage.
Acknowledgments
Financial Support:
NIH R01NS42168
NIH T32GM007518
NIH T32GM008444
NIH F30CA196110
Footnotes
Both authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Omuro A, DeAngelis LM. Glioblastoma and other malignant gliomas: a clinical review. JAMA. 2013;310:1842–50. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.280319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Fulop J, Liu M, Blanda R, et al. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2008–2012. Neuro Oncol. 2015;17(Suppl 4):iv1–iv62. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dubrow R, Darefsky AS. Demographic variation in incidence of adult glioma by subtype, United States, 1992–2007. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:325. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wang Z, Terakawa Y, Goto H, Tsuyuguchi N, Sato H, et al. Glioblastoma in long-term survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Report of two cases. Pediatr Int. 2016;58:520–3. doi: 10.1111/ped.12843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Linet MS, Kim KP, Rajaraman P. Children’s exposure to diagnostic medical radiation and cancer risk: epidemiologic and dosimetric considerations. Pediatr Radiol. 2009;39(Suppl 1):S4–26. doi: 10.1007/s00247-008-1026-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ostrom QT, Bauchet L, Davis FG, Deltour I, Fisher JL, et al. The epidemiology of glioma in adults: a “state of the science” review. Neuro Oncol. 2014;16:896–913. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nou087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hou L, Veeravagu A, Hsu A, Tse V. Recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: a review of natural history and management options. 2006;20:E3. doi: 10.3171/foc.2006.20.4.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Verhaak RG, Hoadley KA, Purdom E, Wang V, Qi Y, et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:98–110. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–96. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:492–507. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0708126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.da Fonseca AC, Badie B. Microglia and macrophages in malignant gliomas: recent discoveries and implications for promising therapies. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:264124. doi: 10.1155/2013/264124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schneider SW, Ludwig T, Tatenhorst L, Braune S, Oberleithner H, et al. Glioblastoma cells release factors that disrupt blood-brain barrier features. Acta Neuropathol. 2004;107:272–6. doi: 10.1007/s00401-003-0810-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wolburg H, Noell S, Fallier-Becker P, Mack AF, Wolburg-Buchholz K. The disturbed blood-brain barrier in human glioblastoma. Mol Aspects Med. 2012;33:579–89. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jain RK, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Loeffler JS, Sorensen AG, Batchelor TT. Angiogenesis in brain tumours. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:610–22. doi: 10.1038/nrn2175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wolf RL, Wang J, Wang S, Melhem ER, O’Rourke DM, et al. Grading of CNS neoplasms using continuous arterial spin labeled perfusion MR imaging at 3 Tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2005;22:475–82. doi: 10.1002/jmri.20415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Alliot F, Godin I, Pessac B. Microglia derive from progenitors, originating from the yolk sac, and which proliferate in the brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1999;117:145–52. doi: 10.1016/s0165-3806(99)00113-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chang AL, Miska J, Wainwright DA, Dey M, Rivetta CV, et al. CCL2 produced by the glioma microenvironment is essential for the recruitment of regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Res. 2016 doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Domingues P, Gonzalez-Tablas M, Otero A, Pascual D, Miranda D, et al. Tumor infiltrating immune cells in gliomas and meningiomas. Brain Behav Immun. 2016;53:1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.07.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yang SH, Hong YK, Yoon SC, Kim BS, Lee YS, et al. Radiotherapy plus concurrent and adjuvant procarbazine, lomustine, and vincristine chemotherapy for patients with malignant glioma. Oncol Rep. 2007;17:1359–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Buckner JC, Shaw EG, Pugh SL, Chakravarti A, Gilbert MR, et al. Radiation plus Procarbazine, CCNU, and Vincristine in Low-Grade Glioma. The New England journal of medicine. 2016;374:1344–55. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1500925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gilbert MR, Dignam JJ, Armstrong TS, Wefel JS, Blumenthal DT, et al. A randomized trial of bevacizumab for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:699–708. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1308573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Phillips AC, Boghaert ER, Vaidya KS, Mitten MJ, Norvell S, et al. ABT-414, an Antibody-Drug Conjugate Targeting a Tumor-Selective EGFR Epitope. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016;15:661–9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Larson SM, Carrasquillo JA, Cheung NK, Press OW. Radioimmunotherapy of human tumours. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15:347–60. doi: 10.1038/nrc3925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Newick K, Moon E, Albelda SM. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for solid tumors. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2016;3:16006. doi: 10.1038/mto.2016.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ren PP, Li M, Li TF, Han SY. Anti-EGFRvIII chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for adoptive cell therapy of glioblastoma. Curr Pharm Des. 2017 doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170316125402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Brown CE, Alizadeh D, Starr R, Weng L, Wagner JR, et al. Regression of Glioblastoma after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:2561–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1610497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Platten M, Offringa R. Cancer immunotherapy: exploiting neoepitopes. Cell Res. 2015;25:887–8. doi: 10.1038/cr.2015.