Figure 3.
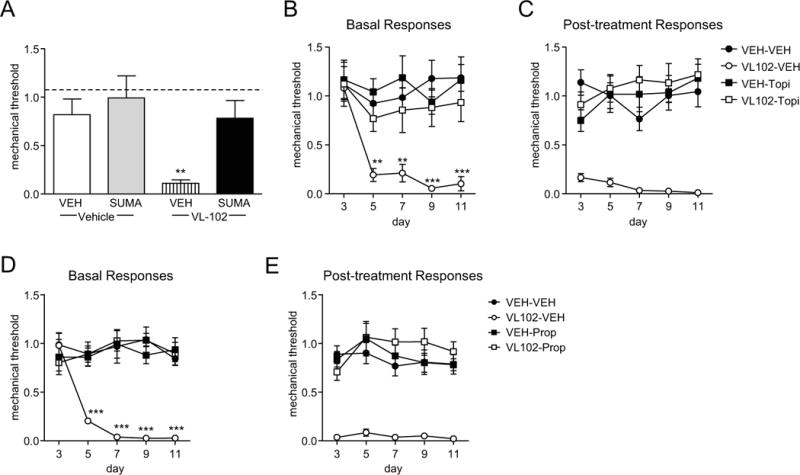
VL-102-induced hyperalgesia is blocked by acute and preventative migraine medications. (A) Sumatriptan significantly inhibited VL-102 evoked hyperalgesia. Mice were treated with vehicle (VEH) or VL-102 (1 mg/kg, IP), and 1h15min later injected with vehicle or sumatriptan (SUMA, 0.6 mg/kg, IP), and tested 45 min later. **p<0.01 as compared to VEH-VEH groups, 2-way ANOVA and Holm-Sidak post-hoc analysis. Dashed line indicates basal naïve responses. (B,C) In a separate group of animals, mice were treated with vehicle (VEH) or topiramate (30 mg/kg IP) daily for 11 days. On days 3,5,7,9, and 11 basal responses were determined (B), and mice were injected with either vehicle (VEH) or VL-102 (1 mg/kg, IP). p<0.05 effect of drug, time and interaction, 2-way RM ANOVA and Holm-Sidak post-hoc analysis. **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 as compared to VEH-VEH controls. (C) Post-treatment responses were assessed 2h following VL-102 administration. p<0.001 effect of drug, but no significant effect of time or interaction, 2-way RM ANOVA. n=6/group. (D,E) A separate group of mice were treated with vehicle (VEH) or propranolol (20 mg/kg IP) daily for 11 days. On days 3,5,7,9, and 11 basal responses were determined (D), and mice were injected with either vehicle (VEH) or VL-102 (1 mg/kg, IP). p<0.05 effect of group, time and interaction, 2-way RM ANOVA and Holm-Sidak post-hoc analysis. **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 as compared to VEH-VEH controls. (C) Post-treatment responses were assessed 2h following VL-102 administration. p<0.001 effect of drug, but no significant effect of time or interaction, 2-way RM ANOVA. n=9/group. Stimulation of soluble guanylyl cyclase produces a migraine-associated pain.
