Abstract
Genetic changes due to dietary intervention in the form of either calorie restriction (CR) or intermittent fasting (IF) are not reported in detail until now. However, it is well established that both CR and IF extend the lifespan and protect against neurodegenerative diseases and stroke. The current research aims were first to describe the transcriptomic changes in brains of IF mice and, second, to determine whether IF induces extensive transcriptomic changes following ischemic stroke to protect the brain from injury. Mice were randomly assigned to ad libitum feeding (AL), 12 (IF12) or 16 (IF16) h daily fasting. Each diet group was then subjected to sham surgery or middle cerebral artery occlusion and consecutive reperfusion. Mid-coronal sections of ipsilateral cerebral tissue were harvested at the end of the 1 h ischemic period or at 3, 12, 24 or 72 h of reperfusion, and genome-wide mRNA expression was quantified by RNA sequencing. The cerebral transcriptome of mice in AL group exhibited robust, sustained up-regulation of detrimental genetic pathways under ischemic stroke, but activation of these pathways was suppressed in IF16 group. Interestingly, the cerebral transcriptome of AL mice was largely unchanged during the 1 h of ischemia, whereas mice in IF16 group exhibited extensive up-regulation of genetic pathways involved in neuroplasticity and down-regulation of protein synthesis. Our data provide a genetic molecular framework for understanding how IF protects brain cells against damage caused by ischemic stroke, and reveal cellular signaling and bioenergetic pathways to target in the development of clinical interventions.
Introduction
Over the last few decades, average calorie intake has steadily risen along with associated age-related diseases. Studies of laboratory animals have shown that caloric restriction can extend lifespan and decrease the incidence of several major age-related diseases (1–3). Similarly, intermittent fasting (IF) can also extend lifespan in rodents, and mitigate age-related neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and ischemic stroke (1–6). The two most commonly applied IF protocols in rodents are alternate day fasting, and daily time-restricted feeding, which involves compressing the time window in which food is consumed to 4–12 h each day (i.e. fasting for 12–20 h daily). IF studies in humans have included those in which the subjects consume approximately 500 calories/day either two days within a week or every other day (4,5).
A chronic positive energy balance resulting from excessive energy intake and a sedentary lifestyle greatly increases the risk of diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease and ischemic stroke (7). It has been established that when maintained under the usual ad libitum feeding conditions, rats and mice develop a metabolic syndrome-like phenotype as they age (8). However, IF can prevent and reverse most aspects of the metabolic syndrome-like phenotype in rodents. For example, IF reduces abdominal fat, inflammation and blood pressure, and increases insulin sensitivity (1,9,10). IF has been demonstrated to lower insulin and leptin levels and elevate adiponectin and ghrelin levels (11,12). In addition, our own studies have demonstrated that IF protects against ischemic stroke-induced brain damage by mechanisms involving suppression of inflammation and cell death pathways (3,10,11,13). Neuroprotection by IF in animal models of stroke is associated with up-regulation of multiple neuroprotective proteins including: the neurotrophic factors brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2); the protein chaperones heat-shock protein 70 (HSP-70) and glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP-78); and the antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase and heme oxygenase-1 (3,10,11,13). Brain tissue affected in ischemic stroke exhibits neuronal death and the presence of multiple types of activated inflammatory cells including microglia and infiltrating lymphocytes (13–17). However, detailed information on time-dependent gene transcriptome responses to ischemic stroke and how such transcriptome responses are modified by IF are lacking.
While experimental evidence indicates that IF exerts protective effects against metabolic syndrome and associated diseases, the underlying mechanisms are largely unknown. Moreover, there is no information available on changes in the cerebral transcriptome that mediate neuroprotective cellular adaptations to IF. We, therefore, designed a study to generate a database of cerebral gene expressions in mice maintained on time-restricted fasting (12 or 16 h per day) or an ad libitum control diet (AL), which were then subjected to experimental stroke. Transcriptome analysis using RNA sequencing revealed that daily fasting for 16 h (IF16) results in changes in the cerebral transcriptome that include pathways involved in cell signaling and neuroplasticity. Major changes in the cerebral transcriptome occurred in response to ischemic stroke in a post-stroke time-dependent manner. IF16 had major effects on the cerebral transcriptome in mice subjected to experimental stroke including up-regulation of pathways involved in intercellular communication, neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity and cellular resistance to cell death. Pathways involved in protein synthesis and inflammation were down regulated by IF16 in the setting of cerebral ischemia. Our findings provide novel insight into the genetic changes by which IF protects the brain against ischemic stress, and provide a resource for investigators in the fields of neuroscience, neurology and energy metabolism.
Results
Intermittent fasting leads to global transcriptome changes
We initially investigated the effects of different time intervals of fasting and refeeding on the cerebral transcriptome using RNA sequencing (Fig. 1A). Male C57BL/6 mice were fed with a normal chow diet (comprised on a caloric basis of 58%, 24% and 18% from carbohydrate, protein and fat, respectively) and were randomly assigned to either AL, daily IF12 or IF16 schedules beginning at 3 months of age. To determine the extent to which IF affected energy metabolism, we measured body weights, and blood glucose and ketone levels, of all mice during the 4 months diet intervention period. Mice in the IF12 and IF16 groups weighed less than mice from AL group throughout the experiment (Supplementary Material, Fig. S1). Mice in the IF16 feeding schedule gained progressively less weight, and weighed significantly less than IF12 mice after 4 months of diet exposure. Compared to the significant difference of body weight among the experimental groups, blood glucose levels were relatively stable with tendency to be decreased only in IF16 group (Supplementary Material, Table S1). This observation is expected to be affected by the concentrated consumption of food during the refeeding hours in IF groups. On the other hand, blood ketone levels were significantly increased in both IF12 and IF16 groups compared to AL group in fasting hours-dependent manner (Supplementary Material, Table S1). It seems like that blood ketone level is more likely to be affected by the duration of fasting hours rather than amount of food consumed during refeeding.
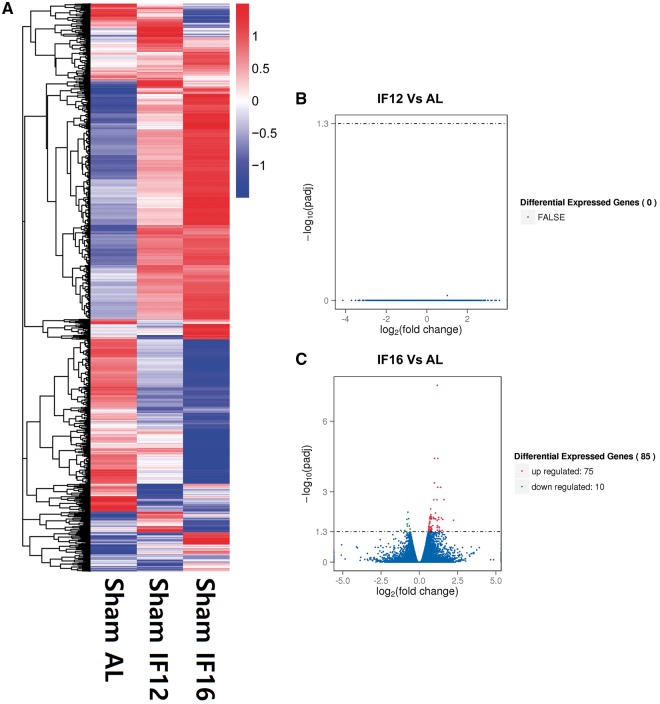
Figure 1.
Genes identified by RNA sequencing as being differentially expressed in the IF12 and IF16 groups compared to the AL group. (A) Heatmap of the differentially expressed genes in AL, IF12 and IF16 groups with up-regulated genes in red and down-regulated genes in blue. The color scale represents the log 10 (FPKM + 1) value. (B and C) Volcano diagrams showing the distribution of differentially expressed genes in IF12 (B) and IF16 (C) groups in comparison with the AL group. The threshold of differential expression is adjusted P-value < 0.05. The horizontal axis is the log 2 fold change of genes. The vertical axis is statistical significance scaled as −log 10 adjusted P-value. Each dot represents an individual gene (blue: no significant difference; red: up-regulated gene; green: down-regulated gene).
Total RNA was isolated from the mid-coronal sections (three tissue sections per mouse) of the ipsilateral hemisphere, which contain both ischemic, and peri-infarct area in order to observe the general transcriptome changes under the direct influence of experimental ischemic stroke. While RNA sequencing revealed that both IF12 and IF16 groups exhibited different heatmap patterns of differentially expressed genes (Fig. 1A), only the IF16 group had genes significantly up-regulated (75 genes) or down-regulated (10 genes) compared to the AL group under sham-operated normal control condition (Fig. 1B and C). We thus analyzed the differentially expressed genes in the IF16 group compared to the AL group. The list of most significantly up-regulated genes includes, Gucy1a2 (guanylate cyclase 1, soluble, alpha 2; log 2 fold change: 1.610); Dok6 (docking protein 6; log 2 fold change: 1.391); Per2 (period circadian clock 2; log 2 fold change: 1.212); Lonrf3 (LON peptidase N-terminal domain and ring finger 3; log 2 fold change: 1.199); Prex2 (phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent Rac exchange factor 2; log 2 fold change: 1.175); Per3 (period circadian clock 3; log 2 fold change: 1.057); Shc3 (Src homology 2 domain-containing transforming protein C3; log 2 fold change: 0.993); Zfc3h1 (zinc finger, C3H1-type containing; log 2 fold change: 0.982); Slc4a7 (solute carrier family 4, sodium bicarbonate cotransporter, member 7; log 2 fold change: 0.945); Lyst (lysosomal trafficking regulator; log 2 fold change: 0.756); Taok1 (TAO kinase 1; log 2 fold change: 0.744); and Slc1a2 (solute carrier family 1, glial high affinity glutamate transporter, member 2; log 2 fold change: 0.609). A full list of genes differentially expressed in the IF16 and AL control groups is provided in Supplementary Material, Table S2. Transcriptome analysis using gene ontology (GO) enrichment helps to identify functional groups of genes that interact with each other to regulate physiological responses. The results of GO analysis of our transcriptome data revealed pathways that may play roles in previously described beneficial effects of IF on brain function and disease resistance (Table 1). These pathways include those involved in cell communication [false discovery rate (FDR) = 0.004], system development (FDR = 0.007), signal transduction (FDR = 0.016), nervous system development (FDR = 0.007), positive regulation of biological process (FDR = 0.023), regulation of cell differentiation (FDR = 0.007), cellular responses to stimuli (FDR = 0.023) and positive regulation of metabolic processes (FDR = 0.041).
