Figure 3. Morphine priming followed by stress causes a loss of DNIC that is ameliorated by systemic nor-BNI.
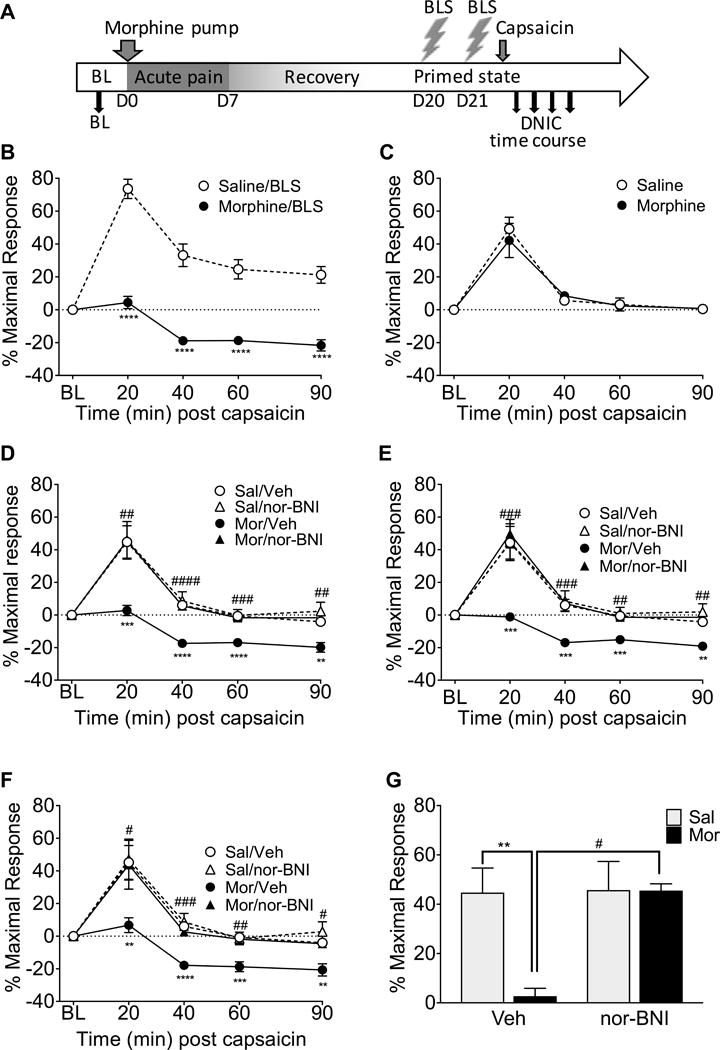
A timeline of experimental procedures is shown for clarity (A). Rats primed with morphine that received bright light stress (BLS) on day 20 and again at day 21 had a significant loss of DNIC compared to saline-primed rats (B). However, morphine-primed rats that were not exposed to BLS did not have a significantly different DNIC response compared to saline-primed rats (C). Nor-BNI administered subcutaneously prior to each BLS period significantly attenuated the loss of DNIC in morphine primed rats (D, E, F). This effect was observed in the left (D), right (E), and combined left and right (averaged together, F) hindpaw measurements. At the 20 minute DNIC timepoint (G), following BLS, the morphine-primed group treated with nor-BNI did not have a significant loss of DNIC whereas the morphine-primed rats treated with vehicle showed a significant loss of DNIC. Also, the morphine primed rats treated with nor-BNI showed significantly higher DNIC than morphine-primed vehicle-treated rats (G). **** p<0.0001, *** p<0.001, ** p<0.01, * p<0.05 significant difference from the saline/BLS group (B), saline group (C), or saline/vehicle group (D-G). #### p<0.0001, ### p<0.001, ## p<0.01, # p<0.05 significant difference between morphine/vehicle and morphine/nor-BNI rats at a timepoint (D-G). B: n= 19 saline, 8 morphine C: n=9 saline, 7 morphine, D-G: n= 10 saline/vehicle, 9 saline/nor-BNI, 10 morphine/vehicle, 6 morphine nor-BNI. Data analyzed by 2-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons in B, C, and G. Data in D, E, and F analyzed by 3-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s correction for multiple comparisons.
