Figure 6.
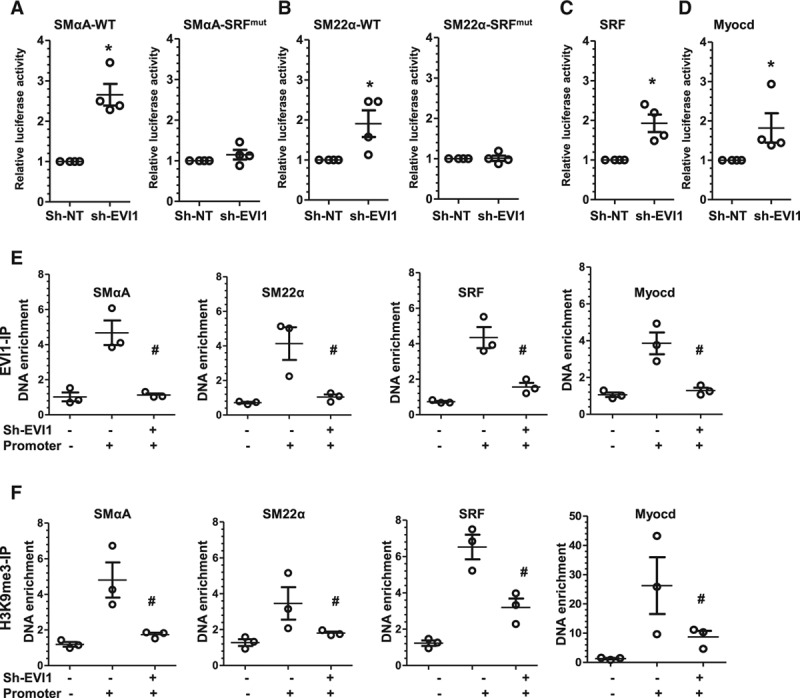
EVI1 functions as a transcriptional repressor for VSMC gene expression. A and B, SRF binding element(s) are required for EVI1-mediated SMαA and SM22α gene promoter activity. Wild-type (SMαA/SM22α) or SRF binding site(s) mutants (SRFmut) of SMαA (A) and SM22α (B) gene promoter reporters were transfected into control (nontarget shRNA, sh-NT) and EVI1 stable knockdown (EVI1 shRNA, sh-EVI1) VSMCs. Transfected cells were subjected to serum starvation for 48 hours, and cell lysates were subjected to luciferase activity assay. C and D, EVI1 inhibition significantly increases SRF and Myocd gene promoter activity. SRF (C) and Myocd (D) gene promoter reporters were transfected into control and EVI1 stable knockdown VSMCs. Transfected cells were subjected to serum starvation for 48 hours, and cell lysates were subjected to luciferase activity assay. E, EVI1 was significantly enriched at the promoter regions of SMαA (far left), SM22α (middle left), SRF (middle right), and Myocd (far right) genes and was significantly decreased by EVI1 knockdown, indicating direct binding of EVI1 to these promoter regions. ChIP assays were performed to measure EVI1 enrichment in the promoter region of its downstream targets. Control (sh-EVI1–) and EVI1 stable knockdown (sh-EVI1+) VSMCs were lysed and incubated with antibody against EVI1 to immunoprecipitate EVI1-bound promoter DNA, followed by qPCR to quantify DNA enrichment. For SMαA and SM22α, genomic DNA without SRF binding sites were amplified as additional control for specific promoter DNA enrichment and designated as Promoter–. For SRF and Myocd, PCR amplification of DNA region adjacent to their promoter was designated as Promoter–. F, H3K9me3 enrichment within the promoter regions of SMαA (far left), SM22α (middle left), SRF (middle right), and Myocd (far right) genes was significantly decreased by EVI1 knockdown. ChIP assays were performed by using an antibody against H3K9me3. Data and error bars are mean±SEM. *P<0.05 (versus sh-NT). #P<0.05 (versus sh-EVI1–, Promoter+). ChIP indicates chromatin immunoprecipitation; EVI1, ecotropic virus integration site 1 protein homolog; qPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction; shRNA, small hairpin RNA; and VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cell.