Table 1.
GO enrichment analysis results of IF16 versus AL groups at sham condition
| Accession no. | GO terms | Expression trend | FDRa | Relevant gene no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0007154 | Cell communication | Up | 0.0042 | 28 |
| 0044700 | Single organism signaling | Up | 0.0042 | 27 |
| 0007399 | Nervous system development | Up | 0.007 | 18 |
| 0007610 | Behavior | Up | 0.007 | 10 |
| 0044707 | Single-multicellular organism process | Up | 0.007 | 32 |
| 0045595 | Regulation of cell differentiation | Up | 0.007 | 16 |
| 0048731 | System development | Up | 0.007 | 26 |
| 0060322 | Head development | Up | 0.0084 | 11 |
| 0007165 | Signal transduction | Up | 0.0159 | 24 |
| 0007275 | Multicellular organismal development | Up | 0.0191 | 27 |
| 0048522 | Positive regulation of cellular process | Up | 0.0205 | 27 |
| 0007632 | Visual behavior | Up | 0.0227 | 4 |
| 0044708 | Single-organism behavior | Up | 0.0227 | 8 |
| 0048518 | Positive regulation of biological process | Up | 0.0227 | 29 |
| 0048856 | Anatomical structure development | Up | 0.0227 | 27 |
| 0051716 | Cellular response to stimulus | Up | 0.0227 | 28 |
| 0061298 | Retina vasculature development in camera-type eye | Up | 0.0241 | 3 |
| 0030097 | Hemopoiesis | Up | 0.0263 | 9 |
| 0009893 | Positive regulation of metabolic process | Up | 0.0407 | 22 |
| 0010604 | Positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process | Up | 0.0407 | 19 |
| 0044767 | Single-organism developmental process | Up | 0.0407 | 28 |
| 0050793 | Regulation of developmental process | Up | 0.0407 | 17 |
| 0048513 | Organ development | Up | 0.043 | 20 |
| 0045596 | Negative regulation of cell differentiation | Up | 0.0459 | 9 |
| 0002520 | Immune system development | Up | 0.0497 | 9 |
FDR value was calculated using Benjamini–Hochberg FDR and considered statistically significant when <0.05.
Cerebral ischemia and reperfusion-induced transcriptome changes reveal novel pathways involved in ischemic stroke
We profiled the effects of cerebral ischemia and reperfusion (I/R) on mRNA levels at different time points in both AL and IF groups to elucidate how brain cells respond to ischemia and how IF might modify these cellular responses. The heatmaps in Figure 2A–E show global changes of RNA expression patterns in the left (ischemic) cerebral hemisphere of the brain as well as the different patterns between AL and IF groups at different time points following I/R.
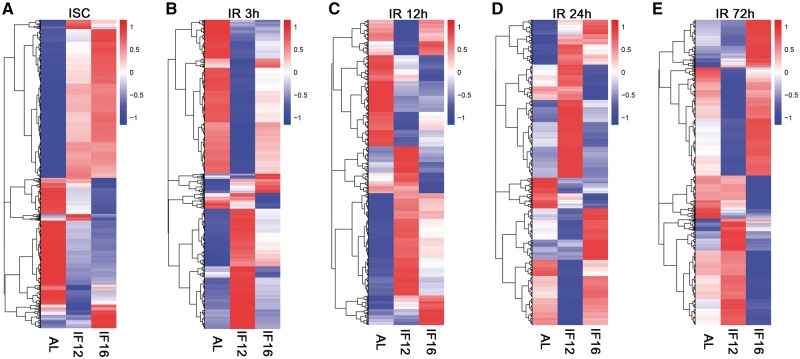
Figure 2.
Heatmaps of differentially expressed genes in AL, IF12 and IF16 groups at each cerebral I/R time point. Heat clusters of differentially expressed genes in the experimental groups at 1 h of ischemia (A), and reperfusion for 3 (B), 12 (C), 24 (D) and 72 h (E). Up-regulated genes in red and down-regulated genes in blue. The color scale represents the log 10 (FPKM + 1) value.
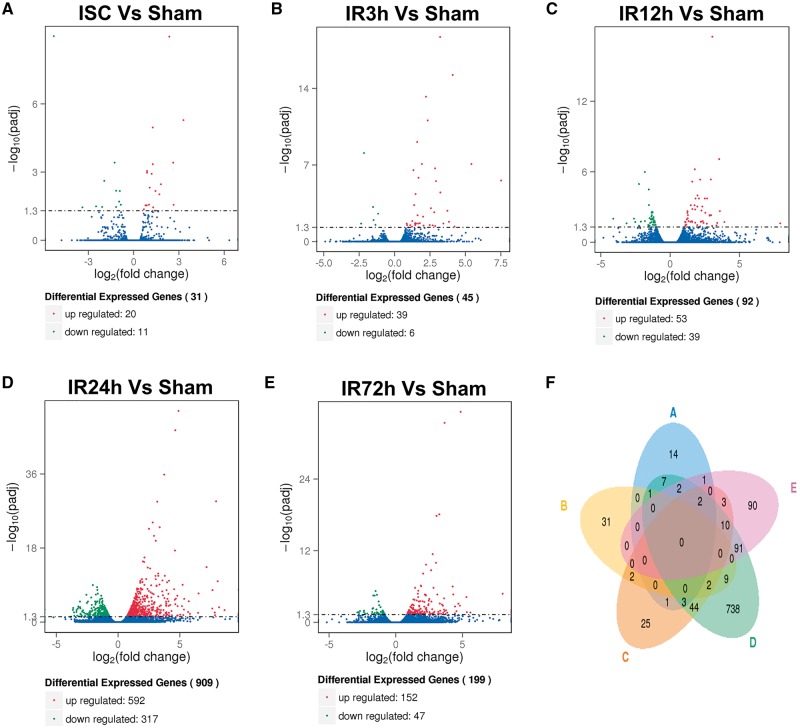
Previous studies of genetic changes to I/R have typically been limited to two time points, but the transition between the acute and chronic phases likely involves more complex waves of gene expression. To investigate transcriptomic responses to ischemia with greater temporal resolution, we performed RNA sequencing immediately after ischemia, and after 3, 12, 24, or 72 h reperfusion in AL group, comparatively analyzed with sham-operated AL group (Fig. 3). Transcriptome analysis of ipsilateral cerebrum revealed significant differences in gene expression at all time points compared to sham-operated normal control. The largest number of differentially expressed genes was detected 24 h after reperfusion (Fig. 3A–E). The results revealed 31 differentially expressed genes at the end of the 1 h ischemia period, and 45, 92, 909 and 199 differentially expressed genes at 3, 12, 24 and 72 h after reperfusion, respectively. The lists of these genes are provided in Supplementary Material, Table S3. Remarkably, the differentially expressed genes were mostly unique to each I/R time point, reflecting the differential progression of ischemic injury over time. Even though the I/R 24 h group shared a number of genes also differentially expressed at neighboring time point groups (61 genes with I/R 12 hour group; 105 genes with I/R 72 hour group), 27%, 81% and 45% of differentially expressed genes were unique to the 12, 24 and 72 h time points, respectively (Fig. 3F).
Figure 3.
Differentially expressed genes in AL group at brain I/R time points compared to the sham-operated control. (A–E) Volcano diagrams showing the distribution of differentially expressed genes in the AL group at 1 h of ischemia (A), and reperfusion for 3 (B), 12 (C), 24 (D) and 72 h (E) in comparison to sham-operated control. The threshold of differential expression is adjusted P-value < 0.05. The horizontal axis is the log 2 fold change of genes. The vertical axis is statistical significance scaled as −log 10 adjusted P-value. Each dot represents an individual gene (blue: no significant difference; red: up-regulated gene; green: down-regulated gene). (F) Venn diagram of differentially expressed genes at the different time points during I/R (A, 1 h of ischemia; B, C, D and E are reperfusion time points of 3, 12, 24 and 72 h, respectively).
Genes differentially expressed at the end of the 1 h ischemia period (31 genes) included: Iyd (iodotyrosine deiodinase; log 2 fold change: 3.305); Crlf1 (cytokine receptor-like factor 1; log 2 fold change: 2.624); Zfp36 (zinc finger protein 36; log 2 fold change: 2.364); Homer3 (homer homolog 3; log 2 fold change: 1.264); Smoc2 (SPARC related modular calcium binding 2; log 2 fold change: 1.262); Cpne6 (copine VI; log 2 fold change: 0.890); Tacr1 (tachykinin receptor 1; log 2 fold change: −1.259); and Oxt (oxytocin; log 2 fold change: −5.286).
Genes significantly affected at 3 h of reperfusion included: Cxcl2 [chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2; log 2 fold change: 7.521]; Atf3 (activating transcription factor 3; log 2 fold change: 5.424); S100a8 (S100 calcium-binding protein A8; log 2 fold change: 3.233); Thbs1 (thrombospondin 1; log 2 fold change: 3.216); S100a9 (S100 calcium-binding protein A9; log 2 fold change: 2.923); Adamts1 (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motif 1; log 2 fold change: 2.340); Epha2 (EPH receptor A2; log 2 fold change: 1.689); Edn1 (endothelin-1; log 2 fold change: 1.481); and Hes5 (transcription factor HES-5; log 2 fold change: -2.156).