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Swartz AM, Li QJ, Sampson JH. Rindopepimut: a promising immunotherapeutic for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Immunotherapy. 2014;6:679–90. doi: 10.2217/imt.14.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Malkki H. Trial Watch: Glioblastoma vaccine therapy disappointment in Phase III trial. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12:190. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2016.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wood CG, Mulders P. Vitespen: a preclinical and clinical review. Future Oncol. 2009;5:763–74. doi: 10.2217/fon.09.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schijns VE, Pretto C, Devillers L, Pierre D, Hofman FM, et al. First clinical results of a personalized immunotherapeutic vaccine against recurrent, incompletely resected, treatment-resistant glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) tumors, based on combined allo- and auto-immune tumor reactivity. Vaccine. 2015;33:2690–6. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.03.095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Phuphanich S, Rudnick J, Chu R, Mazer M, Wang H, et al. A phase I trial of tumor-associated antigen-pulsed dendritic cell immunotherapy for patients with brain stem glioma and glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2032. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Garg AD, Vandenberk L, Koks C, Verschuere T, Boon L, et al. Dendritic cell vaccines based on immunogenic cell death elicit danger signals and T cell-driven rejection of high-grade glioma. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8:328ra27. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aae0105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Akimoto J. Photodynamic Therapy for Malignant Brain Tumors. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2016;56:151–7. doi: 10.2176/nmc.ra.2015-0296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bedrosian I, Mick R, Xu S, Nisenbaum H, Faries M, et al. Intranodal administration of peptide-pulsed mature dendritic cell vaccines results in superior CD8+ T-cell function in melanoma patients. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:3826–35. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.04.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Polyzoidis S, Ashkan K. DCVax(R)-L–developed by Northwest Biotherapeutics. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10:3139–45. doi: 10.4161/hv.29276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Phuphanich S, Wheeler CJ, Rudnick JD, Mazer M, Wang H, et al. Phase I trial of a multi-epitope-pulsed dendritic cell vaccine for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013;62:125–35. doi: 10.1007/s00262-012-1319-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yang L, Guo G, Niu XY, Liu J. Dendritic Cell-Based Immunotherapy Treatment for Glioblastoma Multiforme. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:717530. doi: 10.1155/2015/717530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Goetz C, Dobrikova E, Shveygert M, Dobrikov M, Gromeier M. Oncolytic poliovirus against malignant glioma. Future Virol. 2011;6:1045–58. doi: 10.2217/fvl.11.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Saha D, Ahmed SS, Rabkin SD. Exploring the Antitumor Effect of Virus in Malignant Glioma. Drugs Future. 2015;40:739–49. doi: 10.1358/dof.2015.040.11.2383070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ji N, Weng D, Liu C, Gu Z, Chen S, et al. Adenovirus-mediated delivery of herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase administration improves outcome of recurrent high-grade glioma. Oncotarget. 2016;7:4369–78. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lasek W, Zagozdzon R, Jakobisiak M. Interleukin 12: still a promising candidate for tumor immunotherapy? Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014;63:419–35. doi: 10.1007/s00262-014-1523-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Chiu TL, Wang MJ, Su CC. The treatment of glioblastoma multiforme through activation of microglia and TRAIL induced by rAAV2-mediated IL-12 in a syngeneic rat model. J Biomed Sci. 2012;19:45. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-19-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.He Y, Rivard CJ, Rozeboom L, Yu H, Ellison K, et al. Lymphocyte-activation gene-3, an important immune checkpoint in cancer. Cancer Sci. 2016;107:1193–7. doi: 10.1111/cas.12986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Parry RV, Chemnitz JM, Frauwirth KA, Lanfranco AR, Braunstein I, et al. CTLA-4 and PD-1 receptors inhibit T-cell activation by distinct mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:9543–53. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.21.9543-9553.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Marabelle A, Kohrt H, Sagiv-Barfi I, Ajami B, Axtell RC, et al. Depleting tumor-specific Tregs at a single site eradicates disseminated tumors. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:2447–63. doi: 10.1172/JCI64859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Reardon DA, Gokhale PC, Klein SR, Ligon KL, Rodig SJ, et al. Glioblastoma Eradication Following Immune Checkpoint Blockade in an Orthotopic, Immunocompetent Model. Cancer Immunol Res. 2016;4:124–35. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wang Z, Zhang C, Liu X, Wang Z, Sun L, et al. Molecular and clinical characterization of PD-L1 expression at transcriptional level via 976 samples of brain glioma. Oncoimmunology. 2016;5:e1196310. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1196310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.De Palma M, Lewis CE. Macrophage regulation of tumor responses to anticancer therapies. Cancer Cell. 2013;23:277–86. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Johanns TM, Miller CA, Dorward IG, Tsien C, Chang E, et al. Immunogenomics of Hypermutated Glioblastoma: A Patient with Germline POLE Deficiency Treated with Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2016;6:1230–6. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Graeber MB, Scheithauer BW, Kreutzberg GW. Microglia in brain tumors. Glia. 2002;40:252–9. doi: 10.1002/glia.10147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cai J, Zhang W, Yang P, Wang Y, Li M, et al. Identification of a 6-cytokine prognostic signature in patients with primary glioblastoma harboring M2 microglia/macrophage phenotype relevance. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0126022. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zhai H, Heppner FL, Tsirka SE. Microglia/macrophages promote glioma progression. Glia. 2011;59:472–85. doi: 10.1002/glia.21117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Du R, Lu KV, Petritsch C, Liu P, Ganss R, et al. HIF1alpha induces the recruitment of bone marrow-derived vascular modulatory cells to regulate tumor angiogenesis and invasion. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:206–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.01.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Li M, Li Z, Ren H, Jin WN, Wood K, et al. Colony stimulating factor 1 receptor inhibition eliminates microglia and attenuates brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016 doi: 10.1177/0271678X16666551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Stafford JH, Hirai T, Deng L, Chernikova SB, Urata K, et al. Colony stimulating factor 1 receptor inhibition delays recurrence of glioblastoma after radiation by altering myeloid cell recruitment and polarization. Neuro Oncol. 2016;18:797–806. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Butowski N, Colman H, De Groot JF, Omuro AM, Nayak L, et al. Orally administered colony stimulating factor 1 receptor inhibitor PLX3397 in recurrent glioblastoma: an Ivy Foundation Early Phase Clinical Trials Consortium phase II study. Neuro Oncol. 2016;18:557–64. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Katoh H, Watanabe M. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Therapeutic Strategies in Cancer. Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:159269. doi: 10.1155/2015/159269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Pyonteck SM, Akkari L, Schuhmacher AJ, Bowman RL, Sevenich L, et al. CSF-1R inhibition alters macrophage polarization and blocks glioma progression. Nat Med. 2013;19:1264–72. doi: 10.1038/nm.3337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kloepper J, Riedemann L, Amoozgar Z, Seano G, Susek K, et al. Ang-2/VEGF bispecific antibody reprograms macrophages and resident microglia to anti-tumor phenotype and prolongs glioblastoma survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:4476–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1525360113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Sarkar S, Doring A, Zemp FJ, Silva C, Lun X, et al. Therapeutic activation of macrophages and microglia to suppress brain tumor-initiating cells. Nat Neurosci. 2014;17:46–55. doi: 10.1038/nn.3597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Xu S, Wei J, Wang F, Kong LY, Ling XY, et al. Effect of miR-142-3p on the M2 macrophage and therapeutic efficacy against murine glioblastoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014:106. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Frei K, Gramatzki D, Tritschler I, Schroeder JJ, Espinoza L, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta pathway activity in glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 2015;6:5963–77. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Maxwell M, Galanopoulos T, Neville-Golden J, Antoniades HN. Effect of the expression of transforming growth factor-beta 2 in primary human glioblastomas on immunosuppression and loss of immune surveillance. J Neurosurg. 1992;76:799–804. doi: 10.3171/jns.1992.76.5.0799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Platten M, Wick W, Weller M. Malignant glioma biology: role for TGF-beta in growth, motility, angiogenesis, and immune escape. Microsc Res Tech. 2001;52:401–10. doi: 10.1002/1097-0029(20010215)52:4<401::AID-JEMT1025>3.0.CO;2-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Chen ML, Pittet MJ, Gorelik L, Flavell RA, Weissleder R, et al. Regulatory T cells suppress tumor-specific CD8 T cell cytotoxicity through TGF-beta signals in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:419–24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408197102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Thomas DA, Massague J. TGF-beta directly targets cytotoxic T cell functions during tumor evasion of immune surveillance. Cancer Cell. 2005;8:369–80. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2005.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Wesolowska A, Kwiatkowska A, Slomnicki L, Dembinski M, Master A, et al. Microglia-derived TGF-beta as an important regulator of glioblastoma invasion–an inhibition of TGF-beta-dependent effects by shRNA against human TGF-beta type II receptor. Oncogene. 2008;27:918–30. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Uhl M, Aulwurm S, Wischhusen J, Weiler M, Ma JY, et al. SD-208, a novel transforming growth factor beta receptor I kinase inhibitor, inhibits growth and invasiveness and enhances immunogenicity of murine and human glioma cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7954–61. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ueda R, Fujita M, Zhu X, Sasaki K, Kastenhuber ER, et al. Systemic inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta in glioma-bearing mice improves the therapeutic efficacy of glioma-associated antigen peptide vaccines. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:6551–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Rodon J, Carducci MA, Sepulveda-Sanchez JM, Azaro A, Calvo E, et al. First-inhuman dose study of the novel transforming growth factor-beta receptor I kinase inhibitor LY2157299 monohydrate in patients with advanced cancer and glioma. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:553–60. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Hagner PR, Man HW, Fontanillo C, Wang M, Couto S, et al. CC-122, a pleiotropic pathway modifier, mimics an interferon response and has antitumor activity in DLBCL. Blood. 2015;126:779–89. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-02-628669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


