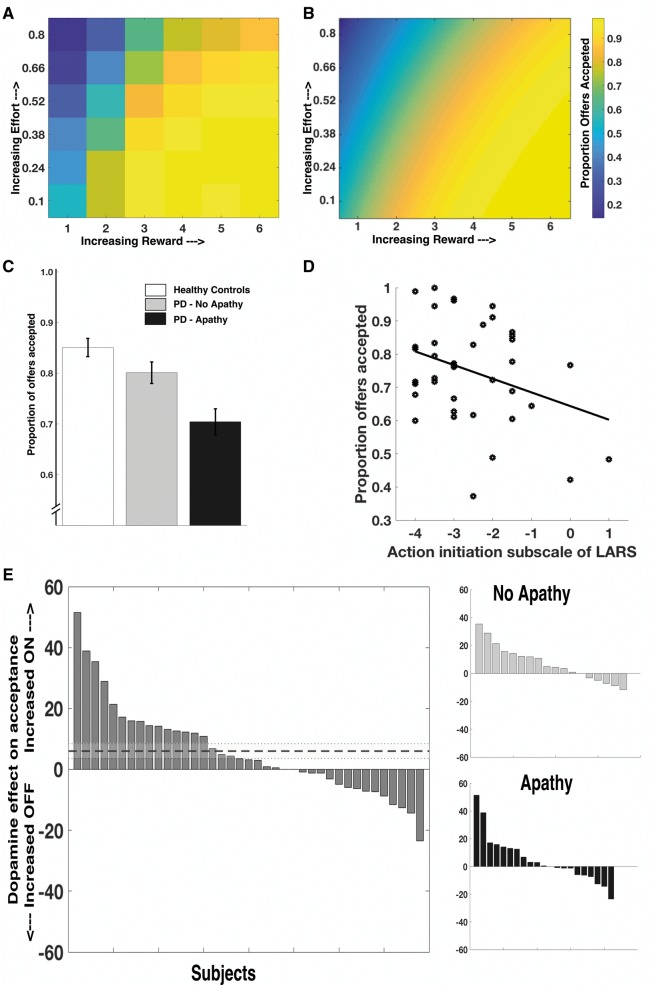
Figure 2.
Raw acceptance results as apathy status, and dopamine state, varied. Mean acceptance rates for all patients, ON and OFF their normal medications. As reward on offer increased, and effort required decreased, the probability of a participant accepting an offer increased, raw data (A) and modelled data (B). Apathetic Parkinson’s disease patients accepted significantly fewer offers than healthy controls or non-apathetic Parkinson’s disease patients (C, ON state shown, error bars are ± SEM). Apathy level (action initiation subscale of LARS) strongly correlated with acceptance rate (D, r = 0.37, P = 0.019; ON state shown). Dopamine depletion (OFF state) was associated with significantly reduced acceptance rates, irrespective of apathy status (E, dotted line is mean effect ± SEM). PD = Parkinson’s disease.