Genes significantly up-regulated at 12 h of reperfusion (92 genes) included: Slc10a6 [solute carrier family 10 (sodium/bile acid cotransporter family) member 6; log 2 fold change: 7.936]; Maff (transcription factor MafF; log 2 fold change: 3.906); Angpt2 (vasoprotective angiopoietin 2; log 2 fold change: 3.584); Ctla2a (cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 2 alpha; log 2 fold change: 3.532); Tnfsf8 [tumor necrosis factor (TNF) (ligand) superfamily member 8; log 2 fold change: 3.394); Ctla2b (cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 2 beta; log 2 fold change: 2.249); Mt2 (metallothionein 2; log 2 fold change: 2.206); Il1r1 [interleukin (IL)-1 receptor type 1; log 2 fold change: 1.602); Mt1 (metallothionein 1; log 2 fold change: 1.592); and Il16 (IL-16; log 2 fold change: 1.569). Significantly down-regulated genes at 12 h reperfusion included Rxrg (retinoid X receptor gamma; log 2 fold change: −2.608) and Chat (choline acetyltransferase; log 2 fold change: −2.111).
The largest number of differentially expressed genes (909 genes) was evident at the 24 h reperfusion time point. Among the genes most up-regulated were: Mmp3 (matrix metallopeptidase 3; log 2 fold change: 8.615); Gp49a (glycoprotein 49A; log 2 fold change: 8.176); Slc10a6 (log 2 fold change: 8.064); Msr1 (macrophage scavenger receptor 1; log 2 fold change: 7.930); Chil3 (chitinase-like 3; log 2 fold change: 7.846); Ccl2 [chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2; log 2 fold change: 7.827]; Il6 (IL-6; log 2 fold change: 6.476); Hcar2 (hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 2; log 2 fold change: 5.818); Timp1 (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1; log 2 fold change: 5.719); Ccl7 [chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 7; log 2 fold change: 5.669]; Ccl4 [chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 4; log 2 fold change: 5.335]; Cxcl10 [chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 10; log 2 fold change: 5.223]; Ptx3 (pentraxin related gene; log 2 fold change: 6.512); Lif (leukemia inhibitory factor; log 2 fold change: 5.170); Atf3 (log 2 fold change: 4.894); Hspa1b (heat shock protein 1B; log 2 fold change: 4.822); and Hmox1 (Heme oxygenase 1; log 2 fold change: 4.800). Highly down-regulated genes at 24 h reperfusion included: Adora2a (adenosine A2a receptor; log 2 fold change: −3.373); Rxrg (retinoid X receptor gamma; log 2 fold change: −3.213); Oxt (log 2 fold change: −3.085); Cd4 (CD4 antigen; log 2 fold change: −3.045); Ntrk1 (neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor, type 1; log 2 fold change: −2.904); Syndig1l (synapse differentiation inducing 1 like; log 2 fold change: −2.903); Ptpn7 (protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 7; log 2 fold change: −2.670); and Chat (log 2 fold change: −2.527).
At 72 h of reperfusion, 199 genes were differentially expressed. Highly up-regulated genes included: Tgm1 (transglutaminase 1, K polypeptide; log 2 fold change: 8.015); Fcgr4 (Fc receptor, IgG, low affinity IV; log 2 fold change: 5.333); Ifi204 (interferon-activated gene 204; log 2 fold change: 5.300); Ifi27l2a (interferon alpha-inducible protein 27 like 2A; log 2 fold change: 4.860); Cst7 (cystatin F; log 2 fold change: 4.687); Cxcl10 (log 2 fold change: 4.446); Serpina3n [Serine (or cysteine) peptidase inhibitor, clade A, member 3N; log 2 fold change: 4.4357]; Cd52 (CD52 antigen; log 2 fold change: 3.531); Casp4 (caspase 4; log 2 fold change: 3.466); Cd44 (CD44 antigen; log 2 fold change: 3.155); Pilra (paired immunoglobin-like type 2 receptor alpha; log 2 fold change: 3.147); and Irf7 (interferon regulatory factor 7; log 2 fold change: 3.056). Highly down-regulated genes at the 72 h reperfusion time point included: Syndig1l (log 2 fold change: −2.799); Rxrg (log 2 fold change: −2.396); Hbb-bt (hemoglobin, beta adult t chain; log 2 fold change: −1.579); Hba-a2 (hemoglobin alpha, adult chain 2; log 2 fold change: −1.510); Hba-a1 (hemoglobin alpha, adult chain 1; log 2 fold change: −1.409); and Hbb-bs (hemoglobin, beta adult s chain; log 2 fold change: −1.281).
Differentially expressed genes at each I/R time point were analyzed with GO enrichment focused on related biological processes in order to elucidate the expected biological changes and possible injury mechanisms following cerebral ischemia. The full results of GO enrichment analysis are provided in Supplementary Material, Table S4. Selected terms of interest show that following 1 h of exposure to ischemia, genes responsible for synaptic transmission and the neurotransmitter biosynthetic process were down-regulated while one related to neuronal axon regeneration was up-regulated (Table 2). Three hours after reperfusion, multiple gene sets involved in the regulation of apoptosis were prominently up-regulated, as were pathways involved in immune cell responses and inflammation (Table 2). At the 12 h post-stroke time point, sphingolipid signaling pathway was up-regulated and a gene set involved in myelination was down-regulated. Consistent with the greatest numbers of individual genes being differentially expressed at the 24 h time point, more GO pathways were significantly affected at this post-stroke time point compared to other time points (Table 2). Pathways up-regulated were especially involved in immune cell responses and inflammation, cellular stress responses and cell death. GO pathways down-regulated at 24 h post-stroke included neurogenesis, cell signal transduction and cell differentiation. At 72 h of reperfusion, pathways involved in immune cell responses and inflammation continued to be strongly up-regulated, including the NLRP3 (NACHT, LRR and PYD domains containing protein 3) inflammasome and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), while the synaptic transmission GO pathway was down-regulated at 72 h (Table 2).
Table 2.
Selected GO enrichment analysis results of AL versus sham group
| Accession no. | GO terms | Expression trend | FDRa | Relevant gene no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At ischemia 1 h | ||||
| 0031102 | Neuron projection regeneration | Up | 0.016 | 3 |
| 0007268 | Synaptic transmission | Down | 0.0012 | 5 |
| 0042136 | Neurotransmitter biosynthetic process | Down | 0.0089 | 2 |
| 0007274 | Neuromuscular synaptic transmission | Down | 0.0226 | 2 |
| At reperfusion 3 h | ||||
| 0042981 | Regulation of apoptotic process | Up | <0.0001 | 13 |
| 0043065 | Positive regulation of apoptotic process | Up | <0.0001 | 9 |
| 0070887 | Cellular response to chemical stimulus | Up | 0.0001 | 13 |
| 0008219 | Cell death | Up | 0.0002 | 10 |
| 0048583 | Regulation of response to stimulus | Up | 0.0008 | 15 |
| 0006915 | Apoptotic process | Up | 0.0009 | 9 |
| 0070488 | Neutrophil aggregation | Up | 0.001 | 2 |
| 0032680 | Regulation of tumor necrosis factor production | Up | 0.0027 | 4 |
| 0010646 | Regulation of cell communication | Up | 0.0028 | 13 |
| 2001233 | Regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | Up | 0.0028 | 6 |
| 0071347 | Cellular response to interleukin-1 | Up | 0.0092 | 3 |
| 0002544 | Chronic inflammatory response | Up | 0.0141 | 2 |
| 0070486 | Leukocyte aggregation | Up | 0.0231 | 4 |
| 0006955 | Immune response | Up | 0.0281 | 6 |
| At reperfusion 12 h | ||||
| 0003376 | Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling pathway | Up | 0.0178 | 3 |
| 0042552 | Myelination | Down | 0.0414 | 4 |
| At reperfusion 24 h | ||||
| 0002376 | Immune system process | Up | <0.0001 | 140 |
| 0006955 | Immune response | Up | <0.0001 | 93 |
| 0006950 | Response to stress | Up | <0.0001 | 175 |
| 0006952 | Defense response | Up | <0.0001 | 96 |
| 0050896 | Response to stimulus | Up | <0.0001 | 260 |
| 0045087 | Innate immune response | Up | <0.0001 | 56 |
| 0034097 | Response to cytokine | Up | <0.0001 | 61 |
| 0098542 | Defense response to other organism | Up | <0.0001 | 50 |
| 0007165 | Signal transduction | Up | <0.0001 | 173 |
| 0001817 | Regulation of cytokine production | Up | <0.0001 | 58 |
| 0006954 | Inflammatory response | Up | <0.0001 | 52 |
| 0042060 | Wound healing | Up | <0.0001 | 36 |
| 0019221 | Cytokine-mediated signaling pathway | Up | <0.0001 | 30 |
| 0008219 | Cell death | Up | <0.0001 | 53 |
| 0002250 | Adaptive immune response | Up | <0.0001 | 19 |
| 0012501 | Programmed cell death | Up | <0.0001 | 51 |
| 0042110 | T cell activation | Up | <0.0001 | 23 |
| 0002221 | Pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway | Up | <0.0001 | 10 |
| 0002224 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | Up | <0.0001 | 8 |
| 0006909 | Phagocytosis | Up | <0.0001 | 12 |
| 0097190 | Apoptotic signaling pathway | Up | <0.0001 | 21 |
| 0001816 | Cytokine production | Up | <0.0001 | 13 |
| 0097193 | Intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Up | 0.0002 | 15 |
| 0019724 | B cell-mediated immunity | Up | 0.0002 | 10 |
| 0000165 | MAPK cascade | Up | 0.0003 | 15 |
| 0002526 | Acute inflammatory response | Up | 0.0012 | 9 |
| 0007249 | I-kappa B kinase/NF-kappa B signaling | Up | 0.0019 | 7 |
| 0000302 | Response to reactive oxygen species | Up | 0.0064 | 12 |
| 0050663 | Cytokine secretion | Up | 0.0078 | 5 |
| 0007267 | Cell–cell signaling | Down | <0.0001 | 39 |
| 0022008 | Neurogenesis | Down | <0.0001 | 49 |
| 0007154 | Cell communication | Down | <0.0001 | 83 |
| 0030154 | Cell differentiation | Down | <0.0001 | 70 |
| 0007218 | Neuropeptide signaling pathway | Down | <0.0001 | 10 |
| At reperfusion 72 h | ||||
| 0006955 | Immune response | Up | <0.0001 | 41 |
| 0045087 | Innate immune response | Up | <0.0001 | 30 |
| 0002376 | Immune system process | Up | <0.0001 | 49 |
| 0006952 | Defense response | Up | <0.0001 | 39 |
| 0002252 | Immune effector process | Up | <0.0001 | 24 |
| 0019882 | Antigen processing and presentation | Up | <0.0001 | 11 |
| 0006950 | Response to stress | Up | <0.0001 | 48 |
| 0035456 | Response to interferon-beta | Up | <0.0001 | 8 |
| 0035455 | Response to interferon-alpha | Up | <0.0001 | 6 |
| 0034097 | Response to cytokine | Up | <0.0001 | 18 |
| 0042063 | Gliogenesis | Up | 0.0197 | 7 |
| 1900225 | Regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly | Up | 0.036 | 2 |
| 0043122 | Regulation of I-kappa B kinase/NF-kappa B signaling | Up | 0.0431 | 7 |
| 0007267 | Cell–cell signaling | Down | 0.0031 | 9 |
| 0050877 | Neurological system process | Down | 0.0084 | 10 |
| 0007268 | Synaptic transmission | Down | 0.025 | 6 |
FDR value was calculated using Benjamini–Hochberg FDR and considered statistically significant when <0.05.
In addition to GO enrichment analysis, we performed Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis of the RNA sequencing data. The results of the KEGG analysis were generally similar to those of the GO analysis, with pathways involved in inflammation, immune cell signaling, cellular stress responses and cell death being up-regulated at the 24 h reperfusion time point (Table 3). Interestingly, the KEGG analysis revealed down-regulation of gene sets related to signaling at multiple types of synapses including those that use gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), acetylcholine, glutamate, serotonin and dopamine as neurotransmitters at the 24 and 72 h time points (Table 3). See Supplementary Material, Table S5 for the complete results of the KEGG pathway analysis.
Table 3.
Selected KEGG pathway analysis results of AL versus sham group
| Pathway ID | Pathway description | Expression trend | FDRa | Relevant gene no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At reperfusion 12 h | ||||
| 4512 | ECM-receptor interaction | Up | 0.0152 | 4 |
| At reperfusion 24 h | ||||
| 4668 | TNF signaling pathway | Up | <0.0001 | 21 |
| 4060 | Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction | Up | <0.0001 | 29 |
| 4151 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | Up | <0.0001 | 30 |
| 4620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | Up | <0.0001 | 16 |
| 4064 | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | Up | <0.0001 | 14 |
| 4066 | HIF-1 signaling pathway | Up | <0.0001 | 15 |
| 4062 | Chemokine signaling pathway | Up | <0.0001 | 19 |
| 4662 | B cell receptor signaling pathway | Up | <0.0001 | 12 |
| 4610 | Complement and coagulation cascades | Up | <0.0001 | 12 |
| 4670 | Leukocyte transendothelial migration | Up | <0.0001 | 15 |
| 4010 | MAPK signaling pathway | Up | <0.0001 | 22 |
| 4145 | Phagosome | Up | <0.0001 | 17 |
| 4630 | Jak-STAT signaling pathway | Up | <0.0001 | 16 |
| 4650 | Natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity | Up | <0.0001 | 13 |
| 4621 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | Up | 0.0006 | 8 |
| 4623 | Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | Up | 0.0009 | 8 |
| 4210 | Apoptosis | Up | 0.0054 | 8 |
| 4622 | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | Up | 0.0084 | 7 |
| 4390 | Hippo signaling pathway | Up | 0.0228 | 10 |
| 4115 | p53 signaling pathway | Up | 0.0283 | 6 |
| 4068 | FoxO signaling pathway | Up | 0.0298 | 9 |
| 4910 | Insulin signaling pathway | Up | 0.0324 | 9 |
| 4080 | Neuroactive ligand–receptor interaction | Down | <0.0001 | 17 |
| 4727 | GABAergic synapse | Down | 0.0008 | 8 |
| 4725 | Cholinergic synapse | Down | 0.0036 | 8 |
| 4721 | Synaptic vesicle cycle | Down | 0.0046 | 6 |
| 4724 | Glutamatergic synapse | Down | 0.0184 | 7 |
| 4728 | Dopaminergic synapse | Down | 0.0262 | 7 |
| 4020 | Calcium signaling pathway | Down | 0.0416 | 8 |
| At reperfusion 72 h | ||||
| 4612 | Antigen processing and presentation | Up | <0.0001 | 7 |
| 4145 | Phagosome | Up | <0.0001 | 9 |
| 4622 | RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | Up | 0.0002 | 6 |
| 4623 | Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | Up | 0.0111 | 4 |
| 4630 | Jak-STAT signaling pathway | Up | 0.0385 | 5 |
| 4728 | Dopaminergic synapse | Down | 0.0007 | 5 |
| 4727 | GABAergic synapse | Down | 0.0289 | 3 |
| 4724 | Glutamatergic synapse | Down | 0.0417 | 3 |
| 4725 | Cholinergic synapse | Down | 0.0417 | 3 |
| 4726 | Serotonergic synapse | Down | 0.0479 | 3 |
FDR value was calculated using Benjamini–Hochberg FDR and considered statistically significant when <0.05.
Daily IF modifies cerebral transcriptomic responses to focal ischemic stroke
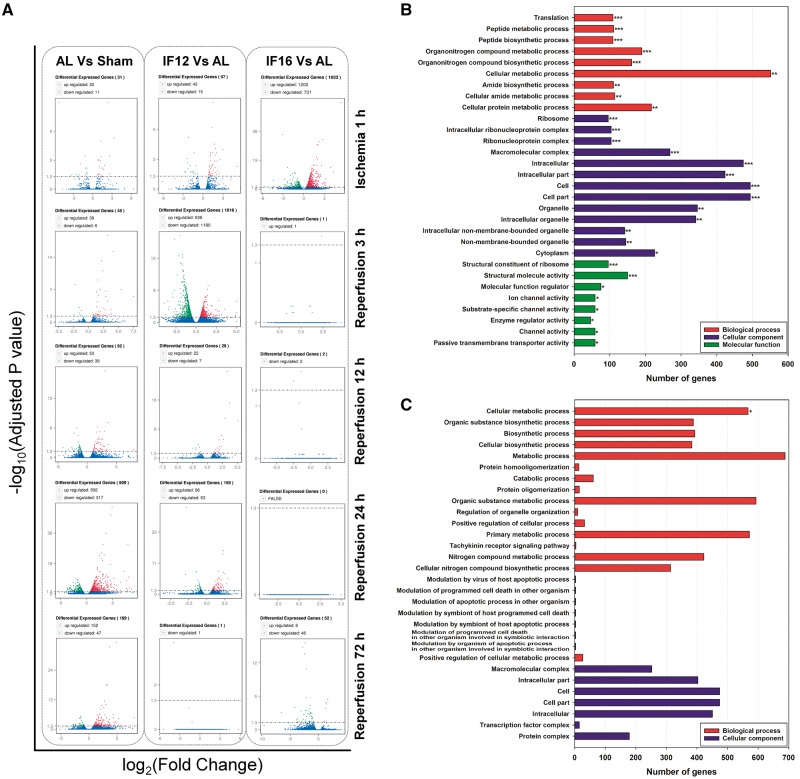
We previously reported that mice maintained on either IF16 or alternate day fasting exhibit less neuronal death and improved neurological outcome following ischemic stroke, compared to mice fed ad libitum (11,13). We therefore applied RNA sequencing analysis of cerebral tissue samples from mice maintained on IF12 and IF16 feeding schedules, and subjected to cerebral I/R. Volcano plots showing the overall results of comparisons of transcriptomes at increasing post-stroke time points of mice in IF12 and IF16 groups compared to AL mice are shown in Figure 4A. The IF12 I/R group showed 57 differentially expressed genes at 1 h of ischemia; 1816, 29, 159 and 1 differentially expressed genes at 3, 12, 24 and 72 h after reperfusion, respectively, compared to the AL group at the same time points after I/R (Fig. 4A; the full list of differentially expressed genes is in Supplementary Material, Table S6). In contrast, the IF16 I/R group displayed 1933 differentially expressed genes at 1 h after ischemia and 52 differentially expressed genes after 72 h of reperfusion compared to the corresponding AL I/R groups (Fig. 4A; the full list of differentially expressed genes is in Supplementary Material, Table S7). Among all the time points, IF12 and IF16 interventions exhibited single I/R time point having exponentially increased number of significantly affected gene expressions which were 3 h of reperfusion or 1 h of ischemia time point, respectively. The full list of genes from each time point of IF12 and IF16 group were initially analyzed for GO enrichment. Multiple number of GO terms were elucidated to be significantly affected in IF12 group at 3 h of reperfusion (Fig. 4B), whereas GO terms from IF16 group at 1 h of ischemia time point were mostly insignificant with the change (Fig. 4C).
Figure 4.
Differentially expressed genes in experimental groups at each brain I/R time points and GO enrichment analysis of IF12 and IF16 groups at the peak gene expression time points. (A) Volcano diagrams showing the distribution of differentially expressed genes in AL group compared to sham-operated control, or IF12 and IF16 groups compared to AL group at each brain I/R time point. The threshold of differential expression is adjusted P-value < 0.05. The horizontal axis is the log 2 fold change of genes. The vertical axis is statistical significance scaled as −log 10 adjusted P-value. Each dot represents an individual gene (blue: no significant difference; red: up-regulated gene; green: down-regulated gene). GO enrichment analysis on differentially expressed genes at the peak time points of 3 h reperfusion in IF12 group (B) and 1 h of ischemia in IF16 group (C) in comparison to AL group. *, **, ***Significantly modulated GO terms within the enrichment analysis (adjusted P < 0.05, adjusted P < 0.01, adjusted P < 0.001).
In order to elucidate the biological processes affected by differentially expressed genes in the IF groups in detail, we performed GO enrichment analyses at each time point in the IF12 I/R (Table 4; full list of GO enrichment analysis is in Supplementary Material, Table S8) and IF16 I/R (Table 6; full list of GO enrichment analysis is in Supplementary Material, Table S10) groups with up- and down-regulated genes separately. GO enrichment analyses showed that after 1 h of ischemia, cellular biosynthetic processes, transcription, regulation of metabolic process and cell proliferation were up-regulated in the IF12 I/R group (Table 4). The most significant change of differentially expressed genes between the IF12 I/R and AL I/R groups was evident at 3 h of reperfusion. Up-regulated GO terms included those involved in protein translation, biosynthetic processes, oxidation-reduction processes, biogenesis, rRNA processing, ATP biosynthesis and responses to cellular stress (Table 4). Down-regulated GO terms include cell communication, cell differentiation, neurogenesis, synaptic transmission and inhibition of apoptosis. Very few GO terms were significantly affected by IF12 I/R compared to AL I/R at 12 or 24 h of reperfusion (Table 4). KEGG pathway analysis of IF12 I/R groups in comparison to the AL I/R group at 3 h of reperfusion revealed up-regulated oxidative phosphorylation, and metabolic and ribosome pathways, whereas calcium signaling, cholinergic, glutamatergic, GABAergic and dopaminergic, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), forkhead box O (FoxO) and mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways were down-regulated (Table 5; the full list of KEGG pathway analysis data are in Supplementary Material, Table S9). At 24 h of reperfusion, KEGG pathway analysis indicated that the IF12 group exhibited down-regulation of inflammatory mediator regulation of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels and calcium-signaling pathways.
Table 4.
Selected GO enrichment analysis results of IF12 versus AL group
| Accession no. | GO terms | Expression trend | FDRa | Relevant gene no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At ischemia 1 h | ||||
| 0006351 | Transcription, DNA template | Up | <0.0001 | 17 |
| 0044249 | Cellular biosynthetic process | Up | 0.0008 | 19 |
| 0010467 | Gene expression | Up | 0.0024 | 17 |
| 0019222 | Regulation of metabolic process | Up | 0.0061 | 22 |
| 0042127 | Regulation of cell proliferation | Up | 0.0168 | 10 |
| At reperfusion 3 h | ||||
| 0006412 | Translation | Up | <0.0001 | 78 |
| 0009058 | Biosynthetic process | Up | <0.0001 | 151 |
| 0055114 | Oxidation–reduction process | Up | <0.0001 | 52 |
| 0042273 | Ribosomal large subunit biogenesis | Up | <0.0001 | 8 |
| 0042254 | Ribosome biogenesis | Up | <0.0001 | 27 |
| 0000028 | Ribosomal small subunit assembly | Up | <0.0001 | 8 |
| 0042274 | Ribosomal small subunit biogenesis | Up | <0.0001 | 13 |
| 0042255 | Ribosome assembly | Up | <0.0001 | 11 |
| 0006364 | rRNA processing | Up | <0.0001 | 21 |
| 0006754 | ATP biosynthetic process | Up | <0.0001 | 9 |
| 0006979 | Response to oxidative stress | Up | 0.0002 | 25 |
| 0000302 | Response to reactive oxygen species | Up | 0.0004 | 16 |
| 0006950 | Response to stress | Up | 0.0005 | 101 |
| 0006417 | Regulation of translation | Up | 0.0011 | 21 |
| 0006119 | Oxidative phosphorylation | Up | 0.0028 | 7 |
| 2001242 | Regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Up | 0.0029 | 14 |
| 0006413 | Translational initiation | Up | 0.0034 | 9 |
| 2001233 | Regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | Up | 0.0058 | 24 |
| 0042773 | ATP synthesis-coupled electron transport | Up | 0.0074 | 6 |
| 2001235 | Positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | Up | 0.0409 | 13 |
| 0034614 | Cellular response to reactive oxygen species | Up | 0.0437 | 9 |
| 0007154 | Cell communication | Down | <0.0001 | 292 |
| 0030154 | Cell differentiation | Down | <0.0001 | 232 |
| 0007165 | Signal transduction | Down | <0.0001 | 252 |
| 0022008 | Neurogenesis | Down | <0.0001 | 141 |
| 0048699 | Generation of neurons | Down | <0.0001 | 136 |
| 0030182 | Neuron differentiation | Down | <0.0001 | 95 |
| 0007268 | Synaptic transmission | Down | <0.0001 | 62 |
| 0007270 | Neuron–neuron synaptic transmission | Down | <0.0001 | 23 |
| 0050768 | Negative regulation of neurogenesis | Down | 0.0002 | 26 |
| 0042981 | Regulation of apoptotic process | Down | 0.0027 | 84 |
| 0010941 | Regulation of cell death | Down | 0.0041 | 88 |
| 0000165 | MAPK cascade | Down | 0.0101 | 18 |
| 1901214 | Regulation of neuron death | Down | 0.0113 | 23 |
| 0017148 | Negative regulation of translation | Down | 0.0131 | 12 |
| 0043523 | Regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Down | 0.0141 | 20 |
| 0043066 | Negative regulation of apoptotic process | Down | 0.0179 | 53 |
| 0032844 | Regulation of homeostatic process | Down | 0.0182 | 30 |
| 0046928 | Regulation of neurotransmitter secretion | Down | 0.0224 | 8 |
| 0060548 | Negative regulation of cell death | Down | 0.0268 | 56 |
| At reperfusion 12 h | ||||
| 0008217 | Regulation of blood pressure | Up | 0.0001 | 5 |
| 0008015 | Blood circulation | Up | 0.0012 | 5 |
| 0007268 | Synaptic transmission | Up | 0.0025 | 5 |
| 0051960 | Regulation of nervous system development | Up | 0.0054 | 6 |
| 0042136 | Neurotransmitter biosynthetic process | Up | 0.007 | 2 |
| 0007218 | Neuropeptide signaling pathway | Up | 0.0145 | 3 |
| At reperfusion 24 h | ||||
| GO.0002588 | Positive regulation of antigen processing and presentation of peptide antigen via MHC class II | Up | 0.033 | 2 |
| GO.0097193 | Intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Up | 0.0396 | 6 |
FDR value was calculated using Benjamini–Hochberg FDR and considered statistically significant when <0.05.
Table 6.
Selected GO enrichment analysis results of IF16 versus AL group
| Accession no. | GO terms | Expression trend | FDRa | Relevant gene no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At ischemia 1 h | ||||
| 0007154 | Cell communication | Up | <0.0001 | 287 |
| 0030154 | Cell differentiation | Up | <0.0001 | 255 |
| 0007165 | Signal transduction | Up | <0.0001 | 254 |
| 0022008 | Neurogenesis | Up | <0.0001 | 124 |
| 0048699 | Generation of neurons | Up | <0.0001 | 116 |
| 0030182 | Neuron differentiation | Up | <0.0001 | 83 |
| 0007268 | Synaptic transmission | Up | <0.0001 | 44 |
| 1902680 | Positive regulation of RNA biosynthetic process | Up | <0.0001 | 142 |
| 1902679 | Negative regulation of RNA biosynthetic process | Up | <0.0001 | 100 |
| 0042127 | Regulation of cell proliferation | Up | <0.0001 | 103 |
| 0008284 | Positive regulation of cell proliferation | Up | <0.0001 | 66 |
| 0032844 | Regulation of homeostatic process | Up | 0.0002 | 37 |
| 0032846 | Positive regulation of homeostatic process | Up | 0.0005 | 20 |
| 0007270 | Neuron–neuron synaptic transmission | Up | 0.0007 | 13 |
| 0043066 | Negative regulation of apoptotic process | Up | 0.0011 | 60 |
| 0017148 | Negative regulation of translation | Up | 0.0017 | 14 |
| 0060548 | Negative regulation of cell death | Up | 0.0022 | 63 |
| 0032007 | Negative regulation of TOR signaling | Up | 0.0029 | 7 |
| 0000165 | MAPK cascade | Up | 0.0059 | 19 |
| 0042981 | Regulation of apoptotic process | Up | 0.0067 | 84 |
| 0010941 | Regulation of cell death | Up | 0.0069 | 89 |
| 0008219 | Cell death | Up | 0.0087 | 65 |
| 0050768 | Negative regulation of neurogenesis | Up | 0.0091 | 22 |
| 0000186 | Activation of MAPKK activity | Up | 0.0096 | 9 |
| 0012501 | Programmed cell death | Up | 0.0143 | 62 |
| 0002520 | Immune system development | Up | 0.0157 | 48 |
| 0042592 | Homeostatic process | Up | 0.0171 | 79 |
| 0032006 | Regulation of TOR signaling | Up | 0.0179 | 9 |
| 0071456 | Cellular response to hypoxia | Up | 0.0181 | 13 |
| 0006915 | Apoptotic process | Up | 0.0195 | 60 |
| 0008283 | Cell proliferation | Up | 0.0394 | 39 |
| 0035722 | Interleukin-12-mediated signaling pathway | Up | 0.0415 | 2 |
| 0071349 | Cellular response to interleukin-12 | Up | 0.0415 | 2 |
| 0006412 | Translation | Down | <0.0001 | 67 |
| 0009058 | Biosynthetic process | Down | <0.0001 | 180 |
| 0043043 | Peptide biosynthetic process | Down | <0.0001 | 68 |
| 0055114 | Oxidation–reduction process | Down | <0.0001 | 60 |
| 0042273 | Ribosomal large subunit biogenesis | Down | <0.0001 | 8 |
| 0042254 | Ribosome biogenesis | Down | 0.0016 | 19 |
| 0001731 | Formation of translation pre-initiation complex | Down | 0.0024 | 6 |
| 0000028 | Ribosomal small subunit assembly | Down | 0.0056 | 5 |
| 0006413 | Translational initiation | Down | 0.0122 | 9 |
| 0042773 | ATP synthesis-coupled electron transport | Down | 0.0192 | 6 |
| 0006417 | Regulation of translation | Down | 0.0246 | 20 |
| 0042255 | Ribosome assembly | Down | 0.0325 | 6 |
| At reperfusion 72 h | ||||
| 0015671 | Oxygen transport | Up | 0.0114 | 2 |
| 0002376 | Immune system process | Down | <0.0001 | 19 |
| 0006955 | Immune response | Down | <0.0001 | 13 |
| 0045087 | Innate immune response | Down | <0.0001 | 10 |
| 0006952 | Defense response | Down | <0.0001 | 12 |
| 0019882 | Antigen processing and presentation | Down | 0.0079 | 4 |
| 0035456 | Response to interferon-beta | Down | 0.0148 | 3 |
| 0045351 | Type I interferon biosynthetic process | Down | 0.0321 | 2 |
FDR value was calculated using Benjamini–Hochberg FDR and considered statistically significant when <0.05.
Table 5.
Selected KEGG pathway analysis results of IF12 versus AL group
| Pathway ID | Pathway description | Expression trend | FDRa | Relevant gene no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At reperfusion 3 h | ||||
| 3010 | Ribosome | Up | <0.0001 | 46 |
| 190 | Oxidative phosphorylation | Up | <0.0001 | 30 |
| 1100 | Metabolic pathways | Up | <0.0001 | 61 |
| 4020 | Calcium signaling pathway | Down | <0.0001 | 39 |
| 4713 | Circadian entrainment | Down | <0.0001 | 28 |
| 4725 | Cholinergic synapse | Down | <0.0001 | 24 |
| 4724 | Glutamatergic synapse | Down | <0.0001 | 24 |
| 4727 | GABAergic synapse | Down | <0.0001 | 21 |
| 4728 | Dopaminergic synapse | Down | <0.0001 | 23 |
| 4010 | MAPK signaling pathway | Down | <0.0001 | 34 |
| 4911 | Insulin secretion | Down | 0.0001 | 15 |
| 4611 | Platelet activation | Down | 0.0001 | 19 |
| 4080 | Neuroactive ligand–receptor interaction | Down | 0.0004 | 30 |
| 4068 | FoxO signaling pathway | Down | 0.0017 | 17 |
| 4150 | mTOR signaling pathway | Down | 0.0135 | 9 |
| 4750 | Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | Down | 0.0232 | 13 |
| At reperfusion 24 h | ||||
| 4911 | Insulin secretion | Down | 0.0009 | 5 |
| 4270 | Vascular smooth muscle contraction | Down | 0.0026 | 5 |
| 4750 | Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels | Down | 0.0206 | 4 |
| 4020 | Calcium signaling pathway | Down | 0.0376 | 4 |
| 4713 | Circadian entrainment | Down | 0.0443 | 3 |
FDR value was calculated using Benjamini–Hochberg FDR and considered statistically significant when <0.05.
Interestingly, the IF16 I/R group had the greatest number of GO pathways affected compared to the AL group after 1 h of cerebral ischemia (Table 6; Supplementary Material, Table S10), suggesting that IF16 has a major impact on the immediate brain cell responses to ischemic stress. Pathways up-regulated in the IF16 I/R group compared to the AL I/R group included those involved in cell communication, cell differentiation, signal transduction, neurogenesis, positive and negative regulation of RNA biosynthetic processes, inhibition of cell death, regulation of mTOR and cellular responses to hypoxia. Down-regulated pathways included: protein translation, biosynthetic processes and oxidative stress reduction (Table 6). At 72 h of reperfusion, eight GO pathways were significantly down-regulated in the IF16 I/R group compared to the AL I/R group with six of the pathways being involved in immune cell responses and inflammation (Table 6). KEGG analysis also identified multiple pathways involved in the modification of the cerebral transcriptome by IF16 within 1 h of ischemia onset. Up-regulated pathways included insulin, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt, MAPK and FoxO signaling, mTOR and 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), neurotrophic factor signaling, calcium signaling and circadian rhythm-related pathways (Table 7). Down-regulated pathways included those involved in energy metabolism (oxidative phosphorylation, glycolysis and gluconeogenesis) and amino acid synthesis (Table 7). The complete results of the KEGG pathway analysis for IF16 versus AL groups at 1 h of ischemia are in Supplementary Material, Table S11.
Table 7.
Selected KEGG pathway analysis results of IF16 versus AL group
| Pathway ID | Pathway Description | Expression Trend | FDRa | Relevant Gene No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At ischemia 1 h | ||||
| 4910 | Insulin signaling pathway | Up | 0.0017 | 19 |
| 4713 | Circadian entrainment | Up | 0.0017 | 15 |
| 4020 | Calcium signaling pathway | Up | 0.0017 | 22 |
| 4068 | FoxO signaling pathway | Up | 0.0021 | 18 |
| 4151 | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | Up | 0.0021 | 34 |
| 4080 | Neuroactive ligand–receptor interaction | Up | 0.0031 | 29 |
| 4725 | Cholinergic synapse | Up | 0.0053 | 15 |
| 4611 | Platelet activation | Up | 0.0088 | 16 |
| 4150 | mTOR signaling pathway | Up | 0.0097 | 10 |
| 4727 | GABAergic synapse | Up | 0.0137 | 12 |
| 4152 | AMPK signaling pathway | Up | 0.0148 | 15 |
| 4010 | MAPK signaling pathway | Up | 0.0158 | 24 |
| 4722 | Neurotrophin signaling pathway | Up | 0.0186 | 14 |
| 4710 | Circadian rhythm | Up | 0.0226 | 6 |
| 4390 | Hippo signaling pathway | Up | 0.0262 | 16 |
| 4724 | Glutamatergic synapse | Up | 0.0331 | 13 |
| 3010 | Ribosome | Down | <0.0001 | 43 |
| 190 | Oxidative phosphorylation | Down | <0.0001 | 26 |
| 1100 | Metabolic pathways | Down | <0.0001 | 83 |
| 480 | Glutathione metabolism | Down | <0.0001 | 11 |
| 1230 | Biosynthesis of amino acids | Down | 0.0091 | 9 |
| 10 | Glycolysis/gluconeogenesis | Down | 0.0117 | 8 |
| 3060 | Protein export | Down | 0.0126 | 5 |
FDR value was calculated using Benjamini–Hochberg FDR and considered statistically significant when <0.05.
Discussion
Previous studies have demonstrated that rats or mice maintained on an alternate day fasting diet prior to cerebral I/R exhibit reduced brain tissue degeneration and improved functional outcome compared to animals fed ad libitum (13,18,19). Daily caloric restriction also improved outcomes in a rat stroke model (20). It was shown that the proteins known to be involved in the cellular stress responses such as protein chaperones (HSP-70 and GRP-78) and neurotrophic factors (BDNF and FGF2) were increased, while concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF, IL-1β and IL-6) were reduced in IF animals compared to AL group (13). The present study is the first to interrogate the impact of any dietary energy restriction protocol on the cerebral transcriptome in the uninjured brain, and during and after focal ischemic stroke. The large datasets generated in our study reveal global transcriptomic responses as the stroke and its aftermath evolves, and furthermore, identifies novel genes and signaling pathways not previously implicated in stroke and neuroprotection. Given the complexity of the experimental design and the large amount of data generated, it is not feasible to discuss all pathways and genes significantly affected by I/R, and modified by IF12 or IF16. We therefore focus our discussion on the pathways and genes most affected by ischemic stroke and/or IF.
Using the same mouse strain and experimental stroke protocol, we previously found that mice on IF16 exhibit markedly reduced brain damage and improved functional outcome following I/R (11). Here we found that IF16 has a significant impact on the expression of genes in multiple pathways in the cerebral region. Most notable was the preponderance of up-regulated pathways involved in cellular plasticity including many known to play important roles in nervous system development and adult neuroplasticity (cell differentiation, neurite outgrowth, neuronal network plasticity). These pathways include those engaged by neurotrophic factors, which had previously been reported to be up-regulated by alternate day fasting (13). Also up-regulated by IF16 were genes in pathways involved in neuronal energy metabolism (Ppar-ɑ, Pdpr and Igf1r), consistent with the known metabolic shift from glucose to fatty acid oxidation during fasting (21). Also consistent with known effects of IF on circadian rhythms (22), we found that Per2 and Per3 were up-regulated in the cerebral region of mice in the IF16 group.
Several novel findings emerged from the current RNA sequencing analyses of cerebral gene expression during ischemia, and at 3, 12, 24 or 72 h of reperfusion in mice fed ad libitum. As reported in many previous studies (23–25), pathways and genes encoding proteins involved in tissue inflammation (both innate and humoral immune system pathways) and cell deaths were prominently up-regulated during reperfusion. Interestingly, neuroinflammatory pathway up-regulation was evident within 3 h of reperfusion, subsided at 12 h, and then was robust at 24 and 72 h. We found that genes encoding proteins involved in major neurotransmitter signaling pathways were down-regulated following cerebral I/R including dopaminergic, serotonergic, noradrenergic and cholinergic pathways. Down-regulation of neuron-specific genes may result, at least in part, from neuronal death occurring during the first 72 h post-stroke. Among the genes most strongly down-regulated by cerebral ischemia was that encoding oxytocin which was reduced by over 40-fold during the 1 h of ischemia and remained reduced through 24 h of reperfusion. Previous studies have shown that oxytocin can protect the heart, skeletal muscle and ovaries against ischemic injury (26–28), and can also protect cultured neural cells against simulated ischemia (29). Because cerebral cortical neurons express oxytocin mRNA (30), down-regulation of oxytocin may contribute to neuronal degeneration in I/R brain injury.
Several major findings emerged from our analyses of the effects of IF12 and IF16 on the cerebral transcriptome responses to I/R. IF16 had major effects on the transcriptome during ischemia and at 72 h of reperfusion, while having little effect at the 3, 12 and 24 h reperfusion time points. Pathways up-regulated during 1 h of cerebral ischemia in mice of the IF16 I/R group compared to the AL I/R group included those that protect neurons against apoptosis, neurogenesis and MAPK signaling, while protein synthesis pathways were down-regulated. The latter effects of IF16 would be expected to increase the survival of neurons, an effect consistent with a previous study showing that IF16 reduces neuronal loss in the same stroke model (11). Interestingly, oxytocin was one of the mRNAs most significantly up-regulated during the 1 h of cerebral ischemia in mice in the IF16 I/R group compared to the AL I/R group, suggesting a role for oxytocin in neuroprotection by IF16. At 72 h of reperfusion, inflammatory pathways were down-regulated in mice on IF16 compared to that fed ad libitum. In contrast to IF16, IF12 had its greatest impact on the cerebral transcriptome at the 3 h reperfusion time point, with pathways involved in ribosome biosynthesis and stress responses being up-regulated and pathways involved in synaptic plasticity and differentiation being down-regulated. As with IF16, oxytocin expression was up-regulated during ischemia in mice in the IF12 group. Whereas IF16 down-regulated inflammatory pathways after I/R, IF12 did not resemble it. It remains to be determined if and to what extent IF12 reduces brain damage and functional deficits following experimental stroke, in comparison with IF16.
Emerging findings suggest that the metabolic switch, which utilizes fatty acids and ketones instead of glucose as a principle energy sources when liver glycogen storage is depleted, plays a major role in adaptive responses of the brain to fasting (21,31). β-hydroxybutyrate, a major ketone produced during fasting has been shown to induce the expression of the neurotrophic factor BDNF in brain neurons (32,33) and can inhibit histone deacetylases and thereby influence the expression of multiple genes (34). During fasting, genes encoding proteins involved in fatty acid synthesis, protein synthesis and insulin signaling are down-regulated, and fatty acid oxidation is up-regulated (31). Ketones may mediate some of these transcriptional responses to fasting (35). We found that blood ketones were elevated to significantly higher levels in mice on IF16 compared to those on IF12, suggesting a potential role for ketones in the differential effects of IF16 and IF12 on the cerebral transcriptome. Indeed, we found that Ppar-ɑ (a gene involved in fatty acid oxidation) was significantly up-regulated and Fabp7 (a gene involved in fatty acid synthesis) was down-regulated in cerebral transcriptome of mice on IF16. We also found that Prex2, a gene that modulates insulin signaling (36) was strongly up-regulated in the cerebral region in response to IF16. Considering our transcriptomic findings, it is noteworthy to mention that the IF16 group was significantly protected against ischemic stroke injury compared to the AL group in our previous study (11).
Our current findings provide novel insight into how the transcriptome of cells in the cerebral region respond to I/R, and how these responses are modified by IF in ways that protect neurons against degeneration. The transcriptomic data sets generated in this study provide a resource for investigators in the fields of neuroscience and nutrition research from which to draw to identify and interrogate specific genes and pathways from the perspectives of both basic science and translational research.
Materials and Methods
Animals and intermittent fasting
C57BL/6NTac male mice were purchased at 2 months of age (InVivos, Singapore) and housed in the animal facilities at the National University of Singapore. All animals were maintained under barrier conditions on a 12 h light: 12 h dark cycle (light during 07:00–19:00). During initiation of dietary interventions, rodent diet pellets (Teklad Global 18% Protein rodent diet #2918, Envigo, Madison, WI, USA) and water were provided ad libitum to all mice. The National University of Singapore Animal Care and Use Committee approved all in vivo experimental procedures performed in the current study (Ethics approval number: R13-6130 and R15-1568). At 3 months of age, mice were randomly assigned to AL, IF12 and IF16 diet groups, 50 mice/group. For IF12 and IF16 groups, mice were fasted daily for either 12 h (19:00–07:00) or 16 h (15:00–07:00) for 4 months, whereas the AL group was provided with food pellets ad libitum. Water was provided ad libitum for all experimental group. All mice were regularly measured with body weight and randomly selected 10 mice from each group were measured with blood glucose and ketone levels using FreeStyle Optium Neo system with FreeStyle Optium blood glucose and β ketone test strips (Abbott Laboratories, Berkshire, UK).
Middle cerebral artery occlusion stroke model
After 4 months of dietary intervention, randomly selected mice from each group underwent transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) procedure to induce experimental ischemic stroke. The mice were anesthetized with isoflurane and a midline incision was made in the neck. The left external carotid and pterygopalatine arteries were exposed and ligated with 6-0 silk thread. The internal carotid artery (ICA) was occluded at the peripheral site of the bifurcation of the ICA and the pterygopalatine artery using a small clip, and the common carotid artery (CCA) was ligated with 6-0 silk thread. The external carotid artery (ECA) was cut, and a 6-0 nylon monofilament with a blunted tip (0.2–0.22 mm) was inserted into the ECA. After the clip at the ICA was removed, the nylon monofilament was advanced to the origin of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) until light resistance was felt. The nylon monofilament and the CCA ligatures were removed after 1 h of occlusion to initiate reperfusion. In the sham-operated control group, these arteries were visualized but not disturbed. Cerebral blood flow was measured by placing the animal’s head in a fixed frame after it had been anesthetized and prepared for surgery. A craniotomy was performed to access the left MCA and was extended to allow positioning of a 0.5 mm Doppler probe (Moor Laboratory, Moor Instruments, Devon, UK) over the underlying parietal cortex approximately 1 mm posterior to the bregma and 1 mm lateral to the midline. The mice were included in the study if they underwent successful MCAO, defined by an 80% or greater drop in cerebral blood flow, and recovery of cortical blood flow to its basal level after reperfusion measured with laser Doppler flowmetry. Following MCAO and initiation of reperfusion, the mice were assessed, and three mice from each group that best displayed signs of brain damage and neurological impairment were included in the study. Mice were excluded if insertion of the thread resulted in perforation of the vessel wall determined by the presence of subarachnoid blood at the scheduled time of euthanasia.
Brain tissue collection
After successful induction of transient MCAO, mice were returned to their cages for designated reperfusion periods of 3, 12, 24 or 72 h before brain tissue collection. For the animals allotted to the 1 h ischemia-only group, the brain tissue was collected without reperfusion. Three coronal sections of ipsilateral brain hemisphere were dissected (1 mm thickness/section), which comprise ischemic core as well as the peri-infarct regions. The collected brain tissues were snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and kept at −80°C until further use.
Total RNA extraction and validation
Total RNA was extracted from the frozen brain tissue samples using a micro-tube tissue homogenizer (Bel-Art, Wayne, NJ, USA) and EZ-10 DNAaway RNA extraction mini-prep kit (Bio Basic, Ontario, Canada) following manufacturer’s instruction. The integrity and quality of extracted total RNA was assessed using agarose gel electrophoresis and Agilent 2100 Bioanalyser (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA); all RNA samples showed RNA integrity numbers above 7, indicating high quality of the extracted total RNA.
cDNA library preparation and RNA sequencing
The mRNA was purified from total RNA using poly-T oligo-attached magnetic beads and it was first fragmented randomly by addition of fragmentation buffer. Then first-strand cDNA was synthesized using random hexamer primer and M-MuLV reverse transcriptase (RNase H-) (New England BioLabs, Ipswish, MA, USA). Second-strand cDNA synthesis was subsequently performed using DNA polymerase I and RNase H. Double-stranded cDNA was purified using AMPure XP beads (Beckman Courter Life Sciences, Indianapolis, IN, USA). Remaining overhangs of the purified double-stranded cDNA were converted into blunt ends via exonuclease/polymerase activities. After adenylation of 3′ ends of DNA fragments, NEBNext adaptor with hairpin loop structure was ligated to prepare for hybridization. In order to select cDNA fragments of preferentially 150–200 bp in length, the library fragments were purified with AMPure XP system. Finally, the library was acquired by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and purification of PCR products by AMPure XP beads. High-throughput sequencing was conducted using HiSeqTM2500 platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
Transcriptome data mapping and differential expression analysis
The RNA sequencing results from the HiSeq system were output as color space fasta and quality files, and these files were mapped to the Ensembl-released mouse genome sequence and annotation. Indexes of the reference genome were built using Bowtie V.2.0.6 and paired-end clean reads were aligned to the reference genome using TopHat V.2.0.9 with mismatch parameter limited to 2. For each sample, approximately 51 million reads were generated and 44 million reads (approximately 88% of total reads) per sample were mapped to the reference genome. For the quantification of gene expression level, HTSeq V.0.6.1 was used to count the read numbers mapped of each gene. Then Reads Per Kilobase of exon model per Million mapped reads (RPKM) of each gene was calculated based on the length of the gene and reads count mapped to the same gene. Differential expression analysis was performed using the DESeq R Package V.1.10.1 and the resulting P-values were adjusted using the Benjamini and Hochberg’s approach for controlling the FDR. Genes with an adjusted P-value lower than 0.05 found by DESeq were assigned as differentially expressed.
Heatmap generation and enrichment analyses
To create heatmaps of differentially expressed genes, R and the R package heatmap3 were used along with the log2Fold-Change output from EdgeR V.3.2.4. To assess the biological significance of gene expression changes, GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses were conducted. GO enrichment analysis, focused on biological processes of differentially expressed genes was implemented by the GOseq R package in which gene length bias was corrected. For KEGG pathway enrichment analysis, we used KEGG Orthology-Based Annotation System (KOBAS) software to test the statistical enrichment. GO terms or KEGG pathways with adjusted P-value less than 0.05 were considered significantly enriched by differentially expressed genes.
Quantitative real-time PCR validation
The RNA sequencing results were validated for randomly selected representative genes among the genes that were differentially expressed in more than three I/R time points used in the AL group study. The cDNA used for real-time qPCR was generated from the reserved total RNA using High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems, Waltham, MA, USA). The PrimePCRTM (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) designed PCR primers for SYBR Green method were used for Aspg (assay ID: qMmuCID0073204), Chat (assay ID: qMmuCID0017045), Gfap (assay ID: qMmuCID0020163), P2ry12 (assay ID: qMmuCID0015382), Rxrg (assay ID: qMmuCID0025416), Serpina3n (assay ID: qMmuCID0024737) and for housekeeping gene, Gapdh (assay ID: qMmuCED0027497). The real-time qPCR assays were all performed in triplicate using StepOnePlus system (Applied Biosystems) in 96-well plate format. A 20 μl reaction volume was used per well, consisting of 10 μl 2× SsoAdvanced Universal SYBR Green supermix (Bio-Rad), 1 μl of 20× PrimePCRTM primer, 100 ng of cDNA sample in 2 μl volume and 7 μl of molecular biology grade nuclease-free water. The amplification was performed as follows: 2 min at 95°C, 40 cycles of 5 s at 95°C and 30 s for 60°C and melt curve from 65 to 95°C with 0.5°C increments for 5 s per step. The qPCR data were analyzed using the method (37). For each of the selected target genes, the mean ΔCT for the three biological replicates in each group being compared was calculated as the mean CT of the target gene minus the mean CT of the housekeeping gene. For each pairwise comparison, ΔΔCT was then calculated as the mean ΔCT of the noncontrol group minus the ΔCT of the control group, and the resulting ΔΔCT value was converted to 2−ΔΔCT, representing fold change. Statistical significance among time points was calculated using ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc analysis (P < 0.05). The qPCR results of selected differentially expressed genes were compared pairwise with fold change of reported fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads (FPKM) values from RNA sequencing data (Supplementary Material, Fig. S2). Up- and down-regulation trends of each gene were well correlated between RNA sequencing and RT-qPCR results.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material is available at HMG online.
Conflict of Interest statement. None declared.
Funding
This work was supported by the Singapore Ministry of Education Tier 1 grants (T1-BSRG-2015–01), ODPRT, National University of Singapore, Singapore National Medical Research Council Research Grants (NMRC-CBRG-0102/2016), and Singapore National Medical Research Council Research Grants (NMRC/OFIRG/0036/2017). Parts of this study were funded by NIH grants RO1 NS101960, RO1 NS099531 and R21 NS095192.
Supplementary Material
References
- 1. Mattson M.P., Longo V.D., Harvie M. (2017) Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes. Ageing Res. Rev., 39, 46–58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Mattson M.P., Wan R. (2005) Beneficial effects of intermittent fasting and caloric restriction on the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems. J. Nutr. Biochem., 16, 129–137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Fann D.Y., Ng G.Y., Poh L., Arumugam T.V. (2017) Positive effects of intermittent fasting in ischemic stroke. Exp. Gerontol., 89, 93–102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Longo V.D., Mattson M.P. (2014) Fasting: molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Cell. Metab., 19, 181–192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Mattson M.P., Allison D.B., Fontana L., Harvie M., Longo V.D., Malaisse W.J., Mosley M., Notterpek L., Ravussin E., Scheer F.A.. et al. (2014) Meal frequency and timing in health and disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 111, 16647–16653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Seimon R.V., Roekenes J.A., Zibellini J., Zhu B., Gibson A.A., Hills A.P., Wood R.E., King N.A., Byrne N.M., Sainsbury A. (2015) Do intermittent diets provide physiological benefits over continuous diets for weight loss? A systematic review of clinical trials. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 418 Pt 2, 153–172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. DeFronzo R.A., Abdul-Ghani M. (2011) Assessment and treatment of cardiovascular risk in prediabetes: impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose. Am. J. Cardiol., 108, 3B–24B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Martin B., Ji S., Maudsley S., Mattson M.P. (2010) “Control” laboratory rodents are metabolically morbid: why it matters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 107, 6127–6133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Gotthardt J.D., Verpeut J.L., Yeomans B.L., Yang J.A., Yasrebi A., Roepke T.A., Bello N.T. (2016) Intermittent fasting promotes fat loss with lean mass retention, increased hypothalamic norepinephrine content, and increased neuropeptide Y gene expression in diet-induced obese male mice. Endocrinology, 157, 679–691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Fann D.Y., Santro T., Manzanero S., Widiapradja A., Cheng Y.L., Lee S.Y., Chunduri P., Jo D.G., Stranahan A.M., Mattson M.P.. et al. (2014) Intermittent fasting attenuates inflammasome activity in ischemic stroke. Exp. Neurol., 257, 114–119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Manzanero S., Erion J.R., Santro T., Steyn F.J., Chen C., Arumugam T.V., Stranahan A.M. (2014) Intermittent fasting attenuates increases in neurogenesis after ischemia and reperfusion and improves recovery. J. Cereb. Blood. Flow. Metab., 34, 897–905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Park S., Yoo K.M., Hyun J.S., Kang S. (2017) Intermittent fasting reduces body fat but exacerbates hepatic insulin resistance in young rats regardless of high protein and fat diets. J. Nutr. Biochem., 40, 14–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Arumugam T.V., Phillips T.M., Cheng A., Morrell C.H., Mattson M.P., Wan R. (2010) Age and energy intake interact to modify cell stress pathways and stroke outcome. Ann. Neurol., 67, 41–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Arumugam T.V., Manzanero S., Furtado M., Biggins P.J., Hsieh Y.H., Gelderblom M., MacDonald K.P., Salimova E., Li Y.I., Korn O.. et al. (2017) An atypical role for the myeloid receptor Mincle in central nervous system injury. J. Cereb. Blood. Flow. Metab., 37, 2098–2111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Tang S.C., Arumugam T.V., Xu X., Cheng A., Mughal M.R., Jo D.G., Lathia J.D., Siler D.A., Chigurupati S., Ouyang X.. et al. (2007) Pivotal role for neuronal Toll-like receptors in ischemic brain injury and functional deficits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 104, 13798–13803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Lok K.Z., Basta M., Manzanero S., Arumugam T.V. (2015) Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) dampens neuronal toll-like receptor-mediated responses in ischemia. J. Neuroinfl., 12, 73.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Wang S., Zhang H., Xu Y. (2016) Crosstalk between microglia and T cells contributes to brain damage and recovery after ischemic stroke. Neurol. Res., 38, 495–503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Yu Z.F., Mattson M.P. (1999) Dietary restriction and 2-deoxyglucose administration reduce focal ischemic brain damage and improve behavioral outcome: evidence for a preconditioning mechanism. J. Neurosci. Res., 57, 830–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Yoon J.S., Mughal M.R., Mattson M.P. (2011) Energy restriction negates NMDA receptor antagonist efficacy in ischemic stroke. Neuromol. Med., 13, 175–178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Ran M., Li Z., Yang L., Tong L., Zhang L., Dong H. (2015) Calorie restriction attenuates cerebral ischemic injury via increasing SIRT1 synthesis in the rat. Brain Res., 1610, 61–68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Camandola S., Mattson M.P. (2017) Brain metabolism in health, aging, and neurodegeneration. EMBO J., 36, 1474–1492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Hatori M., Vollmers C., Zarrinpar A., DiTacchio L., Bushong E.A., Gill S., Leblanc M., Chaix A., Joens M., Fitzpatrick J.A.. et al. (2012) Time-restricted feeding without reducing caloric intake prevents metabolic diseases in mice fed a high-fat diet. Cell. Metab., 15, 848–860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Clark R.K., Lee E.V., Fish C.J., White R.F., Price W.J., Jonak Z.L., Feuerstein G.Z., Barone F.C. (1993) Development of tissue damage, inflammation and resolution following stroke: an immunohistochemical and quantitative planimetric study. Brain. Res. Bull., 31, 565–572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Wang Q., Tang X.N., Yenari M.A. (2007) The inflammatory response in stroke. J. Neuroimmunol., 184, 53–68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Eltzschig H.K., Eckle T. (2011) Ischemia and reperfusion–from mechanism to translation. Nat. Med., 17, 1391–1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Erkanli K., Erkanli Senturk G., Aydin U., Arbak S., Ercan F., Tuncdemir M., Isiksacan N., Bakir I. (2013) Oxytocin protects rat skeletal muscle against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Ann. Vasc. Surg., 27, 662–670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Akdemir A., Erbas O., Gode F., Ergenoglu M., Yeniel O., Oltulu F., Yavasoglu A., Taskiran D. (2014) Protective effect of oxytocin on ovarian ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Peptides, 55, 126–130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Jankowski M., Broderick T.L., Gutkowska J. (2016) Oxytocin and cardioprotection in diabetes and obesity. BMC Endocr. Disord., 16, 34.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Kaneko Y., Pappas C., Tajiri N., Borlongan C.V. (2016) Oxytocin modulates GABAAR subunits to confer neuroprotection in stroke in vitro. Sci. Rep., 6, 35659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Lein E.S., Hawrylycz M.J., Ao N., Ayres M., Bensinger A., Bernard A., Boe A.F., Boguski M.S., Brockway K.S., Byrnes E.J.. et al. (2007) Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature, 445, 168–176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Anton S.D., Moehl K., Donahoo W.T., Marosi K., Lee S.A., Mainous A.G., Leeuwenburgh C., Mattson M.P. (2018) Flipping the metabolic switch: understanding and applying health benefits of fasting. Obesity 26, 254–268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Marosi K., Kim S.W., Moehl K., Scheibye-Knudsen M., Cheng A., Cutler R., Camandola S., Mattson M.P. (2016) 3-Hydroxybutyrate regulates energy metabolism and induces BDNF expression in cerebral cortical neurons. J. Neurochem., 139, 769–781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Sleiman S.F., Henry J., Al-Haddad R., El Hayek L., Abou Haidar E., Stringer T., Ulja D., Karuppagounder S.S., Holson E.B., Ratan R.R.. et al. (2016) Exercise promotes the expression of brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) through the action of the ketone body beta-hydroxybutyrate. eLife, 5, e15092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Newman J.C., Verdin E. (2017) beta-Hydroxybutyrate: a signaling metabolite. Annu. Rev. Nutr., 37, 51–76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Newman J.C., Covarrubias A.J., Zhao M., Yu X., Gut P., Ng C.P., Huang Y., Haldar S., Verdin E. (2017) Ketogenic Diet Reduces Midlife Mortality and Improves Memory in Aging Mice. Cell. Metab., 26, 547–557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Hodakoski C., Hopkins B.D., Barrows D., Mense S.M., Keniry M., Anderson K.E., Kern P.A., Hawkins P.T., Stephens L.R., Parsons R. (2014) Regulation of PTEN inhibition by the pleckstrin homology domain of P-REX2 during insulin signaling and glucose homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 111, 155–160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Livak K.J., Schmittgen T.D. (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods, 25, 402–408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.